#postgres configuration settings
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Is ChatGPT Easy to Use? Here’s What You Need to Know
Introduction: A Curious Beginning I still remember the first time I stumbled upon ChatGPT my heart raced at the thought of talking to an AI. I was a fresh-faced IT enthusiast, eager to explore how a “gpt chat” interface could transform my workflow. Yet, as excited as I was, I also felt a tinge of apprehension: Would I need to learn a new programming language? Would I have to navigate countless settings? Spoiler alert: Not at all. In this article, I’m going to walk you through my journey and show you why ChatGPT is as straightforward as chatting with a friend. By the end, you’ll know exactly “how to use ChatGPT” in your day-to-day IT endeavors whether you’re exploring the “chatgpt app” on your phone or logging into “ChatGPT online” from your laptop.
What Is ChatGPT, Anyway?
If you’ve heard of “chat openai,” “chat gbt ai,” or “chatgpt openai,” you already know that OpenAI built this tool to mimic human-like conversation. ChatGPT sometimes written as “Chat gpt”—is an AI-powered chatbot that understands natural language and responds with surprisingly coherent answers. With each new release remember buzz around “chatgpt 4”? OpenAI has refined its approach, making the bot smarter at understanding context, coding queries, creative brainstorming, and more.
GPT Chat: A shorthand term some people use, but it really means the same as ChatGPT just another way to search or tag the service.
ChatGPT Online vs. App: Although many refer to “chatgpt online,” you can also download the “chatgpt app” on iOS or Android for on-the-go access.
Free vs. Paid: There’s even a “chatgpt gratis” option for users who want to try without commitment, while premium plans unlock advanced features.
Getting Started: Signing Up for ChatGPT Online
1. Creating Your Account
First things first head over to the ChatGPT website. You’ll see a prompt to sign up or log in. If you’re wondering about “chat gpt free,” you’re in luck: OpenAI offers a free tier that anyone can access (though it has usage limits). Here’s how I did it:
Enter your email (or use Google/Microsoft single sign-on).
Verify your email with the link they send usually within seconds.
Log in, and voila, you’re in!
No complex setup, no plugin installations just a quick email verification and you’re ready to talk to your new AI buddy. Once you’re “ChatGPT online,” you’ll land on a simple chat window: type a question, press Enter, and watch GPT 4 respond.
Navigating the ChatGPT App
While “ChatGPT online” is perfect for desktop browsing, I quickly discovered the “chatgpt app” on my phone. Here’s what stood out:
Intuitive Interface: A text box at the bottom, a menu for adjusting settings, and conversation history links on the side.
Voice Input: On some versions, you can tap the microphone icon—no need to type every query.
Seamless Sync: Whatever you do on mobile shows up in your chat history on desktop.
For example, one night I was troubleshooting a server config while waiting for a train. Instead of squinting at the station’s Wi-Fi, I opened the “chat gpt free” app on my phone, asked how to tweak a Dockerfile, and got a working snippet in seconds. That moment convinced me: whether you’re using “chatgpt online” or the “chatgpt app,” the learning curve is minimal.
Key Features of ChatGPT 4
You might have seen “chatgpt 4” trending this iteration boasts numerous improvements over earlier versions. Here’s why it feels so effortless to use:
Better Context Understanding: Unlike older “gpt chat” bots, ChatGPT 4 remembers what you asked earlier in the same session. If you say, “Explain SQL joins,” and then ask, “How does that apply to Postgres?”, it knows you’re still talking about joins.
Multi-Turn Conversations: Complex troubleshooting often requires back-and-forth questions. I once spent 20 minutes configuring a Kubernetes cluster entirely through a multi-turn conversation.
Code Snippet Generation: Want Ruby on Rails boilerplate or a Python function? ChatGPT 4 can generate working code that requires only minor tweaks. Even if you make a mistake, simply pasting your error output back into the chat usually gets you an explanation.
These features mean that even non-developers say, a project manager looking to automate simple Excel tasks can learn “how to use ChatGPT” with just a few chats. And if you’re curious about “chat gbt ai” in data analytics, hop on and ask ChatGPT can translate your plain-English requests into practical scripts.
Tips for First-Time Users
I’ve coached colleagues on “how to use ChatGPT” in the last year, and these small tips always come in handy:
Be Specific: Instead of “Write a Python script,” try “Write a Python 3.9 script that reads a CSV file and prints row sums.” The more detail, the more precise the answer.
Ask Follow-Up Questions: Stuck on part of the response? Simply type, “Can you explain line 3 in more detail?” This keeps the flow natural—just like talking to a friend.
Use System Prompts: At the very start, you can say, “You are an IT mentor. Explain in beginner terms.” That “meta” instruction shapes the tone of every response.
Save Your Favorite Replies: If you stumble on a gem—say, a shell command sequence—star it or copy it to a personal notes file so you can reference it later.
When a coworker asked me how to connect a React frontend to a Flask API, I typed exactly that into the chat. Within seconds, I had boilerplate code, NPM install commands, and even a short security note: “Don’t forget to add CORS headers.” That level of assistance took just three minutes, demonstrating why “gpt chat” can feel like having a personal assistant.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
No tool is perfect, and ChatGPT is no exception. Here are a few hiccups you might face and how to fix them:
Occasional Inaccuracies: Sometimes, ChatGPT can confidently state something that’s outdated or just plain wrong. My trick? Cross-check any critical output. If it’s a code snippet, run it; if it’s a conceptual explanation, ask follow-up questions like, “Is this still true for Python 3.11?”
Token Limits: On the “chatgpt gratis” tier, you might hit usage caps or get slower response times. If you encounter this, try simplifying your prompt or wait a few minutes for your quota to reset. If you need more, consider upgrading to a paid plan.
Overly Verbose Answers: ChatGPT sometimes loves to explain every little detail. If that happens, just say, “Can you give me a concise version?” and it will trim down its response.
Over time, you learn how to phrase questions so that ChatGPT delivers exactly what you need quickly—no fluff, just the essentials. Think of it as learning the “secret handshake” to get premium insights from your digital buddy.
Comparing Free and Premium Options
If you search “chat gpt free” or “chatgpt gratis,” you’ll see that OpenAI’s free plan offers basic access to ChatGPT 3.5. It’s great for light users students looking for homework help, writers brainstorming ideas, or aspiring IT pros tinkering with small scripts. Here’s a quick breakdown: FeatureFree Tier (ChatGPT 3.5)Paid Tier (ChatGPT 4)Response SpeedStandardFaster (priority access)Daily Usage LimitsLowerHigherAccess to Latest ModelChatGPT 3.5ChatGPT 4 (and beyond)Advanced Features (e.g., Code)LimitedFull accessChat History StorageShorter retentionLonger session memory
For someone just dipping toes into “chat openai,” the free tier is perfect. But if you’re an IT professional juggling multiple tasks and you want the speed and accuracy of “chatgpt 4” the upgrade is usually worth it. I switched to a paid plan within two weeks of experimenting because my productivity jumped tenfold.
Real-World Use Cases for IT Careers
As an IT blogger, I’ve seen ChatGPT bridge gaps in various IT roles. Here are some examples that might resonate with you:
Software Development: Generating boilerplate code, debugging error messages, or even explaining complex algorithms in simple terms. When I first learned Docker, ChatGPT walked me through building an image, step by step.
System Administration: Writing shell scripts, explaining how to configure servers, or outlining best security practices. One colleague used ChatGPT to set up an Nginx reverse proxy without fumbling through documentation.
Data Analysis: Crafting SQL queries, parsing data using Python pandas, or suggesting visualization libraries. I once asked, “How to use chatgpt for data cleaning?” and got a concise pandas script that saved hours of work.
Project Management: Drafting Jira tickets, summarizing technical requirements, or even generating risk-assessment templates. If you ever struggled to translate technical jargon into plain English for stakeholders, ChatGPT can be your translator.
In every scenario, I’ve found that the real magic isn’t just the AI’s knowledge, but how quickly it can prototype solutions. Instead of spending hours googling or sifting through Stack Overflow, you can ask a direct question and get an actionable answer in seconds.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Of course, when dealing with AI, it’s wise to think about security. Here’s what you need to know:
Data Retention: OpenAI may retain conversation data to improve their models. Don’t paste sensitive tokens, passwords, or proprietary code you can’t risk sharing.
