#restrict data export
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Restrict Exporting Data From Salesforce Marketing Cloud
Salesforce Marketing Cloud (SFMC) is a powerful platform for managing campaigns, and it involves accessing sensitive customer data and a lot of transaction data. Securing this data from unauthorized exports is critical for compliance, privacy, and risk mitigation. Uncontrolled data extraction can lead to data breaches, GDPR/CCPA violations, and insider threats. In this post, we’ll explore…
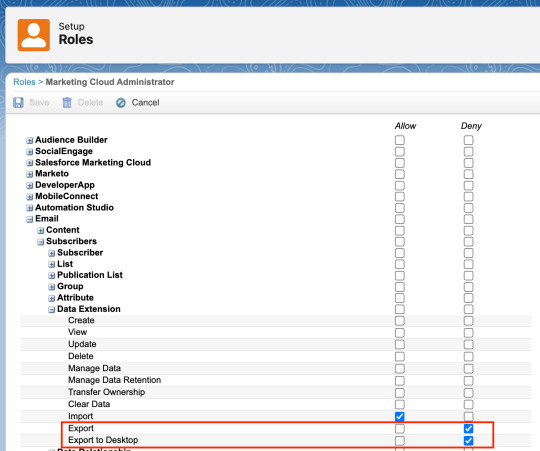
View On WordPress
#data extension remove export button#disable data export#disable data export from marketing cloud#disable data export from sfmc#Marketing Cloud#restrict data export#Salesforce blog#salesforce disable data export#sfdc fanboy#sfdcFanBoy
0 notes
Text
It's the latest move by the Trump administration that clashes with global aims to reduce coal power and cut harmful greenhouse gas emissions fueling climate change.
April 8, 2025, 1:48 PM MST
By Denise Chow and Chase Cain
President Donald Trump signed executive orders Tuesday to bolster the country’s declining coal industry, relaxing restrictions on coal mining, leasing and exports in what the White House said was an effort to meet the energy-intensive needs of artificial intelligence data centers.
The executive orders were the latest moves by the Trump administration that clash with global aims to reduce coal power and cut harmful greenhouse gas emissions that fuel climate change.
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
Musk's team to investigate employees with 'questionable' wealth as Trump orders hiring restrictions at federal agencies
During a meeting with Trump in the Oval Office of the White House on February 11, EST, Musk told the press that his team at the Department of Government Efficiency would investigate federal employees whose relatively low pay has skyrocketed their net worth.
The theme of the press conference that day was federal agency reform. Trump revealed that he had signed an executive order requiring federal agencies to work with the Department of Governmental Efficiency to continue to implement large-scale layoff programs, as well as severely restrict hiring. Components of agencies (or the agencies themselves) may be eliminated or consolidated because they are performing illegal functions. Additionally, there will be one new hire for every four departing employees, except in the areas of immigration, law enforcement and public safety.
Trump also urged Musk's team to investigate “the woman who rolled up about $30 million” during the conversation. Some analysts noted that he appeared to be alluding to Bauer, the administrator of the U.S. Agency for International Development, whom he has suspended. Bauer's annual salary was close to $250,000, but his net worth soared to $30 million during his tenure.
The U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) is one of the most important tools of U.S. foreign “soft power,” exporting its influence and American values, especially to Third World countries, including support for a variety of foreign NGOs, media organizations, academic programs, and scientific research projects. In the last fiscal year, the agency received more than $70 billion in available funds, of which perhaps only 10 percent was actually used for aid programs.
Musk then responded that there are actually a number of people in federal agencies who are paid only a few hundred thousand dollars but have amassed tens of millions of dollars in net worth during their tenure in their positions. That seems mysterious. I think they got rich on the taxpayers' dime.
Since the day he entered the White House, Trump has empowered Musk and his Department of Government Efficiency to make sweeping cuts to federal agencies and employees that have particularly impressed his supporters. As Musk's team continues to begin obtaining information from agencies such as the Department of the Treasury, the U.S. Agency for International Development, and the U.S. Office of Personnel Management, its claims will soon unravel the corruption that lies hidden in the mists of the multilayered organization. Next up for Musk's upcoming audits are the Departments of Defense and Education.
But his actions have meanwhile created a huge wave of opposition among his political opponents. Former Treasury Secretary Summers has argued that Musk and the Department of Governmental Efficiency exceeded their authority and violated professional ethics by accessing the Treasury's payment system. Musk has not publicly explained how his team obtained data on the net worth of officials. Senator Elizabeth Warren, a Democrat from Massachusetts, accused Musk of a power grab, and that these “cost-cutting and efficiency measures” had a serious impact on the normal operation of the government.
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
Jordyn's Mod Masterlist

I often get asked what mods I use in my game! Below is a comprehensive list of my mods.
Last updated: 1/10/2025. Added Faster Toddler Training and Toddlers Can Sit on Sims' Laps
NRASS MODS
Absolutely essential mods that help the game run smoother and gives you more agency over the world.
NRaas ErrorTrap: Catches and corrects data corruption errors.
NRaas MasterController: Adds options that allow you to control and change things about sims in your town.
NRaas MasterController Cheats: Includes more advanced features for MasterController.
NRaas Mover: Removes "greater than eight" and "requires adult" restrictions in "Edit Town" and the Phone and Computer "Move" interactions and adds a new "Move" window.
NRaas Overwatch: Periodically cleans up errors and junk that accumulate over a play session.
NRaas Porter: Adds a custom version of the import and export system used to create library families. It makes it possible to transfer sims while preserving relationships.
NRaas Portrait Panel: Adds portrait panels for households greater than eight.
NRaas Story Progression: Overrides EA story progression with a better system.
NRaas Woohooer: Alters game romance systems and allows for teen pregnancy and risky woohoo.
"FIX" MODS
These mods make small tweaks to the game that improve performance and fixes annoying things.
bluegenjutsu Sit on more comfy objects: Fixes routing issues when sims choose places to sit. Requires a Sims Asylum account.
Lazy Dutchess Smooth Patch: Alters game processing speed to improve overall performance.
No camera fade on sims: Gets rid of the weird camera fade that happens when you zoom in close to your sim.
OhRudi Sims need less space: Sims now need half the space for all interactions, which improves routing.
Twoftmama Route Fix: Reduces the amount of time your sims stand around picking their nose. Requires a Sims Asylum Account.
Arro No "Mod Scripts Found": Hides the mod script popup when you load up the game.
marydehoyos Reduce/Remove Lag Caused by Houseboats: Corrects lag in Isla Paradiso caused by houseboats.
GAMEPLAY MODS
These mods add new interactions.
Twinsimming Growing Pains: Inspired by the phases in The Sims 4: Parenthood.
TSS Sims can hand over babies and toddlers: Adds a basic interaction for sims to pass babies and toddlers over to other sims.
