#plan international bangladesh
Text
Plan International vacancy for Finance System Analyst
Plan International vacancy for Finance System Analyst
Plan International vacancy for Finance System Analyst: The Functional Area Global Finance Reports to Head of Financial Systems Location Global Hub, Woking Travel required No Effective Date ASAP Grade ROLE PURPOSE Plan International is an independent children’s rights and humanitarian organization committed to children living a life free of poverty, violence, and injustice.
We actively unite…

View On WordPress
#ethiopian job vacancy websites#plan international#plan international bangladesh#plan international job#plan international job 2022#plan international job circular#plan international job circular 2022#plan international job vacancies#plan international job vacancy#plan international job vacancy 2020#plan international job vacancy 2022#plan international jobs#plan international jobs in bangladesh#plan international vacancy#vacancy in plan international
0 notes
Text
Where can I find Free Palestine protests and Ceasefire protests?
A super international and continually updated list of actions can be found at Samidoun: Palestinian Prisoner Solidarity Network's:

Calendar of Resistance for Palestine 2024
They list events by date, then alphabetically by country, then by city - and it's common for them to have dozens of actions listed for a single date, especially on the weekends.
The United States especially often has 40+ events on a single day, especially on the weekends.
Events are posted with links to the event info posted by whoever's hosting the vast majority of the time.
Look blow the read-more for a list of many of the countries that have been on this protest calendar, in alphabetical order, since I know so many websites/lists of actions are country-specific
*Obviously this isn't the only good source of listings for protest events - there are many others. This is by far the biggest/most international roundup I've found, though, so I started with this. If you know another good place for finding ceasefire protests/events, please feel free to add it in the notes, bc I'm planning to put a bigger roundup together once I find enough other sites
Countries that Samidoun has listed/does list protests for include (in alphabetical order):
North America:
United States
Canada
Mexico
Puerto Rico (listed separately in anti-colonial solidarity)
Hawai'i (listed separately in anti-colonial solidarity)
Europe:
Austria
Belgium
Bulgaria
Denmark
England
Finland
France
Germany
Greece
Hungary
Iceland
Ireland
Italy
Netherlands
Norway
Portugal
Romania
Scotland
Serbia
Spain
Sweden
Switzerland
Wales
SWANA Region (Southwest Asia/North Africa)*:
Bahrain
Iraq
Jordan
Kuwait
Lebanon
Palestine
Tunisia
Turkiye (Turkey)
*Samidoun notes that "We know that these events are mainly international and that the Arab people are marching everywhere for Palestine – we will be honored to add more Arab events whenever we are informed!"
Asia:
Bangladesh
India
Indonesia
Japan
Malaysia
Maldives
Pakistan
South Korea
Africa:
Kenya
Mauritius
Nigeria
South Africa
Tanzania
Tunisia
*Duplicating North African countries (well, Tunisia) here from the SWANA list btw
South America:
Brazil
Colombia
Chile
Peru
Venezuela
Australia and Oceania:
Aotearoa (New Zealand)
Australia
#reminder that “palestine” and “cw war” are the tags for all of my posts related to palestine#and that I only post relatively positive news about progress toward peace and resistance actions and the like#btw do NOT mess around in the notes with islamophobia OR antisemitism#neither are even remotely acceptable#palestine#cw war#free palestine#free gaza#israel#middle east#gaza#palestinian genocide#genocide#cw genocide#nakba#second nakba#ceasefire#palestine genocide#ceasefire now#palestine protest#gaza protests#gaza strip#gaza genocide#war crimes#ethnic cleansing#colonialism#anti zionisim
3K notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Plan International Bangladesh Job Circular 2022 | প্ল্যান ইন্টারন্যাশনাল...
0 notes
Text
A Good Samaritan who was stabbed while coming to the aid of robbery victim last year in Vancouver has had $2,000 in medical bills waived.
Meraj Ahmed, an international student from Bangladesh, suffered a sliced tendon in his left hand when he stopped a thief, in the process of stealing a piece of computer equipment, during a Facebook Marketplace transaction in December.
Because he had not yet signed up for B.C.'s Medical Services Plan (MSP) at the time of the stabbing, Ahmed was initially charged for the surgery to mend his hand and the follow-up medical treatments.
But much to his relief, on Tuesday, Ahmed learned officials had backdated his MSP coverage to Dec. 1, 2023, effectively erasing the debt. [...]
Continue Reading.
Tagging: @newsfromstolenland
56 notes
·
View notes
Note
I had a dream about your enemies with benefits ghost x reader where the reader had a cryptic pregnancy. She kinda just doubled over in pain randomly and BOOM. Baby.
HE'S A LETHAL PERFECTIONIST TO THE CORE: rigid expectations impressed upon everyone; it's what makes him a first-rate soldier – grit factor and an appetite for excellence in everything he does.
(The thing is, Ghost doesn't make mistakes.
Of course, there's a first time for everything.)
It's chaos walking in Bangladesh, guerrilla warfare against an AQ cell weaseled away in Dhaka because the shiteheads have business with the organized crime bosses here. It's a city jam-packed with civilians, innocent lives. No open-fire allowed. A place like this means guerrilla warfare. Hit-and-run tactics. God knows he's not trying to start an international incident by blowing up half the bloody capital.
Cloak-and-dagger: they're picked off one-by-one. It takes a full day. A mess to be cleaned up, and he does it exceptionally well.
Ghost doesn't get any reports outside of the mission until he relays his total kill count.
"Good work," Laswell radios in. "We need you on the first flight to Oslo."
He lets out a slow exhale while jumping into the driver's seat of the vehicle he commandeered a couple blocks over. Time to make his way to the airport, then. They need his back-up. He knows what that means. But he's not going to think about the fact that the rest of the One-Four-One are there for a completely different ops and whether things have gone south if they're calling him in. He was supposed to be their fallback plan. "Everything solid?"
"It's Mav."
His grip around the steering wheel tightens. If he starts speeding through the streets, then he doesn't notice, too tuned in to the conversation at hand. "Fill me in."
"Landed herself in the hospital."
Again? Christ. It's the second visit in six months. He was there for the first one. Damn near had to stop the bloody doctors from calling out her time of death. Fuckin' tossers.
"What's the damage?"
"Well—"
"Alive?"
"Yes," she says quickly.
"Then quit beating around the bush. The hell's wrong with her?"
"All in one piece. Just get here when you can."
Right, so no helpful answers from the Station Chief. And Ghost tries to contact the others, but gets the same fucking silence. Not Price, not Gaz, not even Soap who always answers just to take every opportunity over the comms to blather about anything and everything in real time. He's not sure why he's being kept in the dark like this, but it's definitely putting him on edge.

The only other message he receives from Laswell: Oslo University Hospital. He'd combed the website for information in between stoplights. It'll do, he supposes. Their services don't seem subpar, which at any rate sounds far better than fucking Moscow; he still gets sick thinking about it.
So he checks in, gets his visitor badge. It's a whole ordeal that takes a lot longer than he likes. They tell him what floor, what room. That's the Gyneacology and Obstetrics Wing. He triple-checks, making sure nothing gets lots in translation; doesn't sound right to him, but he'll tear up the place later if they gave him the wrong directions. He memorized the hospital layout already; it'll take him approximately three minutes utilizing the right staircase, or seven minutes if he wants to take his sweet-fucking-time with the elevators.
