#though some of the works are highly allegorical.
Text
i know it's been brought up how ryoko kui likely knows what autism is based on a past short story in terranium in a drawer, but i also think it's worth pointing out in general that her work shows a good grasp on being disabled.
there's a short story titled "wolves don't lie" in another anthology of hers (seven little sons of the dragon) that's an allegorical but also very literal take on what it means to be disabled with a chronic illness.
(these are pages from a scanalation because I only have the paperback on me, but if there's the official localized version is available, i highly recommend supporting it if you can.)
it's about a young adult named keita who has werewolf syndrome. his mom had become a spokesperson/activist in spreading awareness and info about the condition and the experiences of raising a child with it. meanwhile keita struggles with living an everyday normal life as well as feeling alienated from his mom.





(that page 150 is odd as the official translation i have has him think "she does know me pretty well, doesn't she?" referring to his mom, so im unsure as to which translation is correct)
as a fantasy allegory and short story, it still has its limits, but it's interesting to see how she explores how society tends to let down and stigmatize disabled people, even as they are supported as "respectable" examples that feels very true to real life. having said that though, it's not purely about disability so much as a slight coming of age story about very common parent/child conflict that's through the lens of fantasy and disability.
(and in some ways you can see parallels with izutsumi's blended soul situation.)
as a whole again, i recommend the collection as you can read kui visiting a lot of the same themes that are in delicious in dungeon, even without the core of food and cooking.
#ryoko kui#idk why i wrote all this out........i guess it just popped into my head and i'd like for more ppl to read this anthology....it's v good
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Beast/La Bête (2024) review

Dolls, Blue Moon and… pigeons.
Plot: In the near future where emotions have become a threat, Gabrielle finally decides to purify her DNA in a machine that will immerse her in her previous lives and rid her of any strong feelings. She then meets Louis and feels a powerful connection, as if she has known him forever. A melodrama crossed by the genre, which unfolds over three distinct periods, 1910, 2014 and 2044.
Essentially this is a film that covers every genre possible. From *deep breath* melodrama to romance to thriller to mystery to sci-fi to drama to psychological to surrealism… the list goes on. It is so difficult to stick The Beast (or La Bête as the French title goes) into a specific box, as it’s so many things all at once. This is a bold and audacious piece of filmmaking from French director Bertrand Bonello, based on a Henry James short story/novells “The Beast in the Jungle”. However this film is anything but short. At over 2 and a half hours, this takes you on a disorientating, divergent and daring odyssey through time, and it is both bombastically incredible yet also highly frustrating. Look, this didn’t completely burn out my eye-sockets like Edward Yang’s 1991 epic magnum opus A Brighter Summer Day that was 4 flipping hours long! Don’t get me wrong, that movie has novelistic level of richness in character, narrative and depth, but at that runtime you’re taking the actual mick! So The Beast is nowhere on that scale, but it is definitely a movie that will challenge you mentally, and will make you question everything.
Exhausting is a word I’d choose to use when describing this film. Not in a negative way, but more so how it throws so much at you, but doesn’t explain the half of it. In fact it is very Lynchian in its absurdist style, and reminded me in some ways of Mullholland Drive - a movie at the end of which I too found myself asking the simple yet well earned question of “what the actual f***??”. The Beast feels, especially at the beginning, as if it should have been a piece of poetry, as scenes were happening, and even though there was the loose narrative connection of them being various versions of characters’ past lives, for the most part it seemed like a cluster of random allegorical shorts squeezed together in an anthological format. In the end it does come together granted, but as a collective Parnassus package this movie isn’t supposed to work. It can easily be called out for being pretentious and convoluted and slow, but I do believe this thing somehow, for no genuine explanation, works! It’s a baffling interweaving of the intimate and the spectacular, classicism and modernity, known vs the unknown, yet at this core this is a love story, that is expressed in its varied forms. Essentially The Beast is the answer to the ideology of human connection. Deep.
Wes Anderson darling/Bond girl Lea Seydoux is truly magnetic in this role. She delivers so much through her eyes, and I felt every emotion, even in scenes where I was completely narratively lost. This is easily her best performance I’ve seen from her. George MacKay has less to work with, as he’s more of a foil to Seydoux’s counterpart, but his chemistry with her is solid, and also in the LA segment he absolutely nails this incel character called Louis Lewanski who blogs/monologues on his iPhone about hatred towards women. It’s a performance that is suffused with pitch black humour and a mounting sense of dread. Both Seydoux and MacKay are incredible in this, but also I must applaud the look of this movie. Each shot feels like it should be a painting in a museum. The use of colour to the camera set up to the angle and blocking, with pitch perfect set designs and costumes, this movie looks crisp. The imagery somewhat reflects the movie’s focus on visions and dreams, and honestly this may be the most beautiful looking film this year.
La Bête will stick in my brain and haunt me for a long while, and in fact with how AI is such a current majorly spoken about topic, it does make one wonder if we do become overly reliant on artificial intelligence, will we lose all that is necessary to the human spirit - our emotions, our fears, our doubts? Additionally, the psychological idea of fear and that behind everything that we’re afraid of there is a wish, and the romantic ideal of persistent love…. gosh, this movie is sublime! I do think in parts it does get up its own arse, don’t get me wrong, but this is the type of movie that has something to say, and also is very much the kind of film Letterboxd users would quote as “THIS IS CINEMA!”.
Overall score: 8/10

#the beast#la bete#movie#movie reviews#film#film reviews#thriller#cinema#drama#adventure#romance#science fiction#melodrama#surrealism#ai#lea seydoux#george mckay#bertrand bonello#2024#2024 films#2024 in film#lynchian#mystery#french cinema#la bête#the beast review#dasha nekrasova#guslagie malanda#artificial intelligence#mubi
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
2001: A Space Odyssey still leaves an indelible mark on our culture 55 years on
by Nathan Abrams, Professor of Film Studies at Bangor University

2001: A Space Odyssey is a landmark film in the history of cinema. It is a work of extraordinary imagination that has transcended film history to become something of a cultural marker. And since 1968, it has penetrated the psyche of not only other filmmakers but society in general.
It is not an exaggeration to say that 2001 single-handedly reinvented the science fiction genre. The visuals, music and themes of 2001 left an inedible mark on subsequent science fiction that is still evident today.
When Stanley Kubrick began work on 2001 in the mid-1960s, he was told by studio executive Lew Wasserman: “Kid, you don’t spend over a million dollars on science fiction movies. You just don’t do that.”
By that point, the golden age of science fiction film had run its course. During its heyday, there was a considerable variety of content within the overarching genre. There had been serious attempts to foretell space travel. Destination Moon, directed by Irving Pichel and produced by George Pal in 1950, and, in mid-century, Byron Haskin’s Conquest of Space both fantasised space travel and, in Haskin’s film, a space station, which Kubrick would elaborate on in 2001.
youtube
Most 1950s science fiction films, though, were cheap B-movie fare and looked it. They involved alien invasions with an ideological and allegorical subtext. They were cultural, cinematic imaginations of the danger of communism, which in the overheated political atmosphere of the time was seen as an imminent threat to the American way of life.
The aliens in most science fiction films were out simply to destroy or take over humanity; they were expressions, to use the title of a Susan Sontag essay, of “the imagination of disaster”. There were some exceptions, including Byron Haskin’s film version of The War of the Worlds and Robert Wise’s The Day the Earth Stood Still.
By 1968, then, as the lights went down, very few people knew what was about to transpire and they certainly were not prepared for what did. The film opened in near darkness as the strains of Thus Spake Zarathustra by Richard Strauss were heard. The cinema was dazzled into light, as if Kubrick had remade Genesis.
The subsequent 160 or so minutes (the length of his original cut before he edited 19 minutes out of it) took the viewer on what was marketed as “the ultimate trip”. Kubrick had excised almost every element of explanation leaving an elusive, ambiguous and thoroughly unclear film. His decisions contributed to long silent scenes, offered without elucidation. It contributed to the film’s almost immediate critical failure but its ultimate success. It was practically a silent movie.
2001 was an experiment in film form and content. It exploded the conventional narrative form, restructuring the conventions of the three-act drama. The narrative was linear, but radically, spanning aeons and ending in a timeless realm, all without a conventional movie score. Kubrick used 19th-century and modernist music, such as Strauss, György Ligeti and Aram Khachaturian.
Vietnam
The movie was made during a tumultuous period of American history, which it seemingly ignored. The war in Vietnam was already a highly divisive issue and was spiralling into a crisis. The Tet offensive, which began on January 31 1968, had claimed tens of thousands of lives. As US involvement in Vietnam escalated, domestic unrest and violence at home intensified.
Increasingly, young Americans expected their artists to address the chaos that roared around them. But in exploring the origins of humanity’s propensity for violence and its future destiny, 2001 dealt with the big questions and ones that were burning at the time of its release. They fuelled what Variety magazine called the “coffee cup debate” over “what the film means”, which is still ongoing today.
The design of the film has touched many other films. Silent Running by Douglas Trumbull (who worked on 2001’s special effects) owes the most obvious debt but Star Wars would be also unthinkable without it. Popular culture is full of imagery from the film. The music Kubrick used in the film, especially Strauss’s The Blue Danube, is now considered “space music”.
Images from the movie have appeared in iPhone adverts, in The Simpsons and even the trailer for the new Barbie movie.
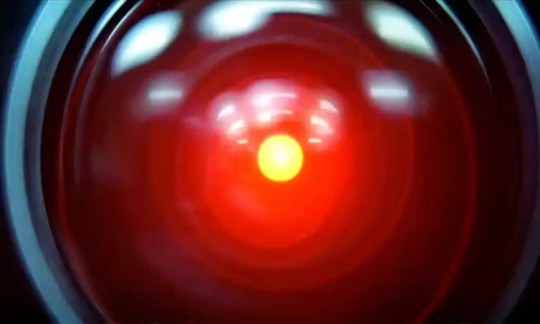
The warnings of the danger of technology embodied in the film’s murderous supercomputer HAL-9000 can be felt in the “tech noir” films of the late 1970s and 1980s, such as Westworld, Alien, Blade Runner and Terminator.
HAL’s single red eye can be seen in the children’s series, Q Pootle 5, and Pixar’s animated feature, Wall-E. HAL has become shorthand for the untrammelled march of artificial intelligence (AI).
In the age of ChatGPT and other AI, the metaphor of Kubrick’s computer is frequently evoked. But why when there have been so many other images such as Frankenstein, Prometheus, terminators and other murderous cyborgs? Because there is something so uncanny and human about HAL who was deliberately designed to be more empathic and human than the people in the film.
In making 2001, Stanley Kubrick created a cultural phenomenon that continues to speak to us eloquently today.
#movies#science fiction#2001: a space odyssey#stanley kubrick#space#technology#artificial intelligence#space exploration#tet offensive#featured#Youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
More about the trans Shu fic
I forgor where I left off and I’m not gonna look 😎
Anyways I’ve decided that all the nobles are vampires. mostly for class divide and allegorical strength (that’s bullshit you fucking asshole I know this is so Shu can bite Mika at some point and Mika can be weird about it)
Anyways back to the queer shitlet children.
the abbey is real close to the capital ain’t it? I wonder if that has any affect on how the abbey is run. It’s highly corrupt 🥰. Most of the kids are being trafficked as servants or contract killers or any other manner of unsavory lines of work that these kids wouldn’t choose otherwise. Mika has killed before.
anyways Shu and Mika grow way closer. Mika doesn’t know who Shu is, and Shu doesn’t know that the abbey is corrupt or that his best friend is a contract killer. Good for them. They’re each other’s escape from their shitty realities.
Shu is still being forced to present extremely femininely and assume feminine roles even though he’s prefer to be treated like a human being that can make his own decisions. Also he is being passed up for the throne in favor of his younger step brother because he isn’t a man in the eyes of his father. Shu is obviously not happy about any of this. Also he isn’t allowed to make clothing at the castle because he got caught making “clothing unbefitting a lady of his social standing”.
So in response to that Mika has been learning how to sew and he made Shu a couple things with the help of the ladies at the abbey. Shu is really grateful but it is Shu so he does take the garments and alter them a bit to be more to his liking. Shu worries that Mika will be upset about this but Mika isn’t. It’s Mika, he’s actually quite happy because he was really worried about how they would turn out and having Shu compliment them and then show him how to improve makes him really really happy, because it means that the basic stuff he made is good enough for Shu to deem them of high enough quality for him to wear.
Anyways Shu starts sewing at the abbey in secret, away from the prying eyes of his father.
Shu makes a couple “jokes” about how he wishes he could just run away from his home and marry a guy to get him out of here. Mika jokes back that if it weren’t for him being a commoner, and a human they could do that together. Mika is actually joking, Shu is not.
Shit happens, these mfers get older they’re sixteen now. Shu is being married off to another guy and he is very unhappy about this. So is his betrothed, because it is Rei. They’re both upset about this.
Shu talks to Mika about this and is like, “wait, why don’t we run away and get married when we’re older. We can go across the border and be long gone before anyone can catch us.”
and Mika is like “I’m sorry, we can’t. I’m not worthy of any of that. I can’t do that to you, you’re a noble and I’m a commoner, we can’t just-”(he doesn’t know that Shu is royalty) and Shu gets mad and reveals his royal title and they both leave for the day because they’re both upset.
Shu causes a scene at the wedding ceremony and the wedding is called off. Bitch convinces the court he is hysterical (bitch has woman who talks too much disease 🙄).
anyways his step mom is now plotting to have him killed 🥰🥰.
I’m done for now, I’ll be back.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
On Kawara (1932-2014)
On Kawara, a Japanese born artist based in New York, became a household name after gaining sensational response from his contemporaries for his graphic images. He came to stand for the new generation of social realism which was determined to confront the reality of Japan’s postwar society with a vision unclouded by the older generations' nostalgia for the prewar past.
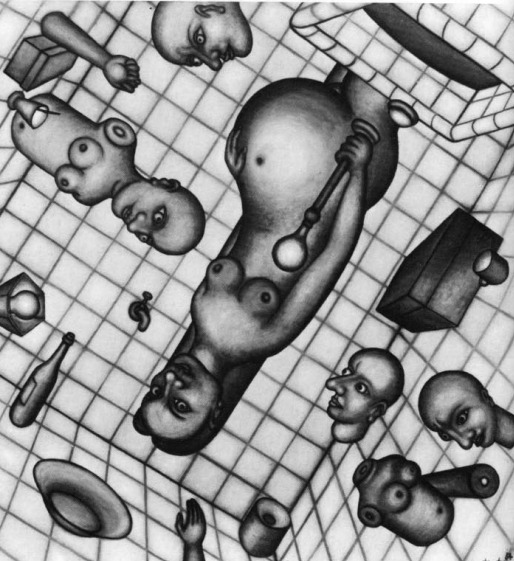
The Bathroom series, 1953
In these pencil sketches, the bathroom is a distorted, claustrophobic space filled with scenes of murder, dismembered bodies and Matricidal images. The naked bodies of wide-eyed men and women are cut into pieces with various body parts floating inside a neatly tiled bathroom.
It is not difficult to see that Kawara's drawings are associated with the tumultuous state of the Japanese nation during his time. A close examination of the conflict betwen the subject of brutality and the formal strategy of indifference (the subjects seem indifferent to their their own murder) allows us to infer that the disrupted representation of Kawara's Bathroom series echoes the psychological effect of the nuclear explosion and its social aftermath. Some images can be seen below.