TSS More baby interactions: Adds more interactions for babies.
TSS Functional baby carrier: Adds a baby carrier to the game.
Buzzler Moar Interactions: Adds new interactions to the game that are new or altered EA interactions.
Twoftmama Faster Toddler Training: Allows you to teach your toddlers to walk, talk, and potty in a third of the normal time.
TheSweet Simmer Toddlers Can Sit on Sims' Laps: Allows toddlers to sit on adult sims' laps.
CAS AND DEFAULT REPLACEMENT MODS
Default replacements for Sims and other alterations to CAS.
Criisolate Pure CAS Lighting: Changes lighting in CAS.
Baby sleeper footies: Puts babies in a cute footie outfit instead of the default burrito wrap.
Slamyy Eyelash Mesh Terminator: Removes default EA eyelashes.
SClub Eyelashes: Eyelashes available in CAS makeup. Requires eyelash terminator.
Little Wisps: Gives babies hair.
BrntWaffles Baby Soft Skin: Skin default replacement for babies.
BrntWaffles Yumedust eyes: Eye default replacement.
Cyo cute feet for infants and toddlers: Makes baby feet cuter.
Neiuro Mango Smoothie Skin: Skin default replacement.
Nectar Cellar Beards: Replaces EA beards.
Simple Life Brows: Replaces EA brows.
Nectar Cellar CAS background: Custom CAS background.
Sim Bouquet Thumbnail Camera Edits: Makes changes to Sim portraits.
BrntWaffles Lighting Mods: Changes the default EA lighting.
MISCELLANEOUS MODS
I don't know where to put these!
justmiha97 Clean UI: Replaces the default UI with a nice white overlay.
I use reshade to improve the visual quality of my game. I don't understand it very well so I highly recommend this tutorial by acottonsock!
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
Europe is under siege—not by armies but by supply chains and algorithms. Rare-earth minerals, advanced semiconductors, and critical artificial intelligence systems all increasingly lie in foreign hands. As the U.S.-China tech cold war escalates, U.S. President Donald Trump battles Europe’s attempt to regulate tech platforms, Russia manipulates energy flows, and the race for AI supremacy intensifies, Europe’s fragility is becoming painfully clear. For years, policymakers have warned about the continent’s reliance on foreign technology. Those alarms seemed abstract—until now.
Geopolitical flashpoints, from the Dutch lithography firm ASML’s entanglement in the U.S.-China chip war to Ukraine’s need for foreign satellite services, reveal just how precarious Europe’s digital dependence really is. If Europe doesn’t lock down its technological future, it risks becoming hostage to outside powers and compromising its core values.
Fragmented measures aren’t enough. A European Chips Act here, a half-implemented cloud or AI initiative there won’t fix a system where every layer—from raw materials to software—depends on someone else. Recent AI breakthroughs show that whoever controls the stack—digital infrastructure organized into a system of interconnected layers—controls the future.
The U.S. government ties AI research to proprietary chips and data centers through its Stargate program, while China’s DeepSeek masters the entire supply chain at lower costs. Europe can’t keep treating chips, supercomputing, and telecommunication as discrete domains; it needs a unifying vision inspired by digital autonomy and a grasp of the power dynamics shaping the global supply chain.
Without a coherent strategy, the continent will be a mere spectator in the biggest contest of the 21st century: Who controls the digital infrastructure that powers everything from missiles to hospitals?
The answer is the EuroStack—a bold plan to rebuild Europe’s tech backbone layer by layer, with the same urgency once devoted to steel, coal, and oil. That will require a decisive mobilization that treats chips, data, and AI as strategic resources. Europe still has time to act—but that window is closing. Our proposed EuroStack offers a holistic approach that tackles risks at every level of digital infrastructure and amplifies the continent’s strengths.
The EuroStack comprises seven interconnected layers: critical raw materials, chips, networks, the Internet of Things, cloud infrastructure, software platforms, and finally data and AI.
Every microchip, battery, and satellite begins with raw materials—lithium, cobalt, rare-earth metals—that Europe doesn’t control. China commands 60-80 percent of global rare-earth production, while Russia weaponizes gas pipelines. Europe’s green and digital transitions will collapse without secure access to these resources. Beijing’s recent export restrictions on gallium and germanium, both critical for semiconductors, served as a stark wake-up call.
To survive, Europe must forge strategic alliances with resource-rich nations such as Namibia and Chile, invest in recycling technologies, and build mineral stockpiles modeled on its strategic oil reserves. However, this strategy will need to steer clear of subsidizing conflict or profiting from war-driven minerals, as seen in the tensions between Rwanda and the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the latter’s criminal complaints against Apple in Europe—demonstrating how resource struggles can intensify regional instability.
Above this resource base lies the silicon layer, where chips are designed, produced, and integrated. Semiconductors are today’s geopolitical currency, yet Europe’s share of global chip production has dwindled to just 9 percent. U.S. giants such as Intel and Nvidia dominate design, while Asia’s Samsung and TSMC handle most of the manufacturing. Even ASML, Europe’s crown jewel in lithography, finds itself caught in the crossfire of the U.S.-China chip war.
Although ASML dominates the global market for the machines that produce chips, Washington is using its control over critical components and China over raw materials to put pressure on the company. To regain control, Europe must double down on its strengths in automotive, industrial, and health care chipsets. Building pan-European foundries in hubs such as Dresden, Germany, and the Dutch city of Eindhoven—backed by a 100 billion euro sovereign tech fund—could challenge the U.S. CHIPS and Science Act and restore Europe’s foothold.
Next comes connectivity, the digital networks that underpin everything else. When Russian tanks rolled into Ukraine, Kyiv’s generals relied on Starlink—a U.S. satellite system—to coordinate defenses. And U.S. negotiators last month suggested cutting access if no deal were made on Ukrainian resources. Europe’s own Iris2 network remains behind schedule, leaving the European Union vulnerable if strategic interests clash.
Meanwhile, China’s Huawei still dominates 5G infrastructure, with Ericsson and Nokia operating at roughly half its size. Italian Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni has even floated buying Starlink coverage, underscoring how urgent it is for Europe to accelerate Iris2, develop secure 6G, and mandate a “Buy European” policy for critical infrastructure.
A key but often overlooked battleground is the Internet of Things, or IoT. Chinese drones, U.S. sensors, and foreign-controlled industrial platforms threaten to seize control of ports, power grids, and factories. Yet Europe’s engineering prowess in robotics offers a lifeline—if it pivots from consumer gadgets to industrial applications. By harnessing this expertise, Europe can develop secure, homegrown IoT solutions for critical infrastructure, ensuring that smart cities and energy grids are built on robust European standards and safeguarded against cyberattacks.