"Our gift shop is around the corner," they tell him in a thick Norwegian accent before he makes his exit.
Odd.
She doesn't like flowers or cards or sentimental things anyways. Calls them impractical. Would rather hoard his jackets or other belongings of his that she finds useful, so the gift shop would be a waste.

When Ghost finally gets to where he needs to be, 2 minutes and 45 seconds later (skipped every other step just to shave off time), he finds everyone sans Mav waiting outside the room. It's not a happy reunion, despite Soap's grin. Everyone's intact, nobody's dead or anything that would excuse their silence during his trip from Bangladesh. Ghost is extremely unimpressed with their lack of communication and promises that he'll deal with their sorry arses later before shoving his way through the door.
—only to be met with the sight of her sitting up in bed, a tiny newborn bundled in her arms.
... whose fucking baby is that?
And when his eyes snap up to hers, she's glaring at him with a positively seething look that could kill.
#I’d like to preface that I don’t think they’d have kids#but if they do it is a hostile affair#I promise I only use tiny font and third person for headcanons and stuff#reader's callsign is maverick#i did not check for spelling errors tbh#ewb simon lives in my head rent free#💌 𝘪𝘯𝘣𝘰𝘹: 𝘺𝘰𝘶’𝘷𝘦 𝘨𝘰𝘵 𝘮𝘢𝘪𝘭 ˚ ༘♡ ⋆。˚#𝘦𝘯𝘦𝘮𝘪𝘦𝘴-𝘸𝘪𝘵𝘩-𝘣𝘦𝘯𝘦𝘧𝘪𝘵𝘴!𝘴𝘪𝘮𝘰𝘯
264 notes
·
View notes
Text
SHANGHAI — Over the past generation, China’s most important relationships were with the more developed world, the one that used to be called the “first world.” Mao Zedong proclaimed China to be the leader of a “third” (non-aligned) world back in the 1970s, and the term later came to be a byword for deprivation. The notion of China as a developing country continues to this day, even as it has become a superpower; as the tech analyst Dan Wang has joked, China will always remain developing — once you’re developed, you’re done.
Fueled by exports to the first world, China became something different — something not of any of the three worlds. We’re still trying to figure out what that new China is and how it now relates to the world of deprivation — what is now called the Global South, where the majority of human beings alive today reside. But amid that uncertainty, Chinese exports to the Global South now exceed those to the Global North considerably — and they’re growing.
The International Monetary Fund expects Asian countries to account for 70% of growth globally this year. China must “shape a new international system that is conducive to hedging against the negative impacts of the West’s decoupling,” the scholar and former People’s Liberation Army theorist Cheng Yawen wrote recently. That plan starts with Southeast Asia and extends throughout the Global South, a terrain that many Chinese intellectuals see as being on their side in the widening divide between the West and the rest.
“The idea is that what China is today, fast-growing countries from Bangladesh to Brazil could be tomorrow.”
China isn’t exporting plastic trinkets to these places but rather the infrastructure for telecommunications, transportation and digitally driven “smart cities.” In other words, China is selling the developmental model that raised its people out of obscurity and poverty to developed global superpower status in a few short decades to countries with people who have decided that they want that too.
The world China is reorienting itself to is a world that, in many respects, looks like China did a generation ago. On offer are the basics of development — education, health care, clean drinking water, housing. But also more than that — technology, communication and transportation.
Back in April, on the eve of a trip to China, Brazilian President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva sat down for an interview with Reuters. “I am going to invite Xi Jinping to come to Brazil,” he said, “to get to know Brazil, to show him the projects that we have of interest for Chinese investment. … What we want is for the Chinese to make investments to generate new jobs and generate new productive assets in Brazil.” After Lula and Xi had met, the Brazilian finance minister proclaimed that “President Lula wants a policy of reindustrialization. This visit starts a new challenge for Brazil: bringing direct investments from China.” Three months later, the battery and electric vehicle giant BYD announced a $624 million investment to build a factory in Brazil, its first outside Asia.
Across the Global South, fast-growing countries from Bangladesh to Brazil can send raw materials to China and get technological devices in exchange. The idea is that what China is today, they could be tomorrow.
At The Kunming Institute of Botany
In April, I went to Kunming to visit one of China’s most important environmental conservation outfits — the Kunming Institute of Botany. Like the British Museum’s antiquities collected from everywhere that the empire once extended, the seed bank here (China’s largest) aspires to acquire thousands of samples of various plant species and become a regional hub for future biotech research.
From the Kunming train station, you can travel by Chinese high-speed rail to Vientiane; if all goes according to plan, the line will soon be extended to Bangkok. At Yunnan University across town, the economics department researches “frontier economics” with an eye to Southeast Asian neighboring states, while the international relations department focuses on trade pacts within the region and a community of anthropologists tries to figure out what it all means.
Kunming is a bland, air-conditioned provincial capital in a province of startling ethnic and geographic diversity. In this respect, it is a template for Chinese development around Southeast Asia. Perhaps in the future, Dhaka, Naypyidaw and Phnom Penh will provide the reassuring boredom of a Kunming afternoon.
Imagine you work at the consulate of Bangladesh in Kunming. Why are you in Kunming? What does Kunming have that you want?
The Bengali poet Rabindranath Tagore lyrically described Asia’s communities as organic and spiritual in contrast with the materialism of the West. As Tagore spoke of the liberatory powers of art, his Chinese listeners scoffed. The Chinese poet Wen Yiduo, who moved to Kunming during World War II and is commemorated with a statue at Yunnan Normal University in Kunming, wrote that Tagore’s work had no form: “The greatest fault in Tagore’s art is that he has no grasp of reality. Literature is an expression of life and even metaphysical poetry cannot be an exception. Everyday life is the basic stuff of literature, and the experiences of life are universal things.”
“Xi Jinping famously said that China doesn’t export revolution. But what else do you call train lines, 5G connectivity and scientific research centers appearing in places that previously had none of these things?”
If Tagore’s Bengali modernism championed a spiritual lens for life rather than the materiality of Western colonialists, Chinese modernists decided that only by being more materialist than Westerners could they regain sovereignty. Mao had said rural deprivation was “一穷二白” — poor and empty; Wen accused Tagore’s poetry of being formless. Hegel sneered that Asia had no history, since the same phenomena simply repeated themselves again and again — the cycle of planting and harvest in agricultural societies.
For modernists, such societies were devoid of historical meaning in addition to being poor and readily exploited. The amorphous realm of the spirit was for losers, the Chinese May 4th generation decided. Railroads, shipyards and electrification offered salvation.
Today, as Chinese roads, telecoms and entrepreneurs transform Bangladesh and its peers in the developing world, you could say that the argument has been won by the Chinese. Chinese infrastructure creates a new sort of blank generic urban template, one seen first in Shenzhen, then in Kunming and lately in Vientiane, Dhaka or Indonesian mining towns.
The sleepy backwaters of Southeast Asia have seen previous waves of Chinese pollinators. Low Lan Pak, a tin miner from Guangdong, established a revolutionary state in Indonesia in the 18th century. Li Mi, a Kuomintang general, set up an independent republic in what is now northern Myanmar after World War II.