#The Decoy#—the humiliation of occupation#collusion in a neighboring war#political entrapment#and social inequality#though some of the works are highly allegorical.#Some of his works are shown below.#The unattractive head depicts Kishi Nobusuke#who became prime minister in 1957 and negotiated the renewal of the security treaty in 1960. Kishi was imprisoned as an accused war crimina#but never brought to trial.#In several works#Ishii set his sights on specific targets#such as war profiteers in his untitled painting below.#japan#japanese history#art#literature#tumblarians#writers#japanese#japanese culture#japanese art history#art history#art exhibition#illustration#contemporary japanese art#post war#art revolution#world war 2#world war second
0 notes
Text
“Entertainment held an important place at the English royal court under Eleanor and Henry II, in contrast to Louis VII’s court, known for its sobriety and solemnity. Eleanor’s second husband invited jongleurs and performers of all sorts to his court, doubtless encouraged by her. English moralists, much like critics of the court of Eleanor’s grandfather at Poitiers, condemned the Plantagenet court for immorality, complaining of actors, mimes, and dancers who fostered debauched conduct among the courtiers.
Just as with other princes new to power, Henry Plantagenet, after winning the English Crown, attracted to his court singers and writers to compose poems and songs, glorifying him and his lineage. Among the crowd of courtiers were serious writers in Latin and in the Anglo-Norman vernacular, and during Eleanor’s years as English queen, troubadour lyric poetry, courtly love, and courtly romances spread to the Anglo-Norman world. A former poet turned monk at Eleanor and Henry’s court noted ruefully, “When I frequented the court with the courtiers, I made sirventes, chansons, rimes and saluts [types of secular lyrics], among the lovers and their mistresses.”
Yet a cause and effect relationship between Eleanor’s arrival in England and the advent of courtly literature there is dubious. Certainly a uniquely productive literary culture flourished at the royal court under Eleanor and Henry, and learned men flocked there, as evidenced by an extraordinary flowering of literary works in several genres. The queen, of course, had grown up at a court where literature and learning were valued, as had Henry. A contemporary described his father Geoffrey le Bel as “most highly lettered, commanding eloquence which set him far above both clerics and laymen, replete with all good manners.” Even before Henry became king, writers were dedicating works to him.
It is unlikely that the young duke of Normandy commissioned their works, however; they were dedicated to him in anticipation of his patronage once he took the English throne. Certainly, the court of Eleanor and Henry II earned a reputation as a beacon for courtly writers. As king of England, Henry was eager to encourage authors writing on varied subjects, no doubt expecting their works to reflect favorably on him as a powerful monarch. He sponsored both Latin language and Anglo-Norman vernacular works, among them historical works written in England and Normandy and also in Anjou that would give an illustrious past to both his Plantagenet predecessors as counts of Anjou and his Norman ancestors who had captured England’s royal Crown.
He wished during his quarrel with his archbishop of Canterbury to shore up the English monarchy’s sacred character with writings pointing up the sanctity of his predecessors. In his competition with the Capetian kings he needed to claim as forebear some heroic figure equaling their prestigious predecessor Charlemagne, and King Arthur or Edward the Confessor could potentially fulfill that need. Both of Henry I’s wives had been known as patrons of literature, and Henry II, who modeled himself on his grandfather, associated his queen with him in extending patronage to writers, even if no explicit evidence for their commissions of works survives.
Yet dedications or eulogies inserted by authors into their works afford indirect evidence that they viewed their monarch or his queen as prospective if not actual sources of patronage. Not all clerics wrote in search of material gain, however; some were impelled to write in the hope of instructing and correcting their prince, and others simply sought to show themselves loyal subjects through passages praising their ruler. There is no evidence that the nun of Barking who translated a Latin life of Edward the Confessor into Anglo-Norman had a commission from Henry II or his queen, although she would have known of the king’s support for the Confessor’s canonization. Perhaps she hoped to win their favor for her convent through her work. She inserted into her translation a passage calling on God’s protection for the king, the queen, and their lineage, and their divine sustenance in sanctity, peace, joy, and plenty.
For clerical authors at court who often doubled as royal clerks, it is impossible to separate patronage of their literary activity from payment for their secretarial services. Their reward from Eleanor or Henry often came in indirect forms, as presentations to churches or to cathedral prebends, whether in return for activities as royal scribes or as authors. Best known are clerics writing in Latin at the court of Eleanor and Henry, such as Gerald of Wales, Peter of Blois, or Roger of Howden; but Wace, a writer of histories in Anglo-Norman, was awarded by the king with a prebend at Bayeux Cathedral in the 1160s.
Eleanor had grown up at the Poitevin court that gave birth to troubadour poetry, and she certainly heard, read, and encouraged courtly literature. The royal court of Henry II attracted singers of songs, viol players, pipers, and other musicians; and among these entertainers were poets and composers. No doubt scores of songs were commissioned as propaganda in praise of the monarch and his queen or to commemorate special events such as celebrations of victories or the births and marriages of royal offspring, and once sung were soon forgotten.
Occasionally a pipe roll entry records payments to a storyteller (fabulator) or a harpist (citharidus). Although no documents survive to register Eleanor’s own commissions of literary works, handsome sums were regularly handed over to her from the royal treasury that could be used for distributing patronage to writers without leaving any trace in the exchequer accounts. The absence of documents recording Eleanor’s payments to writers does not preclude her showing favor to them with cash from her personal treasury or with gifts of precious objects.
Royal reward to writers, like favors to other courtiers, could take the form of gifts of robes or other clothing, gold cups, or even horses and mules. A Catalan troubadour writing a decade or more after Henry II’s death wrote of hearing how “Sir Henry, a king of England, gave horses and mules as gifts.” A week spent entertaining a generous patron could win a singer or poet robes worth more than most peasants earned in a year. Lacking other documentation, however, the poems themselves must bear witness that their authors expected to win the English queen’s favor through their writings.
…During Eleanor’s early years as English queen, she seems to have shared her husband’s taste for histories, especially those written in the Anglo-Norman vernacular. Henry II commissioned writers experienced at composing romances who could make historical writings available to a courtly audience not well educated in Latin. In about 1155 a royal clerk Wace won a commission to write the Roman de Brut, an Anglo-Norman adaptation of Geoffrey of Monmouth’s Latin history. Layamon, a priest who translated the Brut into English in the first decades of the thirteenth century, claims that Wace had dedicated it to Queen Eleanor and that he wrote of her, “Generous is Eleanor, gracious and wise.”
Possibly Layamon had seen a now lost presentation copy that contained a dedication to the queen. While his statement is no direct proof for Eleanor’s patronage, at least it indicates that she was thought to be a queen interested in literature and capable of offering favors to authors attracting her attention. Hardly accurate history, the Roman de Brut presents the story of the early Britons from the arrival of Brutus, a refugee from the Trojan War, to the Saxon invasions as if a translation of an ancient book in Breton (or Welsh). Although Wace incorporated oral traditions transmitted in minstrels’ songs, Geoffrey of Monmouth’s History of the Kings of Britain was his chief source.
His vernacular reworking of legends of the ancient Britons, adding courtly elements, would play a pivotal part in medieval literature as the source for the “matter of Britain,” for it proved appealing to composers of later twelfth-century romances centering on King Arthur, Guinevere, and the knights of the Round Table. As a result, the legendary Arthur, his queen, and his knights became as much a part of history for twelfth-century readers as biblical personages or as heroes from the Latin classics, and Wace may have modeled his depiction of Arthur’s queen on Eleanor.
Perhaps courtiers hearing or reading these romances were tempted to see Henry and Eleanor in the portraits of Arthur and Guinevere. If modern readers can see parallels between fictional characters and historical personalities in twelfth-century romances, then Eleanor and Henry’s contemporaries could have seen them even more clearly. Medieval readers expected to uncover more than one level of meaning during their reading, and they were attuned to the allegorical nature of poetry.
Henry II, though materially more powerful than his rival Louis VII, felt himself “ideologically inferior” because of the Capetian king’s prestigious ancestry, traced back to Charlemagne. Arthurian material is sometimes said to have provided useful propaganda for Henry in his rivalry with Louis and later with his son Philip II, offering King Arthur as a prestigious royal predecessor from an even earlier time than the Capetians’ Frankish predecessors. Yet Henry made only fitful and desultory attempts at constructing an Arthurian ideology to counteract the Capetians’ use of Charlemagne.
Seeking ideological advantage from Arthurian material was not without risks, for King Arthur and Arthurian legends could serve better the purposes of rebellious English nobles, who found in Arthur and his faithful men gathered at the Round Table an idealized view of earlier kingship. Arthur was closely identified with the inhabitants of the Celtic fringes, people looked on by the English as savages, and Arthurian tales had an especially subversive effect on the Welsh and the Bretons. Henry II commissioned another book from Wace, the Roman de Rou, a history praising his Norman ducal ancestors from Rollo (or Rou), the Viking invader of Normandy, down to his grandfather Henry I; and the clerk prepared himself for the task by reading early Norman chronicles, listening to epic poetry, and even examining charters in Norman churches.
…Eleanor may have had some connection with another scientific work, a medical text in Latin brought from Sicily to England by Robert Cricklade, prior of Saint Fridewide’s, Oxford (d. c.1171). He was the compiler of a scientific text, an abridgement of Pliny’s natural history, that he had dedicated first to King Henry I, then later to Henry II. Like a number of English scholars, Robert traveled in Italy, going to Rome and Sicily in 1156 and returning in 1158. While in Sicily, he was given a copy of the Gynaecia Cleopatrae, originating in Constantinople, to take back to England to the queen.
Eleanor would have learned of the reputation of Greek medical learning while in Constantinople during the Second Crusade. It is plausible that the English queen, anxious after the early death of her son William, had asked the prior to bring from Sicily medical books on childbirth, care of children, and female disorders. At the time of Robert’s departure, Eleanor was left with only one boy, Young Henry. Given her record of bearing only daughters in her first marriage, she may have had dynastic concerns about producing more sons. If so, her fears proved unrealistic, for she quickly produced two more sons in 1157 and 1158.”
- Ralph V. Turner, “ A Queen’s Work: Regent for an Absentee King, 1155–1168.” in Eleanor of Aquitaine: Queen of France, Queen of England
#eleanor of aquitaine#eleanor of aquitaine: queen of france queen of england#history#high middle ages#medieval literature#ralph v. turner#henry ii of england
36 notes
·
View notes
Photo
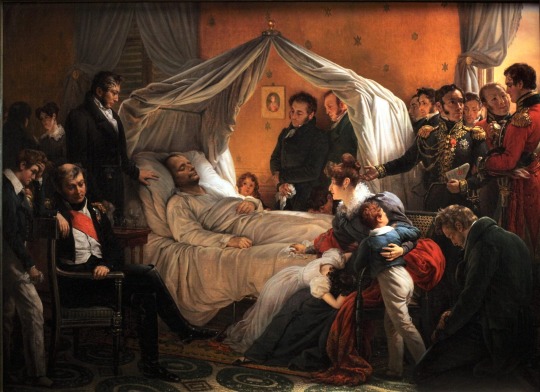
Vivant, il a manqué le monde ; mort, il le possède.
- François René de Chateaubriand (1768-1848), Vie de Napoléon, livres XIX à XXIV des Mémoires d’outre-tombe (posthume)
Of course we don’t have any photograph or film of Napoleon’s death on 5 May 1821 on Saint Hélène. But we do have the next best thing: a painting. Charles de Steuben depiction of Napoleon's deathbed and his faithful entourage that served as witnesses to his dying moments became the one of the most important paintings of the post-Napoleonic era but then faded from modern memory.
I first came across it by accident when I was in my teens at my Swiss boarding school. There were times I found myself with school friends going away on hiking trips around the high Alpine chain of the Allgäu Alps and we would drive through Lake Constance to get there, or we would hike around the Lake itself through the Bodensee-Rundwanderweg.
Perched high above Lake Constance and nestled in large parklands, stood Schloss Arenenberg which overlooks the lower part of Lake Constance. At first, it appears a relatively modest country house. But this was no usual pretty looking house. Arenenberg was owned by well-heeled families before it was sold to Hortense de Beauharnais, the adopted daughter and sister-in-law of the French Emperor himself, Napoleon Bonaparte. She had it rebuilt in the French Empire style and lived there from 1817 with her son Louis Napoleon, later Emperor Napoleon III, who is said to have spoken the Thurgau dialect in addition to French. This elegantly furnished castle then was once the residence of the last emperor of France.

The alterations made first by Queen Hortense and later by Empress Eugénie have been carefully preserved and the house still bears the marks of both women. Queen Hortense's drawing room is perfectly preserved and visitors can still admire her magnificent library (all marked with the Empress' cipher) containing over one thousand books. Likewise, in the room where the queen died, every object has been maintained in its original condition: pieces of furniture and personal belongings are gathered here to evoke her memory in a very touching manner. As for Empress Eugénie's rooms, they too have been very carefully preserved. Her private drawing room is a perfect illustration of the Second Empire style with sculptures by Carpeaux and portraits of the imperial family by Winterhalter.
After 1873, the Empress and the Imperial Prince brought the palace back to life by making regular summer visits, which they continued until 1878. However, on the tragic death of her son in 1879, Eugénie found it difficult to return to a place so full of painful memories. And so in 1906 she donated the estate to the canton of Thurgovie as a testimony of her gratitude for the region's faithful hospitality towards the Napoleon family. And in accordance with the Empress' wishes, the residence was turned into a museum devoted to Napoleon.
In what is now the Napoleonic Museum, the original furnishings have been preserved, and the palace gardens had been fully restored. This in itself might be worth a visit for the view over Lake Constance which is stunning. For Napoleonic era buffs though its the incredible art collection which is its real treasure. It houses an important art collection including works by the First-Empire artists Chinard Canova, Gros, Robert Lefèvre, Gérard, Isabey and Girodet-Trioson, and by the Second-Empire painters and sculptors Alfred de Dreux, Winterhalter, Carpeaux, Meissonier, Hébert, Flandrin, Detaille, Nieuwerkerke and Giraud.
But what caught my eye was this painting, ‘La Mort de Napoléon’ by Charles de Steuben. I didn’t know anything about it or the artist for that matter, but one of my more erudite school friends who, being French, was into Napoleonic stuff in a huge way, and she explained it all to me. Of course I knew a fair bit about Napoleon growing up because my grandfather and father, being military men themselves, were Napoleonic warfare buffs and it rubbed off onto me. I just knew about Napoleon the military genius. I never thought about him once he was beaten at Waterloo in 1815. So I never really engaged with Napoleon the man. And yet here I was staring at his last breath of mortality caught forever in time through art. Not for the first time I had mixed feelings about Napoleon Bonaparte, both the man and the myth (built up around him since his death).

On 5 May, 1821, at 5.49pm in Longwood House on the remote island of St Helena, in the words of the famed French man of letters, François-René de Chateaubriand, ‘the mightiest breath of life which ever animated human clay’ came no more. To the British, Dutch, and Prussian coalition who had exiled Naopleon Bonaparte there in 1815, he was a despot, but to France, he was seen as a devotee of the Enlightenment.
In the decade following his demise, Napoleon’s image underwent a transformation in France. The monarchy had been restored, but by the late 1820s, it was growing unpopular. King Charles X was seen as a threat to the civil liberties established during the Napoleonic era. This mistrust revived Napoleon’s reputation and put him in a more heroic light.
Fascination with the French leader’s death led Charles de Steuben, a German-born Romantic painter living in Paris, to immortalise the momentous event. Steuben’s painting depicts the moment of Napoleon’s death and seeks to capture the sense of awe in the room at the death of a man whose legendary career had begun in the French Revolution. It was this, ultimate moment that Steuben wished to immortalise in a painting which has since become what could almost be described as the official version of the scene.
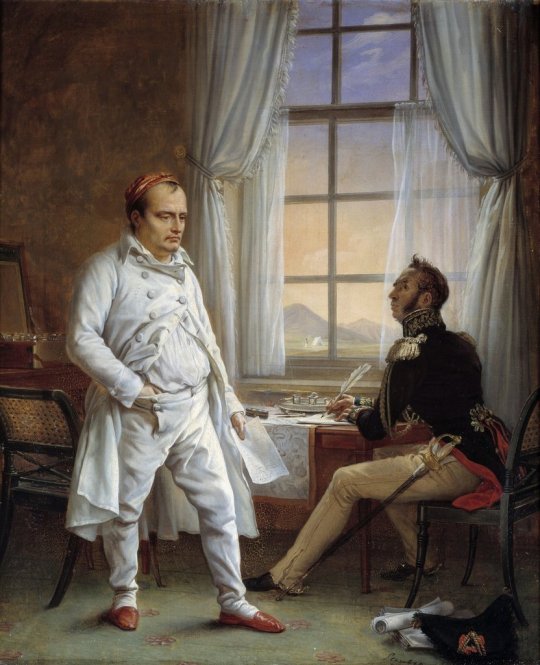

There is no question that Steuben’s painting became the most famous and most iconic depiction of Napoleon’s death in art history. In another painting, executed during the years 1825-1830, Steuben was to give a realistic view of the emperor dictating his memoirs to general Gourgaud. This same realism also pervades his version of Napoleon’s death, and it is totally unlike Horace Vernet’s, Le songe de Bertrand ou L’Apothéose de Napoléon (Bertrand’s Dream or the apotheosis of Napoleon) which, although painted in the same year, is an allegorical celebration of the emperor’s martyrdom and as such the first stone in the edifice of the Napoleonic legend.
And what a legend Napoleon’s life was turned into for time immemorial. Napoleon declared himself France’s First Consul in 1799 and then emperor in 1804. For the next decade, he led France against a series of European coalitions during the Napoleonic Wars and expanded his empire throughout much of continental Europe before his defeat in 1814. He was exiled to the Mediterranean island of Elba, but he escaped and briefly reasserted control over France before a crushing final defeat at the Battle of Waterloo in 1815.
Napoleon’s military prowess earned him the fear of his enemies, but his civil reforms in France brought him the respect of his people. The Napoleonic Code, introduced in 1804, replaced the existing patchwork of French laws with a unified national system built on the principles of the Enlightenment: universal male suffrage, property rights, equality (for men), and religious freedom. Even in his final exile on St. Helena, Napoleon proved a magnetic presence. Passengers of ships docked to resupply would hurry to meet the great general. He developed strong personal bonds with the coterie who had accompanied him into exile. Although some speculate that he was murdered, most agree that Napoleon’s death in 1821, at the age of 51, was the result of stomach cancer.

By contrast, Charles de Steuben was born in 1788, his youth and artistic training coinciding with Napoleon’s rise to power. He was the son of the Duke of Württemberg officer Carl Hans Ernst von Steuben. At the age of twelve he moved with his father, who entered Russian service as a captain, to Saint Petersburg, where he studied drawing at the Art Academy classes as a guest student. Thanks his father's social contacts in the court of the Tsar, in the summer of 1802 he accompanied the young Grand Duchess Maria Pavlovna of Russia (1786–1859) and granddaughter of Frederick II Eugene, Duke of Württemberg, to the Thuringian cultural city of Weimar, where the Tsar's daughter two years later married Charles Frederick, Grand Duke of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (1783–1853). Steuben, then fourteen years old, was a Page at the ducal court, a position for which the career prospects would be in the military or administration. The poet Friedrich Schiller was a family friend who at once recognised De Steuben's artistic talent and instilled in him his political ideal of free self-determination regardless of courtly constraints.
At the behest of Pierre Fontaine in 1828 de Steuben painted La Clémence de Henri IV après la Bataille d'Ivry, depicting a victorious Henry IV of France at the Battle of Ivry. De Steuben's Bataille de Poitiers, en octobre 732, painted between 1834 and 1837, shows the triumphant Charles Martel at the Battle of Tours, also known as the Battle of Poitiers. He painted Jeanne la folle around the same time and he was commissioned by Louis Philippe to paint a series of portraits of past Kings of France.

Life in the French capital was a repeated source of internal conflict for Steuben. The allure of bohemian Paris and his military-dominated upbringing made him a wanderer between worlds. As an official commitment to his adopted country he became a French citizen in 1823. However, the irregularity of his income as a freelance artist was in contrast to his sense of duty and social responsibility. To secure his family financially, he took a job as an art teacher at École Polytechnique, where he briefly trained Gustave Courbet. In 1840 he was awarded a gold medal at the Salon de Paris for his highly acclaimed paintings.
The love of classical painting was a lifelong passion of Steuben. He was a close friend to Eugène Delacroix, the leader of the French Romantic school of painting, whom he portrayed several times. Steuben was also part of this artistic movement, which replaced classicism in French painting. "The painter of the Revolution," as Jacques-Louis David was called by his students, joined art with politics in his works. The subjects of his historical paintings supported historical change. He painted mainly in sharp colour contrasts, heavy solid contours and clear outlines. The severity of this style led many contemporary artists - including Prud'hon - to a romanticised counter movement. They preferred the shadowy softness and gentle colour gradations of Italian Renaissance painters such as Leonardo da Vinci and Antonio da Correggio, whose works they studied intensively. Steuben, who had begun his training with David, felt the school was becoming increasingly rigid and dogmatic. Critics praised his deliberate compositions, excellent brush stroke and impressive colour effects. But some of his critics felt that his pursuit of dramatic design of rich people also showed, at times, a pronounced tendency toward the histrionic.