Internal Policies: If you work for a company with strict data guidelines, check whether sending internal data to a third-party service complies with your policy.
Public Availability: Remember that anyone else could ask ChatGPT similar questions. If you need unique, private solutions, consult official documentation or consider an on-premises AI solution.
I routinely use ChatGPT for brainstorming and general code snippets, but for production credentials or internal proprietary logic, I keep those aspects offline. That balance lets me benefit from “chatgpt openai” guidance without compromising security.
Is ChatGPT Right for You?
At this point, you might be wondering, “Okay, but is it really easy enough for me?” Here’s my honest take:
Beginners who have never written a line of code can still ask ChatGPT to explain basic IT concepts no jargon needed.
Intermediate users can leverage the “chatgpt app” on mobile to troubleshoot on the go, turning commute time into learning time.
Advanced professionals will appreciate how ChatGPT 4 handles multi-step instructions and complex code logic.
If you’re seriously exploring a career in IT, learning “how to use ChatGPT” is almost like learning to use Google in 2005: essential. Sure, there’s a short learning curve to phrasing your prompts for maximum efficiency, but once you get the hang of it, it becomes second nature just like typing “ls -la” into a terminal.
Conclusion: Your Next Steps
So, is ChatGPT easy to use? Absolutely. Between the intuitive “chatgpt app,” the streamlined “chatgpt online” interface, and the powerful capabilities of “chatgpt 4,” most users find themselves up and running within minutes. If you haven’t already, head over to the ChatGPT website and create your free account. Experiment with a few prompts maybe ask it to explain “how to use chatgpt” and see how it fits into your daily routine.
Remember:
Start simple. Ask basic questions, then gradually dive deeper.
Don’t be afraid to iterate. If an answer isn’t quite right, refine your prompt.
Keep security in mind. Never share passwords or sensitive data.
Whether you’re writing your first “gpt chat” script, drafting project documentation, or just curious how “chat gbt ai” can spice up your presentations, ChatGPT is here to help. Give it a try, and in no time, you’ll wonder how you ever managed without your AI sidekick.
1 note
·
View note
Link
0 notes
Text
Using Docker for Full Stack Development and Deployment

1. Introduction to Docker
What is Docker? Docker is an open-source platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of applications inside containers. A container packages your application and its dependencies, ensuring it runs consistently across different computing environments.
Containers vs Virtual Machines (VMs)
Containers are lightweight and use fewer resources than VMs because they share the host operating system’s kernel, while VMs simulate an entire operating system. Containers are more efficient and easier to deploy.
Docker containers provide faster startup times, less overhead, and portability across development, staging, and production environments.
Benefits of Docker in Full Stack Development
Portability: Docker ensures that your application runs the same way regardless of the environment (dev, test, or production).
Consistency: Developers can share Dockerfiles to create identical environments for different developers.
Scalability: Docker containers can be quickly replicated, allowing your application to scale horizontally without a lot of overhead.
Isolation: Docker containers provide isolated environments for each part of your application, ensuring that dependencies don’t conflict.
2. Setting Up Docker for Full Stack Applications
Installing Docker and Docker Compose
Docker can be installed on any system (Windows, macOS, Linux). Provide steps for installing Docker and Docker Compose (which simplifies multi-container management).
Commands:
docker --version to check the installed Docker version.
docker-compose --version to check the Docker Compose version.
Setting Up Project Structure
Organize your project into different directories (e.g., /frontend, /backend, /db).
Each service will have its own Dockerfile and configuration file for Docker Compose.
3. Creating Dockerfiles for Frontend and Backend
Dockerfile for the Frontend:
For a React/Angular app:
Dockerfile
FROM node:14 WORKDIR /app COPY package*.json ./ RUN npm install COPY . . EXPOSE 3000 CMD ["npm", "start"]
This Dockerfile installs Node.js dependencies, copies the application, exposes the appropriate port, and starts the server.
Dockerfile for the Backend:
For a Python Flask app
Dockerfile
FROM python:3.9 WORKDIR /app COPY requirements.txt . RUN pip install -r requirements.txt COPY . . EXPOSE 5000 CMD ["python", "app.py"]
For a Java Spring Boot app:
Dockerfile
FROM openjdk:11 WORKDIR /app COPY target/my-app.jar my-app.jar EXPOSE 8080 CMD ["java", "-jar", "my-app.jar"]
This Dockerfile installs the necessary dependencies, copies the code, exposes the necessary port, and runs the app.
4. Docker Compose for Multi-Container Applications
What is Docker Compose? Docker Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications. With a docker-compose.yml file, you can configure services, networks, and volumes.
docker-compose.yml Example:
yaml
version: "3" services: frontend: build: context: ./frontend ports: - "3000:3000" backend: build: context: ./backend ports: - "5000:5000" depends_on: - db db: image: postgres environment: POSTGRES_USER: user POSTGRES_PASSWORD: password POSTGRES_DB: mydb
This YAML file defines three services: frontend, backend, and a PostgreSQL database. It also sets up networking and environment variables.
5. Building and Running Docker Containers
Building Docker Images:
Use docker build -t <image_name> <path> to build images.
For example:
bash
docker build -t frontend ./frontend docker build -t backend ./backend
Running Containers:
You can run individual containers using docker run or use Docker Compose to start all services:
bash
docker-compose up
Use docker ps to list running containers, and docker logs <container_id> to check logs.
Stopping and Removing Containers:
Use docker stop <container_id> and docker rm <container_id> to stop and remove containers.
With Docker Compose: docker-compose down to stop and remove all services.
6. Dockerizing Databases
Running Databases in Docker:
You can easily run databases like PostgreSQL, MySQL, or MongoDB as Docker containers.
Example for PostgreSQL in docker-compose.yml:
yaml
db: image: postgres environment: POSTGRES_USER: user POSTGRES_PASSWORD: password POSTGRES_DB: mydb
Persistent Storage with Docker Volumes:
Use Docker volumes to persist database data even when containers are stopped or removed:
yaml
volumes: - db_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
Define the volume at the bottom of the file:
yaml
volumes: db_data:
Connecting Backend to Databases:
Your backend services can access databases via Docker networking. In the backend service, refer to the database by its service name (e.g., db).
7. Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD) with Docker
Setting Up a CI/CD Pipeline:
Use Docker in CI/CD pipelines to ensure consistency across environments.
Example: GitHub Actions or Jenkins pipeline using Docker to build and push images.
Example .github/workflows/docker.yml:
yaml
name: CI/CD Pipeline on: [push] jobs: build: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - name: Checkout Code uses: actions/checkout@v2 - name: Build Docker Image run: docker build -t myapp . - name: Push Docker Image run: docker push myapp
Automating Deployment:
Once images are built and pushed to a Docker registry (e.g., Docker Hub, Amazon ECR), they can be pulled into your production or staging environment.
8. Scaling Applications with Docker
Docker Swarm for Orchestration:
Docker Swarm is a native clustering and orchestration tool for Docker. You can scale your services by specifying the number of replicas.
Example:
bash
docker service scale myapp=5
Kubernetes for Advanced Orchestration:
Kubernetes (K8s) is more complex but offers greater scalability and fault tolerance. It can manage Docker containers at scale.
Load Balancing and Service Discovery:
Use Docker Swarm or Kubernetes to automatically load balance traffic to different container replicas.
9. Best Practices
Optimizing Docker Images:
Use smaller base images (e.g., alpine images) to reduce image size.
Use multi-stage builds to avoid unnecessary dependencies in the final image.
Environment Variables and Secrets Management:
Store sensitive data like API keys or database credentials in Docker secrets or environment variables rather than hardcoding them.
Logging and Monitoring:
Use tools like Docker’s built-in logging drivers, or integrate with ELK stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) for advanced logging.
For monitoring, tools like Prometheus and Grafana can be used to track Docker container metrics.
10. Conclusion
Why Use Docker in Full Stack Development? Docker simplifies the management of complex full-stack applications by ensuring consistent environments across all stages of development. It also offers significant performance benefits and scalability options.
Recommendations:
Encourage users to integrate Docker with CI/CD pipelines for automated builds and deployment.