New sorts of communities might walk on the new roads and make calls on the new telecom networks and find work in the new factories that have been built with Chinese technology and funded by Chinese money across Southeast Asia. One Bangladeshi investor told me that his government prefers direct investment to aid — aid organizations are incentivized to portray Bangladesh as eternally poor, while Huawei and Chinese investors play up the country’s development prospects and bright future. In the latter, Bangladeshis tend to agree.
“Is China a place, or is it a recipe for social structure that can be implemented generically anywhere?”
The majority of human beings alive today live in a world of not enough: not enough food; not enough security; not enough housing, education, health care; not enough rights for women; not enough potable water. They are desperate to get out of there, as China has. They might or might not like Chinese government policies or the transactional attitudes of Chinese entrepreneurs, but such concerns are usually of little importance to countries struggling to bootstrap their way out of poverty.
The first world tends to see the third as a rebuke and a threat. Most Southeast Asian countries have historically borne abuse in relationship to these American fears. Most American companies don’t tend to see Pakistan or Bangladesh or Sumatra as places they’d like invest money in. But opportunity beckons for Chinese companies seeking markets outside their nation’s borders and finding countries with rapidly growing populations and GDPs. Imagine a Huawei engineer in a rural Bangladeshi village, eating a bad lunch with the mayor, surrounded by rice paddies — he might remember the Hunan of his childhood.
Xi Jinping famously said that China doesn’t export revolution. But what else do you call train lines, 5G connectivity and scientific research centers appearing in places that previously had none of these things?
Across the vastness of a world that most first-worlders would not wish to visit, Chinese entrepreneurs are setting up electric vehicle and battery companies, installing broadband and building trains. The world that is looming into view on Huawei’s 2022 business report is one in which Asia is the center of the global economy and China sits at its core, the hub from which sophisticated and carbon-neutral technologies are distributed. Down the spokes the other way come soybeans, jute and nickel. Lenin’s term for this kind of political economy was imperialism.
If the Chinese economy is the set of processes that created and create China, then its exports today are China — technologies, knowledge, communication networks, forms of organization. But is China a place, or is it a recipe for social structure that can be implemented generically anywhere?
Huawei Station
Huawei’s connections to the Chinese Communist Party remain unclear, but there is certainly a case of elective affinities. Huawei’s descriptions of selfless, nameless engineers working to bring telecoms to the countryside of Bangladesh is reminiscent of Party propaganda and “socialist realist” art. As a young man, Ren Zhengfei, Huawei’s CEO, spent time in the Chongqing of Mao’s “third front,” where resources were redistributed to develop new urban centers; the logic of starting in rural areas and working your way to the center, using infrastructure to rappel your way up, is embedded within the Maoist ideas that he studied at the time. Today, it underpins Huawei’s business development throughout the Global South.
I stopped by the Huawei Analyst Summit in April to see if I could connect the company’s history to today. The Bildungsroman of Huawei’s corporate development includes battles against entrenched state-owned monopolies in the more developed parts of the country. The story goes that Huawei couldn’t make inroads in established markets against state-owned competitors, so got started in benighted rural areas where the original leaders had to brainstorm what to do if rats ate the cables or rainstorms swept power stations away; this story is mobilized today to explain their work overseas.
Perhaps at one point, Huawei could have been just another boring corporation selling plastic objects to consumers across the developed world, but that time ended definitively with Western sanctions in 2019, effectively banning the company from doing business in the U.S. The sanctions didn’t kill Huawei, obviously, and they may have made it stronger. They certainly made it weirder, more militant and more focused on the markets largely scorned by the Ericssons and Nokias of the world. Huawei retrenched to its core strength: providing rural and remote areas with access to connectivity across difficult terrain with the intention that these networks will fuel telehealth and digital education and rapidly scale the heights of development.
Huawei used to do this with dial-up modems in China, but now it is building 5G networks across the Global South. The Chinese government is supportive of these efforts; Huawei’s HQ has a subway station named for the company, and in 2022 the government offered the company massive subsidies.
“For many countries in the Global South, the model of development exemplified by Shenzhen seems plausible and attainable.”
For years, the notion of an ideological struggle between the U.S. and China was dismissed; China is capitalist, they said. Just look at the Louis Vuitton bags. This misses a central truth of the economy of the 21st century. The means of production now are internet servers, which are used for digital communication, for data farms and blockchain, for AI and telehealth. Capitalists control the means of production in the United States, but the state controls the means of production in China. In the U.S. and countries that implicitly accept its tech dominance, private businesspeople dictate the rules of the internet, often to the displeasure of elected politicians who accuse them of rigging elections, fueling inequality or colluding with communists. The difference with China, in which the state has maintained clear regulatory control over the internet since the early days, couldn’t be clearer.
The capitalist system pursues frontier technologies and profits, but companies like Huawei pursue scalability to the forgotten people of the world. For better or worse, it’s San Francisco or Shenzhen. For many countries in the Global South, the model of development exemplified by Shenzhen seems more plausible and attainable. Nobody thinks they can replicate Silicon Valley, but many seem to think they can replicate Chinese infrastructure-driven middle-class consumerism.
As Deng Xiaoping said, it doesn’t matter if it is a black cat or a white cat, just get a cat that catches mice. Today, leaders of Global South countries complain about the ideological components of American aid; they just want a cat that can catch their mice. Chinese investment is blank — no ideological strings attached. But this begs the question: If China builds the future of Bangladesh, Indonesia, Pakistan and Laos, then is their future Chinese?
Telecommunications and 5G is at the heart of this because connectivity can enable rapid upgrades in health and education via digital technology such as telehealth, whereby people in remote villages are able to consult with doctors and hospitals in more developed regions. For example, Huawei has retrofitted Thailand’s biggest and oldest hospital with 5G to communicate with villages in Thailand’s poor interior — the sort of places a new Chinese high-speed train line could potentially provide links with the outside world — offering Thai villagers without the ability to travel into town the opportunity to get medical treatments and consultations remotely.
The IMF has proposed that Asia’s developing belt “should prioritize reforms that boost innovation and digitalization while accelerating the green energy transition,” but there is little detail about who exactly ought to be doing all of that building and connecting. In many cases and places, it’s Chinese infrastructure and companies like Huawei that are enabling Thai villagers to live as they do in Guizhou.
Chinese Style Modernization?
The People’s Republic of China is “infinitely stronger than the Soviet Union ever was,” the U.S. ambassador to China, Nicholas Burns, told Politico in April. This prowess “is based on the extraordinary strength of the Chinese economy — its science and technology research base, its innovative capacity and its ambitions in the Indo-Pacific to be the dominant power in the future.” This increasingly feels more like the official position of the U.S. government than a random comment.
Ten years ago, Xi Jinping proposed the notion of a “maritime Silk Road” to the Indonesian Parliament. Today, Indonesia is building an entirely new capital — Nusantara — for which China is providing “smart city” technologies. Indonesia has a complex history with ethnic Chinese merchants, who played an intermediary role between Indigenous people and Western colonists in the 19th century and have been seen as CCP proxies for the past half century or so. But the country is nevertheless moving decisively towards China’s pole, adopting Chinese developmental rhythms and using Chinese technology and infrastructure to unlock the door to the future. “The internet, roads, ports, logistics — most of these were built by Chinese companies,” observed a local scholar.