The portrayal of key moments in Napoleon’s dramatic military career would feature among some of Steuben’s best known works. But it is this death scene that Steuben is most remembered for.
Using his high-level contacts among figures in Napoleon’s circle, Steuben interviewed and sketched many of the people who had been present when Napoleon died at Longwood House on St. Helena. He wanted to attempt o give the most accurate representation of the scene possible. Indeed, the painter interviewed the companions of Napoleon’s captivity on their return to France and had them pose for their portraits. Only the Abbé Vignali, captain Crokat and the doctor Arnott were painted from memory. The Grand maréchal Bertrand made sketches of the plan of the room, noting the positions of the different pieces of furniture and people in the room. All the protagonists within the painting brought together some of their souvenirs and in posing for the painter, each person can be seen contributing to a work of collective memory, very much with posterity in mind.
Painstakingly researched, Steuben painted a carefully composed scene of hushed grief. Notable among the figures are Gen. Henri Bertrand, who loyally followed Napoleon into exile; Bertrand’s wife, Fanny; and their children, of whom Napoleon had become very fond.
The best known version of “La Mort de Napoléon” was completed in 1828. French writer Stendhal considered it “a masterpiece of expression.” In 1830 the installation of a more liberal monarchy in France further boosted admiration of Napoleon, who suddenly became a wildly popular figure in theatre, art, and music. This fervour led to the diffusion of Steuben’s deathbed scene in the form of engravings throughout Europe in the 1830s. As Napoleon’s stock arose within French culture and arts, so did Steuben’s depiction of Napoleon’s death. It became a grandeur of vision that permeated Steuben’s masterpiece of historical reconstruction.
Initially forming part of the collection of the Colonel de Chambrure, the painting was put up for auction in Paris, on 9 March 1830, with other Napoleonic works, notably Horace Vernet’s Les Adieux de Fontainebleau (The Fontainebleau adieux) and Steuben’s Retour de l’île d’Elbe (The return from the island of Elba). The catalogue noted that the painting had already been viewed in the colonel’s collection by “three thousand connoisseurs” – which alone would have made it a success -, but its renown was to be further amplified by the production of the famous engraving. The diffusion of this engraving by Jean-Pierre-Marie Jazet (1830-1831, held at the Musée de Malmaison), reprinted and copied countless times throughout the 19th century, made the scene a classic in popular imagery, on a level of popularity with paintings such as Millet’s Angelus.
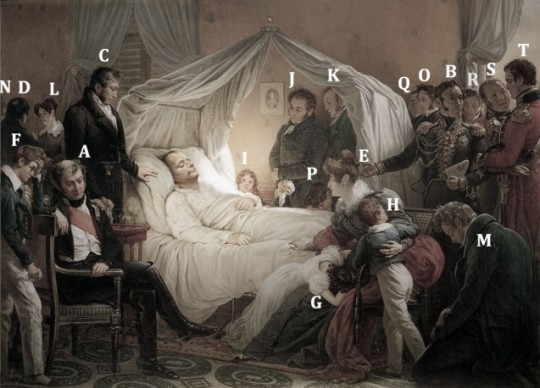
A / Grand Marshal Henri-Gatien Bertrand. Utterly loyal servant of Napoleon’s to the last. His memoirs of the exile on St Helena were not published until 1849. Only the year 1821 has ever been translated into English.
B / General Charles Tristan de Montholon. Courtier and companion of Napoleon’s exile. Montholon managed to ease Bertrand out and become Napoleon’s closest companion at the end, highly rewarded in Napoleon’s will, which Montholon helped write. Montholon’s untrustworthy memoirs were published in 1846/47.
C / Doctor Francesco Antommarchi. Corsican anatomy specialist. Sent by Napoleon’s mother from Rome to St Helena to be Napoleon’s personal physician on the expulsion of Barry O’Meara. Napoleon disliked and distrusted Antommarchi. Antommarchi’s untrustworthy memoirs were very influential and published in 1825.
D / Angelo Paolo Vignali, Abbé. Corsican assistant-chaplain, sent by Madame Mère from Rome to St Helena in 1819.
E / Countess Françoise Elisabeth “Fanny” Bertrand and her children: Napoléon (F), who carried the censer at Napoleon’s funeral; Hortense (G); Henry (H); and Arthur (I), youngest by six years of all the Bertrand children and born on the island. She was wife of the Grand Marshal, very unwilling participant in the exile on St Helena. Her relations with Napoleon were difficult since she refused to live at Longwood. She spoke fluent English. Was however very loyal to Napoleon.
J / Louis Marchand. Napoleon’s valet from 1814 on and one of his closest servants. As Napoleon noted in his will, “The service he [Marchand] rendered were those of a friend”.
K / “Ali”, Louis Étienne Saint-Denis. Known as “the Mamluk Ali”, one of Napoleon’s longest-serving and intimate servants; He became Librarian at Longwood and was an indefatigable copyist of imperial manuscripts.
L / Ali’s English (Catholic) wife, Mary ‘Betsy’ Hall. She was sent out from England by UK relatives of the Countess Bertrand to be governess/nursemaid to the Bertrand children. Married Ali aged 23 in October 1819.
M / Jean Abra(ha)m Noverraz. From the Vaud region in Switzerland. Very tall and imposing figure that Napoleon called his “Helvetic bear”. He was himself ill during Napoleon’s illness.
N / Noverraz’s wife, Joséphine née Brulé. They married in married in July 1819, and she was the Countess Montholon’s lady’s maid. Noverraz and Saint-Denis had a fist fight for the hand of Joséphine.
O / Jean Baptiste Alexandre Pierron. The cook, dessert specialist, long in Napoleon’s service and who had accompanied Napoleon to Elba.
P /Jacques Chandelier. Iincorrectly identified on the picture as Santini who had left the island in 1817. A cook, from the service of Pauline Bonaparte, Napoleon’s sister, who arrived on St Helena with the group from Rome in 1819.
Q /Jacques Coursot. Butler, from the service of Madame Mère, Napoleon’s mother, he arrived on St Helena with the group from Rome in 1819.
R / Doctor Francis Burton. Irish surgeon in the 66th regiment who had arrived on St Helena only on 31st March 1821. He is renowned for having made Napoleon’s death mask (with ensign John Ward and Antommarchi).
S/ Doctor Archibald Arnott. Surgeon in the 20th regiment. Brought in to tend to Napoleon in extremis on 1 April 1821.
T/ Captain William Crokat. A Scot, orderly officer at Longwood for less than a month, having replaced Engelbert Lutyens on 15 April. He received the honour of carrying the news of Napoleon’s death back to London and also the reward, namely, a promotion and £500, privileges of which Lutyens was deliberately deprived by the governor.
#charles de steuben#art#painting#napoleon#bonaparte#st helena#life#death#chateaubriand#french#france#emperor#artist#aesthetics#war#politics#society#culture#arts#personal
38 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Ginger angel., Z E D
Ginger angel, oil, canvas, 70×70, 2012, Painting on canvas, canvas on stretcher, stretcher thickness of 2.5 cm, sides painted, can be exposed without a frame. EDUARD ZENTSIK Paintings Eduard Zentsik is an exceptionally prolific Estonian-based artist of many faces. One might call him a greedy painter, as he is traveling quite a few creative lanes simultaneously, refusing to stick to a single signature style, technique, or theme; instead, Zentsik keeps confusing critics and audiences alike by choosing to explore all available options, exercise all styles, play diverse and almost conflicting roles. Some of Zentsik’s endeavors, like the mildly macabre art brut series, focus on physical metamorphoses and flourishes of the flesh; others zoom in on the mysteries of the mind; elsewhere, the artist indulges in formless Pollockian color drippings or flirts with digital media. Hope for Love, his latest solo show, accentuates the spiritual aspects in Zentsik’s enormous oeuvre. Tied together with recurring themes and symbols, the collection presents 37 allegorical paintings made in the surrealistic canon. Hope for Love captures a distinctly magical reality populated by gracious entities and precious objects. The scenes are static and peaceful, shrouded in dark ambience created by the palette of caramel and caked blood harking back to Renaissance masterpieces; the saccharine decor would be perhaps quite familiar to Vienna crowds. The entire universe of the series is feminine and deeply erotic, with no male figures to be seen. Flowers and jewels, birds and eggs, pups and bunnies—the inventory borders banal, but the images stand for something else, promising to unfold hidden meanings and clues. Indeed, Hope for Love is highly symbolic. Zentsik’s paintings are trim and disciplined, low on noise; however, within the frame resides an open-ended space, where almost any artifact or concept, from any era or culture, may appear with a certain albeit enigmatic purpose. No mythology or esoteric teaching is immune to the artist’s tactful manipulations—Zen in Zentsik goes hand in hand with Tao, Krishna, Christ, and the Twelve Olympians. The eclectic mystical trappings seem to glorify life, with translucent eggs, lavish grains of red caviar, and lustful petals among the major motifs, while objects within objects apparently signify the fractal structure of the universe. In Hope for Love, Zentsik confirms his reputation as an artist who mixes genres and media, playfully subverting the traditions of old. He deconstructs (and reinvents) the genre of landscape by placing images of nature inside female characters and random objects or projecting them onto virtual surfaces. His portrait of a haloed crinoline-clad cat of six eyes is a genial yet ironic comment on icon painting. As an appropriately mystical reference, more than a few times the compositions of artworks bring to mind Tarot cards where depicted occult characters peer into our reality from esoteric domains. However, Zentsik’s main daring lies in using self-aware decorative strategies and deceptively simple tropes to convey his big ideas—some will find his work pretentious. This is not an intellectual game, though. Those willing to unlock the code are likely (and welcome) to reveal metaphysical depths. Hope for Love is a visual poem to the great God of Beauty Zentsik has worshipped in earnest for a long time. Behind the images, there is a powerful coherent cosmology explaining the underlying natural order, the ulterior essence of everything. This is true spiritual art with a transcendental message, ostensibly co-created and inhabited by the spirit of the Creation itself (all artworks have always existed, you know). Zentsik’s mission is to cut open two-way windows between our world and the fantastical realm through which mystical figures and phenomena on the other side meet our gaze. Could they be the proverbial Platonic ideas represented on canvas in vaguely familiar forms? Hope for Love, therefore, is a slightly misleading title. Eduard Zentsik is not questioning the existence of Love—he knows it already exists. Everything to hope for already exists. Snap your fingers, wink, whisper a wish. Let yourself believe in the eternal, never-ending beauty, and let Hope be your guide to the whole world of love.
https://www.saatchiart.com/art/Painting-Ginger-angel/733440/2767180/view
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Modern critics of The Arnolfini Portrait painted by Jan van Eyck are baffled by some of its symbolism, and have engaged in debate about the symbols and meanings behind the double portrait for some time. Many have attempted to analyze these symbols in the context of societal norms of the time, and yet the controversy continues. I propose that there is another, most obvious, though scandalous, and even heretical viewpoint that could settle the debate once and for all.
Erwin Panofsky views the painting as a record of a "marriage by a marital oath, more particularly by joining hands," as the two figures in this double portrait are indeed touching hands in the very center of the image. He assumes the identity of the female figure to be that of Giovanna Cenami, whom a Giovanni Arnolfini living in Flanders at the time did not legally marry until 13 years after van Eyck's painting was completed (Chipps Smith, p. 102-103.) I believe this assumption to be a mistake, because it precludes other possibilities as to the identity of the female figure portrayed by the artist. I do believe that he is correct in the analysis that the painting is a record of some kind of societal contract, akin to a marriage, taking place in the private space of Arnolfini's domicile. I believe it to be more of an allegory to marriage, however, since the historical identity of this female figure remains a mystery, and for all of the historical evidence available, did not exist in live human form at the time that the portrait was painted, in 1434 AD.
Art historian Craig Harbison wrote about The Arnolfini Portrait that, as a wealthy merchant Giovanni Arnolfini was well known for a "pretension to noble status" and that "Arnolfini apparently spent much time courting the Flemish nobility." Harbison comments on the luxurious nature of the couple's dress to support this claim. He relays details of how their dress mimics that of Royalty when he writes, "The somber colors of the man's clothing, dark purple, brown, and black, appropriately mirror the taste of the duke of Burgundy. Cenami's pale complexion is no doubt due to heavily applied makeup favored by courtly women to give a refined impression. Her robe, while not made of particularly costly fabric, has an elegant white fur lining and enormous sleeves decorated with applied dagging." Harbison has overlooked, however, critical details of the female figure's dress that tell of how she is not merely attired luxuriously, but in the exact manner of the Burgundian courtly trends of the time. Isabeau of Bavaria, wife and Queen to Charles VI, was the first woman in recorded history to wear a linen petticoat, and this item was considered the ultimate symbol of luxury and status in her court. Burgundian Ladies, in an effort to display their status, would wear overcoats, the gender neutral houppelande, with cutouts and sleeves designed to give a glimpse of their luxurious linen undergarments. The truncated sleeve of the emerald green houppelande worn by the female figure in The Arnolfini Portrait performs this service perfectly. Yes, it is lined with white fur, as Harbison noted, but more importantly, it shows quite a good portion of the fine linen of her undergarment. Isabeau was also the Queen of wearing high headdresses, particularly heart in shape, and the architecture of palaces was altered to allow ladies of her court ease and comfort in traversing the walkways in their headgear. True to Royal form, the womanly figure that van Eyck portrays in this double portrait is adorned with an elaborate headdress, which accentuates her high forehead. The Burgundian courts valued high foreheads above all other adornments on a noble woman, and the feature was emphasized and valued in portraiture painting of the time. Like the symbol of fertility in gathering the houppelande skirts to one's waistline, the high forehead indicated survival of the plague that had wiped out viable brides of the Royal line. The combination of these details convey to the viewer that the female figure in this painting is of Royal descent, and is likely to continue the Royal bloodline. This figure was painted as if she were nobility, not merely imitating royal descent, and she is declared fertile by her dress. Harbison, like Panofsky, assumed her identity to be that of Arnolfini's future bride, Giovanna Cenami, but I do not believe that she would have worn these styles in exactly this way, having come from the burgher class herself. In fact, Wikipedia states that this marriage was assumed by art historians entirely, and that Arnolfini was never married a second time, as his first wife had deceased before this painting was commissioned.
Why would art historians assume a marriage? I believe it is because they are too literal. Of much debate and mystery is the inscription that the painter placed above the mirror, between the eyes of the two figures, and at eye level in the composition. The inscription reads, "Jan van Eyck was here." It is also situated between the chandelier, which critics claim to represent God, and the mirror, which has been painted in great detail with scenes from the Passion of Christ. Essentially, the artist has placed himself as an authority between the Heavenly and the Earthly realms. Most art historians agree that this inscription is some kind of witness statement, but they cannot agree on what exactly is being witnessed. When I consider that the female figure in this painting is an allegory, a symbol unto herself, of the Burgundian courts and Royalty, I begin to consider that the painter understood that he had been commissioned to document an unprecedented moment in History: the marriage of the burgher class and the nobility. He may have understood that this was a fantasy in Arnolfini's mind, but he also recognized that it was a powerful political statement, and he wanted recognition as offering support to his patron in making this statement. He was indeed an authority to validate the marriage, for as a member of the burgeoning Flemish society of the time, he witnessed the economic exchanges with Royalty and the growing power of the burgher class, quite literally, and on a daily basis.
I believe that it is not an accident that this particular Flemish portrait of the Renaissance has survived, while others have not, for it carries meaning and power of great significance to the evolution of European economics and society. In commissioning Jan van Eyck to paint a portrait of himself marrying Royalty, Giovanni Arnolfini was claiming that his wealth and status as a merchant afforded him the same amount of sovereignty and religiosity of the rulers of the time. This painting documents the beginnings of New Money, and the destruction of the old system, as we saw with the entrenne, where money could not buy power or recognition. The Arnolfini Portrait is so named because it is actually the portrait of one man taking a revolutionary stand in society. The second figure in the double portrait is that of an institution, not an individual person. The allegorical marriage in the painting was conducted in private chambers, an act of defiance in itself, and an official statement that a commoner was procreating with Royalty, with or without sanction. Jan van Eyck was there, and his legacy lives on because he dared to join a contemporary burgher in fighting the status quo. I mean, the strategically placed inscription, which art historians call "odd," rendered him infamous, for centuries, as World War II graffiti can attest. The religious symbols abundant in the painting hint that the commission of this work was indeed sanctioned by a higher authority, a Bishop perhaps, but we lack evidence of this detail, and so the debate continues.
I have no doubt in my mind, however, after reviewing the writings of the aforementioned authors, and others, that Jan van Eyck documented the conception of Modern Capitalism with The Arnolfini Portrait. To take a cue from Vicki Saxon, this painting was more like the Royal Wedding portrait of Harry and Meghan than a Kardashian family portrait. The artist threw in all of those debated symbols of wealth and fertility specifically to inform the audience that they were viewing the birth of a New Age, one resilient with prosperity for the common man, not born to nobility, but married into it by wealth. Jan van Eyck was a master of hyper realistic detail, which was highly valued then and is now, but his genius is in his apparent knowledge of his place in History, as the midwife, or St. Catherine, of the Art World. One need only look to the era of Kilroy to see how the portent of this masterpiece played out. With oil barons buying up noble estates, and the daughters of shipping magnates salvaging the old family name, the Merchant and his Royal Bride were more relevant in the 20th Century than they were in the 15th. Somehow painter and subject were both aware of this, because the state of solemnity that Jan van Eyck painted on Arnolfini's face is so priceless, as he was a visionary looking to a future, centuries and centuries beyond his Worldly grasp. Those unknown figures reflected in the mirror? That is you and me.
Rachel Schultz
Course ARH361U : The Northern Renaissance
Portland State University
Spring 2020
#dark acadamia aesthetic#art in the time of corona#art history#mine#late capitalism#academia aesthetics#chandelier
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Pair of Very Fine Werewolf Films from the 2000s
Werewolves have been more prolific in cinema than I ever realized. They are, indeed, a bit of a horror movie darling, appearing in a number of movies from the very advent of modern cinema. Perhaps it’s because the challenge of designing a werewolf transformation is just too tantalizing for special effects teams to resist. Perhaps it’s because werewolves can mean so many things in so many contexts.
Whatever the reason, there are a lot of werewolf movies through the decades, and we’ve seen quite a few of them! But we recently watched what are often considered two of the best.
youtube
Dog Soldiers (2002) was the directorial debut of Neil Marshall, who has gone on to make more movies but may be better known for the work he’s done on major TV shows like Game of Thrones, Hannibal and Lost in Space.
For a debut, all I can say is -- wow. This is a very well-made film.
The story is about a group of British soldiers sent to the remote Scottish highlands for a training exercise. Instead of the special ops team they’re supposed to meet, they instead encounter a different type of threat -- a whole pack of werewolves intent on killing them.
There are a couple of things this movie does that are just very very good. For one, it makes a point of humanizing its characters, letting the viewer get to know and care about everyone first before putting them into danger. It’s a big ensemble cast, so taking the time to do that is super important (and something a lot of movies fail to do). It’s also extremely tightly plotted, with pretty much everything having a setup and pay-off, making it very satisfying to watch. Also, Liam Cunningham (of Ser Davos Seaworth fame) is in this movie, and he’s spectacular.
Dog Soldiers does something else interesting -- It’s the first of the werewolf movies we’ve seen where the wolves are 100% the “other.” Most werewolf stories are about the drama and conflict of turning into a wolf yourself. Here, the wolves are monsters, posing a predominantly external threat. It makes the format more of a zombie movie than a werewolf movie, but it’s still quite good (and much better than zombies because the werewolves are cunning and extremely dangerous).
Also the werewolf design is pretty unique. They’re not my favorite werewolves -- they have the problem that most movie werewolves have, of being just too static and lacking in expression -- but they are designed in a genuinely creepy and monstrous way, with exaggerated proportions and well-made heads and faces that are all distinct and have character and personality.
Overall, A+ wonderful film, highly recommended.
youtube
Ginger Snaps (2000) is a Canadian horror movie directed by John Fawcett who you might know as being one of the co-creators of the TV show Orphan Black.
The film is about two sisters, Ginger and Brigitte. Death-obsessed social outcasts, they have a suicide pact and a dream to get out of their boring suburban life. But when Ginger is attacked by a werewolf, she begins to experience some changes that tear a rift into the girls’ relationship...
Ginger Snaps is one of those movies that is frustrating because it was so close to being perfect, but falls short in a way that would have been less disappointing if the film weren’t so good. The first parts of it are excellent, and really ahead-of-its-time for the year 2000: We’ve got two strong female leads, a story centered almost entirely around a family relationship, a story that’s outspokenly about female sexuality. It’s werewolf-as-puberty metaphor, but it’s so much deeper than that.
The werewolf effects are...not my favorite. Right up until the final transformation, though, the makeup is top notch -- slowly converting Ginger into an inhuman creature, one horrifying body change at a time. It’s Cronenberg-esque and deeply human and beautifully acted...
...And then the film kind of falls apart a bit in the third act. It’s not terrible, it just suffers from the problem of allegorical filmmaking where your metaphors start to break down when applied in a literal sense, which can muddle your themes. The pacing is off, and the excellent family drama starts to give way to something that feels a bit more like The Craft. Still good! But not as good.
I guess there’s a sequel and a prequel, which I haven’t seen, but I’m willing to give them a shot.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
I flicked through the Tuula Karjalainen book and read bits and pieces of it already and there’s this one section about homosexuality in it that I found really interesting so I thought I’d post it here, even though it’s a bit long oops, in case any of y’all were interested in reading it! Like, I never knew Tove had a gay cousin whom Tove was supportive of in terms of her lesbian identity and whose partner wrote a dissertation on Tove’s books?? So fascinating! Also was not expecting the sentence “The Hattifatteners resemble a wandering flock of penises or condoms”; usually they’re referred to more subtly with words like ‘phallic’ but not here xD
OPEN AND CLOSED
Many researchers have looked for references to homosexuality in Tove’s writings. Although she did not talk about it in public, she made no attempt to conceal it either, and her relationship with Tuulikki Pietilä was known to everyone. The two women took part in official state events such as the President’s Independence Day ball, where they were clearly the first to attend the event officially as a lesbian couple. Their relationship was so open and obvious it was that it was not newsworthy. It was hard to build a scandal on something that everyone knew - even the press, which liked to chase stories of that kind.
Psychological explanations of various kinds often have a chapter of their own in the analyses of Tove’s books, and sometimes unusual views have been expressed. The Swedish scholar Barbro K. Gustafsson earned her doctorate in 1992 from Uppsala University’s Theological Faculty with a dissertation on Tove’s books for adults. She made a special study of The Doll’s House, Sun City, ‘The Great Journey’ and Fair Play, and although her thesis also covered the Moomin stories, they were dealt with more briefly.
Perhaps surprisingly, Tove agreed to be interviewed by Gustafsson during her research work, and even participated in it actively by attending Gustafsson’s dissertation defence. The fact that Tove was prepared to do this may partly be explained by a family connection: Gustafsson was the partner of Tove’s beloved cousin Kerstin. When Kerstin, from a religious family, had realised that she was lesbian, Tove had been extremely supportive. Tove and her friends also helped Kerstin with many issues related to her lesbian identity.
Tove refused to give any public interviews about the dissertation defence, and did not want to talk about her private life or relationships. She returned to Finland as soon as the defence and the celebrations for Gustafsson’s Ph.D. were over, though she did issue a press release. In it she followed convention, thanking Gustafsson for the clarity of her book and her extensive knowledge of the subject - she had, Tove thought, succeeded in uncovering a rarely explored area of the unconscious. She also said that though much was written about authors, it was perhaps best done after their death, if at all. As if to soften the blow, she stressed the degree of trust between herself and Gustafsson. She said that following the progress of the research had been like an adventure, and that it had almost allowed her to see herself as a pioneer.
In her study, Gustafsson focuses on a dream that Tove had in the 1930s and found strangely threatening. In it she had seen large, black, wolf-like dogs on a seashore at sunset. A psychologist had explained to her that the dream was about repressed drives and forbidden sensuality.
In her thesis, Gustafsson is perhaps prone to detect elements of homosexuality too easily in very ordinary matters connected with the sea and archipelago life. She also discussed the wild animals that Tove often returned to both in the Moomin books and in her works for adults. In Moominland Midwinter the dog Sorry-oo wants to join the wolves and learn to howl like them. The story concerns the desire to leave the species into which one has been born, something that proves impossible. In The True Deceiver, the wolfhound plays a central role in the power relationship between the two women. Numerous readers have seen allusions to homosexuality in the comic strip about a little dog that falls in love with a cat. It realises that the love is wrong and becomes depressed. In the end the cat turns out to be a dog in disguise. This time the problem has a simple solution.
In Tove’s books there are repeated descriptions of people or Moominvalley creatures becoming ‘electric’, and this is clearly an important theme in her writing. The Hattifatteners resemble a wandering flock of penises or condoms - in thunderstorms they become electric, and then burn anyone who gets close to them. It is very easy to imagine that the electrification is an allegory for oestrus. The Mymble is also able to become electric - with her countless children she is the most sensual character in Moominvalley. The Whomper Toft in Moominvalley in November is the master of thunder and lightning. He lets the Creature out of a locked cupboard, and all that remains is a smell of electricity. The Creature runs away and grows even larger during thunderstorms, when lightning fills the sky, but is too big, angry and bewildered to be so big and angry. In ‘The Doll’s House’, electrification brings about a drama of jealousy between three men that leads to violence. There is a similar outcome in ‘The Great Journey’, where the mother feels the electrifying presence of her daughter’s female friend, whereupon the daughter becomes jealous.
Fair Play is a book about the relationship between two women in their seventies who are set in their ways, and their daily life together. Gustafsson uses the narrative to examine their mutual roles in the light of the old custom of categorising lesbians either as ‘femmes’ or ‘butches’, the latter having more masculine traits - a way of seeing a relationship between two women as a copy of a heterosexual one. Jonna and her prototype Tuulikki correspond to the ‘butch’ profile. Tove also portrayed Tuulikki as Moominvalley’s Too-ticky, a rather burly, masculine figure who keeps a knife in her belt.
Quoting Lord Alfred Douglas and the line of verse that was mentioned at the indecency trial of Oscar Wilde, Gustafsson writes that homosexual love is the love that does not dare speak its name. Although the time in which Tove lived was quite different from Wilde’s, there were similar prejudices and tensions in society - and, of course, they influenced her writing. Over the centuries women were not expected to write blatant erotic descriptions, but had instead to express themselves in allegorical terms. It was supposed that they did experience such feelings - and even more so when they were the result of unlawful love.
Tove’s books contain no openly erotic episodes or writing of a sexual nature and in this her writing is typical of women’s literature of her time. Sometimes it feels as though the characters in her books have to some extent been freed from sexuality. Their relationships are based more on understanding and friendship than on ardent passion, though their jealousy can sometimes take violent forms. Many things are veiled in highly metaphorical language. In the books that Tove wrote for adults, male and female couples are portrayed interchangeably without particular emphasis. In many of her books, as in her life, homosexuality was so natural that there was no need to make a fuss about it. While it was not to be denied, it was not to be given a high profile either. It was almost as though she backed out of dealing with her sexuality too openly, and in fact she forbade her biographer to write about her love affairs. Since the biography was written for children, this kind of advance censorship was possible.
In the story ‘The Great Journey’ (’Den stora resan’), two women in their seventies, Rosa and Elena, together with Rosa’s mother, live a life of humdrum joys and sorrows and work on their creative tasks. Among all three, physical love is a taboo subject. Elena asks Rosa: ‘What does she know, in any case? Nothing. She doesn’t know anything about such matters.’ The two women are unable to show their feelings for each other if Rosa’s mother is present. They plan a holiday together, but Rosa changes her mind and goes away with her mother instead. She remembers the promise she made in the nursery: ‘I’ll take you with me, I’ll steal you from Papa, we’ll go to a jungle or sail out on the Mediterranean... I’ll build you a castle where you shall be queen.’
Organisations that promoted sexual equality in Finland and the Nordic countries gave Tove awards for her pioneering work on behalf of sexual minorities, and she has certainly been an extremely important role model and author in the gay community. She had the ability to be completely open, yet at the same time quite private - as in the case of the dissertation, when she gave Gustafsson interviews and took part in the defence, but would not agree to answer questions from journalists who were interested in her private life. In relation to her lesbian identity, as shown by this very situation, she sometimes came out of the closet, and at other times she concealed the truth.
Tove’s homosexuality inspired a great many researchers and readers to look for the most varied interpretations. Perhaps her slightly sardonic attitude to this excessive interest can be seen in her song ‘Psychomania’ (’Psykofnattvisan’), written in 1963 for the revue Krasch and set to music by Erna Tauro. The song is like an obscure parody, in which psychoanalytic terms form a wild, cacophonous reality all of their own. It is as though she is drifting among people who are intently looking for something and who begin to see the signs of it everywhere. In fact, they can no longer see anything else because their heads are filled with ‘psychomania’. The song is a lengthy one, and operates on many levels. It also demonstrates that its author was familiar with the psychological terminology of the day - Tove had always been fascinated by interpretations of the human mind and she knew the terminology back to front, so well in fact that she could play with it:
I pore and pore
and where I pore
the symbols gather more and more
I sink right through the floor
into depression
and tendentious apperception...
-Tove Jansson: Work and Love by Tuula Karjalainen
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
Michael After Midnight: C.H.U.D. & Us