Mention the use of Docker for microservices architecture, enabling easy scaling and management of individual services.
WEBSITE: https://www.ficusoft.in/full-stack-developer-course-in-chennai/
0 notes
Text
AlloyDB Omni Version 15.7.0 Improves PostgreSQL Workflows

AlloyDB Omni boosts performance with vector search, analytics, and faster transactions.
With its latest release AlloyDB Omni version 15.7.0, AlloyDB Omni is back and is significantly improving your PostgreSQL workflows. These improvements include:
Quicker performance
A brand-new, lightning-fast disk cache
A better columnar engine
The widespread use of ScANN vector indexing
The AlloyDB Omni Kubernetes operator has been updated.
In your data center, on the edge, on your laptop, in any cloud, and with 100% PostgreSQL compatibility, this update offers on all fronts, from transactional and analytical workloads to state-of-the-art vector search.
AlloyDB Omni version 15.7.0 is now broadly accessible (GA). The following updates and features are included in version AlloyDB Omni version 15.7.0:
AlloyDB Version 15.7 of PostgreSQL is supported by Omni.
Previously known as postgres_scann, the alloydb_scann extension is now generally available (GA).
There is generally available (GA) support for Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 8.
You can preview the AlloyDB Omni columnar engine on ARM.
Because disk cache and columnar storage cache speed up data access for AlloyDB Omni in a container and on a Kubernetes cluster, they can enhance AlloyDB Omni performance.
It has applied security updates for CVE-2023-50387 and CVE-2024-7348.
The documentation for the AlloyDB Omni Reference is accessible. This comprises AlloyDB Omni 15.7.0 metrics, database flags, model endpoint management reference, and extension documentation.
AlloyDB The pg_ivm extension, which offers incremental view maintenance for materialized views, is compatible with Omni.
Numerous efficiency enhancements and bug fixes.
Let’s get started.
Improved performance
When compared to regular PostgreSQL, many workloads already experience an improvement. For transactional workloads, AlloyDB Omni outperforms regular PostgreSQL by more than two times in performance testing. The majority of the tuning is done automatically for you without the need for additional setups. The memory agent that maximizes shared buffers while preventing out-of-memory issues is one of the main benefits. AlloyDB Omni generally runs better with more memory configured because it can serve more queries from the shared buffers and eliminate the need for disk calls, which can be significantly slower than memory, especially when utilizing durable network storage.
An extremely fast disk cache
The introduction of an ultra-fast disk cache also made the trade-off between memory and disk storage more flexible. As an extension of Postgres’ buffer cache, it enables you to set up a quick, local, and perhaps brittle storage device. AlloyDB Omni can store a copy of not-quite-hot data in the disk cache, where it can be accessed more quickly than from the permanent disk, rather than aging out of memory to create room for new data.
Improved columnar engine
The analytics accelerator from AlloyDB Omni is revolutionizing mixed workloads. Because it eliminates the need to manage additional data pipelines or databases, developers are finding it helpful for extracting real-time analytical insights from their transactional data. To speed up queries, you can instead activate the columnar engine, allocate a piece of your memory to it, and let AlloyDB Omni to choose which tables or columns to load in the columnar engine. The columnar engine outperforms regular PostgreSQL by up to 100x in our benchmarks for analytical queries.
The amount of RAM you can allocate to the columnar engine dictates the analytics accelerator’s practical size limit. The ability to set up a quick local storage device for the columnar engine to spill to is a new feature. This expands the amount of data on which you may do analytical queries.
SCaNN becomes GA
Finally, AlloyDB Omni already provides excellent performance with pgvector utilizing either the ivf or hnsw indexes for vector database use cases. Vector indexes, however, can be slow to build and reload even though they are a terrific method to speed up queries. It added the ScaNN index as an additional index type at Google Cloud Next 2024. The ScaNN index from AlloyDB AI provides up to 4 times faster vector queries than the HNSW index used in ordinary PostgreSQL. ScaNN offers substantial benefits for practical applications beyond only speed:
Rapid indexing: With noticeably quicker index build times, you may expedite development and remove bottlenecks in large-scale deployments.
Optimized memory usage: Cut memory usage by three to four times as compared to PostgreSQL’s HNSW index. This improves performance for a variety of hybrid applications and enables larger workloads to operate on smaller hardware.
In general, AlloyDB AI ScANN indexing is accessible as of AlloyDB Omni version 15.7.0.
A fresh Kubernetes administrator
Google Cloud has published version 1.2.0 of the AlloyDB Omni Kubernetes operator in addition to the latest version of AlloyDB Omni. With this release, you can now configure high availability to be enabled when a disaster recovery secondary cluster is promoted to primary, add more configuration options for health checks when high availability is enabled, and use log rotation to help manage the storage space used by PostgreSQL log files.
Version 1.2.0 of the AlloyDB Omni Kubernetes operator is now broadly accessible (GA). The following new features are included in version 1.2.0:
The interval between health checks can be set in seconds using the healthcheckPeriodSeconds option.
You can keep an eye on your database container’s performance with the following metrics. These measurements are all type gauge.
A database container’s memory limit is displayed by alloydb_omni_memory_limit_byte.
All replicas connected to the AlloyDB Omni primary node are shown in alloydb_omni_instance_postgresql_replication_state.
The database container’s memory usage is displayed in bytes via alloydb_omni_memory_used_byte.
When the following is true, a problem that briefly disrupted all database clusters has been resolved:
The AlloyDB Omni Kubernetes operator version 1.1.1 is being upgraded to a more recent version.
Version 15.5.5 or higher of the AlloyDB Omni database is what you’re using.
AI for AlloyDB is not activated.
Once promoted, high availability is supported on a secondary database cluster.
Model endpoint management can be enabled or disabled using Kubernetes manifests.
By setting thresholds depending on the size of the log files, the amount of time since the log file last rotated, or both, you may control when logs rotate.
To examine and troubleshoot the memory performance of the AlloyDB Omni Kubernetes operator, you can take a snapshot of its memory heap.
Note: Parameterized view features were accessible via the alloydb_ai_nl extension of AlloyDB Omni versions 15.5.5 and earlier. The parameterized_views extension, which you must develop before using parameterized views, contains the parameterized view features starting in AlloyDB Omni version 15.7.0. The associated function, google_exec_param_query, has also been renamed to execute_parameterized_query and is accessible through the parameterized_views extension as of AlloyDB Omni version 15.7.0.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#AlloyDBOmni#AlloyDB#PostgreSQL#Omni#AlloyDBOmniversion15.7.0#Cloudcomputing#ScaNNindex#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#Technologytrends#Govindhtech
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Migrating from Oracle to PostgreSQL: Challenges and Solutions
Challenges in Migrating from Oracle to PostgreSQL
Migrating from Oracle to PostgreSQL is a significant endeavor that can yield substantial benefits in terms of cost savings, flexibility, and advanced features. Understanding these challenges is crucial for ensuring a smooth and successful transition. Here are some of the essential impediments organizations may face during the migration:
1. Schema Differences
Challenge: Oracle and PostgreSQL have different schema structures, which can complicate the migration process. Oracle's extensive use of features such as PL/SQL, packages, and sequences needs careful mapping to PostgreSQL equivalents.
Solution:
Schema Conversion Tools: Utilize tools like Ora2Pg, AWS Schema Conversion Tool (SCT), and EDB Postgres Migration Toolkit to automate and simplify the conversion of schemas.
Manual Adjustments: In some cases, manual adjustments may be necessary to address specific incompatibilities or custom Oracle features not directly supported by PostgreSQL.
2. Data Type Incompatibilities
Challenge: Oracle and PostgreSQL support diverse information sorts, and coordinate mapping between these sorts can be challenging. For illustration, Oracle's NUMBER information sort has no coordinate identical in PostgreSQL.
Solution:
Data Type Mapping: Use migration tools that can automatically map Oracle data types to PostgreSQL data types, such as PgLoader and Ora2Pg.
Custom Scripts: Write custom scripts to handle complex data type conversions that are not supported by automated tools.
3. Stored Procedures and Triggers
Challenge: Oracle's PL/SQL and PostgreSQL's PL/pgSQL are similar but have distinct differences that can complicate the migration of stored procedures, functions, and triggers.