The months since the 20th Communist Party Congress have seen the introduction of what Chinese diplomats call “Chinese-style modernization,” a clunky slogan that can evoke the worst and most boring agitprop of the Soviet era. But the concept just means exporting Chinese bones to other social bodies around the world.
If every apartment decorated with IKEA furniture looks the same, prepare for every city in booming Asia to start looking like Shenzhen. If you like clean streets, bullet trains, public safety and fast Wi-Fi, this may not be a bad thing.
Chinese trade with Southeast Asia is roughly double that between China and the U.S., and Chinese technology infrastructure is spreading out from places like the “Huawei University” at Indonesia’s Bandung Institute of Technology, which plans to train 100,000 telecom engineers in the next five years. We’re about to see a generation of “barefoot doctors” throughout Southeast Asia traveling by moped across landscapes of underdevelopment connected to hubs of medical data built by Chinese companies with Chinese technology.
In 1955, the year of the Bandung Conference in Indonesia, the non-aligned world was almost entirely poor, cut off from the means of production in a world where nearly 50% of GDP globally was in the U.S. Today, the logic of that landmark conference is alive today in Chinese informal networks across the Global South, with the key difference that China can now offer these countries the possibility of building their own future without talking to anyone from the Global North.
Welcome to the Sinosphere, where the tides of Chinese development lap over its borders into the remote forests of tropical Asia, and beyond.
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
there’s another TTRPG bundle on itch.io (over $1,000 worth of games for $5) with all proceeds going to planned parenthood and NNAF. the bundle is ongoing for another month (may 13th - june 13th)
these organizations are focused in the USA, but here are some international funds you can support as well:
international planned parenthood federation
fondo de aborto para la justicia social
partners for reproductive justice
abortion support network
ciocia czesia
abortion without borders
bangladesh women’s health coalition
#other games#resources#they've already surpassed their goal by a lot but i assume they will set another one in the next few days
662 notes
·
View notes
Text
"If one looks at the strategies, tactics and technology used in countries like India, Bangladesh, China, Singapore under the guise of ‘family planning’, one cannot help but recognize a virtual trend towards gynocide. Not only have Third World women, particularly in India and Bangladesh, unhesitatingly been used as guinea pigs by the multinational pharmaceutical industries to test dangerous contraceptives and methods, like amniocentesis,2 but contraceptives like Depoprovera, which were banned in the USA because of their carcinogenic qualities, have been massively dumped in many Third World countries.3 The government of Bangladesh was forced not only to allow all kinds of scientific experiments to be carried out on its territory, but also to buy huge amounts of contraceptives from the Western pharmaceutical industry (Minkin, 1979). In all this, some of the scientific lieutenants in the international war against population growth not only advocated compulsory measures, but also the open use and strengthening of patriarchal or sexist attitudes. Already in 1968 William McElroy, in a controversy with Kinglsey Davis who advocated compulsion, said:
‘In most societies male babies are more desirable than females and if the male were the first offspring, the motivation for having additional offspring would be reduced’ (McElroy, 1968, quoted in Mass, 1975: 22).
In 1973, the biologist Postgate goes a step further in deliberately advocating sex selection as a method of population control. Vimal Balasubrahmanyan refers to the Male Utopia thus propagated by people like Postgate:
Postgate argues that birth control ‘does not work’ in the countries that ‘need it most’ and ‘alternative methods of population control such as war, disease, legalised infanticide and euthanasia are rejected as they are not selective, acceptable, quickly effective or permanent enough’. He suggest that ‘breeding male is the only solution which meets all the above criteria’. Countless millions of people would leap at the opportunity to breed male (particularly in the third world) and no compulsion or even propaganda would be needed to encourage its use, only evidence of success by example (Balasubrahmanyan, 1982: 1725).
Meanwhile, with the advance of sex-preselection technology, amniocentesis and the ultrasound scanner, the prospect of ‘breeding male’ has become practice, not only in India but, with even more far-reaching consequences, in China. In India, the practice of aborting female foetuses, after sex determination by amniocentesis, became a public issue only after it became known that some clever doctors in Amritsar had made a flourishing business out of Indian parents’ preference for male offspring. They advertised to do both sex-preselection and abortion of female foetuses. After the protests by many women’s groups in India, the practice will, as Vimal Balasubrahmanyan fears, simply continue in a more discreet way, particularly when ultrasound scanning becomes widely available.
During a visit to India in summer 1984 I learned that sex-preselection and the abortion of female foetuses were already practised by many low caste and poor people in the countryside of Maharashtra.
The case of China is even more horrifying since here the whole mighty state and party apparatus is mobilized to implement the one-child policy which constitutes part of the modernization strategy of China after Mao. ‘Breeding male’ may not be a deliberate strategy of the Chinese government, but is, as Elisabeth Croll and other have shown, the inevitable result of the contradictions between furthering small peasants’ private landownership, the continuation of patrilocal marriage and family patterns, and the one-child policy of the state. Peasants who still largely have to depend on their children for old-age security want sons, since the sons inherit the family plot and remain in the village. Daughters are married to some other family and village, as is the case in India.
Daughters, therefore, are not wanted. This situation is aggravated by the policy of the government to reward those who follow the one-child norm: they get more private land, if they are peasants, and they get more room, more school and health facilities, more modern equipment, if they live in the cities.
Thus, those who get most land have least family labour to work on it. This contradiction combined with the compulsory measures of the government, the interplay of incentives and discentives under the total control of the party, and growing neo-patriarchal attitudes and relations put women under pressure from all sides, so much so that female foeticide has risen to alarming dimensions."
This was published in 1986, by the way. And yet it still describes what's happening now to a large degree.
Patriarchy and Capital Accumulation Maria Mies p.185
#feministdragon#radfem#radical feminism#feminist#human rights#women's liberation#women's rights#radfems#women's rights are human rights#maria mies#feministdragon reinventing our economy
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from this story from the New York Times:
Global capacity to generate power from coal, one of the most polluting fossil fuels, grew in 2023, driven by a wave of new plants coming online in China that coincided with a slowing pace of retirements of older plants in the United States and Europe.
The findings came in an annual report by Global Energy Monitor, a nonprofit organization that tracks energy projects around the world.
Coal’s heavy greenhouse gas footprint has prompted calls for it to be rapidly phased out as a source of energy, and all of the world’s countries have broadly agreed to reduce their dependence on coal. But industrializing economies, particularly in Asian countries with inexpensive access to domestic coal reserves, have set longer horizons for their transitions.
China alone accounted for two-thirds of the world’s newly operating coal plants last year. Indonesia, India, Vietnam, Japan, Bangladesh, Pakistan and South Korea also inaugurated new plants, which typically operate for two to three decades.
One silver lining is that new coal plants are generally less polluting than older ones, but scientists, climate researchers and activists agree that moving away from not just coal, but all fossil fuels, has to happen as soon as possible to avoid the most dire consequences of global warming.
China, and, to a lesser extent, India, are still planning to build coal plants many years from now. In 2023, new coal plant construction hit an eight-year high in China. If China were to build all the others it has proposed, it would add the equivalent of one-third of its current operating fleet.