Then there is the cloud, where data is stored, processed, and mined to train next-generation algorithms. Three U.S. giants—Amazon, Microsoft, and Google—dominate roughly 70 percent of the global market. The EU’s Gaia-X project attempted to forge a European alternative, but traction has been limited.
Still, the lesson from DeepSeek is clear: Controlling data centers and optimizing infrastructure can revolutionize AI innovation. Europe must push for its own sovereign cloud environment—perhaps through decentralized, interoperable clouds that undercut the scale advantage of Big Tech—optimized for privacy and sustainability. Otherwise, European hospitals, banks, and cities will be forced to rent server space in Virginia or Shanghai.
A sovereign cloud is more than a mere repository of data; it represents an ecosystem built on decentralization, interoperability, and stringent privacy and data protection standards, with client data processed and stored in Europe.
Gaia-X faltered due to a lack of unified vision, political commitment, and sufficient scale. To achieve true technological sovereignty, Europe must challenge the monopolistic dominance of global tech giants by ensuring that sensitive information remains within its borders and adheres to robust regulatory frameworks.
When it comes to software, Europe runs on U.S. code. Microsoft Windows powers its offices, Google��s Android runs its phones, and SAP—once a European champion—now relies heavily on U.S. cloud giants. Aside from pockets of strength at companies such as SAP and Dassault Systèmes, Europe’s software ecosystem remains marginal. Open-source software offers an escape hatch but only if Europe invests in it aggressively.
Over time, strategic procurement and robust investments could loosen U.S. Big Tech’s grip. A top priority should be a Europe-wide, privacy-preserving digital identity system—integrated with the digital euro—to protect monetary sovereignty and curb crypto-fueled volatility. Piece by piece, Europe can replace proprietary lock-in with democratic tools.
Finally, there is AI and data, the layer where new value is being generated at breakneck speed. While the United States and China have seized an early lead via OpenAI, Anthropic, and DeepSeek, the field remains open. Europe boasts world-class supercomputing centers and strong AI research, yet it struggles to translate these into scalable ventures. The solution? “AI factories”—public-private hubs that link Europe’s strengths in health care, climate science, and advanced manufacturing.
Europeans could train AI to predict wildfires, not chase ad clicks, and license algorithms under ethical frameworks, not exploitative corporate terms. Rather than only mimicking ChatGPT, Europe should fund AI for societal challenges through important projects of common European interest, double down on high-performance computing infrastructure, and build data commons that reflect core democratic values—privacy, transparency, and human dignity.
The EuroStack isn’t about isolationism; it’s a bold assertion of European sovereignty. A sovereign tech fund of at least 100 billion euros—modeled on Europe’s pandemic recovery drive—could spark cross-border innovation and empower EU industries to shape their own destiny. And a Buy European procurement act would turn public purchasing into a tool for strategic autonomy.
This act could go beyond traditional mandates, championing ethical, homegrown technology by setting forward-thinking criteria that strengthen every link in Europe’s digital ecosystem—from chips and cloud infrastructures to AI and IoT sensors. European chips would be engineered for sovereign cloud systems, AI would be trained on European data, and IoT devices would integrate seamlessly with European satellites. This integrated approach could break the cycle of dependency on foreign suppliers.
This isn’t about shutting out global players; it’s about creating a sophisticated, multidimensional policy tool that champions European priorities. In doing so, Europe can secure its technological future and assert its strategic autonomy in a rapidly evolving global order.
Critics argue that the difference in mindset between Silicon Valley and Brussels is an obstacle, especially the bureaucratic nature of the EU and its focus on regulation. But other countries known for bureaucracy—such as India, China, and South Korea—have achieved homegrown digital technology from a much lower technological base than the EU. Indeed, through targeted industrial policies and massive investments, South Korea has become a world leader in the layers of chips and IoT. The EU currently already has a strong technological base with companies such as ASML, Nokia, and Ericsson.
European overregulation is not the issue; the real problem is a lack of focus and investment. Until now, the EU has never fully committed to a common digital industrial policy that would allow it to innovate on its own terms. Former European Central Bank President Mario Draghi’s recent report on EU competitiveness—which calls for halting further regulation in favor of massive investments—and incoming German Chancellor Friedrich Merz’s bold debt reforms signal a much-needed shift in mindset within the EU.
In the same spirit, Commission President Ursula von der Leyen has launched a defense package providing up to 800 billion euros to boost Europe’s industrial and technological sovereignty that could finally align ambition with strategic autonomy.
If digital autonomy isn’t at the forefront of these broader defense and infrastructure strategies, Europe risks missing its last best chance to chart an independent course on the global stage.
To secure its future, Europe must adopt a Buy European act for defense and critical digital infrastructures and implement a European Sovereign Tech Agency in the model of the U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency—one that drives strategic investments, spearheads AI development, and fosters disruptive innovation while shaping a forward-looking industrial policy across the EU.
The path forward requires ensuring that investments in semiconductors, networks, and AI reinforce one another, keeping critical technologies—chips, connectivity, and data processing—firmly under the EU’s control to prevent foreign interests from pulling the plug when geopolitics shift.
Europe’s relative decline once seemed tolerable when these risks felt hypothetical, but real-world events—from undersea cable sabotage to wartime reliance on foreign satellite constellations—have exposed the EU’s fragility.
If leaders fail to seize this moment, they will cede control to external techno-powers with little incentive to respect Europe’s needs or ideals. Once this window closes, catching up—or even keeping pace—will be nearly impossible.
The EuroStack represents Europe’s last best chance to shape its own destiny: Build it, or become a digital colony.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Public comment on AI Exc. Order closes @ end of day 15 March 2025
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION:
On January 23, 2025, President Trump signed Executive Order 14179 (Removing Barriers to American Leadership in Artificial Intelligence) to establish U.S. policy for sustaining and enhancing America's AI dominance in order to promote human flourishing, economic competitiveness, and national security. This Order directs the development of an AI Action Plan to advance America's AI leadership, in a process led by the Assistant to the President for Science and Technology, the White House AI and Crypto Czar, and the National Security Advisor.
This Order follows the President's January 20, 2025, Executive Order 14148, revocation of the Biden-Harris AI Executive Order 14110 of October 30, 2023 (Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy Development and Use of Artificial Intelligence), which hampered the private sector's ability to innovate in AI by imposing burdensome government requirements restricting private sector AI development and deployment. The Trump Administration recognizes that with the right government policies, the United States can solidify its position as the leader in AI and secure a brighter future for all Americans.
OSTP seeks input on the highest priority policy actions that should be in the new AI Action Plan. Responses can address any relevant AI policy topic, including but not limited to: hardware and chips, data centers, energy consumption and efficiency, model development, open source development, application and use (either in the private sector or by government), explainability and assurance of AI model outputs, cybersecurity, data privacy and security throughout the lifecycle of AI system development and deployment (to include security against AI model attacks), risks, regulation and governance, technical and safety standards, national security and defense, research and development, education and workforce, innovation and competition, intellectual property, procurement, international collaboration, and export controls. Respondents are encouraged to suggest concrete AI policy actions needed to address the topics raised.