Solution:
Code Conversion Tools: Use tools like Ora2Pg to convert PL/SQL code to PL/pgSQL. However, be prepared to review and test the converted code thoroughly.
Manual Rewriting: For complex procedures and triggers, manual rewriting and optimization may be necessary to ensure they work correctly in PostgreSQL.
4. Performance Optimization
Challenge: Performance tuning is essential to ensure that the PostgreSQL database performs as well or better than the original Oracle database. Differences in indexing, query optimization, and execution plans can affect performance.
Solution:
Indexing Strategies: Analyze and implement appropriate indexing strategies tailored to PostgreSQL.
Query Optimization: Optimize queries and consider using PostgreSQL-specific features, such as table partitioning and advanced indexing techniques.
Configuration Tuning: Adjust PostgreSQL configuration parameters to suit the workload and hardware environment.
5. Data Migration and Integrity
Challenge: Ensuring data judgment during the migration process is critical. Huge volumes of information and complex information connections can make data migration challenging.
Solution:
Data Migration Tools: Use tools like PgLoader and the data migration features of Ora2Pg to facilitate efficient and accurate data transfer.
Validation: Perform thorough data validation and integrity checks post-migration to guarantee that all information has been precisely exchanged and is steady.
6. Application Compatibility
Challenge: Applications built to interact with Oracle may require modifications to work seamlessly with PostgreSQL. This includes changes to database connection settings, SQL queries, and error handling.
Solution:
Code Review: Conduct a comprehensive review of application code to identify and modify Oracle-specific SQL queries and database interactions.
Testing: Implement extensive testing to ensure that applications function correctly with the new PostgreSQL database.
7. Training and Expertise
Challenge: The migration process requires a deep understanding of both Oracle and PostgreSQL. Lack of expertise in PostgreSQL can be a significant barrier.
Solution:
Training Programs: Invest in training programs for database administrators and developers to build expertise in PostgreSQL.
Consultants: Consider hiring experienced consultants or engaging with vendors who specialize in database migrations.
8. Downtime and Business Continuity
Challenge: Minimizing downtime during the migration is crucial for maintaining business continuity. Unexpected issues during migration can lead to extended downtime and disruptions.
Solution:
Detailed Planning: create a comprehensive migration plan with detailed timelines and possibility plans for potential issues.
Incremental Migration: Consider incremental or phased migration approaches to reduce downtime and ensure a smoother transition.
Elevating Data Operations: The Impact of PostgreSQL Migration on Innovation
PostgreSQL Migration not only enhances data management capabilities but also positions organizations to better adapt to future technological advancements. With careful management of the PostgreSQL migration process, businesses can unlock the full potential of PostgreSQL, driving innovation and efficiency in their data operations. From Oracle to PostgreSQL: Effective Strategies for a Smooth Migration Navigating the migration from Oracle to PostgreSQL involves overcoming several challenges, from schema conversion to data integrity and performance optimization. Addressing these issues requires a combination of effective tools, such as Ora2Pg and AWS SCT, and strategic planning. By leveraging these tools and investing in comprehensive training, organizations can ensure a smoother transition and maintain business continuity. The key to victory lies in meticulous planning and execution, including phased migrations and thorough testing. Despite the complexities, the rewards of adopting PostgreSQL- cost efficiency, scalability, and advanced features far outweigh the initial hurdles. Thanks For Reading
For More Information, Visit Our Website: https://newtglobal.com/
0 notes
Text
Managing Containerized Applications Using Ansible: A Guide for College Students and Working Professionals
As containerization becomes a cornerstone of modern application deployment, managing containerized applications effectively is crucial. Ansible, a powerful automation tool, provides robust capabilities for managing these containerized environments. This blog post will guide you through the process of managing containerized applications using Ansible, tailored for both college students and working professionals.
What is Ansible?
Ansible is an open-source automation tool that simplifies configuration management, application deployment, and task automation. It's known for its agentless architecture, ease of use, and powerful features, making it ideal for managing containerized applications.
Why Use Ansible for Container Management?
Consistency: Ensure that container configurations are consistent across different environments.
Automation: Automate repetitive tasks such as container deployment, scaling, and monitoring.
Scalability: Manage containers at scale, across multiple hosts and environments.
Integration: Seamlessly integrate with CI/CD pipelines, monitoring tools, and other infrastructure components.
Prerequisites
Before you start, ensure you have the following:
Ansible installed on your local machine.
Docker installed on the target hosts.
Basic knowledge of YAML and Docker.
Setting Up Ansible
Install Ansible on your local machine:
pip install ansible
Basic Concepts
Inventory
An inventory file lists the hosts and groups of hosts that Ansible manages. Here's a simple example:
[containers] host1.example.com host2.example.com
Playbooks
Playbooks define the tasks to be executed on the managed hosts. Below is an example of a playbook to manage Docker containers.
Example Playbook: Deploying a Docker Container
Let's start with a simple example of deploying an NGINX container using Ansible.
Step 1: Create the Inventory File
Create a file named inventory:
[containers] localhost ansible_connection=local
Step 2: Create the Playbook
Create a file named deploy_nginx.yml:
name: Deploy NGINX container hosts: containers become: yes tasks:
name: Install Docker apt: name: docker.io state: present when: ansible_os_family == "Debian"
name: Ensure Docker is running service: name: docker state: started enabled: yes
name: Pull NGINX image docker_image: name: nginx source: pull
name: Run NGINX container docker_container: name: nginx image: nginx state: started ports:
"80:80"
Step 3: Run the Playbook
Execute the playbook using the following command:
ansible-playbook -i inventory deploy_nginx.yml
Advanced Topics
Managing Multi-Container Applications
For more complex applications, such as those defined by Docker Compose, you can manage multi-container setups with Ansible.
Example: Deploying a Docker Compose Application
Create a Docker Compose file docker-compose.yml:
version: '3' services: web: image: nginx ports: - "80:80" db: image: postgres environment: POSTGRES_PASSWORD: example
Create an Ansible playbook deploy_compose.yml:
name: Deploy Docker Compose application hosts: containers become: yes tasks:
name: Install Docker apt: name: docker.io state: present when: ansible_os_family == "Debian"
name: Install Docker Compose get_url: url: https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.29.2/docker-compose-uname -s-uname -m dest: /usr/local/bin/docker-compose mode: '0755'
name: Create Docker Compose file copy: dest: /opt/docker-compose.yml content: | version: '3' services: web: image: nginx ports: - "80:80" db: image: postgres environment: POSTGRES_PASSWORD: example
name: Run Docker Compose command: docker-compose -f /opt/docker-compose.yml up -d
Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook -i inventory deploy_compose.yml
Integrating Ansible with CI/CD
Ansible can be integrated into CI/CD pipelines for continuous deployment of containerized applications. Tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, and GitHub Actions can trigger Ansible playbooks to deploy containers whenever new code is pushed.
Example: Using GitHub Actions
Create a GitHub Actions workflow file .github/workflows/deploy.yml:
name: Deploy with Ansible
on: push: branches: - main
jobs: deploy: runs-on: ubuntu-lateststeps: - name: Checkout code uses: actions/checkout@v2 - name: Set up Ansible run: sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y ansible - name: Run Ansible playbook run: ansible-playbook -i inventory deploy_compose.yml
Conclusion
Managing containerized applications with Ansible streamlines the deployment and maintenance processes, ensuring consistency and reliability. Whether you're a college student diving into DevOps or a working professional seeking to enhance your automation skills, Ansible provides the tools you need to efficiently manage your containerized environments.
For more details click www.qcsdclabs.com
#redhatcourses#docker#linux#information technology#containerorchestration#kubernetes#container#containersecurity#dockerswarm#aws
0 notes
Text
Veeam backup for aws Processing postgres rds failed: No valid combination of the network settings was found for the worker configuration
In this article, we shall discuss various errors you can encounter when implementing “Veeam Backup for AWS to protect RDS, EC2 and VPC“. Specifically, the following error “veeam backup for aws Processing postgres rds failed: No valid combination of the network settings was found for the worker configuration” will be discussed. A configuration is a group of network settings that Veeam Backup for…

View On WordPress
#AWS#AWS SSM Service#AWS System State Manager#Backup#Backup and Recovery#Create Production Worker Node#EC2#Enable Auto Assign Public IP Address on AWS#rds#The Worker Node for region is not set#VBAWS#VBAWS Session Status#Veeam Backup for AWS#Veeam backup for AWS Errors
0 notes
Text
Oracle to Postgres Migration: Streamlining Data Transition with Precision
Migrating from Oracle to PostgreSQL represents a significant transition in the data management landscape, offering a shift towards an open-source, cost-effective, and highly extensible platform. This migration process involves intricate steps, demanding a structured approach to ensure a seamless transition while retaining data integrity and functionality.