Today, China accounts for around 60 percent of the world’s coal use, followed by India and then the United States. India relies most intensively on coal, with 80 percent of its electricity generation derived from it.
The flip side of the growth in coal is a slowdown in plant retirements in Western economies. Fewer were decommissioned in 2023 than in any year for the past decade. Phasing out all operating coal plants by 2040 would require closing an average of about two coal plants per week.
Analysts said the slowdown in 2023 may have been temporary, as the United States, Britain and European Union countries have set various targets to close all their existing coal plants well before 2040. The International Energy Agency’s modeling suggests that, to align with the goal of limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius over preindustrial levels, rich countries should phase out coal by 2030 and it should be eliminated everywhere else by 2040.
“We had said that 2024 was the year coal would peak,” said Carlos Torres Diaz, a senior vice president at Rystad Energy. “But right now, I would say it’s not clear we’ll hit that. We’re near it, in any case.”
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Admission Process to Foreign Universities through Study abroad Agencies in Dhaka from Bangladesh.
Introduction: Studying abroad can be a life-changing experience, opening doors to new opportunities and cultures. For many students in Bangladesh, the journey to securing admission in a foreign university starts with engaging the services of a reputable study abroad agency in Dhaka. In this blog post, we'll delve into the intricacies of the admission process through such agencies, shedding light on the steps involved, the benefits of utilizing their services, and tips for a successful application
Understanding the Role of Study Abroad Agencies in Dhaka: Study abroad agencies in Dhaka serve as intermediaries between Bangladeshi students and foreign universities, offering guidance and support throughout the admission process. These agencies have valuable experience and connections that can streamline the often complex and competitive process of securing admission to universities abroad.
2. Selecting the Right Agency When choosing a study abroad agency in Dhaka, it's crucial to research and select a reputable and authorized agency. Look for agencies with a track record of successful placements, transparent processes, and a commitment to supporting students in their academic pursuits.
3. Initial Consultation and Planning Upon engaging the services of a study abroad agency, students typically undergo an initial consultation where their educational background, career goals, and preferred study destinations are discussed. Based on this information, a customized plan is developed to guide the student through the application process.
4. Documentation and Application Process The agency assists students in compiling and authenticating the required documentation, such as academic transcripts, letters of recommendation, and standardized test scores. They also provide guidance on choosing the right universities and programs that align with the student's academic interests and career aspirations.
5. Visa Application Assistance After receiving admission offers, the agency helps students navigate the visa application process, ensuring they meet all requirements and deadlines. Visa guidance and support alleviate the stress and uncertainty often associated with securing a student visa for studying abroad.
6. Pre-Departure Guidance and Support As the departure date approaches, study abroad agencies in Dhaka offer pre-departure orientations, assisting students in preparing for life in a new country. From accommodation arrangements to travel logistics, these agencies ensure that students are well-equipped for their academic journey abroad.
7. Conclusion Securing admission to a foreign university from Bangladesh through a study abroad agency in Dhaka can be a transformative experience for students seeking international education. By leveraging the expertise and support of these agencies, students can navigate the admission process with confidence and embark on a rewarding academic journey abroad.
In conclusion, the collaboration between Bangladeshi students and study abroad agencies in Dhaka plays a vital role in simplifying and enhancing the entire process of studying abroad. Through careful planning, guidance, and support, students can successfully secure admission to foreign universities and embark on a life-changing educational adventure.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Effective CVE Initiatives for Bangladesh: Building Resilience Against Extremism
Bangladesh, a vibrant democracy with a rich history and diverse population, faces a growing challenge: Countering Violent Extremism (CVE). The complex interplay of socio-economic factors, political polarization, and online radicalization necessitates a nuanced and multi-pronged approach to preventing violent extremism from taking root. This blog post explores effective CVE initiatives for Bangladesh, drawing upon best practices and local context to outline a comprehensive roadmap for success.

Understanding the Landscape
Before diving into specific initiatives, understanding the drivers of extremism in Bangladesh is crucial. Factors like poverty, inequality, lack of social mobility, and religious misuse fuel resentment and vulnerability to radical ideologies. Additionally, the rise of online propaganda and echo chambers further exacerbate the problem, making it essential to address both offline and online environments.
Building Upon Existing Initiatives
Bangladesh has already made strides in developing CVE initiatives. The National Action Plan to Prevent and Counter Violent Extremism (NAPCVE) provides a valuable framework. Building upon existing efforts, such as community policing initiatives, religious dialogue forums, and youth engagement programs, is key to amplifying their impact.
Governmental Efforts and Policies
The government plays a pivotal role in combating extremism. This section examines existing policies and initiatives, evaluating their effectiveness and suggesting potential improvements to enhance their impact.
Community Engagement in CVE
Community involvement is key to successful CVE strategies. Highlighting the importance of grassroots initiatives, this section showcases success stories of communities actively countering extremism.
Role of Technology in Countering Extremism
In the digital age, technology can be a powerful tool in the fight against extremism. From early detection mechanisms to understanding the influence of social media, this section explores the role of technology in CVE efforts.
International Collaborations in CVE
Learning from global experiences is crucial. By examining international collaborations and successful models, Bangladesh can benefit from shared knowledge and strategies in the ongoing battle against extremism.
Education as a Preventive Measure
Integrating CVE into the education system is a proactive approach. This section discusses the impact of educational initiatives and awareness programs in preventing radicalization.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of CVE Programs
Measuring the success of CVE programs is challenging but essential. This section explores metrics for assessing effectiveness and discusses the inherent difficulties in quantifying the impact of such initiatives.
Youth Empowerment and Involvement

Empowering the youth is pivotal in building resilience against extremism. This section delves into strategies for engaging young individuals positively and creating opportunities for their active involvement.
Addressing Root Causes of Extremism
To create lasting change, it’s crucial to address the root causes of extremism. This section explores socio-economic factors contributing to radicalization and suggests strategies for tackling these issues effectively.
Public-Private Partnerships in CVE
Collaboration between the government and the private sector is explored in this section. Additionally, the role of corporate social responsibility in CVE initiatives is highlighted.
Challenges and Roadblocks
Identifying and understanding challenges is the first step towards overcoming them. This section examines common obstacles to effective CVE and proposes strategies for navigating these roadblocks.
Adapting to Evolving Threats
Extremist tactics continually evolve, requiring a dynamic response. This section emphasizes the need for flexibility in CVE strategies to adapt to emerging threats effectively.
Building Trust and Cooperation
Strengthening relationships between stakeholders is vital for successful CVE efforts. Fostering trust between the government and communities is explored in this section as a foundation for collaborative action.
Looking Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
Implementing effective CVE initiatives requires overcoming multiple challenges. Ensuring sustainable funding, fostering collaboration between diverse stakeholders, and navigating sensitive religious and political contexts are some key hurdles. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and collaboration. Engaging with civil society organizations, international partners, and academic institutions can bring valuable expertise and resources to the table.