Do you like horror? Do you feel for the plight of homeless people? Do you despise Ronald Reagan and everything he represents? Well congratulations! You have a functioning heart and mind! But you also might be in to the B-movie cult classic that is C.H.U.D. This is a film that has at least partially wormed its way into the cultural consciousness as the titular monsters have become something of a go-to descriptor for any sort of sewer-dweller as well as an insult used to describe alt-righters and other nasty bastards (it works too since alt-right people do often look like they crawled out of a sewer). Unless you’re a cult film aficionado though, you may not have actually sat down and watched this film, which is a shame, as it definitely has quite a bit to offer.
But you know who almost certainly HAS watched this film? Beloved filmmaker, comedian, and actor Jordan Peele! And I know this because his second feature film Us is pretty much a semi-remake of C.H.U.D. No, I’m not joking. I would never fuck around about something as serious as trashy B-movies and Jordan Peele films. This is serious business right here. These movies are pretty similar thematically and even slightly plot-wise, but at the same time their different approaches really help set them apart and make each film great in their own right.
The big thing with C.H.U.D. is its function as a criticism towards the Reagan-era treatment of the homeless and the mentally ill. Homeless people are portrayed very sympathetically, with them going missing being what really kicks things off… or it would be, if anyone in power gave a damn. No, the people in power only start caring when people they start caring about go missing. Things go from bad to worse when it’s revealed that the C.H.U.D.s are not only mutated homeless people, but that the United States government is complicit in their transformation, having decided to dump toxic waste into the sewers. Aside from giving Jason Takes Manhattan’s ending some level of plausibility, this is a pretty brutal showcase of how society treats the less fortunate, and especially how the government treats them. As far as B-movies go, this one has the most instantly believable problem causing the monsters.
And it is similar with Us. The film has a much broader application than Peele’s previous film Get Out, which is pretty blatantly about left-wing condescending racism. But the way the Tethered function, their nature as failed experiments left behind by the government to rot, and their desire to simply be given all that they had been denied because the powers that be deemed them less worthy is not just stellar thematically, it is the sort of message that in this day and age is needed more than ever. Reagan is long dead and burning in Hell, but the evil he perpetuated still stands.
The big reveal at the end – which I WILL refrain from spoiling – changes the entire perspective of the film and showcases the Tethered as not just victims, but people who if given half a chance could easily excel in the upper world. But they were denied this chance, shunned as mindless monsters, and then are we to vilify them when they rise up to take what they deserve? Both of these films certainly show their “monsters” as vicious and violent, but ultimately they are merely scared, terrified beings lashing out at those who have oppressed and hurt them, intentionally or otherwise.
Both films certainly do show the oppressed commit monstrous actions, but it never really stops sympathizing with them, instead (rightfully) demonizing the government and the people who constantly put them in those positions of oppression. C.H.U.D. certainly is more cathartic, featuring the major government antagonist being not only shot but blown up, but it also tends to feel a tad more exploitative, what with literal homeless people being mutated, though I must stress the movie doesn’t demonize the homeless and paints them as sympathetic victims of a cruel, unfeeling government who just decides to kill ‘em all to cover up their own fuckup. This is one of the single most realistic depictions of government ever put on film, and for that C.H.U.D. deserves some praise. Us certainly paints a more sympathetic picture for its “monsters,” beginning with the story Red tells her captive audience, and while the reveal of their true nature is a bit more sloppily executed than the reveal of C.H.U.D. it still manages to bear down with the full weight of its allegorical impact with late-game revelations.
Another interesting thing with C.H.U.D.: the monsters don’t even appear all that much. When they do, they look absolutely fantastic; the suits are stunning achievements of practical effects, though the scene where one stretches its neck out is a bit dubious. But for the most part, even at the film’s climax, the C.H.U.D.s are mostly absent, with a “less is more” approach being used in regards to them. I don’t recall there ever really being more than four or so onscreen at once, and there’s no massive invasion of monsters. Honestly, it helps keep the film from feeling like a bloated spectacle, and the fact the film slowly builds up to the monsters appearing after a brief appearance in the start really helps them feel more memorable and iconic than other forgotten throwaway monsters of the 80s, while at the same time letting the mystery, atmosphere, and grimy New York backdrop congeal and allowing the message of the film to just ooze over and permeate you.
Us, on the other hand, keeps the Tethered front and center starting at the second act, but in this case this is a good thing; the Tethered have a lot more personality, seeing as they are essentially fully human, where the C.H.U.D.s are mutated humans whose last vestiges of humanity were washed away by the waste the government hid beneath the streets. Lupita Nyong’o in particular is masterful as Red, and is incredibly skilled to be able to pull off playing two roles who frequently share the screen and who are essentially copies of each other while still managing to make them distinct and different. Tim Heidecker and Winston Duke too really do a grand job as their Tethered counterparts, in Heidecker’s case probably more than his regular person character (not to say he’s bad, but seeing Heidecker selling a creepy killer is a lot more impressive than seeing him play a douchebag husband).
Out of the two, I think it goes without saying that Us is the better film. It has all around better acting, it has the most incredible foreshadowing I have ever seen with every little thing foreshadowed getting a satisfying payoff, it has a great soundtrack, it has some moderately enjoyable humor, it’s paced very well… but here’s the thing: C.H.U.D.s big reveal of the true nature of its monsters is a bit better executed. A lot of people get hung up on how Us overexplains the origin of its monsters, and while it certainly doesn’t bother me because the Tethered are still an effective allegorical implement regardless of their in-universe origin, I can’t help but feel the reveal that the government mutating homeless people into cannibalistic sewer monsters and then just… not giving a shit about it was just a bit better executed. However, I feel like watching C.H.U.D. actually helps improve the big reveal at Us by token of being so similar that the latter’s twist becomes far easier to swallow.
Both of these movies are great for what they’re going for. Jordan Peele’s Us is a fantastic horror film that uses the genre as a way to showcase the effect privilege has on those without it, whether you intend it to or not; C.H.U.D. is a classic B-movie that, while perhaps still a bit exploitative, is ultimately incredibly sympathetic to the plight of the homeless as well as extremely critical of the government that would put them in such danger. Both films are fantastic in their own right, and I highly recommend both to any horror fans, especially those who love some sweet, sweet allegory alongside their brutal murders.
Both of these films are some of my favorites for really pushing the boundaries of what a horror film can do, story-wise. I think C.H.U.D. is a bit more ambitious in some ways, being a pretty direct attack on the Reagan-era government, as well as being relatively sympathetic to lower class people in a time when that wasn’t really the norm. For its time, it really is an impressive work, while Us, while certainly delivering a message that has strong impact, is a bit more open to interpretation and honestly lacking a bit of the gut punch that Peele’s Get Out had in terms of conveying and delivering said message. Still, I think Us is just better for refining what C.H.U.D. was trying to do and delivering it in a more polished form with better actors, a better budget, and just overall more intelligence and visual flair… which is not to say C.H.U.D. was lacking either, as it paints an incredibly dark and grimy picture of New York that I absolutely love, it’s just that it’s hard to deny that Peele is just a better filmmaker than the director of C.H.U.D. and really knew what he was doing. But again: both fantastic films in their own right, and both definitely worth watching.
#Michael After Midnight#Review#Movie review#C.H.U.D.#Chud#B-movie#horror movie#horror#monster movie#social commentary#Jordan Peele#us
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
12/09/2020 DAB Transcript
Joel 1:1-3:21, Revelation 1:1-20, Psalms 128:1-6, Proverbs 29:18
Today is the 9th day of December welcome to the Daily Audio Bible I am Brian and it is a joy and an honor and a privilege to be here with you today just like it is every day of the year. I'm excited for us to take our next step forward in the Scriptures. That next step forward is actually going to lead us into new territory in both old and new Testaments. So, we have two books that we are entering into today that we need to talk about and the first one that we will encounter is the next of the minor prophets in the Old Testament, and this book is known as Joel and we’ll read the entire book of Joel in our reading today. So, let’s just kind of get a little bit of understanding of what we’re reading.
Introduction to the book of Joel:
Nobody really knows exactly which Joel wrote the book of Joel. There are people…other people in the Bible that have the name Joel but…but scholars believe that these are the…any of them are the author of this prophetic book although the language of the book does share kind of a style with other prophets, prophets, like Ezekiel or Jeremiah or Amos or Micah in the minor prophets or Zephaniah. So, that leads to conjecture like so much of the scholarship that surrounds the origins of the Bible. On the one hand it…it could be that the book of Joel is the work of more than one prophet or it could be that the writer of Joel, Joel, this Joel that we’re talking about was in fellowship with other prophets, maybe even in close proximity to other prophets, so they shared kind of a common vernacular. And, so, with repeated readings of these texts these similarities become apparent. But those are like plausible ideas. The text itself doesn't really give any historical clues. So, dating the book is really, really difficult at least with any precision. If we’re just kind of like aggregating the ideas, somewhere between 500 and 800 B.C. like a three-century span here, somewhere between 500 and 800 years before Jesus came. And what we’ll see is that Joel wrote of this massive overwhelming horde of locusts that invaded the land and just destroyed the vegetation of the land, including all the crops. And, so, following that, as you can imagine, famine because there's no food. And, so, a plague and then a great famine. And Joel uses this as the backdrop to call the children of Israel to repentance. And its thought that the locusts…like this isn’t a vision, this isn't like a metaphor or an allegory. There probably was this type of locust invasion and people knew of the circumstances and had endured these things. And, so, when Joel's speaking of these things people know exactly what he's talking about and so they’re listening. And as is the case with the other prophets, the prophet is essentially announcing a fork in the road like that. Things have reached a point where like this is the last stop. This is where you either get off the train or you stay on the train and go straight into destruction. And if they stay on the train headed for destruction, then…then they will encounter the great and terrible day of the Lord as Joel describes it. But there is an alternative path as there typically is in the prophets, a path of restoration, a path of repentance. And following that path in the book of Joel leads us to some of the most encouraging and famous passages in the Scriptures, things like “I'll pour out my spirit upon all people and your sons and your daughters will prophesy, and your old men will dream dreams, and your young men will see visions”, stuff like that. So, God through Joel is saying, “you can have the great and terrible day of the Lord, or you can have Me pouring out my spirit upon all of you. The choice is yours.” And friends, the choice is still ours. And, so, let's dive into the book of Joel understanding that not matter what's been going on, no matter what the locusts have eaten, restoration is still always possible. And, so, we’re reading from the English Standard Version this week. Joel its entirety, which is three chapters.
Introduction to the book of Revelation:
Okay. So, that is Joel in its entirety and now we flip the page or flip several pages into the New Testament, and we find ourselves at the very final book in the New Testament, and this book is called Revelation. And there isn’t a book in the Bible that seems to have captured the fascination of…of its readers more than this book. And it's been interpreted many, many various ways through many various lenses over many centuries, in fact, over thousands of years. And these interpretations can be fantastic just wild stuff and then there are more pragmatic attempts to try to find out what's going on in this book. And, so, revelation tells us, it self-identifies the author as is John. It's just…we don’t have like a last name. We didn't have those then. And, so, which John are we talking about because this is not particularly an uncommon name? So, traditionally we would accept the author being the apostle John who wrote other portions of the New Testament as well - the gospel of John and first, second and third John. But this isn’t like a straight line and this isn't like modern scholarship trying to tear things apart. that's been questioned since at least the third century and that debate continues to the presence but without, you know, without new evidence, without something archaeologically being discovered that would give more clues or that would paint a more complete picture, the tradition…the tradition holds just as strongly as any other explanation that the…it was the apostle John who probably wrote this text. So, this being the case, it's not just any John who was exiled to the island of Patmos it's…it’s John the evangelist, the disciple of Jesus who was banished to the island of Patmos where Revelation was written. And it’s believed that Patmos, it…Patmos still exists, it’s still an island today. But at the time it's…it's like a Roman penal colony, a place of criminal and political exile. So, rather than just dealing with all these people they just put em’ on this island and let them sort it out under the guard of the Roman…Roman military. And like I said, it’s still an island. You can still go there. You can visit Patmos. It’s in the Aegean Sea. It’s like between modern-day Greece and Turkey and not too far actually from Ephesus where the tradition holds that John spent the elder…elderly years of his life. But here's where it gets interesting. Here's where the intrigue about the book of Revelation begins. It is a work in the genre of literature known as apocalyptic literature. This type of literature is highly symbolic, highly allegorical. And, so, when you read the book of Revelation and you have to kind of have your discerner…if that’s a word…you have to have discernment, you have to be paying attention because you find that as you go through this, you're taking certain things to be literal, you’re taking other things to be allegorical or symbolic and you have to wonder why you're doing that. How is that happening? How do you decide? And because we have so much seemingly symbolic language and be…because it appears that the subject matter here is the end of all things as we know it, like the end of the world and the beginning of the next, well then you’ve got a good recipe because everybody’s interested in that topic. Like if there's going to be the end of the world then we should probably have as much understanding about that as we can get. So, we would read this at different than say a poetic allegorical poem like the Song of Songs, right? So, we can read Song of songs and put different lenses on and go, “this is Christ's love for His bride, this is God's love for His people. This is just a beautiful portrayal of love between a man and a woman.” And we could be fine with that but you overlay the end of the world into that mix and you’re paying attention, but you still have highly symbolic language to…to discern and work your way through. And, so, as you can imagine, there have been thousands of very unique diverse interpretations over thousands of years. So, some scholars would say this is a very, very important book. Obviously, it's in the New Testament. Pulling it apart and trying to lay the pieces, the components out and then put them back together, this is indeed a prophetic utterance, but it is meant for people in the first century and contains a first century perspective and the sym…symbolism is something that would be understood better in the first century context. And, so, they conclude that the book of Revelation is already been completely fulfilled. That's like one way of looking at it. Others see like that Revelation outlines a chain of events that starts when this was written in the first century but lasts until…well…until the end of the world. And then others believe that the symbolism is the thing that keeps the relevance. It's…it's poetic and so can be interpreted and brought into any time period. So, it's timeless, and is ultimately describing the overarching cosmic struggle that we find in the Bible between good and evil. And the thing is, all of that can be legitimate. Like all of that can be right but even knowing that we still pretty much have only ever gotten it wrong because what happens is that we get intrigued in all these details and we’re trying to fit them together and overlay them into the time that we live in and come to some sort of conclusion that this is it…this is all going down right now. The problem is that's what's been going on for 2000 years. So many, many, many, many generations have looked into this and overlaid it into their time and said this is happening now. And yet 100% of the time until right now they've been wrong. One thing that I can tell you that is a right though, remember when we started getting into the letters and started to move to Paul and I'm telling you like this theme of endurance is going to show up and it's going to be unrelenting all the way until we end the Scriptures and understand how important that word, endurance, actually is to our faith journey, that is probably as clear as it can get in the book of Revelation, the final book of the Bible because it's a fundamental theme in the book of Revelation. In some ways, it almost feels like we've been pulled forward in this theme of endurance all the way to this point where we can see its enduring, not just kind of enduring healing because you broke your leg or enduring the transition of a job. It's…it's enduring until the very, very end, enduring until the end of all things. And Revelation ultimately tells us that those who stay faithful, those who endure and stay faithful to the testimony of Jesus until the very end will then experience eternal victory. And that brings us to one of the famous passages in the book of Revelation –“they overcame, they defeated evil by the blood of the Lamb and the word of their testimony.” Here's the thing, this theme of endurance that we’ve been working our way through for months, and it has probably encouraged us on days that we needed to endure and enduring is never easy, but as we kind of come to the end of the Bible and this theme becomes dominant, we begin to realize that this is…endurance isn't just sitting still and suffering until something is over. It’s not a passive waiting thing. It's not like some sort of defensive posture. It's actually a very conscious active thing that we are doing understanding that it's going somewhere. It's our endurance in the face of deception, our holding true to the blood of the lamb and the word of our testimony. In the face of the entire world being dissected around us, we’re to remain true. When I say, “we are to remain true” I’m talking about the people at the very end that are spoken of in this book. It's their witness that remains until the very end so that there was always a chance for anyone to turn. And when everyone who is going to turn has turned then things get very bleak and they come to an end and a new beginning emerges. And, so, let's dive into the book of Revelation. This will carry us until December 31st in the New Testament, until the end of our year. And we will notice that as we begin the book of Revelation, we begin by hearing from Jesus. Jesus writes some letters to some churches and that sets the backdrop. Revelation 1.
Prayer:
Father, we thank you for your word. We thank you for bringing us into this territory, this new territory across the board…board in both old and new Testaments. And Lord we invite your Holy Spirit as we now encounter and move into and move through the final book in the New Testament, the book of Revelation. Show us what we need to see. Give us what we need to take with us into the future. From the very beginning of this year we've been asking for something specific because it's something that you told us Jesus that we need - eyes to see, ears to hear. And, so, this is again our prayer as we move through the rest of this month, as we move through the territory that we’re moving through in the Bible. Give us eyes to see and ears to hear what you're saying. We pray this in the incomparable immeasurable name of our Savior Jesus. Amen.
Announcements:
dailyaudiobible.com is home base, it’s the website, it’s where you find out what’s going on around here.
And really, the things to talk about are Christmas related because that's where this is headed. That's where we’re going. And, so, the first thing is we have an annual program and …sort of like our annual Christmas party. And, so, for the next week beginning yesterday you can call in your holiday greetings to the community that you’ve been spending the year going to the Bible together with. And you can use the Hotline button for that or the phone number 877-942-4253. And that might sound familiar because that's how we send in our prayer requests and encouragements to each other. And, so, we’re gonna use that same apparatus to collect our holiday greetings. There's just one kind of rule…rule about it. Don’t call a holiday greeting mixed with a prayer request or anything like that. If you’re gonna call in a holiday greeting, call in a holiday greeting and let that be that. If you have some other things going on or you wanna pray for somebody or you want to ask for prayer, do that separately. This is like the only time year that you can do like multiple…like you can do that, call and then call right back. We’ll take those calls for the next week and then we’ll start assembling everything and create our annual Christmas gathering and I can't wait for it. It's always virtual because we’re a virtual community but this year, especially. It’s like we get to do this without a…we don’t have to change a thing. There can be viruses running around the world or pandemics. We don't have to change a thing. We’re gonna do what we always do and it’s gonna be beautiful as it always is. So, you can call those in now.
And then the other thing is the Daily Audio Bible Shop and shopping. Go there and look for resources that you might want to use to invite others along for the journey, or just to encourage their…their faith. There are written resources in book form, like the God of Your Story or Sneezing Jesus or Reframe or Passages. Like, there's there are books there. There are all kinds resources from things to wear to things to write with, to things to write in. Our Global Campfire candle is in the Shop. We worked so hard on that with a perfumer last year, with a sent a designer to get a candle that smells like a campfire but still smells good, not like ashy, like still smells good like a campfire to remind us. It's amazing how aroma actually brings us to a place. And, so, to have the Global Campfire candle reminds us that we’re in community together. All kinds resources like that. The Daily…or the Wind Farm coffee, our entire line of coffee that we roast fresh and send you our entire line of tea because these are activities that we do most every day. We drink something warm…not everybody…but most people drink either a cup of coffee or a cup of tea in the morning and maybe even throughout the day. I do. Everyone around here does. And, so, we created this line well over a decade ago because it's kind of part of the journey. It's nice to have a cup of coffee and allow God's word to be spoken over us and gives some things to think about and move into our day. It’s just part of the rhythm. All those resources and more are available in the Shop. If you spend $40 or more in the Shop, we will send you this year the 2020 Christmas ornament for the Daily Audio Bible included in your order. So, check that out.
If you want to partner with the Daily Audio Bible here in the latter part of the year, then thank you. Thank you humbly and deeply. Sincerely, we wouldn't be here if we weren't in this together. So, thank you. If this has made a difference, then thank you for your partnership. There is a link on the homepage at dailyaudiobible.com. If you’re using the app, you can press the Give button in the upper right-hand corner, or the mailing address is PO Box 1996 Spring Hill Tennessee 37174.
And, as always, if you have a prayer request or encouragement, or right now holiday greeting then you can hit the Hotline button in the app, or you can dial 877-942-4253.
And that's it for today. I’m Brian I love you and I'll be waiting for you here tomorrow.
Community Prayer ad Praise:
Hi everybody it’s Lisa the Encourager I just wanted to remind everyone of something that I wrote down after Brian read the last part of second Peter and I just called it when I wrote it down in my notes I just wrote it down as Peter’s charge. And I thought it’s…it was so good the way he reminded us that, you know, we should honor Peter in this last message that he gave to us as followers of Christ and basically telling us that, you know, this would be things that you would follow in the gift of having the rich welcome into the kingdom of Jesus Christ. And, so, I love that. And, so, there are seven beautiful principles to follow. And, so, the first one is goodness and the second one is knowledge. And we’re certainly getting all that through Brian and also reading the Bible every day. Self-control, which we could all use that especially with the busy holidays and busy traffic and even with our families continuing to have self-control with those that we love the most. Perseverance and walking with Christ, mutual affection and respect for all. I love that…just…just having mutual affection for, you know, people that we interact with. And then godliness, mirroring the way we are like Jesus, so continuing to have godliness. And then the last one is love. Again, just reminding us to show love to all and everything we do and all of our actions, like put those word to action. So, I wrote them down because I need reminding of this. So, I hope it helps you. I also shared them with my children…
Good morning DAB family my name is Pamela and I’m calling from Toronto Canada. It’s December 5th 130 in the morning and I’m calling for prayers, to ask for prayers for my son in Jamaica. His name is Ray. For him to turn his life over to Jesus because it’s the only way. And I’m praying for my other family members, nephews, and nieces, sisters, brothers. And I am also praying…asking for prayer for myself. I’m having pain all over my body. Sciatica pain, arthritis pain. So, I’m asking for your prayers and I just want to say thank you Brian and your family for the beautiful work you’ve been doing through Jesus. Thank you. I love you all. In Jesus name. Amen.
Hi DAB family this is Radiant Rachel and like Jane in the Everglades I’m going to pray Psalm 191 over us and with us for anybody who is in battle against demonic attacks. And I’m also specifically calling out protection and clarity for Janna and her family - Billy, Amber, Roland, Braden and Izzy. I may have one of those names wrong, but God knows his name and also over the state of Washington where they currently reside. Lord, we choose to live in the shelter of the most-high where we will find rest in the shadow of the Almighty. You alone Lord are our refuge, our place of safety. You are our God we trust You. Thank You, Lord for rescuing us from every trap and protecting us from deadly disease. We are covered with Your feathers. You shelter us with Your wings. Your faithful promises Lord are our armor and protection. We will not be afraid of the terrors of the night nor the arrows that fly in the day. We do not dread the disease that stocks in the darkness nor the disaster that strikes at midday. Though 10,000 fall at our side, though 10,000s are dying around us these evils will not touch us. Open our eyes Lord that we may see all the wicked are punished. You are our refuge. You Lord are the most-high and You are our shelter. No evil will conquer us. No plague will come near our home. You Lord have ordered the angels to protect us wherever we go. They hold us up with their hands so that we won’t hurt our foot on the stone. Thank You, Lord for the strength to trample lions and cobras and the strength to crush fierce lions and serpents under our feet. You tell us Lord that You will rescue those that love You. We love You Lord. You will protect those who trust in You name. We trust in You. Thank You for answering when we call on Your name. Thank You for being with us when we are in trouble. Lord, thank You for rescuing and honoring us and rewarding us with a long life and giving us salvation. In Jesus’ name we pray all these things. And we thank You for all these things. Amen.
I recently learned the lesson of the bamboo tree
and the many parallel analogies between that tree and me
that tree can grow so tall so fast that it mystifies the mind
90 feet or more in the first five years much faster than any other tree you’ll find
but for the first 4 ½ years you’ll only see a sprout
just a tiny shoot above the ground is all that’ll be sticking out
but in the last six months of that last 5th year it grows 90 feet and more
only the most faithful and loyal cultivators would stick it out to see what’s in store
but God is like that in our lives he’s faithful and he’s true
and even when we show little or no growth he still gives grace and mercy too
most would say just let it die it looks like it’s dead already
but God never loses hope for us his hands are true and steady
great is his faithfulness morning by morning new mercies we see
God changes not his compassions they fail not and as he has been he forever will be
and when all our worldly hope is gone and no more friends are left around
that sprout we had left for dead becomes a tree high above the ground
with roots so deep that the fiercest of storms could never erode its grip
it bends it sways some branches may break but mostly it’ll just dip
while we see nothing above the ground there’s continual growth below
only God can make a tree there so much that we just don’t know
but I also know that sometimes it looks like there’s little or no growth in me
so I’m thankful for his loving hands and I’m sure in time all will see
that growth was present all the time and God was present too
carefully nurturing day by day so my roots would hold fast too
don’t be so quick to judge that shoot that’s barely out of the ground
God has the power to make it as strong as any of the tree that’s around
This is from junk to treasure. I want to talk about our voices for couple minutes. I have heard so many people on the DAB mention of a miss the voice of someone who used to call in for prayers or someone who will comment about how they love to hear from those who call in regularly. The study of the voice and the ability to recognize voices is so complex and amazing. Like our unique fingerprints everyone has a voice identity due to pitch and tone rhythm and tempo and texture and so on. Also, many of us have little catchphrases that are used for their own special way of expression like when I say “kiss kiss”, “shalom shalom”, “okay Holy Spirit let’s roll”, or “in the name of Jesus!” You would know exactly who I’m referring to without me even using their name. I love to hear Grandpa Bob on here. His voice is so calming and soothing. He expresses such a sense of sincerity that you want to hear from him more and more. But there is one voice that is above all others and that is the voice of the One who has the power of creation and judgment, that of healing and forgiveness. It calms a raging storm and raises people from the dead. How do we recognize the voice of the Lord? By spending quiet time contemplating in His word. I believe we also hear from God in the voices of those who call in for prayer and encouragement every time they throw their log in the community campfire. Each day I find that I long to hear and get into the word with Brian every day and to hear the wonderful unique voices of my DAB family and I praise God for the ability to recognize and to hear from each and every one of you.
Hello DAB family this is Russell from superior. I just had a call talking to my daughter. She told me she’s injecting drugs. Ask you all to pray for her and keep her safe. Thank you.
1 note
·
View note
Text
The 20 Best Horror Movies on Netflix UK – Scary Films to Watch Right Now
https://ift.tt/2RE5emn
Netflix is an ever-changing, constantly growing treasure trove of hidden gems and secret delights (here’s everything new on Netflix UK this month). Sometimes, a teeny bit too secret though.
Who hasn’t sat down to watch a horror movie and found themselves scrolling endlessly, either not being able to find something they’re in the mood for, or not really knowing what half the titles are, or if they’re any good?
We’ve scoured the full current catalogue available to watch in the UK now and picked out the best scary movies. It’s a mix of classic and new, and a range of slashers, horror-coms, mumblegore, monster movies and more to hopefully scratch that itch with ease.
We’ll keep this updated as and when titles drop in and out of the service.
Hereditary (2018)
If you haven’t seen this slice of trauma, the feature debut of Ari Aster, you probably should. If you have seen it, you probably won’t want to again. Toni Collette stars as a woman whose controlling mother has just passed away setting of a series of horrible events. Aster says the film was partly inspired by his own sense of his family being cursed – this a movie absolutely drenched in grief and pain with astonishing performances all round. It’s tough going, but it’s a masterpiece. Read our review.
The Platform (2019)
This existential Spanish horror made a splash at the start of lockdown with it’s tale of prisoner trapped in an enormous vertical prison with a platform at it’s centre which delivers food to the inmate floor by floor starting at the top, so that each floor only gets what the floor above has left over. It’s political, allegorical, it’s clever and it’s very violent.
The Endless (2017)
Justin Benson and Aaron Moorhead’s gorgeous sci-fi horror stars the two as brother who escaped from a cult ten years ago and are drawn back in in search of answers when a strange videotape arrives. This is their third movie after Resolution and Spring and the two are only growing in strength as directors – The Endless is rammed with indelible imagery and deeply unsettling moments within a plot that is a joy to unpick.
What Keeps You Alive (2018)
Couple Jackie and Jules head to a remote woodland cabin to celebrate their first wedding anniversary but things go bad… Ok this sounds like the most generic slasher in the world but trust us it’s not. Twists hit early on (that we’d hate to spoil) and the tension ramps up fast in a very effective cat and mouse chase with a female bent. This comes from Colin Minihan who made Grave Encounters – this isn’t similar but both have a disorientating sense of place. Read our review.
Orphan (2009)
Released during the heyday of Dark Castle’s mid-budget horror splurge, Orphan is one of those genre films with an absolutely ludicrous (and therefore thoroughly enjoyable) twist, which we will not spoil for you. Peter Sarsgaard and Vera Farmiga star as a couple mourning the loss of their baby, who decided to adopt a little Russian girl called Esther from the local orphanage. Things quickly start to go very, very wrong as the pair start to suspect that wee Esther – who insists on dressing like a spooky doll – isn’t all she appears to be. Check out our review.
Insidious (2010)
The many sequels may have yielded diminishing returns but the first of this franchise, about a couple (Patrick Wilson and Rose Byrne) whose comatose son appeared to be trapped in another realm by a evil spirit, is a very effective chiller. Horror genius James Wan directs, and the first half of this movie at least is pretty much guaranteed to make you jump out of your skin.
Annihilation (2018)
An all star cast including Natalie Portman, Jennifer Jason Leigh and Tessa Thompson, plus the quality direction of Alex Garland wasn’t enough to secure this horror sci-fi based on Jeff Vandermeer’s novel a theatrical release in the UK. Nevermind, that just means you can watch it for free on Netflix. Portman joins a crew of women exploring the mysterious Area X where he husband ventured some time before and came back changed. It’s a weird, unfamiliar landscape of beautiful flora and terrifying fauna defying explanation until the strange, indelible finale (not sure what it means? Have a read of this explainer). And you can check out our review, too if you like.
Daybreakers (2009)
You’ll get a little bit of everything with this Spierig Brothers curio. It was the film that really got the directing team noticed and it’s not hard to see why. Set in a dystopian world where basically everyone has been turned into a vampire, one corporation thinks it’d be a bloody (sorry) good idea to track down all the surviving humans and…well, basically milk them. Ethan Hawke stars as a vampire haematologist who starts to think there might be another way for this story to go after he’s collared by a former vampire (Willem Dafoe), who can cure everyone. (Living) dead good. Check out our review.
The Bar (2017)
Slightly bonkers Spanish horror thriller which sees a bunch of strangers stuck in a busy Madrid cafe when snipers begin shooting anyone who tries to leave. Confusion and personality clashes abound in this economical single location chiller with a dark sense of human as the inhabitants slowly discover what’s going on, who’s responsible and try to work out if and how they will survive.
Read more
TV
Netflix UK: What’s New in April 2020?
By Kirsten Howard
TV
21 underappreciated films to watch on Netflix UK
By Paul Bradshaw and 2 others
The Cabin in the Woods (2012)
Drew Goddard and Joss Whedon’s love/hate letter to the horror genre felt like something of a game changer when it finally arrived (it was shelved for several years because of financial issue with original distributor MGM). Chris Hemsworth and Haley Bennett star in a double layer story about ordinary kids vacationing in a woodland cabin, with Bradley Whitford and Richard Jenkins as very particular kinds of bureaucrats up to something in the background. No spoilers, just watch. Here’s our review.
Cargo (2017)
Martin Freeman stars in this Netflix original developed from a short directed by Ben Howling and Yolanda Ramke. Set in the Australian outback, Freeman is a father trying to find someone to protect his child in the middle of a zombie apocalypse. More wistful and emotional than that sounds on paper, there’s a fascinating subplot about an Aboriginal girl mourning her father and the final set piece is unforgettable. Check out our review.
Lifeforce (1985)
A Cannon Films classic directed by late Texas Chain Saw legend Tobe Hooper, people are still discovering the ’80s madness that is Lifeforce. Originally entitled Space Vampires, it’s exactly what you’d expect, and so much more. Nude, energy sucking bat creatures are brought back to Earth after an interstellar mission finds a gaggle of them lying dormant in Halley’s Comet, and it all goes very badly for the planet. You can expect a scenery-chewing Patrick Stewart to pop up in between the tits and gore. Not literally! Although, sometimes literally.
Creep (2014)
No, not the one set on the tube, this ‘mumblegore’ horror is far weirder than that. Director Patrice Brice plays Aaron, a videographer hired by Mark Duplass’s Josef to make a video for his kid to watch after he’s died of a terminal illness. Or does he? Playing on the power of politeness and the awkwardness of male relationships this is a highly original, itchily uncomfortable watch. Creep 2 is also on Netflix, and also good!
Read more
TV
17 of the best TV series on Netflix UK
By Louisa Mellor
TV
Underappreciated comedy movies on Netflix UK to watch now
By Mark Harrison and 1 other
Hush (2016)
Another smart sensory-based horror, this time from Oculus and Doctor Sleep man Mike Flanagan. This home invasioner sees deaf writer Maddie (Kate Siegel) attacked in her woodland retreat by a masked stranger. He uses her inability to hear to sneak around and terrorise her, but she has tricks of her own up her sleeve. Check out our review.
The Invitation (2015)
Karyn Kusama (Jennifer’s Body, Destroyer) just keeps knocking it out of the park (and she’s recently been attached to a Dracula movie from Blumhouse Productions), and with The Invitation she continued to secure her place as one of the best directors around. Here, Will (Logan Marshall-Green) and his girlfriend go to a party held by his formerly suicidal ex-wife, and discover that she seems to be happier than she ever was, but Will starts to suspect that rather than healthily coping with her mental illness, she may well have joined a doomsday cult instead, and be planning to kill them all. Paranoia and tension are at the max in this bad boy. Here’s our review.
Little Evil (2017)
Comedy horror from Eli Craig who made the wonderful Tucker and Dale Vs Evil. This time he’s playing on creepy kid tropes, particular those from The Omen movies. Adam Scott plays a man who discovers his new wife’s (Evangeline Lilly) son might actually be the anti-christ. And because it’s Eli Craig, of course it’s funny and very good natured as well as playing with the genre.
Gerald’s Game (2017)
Another Mike Flanagan offering here – what can we say? he’s damn good! – as Jessie (a spectacular Carla Guigino) and her husband Gerald drive to a remote house to try and spice up their marriage with a bit of gentle BDSM. One problem: Jessie is not into it. At all. Two problems: Gerald carks it, leaving her tied up with only her cunning to help her free herself from her prone, handcuffed predicament. Three problems: a mythical, supernatural killer may be in the house. Stephen King, you’ve done it again. Read our review.
Ravenous (2017)
Unusual Canadian zombie movie (in French) which sees remaining stragglers after an outbreak of the infected band together in disparate groups travelling to find other survivors. Ravenous sets up its infected as worshipping a sort of new religion of found items (chairs, TVs etc.) making comment on the zombification of society. It’s also funny and quite scary, so there’s that.
Veronica (2017)
Loosely based on a true story, Veronica is set in Madrid in 1991 and follows a young woman who messes with a Ouija board who thinks she’s accidentally summoned an evil spirit. Director by Paco Plaza, one of the two directors behind [REC], the movie gained minor notoriety when it first landed on Netflix because of a few viewers finding it overly scary. It’s true there are some seriously creepy bits (but you’ll be fine!).
The Perfection (2018)
Get Out‘s Allison Williams and Dear White People‘s Logan Browning star in this twisty, trashy but nonetheless enjoyable tale of two musical prodigies hothoused at a mysterious academy. It’s lurid and lavish (and it’s got some fairly dodgy sexual politics, we’d warn you) but great lead performances and a tricksy three act structure that keeps you guessing, make this an entertaining and unusual Friday night pick. Read our review.
Want more horror? Here’s our list of 81 genuinely creepy horror movies. Here are some horror movies it’s safe to watch with your kids. And here are some underappreciated Scream-inspired horror movies of the 90s.
cnx.cmd.push(function() { cnx({ playerId: "106e33c0-3911-473c-b599-b1426db57530", }).render("0270c398a82f44f49c23c16122516796"); });
The post The 20 Best Horror Movies on Netflix UK – Scary Films to Watch Right Now appeared first on Den of Geek.
from Den of Geek https://ift.tt/33vglD3
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Not-So-Amazing Mary Jane Part 3: The Birth of Mysterio