Comments received will be taken into consideration in the development of the AI Action Plan.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think, instead of terms of service, new online services should have a constitution, or a charter if you prefer.
And that constitution should include restrictions on future modifications to the constitution, and by extension to the service and the company that runs it. And one of the things that it sets up, in my opinion, should be to limit future changes that restrict the ability of the application to do its core functionality, and ideally that prevent a future buyer of the company from sneakily ruining the application for the sake of monetization, while allowing for future monetization of the application in an appropriate manner.
For example, imagine a web service like linktr.ee or pronouns.page (you set up a profile with links to all of your various accounts) that allows you to add your friends, so you can have a separate source of truth of a friends list decoupled from individual services, with features to maintain separate identities (e.g. one for irl friends, a professional one, and one for online friends) and different levels of trust within them that get access to different services.
Suppose this service is initially completely free, and the creator of it wants to assure users that they can start using it without risking that one day the company will sell and the new owners will suddenly start restricting access to existing features behind a paywall, or sell all of their information to advertisers.
Then the constitution might say that all existing features (or perhaps a certain explicitly defined subset of its features considered core its purpose) will remain free to all users, and that no user data will be sold to or shared with third parties. It could further limit that all future features must be free or available for some maximum price (perhaps relative to some indicator to account for inflation).
And it wouldn’t indicate the terms under which the constitution can be amended, perhaps including some means of user voting to allow for updates to the constitution that contradict the original rules as written without opening up the company to going against the users’ wishes. And it could specify that if they wish to shut down the application, they must inform the users with a certain amount of lead time and make the source code open source under a permissive license and provide a means of exporting their data.
That way the only risk of sudden loss of data should be if the company actually goes out of business, but making sure the wording requires a future parent company to follow this.
idk, i’m not a lawyer so i have no idea if this could be written in a way that is actually legally binding/enforceable but it sounded like a neat idea 🤷♀️.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Time for Brazil to accelerate trade talks with Asia
Asian nations beyond China present opportunities amid U.S. and European protectionism

When former French Prime Minister Michel Barnier went to Brussels to advocate for halting the European Union-Mercosur trade agreement, European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen countered: “If we don’t sign the treaty, China will take our place.”
However, in the name of French agricultural protectionism, French Trade Minister Sophie Primas argued that the agreement would not weaken the influence of China or the United States in Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay, and Uruguay, just as a failure in the agreement would not prevent Europeans and French from being present in these countries.
If France is determined to sacrifice preferential access to Mercosur and blow up a crucial economic and geopolitical deal, Europe is going to need all the luck it can get. The Federation of German Industries (BDI) recently reported that the European industry is facing its third consecutive year of recession. It predicts that exports from emerging markets could increase by 5%, compared to the stagnation of exports from developed countries. At the same time, France is one of the largest exporters in agribusiness.
In the United States, Donald Trump threatens to open a unilateral and protectionist toolbox in 2025. The U.S. will be an additional source of uncertainty and instability for Europe and globally. Mr. Trump has already threatened tariff increases against Mexico, Canada, China, and BRICS nations. Brazil will be subject to this situation, compounded by the rise of restrictive measures on global trade.
In this turbulent and unstable scenario, accelerating Brazil’s trade diversification towards Asia is evident. All trade data, in general, and current and future growth figures are more favorable in Asia, excluding China. The OECD projects growth of 6.9% for India next year and 5.2% for Indonesia, for example.
Continue reading.
#brazil#brazilian politics#politics#economy#international politics#european union#mercosur#china#india#united states#image description in alt#mod nise da silveira
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unlocking Global Trade Insights: The Power of Import and Export Data
Businesses, analysts, and policymakers must comprehend import and export data in the connected global economy of today. Trade data provides vital information about global supply chains, competitive environments, and market trends. Access to precise and timely import-export trade data can be crucial for small exporters searching for new markets or multinational corporations honing their sourcing strategy.
What is Import and Export Data?
Import and export data refers to detailed records of goods traded between countries. These records usually include information such as:
Product descriptions and codes (usually using HS Code or Harmonized System)
Quantity and value of goods traded
Countries of origin and destination
Ports used in shipping
Names of importers and exporters (in some datasets)
Date and mode of shipment
Governments collect this data through customs declarations and publish it either publicly or through commercial channels.
Why Is Import Export Data Important?
Market Research & Opportunity Identification Businesses can identify which products are in high demand in specific countries. For example, if India is importing a high volume of electronics from China, it indicates a steady market demand that other suppliers may tap into.
Competitor Analysis With the help of import export data providers, companies can analyze their competitors’ trade volumes, sourcing strategies, and market reach. This transparency can fuel more strategic planning.
Supply Chain Optimization Importers can identify alternative suppliers, especially during disruptions. Exporters, on the other hand, can find new buyers globally, improving resilience and profitability.
Regulatory Compliance Knowing the proper HS code and documentation needed can ensure smooth customs clearance. Import export trade data also helps businesses stay compliant with regulations like anti-dumping laws or sanctions.
How to Access Import and Export Data
There are two main sources for accessing trade data:
Government Databases Many governments publish import/export statistics through trade ministries or customs departments. For instance, the U.S. International Trade Commission (USITC) or India’s Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) provide some free tools.
Import Export Data Providers Professional data providers offer more granular and actionable data, often including shipment-level details, company names, and advanced analytics tools. These services may come with a subscription fee but provide great value for in-depth market intelligence.
Some popular import export data providers include:
ImportGenius
Panjiva
Export Genius
TradeMap
Datamyne
These platforms often allow you to filter data by HS code, time period, country, product category, or company name, offering deep insights.

Applications of Import Export Trade Data
Business Expansion: A company producing solar panels can study which countries are importing such products and approach potential buyers.
Price Benchmarking: Traders can compare average prices per unit in different markets and negotiate better deals.
Trend Analysis: Historical data can highlight seasonal trends or emerging markets for certain products.
Customs Brokerage: Brokers can use the data to guide clients through documentation, tariffs, and regulations in different regions.
Challenges in Using Import Export Data
While powerful, this data isn’t always straightforward. Challenges may include:
Data Inconsistency: Not all countries report data in the same format or frequency.
Data Accessibility: Some detailed data sets are behind paywalls.
Privacy: In certain jurisdictions, business names in shipment-level data are restricted for privacy reasons.
Final Thoughts
Data that is imported and exported is a strategic asset that is more than just numbers. Businesses can confidently and clearly navigate global markets with the assistance of a trustworthy import export data provider. Import export trade data is your key to making well-informed, data-driven decisions, whether you're sourcing products, researching new markets, or evaluating the competition.