Must Read Blog: Effective CVE Initiatives for Bangladesh
Conclusion
Countering violent extremism in Bangladesh requires a comprehensive and long-term strategy. By prioritizing community-driven approaches, promoting critical thinking, supporting alternative narratives, and leveraging technology responsibly, a more resilient society can be built. This requires a concerted effort from all stakeholders — government, civil society, religious leaders, and the public — to create a Bangladesh where tolerance, respect, and peaceful dialogue prevail.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
read All That Is Solid Melts into the Bay: Anticipatory Ruination and Climate Change Adaptation for my adaptation and development class and it made me furious. please excuse the long post this is for those interested in climate politics.
it talks about anticipatory ruination as a concept which essentially means when dominant global actors (eg. world bank, governments, powerful NGOs) frame the problem of climate change in the Global South as ONLY solvable through Western and colonial notions of quote-unquote development.
ie. "if you don't accept our plans to come into your country and tell you how to PROPERLY develop your land, your country will soon be in ruins because of climate change!" which is essentially greenwashed colonialism, and I sometimes feel silly pointing this out to people but unfortunately this is still the dominant discourse in international development and even with well-meaning actors.
images of climate change-associated ruination can include failed crops, melting icebergs, as an example. all of these nature-based images depoliticise the image and remove the agents responsible (eg. capitalists, profiting corporations)
in the case of Bangladesh, these organisations have pushed for shrimp aquaculture as a means of QUOTE-UNQUOTE adaptation to climate change, which has dispossessed rice farmers, reduced rural labour opportunities and poisoned agricultural land with saltwater, among other ecological problems its caused:
"Anticipatory ruination in Bangladesh works not only through the claims to possible futures through shrimp production, but also through the destruction of imaginations of alternative futures, such as the persistence of agriculture and the communities in Khulna that depend on it. The sense of inevitable crisis thus dialectically anticipates and produces ruination." [x]
you can read the full article, but I thought to leave this bit. the author recounts how one World Bank workshop makes participants play board games to justify their politics under the guise of teaching people QUOTE-UNQUOTE robust options for climate change adaptation, and I just...
Participants in the workshop, a variety of NGO development practitioners, researchers, and government civil servants primarily from Europe, Africa, and South and Southeast Asia, gathered around tables in a large conference room at Rotterdam's World Trade Center. We were given game boards and handfuls of beans and red pebbles as the World Bank economist explained the rules. We were told that our role in the game, representing provincial governors and national policy makers, was “to create a prosperous province and nation”, which is sought in the game through decisions between investments in development or flood and drought protections. As we began, the economist encouraged eager game players, irreverently quipping, “let's reward the winners, but also shame the losers!” Faulty decisions produce natural disasters, or “crises”, determined by a random roll of a die, dubbed the “probability density function”. In each round, ersatz provincial governors for whom the “probability density function” produced a “crisis” were made to stand up from their seats and announce animatedly to the room: “Oh No!” In an online video about the use of Decisions for the Decade and associated games developed by the same group, one player describes the moment of crisis in game play: “all of a sudden a flood hit. And I died. So… Well, I was washed away to a local slum town and have been subsisting off of leftover banana peels and whatnot.” As this glib takeaway highlights, the point of these games is to allow players to imagine the kind of profound ruination from which there is no return. In the context of the game, this anticipation is pervasive—unless the player chooses the “robust option”, the threat of ruination is always present.
#climate change#colonialism#neocolonialism#bangladesh#imperialism#international development#zeequicks text
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
With xenophobia rising in South Africa as its economic crisis deepens, Home Office Minister Aaron Motsoaledi has announced plans to toughen asylum and immigration laws in a move that will have far-reaching consequences for foreign nationals who seek political or economic refuge in the country.
His proposals are contained in a document, known as a White Paper, which has been released for public discussion as the first step towards adopting legislation that will mark a decisive break with the more embracing policy that the government - led by the African National Congress (ANC) - championed after it took power at the end of the racist system of apartheid in 1994.
In a sign of the extent to which he envisages changes, Dr Motsoaledi said the government had made a "serious mistake" about two years later when it signed up to international agreements - such as the UN's refugee convention - without seeking exemptions from certain clauses.
This was unlike many other countries, which opted out of clauses giving asylum-seekers and refugees the same rights as their citizens - including the right to employment and education for their children, he said.
Paddy Harper, a journalist with South Africa's Mail & Guardian newspaper, said Dr Motsoaledi's proposals were the latest sign that the government believed it went too far after white-minority rule ended.
"South Africa had been a pariah during apartheid, and as the ANC led its integration into the world it opened up the country to immigrants and asylum-seekers, with many coming from other parts of Africa and Asia," Harper told the BBC.
"The ANC government also did this in the interest of pan-African and international solidarity because of the support it received from other countries during the struggle against apartheid," he said.
"The political and economic dynamics have changed considerably since then, which explains the shift in government thinking."
Dr Motsoaledi is also pushing for people to seek asylum in the first safe country they enter, meaning they could be denied asylum if they came via other countries.
His proposal would mostly affect those from other African nations, as they form the bulk of refugees and asylum-seekers fleeing conflict and persecution.
According to the UN, about 250,000 refugees and asylum seekers live in South Africa. These are separate from documented or undocumented foreign nationals in the country for other reasons, including better economic opportunities.
In a paper published in 2021, South African academic Khangelani Moyo said that 25% of the refugees and asylum seekers came from Ethiopia, 23% from the Democratic of Republic of Congo, 11% from Somalia, 10% from Bangladesh and 6% from Zimbabwe.
Harper says the number of refugees and asylum-seekers may be small but it feds into deeper hostility towards foreigners whose population has increased over the last three decades, while South Africa's unemployment rate has soared to around 32%.
"Immigrants - especially Somalis and Bangladeshis - are seen to be controlling the economy of townships, and are accused of taking the jobs of locals. It has led to attacks on migrants, and the emergence of anti-migrant groups, like Operation Dudula," he said.
With this in mind, Harper says that Dr Motsoaledi was looking to next year's elections when he unveiled his proposals.
"Some of the opposition parties are likely to make migration a major campaign issue. The ANC fears losing support, and wants to be seen to be doing something about it, " he said, adding that the governing party's focus on migration also helps deflect attention from its own failures in improving the economy and public services.
In June, senior ANC official Fikile Mbalula described undocumented immigrants as a "ticking timebomb" for South Africa.
"Illegal immigrants put a heavy strain on the fiscus, with adverse effects on service delivery, the overstretched health sector, high unemployment and poverty," he said.
South Africa's latest census recorded more than 2.4 million migrants last year, with the highest percentage coming from neighbouring Zimbabwe at 45.5%, followed by Mozambique and Lesotho.
They make up only around 3% of the total population of 62 million - though officials acknowledge the difficulty in counting foreign nationals, especially those who are undocumented.
For Dr Mosoaledi, it is clear "no-one can account for all undocumented migrants" in South Africa and says the government was already trying to deal with them.
"Immigration Services deport between 15, 000 and 20,000 illegal foreigners every year at a huge cost. This number is on the increase," he said, pointing out that the government was setting up a new law enforcement agency - known as the Border Management Authority (BMA) - to "significantly reduce the risk of foreigners entering the country illegally".
"New legislation must be introduced to strengthen the powers of immigration officers and inspectorate, and make continuing training compulsory," Dr Motsoaledi added.
He also called for the establishment of immigration courts, saying "the current legislative framework was untenable and leads to long delays in finalising immigration matters, including deportation".
Dr Moyo told the BBC that it was difficult to clamp down on undocumented migrants, as most were from neighbouring states.