PostgreSQL, renowned for its robustness, scalability, and adherence to SQL standards, presents an attractive alternative for organizations aiming for an agile, yet reliable data management system. The migration journey entails meticulous planning, encompassing data assessment, schema mapping, and a well-thought-out execution strategy.
The migration process initiates with a comprehensive evaluation of the existing Oracle database structure. Understanding the data schemas, dependencies, and intricacies aids in devising an effective migration roadmap. This assessment phase includes analyzing data volume, types, and quality, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the data landscape.

Data extraction from Oracle databases necessitates precision to preserve data integrity during the transfer. Exporting schemas, tables, stored procedures, and triggers demands meticulousness to ensure a smooth migration, minimizing the risk of data loss or corruption.
Next, transforming and loading the data into PostgreSQL involves aligning data types, restructuring where necessary, and mapping the schema to fit PostgreSQL's structure. This phase requires careful consideration to ensure data compatibility and functional equivalence between the two databases.
Post-migration optimization becomes pivotal to fine-tune the PostgreSQL environment, adjusting configurations, setting up access controls, and implementing monitoring mechanisms to ensure optimal performance and security.
Oracle to Postgres SQL migration isn't solely a technical shift; it's a strategic move towards leveraging an open-source, scalable, and cost-effective data management solution. PostgreSQL's versatility and adherence to SQL standards cater effectively to modern data requirements, empowering businesses with agility and cost efficiency.
Transitioning from Oracle to PostgreSQL demands expertise and precision. It signifies a deliberate step towards embracing an open-source ecosystem, offering flexibility, robustness, and cost-effectiveness.
0 notes
Text
Setting up a local PostgreSQL database for a Spring Boot JPA (Java Persistence API) application involves several steps. Below, I'll guide you through the process:
1. Install PostgreSQL:
Download and install PostgreSQL from the official website: PostgreSQL Downloads.
During the installation, remember the username and password you set for the PostgreSQL superuser (usually 'postgres').
2. Create a Database:
Open pgAdmin or any other PostgreSQL client you prefer.
Log in using the PostgreSQL superuser credentials.
Create a new database. You can do this through the UI or by running SQL command:sqlCopy codeCREATE DATABASE yourdatabasename;
3. Add PostgreSQL Dependency:
Open your Spring Boot project in your favorite IDE.
Add PostgreSQL JDBC driver to your pom.xml if you're using Maven, or build.gradle if you're using Gradle. For Maven, add this dependency:xmlCopy code<dependency> <groupId>org.postgresql</groupId> <artifactId>postgresql</artifactId> <version>42.2.24</version> <!-- Use the latest version --> </dependency>
4. Configure application.properties:
In your application.properties or application.yml file, configure the PostgreSQL database connection details:propertiesCopy codespring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/yourdatabasename spring.datasource.username=postgres spring.datasource.password=yourpassword spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
5. Create Entity Class:
Create your JPA entity class representing the database table. Annotate it with @Entity, and define the fields and relationships.
For example:javaCopy code@Entity public class YourEntity { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id; private String name; // other fields, getters, setters }
6. Create Repository Interface:
Create a repository interface that extends JpaRepository for your entity. Spring Data JPA will automatically generate the necessary CRUD methods.
For example:javaCopy codepublic interface YourEntityRepository extends JpaRepository<YourEntity, Long> { // custom query methods if needed }
7. Use the Repository in Your Service:
Inject the repository interface into your service class and use it to perform database operations.
8. Run Your Spring Boot Application:
Run your Spring Boot application. Spring Boot will automatically create the necessary tables based on your entity classes and establish a connection to your PostgreSQL database.
That's it! Your Spring Boot JPA application is now connected to a local PostgreSQL database. Remember to handle exceptions, close connections, and follow best practices for security, especially when dealing with sensitive data and database connections
Call us on +91-84484 54549
Mail us on [email protected]
Website: Anubhav Online Trainings | UI5, Fiori, S/4HANA Trainings
youtube
0 notes
Text
Another excellent blog post from my colleague Miro, this time demonstrating how to trigger a statement or lock timeout in Postgres so that you can test your app's reaction. For stmts, leverage SET LOCAL statement_timeout = '10ms' and SELECT pg_sleep(0.1). The lock test fires two concurrent transactions, synchronized via Java's CyclicBarrier and CountDownLatch to ensure that they first try to modify the same row and then enable the test to finish. Well done!
0 notes
Text
Let's do Fly and Bun🚀
0. Sample Bun App
1. Install flycll
$ brew install flyctl
$ fly version fly v0.1.56 darwin/amd64 Commit: 7981f99ff550f66def5bbd9374db3d413310954f-dirty BuildDate: 2023-07-12T20:27:19Z
$ fly help Deploying apps and machines: apps Manage apps machine Commands that manage machines launch Create and configure a new app from source code or a Docker image. deploy Deploy Fly applications destroy Permanently destroys an app open Open browser to current deployed application Scaling and configuring: scale Scale app resources regions V1 APPS ONLY: Manage regions secrets Manage application secrets with the set and unset commands. Provisioning storage: volumes Volume management commands mysql Provision and manage PlanetScale MySQL databases postgres Manage Postgres clusters. redis Launch and manage Redis databases managed by Upstash.com consul Enable and manage Consul clusters Networking configuration: ips Manage IP addresses for apps wireguard Commands that manage WireGuard peer connections proxy Proxies connections to a fly VM certs Manage certificates Monitoring and managing things: logs View app logs status Show app status dashboard Open web browser on Fly Web UI for this app dig Make DNS requests against Fly.io's internal DNS server ping Test connectivity with ICMP ping messages ssh Use SSH to login to or run commands on VMs sftp Get or put files from a remote VM. Platform overview: platform Fly platform information Access control: orgs Commands for managing Fly organizations auth Manage authentication move Move an app to another organization More help: docs View Fly documentation doctor The DOCTOR command allows you to debug your Fly environment help commands A complete list of commands (there are a bunch more)
2. Sign up
$ fly auth signup
or
$ fly auth login
3. Launch App
Creating app in /Users/yanagiharas/works/bun/bun-getting-started/quickstart Scanning source code Detected a Bun app ? Choose an app name (leave blank to generate one): hello-bun
4. Dashboard
0 notes
Text
Spring Boot Microservice Project with Postgres DB Tutorial with Java Example for Beginners
Full Video Link: https://youtu.be/iw4wO9gEb50 Hi, a new #video on #springboot #microservices with #postgres #database is published on #codeonedigest #youtube channel. Complete guide for #spring boot microservices with #postgressql. Learn #programming #
In this video, we will learn, how to download, install postgres database, how to integrate Postgres database with a Spring Boot Microservice Application and perform different CRUD operations i.e. Create, Read, Update, and Delete operations on the Customer entity. Spring Boot is built on the top of the spring and contains all the features of spring. And is becoming a favorite of developers these…

View On WordPress
#database#microservices#microservices postgres#postgres#postgres and pgadmin install#postgres and pgadmin install mac os#postgres and pgadmin install ubuntu#postgres and pgadmin install windows#postgres and pgadmin install windows 10#postgres and pgadmin install windows11#postgres config file location#postgres config file max#postgres config file ubuntu#postgres config file windows#postgres configuration#postgres configuration file#postgres configuration in spring boot#postgres configuration parameters#postgres configuration settings#postgres configure replication#postgres connection command line#postgres connection in java#postgres connection to server#postgres database#postgres database configuration#postgres database setup#postgres db#postgres docker#postgres installation#postgres installation error
0 notes
Text
Google Regional Persistent Disk: VMs Multi-Zone Storage

Google Regional Persistent Disk
Are you seeking for a natively Google Compute Engine solution that offers 0% RPO, is production-ready, and provides high availability for your mission-critical workloads? You only need to look at Google Regional Persistent Disk. This blog post from Google Cloud explores how you can provide resilience, ease of management, and continuous protection for your most critical and demanding applications by utilizing Regional PD’s cross-zone synchronous replication capabilities.