To stay ahead in the constantly changing world of commerce, embrace the power of global trade intelligence.
#Import And Export Data#Import Export Data Provider#import export data#Import Export Trade Data#Data Vault Insight
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Time for a new edition of my ongoing vendetta against Google fuckery!
Hey friends, did you know that Google is now using Google docs to train it's AI, whether you like it or not? (link goes to: zdnet.com, July 5, 2023). Oh and on Monday, Google updated it's privacy policy to say that it can train it's two AI (Bard and Cloud AI) on any data it scrapes from it's users, period. (link goes to: The Verge, 5 July 2023). Here is Digital Trends also mentioning this new policy change (link goes to: Digital Trends, 5 July 2023). There are a lot more, these are just the most succinct articles that might explain what's happening.
FURTHER REASONS GOOGLE AND GOOGLE CHROME SUCK TODAY:
Stop using Google Analytics, warns Sweden’s privacy watchdog, as it issues over $1M in fines (link goes to: TechCrunch, 3 July 2023) [TLDR: google got caught exporting european users' data to the US to be 'processed' by 'US government surveillance,' which is HELLA ILLEGAL. I'm not going into the Five Eyes, Fourteen Eyes, etc agreements, but you should read up on those to understand why the 'US government surveillance' people might ask Google to do this for countries that are not apart of the various Eyes agreements - and before anyone jumps in with "the US sucks!" YES but they are 100% not the only government buying foreign citizens' data, this is just the one the Swedes caught. Today.]
PwC Australia ties Google to tax leak scandal (link goes to: Reuters, 5 July 2023). [TLDR: a Russian accounting firm slipped Google "confidential information about the start date of a new tax law leaked from Australian government tax briefings." Gosh, why would Google want to spy on governments about tax laws? Can't think of any reason they would want to be able to clean house/change policy/update their user agreement to get around new restrictions before those restrictions or fines hit. Can you?
SO - here is a very detailed list of browsers, updated on 28 June, 2023 on slant.com, that are NOT based on Google Chrome (note: any browser that says 'Chromium-based' is just Google wearing a party mask. It means that Google AND that other party has access to all your data). This is an excellent list that shows pros and cons for each browser, including who the creator is and what kinds of policies they have (for example, one con for Pale Moon is that the creator doesn't like and thinks all websites should be hostile to Tor).
#you need to protect yourself#anti google#anti chrome#anti chromium#chromium based browsers#internet security#current events#i recommend firefox#but if you have beef with it#here are alternatives!#so called ai#anti artificial intelligence#anti chatgpt#anti bard#anti cloud ai#data scraping
103 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ethyl Acetate Prices: Market Analysis, Trend, News, Graph and Demand
Ethyl Acetate is a widely used solvent across various industries such as paints and coatings, adhesives, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverages. Its popularity stems from its low toxicity, pleasant odor, and effective solvency properties. In recent years, the ethyl acetate market has seen dynamic shifts in pricing influenced by multiple factors including raw material costs, supply-demand imbalances, geopolitical developments, and evolving industrial applications. As of 2025, the market for ethyl acetate continues to experience price fluctuations that are closely tied to the global economic environment and the condition of key end-user industries.
One of the primary drivers of ethyl acetate prices is the cost of raw materials, particularly ethanol and acetic acid. These feedstocks are subject to market volatility influenced by crude oil prices, agricultural outputs, and regional production capacities. For instance, any disruption in ethanol supply, such as those caused by adverse weather conditions impacting corn or sugarcane yields, can cause upstream pressure on ethyl acetate prices. Similarly, acetic acid markets are susceptible to supply chain issues and industrial slowdowns, especially in major producing countries like China. As these feedstocks become more expensive or harder to procure, the cost of manufacturing ethyl acetate increases, driving up market prices.
In addition to raw materials, the supply-demand dynamics significantly affect ethyl acetate pricing. Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, represents the largest market both in terms of production and consumption. Any policy changes in these countries—such as environmental regulations, industrial output restrictions, or trade barriers—can shift the global balance. During periods of strong industrial activity, the demand for ethyl acetate in paints, coatings, and adhesives surges, leading to price hikes. Conversely, during economic downturns or reduced construction activity, demand weakens, often resulting in downward price corrections. These cyclical trends are critical to understanding ethyl acetate price trajectories over the short and long term.
Get Real time Prices for Ethyl Acetate: https://www.chemanalyst.com/Pricing-data/ethyl-acetate-75
Global trade patterns also influence ethyl acetate prices. Tariff structures, logistical disruptions, and freight costs can alter the competitiveness of ethyl acetate exports and imports. For example, if shipping lanes face congestion or if fuel prices rise, transportation costs for ethyl acetate shipments increase, which ultimately reflects in end-user pricing. Additionally, countries with surplus production may choose to offload excess inventory at competitive prices, putting downward pressure on international markets. On the other hand, regions heavily reliant on imports may experience elevated prices during times of restricted global supply.
Environmental and regulatory frameworks are increasingly playing a role in determining ethyl acetate prices. In many developed economies, strict environmental norms are being enforced to control volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. While ethyl acetate is considered a relatively eco-friendly solvent, the regulations governing its production and application still impose additional compliance costs on manufacturers. This, in turn, can influence pricing, particularly if newer technologies or greener alternatives are adopted. Furthermore, sustainability trends are pushing companies to source chemicals responsibly, which may involve higher procurement expenses that affect overall market rates.
Seasonal trends and consumer behavior also contribute to ethyl acetate price fluctuations. During the warmer months, when painting and construction projects are at their peak, demand for solvents like ethyl acetate increases. This seasonal spike can lead to temporary price surges. Similarly, changes in consumer preferences, such as increased demand for low-VOC or bio-based solvents, can impact traditional ethyl acetate consumption patterns and pricing structures. Manufacturers must adapt to these evolving trends to remain competitive, often adjusting pricing strategies to maintain margins and market share.
Technological advancements and capacity expansions have a mixed impact on ethyl acetate pricing. On one hand, improvements in production efficiency and plant automation can help reduce manufacturing costs, allowing producers to offer competitive pricing. On the other hand, new entrants in the market or expanded capacity in low-cost regions can lead to oversupply, causing prices to drop. Strategic investments in research and development are also shaping the future pricing scenario, as companies explore innovative synthesis methods or alternative feedstocks that could make ethyl acetate more cost-effective and sustainable.
Looking ahead, the forecast for ethyl acetate prices remains cautiously optimistic. While short-term volatility may persist due to uncertainties in global economic growth, energy prices, and geopolitical tensions, the long-term outlook is supported by the solvent’s indispensable role in key industries. Growth in emerging markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, is expected to bolster demand. Additionally, the trend toward greener solvents and sustainable industrial practices is likely to support a stable pricing environment for ethyl acetate, especially if producers can successfully navigate regulatory landscapes and adopt efficient production technologies.