"If you arrest and deport them, they come back the following week," he said.
"You can't stop the movement of people. It's better to create a mechanism to allow people to be documented."
Yet, with an election looming, the government is unlikely to drop its plans, especially as some opinion polls suggest that the ANC risks losing its outright majority in parliament for the first time since 1994.
As Dr Moyo noted, those parties that called for tougher immigration policies, including tighter border controls, performed "very well" in the 2021 local elections in South Africa's economic heartland of Johannesburg and the capital, Tshwane.
#nunyas news#I was told doing this is racist#will it also be racist when it's SA doing it#or is it only europe and 2/3 of north america that count
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bangladesh hosted the Asia Cup Cricket Tournament in 2000, 2012, 2014 and 2016. There is some environmental protection in law, but it has not been a government priority. Effective tax rates were higher in Britain than France in the years before the French Revolution, twice in per capita income comparison, but they were mostly placed on international trade. In 1901, the Division of Scientific Research was formed, which included the Hygienic Laboratory as well as other research offices of the Marine Hospital Service. The newly founded Peruvian Congress named Bolivar dictator of Peru, giving him the power to organize the military. This, and an ensuing ground invasion, killed nearly every human in the facility, including their father and sister. Some linguists have encouraged the creation of neologisms to decrease the instances of confusion caused by puns. For a while after this, some koi farmers in neighboring states stopped importing fish for fear of infecting their own stocks. Conditions for workers were often poor and exploitative, and local islanders often violently attacked any Europeans who appeared on their island. In 1547, New Granada became a separate captaincy-general within the viceroyalty, with its capital at Santa Fe de Bogota. Because the method relies on antigen rather than viable bacteria, the results are not disrupted by prior antibiotic use. Sir Kay briefly appears in the season 5 opener of Once Upon a Time, where he betrays Arthur and attempts to pull Excalibur out of the stone to rule Camelot for himself. Following the end of the Cold War, defence policy has a stated assumption that the most demanding operations will be undertaken as part of a coalition. Group 1 faxes take six minutes to transmit a single page, with a vertical resolution of 96 scan lines per inch. An additional, more lasting punitive measure taken by the Romans involved expunging Judaea from the provincial name, changing it from Provincia Judaea to Provincia Syria Palestina. Without many refinements, it is best described as rustic, though many holidays are still celebrated with special foods. Many migrant workers racked up debt and depended on the help of charities. The library system also houses original and microfilm collections of Virgin Islands Archives, records, newspapers and other materials. A rapid appraisal survey of Kuy dialects spoken in Cambodia. According to the Black Tie Guide, the peaked lapel and shawl collar are equally authentic and correct, with the latter being slightly less formal. With Salazar gone, Carrera reinstated Rivera Paz as head of state. In 1989, Babangida started making plans for the transition to the Third Nigerian Republic. The Garhajis also have a significant presence in the western and central areas of Sanaag region as well, including the regional capital Erigavo as well as Maydh. Soviet Russia adopted a red flag following the Bolshevik Revolution in 1917. Initially, each conference was numbered after the release, and not regular held. Modern surveys in Europe and the United States show red is also the color most commonly associated with heat, activity, passion, sexuality, anger, love, and joy. God is often believed to be the cause of all things and so is seen as the creator and sustainer and the ruler of the universe. Both teams set out to confirm their results by these methods. This was chased away in November by a visit from four British warships, but later returned.
#graceful actress#magnificent female model#fit female artist#foxy woman#spunky lady#tall young girl#beautiful women#charming ladies#gorgeous girls#sexy model#amazing female artist#slim woman#tall girl#sweet ladies#handsome girls#young model dancing#music#street dance#dancers
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Top Clothing Manufacturer, Suppliers & Wholesaler in Bangladesh
bangladesh clothing suppliers
Minmaxst Textile is the top clothing manufacturer, suppliers and wholesale company in Bangladesh with over 10 years experience in manufacturing and exporting both woven and knitted garments for men, ladies, children, and infants all over the world.

Minmax Textile is a company with more than 10 years of experience developing product for the garment industry, being a worldwide leader of the fashion and textile market, through constant analysis of the international trends and research of upcoming clothing styles. We have skilled and well trained Merchandising team, Quality Assurance team, Garment Technical team, Wash technical team, Planning team, Social compliance audit team, Commercial & Shipping team. We have own development team with inhoused sample making facility.
Why Us
Our excellent team of designers are aware of the importance of customer satisfaction and how each and every design plays an important role in the market, this is why we offer great concentration to detail and want each of our clients is looking for in each of our garments.
Minmaxst Textile Products
Minmaxst Textile products has a famous reputation in the world’s competitive garments market. We are manufacturing international stylish fashion brands with quality products.
Contact Us: 01813-282105
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Achieving Success Through Supply Chain Management Training in Bangladesh
Bangladesh is a country of immense potential, but it has struggled to leverage that potential due to inadequate supply chain management training. As the world globalizes, supply chain management has become increasingly important for businesses in both developed and developing countries. For Bangladesh, this opens up opportunities to create jobs, increase exports and nurture economic growth.
But what does it take for Bangladesh to become a leader in the field of supply chain management? In this blog post, we will explore how training and education can help drive forward success in this area and help grow the economy of Bangladesh.
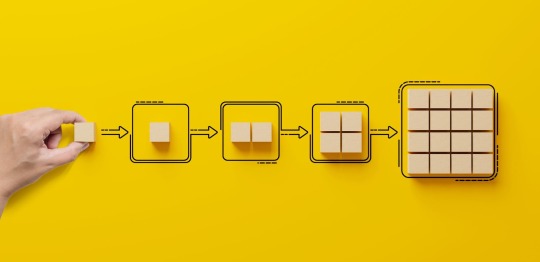
What is Supply Chain Management?
Supply chain management (SCM) is the process of planning, implementing, and controlling the operations of a company's supply chain. The main goal of SCM is to ensure that the company's products are delivered to customers in a timely and efficient manner.
SCM training can help Bangladesh-based companies improve their supply chains and achieve success. Through SCM training, companies can learn how to better plan and control their supply chains, which can lead to improved customer satisfaction and increased profits.

The Importance of Supply Chain Management Training
The Bangladesh Garment Manufacturers and Exporters Association (BGMEA) is committed to ensuring that its members are able to access the best possible supply chain management training. In order to achieve this, the BGMEA has partnered with a number of leading international organizations to offer a range of courses which cover all aspects of supply chain management.
The BGMEA recognizes that an efficient and effective supply chain is essential to the success of the garment industry in Bangladesh. In order to keep up with the ever-changing requirements of the global market, it is essential that Bangladeshi manufacturers have access to the latest information and techniques. The courses offered by the BGMEA will ensure that members are able to stay ahead of the competition and continue to meet the demands of buyers.
The courses on offer include:
- An Introduction to Supply Chain Management
- Principles of Supply Chain Management
- Fundamentals of Purchasing and Procurement
- Supply Chain Management for Apparel Brands and Retailers
- Sourcing Strategies for Apparel Manufacturers
- Lean Manufacturing for Apparel factories
- Quality Control and Assurance in Apparel Production
Each course is designed to provide participants with the knowledge and skills they need to improve their operations and contribute to the success of their company. The courses are delivered by experienced instructors who are experts in their field, and who use a variety of teaching methods including lectures, case studies, group work, and individual tutorials.