Previous Part
Next Part
Master Post
Before we dive into specifics of Amazing Mary Jane, there is a large chunk of context we need to establish about Mysterio’s history. Specifically who he is and some of the crimes he’s committed over the years. I will generally be emphasising stuff that Mary Jane would likely or definitely be aware of; or at least could easily learn about with a little research. This is important to bear in mind when we look at MJ’s attitude to Beck in AMJ.
For starters, let’s consider how and why Beck ventured into a life of crime in the first place.
Life before Mysterio
Quentin Beck before he became a criminal had a college education to some extent and had major technical and chemical skills at his disposal. He became an accomplished special effects artists and stuntman and had regular employment. Long story short, he got bored and after failing to transition into acting (though he obviously had some acting talent) he was inspired to get involved with costume villainy.
Due to retcons in BND, it was established that he went back to work in Hollywood. However, he later got blacklisted when one of his effects injured someone. As originally presented and intended though, he basically turned to villainy out of boredom and frustration.
After being blacklisted Beck undertook his first major campaign against Spider-Man, whom (due to other retcons) he resented for foiling some of his crimes during his first foray into villainy.
Whether you look at him as originally presented or in the wake of all these retcons it’s clear that Beck didn’t get pushed into crime. It was a pure ego trip for him. Even with the retcon in mind realistically his skills and intelligence would garner him legitimate work elsewhere. In fact in the ‘Guardian Devil’ arc of Daredevil it’s established he was instrumental in developing certain technologies and processes that made advances in film making possible.
In short Quentin Beck became a criminal because he LIKED it. He is 100% not a tragic figure like the Lizard. He is not someone who’s environment made it difficult for him to be anything but a criminal, as is often the case for people in poverty stricken parts of the world. He wasn’t even someone like Doc Ock or Norman Osborn whose minds were (arguably) inadvertently affected by some kind of extenuating circumstance. Nor is he someone diagnosed with some kind of anti-social personality disorder like Cletus Kasady or Eddie Brock.
Regardless of whether you feel such mental conditions mitigate those villains, my point is Beck DEFINIETLY cannot be excused for his choice of becoming a criminal.
Virtually every crime he ever committed were the actions of a sane, rationale and intelligent person who happened to also be selfish, egotistical, greedy and often nasty. Maybe not nasty the way Carnage or the Green Goblin are, but nasty nevertheless.
I’m saying he’s not just ‘a villain’ but also an outright bad person.
And he’s been a bad person since basically the start of Spider-Man’s superhero career. That’s anywhere from 10-25 years, depending upon whose math you want to use.
The 1960s: Making an Entrance
Were we to take retcons into account, Mysterio’s first crime was his involvement with the Tinkerer way back in ASM #2, circa 1964! This was literally the fifth ever Spider-Man story to be created.