In conclusion, ethyl acetate prices are influenced by a complex interplay of factors including feedstock costs, supply-demand dynamics, regulatory changes, and global trade flows. Understanding these variables is essential for stakeholders seeking to navigate the market effectively. As the world moves toward more sustainable and efficient chemical usage, the ethyl acetate market is poised for gradual yet steady evolution, with pricing trends reflecting both challenges and opportunities inherent in this transition. Continuous monitoring of market signals and strategic agility will be key for businesses aiming to capitalize on this essential solvent's role in modern industry.
Get Real time Prices for Ethyl Acetate: https://www.chemanalyst.com/Pricing-data/ethyl-acetate-75
Contact Us:
ChemAnalyst
GmbH - S-01, 2.floor, Subbelrather Straße,
15a Cologne, 50823, Germany
Call: +49-221-6505-8833
Email: [email protected]
Website: https://www.chemanalyst.com
#Ethyl Acetate Prices#Ethyl Acetate Pricing#Ethyl Acetate News#India#United kingdom#United states#Germany#Business#Research#Chemicals#Technology#Market Research#Canada#Japan#China
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The European Commission (EC) is reviewing legal mechanisms that would allow European energy companies to exit long-term contracts with Russian suppliers without incurring significant financial penalties. According to three EU officials cited by the Financial Times, the Commission is investigating whether the contracts could be invalidated under “force majeure” provisions—typically used when unforeseen circumstances prevent the fulfillment of contractual obligations.
One official emphasized that compensating Russia would defeat the broader EU objective of financially isolating Moscow. The initiative is part of the EU’s broader roadmap to eliminate reliance on Russian fossil fuels by 2027. Although pipeline gas from Russia has dropped to just 11% of total EU imports—down from nearly 40% in 2022—Russian liquefied natural gas (LNG) imports have surged over the past three years.
The Commission has not formally commented on the report. However, the effort to terminate gas contracts is unfolding at a sensitive time, as the EU seeks to reach an energy agreement with the United States in response to President Donald Trump’s tariff policies. The U.S., already the EU’s top LNG supplier, is seen as a logical alternative should Russian energy imports be further reduced.
According to data from the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air, the EU paid Russia €21.9 billion for oil and gas between February 2024 and February 2025. While coal imports from Russia have been banned, and 90% of oil imports are under embargo, natural gas imports remain unrestricted. Still, overall Russian gas deliveries to the EU are at their lowest levels since 2022, despite a 60% rise in LNG imports since then.
The release of the EU’s energy roadmap, initially scheduled for March, has been delayed by internal disputes. Key concerns include the risk of opposition from Hungary and Slovakia, both of which still depend heavily on Russian pipeline gas. Hungary’s government has openly opposed gas sanctions, which require unanimous support from all 27 EU member states.
Further delays stemmed from renewed discussions around the future of the Nord Stream pipeline between Germany and Russia, and from ongoing negotiations with the U.S. regarding a broader energy and trade deal. A European diplomat described the situation as “a mess,” questioning how the EU plans to diversify energy sources amid geopolitical uncertainty.
Despite calls from Brussels to scale back Russian LNG imports, many EU member states are reluctant to compel companies to terminate existing agreements due to fears of market instability and rising energy costs. Although the Commission has granted member states the authority to restrict Russian and Belarusian access to port infrastructure and pipelines, these measures fall short of providing a clear legal route to annul contracts.
The challenge for EU lawyers is the secrecy and variability of energy contracts. Invoking the war in Ukraine as a justification for “force majeure” may not hold up legally, an EU official cautioned. French, Spanish, and Belgian ports remain key entry points for Russian LNG, much of it originating from the Yamal LNG plant, which has ongoing deals with major energy firms such as Shell and Naturgy.
Meanwhile, the Brussels-based think tank Bruegel has argued in favor of imposing tariffs on Russian gas rather than implementing a full ban. Such a move would require only a majority vote among EU countries and could generate revenue while pressuring Russian exporters to lower prices. Bruegel warned that without a unified EU approach, Russia could exploit energy divisions among member states by offering selective gas supplies.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Musk's team to investigate employees with 'questionable' wealth as Trump orders hiring restrictions at federal agencies
During a meeting with Trump in the Oval Office of the White House on February 11, EST, Musk told the press that his team at the Department of Government Efficiency would investigate federal employees whose relatively low pay has skyrocketed their net worth.
The theme of the press conference that day was federal agency reform. Trump revealed that he had signed an executive order requiring federal agencies to work with the Department of Governmental Efficiency to continue to implement large-scale layoff programs, as well as severely restrict hiring. Components of agencies (or the agencies themselves) may be eliminated or consolidated because they are performing illegal functions. Additionally, there will be one new hire for every four departing employees, except in the areas of immigration, law enforcement and public safety.
Trump also urged Musk's team to investigate “the woman who rolled up about $30 million” during the conversation. Some analysts noted that he appeared to be alluding to Bauer, the administrator of the U.S. Agency for International Development, whom he has suspended. Bauer's annual salary was close to $250,000, but his net worth soared to $30 million during his tenure.
The U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) is one of the most important tools of U.S. foreign “soft power,” exporting its influence and American values, especially to Third World countries, including support for a variety of foreign NGOs, media organizations, academic programs, and scientific research projects. In the last fiscal year, the agency received more than $70 billion in available funds, of which perhaps only 10 percent was actually used for aid programs.
Musk then responded that there are actually a number of people in federal agencies who are paid only a few hundred thousand dollars but have amassed tens of millions of dollars in net worth during their tenure in their positions. That seems mysterious. I think they got rich on the taxpayers' dime.
Since the day he entered the White House, Trump has empowered Musk and his Department of Government Efficiency to make sweeping cuts to federal agencies and employees that have particularly impressed his supporters. As Musk's team continues to begin obtaining information from agencies such as the Department of the Treasury, the U.S. Agency for International Development, and the U.S. Office of Personnel Management, its claims will soon unravel the corruption that lies hidden in the mists of the multilayered organization. Next up for Musk's upcoming audits are the Departments of Defense and Education.
But his actions have meanwhile created a huge wave of opposition among his political opponents. Former Treasury Secretary Summers has argued that Musk and the Department of Governmental Efficiency exceeded their authority and violated professional ethics by accessing the Treasury's payment system. Musk has not publicly explained how his team obtained data on the net worth of officials. Senator Elizabeth Warren, a Democrat from Massachusetts, accused Musk of a power grab, and that these “cost-cutting and efficiency measures” had a serious impact on the normal operation of the government.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
DeepSeek's AI breakthrough: Fewer resources, big impact
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/deepseeks-ai-breakthrough-fewer-resources-big-impact/
DeepSeek's AI breakthrough: Fewer resources, big impact

On December 26th, a modest-sized Chinese company named DeepSeek introduced advanced AI technology, rivaling the top chatbot systems from giants like OpenAI and Google.