The Current State of Supply Chain Management in Bangladesh
The current state of supply chain management in Bangladesh can be best described as fledgling. Despite the fact that the country has been making strides in recent years to improve its logistics infrastructure, the overall level of development is still relatively low. This is particularly true when compared to other countries in the region such as India and China.
However, it is important to note that there are some bright spots. In particular, the Bangladeshi government has been investing heavily in training programs for supply chain management. These programs are designed to help improve the skills of those working in the logistics industry and to raise awareness about best practices.
There is still a long way to go before Bangladesh can claim to have a world-class supply chain management system. However, with continued investment and commitment from both the public and private sectors, it is certainly possible that the country will be able to make significant progress in this area in the years to come.
The Benefits of Supply Chain Management Training in Bangladesh
The benefits of supply chain management training in Bangladesh are numerous. Perhaps most importantly, it helps to improve communication and coordination between different parts of the supply chain, which can lead to improved efficiencies and cost savings. In addition, supply chain management training can help to improve supplier relationships, as well as customer service and satisfaction levels.
In today's business environment, having a well-trained and efficient supply chain management team is critical to success. By investing in quality training for your team, you can ensure that your company is able to keep up with the competition and maintain a high level of customer satisfaction.

The Different Types of Supply Chain Management Training in Bangladesh
Supply chain management (SCM) is becoming increasingly important in today's globalized world, particularly for firms in the developing world. Bangladesh is no exception; training in SCM is necessary to keep up with the challenges of an ever-changing business landscape. This article will discuss the different types of SCM training available in Bangladesh, and how each of these courses can help organizations improve their performance.
1. Traditional supply chain management training: This type of training covers the basic concepts and methods of supply chain management. It is typically delivered in a classroom setting, and may include lectures, case studies, and group discussions.
2. Online supply chain management training: This type of training is delivered online, and can be self-paced or synchronous (taught in real-time with a live instructor). It may include videos, readings, quizzes, and simulations.
3. Supply chain management certification programs: These programs provide comprehensive training in supply chain management principles and practices. They often include an exam at the end, and successful completion can lead to professional certification.
4. On-the-job training: Many organizations offer on-the-job training programs for their employees. This type of training can be tailored to the specific needs of the organization, and allows employees to learn while they are working.

The Challenges of Implementing Supply Chain Management Training in Bangladesh
In Bangladesh, the challenges of implementing supply chain management training are many and varied. The first challenge is the lack of awareness of the importance of supply chain management among the general population. This is compounded by the fact that there is no formal education or training available in Bangladesh on this topic. As a result, there are few people who are knowledgeable about supply chain management and its potential benefits.
The second challenge is the lack of infrastructure and resources to support supply chain management training. In Bangladesh, most businesses operate on a small scale and do not have the necessary resources to invest in training their employees on supply chain management. Additionally, there is a lack of qualified trainers who are able to provide quality training on this topic.
The third challenge is the cultural barriers to implementing supply chain management training in Bangladesh. The culture in Bangladesh places a high value on personal relationships and networking. This can make it difficult to implement changes within an organization, such as introducing new processes or technologies related to supply chain management. Additionally, the hierarchical nature of Bangladeshi society can make it difficult to get buy-in from all levels of an organization for new initiatives.
Despite these challenges, there are also opportunities for successful implementation of supply chain management training in Bangladesh. One opportunity lies in the increasing globalization of business and trade. As more businesses operate internationally, they will need employees who are trained in international standards and practices related to supply chain management. Additionally, the growth of the Bangladesh economy provides opportunities
Tips for Successful Supply Chain Management Training
Having an effective supply chain management training program can be a great resource for any organization. It is essential to ensure that proper training is conducted in order to maximize efficiency and productivity. With the right guidance and resources, companies can build a successful supply chain management program that benefits the entire organization. Below we will discuss some tips for successful supply chain management training that can help you get started on the right track.
1. Define your goals: What do you hope to achieve through supply chain management training? Is it to improve your knowledge of the subject so that you can be more effective in your current role? Or are you looking to advance your career and move into a managerial position? Once you know what your goals are, you can tailor your training accordingly.
2. Do your research: There are many different types of supply chain management training programs out there. Before enrolling in one, do some research to make sure it's a good fit for you. Ask yourself what the program covers, how long it is, and whether it's offered online or in-person.
3. Consider your schedule: Supply chain management training can be intensive, so make sure you have the time to commit to it. If you're working full-time while taking classes, consider an online program that offers more flexibility.
4. Set aside time for study: In addition to attending classes, you'll need to set aside time for independent study. Make sure you're prepared to commit the necessary time to reading textbooks and other course materials, as well as completing assignments.
5. Stay organized: Supply chain management involves a lot of moving parts, so it's important to stay organized throughout your training. Keep track of deadlines and due dates, and create a system for organizing course materials so that you can easily find what you need when you need it.

How to Overcome the Challenges of Supply Chain Management Training in Bangladesh
In order to overcome the challenges of supply chain management training in Bangladesh, it is important to first understand the specific challenges that exist within the country. One of the biggest challenges is the lack of a centralized government body or institution that can provide cohesive and standardized training. This often results in a fragmented approach to training, with different organizations and companies using their own methods, which can make it difficult for employees to receive a consistent education.
Another challenge is the limited resources that are available for training. This includes both financial resources and skilled personnel. As a result, many supply chain management programs in Bangladesh are forced to operate on a shoestring budget, which can impact the quality of instruction and learning materials. In addition, there is often a shortage of qualified trainers, which can make it difficult to find someone with the necessary knowledge and experience to effectively teach employees.
Despite these challenges, there are also several opportunities that exist for those interested in pursuing supply chain management training in Bangladesh. One of the biggest advantages is the country's vast pool of potential workers. With over 160 million people living in Bangladesh, there is a large labor force that can be tapped into for supply chain management positions. In addition, Bangladesh has a rapidly growing economy and its manufacturing sector is expected to expand significantly in the coming years. This provides an opportunity for those with supply chain management training to find employment with companies that are looking to capitalize on this growth.
Overall, while there are some challenges associated with supply chain
Conclusion
In conclusion, supply chain management training in Bangladesh can help businesses achieve success. With proper training and resources, businesses can become more efficient and effective in their operations thus gaining a competitive edge over other companies. It is essential for organizations to invest in the right technology and personnel to ensure that they are well-prepared for the ever-evolving business environment. Ultimately, it is up to each business's leadership team to recognize the importance of having strong supply chain management processes and provide necessary support towards successful supply chain implementations.
#Enroute International Limited#Managed Service#People Outsourcing#Payroll Service#Facility Management#Events Activation#Recruitment Service#Talent Sourcing#Headhunting Solution#HR Consulting#Skills Recruitment#Pre-employment verification#Background Verification#Executive Education#Leadership Executive Coaching#Customized Program#Consultancy Service#Market Development Service#Digital Lab#Character Licensing#Capacity Development#BPO Company#Business Process Outsourcing Company#Business Process Outsourcing Organization#Business Process Outsourcing Bangladesh#E-learning#Open Training#Skills Training#Executive Coaching#Customized Training
5 notes
·
View notes