However, retcons not withstanding Mysterio’s first major crime was impersonating and framing Spider-Man, back in ASM #13.


He then went on to bill himself as a hero and defeated Spider-Man.






These events were a huge news story at the time and thus it’s not unbelievable that MJ would know about them via osmosis. Granted, there is leeway on that because MJ was not living in NYC at this time but she was making sporadic trips there and had taken a casual interest in Spider-Man’s adventures; this was partially because she knew Peter was Spider-Man.
However, one would imagine that it’d likely come up in conversation with Peter over the years given how this was his first (known) encounter with Mysterio and MJ was present for several consequent ones. It’d also be believable given that it’s just common sense for Peter to inform MJ of any enemies who could possibly impersonate him. Forewarned is forearmed (as arguably Gwen’s death proved) so knowing about Mysterio could help MJ ensure the safety of herself and her loved ones; for example MJ’s Aunt Anna and cousin Kristy.
Furthermore it is important to note that Mysterio’s very first major solo effort was a form of identity theft (there is probably a more accurate descriptor but I don’t know of one). The crime was intentionally designed so that he could build up his own reputation off the back of someone else’s. Does this perhaps remind you of another time Mysterio might’ve tried to selfishly benefit at the expense of another person’s reputation, not caring if he damaged it along the way? Like for example any female-led comic books released in 2019 for example?
The next time Mysterio duelled Spidey he used highly convincing robot duplicates of the (3 of the original 5) X-Men.




So, Mysterio is an expert in robotics and can create loyal and dangerous robotic servants. These robots can also trick people into thinking they are a real person, including Mysterio himself. Thus it’s very possible for Beck to convince someone he’s in one place when he’s actually in another, or alternatively get his robots to do something on his behalf when he’s otherwise indisposed.
Mary Jane 100% knows about these robot duplicates because versions of them (plus Iceman and Jean Grey) appear in Amazing Mary Jane #1.

It would suuuuuuuuure be illogical for MJ to just presume Mysterio would definitely NEVER misuse such robots for any nefarious schemes, or use them to slip under the noses of the press monitoring the movie. Or if he or his crew maybe used them to violate/evade justice somehow…
Also, just for the record, Mysterio was potentially risking damaging the reputation of the X-Men/mutants in general by creating duplicates of them. Yet another example of Mysterio is selfishly cavalier with someone else’s reputation.
Arguably (because I’m not an X-Men expert) this was especially awful because of how the general public already hated and feared mutants, who were of course chiefly allegorical to African Americans back in the 1960s. In this sense Mysterio could be viewed as exploiting societal bigotry or at least caring so little about it he doesn’t realise he’s potentially going to make it far worse. *
Mysterio’s third major encounter with Spidey was in a lot of ways one of his most twisted efforts.
His plan was to learn Spider-Man’s identity by convincing him that he was mentally ill…yeah…
Posing as psychiatrist Doctor Ludwig Rinehart, he convinced Jameson to publish an article claiming Spider-Man was heading for a major mental breakdown.


To make this more convincing he used his illusions to make Spider-Man believe he was seeing things that weren’t really there. His efforts bore fruit as Peter genuinely began to doubt his own sanity.



Beck’s endgame was for Spider-Man to seek out treatment from ‘Rinehart’ and in his vulnerable state divulge his secret identity. It was only through Jameson’s inadvertent intervention that Peter’s secret (and loved ones) remained safe.




I’m not suggesting Mary Jane necessarily knows about this incident; though it’s possible Peter told her. It’s more relevant because it illustrates what a twisted person Mysterio is to try and get to Spider-Man in such a way. It also illustrates the distress his illusionary skills can cause to people, both mentally and emotionally. This is a fact that Mary Jane need not have studied psychology to grasp; it’s just common sense. She knows Mysterio’s M.O. is tricking people into believing things that aren’t real and she’d know how believing something uncomfortable or frightening (even if it isn’t real) can be a dangerous and unhealthy thing. Her friend Harry Osborn had mental health problems that caused him to believe things that weren’t true and (for a time anyway) it destroyed him and harmed his family.
If you still think this is a concept MJ wouldn’t have grasped, then Mysterio’s next exploit would’ve likely convinced her.
During the course of Webspinners: Tales of Spider-Man #1-2 Mysterio intentionally attacked the mind of MJ’s acquaintance J. Jonah Jameson. He did this by tricking Jonah into believing he’d been killed and gone to Hell. Simultaneously he also framed Spidey for Jameson’s alleged murder.







Events from this story formed part of the screenplay for Mysterio’s biopic. Proof of this can be found in ASM v5 #29 wherein Peter and MJ are rehearsing Mysterio’s script and the dialogue is almost verbatim from the Webspinners story in question.
As such it is very possible that MJ would know about what Beck did to Jameson. One would imagine Peter would at least tell her about that in the course of rehearsing with her.

We are skipping ahead a bit, but another instance of Mysterio using his illusions to cause terror can be found in ASM #66. In the issue he hijacks TV airwaves and essentially delivers a terrorist message to the city at large. He depicts scenes of New York decimated and threatens to make them a reality unless Spidey confronts him. The incident upsets Aunt May (a woman with an underlying heart condition) and realistically would’ve distressed other people too. This might’ve included MJ’s Aunt Anna who was living with May at the time.

Given the public nature of this broadcast and the distress it caused Aunt Anna’s roommate, the chances are MJ would be aware of it. Even if she failed to catch it initially she’d have heard about it via sheer osmosis.
Even if you disagree, it’s yet another example of Mysterio selfishly and callously causing distress to people for his own ends. If one buys into Marvel’s sliding timescale these events also pack more of a punch since they would've happened post 9/11.
The 1970s: Scamming Seniors
We’re skipping ahead again all the way into the 1970s.
In ASM #141 Betty Brant and Ned Leeds inform Peter that Mysterio died a year earlier in prison. This horrifies Peter because he fought Mysterio earlier that very night.

This was public knowledge meaning there is a chance MJ would’ve heard about it in the news. But even if it wasn’t widely reported or if she just missed it, she’d have still likely heard about it. After all she was dating Peter at the time and was also very friendly with Betty (even serving as her Maid of Honour not too long after this). This is important to remember for the next section.
As it turns out he actually battled a new Mysterio, Danny Berkhart. Berkhart believed himself Beck’s friend and inherited some of his equipment after the latter’s death. He decided to take down Spider-Man out of respect for Beck.**

Much later it was revealed that Beck hadn’t really died, he’d merely used Berkhart to fake his own death. In the guise of Doctor Reinhardt he took over a nursing home. Consequently he swindled vulnerable elderly people out of their life savings, amassing almost $8 million. According to this inflation calculator, in 2019 that’d be about $40,780,313.20.



My, what a sympathetic individual…
This scheme snowballed into Beck faking Aunt May’s death on behalf of the burglar who killed Uncle Ben.

To be fair to him, The Burglar was threatening his life. However given Mysterio’s technology and intelligence it’s highly unbelievable that he couldn’t have taken the Burglar down if he wanted to. He does exactly this in ASM #198 once he’s learned the Burglar was after a fortune hidden in Aunt May’s old home, opting to seek out the fortune himself (see above).
It goes without saying how devastating it was for Peter and May’s friends (chiefly Aunt Anna) to believe she’d passed away.




It beguiles belief that, between MJ’s closeness to Peter, their mutual friends (like Harry and Flash), Aunt May and Aunt Anna, that MJ wouldn’t at some point have learned about May’s ‘death’. By extension she would’ve learned of the circumstances of it being faked and surely have been at least miffed about it! Thus she’d have deduced that Beck had faked his death, as she’d likely have heard about his alleged death in prison.
Even if MJ didn’t hear about any of this during the incident itself, considering that this was all a matter of public record and would’ve been reflected in May’s medical history MJ realistically would have learned about this at some point. This would especially be the case because May’s death was faked a further two times; and that was when MJ married to Peter.
After all, if it was public record that May’s death had been faked before then her consequent ‘death’ (it was actually an imposter) in ASM #400 would require a degree of verification that’d go beyond most patients.*** And it’s highly unlikely that Peter and MJ wouldn’t have been informed about this process. ; or that they themselves didn’t inform the doctors that they should triple check given May’s history. This is literally the reason the actress impersonating her in ASM #400 was specified as being ‘genetically altered’ so her DNA would read as Aunt May’s.
All this means that there is simply NO WAY MJ wouldn’t know Mysterio caused this kind of harm to two of the people she loved most in the world (Peter and May).
The 1980s: Old Tricks
We skip ahead again all the way into the 2010s, albeit an untold tale set circa the 1980s. In Symbiote Spider-Man #1 Mysterio’s attempts to rob a bank inadvertently led to an innocent woman (with kids no less) being shot and killed.