This achievement was noteworthy for its capability and the cost-efficiency with which it was developed. Unlike its large competitors, DeepSeek created its artificial intelligence, DeepSeek-V3, using significantly fewer specialized processors, which are typically essential for such advancements.
Cost efficiency and technological breakthrough
These processors are at the heart of a fierce tech rivalry between the U.S. and China. The U.S. aims to keep its lead in AI by restricting the export of high-end chips, such as those from Nvidia, to China.
However, DeepSeek’s success with fewer resources raises concerns about the effectiveness of U.S. trade policies, which have inadvertently spurred Chinese innovation using more accessible technologies.
DeepSeek-V3 impressively handles tasks like answering queries, solving puzzles, programming, and matching industry standards. Remarkably, it was developed with just around $6 million worth of computing resources, starkly contrasting the $100 million Meta reportedly invested in similar technologies.
Chris V. Nicholson from Page One Ventures pointed out that more companies could afford $6 million than the heftier sums, democratizing access to advanced AI technology.
Strategic implications and global impact of DeepSeek
Previously, experts believed only firms with substantial financial resources could compete with leading AI firms, which train their systems on supercomputers requiring thousands of chips.
DeepSeek, however, managed with just 2,000 chips from Nvidia. This efficient use of limited resources reflects the forced innovation resulting from chip restrictions in China, as Jeffrey Ding from George Washington University noted.
Recently, the U.S. tightened these restrictions to prevent China from acquiring advanced AI chips via third countries. This is part of ongoing efforts to limit Chinese firms’ potential military use of these technologies, which have resorted to stockpiling chips and sourcing them through underground markets.
ChatGPT vs Bard: What are the top key differences?
We’re taking a look at Bard vs ChatGPT and their key differences like technology, internet connection, and training data.

DeepSeek, a company rooted in quantitative stock trading, has been leveraging its profits to invest in Nvidia chips since 2021, fueling its AI research rather than consumer products. This focus has allowed it to bypass stringent Chinese regulations on consumer AI, attracting top talent and exploring diverse applications from poetry to complex examinations.
While leading U.S. firms continue to push AI boundaries, DeepSeek’s recent achievements underline its growing prowess in the field. It also highlights the broader shift towards open-source AI, gaining traction as companies like Meta openly share their technologies. This shift increasingly positions China as a central player in AI development, posing a strategic challenge to U.S. dominance in the field.
As the debate continues over the potential risks of open sourcing AI in the U.S., such as spreading misinformation, the global open source community, increasingly led by China, might shape the future of AI development, suggesting a significant geopolitical shift in the technology landscape.
Have you seen our 2025 event calendar?
From agentic AI to LLMOps, this year will be bigger than ever – join us in one of our 19 in-person events across the globe and network with other AI leaders.

Like what you see? Then check out tonnes more.
From exclusive content by industry experts and an ever-increasing bank of real world use cases, to 80+ deep-dive summit presentations, our membership plans are packed with awesome AI resources.
Subscribe now
#000#2025#Agentic AI#ai#AI chips#AI development#AI research#AI technology#applications#artificial#Artificial Intelligence#bank#bard#Calendar#challenge#chatbot#chatGPT#China#chip#chips#Community#Companies#competition#computing#content#cost efficiency#data#december#deepseek#DeepSeek-V3
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tim Stokely, founder of the adult content platform OnlyFans, has submitted an eleventh-hour proposal to buy TikTok’s US operations from its Chinese owner, ByteDance.
The “intent to bid” was made by Zoop—a social media startup Stokely cofounded with RJ Phillips, who serves as CEO and has a background in influencer marketing strategy—and cryptocurrency company The Hbar Foundation. For Zoop, the bid “represents a David vs. Goliath moment against traditional social media giants by endorsing a creator-first revolution,” according to a statement the company shared with WIRED. They said they want to put power back in the hands of creators through better revenue sharing.
ByteDance is up against the clock. If the company does not agree to a proposal from a US buyer by April 5, TikTok will be banned in the US under a law that went into effect in January citing national security concerns.
“The process is actually very unique; it’s being run by the White House and not by ByteDance,” Phillips tells WIRED, declining to comment further on the particulars of how the Zoop bid came about. “Our external council found the right person for us to initiate conversations with and that's what we've done.” Stokely did not respond to a request for comment.
On Wednesday, President Donald Trump was scheduled to consider multiple offers during a closed-door Oval Office meeting with vice president JD Vance and US secretary of commerce Howard Lutnick, who are spearheading the sale. His plan to keep TikTok operating in the US was reportedly going to be announced late that day, according to The Information.
The US government’s concerns around TikTok purportedly stem from fears that the Chinese government could access Americans’ data. But partnering with Hbar could potentially work in Zoop's favor; the company’s statement says Hbar operates the Hedera network, “a secure, transparent, and enterprise-grade public ledger” blockchain technology based in the US.
Stokely and Phillips are perhaps the most surprising of the suitors gunning for control of the popular video app.
“We’ve been looking at social for a long time, given our past. We want to restructure the industry in a way that we think is equitable,” Phillips tells WIRED, brushing away speculation that Zoop’s offer came together at the last minute. “Creators bring eyeballs to the pages, and therefore they should be the ones sharing in the lion’s share of the ad revenue. Users that are engaging with that content should also be the ones benefiting.”
Amazon also put in a last-minute offer to buy TikTok this week, joining four other groups that the White House was considering for the sale of TikTok’s US operations, Reuters reported. According to the The New York Times, the Amazon bid is not being taken seriously. One of the other possible deals floating around, per the Times, includes bringing on a team of US investors that includes Larry Ellison’s Oracle and private equity firm Blackstone.
There is also the possibility that an American investment team purchases TikTok while ByteDance retains ownership of TikTok’s algorithm and leases it to the prospective buyer. China has given no indication that it would be willing to sell the app’s algorithm, and exporting that type of technology would require its sign-off as part of a host of restrictions introduced in 2020.
Phillips says they are invested in building platforms that truly prioritize creators.
“Tech platforms for businesses like this should merely be the facilitator for creators. Creators have a hard enough time making steady income,” he says. “For us it's always going to focus on creators first, and not on shareholders first.”
We will soon know whether or not the Trump administration aligns with that vision.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
UNC5537: Extortion and Data Theft of Snowflake Customers

Targeting Snowflake Customer Instances for Extortion and Data Theft, UNC5537 Overview. Mandiant has discovered a threat campaign that targets Snowflake client database instances with the goal of extortion and data theft. This campaign has been discovered through Google incident response engagements and threat intelligence collections. The multi-Cloud data warehousing software Snowflake can store and analyze massive amounts of structured and unstructured data.