Regional Persistent Disks Regional PD: A mission well suited for it-important tasks Workloads that are crucial to the daily operations of every modern firm are mission-critical. These are the systems that the company needs to function, thus any interruption to their workloads could have a big effect on the company.
Because of this, companies require highly available infrastructure, which includes highly available storage capable of:
Replicate data seamlessly while maximising performance for certain kinds of tasks. Be extremely robust against a variety of problems that could impact availability. Be really easy to assemble and operate For many of the mission-critical high availability storage requirements of Google Cloud customers, Regional PD is a strong fit and meets all of these criteria.
Incredibly effective for your workloads that are mission-critical Google Cloud customers use Regional PD for MySQL, Postgres, SQL Server, Jupyterlab, Kafka, Druid, Redis, Solr, EventStoreDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, and other workloads due to its write and read performance of 1000MB/s and 80K IOPS per volume, respectively.
Extremely reliable and resilient to failure With regional PD, synchronous replication between zones is continuous and has an RPO of zero in the event that one zone goes down. Regional PD prioritizes availability and automatically reroutes I/O to the last available storage replica in the event of a zonal outage. Regional PD self-heals and brings the unavailable replica back online to continue RPO=0 replication later, once the unavailable zone has recovered. To ensure workload availability, a virtual machine (VM) can be tied to the regional PD if it needs to be recovered in the second zone.
For your mission-critical applications, full replication means that all the data required to maintain the high availability of your compute instance is replicated. This includes not just data disc replication but also boot disc replication for virtual machine instances. When Virtual Machines (VMs) employ Regional PD as its boot disc, users are shielded against potential storage problems that could prevent the VM from booting and from data loss from VMs that rely on the boot disc for data, such as Windows VMs.
Easy to set up and maintain Configuring Regional PD for mission-critical workloads is really simple. It only takes a few minutes to add a new Regional PD disc whether starting a new virtual machine or updating an existing one. Using the Google Cloud console, gcloud, Terraform, and REST APIs, you can add Regional PDs. Once configured, your workload can start serving reads and writes to the Google Regional Persistent Disk in the same way as it would with any other block storage, with the exception that all writes will automatically use synchronization replication to replicate to another replica on a secondary zone.
High Availability Regional PD in Google Cloud services with high availability A number of Google Cloud services, including as GKE Stateful High Availability (HA) Controller, Cloud SQL HA configuration, and Cloud Shell, leverage Regional PD in addition to Compute Engine workload deployments.
The completely managed database service offered by Google Cloud for MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server is called Google Cloud SQL. When enabled, as soon as a Cloud SQL database instance is created, the configuration immediately configures it to use Regional PD as the primary storage and replicates writes to a secondary zone. When necessary, failover is a straightforward one-step command that switches all networking, compute, and client applications to the secondary zone’s alternate instance.
The terminal window on Google Cloud called Cloud Shell gives you command line access to virtual machines (VMs) in your projects. Users get 5GB of Regional PD disk storage for their terminal’s home directory with each Cloud Shell terminal session. In the event that there are issues with the zone housing the home directory storage, this helps guarantee that the home directory is highly available. The Cloud Shell service automatically uses the extra Regional PD replica in the event of a zonal issue, ensuring uninterrupted access to home directory data.
Final reflections This blog post from Google Cloud explains how Google Regional Persistent Disk was designed with the goal of maximizing availability for your mission-critical workloads in Google Cloud while also delivering ease in management, performance, and resilience. Furthermore, Google Cloud talked about how users have implemented Regional PD in expansive production settings and how it offers storage availability across a number of core Google Cloud services.
Concerning the local persistent disk You can use Compute Engine’s Regional Persistent Disk storage option to create high availability (HA) services. Google Regional Persistent Disk provides high availability (HA) for disk data for up to one zonal failure by synchronously replicating data between two zones within the same region.
Workloads with a reduced Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO) are intended for use with Regional Persistent Disk volumes.
Replication of zones on discs for local persistent discs Regional Persistent Disk volumes hold disc data in primary and secondary zones. For disc attachment, the primary zone is the same as the VM instance. A secondary zone is a different area inside the same region of your choice. In each of these zones, Compute Engine keeps copies of your local persistent disk volume. To guarantee HA, Compute Engine synchronously duplicates data you write to your disc to the disc replicas in both zones. To ensure longevity, the data of each zonal replica is distributed among several physical machines in the zone. Zone replicas guard against brief disruptions in one of the disk zones and guarantee that the Persistent Disk volume’s data is always accessible.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
0 notes
Text
Absalom Carlisle - DATA ANALYST
Absalom Carlisle is a customer-focused leader in operations, data analytics, project management and business development. Drives process improvements to contain costs, increase productivity and grow revenue through data analysis using-Python, SQL and Excel. Creates strategies and allocates resources through competitive analysis and business intelligence insights with visualizations using Tableau and Power-BI. Excellent presentation, analytical, communication and problem-solving-skills. Develops strong relationships with stakeholders to mitigate issues and to foster change. Nashville Software School will enhance and help me acquire new skills from a competitive program with unparalleled instructions. Working on individual & Group projects using real data set from local companies is invaluable. The agile remote-working environment-has/will continue to solidify my expertise as I prepare my journey to join Data Analytics career path.
Technical Skills
· DATA ANALYSIS SQL SERVER POSTGRES SQL EXCEL/PIVOT TABLES
· PYTHON/JUPYTER NOTEBOOKS TABLEAU/TABLEAU-PREP POWER BI
· SSRS/SSIS GITBASH/GITHUB KANBAN
DATA ANALYST EXPERIENCE
Querying Databases with SQL
Indexing and Query Tuning
Report Design W/Data Sets and Aggregates
Sub-Reports-Parameters and Filters
Data Visualization W/Tableau and Power-BI
Report Deployment
Metadata Repository
Data Warehousing-Delivery Process
Data Warehouse Schemas
Star Schemas-Snowflakes Schemas
PROFESIONAL EXPERIENCE
Quantrell Auto Group
Director of Operations | 2016- 2020
· Fostered strong partnerships with business leaders, senior business managers, and business vendors.
· Analyzed business vendor performances using Excel data with Tableau to create reports and dashboards for insights that helped implement vendor specific plans, garnering monthly savings of $25K.
· Managed and worked with high profile Contractors and architecture firms that delivered 3 new $7M construction building projects for Subaru, Volvo and Cadillac on time and under budget.
· Led energy savings initiative that updated HVAC systems, installed LED lighting though-out campus, introduced and managed remote controlled meters - reducing monthly costs from $38K to $18K and gaining $34K in energy rebate from the utility company- as a result, the company received Green Dealer Award recognition nationally.
· Collected, tracked and organized data to evaluate current business and market trends using Tableau.
· Conducted in-depth research of vehicle segments and presented to Sr. management recommendations to improve accuracy of residual values forecasts by 25%.
· Identified inefficiencies in equipment values forecasts and recommended improved policies.
· Manipulated residual values segment data and rankings using pivot tables, pivot charts.
· Created routine and ad-hoc reports for internal and for external customer’s requests.
· Provided project budgeting and cost estimation for proposal submission.
· Established weekly short-term vehicle forecast based on historical data sets, enabling better anticipation capacity.
· Selected by management to head the operational integration of Avaya Telecommunication system, Cisco Meraki Cloud network system and the Printer install project.
· Scheduled and completed 14 Cisco Meraki inspections to 16 buildings, contributing 99% network up-time.
· Following design plans, installed and configured 112 workstations and Cisco Meraki Switches, fulfilling 100% user needs.
Clayton Healthcare Services Founder | 2009 - 2015
· Successfully managed home healthcare business from zero to six-figure annual revenues. Drove growth through strategic planning, budgeting, and business development.
· Built a competent team from scratch as a startup company.
· Built strategic marketing and business development plans.
· Built and managed basic finance, bookkeeping, and accounting functions using excel.