Now to be fair, this wasn’t intentional and he felt bad about it. But it wouldn’t have happened if he hadn’t committed a crime in the first place. He also wasn’t exactly turning himself in due to remorse or giving up a life of crime. MJ might not have known about this but it’s the first time (to my recollection) Beck was involved with someone actually dying. So you know, he’s definitely a killer and is unwilling to face the consequences of his crime. Real sympathetic right?
I will admit this is something of a contentious example as this series doesn’t exactly fit into continuity and so could be arguably discounted. Nevertheless it definitely offers food for thought. An insight into how Mysterio likely would act under these circumstances.
Jumping back to the 1980s proper, in a much later encounter with Spidey Mysterio once again attacked Peter’s mind. This time he tricked him into believing that an innocent person had died on his watch.


MJ again definitely knew about this because a guilt-ridden Peter talked to her about it before he learned the truth. Later she tried to talk him out of his guilt ridden state.
I think I will leave it there for now. We’ll continue our look at Mysterio in the next post as we enter the 21st century.
*I’ve got no place for this in future instalments so I’ll just say put it here as an aside.
MJ to my recollection has no experience with the X-Men (sans Wolverine), but she is definitely no anti-mutant bigot. Wouldn’t it be logical for her to be wary or at least conscious about how Beck is playing with the optics of the X-Men/mutants in general in his vanity project?
Not to mention their inclusion I’d imagine would be in reference to ASM Annual #1 where he tried to use them to kill her boyfriend. She has no qualms about the guy responsible for that recreating that event on film in an effort to glorify him self?
On the other hand we don’t know exactly how they are being used in the movie so I’ll let that slide.
**Berkhart isn’t all that relevant at the moment but he will be in the next instalment, so bear him in mind.
***Alternatively one would imagine in a world where the fantastical is a matter of fact, death would be checked to a greater degree than practiced in real life.
Previous Part
Next Part
Master Post
#Amazing Mary Jane#Mysterio#Quentin Beck#mjwatsonedit#mary jane watson#Mary Jane Watson Parker#Spider-Man#MJ Watson#peter parker#Symbiote Spider-Man#Betty Brant#Ned Leeds#Tinkerer#Brand New Day#Marvel#Marvel Comics
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Only a day or two ago I was notified that I was in contact with some people tested for and found positive for Covid-19, this came as nothing un expected, I was in contact with hundreds of people many from Europe recently. Then, as you know we are experiencing, most Universities, Libraries and Book Shows have been indefinitely closed, and because of this; many of us find or try lively-hood’s challenged. In a situation where it seems that there is little to do that will improve the current situation any faster than time will take its course, I have turned to reading and writing. I have been researching, as best as I can from home, fifteen books which are new to my stock. There are many more stuck in Europe and this gives me hope. It is the first day of spring and I awoke to a beautiful snow squall… In like a Lion..
And here are the fruits…

1). 355J Bible Saint Jerome, Gabriello Bruno (active 1480-1514.)
Biblia cum summariis concordantiis : diuisionibus: quattuor repertoriis p[ro]positis: numeriq[ue] foliorum distinctione: terse et fidelit[er] imp[re]ssa. { With table of Gabriel Brunus }
[Lyons]: Jean Pivard, 29 Jan. 1500 & 1. $ 15,000.

Impresserunt aute[m] solertes viri Franciscus Fradin et Ioha[n]nes Piuard socij impressores. …,]
Folio inches, &8 ç8 , a8 b6, c-z8 A-Z8 Aa8 Bb8; aa-cc8 dd10. Bound in original full calf over wooden boards with 10 brass bosses.
This edition corresponds with the edition printed by Fradin and Pivard in 1497. There are the same tables, summaries, &c.; and the arrangement of the books and the readings are alike. At the end of the subscription we read: “Impressit autem solers ori Johänes Pivard impressor. Deo sint sempiterne gratie.”
Pivard,who was working alone from 7 March 1498 to 1501, Started printing with François Fradin in 1497 (Goff B602) ISTC lists15 titles solely printed by Privard.
Goff B604; HC 3128; GfT 1883, 1884; Pell 2341; CIBN B-426; Arnoult 288; Girard 108; Parguez 213; Polain(B) 4210; IBE 1040; SI 764; Martín Abad B-134; Sallander 2098; Bod-inc B-312; Sheppard 6736; Pr 8670; GW 4281. (Gutenberg-Jahrbuch 1965 p140-3)

Copinger, Incunabula Biblica, 120; Darlow–Moule 6090; Sheppard 6736.
U.S. copies: Boston Public Library, General Theological Seminary, Jewish Theological Seminary of America, Library of Congress, Rare Book Division, Southern Methodist Univ., Bridwell Library (418 ff)

https://data.cerl.org/istc/ib00604000
◊
◊ ◊
◊
2) 353J Alberto da Castello (ca. 1460-1522)
Rosario della gloriosa Vergine Maria : con lle sttattiionii & iindullgenttiie delllle chiiese di Roma perr tutto L’’anno.
In Venetia : Presso la compagnia de gli Vniti,1585. $7,800

Octavo. 6 x 3 3/4. A-Z, Aa-Ii8. A later edition of the first ‘Rosary Book” in Italian.
This book has a wonderful contemporary binding, recently expertly rebacked. It is of red Morocco with gilt center images and borders gilt, with angels. Certainly these books were

very popular, that said, very few copies have survived. This edition is represented on OCLC by only two copies worldwide. 1 US copy Saint Benedict/Saint John’s University. (SJU Alcuin Arca Artium Rare BookBX2163 .C37 1585). [The authorship of the work and the woodcuts are attributable to the Dominican Friar Alberto da Castello, identified as author or editor at the authorizations of the Venecian Inquisition, given 5 April 1521. (Francesco Pisano)]

Over 150 woodcuts (including repeats) comprising almost full-page cuts (1 on t.p.) within borders. All had previously appeared in earlier editions. Ornamental and pictorial border pieces on almost every leaf. ( The wood cut on leaf 173v is upside down in the border!) Each wood cuts represent the “Mysteries of the Rosary”
“From the beginning, publications on the Rosary came accompanied by lavish xilographic illustrations. The most striking of these can be found in the edition of the Rosario della gloriosa Vergine Maria by Alberto da Castello from 1521 [Fig. 14.1], which contains a wealth of illustrations. This clearly shows that the Rosary was not just an oral recitation, but was also a contemplative prayer engaging the imagination, a combination later mirrored by the exercises of Ignatius of Loyola.
Alberto da Castello, born in the middle of the fifteenth century in Venice, joined the Dominican order around 1470 and wrote several devotional, liturgical, historical and canonical texts. In the Epistola prohemiale of his Rosario della gloriosa Vergine Maria he says that he wrote the meditations and organised the images ‘acciò che gli idioti che non sanno legere habbino el modo de contemplare gli divini beneficii et de questa contemplatione ne habbino qualche frutto spirituale’.( fol. 6r. ‘So that even the illiterate have a means to contemplate gifts of the divine and to receive spiritual fruits from such contemplation’ (translations are mine).He states that he writes especially for the ‘ignoranti, illetterati, idioti’, and that a good Christian must hold the mysteries of the Rosary deep in his heart. (Literary and Visual Forms of a Domestic Devotion: The Rosary in Renaissance Italy. Erminia Ardissino)

The mysteries of the rosary were introduced by Dominic of Prussia sometime between 1410 and 1439. This gave each decade of the rosary a unique quality. Each mystery leads us to ponder very specific events in the lives of Jesus and Mary and the lessons they hold for our own lives today.
The Rosary has a ritual aspect that individual prayers lack, and it is highly structured. It entails the recitation of 150 Ave Marias, clustered in groups of ten, preceded by a Pater noster and the proposition of a ‘mystery’ upon which to meditate. This number of 150

Ave Marias seems to be designed to correspond to the 150 psalms in the Davidic psalter, which is why the Rosary is also known as the ‘Virgin’s psalter’. It does not consist only of repetitive prayers, however, but also entails meditations. Indeed, the Rosary created by Dominic of Prussia was a kind of meditation on the life of Christ and Mary. In his Liber experientiarum he ‘explicitly claimed to be the first to have composed a series of fifty points on the life of Christ that were to be meditated on while reciting the Ave Marias’.
Sander 6572-6573. See: Essling 2124
)0(
100 full page plates and a volvelle!
3) 382J Jan David. 1545?-1613.
Veridicus christianus: auctore P. Joanne David … Editio altera, auctior.
Antverpiæ ex officina Plantiniana, M. DCVI. $6,500

Quarto 8 1/2 X 6 inches ‡4, ‡‡4, A-Z4, a-z4, Aa-Ee4.+ 100 Numbered Plates. Withspecial engraved t.p. with allegorical depiction of Christ carrying the cross, surrounded by ten artists at easels painting scenes from his life (as well as a few questionable profane subjects).

The text is divided into 100 chapters, each with an allegorical engraving incorporating letters keyed to the explanatory text and with marginal references. Each of the 100 numbered plates has a single line of Latin at the head giving the subject, with two-line explanatory verses below the allegorical engraving in Latin (roman letter), Dutch (civilité) and French (italic) First plate (following [2 daggers]4) is added title leaf for the ill., which were also published separately; see Bibliotheca Belgica. The added title reads: Icones ad Veridicvm Christianvm P. Ioannis David e Societate Iesv At the end is Device with compasses and the motto “constantia et labore” on Ee4r . This book is notoriously found defective in one way or another, this copy is perfect and complete.

This copy is bound in full contemporary blind stamped calf over wooden boards with two working clasps.
The Veridicus christianus: is followed by the “Orbita probitatis ad Christi imitationem veridico Christano subserviens”: p. 351-374; which preceds a volvelle plate for use in locating specific passages.

This text contains a series of images with accessible (sometimes to a fault) moral or religious messages. These illustration swarns against opening the senses to temptation lest death and moral decay take up residence in one’s soul.
The Veridicus Christianus emphasizes the Society of Jesus’ investment in thinking in, though, and about visual images that exemplify the supreme mystery of God. Published as a tool of devotion and meditations, it features one hundred chapters that encompass a wide range of topics for reflection. Each chapter incorporates an extensive commentary that interprets the emblematic image David too follows the order in which we apprehend things with our senses, beginning with a visual representation at the head of each chapter. Then comes the explication. The symboli explicatio was considered necessary because cultivated readers would be more susceptible to a reasoned argument than a picture.
Here are images of the vovell. The centers of the engraving and the volvelle (through which a string passes) are reinforced with small paper roundels printed with the monograms of Christ. The numbers are keyed to an “Indiculus orbitae” that follows (Bb1r-Bb2r). There a number, having been selected, is provided with a phrase from various Latin authors (listed on Bb2v), and a reference to one of the hundred sections that comprise the main text. It is suggested in Bibliotheca Belgica that this game may have been intended as a pious alternative to such superstitious books as Thuys der fortvnen.
)0(
4) 312J. Domenico Cavalca. (1270?-1342)
Pungi lingua
[Baptista de Tortis]: Venexia, Adi .viiii. de Octubrio. 1494 $12,000

Quarto (200 x 145 mm); [80] pages. a-k8. Large woodcut depicting the crucifixion on the frontispiece, First Venetian edition with the beautiful woodblock published here for the first time. This copy has a beautiful initial “A” in gold, blue, red and green, a colorful coat of arms. This copy is bound in modern carta rustic with a gold title on an orange label

This is a treatise on the dangers of the misuse of the language it was, as you might expect quite popular . Written by the Dominican monk who was a contemporary of Dante and among the first to write in the vernacular, and one of the most successful translators of holy texts.
Aside from Biblical illustrations, the Pungilingua has many exempla drawn from many other sources including some not includes in the Alphabetum narratinum. Most of the stories are told in one to three lines, and many contain commerce with the Devil, one time disguised as a horse. In the prologue Cavalca mentions that he gathered his exempla from many sources “alcune poche cose” . One of the major sources is the Summa Vitiorum by Peraldus. but he also quite a few profane authors , Seneca, Socrates, Cicero, Valerius Maximus. That said, quite often Cavalca attributes the wrong author. Cavalca writes as though he was speaking to the reader in person useing phrases like “Io per me credo” and “Oimé “ Introducing unique stories and words, He refers to someone as double-tongued as a “tecomeco” (bilingue) . He refers to a sleight of hand trick ,called “gherminella” a word which was used later by Boccaccio. This is an important book in Italian literary history, and the Italian vocabulary leaving many contemporary proverbs and descriptions of medieval life.
Goff C342; H(Add)C 4776a; R 116; Pell 3448; CIBN C-195; IGI 2637; Essling 750; Sander 1853;
Pr 4649; BMC V 328; GW 6413
One copy in Goff.
Huntington Library.
Queried Location: New York NY, Manhattan College: sold Christie’s (NY) 1 June 1991 lot 41 (current whereabouts unknown)

***
***
5) 350J. Richard FitzRalph (Ricardus Radulphus Armacanus pseudonym) (circa 1300-1360)
Summa Domini Armacani in Questionibus Armenorum noviter impressa et Correcta a magistro nostro Johanne Sudoris. Cum aliquibus Sermonibus eiusdem de Christi dominio.
Paris: Jehan Petit et ponset le Preux, (Venales habentur in vico divi Jacobi sub Lilio aureo) 1512. [Privilège octroyé à Jean Petit et Poncet Le Preux daté du 12 mars 1511 (1512 n. st.) et prenant effet le 15 juillet 1512.]. $24,000

Small Folio 275 x 201 mm. A6 a-z6 &6 A-E6 F4. [6], 177 [i. e., 178] leaves. This copy is bound in a Remboîtage of later limp vellum; contents toned and brittle, lightly damp wrinkled with marginal damp staining at beginning and end, contemporary inscriptions on title and scattered underscoring and marginalia, wormhole through blank outer margin of approximately the first 30 leaves, paper crack in o1 not affecting text, last leaf reinforced in outer margin on verso. A Mexican Augustinian branded ownership mark on bottom edge.
This is the only printed edition of the Summa in Questionibus Armenorum which is an examination of alleged Armenian doctrinal errors, the chief dogmatic work by an Irish theologian and prelate involved in negotiations between the papal court at Avignon and Armenian representatives over the reconciliation of the Roman and Armenian churches.
FitzRalph, whose Defensorium curatorum was first published circa 1483, was one of the earliest Irish authors to appear in print. Renouard-Moreau II, 314;
Shaaber M119; not in RBH or ABPC. Moreau, B. Inventaire 1512- 314; Index des livres interdits, t. IX, p. 86 (n° 50/499; Page de titre en rouge et noir dans un encadrement de plaques gravées sur métal, marque de Jean Petit (Renouard, 890) Adams, F-550


><><><><><
6) 358J Jacobus de Gruytrode 1400-1475
Speculum animae peccatricis
[Memmingen : Albrecht Kunne, about 1490] $6,500

Quarto , [28] ff, 33 lines, the first initial (5 lines) is painted in white and blue on a golden background, upper and left margin richly decorated in red, purple, blue and gold and with two red beasts. 19th c. binding in half leather, title gilt on spine, all edges gilt. Sometimes falsely attributed to Dionysius Carthusiensis, the Speculum is now attributed either to Jacobus de Gruytrode (cf. Bloomfield) or to Jacobus de Clusa (cf. L. Meier, Die Werke des Erfurter Karthäusers Jakob von Jüterbog, Münster, 1955).

Speculum animae peccatricis is a work of spiritual edification which consists of seven sections: on human misery, sin (especially lechery), penance, rejection of the world, the vanity of human wishes, death and hell and heaven.
Firste of the filthenes and miserie of man. Below are the chapter in English
Secounde of the synnes ingeneralle and of their effectis.
Thyrde howe they ought hastely with all diligence to do penaunce.
Fourth howe they ought to fle the world.
Fyfthe of the false Riches and vayne ho∣noures of the worlde.
Sixt howe they ought to drede deth.
Seuenth of the Ioyes of paradyse and of the paynes of hell.
There is no modern critical edition of the text. Among the devotional books by the Flemish mystical writers of the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries, none was more popular on the Continent and in England during the early Renaissance than the Speculum aureum animae peccatricis or The mirroure of golde for the synfull soule, which Lady Margaret Beaufort translated into English. Since the sixteenth century, bibliographers have listed the Speculum as the work of the Carthusian monk Jacobus de Gruytroede, prior of the Liége Charterhouse from 1440 to 1475, yet the English version is always attributed to his friend Denis de Leuwis or Dionysius the Carthusian, as he is better known. The question of authorship may be satisfactorily settled as the result of recent research by an English Carthusian scholar in the library of the Certosa in Farneta. He noted that the editors of Dionysius’s Opera omnia (Tournai, 1913) explain how the error in authorship began. In volume xlii they point out that, owing to the Carthusian tradition of anonymity during a monk’s lifetime, the Speculum was printed anonymously until 1495, in which year the Nuremberg printer Paul Wagner first issued it as a work by Dionysius. He found the manuscript of the Speculum in the library at Ruremond, where Dionysius was prior until his death in 1471, and supposed it was written by him, as were the other works he intended to print. The two priors were close friends, and dedicated several of their works to each other. Nugent E.M. (1969) Jacobus de Gruytroede. In: Nugent E.M. (eds) The Thought & Culture of the English Renaissance. Springer, Dordrecht
Goff S644; HC 14899*; Pell 4313; CIBN S-333; IGI 5001; IDL 2532; Schlechter-Ries 1003; Voull(B) 1617,5; Schmitt I 1614,2; Hubay(Augsburg) 1141; Hubay(Eichstätt) 538; Sack(Freiburg) 1951; Walsh 988; Bod-inc S-258; Sheppard 2032; Pr 2804; BMC II 608; BSB-Ink I-23; GW M10734
U.S. copies;Harvard ,Emory, Columbia ,Huntington Library
Southern Methodist Univ, Univ. of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Library
)0(
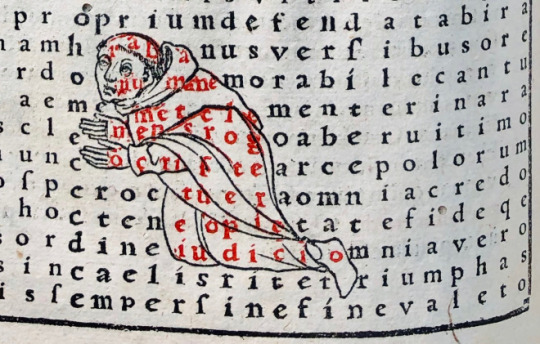
Nam digiti scripto laetantur, lumina visu Mens volvet sensu mystica verba Dei
“The fingers rejoice in writing, the eyes in seeing,
and the mind at examining the meaning of God’s mystical words.”
The first printed facsimile of a manuscript.
7) 351J. Hrabanus Maurus. 784-856?
Magnencij Rabani Mauri De Laudib[us] sancte Crucis opus. erudicione versu prosaq[ue] mirificum.
Phorçheim. [Pforzheim] : In ædibus Thom[ae] Anshelmi., 1503. $10,700

Folio Aa6, Bb4, a-k6, A-B6, C4 (last leaf blank).
THIS COPY LACKING [four leaves] A5 & 6, Bb1 and a1. [two woodcuts of Alcuin interceding on behalf of Rabanus before Pope Gregory iv, and of Rabanus presenting his poems to the Pope; and two figured dedicatory poems the first to Louis the Pious the next christ crucified] It is bound in a full vellum modern binding. First Edition (for a second edition see below)
Types 3:109R, 4:180G; 40 lines of transcribed verse + headline, 40 lines of commentary + headline, red and black printing throughout, calligraphic woodcut initial (Proctor, fig. 24) M on title page, woodcut initials printed in red, and a figured prefatory poem, 28 carmina figurata, the first entirely xylographic, the remaining poems combining printed and xylographic letters with the versus intexti printed in red (except fig. xvi), enclosed by either woodcut figures (of the emperor, Christ, the Evangelists, Cherubim, etc.) printed in black or by Christian symbols and characters, most defined by metal rules in red.
This is a remarkable typographical achievement, probably the earliest attempt to reproduce a medieval manuscript. The greater portion of the work comprises a preface in verse and twenty-eight poems. “Hrabanus Maurus, the abbot of Fulda, wrote in the midst of the ‘new monasticism,’ a period associated with a revival of literacy and learning. In religious and secular spheres. This ‘script culture,’ as Rosamond McKitterick has it, used the written word not only as a mode of communication but as ‘a resource, a guide, a key, and an inspiration,’ especially in the devotional practice of Christianity.