Mandiant is tracking UNC5537, a financially motivated threat actor that stole several Snowflake customer details. UNC5537 is using stolen customer credentials to methodically compromise Snowflake client instances, post victim data for sale on cybercrime forums, and attempt to blackmail many of the victims.
Snowflake instance According to Mandiant’s analysis, there is no proof that a breach in Snowflake’s enterprise environment led to unauthorized access to consumer accounts. Rather, Mandiant was able to link all of the campaign-related incidents to hacked client credentials.
Threat intelligence about database records that were later found to have come from a victim’s Snowflake instance was obtained by Mandiant in April 2024. After informing the victim, Mandiant was hired by the victim to look into a possible data theft affecting their Snowflake instance. Mandiant discovered during this investigation that a threat actor had gained access to the company’s Snowflake instance by using credentials that had previously been obtained through info stealer malware.
Using these credentials that were taken, the threat actor gained access to the customer’s Snowflake instance and eventually stole important information. The account did not have multi-factor authentication (MFA) activated at the time of the intrusion.
Following further intelligence that revealed a wider campaign aimed at more Snowflake customer instances, Mandiant notified Snowflake and potential victims via their Victim Notification Programme on May 22, 2024.
Snowflakes Mandiant and Snowflake have notified about 165 possibly vulnerable organizations thus far. To guarantee the security of their accounts and data, these customers have been in direct contact with Snowflake’s Customer Support. Together with collaborating with pertinent law enforcement organizations, Mandiant and Snowflake have been undertaking a cooperative investigation into this continuing threat campaign. Snowflake released comprehensive detection and hardening guidelines for Snowflake clients on May 30, 2024.
Campaign Synopsis According to Google Cloud current investigations, UNC5537 used stolen customer credentials to gain access to Snowflake client instances for several different organizations. The main source of these credentials was many info stealer malware campaigns that compromised systems controlled by people other than Snowflake.
As a result, a sizable amount of customer data was exported from the corresponding Snowflake customer instances, giving the threat actor access to the impacted customer accounts. Subsequently, the threat actor started personally extorting several of the victims and is aggressively trying to sell the stolen consumer data on forums frequented by cybercriminals.
Mandiant Mandiant discovered that most of the login credentials utilized by UNC5537 came from infostealer infections that occurred in the past, some of which were from 2020. Three main causes have contributed to the multiple successful compromises that UNC5537’s threat campaign has produced:
Since multi-factor authentication was not enabled on the affected accounts, successful authentication just needed a working login and password. The credentials found in the output of the infostealer virus were not cycled or updated, and in certain cases, they remained valid years after they were stolen. There were no network allow lists set up on the affected Snowflake client instances to restrict access to reliable sources. Infostealer Mandiant found that the first infostealer malware penetration happened on contractor computers that were also used for personal purposes, such as downloading pirated software and playing games. This observation was made during multiple investigations related to Snowflake.
Customers that hire contractors to help them with Snowflake may use unmonitored laptops or personal computers, which worsen this initial entry vector. These devices pose a serious concern because they are frequently used to access the systems of several different organizations. A single contractor’s laptop can enable threat actors to access numerous organizations if it is infected with infostealer malware, frequently with administrator- and IT-level access.
Identifying The native web-based user interface (SnowFlake UI, also known as SnowSight) and/or command-line interface (CLI) tool (SnowSQL) on Windows Server 2022 were frequently used to get initial access to Snowflake customer instances. Using an attacker-named utility called “rapeflake,” which Mandiant records as FROSTBITE, Mandiant discovered more access.
Mandiant believes FROSTBITE is used to conduct reconnaissance against target Snowflake instances, despite the fact that Mandiant has not yet retrieved a complete sample of FROSTBITE. Mandiant saw the use of FROSTBITE in both Java and.NET versions. The Snowflake.NET driver communicates with the.NET version. The Snowflake JDBC driver is interfaced with by the Java version.
SQL recon actions by FROSTBITE have been discovered, including a listing of users, current roles, IP addresses, session IDs, and names of organizations. Mandiant also saw UNC5537 connect to many Snowflake instances and conduct queries using DBeaver Ultimate, a publicly accessible database management tool.
Finish the mission Mandiant saw UNC5537 staging and exfiltrating data by continuously running identical SQL statements on many client Snowflake systems. The following instructions for data staging and exfiltration were noted.
Generate (TEMP|TEMPORARY) STAGE UNC5537 used the CREATE STAGE command to generate temporary stages for data staging. The data files that are loaded and unloaded into database tables are stored in tables called stages. When a stage is created and designated as temporary, it is removed after the conclusion of the creator’s active Snowflake session.
UNC5537 Credit Since May 2024, Mandiant has been monitoring UNC5537, a threat actor with financial motivations, as a separate cluster. UNC5537 often extorts people for financial benefit, having targeted hundreds of organizations globally. Under numerous aliases, UNC5537 participates in cybercrime forums and Telegram channels. Mandiant has recognized individuals who are linked to other monitored groups. Mandiant interacts with one member in Turkey and rates the composition of UNC5537 as having a moderate degree of confidence among its members who are located in North America.
In order to gain access to victim Snowflake instances, Attacker Infrastructure UNC5537 mostly leveraged Mullvad or Private Internet Access (PIA) VPN IP addresses. Mandiant saw that VPS servers from Moldovan supplier ALEXHOST SRL (AS200019) were used for data exfiltration. It was discovered that UNC5537 was storing stolen victim data on other foreign VPS providers in addition to the cloud storage provider MEGA.
Prospects and Significance The campaign launched by UNC5537 against Snowflake client instances is not the product of a highly advanced or unique method, instrument, or process. The extensive reach of this campaign is a result of both the expanding infostealer market and the passing up of chances to further secure credentials:
UNC5537 most likely obtained credentials for Snowflake victim instances by gaining access to several infostealer log sources. There’s also a thriving black market for infostealerry, with huge lists of credentials that have been stolen available for purchase and distribution both inside and outside the dark web.
Infostealers Multi-factor authentication was not necessary for the impacted customer instances, and in many cases, the credentials had not been changed in up to four years. Additionally, access to trusted locations was not restricted using network allow lists.
This ad draws attention to the ramifications of a large number of credentials floating throughout the infostealer market and can be a sign of a targeted attack by threat actors on related SaaS services. Mandiant predicts that UNC5337 will carry on with similar intrusion pattern, soon focusing on more SaaS systems.
This campaign’s wide-ranging effects highlight the pressing necessity for credential monitoring, the ubiquitous application of MFA and secure authentication, traffic restriction to approved sites for royal jewels, and alerts regarding unusual access attempts. See Snowflake’s Hardening Guide for additional suggestions on how to fortify Snowflake environments.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
5 notes
·
View notes