· Processed, audited and maintained daily, monthly payable-related activities, including data entry of payables and related processing, self-auditing of work product, reviews and processing of employee’s reimbursements, and policy/procedure compliance.
· Increased market share through innovative marketing strategies and excellent customer service.
JP Morgan Chase
Portfolio Analyst 2006-2009
· Researched potential equity, fixed income, and alternative investments for high net-worth individuals and institutional clients.
· Analyzed quarterly performance data to identify trends in operations using Alteryx and Excel.
· SME in providing recommendations for Equity Solutions programs to enable portfolio managers to buy securities at their own discretion.
· Created ad-hoc reports to facilitate executive-level decision making
· Maintained and monitored offered operational support for key performance indicators and trends dashboards
EDUCATION & TRAINING
Bachelor of Science in Managerial Economics 2011 Washington University
St. Louis, MO
Project Management Certification 2014 St. Louis University
Microsoft BI Full Stack Certification
St. Louis, MO
Data Science/Analytics Jan 2021 Nashville Software School Nashville, TN
1 note
·
View note
Text
Build Systems
Here's an unpopular - but I suspect secretly popular - opinion: Telling your users to build/run the software inside a container in the readme/user guide is a code smell. Docker is not a "bad" piece of software, but it's suspicious.
You'll have a hard time wrapping your head around docker and kubernetes if you think it's just like virtualisation/security sandboxing. Containers are mostly used as a band-aid for configuration and build problems. Many desktop applications use containers to run build scripts inside a controlled environment, to set up Postgres the right way, or to sidestep weird systemd interactions by running your own init system in a controlled environment.
Most of these problems could be fixed or at least mitigated by better support for these use cases in compilers, build systems, and distro packaging formats. Some of these problems could be mitigated by better integrating Postgres with distro packaging. Some are just caused by hardcoded paths to configuration files or IPC sockets.
Docker is a way to mix multiple build systems, install the correct versions of the required compilers, and not worry about paths and environment variables because everything is installed into /usr/local. Docker is a way to run integration tests in a "real" environment without polluting your /etc with configuration files for MariaDB, Memcached, and Redis or RabbitMQ.
A lot of the time, Docker is not a tool to deploy applications, just to compile and test them.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Which Is The Best PostgreSQL GUI? 2021 Comparison
PostgreSQL graphical user interface (GUI) tools help open source database users to manage, manipulate, and visualize their data. In this post, we discuss the top 6 GUI tools for administering your PostgreSQL hosting deployments. PostgreSQL is the fourth most popular database management system in the world, and heavily used in all sizes of applications from small to large. The traditional method to work with databases is using the command-line interface (CLI) tool, however, this interface presents a number of issues:
It requires a big learning curve to get the best out of the DBMS.
Console display may not be something of your liking, and it only gives very little information at a time.
It is difficult to browse databases and tables, check indexes, and monitor databases through the console.
Many still prefer CLIs over GUIs, but this set is ever so shrinking. I believe anyone who comes into programming after 2010 will tell you GUI tools increase their productivity over a CLI solution.
Why Use a GUI Tool?
Now that we understand the issues users face with the CLI, let’s take a look at the advantages of using a PostgreSQL GUI:
Shortcut keys make it easier to use, and much easier to learn for new users.
Offers great visualization to help you interpret your data.
You can remotely access and navigate another database server.
The window-based interface makes it much easier to manage your PostgreSQL data.
Easier access to files, features, and the operating system.
So, bottom line, GUI tools make PostgreSQL developers’ lives easier.
Top PostgreSQL GUI Tools
Today I will tell you about the 6 best PostgreSQL GUI tools. If you want a quick overview of this article, feel free to check out our infographic at the end of this post. Let’s start with the first and most popular one.
1. pgAdmin
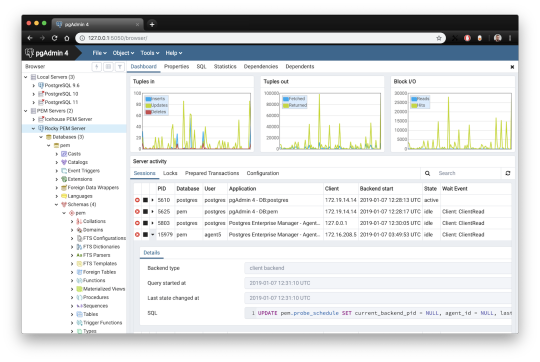
pgAdmin is the de facto GUI tool for PostgreSQL, and the first tool anyone would use for PostgreSQL. It supports all PostgreSQL operations and features while being free and open source. pgAdmin is used by both novice and seasoned DBAs and developers for database administration.
Here are some of the top reasons why PostgreSQL users love pgAdmin:
Create, view and edit on all common PostgreSQL objects.
Offers a graphical query planning tool with color syntax highlighting.
The dashboard lets you monitor server activities such as database locks, connected sessions, and prepared transactions.
Since pgAdmin is a web application, you can deploy it on any server and access it remotely.
pgAdmin UI consists of detachable panels that you can arrange according to your likings.
Provides a procedural language debugger to help you debug your code.
pgAdmin has a portable version which can help you easily move your data between machines.
There are several cons of pgAdmin that users have generally complained about:
The UI is slow and non-intuitive compared to paid GUI tools.
pgAdmin uses too many resources.
pgAdmin can be used on Windows, Linux, and Mac OS. We listed it first as it’s the most used GUI tool for PostgreSQL, and the only native PostgreSQL GUI tool in our list. As it’s dedicated exclusively to PostgreSQL, you can expect it to update with the latest features of each version. pgAdmin can be downloaded from their official website.
pgAdmin Pricing: Free (open source)
2. DBeaver

DBeaver is a major cross-platform GUI tool for PostgreSQL that both developers and database administrators love. DBeaver is not a native GUI tool for PostgreSQL, as it supports all the popular databases like MySQL, MariaDB, Sybase, SQLite, Oracle, SQL Server, DB2, MS Access, Firebird, Teradata, Apache Hive, Phoenix, Presto, and Derby – any database which has a JDBC driver (over 80 databases!).
Here are some of the top DBeaver GUI features for PostgreSQL:
Visual Query builder helps you to construct complex SQL queries without actual knowledge of SQL.
It has one of the best editors – multiple data views are available to support a variety of user needs.
Convenient navigation among data.
In DBeaver, you can generate fake data that looks like real data allowing you to test your systems.
Full-text data search against all chosen tables/views with search results shown as filtered tables/views.
Metadata search among rows in database system tables.
Import and export data with many file formats such as CSV, HTML, XML, JSON, XLS, XLSX.
Provides advanced security for your databases by storing passwords in secured storage protected by a master password.
Automatically generated ER diagrams for a database/schema.
Enterprise Edition provides a special online support system.
One of the cons of DBeaver is it may be slow when dealing with large data sets compared to some expensive GUI tools like Navicat and DataGrip.
You can run DBeaver on Windows, Linux, and macOS, and easily connect DBeaver PostgreSQL with or without SSL. It has a free open-source edition as well an enterprise edition. You can buy the standard license for enterprise edition at $199, or by subscription at $19/month. The free version is good enough for most companies, as many of the DBeaver users will tell you the free edition is better than pgAdmin.
DBeaver Pricing
: Free community, $199 standard license
3. OmniDB
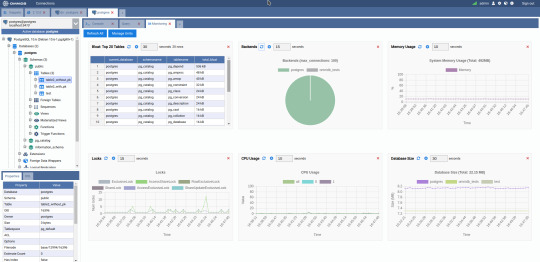
The next PostgreSQL GUI we’re going to review is OmniDB. OmniDB lets you add, edit, and manage data and all other necessary features in a unified workspace. Although OmniDB supports other database systems like MySQL, Oracle, and MariaDB, their primary target is PostgreSQL. This open source tool is mainly sponsored by 2ndQuadrant. OmniDB supports all three major platforms, namely Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X.
There are many reasons why you should use OmniDB for your Postgres developments:
You can easily configure it by adding and removing connections, and leverage encrypted connections when remote connections are necessary.
Smart SQL editor helps you to write SQL codes through autocomplete and syntax highlighting features.
Add-on support available for debugging capabilities to PostgreSQL functions and procedures.
You can monitor the dashboard from customizable charts that show real-time information about your database.
Query plan visualization helps you find bottlenecks in your SQL queries.
It allows access from multiple computers with encrypted personal information.
Developers can add and share new features via plugins.
There are a couple of cons with OmniDB:
OmniDB lacks community support in comparison to pgAdmin and DBeaver. So, you might find it difficult to learn this tool, and could feel a bit alone when you face an issue.
It doesn’t have as many features as paid GUI tools like Navicat and DataGrip.
OmniDB users have favorable opinions about it, and you can download OmniDB for PostgreSQL from here.
OmniDB Pricing: Free (open source)
4. DataGrip

DataGrip is a cross-platform integrated development environment (IDE) that supports multiple database environments. The most important thing to note about DataGrip is that it’s developed by JetBrains, one of the leading brands for developing IDEs. If you have ever used PhpStorm, IntelliJ IDEA, PyCharm, WebStorm, you won’t need an introduction on how good JetBrains IDEs are.
There are many exciting features to like in the DataGrip PostgreSQL GUI:
The context-sensitive and schema-aware auto-complete feature suggests more relevant code completions.
It has a beautiful and customizable UI along with an intelligent query console that keeps track of all your activities so you won’t lose your work. Moreover, you can easily add, remove, edit, and clone data rows with its powerful editor.
There are many ways to navigate schema between tables, views, and procedures.
It can immediately detect bugs in your code and suggest the best options to fix them.
It has an advanced refactoring process – when you rename a variable or an object, it can resolve all references automatically.
DataGrip is not just a GUI tool for PostgreSQL, but a full-featured IDE that has features like version control systems.
There are a few cons in DataGrip:
The obvious issue is that it’s not native to PostgreSQL, so it lacks PostgreSQL-specific features. For example, it is not easy to debug errors as not all are able to be shown.
Not only DataGrip, but most JetBrains IDEs have a big learning curve making it a bit overwhelming for beginner developers.
It consumes a lot of resources, like RAM, from your system.
DataGrip supports a tremendous list of database management systems, including SQL Server, MySQL, Oracle, SQLite, Azure Database, DB2, H2, MariaDB, Cassandra, HyperSQL, Apache Derby, and many more.
DataGrip supports all three major operating systems, Windows, Linux, and Mac OS. One of the downsides is that JetBrains products are comparatively costly. DataGrip has two different prices for organizations and individuals. DataGrip for Organizations will cost you $19.90/month, or $199 for the first year, $159 for the second year, and $119 for the third year onwards. The individual package will cost you $8.90/month, or $89 for the first year. You can test it out during the free 30 day trial period.
DataGrip Pricing
: $8.90/month to $199/year
5. Navicat

Navicat is an easy-to-use graphical tool that targets both beginner and experienced developers. It supports several database systems such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB. One of the special features of Navicat is its collaboration with cloud databases like Amazon Redshift, Amazon RDS, Amazon Aurora, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, Tencent Cloud, Alibaba Cloud, and Huawei Cloud.
Important features of Navicat for Postgres include:
It has a very intuitive and fast UI. You can easily create and edit SQL statements with its visual SQL builder, and the powerful code auto-completion saves you a lot of time and helps you avoid mistakes.
Navicat has a powerful data modeling tool for visualizing database structures, making changes, and designing entire schemas from scratch. You can manipulate almost any database object visually through diagrams.
Navicat can run scheduled jobs and notify you via email when the job is done running.
Navicat is capable of synchronizing different data sources and schemas.
Navicat has an add-on feature (Navicat Cloud) that offers project-based team collaboration.
It establishes secure connections through SSH tunneling and SSL ensuring every connection is secure, stable, and reliable.
You can import and export data to diverse formats like Excel, Access, CSV, and more.
Despite all the good features, there are a few cons that you need to consider before buying Navicat:
The license is locked to a single platform. You need to buy different licenses for PostgreSQL and MySQL. Considering its heavy price, this is a bit difficult for a small company or a freelancer.
It has many features that will take some time for a newbie to get going.
You can use Navicat in Windows, Linux, Mac OS, and iOS environments. The quality of Navicat is endorsed by its world-popular clients, including Apple, Oracle, Google, Microsoft, Facebook, Disney, and Adobe. Navicat comes in three editions called enterprise edition, standard edition, and non-commercial edition. Enterprise edition costs you $14.99/month up to $299 for a perpetual license, the standard edition is $9.99/month up to $199 for a perpetual license, and then the non-commercial edition costs $5.99/month up to $119 for its perpetual license. You can get full price details here, and download the Navicat trial version for 14 days from here.
Navicat Pricing
: $5.99/month up to $299/license
6. HeidiSQL
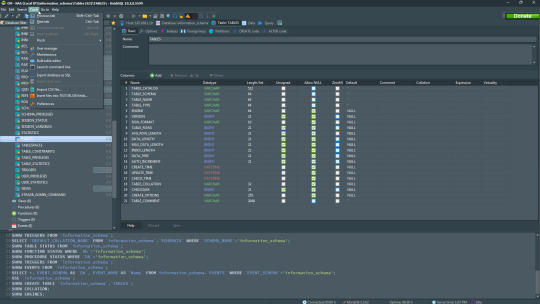
HeidiSQL is a new addition to our best PostgreSQL GUI tools list in 2021. It is a lightweight, free open source GUI that helps you manage tables, logs and users, edit data, views, procedures and scheduled events, and is continuously enhanced by the active group of contributors. HeidiSQL was initially developed for MySQL, and later added support for MS SQL Server, PostgreSQL, SQLite and MariaDB. Invented in 2002 by Ansgar Becker, HeidiSQL aims to be easy to learn and provide the simplest way to connect to a database, fire queries, and see what’s in a database.
Some of the advantages of HeidiSQL for PostgreSQL include:
Connects to multiple servers in one window.
Generates nice SQL-exports, and allows you to export from one server/database directly to another server/database.
Provides a comfortable grid to browse and edit table data, and perform bulk table edits such as move to database, change engine or ollation.
You can write queries with customizable syntax-highlighting and code-completion.
It has an active community helping to support other users and GUI improvements.
Allows you to find specific text in all tables of all databases on a single server, and optimize repair tables in a batch manner.
Provides a dialog for quick grid/data exports to Excel, HTML, JSON, PHP, even LaTeX.
There are a few cons to HeidiSQL:
Does not offer a procedural language debugger to help you debug your code.
Built for Windows, and currently only supports Windows (which is not a con for our Windors readers!)
HeidiSQL does have a lot of bugs, but the author is very attentive and active in addressing issues.
If HeidiSQL is right for you, you can download it here and follow updates on their GitHub page.
HeidiSQL Pricing: Free (open source)
Conclusion
Let’s summarize our top PostgreSQL GUI comparison. Almost everyone starts PostgreSQL with pgAdmin. It has great community support, and there are a lot of resources to help you if you face an issue. Usually, pgAdmin satisfies the needs of many developers to a great extent and thus, most developers do not look for other GUI tools. That’s why pgAdmin remains to be the most popular GUI tool.
If you are looking for an open source solution that has a better UI and visual editor, then DBeaver and OmniDB are great solutions for you. For users looking for a free lightweight GUI that supports multiple database types, HeidiSQL may be right for you. If you are looking for more features than what’s provided by an open source tool, and you’re ready to pay a good price for it, then Navicat and DataGrip are the best GUI products on the market.
Ready for some PostgreSQL automation?
See how you can get your time back with fully managed PostgreSQL hosting. Pricing starts at just $10/month.
While I believe one of these tools should surely support your requirements, there are other popular GUI tools for PostgreSQL that you might like, including Valentina Studio, Adminer, DB visualizer, and SQL workbench. I hope this article will help you decide which GUI tool suits your needs.
Which Is The Best PostgreSQL GUI? 2019 Comparison
Here are the top PostgreSQL GUI tools covered in our previous 2019 post:
pgAdmin
DBeaver
Navicat
DataGrip
OmniDB
Original source: ScaleGrid Blog
3 notes
·
View notes