Each of the twenty-eight picture poems that form In honorem sanctae crucis explores a different theme relating to the Cross through a complex interplay of word and image. The poems each have an equal number of letters per line, written continuously like a grid. By following the letters in the usual direction for a Latin text—from left to right, top to bottom—each grid reads as one long poem. But within each grid, certain letters are also marked out with colour and drawings to form pictures. The letters that make up these pictures read as separate short poems embedded within the larger poem. As such, each page of In honorem sanctae crucis presents not just a puzzle of words and pictures, full of hidden and interrelated messages for the reader to decode bout a meditation exercise.
“Hrabanus created the various shapes and figures by highlighting individual letters in underlying poens in colour (in the printed editions red), and theses individual letters together make up meaningful text , ranging from simple declarations to very elaborate ones. For example, Carmina 2 contains a simple cross inside a square (Hrabanus calls it a “tetragonum”)whose sides form a border for the poem as a whole. The textfrom the underlying poen that makes up the figure consists of six hexameters, each one an address to the cross beginning with the words ‘O crux…’ When we follow Hrabanus’s instruction in the accompanying prose text for reading these hexameters, we find the following: even though the verse that forms the top of the square is also the opening of the underlying poem, he insists that we begin reading with the stem of the cross, from top to bottom.” (Schipper)

Sunt quoque uersus duo in ipsa ccruceconscripti, quorum prior est:
O CRVX QVAE SVMMI ES NOTO DEDICATA TROPAEO
a summo in ima descendens. Alter uero:
O CRVX QVAE CHRISTI ES CARO BENEDICTA TRIVMPHO
a dextra in sinistram crucis tendens ‡
‡“there are also two verses inscribed in the cross, the first of which is :
“ O cross , thou who art at the height of fame, a dedicated moment”
‘running from the top down. And a second’
“O Cross thou who through the body of Christ art the blessed triumph”
‘running from the right to the left.’
Further more Hrabanus flips left and right the texts point of view alternates , Hrabanus tells us the cross is looking out at the reader, not the other way around. “ Only after we have read the hexameters in the cross are we free to read the verses in the four sides of the tetragon, and even then Hrabanus constrains the order in which they are to be read: first the top, then the bottom, then the right side then finally the left side.”
More complex figures present further challenges in reading. The figure in Carmen 25, for example, consists of eight letters of the word ‘ALLEVIA’ arranged around a small cross. It does not take much effort to notice that we need to start with the A, read down to the E, continue on the left, and end on the right of the figure; and that each time we trace out those letters we make the sign of the cross. It becomes more difficult when we also try and read the text that is enclosed in the figures.

The letters of ALLEVIA are made of the following letters from the underlying poem.
A crux[a
L eter
L na[de
E i]es[lave[v L ivis
V in]arc
I e]po
A lorvm
CRUX AETERNA DEI ES LAVS VIVIS IN ARCE POLORUM
‡ Eternal cross, thou art the praise of God, thou livest in the arc of the skies.

Peter Godman, Poetry of the Carolingian Renaissance (Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 1985), 249.
A. G. Rigg and G. R. Wieland, ‘A Canterbury Classbook of the Mid-eleventh Century Anglo-Saxon England 4 (1974), 113-30.
William Schipper, ‘Hrabanus Maurus in Anglo-Saxon England: In Honorem Sanctae Crucis’, in Early Medieval Studies in Memory of Patrick Wormald, ed. Stephen Baxter, Catherine Karkov, Janet L. Nelson, David Pelteret (Farnham, Surrey; Burlington, Vt.: Ashgate 2009), 283-98.

Proctor, R. Index to the early printed books in the British Museum,; 11747; Adams, H.M. Catalogue of books printed on the continent of Europe, 1501-1600, in Cambridge libraries,; R3; Catalogue of a collection of early German books in the library of C. Fairfax Murray,; 350; Panzer, G.W.F. Annales typographici,; VIII 227, 2; Pollard, A.W. Catalogue of books mostly from the presses of the first printers … collected by Rush C. Hawkins,; 189 Panzer, VIII, 227, no. 2. Proctor 11747. Fairfax Murray 350./ Last leaf blank./ Edited by Jakob Wimpheling.–cf. title page verso./ Illustrations: 2 woodcuts of the author presenting his book to the pope, and many woodcut figures (Christ, cherubs, crosses, symbols, etc.) printed on 28 pages of text. Some of the text within and near the outline figures is xylographic, the rest printed. The letters within the outlines are printed in red and may be read separately in a different sense. Printed in red and black, initials (except on t.p.) in red./ With label of Sinclair Hamilton. Peter Godman, Poetry of the Carolingian Renaissance (Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 1985), 249.
A. G. Rigg and G. R. Wieland, ‘A Canterbury Classbook of the Mid-eleventh Century Anglo-Saxon England 4 (1974), 113-30. William Schipper, ‘Hrabanus Maurus in Anglo-Saxon England: In Honorem Sanctae Crucis’, in Early Medieval Studies in Memory of
Patrick Wormald, ed. Stephen Baxter, Catherine Karkov, Janet L. Nelson, David Pelteret (Farnham, Surrey; Burlington, Vt.: Ashgate,
^)^)^)^(^(^(^
The second edition One-Hundred and three years later.
8). 354J Hrabanus Maurus. 784-856?
Magnencij Rabani Mauri De Laudib[us] sancte Crucis opus. erudicione versu prosaq[ue] mirificum. Cum antiqviate avctoris <annis abhinc prope octingentis abbatis primum fuldensis, archiepiscopi postea moguntini. tum noitate scriptionis memorabile. Qvo figvris sive imaginibvs XXVIII. multi fedei christianae mysteria, multi mystici numeri; angelorum, virtutum, VII. donorum Spiritus Sancti, VIII. Beatitudinum, IV. elementorum, IV. temorum anni, VI euangelistarum & agni, mensium, ventorum, V librorum Moysis, nominis Adam, alleluia, & amen, aliarumq[ue] rerum vis & dignitas in formam crvis reedacta, subtiliter et ingeniose explicantur.
Augustæ Vindelicorvm e typographeo Praetoriano. , 1605. $9,000

Folio Aa6, Bb4, a-k6, a6, B4, c4. (complete). Printers mark on title page, woodcut initials printed in red, two woodcuts of Alcuin interceding on behalf of Rabanus before Pope Gregory iv, and of Rabanus presenting his poems to the Pope; a figured dedicatory poem to Louis the Pious and a figured prefatory poem, 28 carmina figurata, the first entirely xylographic, the remaining poems combining printed and xylographic letters with the versus intexti printed in red (except fig. xvi), enclosed by either woodcut figures (of the emperor, Christ, the Evangelists, Cherubim, etc.) printed in black or by Christian symbols and characters, most defined by metal rules in red. Bound in contemporary deer skin.
This aside from the prologue this edition is a re-set reproduction of the first printed edition (see above)
#######+++++#######
9) 383J Johannes de Anania
Commentaria super prima et secunda parte libri quinti Decretalium. Add: Repertorium
Bologna : Henricus de Colonia, 7 Dec. 1479, 5 Jan. 1480. $17,000
Large folio 422 x 285mm
Pars III (bound first) a8,b6,c10,d6,e8,f4,g8.(lacking a1Blank)
Pars I (bound second) a10,b8,i8,k6,l8,m8,n6,o6,p8,q8,r10s 10.
Pars II (bound third) A8,-F8,G6,H8,-L8,M6,N8,O8P6,Q8,R8,S6,T8,U10,X8-Z8, &8, ¶8,€8,¡8. In three parts, dated: 7 Dec. 1479 (Commentaria, partes I-II); 5 Jan. 1480 (Repertorium)
No copy of parts II & III in the US.
The margin of a2 of the Repertorium cut off with no text loss (see image) This is a very very wide margined copy, with strong and crisp paper. The first leaf is stroked in red and blue. Throughout the rest of the books capital spaces are left blank. This copy is bound in 19th century vellum.
ANANI’A, JOHANNES DE : his family name, Anagni. implies that he was of the family of the Catani, and that his father’s name was Leonardo. He taught canon law in Bologna, and had the reputation of a conscientious man. He studied under Floriano di San Pietro. Alexander Tartagni and Andreas Barbati were his scholars; the former became his step-son, and the latter inherited his library. According to Orlandi, Anania was sent ambassador from the city of Bologna to Pope Martin V. in 1425, and he was also employed to conduct negotiations with other princes. Johannes de Anania at the time of his death, in 1455 or 1458, was archdeacon at Bologna. Spangenberg enumerates four of his works, three of which were published at Lyon between 1521 and 1555 : — 1. A Commentary on the fifth book of the Decretals, published in folio at Lyon in 1521, and reprinted there in 1553. 2. Consilia, discovered and edited by Ludovico Bolognini, in folio, at Lyon in 1555, reprinted at Venice in 1570. 3. “De Revocatione Feudi alienati,” in octavo, at Lyon, in 1546, reprinted at Basle in 1564. 4. A Collection of the Decisions of the Roman Rota, at Venice, in folio, in 1496. Mazzuchelli mentions a treatise on the law as to salaries, “Allegatio de Salario et Stipendio ac de Obligatione et Promissione Domini,” which is preserved in MS. at Bologna in the library of the Collegio di Spagna. In addition to these Lipenius ascribes to Johannes de Anania a legal tract on church patronage, “De Jure Patronatus Ecclesiastico,” published at Amsterdam in 1640; and a collection of cases (” Quaestiones”) at Cologne in 1570. To the folio edition of Baldus, “In Usus Feudorum Commentaria,”

published at Lyon in 1550, there is appended a thesis on the law regarding the alienation of fiefs, maintained by Johannes de Anania at a public disputation in Bologna. The date is not given, but he is styled “Doctor et Canonicus,” and his opponent is said to have been Secundinus de Natis; and the publisher intimates that the MS. had been preserved in the library of Johannes Nevizanus at Asti. No. 446. of the Arundel MSS. in the library of the British Museum contains a treatise “De Usuris” by Johannes de Anania. The volume is of a large folio form, and the ” De Usuris,” written in a small character with numerous contractions, occupies the folios 93. to 164. inclusive, each folio containing four columns. These treatises are the only compositions of the author we have seen, and they leave a favourable impression of his skill in selecting authorities to support and elucidate his positions, and of his talent for lucid arrangement. (Mazzuchelli, Scrittori d’ Italia; Spangenberg, in Ersch und Gruber’s Allgemeine Encyclopadie; Alidosi, Appendice alli Dottori Bolognesi de Legge Canonica e Civile; Orlandi, Notizie degli Scrittori Bolognesi; Baldus Perusinus, in Usus Feudorum Commentaria doctissima, quibus accesserunt Andr. Siculi Adnotationes una cum Joan. de Anania eleganti Disputatione in tres secta Quastiones, Lugduni, 1550, fol.; Arundel MSS. in the British Museum, No. 446.) W. W
Not in Goff: ISTC ij00250150; H 938*; Torchet 521; IGI 5245; IBE 3188; Kotvan 702; Sajó-Soltész 1881; Martín Abad J-44; Voull(B) 2735,20; Walsh 3188; BSB-Ink I-365; GW M12841
Holdings: United States Harvard University, Law School Library (I) only.

)0(
)0(

10) 381J Athanasius Kircher 1602-1680
Physiologia Kircheriana Experimentalis, Qua Summa Argumentorum Multitudine & Varietate Naturalium rerum scientia per experimenta Physica, Mathematica, Medica, Chymica, Musica, Magnetica, Mechanica comprobatur atque stabilitur. Quam Ex Vastis Operibus Adm. Revdi. P. Athanasii Kircheri extraxit, & in hunc ordinem per classes redegit Romæ, Anno M. DC. LXXV. Joannes Stephanus Kestlerus Alsata, Authoris discipulus, & in re litterariâ assecla, & coadjutor.
Amsterdam: Ex Officinâ Janssonio-Waesbergiana. Anno 1680 $9,500

Folio. 15 x 9 3/4 inches. *4, A-Z4, Aa-Ii4. First edition.mmThis copy is quite clean and crisp throughout, never having been washed or pressed. There is some occasional spotting and browning. but none is too extensive. The binding is twentyth century full vellum with title on spine. an impressive and large copy!
“Thus in the must varied branches of science Kircher played the role of pioneer. Even medicine received his attention, as is shown for example by his treatise, ‘Scrutinium phyisco-medicum contagiosæ luis, quæ pestis dicitur’ (Rome, 1663). His scientific activities brought him into scientific correspondence with scholars laboring in the most different fields, as the numerous volumes of his extant letters show. It is to his inventive mind that we owe one of the earliest of our counting machines: the speaking-tube and æolian harp were perfected by him. He was also the inventor of the magic lantern which has since been brought to such perfection and is and is today almost indispensable. [All of these devices are illustrated in the present work, compiled in the year of the author’s death by Kircher and his student Johann Stephan Kestler, including three large and striking engravings of magic lanterns.]”
May I ask the reader to take the following quote with a measure of indulgence for its closed minded author [circa 1913] with the hope that modern folk of the last decade of the second millennium have a bit more tolerance for the many sciences that we have yet to master.
“That the most varied judgments should be formed and expressed on a man of such encyclopædic knowledge was only to be expected. He tried to find a grain of truth even in the false sciences of alchemy, astrology, and horoscopy, which were still in his time much in vogue, nor is it surprising that in the province of astronomy he did not at this early date defend the Copernican System.” (the above two quoted taken from the Catholic Encyclopedia, vol. viii, page 662) Kircher was an accomplished and versatile scholar who applied his intellectual abilities to a myriad of scientific problems. This work is a fascinating compendium of scientific experiments and principles which documents the accomplishments of early modern thinkers of the west.
^)^)^)^(^(^(^

11) 380J Francis Molloy. fl 1660
Lucerna fidelium, seu, Fasciculus decerptus ab authoribus magis versatis, qui tractarunt de doctrina Christiana : divisus in tres partes.
Romæ : Typis Sacræ Congreg. de Propaganda Fide, M DC LXXVI [1676] $4,500
Octavo 6 X 4 inches : A-2B8 2C2. complet, signature ) is mis-signed . This copy is bound in early 20th century sheep.

MOLLOY or O’MAOLMHUAIDH, FRANCIS (Jl. 1660), theologian and grammarian, was a native of the county of Meath, Ireland. The family of which he was a member had extensive landed possessions in the district known as O’Molloys’ Country, and some of them engaged actively in the Irish movements from 1641 to 1652.
Francis Molloy entered the order of St. Francis, became a priest, was appointed professor of theology at St. Isidore’s College, Rome, and acted as agent for the Irish catholics at the papal court in the reign of Charles II. His first published work was entitled ‘Tractatus de Incarnatione ad mentern Scoti,’ 1645. This was followed in 1658 by ‘ Jubilatia genethliaca

in honorem Prosperi Balthasaris Philippi, Hispani principis, carmine,’ and by a Latin treatise on theology in 1666.
A catechism of the doctrines of the catholic church in the Irish language was published by Molloy in 1676 with the title: ‘Lucerna tidelium, seu fasciculus decerptus ab authoribus magis versatis qui tractarunt de doctrina Christiana.’ It was printed at Rome at the press of the Congregation ‘de propaganda fide,’ ( This book is the first book they printed in Irish Type) from which, in 1677, issued another book by Molloy, entitled ‘Grammatica Latino-Hibernica,’ 12mo, the first printed grammar of the Irish language.
Edward Lhuyd [q. v.], in his’ Archaeologia Britannica,’published at Oxford in 1707, mentioned that he had seen a manuscript grammar of the Irish language copied at Louvain in 1669 which partially corresponded with that of Molloy. He added that Molloy’s grammar, although the most complete exta’nt in his time, was deficient as to syntax and the variation of the nouns and verbs. The date of Molloy’s death has not been ascertained.
In 1626 Propaganda Fide had installed a printing press for the foreign missions and not much later another one was brought to Louvain where books and catechisms were printed for both the local college and the Irish mission.* The problem with the Propaganda printing press was that only books in Latin and Italian were allowed to be printed so it took until 1674 when Francis Molloy asked for permission to print a catechism there in Irish with the explanation “che altra malamente capisce e vacilla assai per mancanza d’intruttore e d’intruttion sana.”**.
[“Irish priests at Rome had a new Irish type cut about 1675 … [this was] their first book.”- -H. Reichner, Catalogue 34, Jan. 1968]

Wing O291C, English short title catalogue,; R41480; Clancy, T.H. English Catholic books, 1641-1700 (rev. ed.),; entry 743; Catalogue of seventeenth century Italian books in the British Library,; page 628
*& ** ;Egan, Bartholomew (ed.): Notes on Propaganda Fide Printing Press and Correspondence concerning Francis Molloy O.F.M., in: Collectanea Hibernica, No. 2 (1959), pp. 115-124.
)0(
)0()0(
With a reference to the invention of printing on the verso of Folio 64.
12) 359J Werner Rolewinck 1425-1502
Fasciculus temporu[m] omnes antiquo[rum] chronicas strictim complectens felici numine incipit. Prologus.
Venice : Erhard Ratdolt, 8 Sept. 1485 $16,000

Folio (275 x 195 mm). [A]8 [a-g]8 [h]10 75 leaves without signatures or page numbers (9 leaves, 1-66 foliated ), 3 columns in table, 59 lines and foliation, gothic letter, 2 large ornamental initials, 59 woodcuts, one full-page, woodcut diagram. Fifth and last Venetian edition, and fourth Ratdolt edition being the most complete edition of Rolewinck s chronological history of the world. The chronology follows a double time-line, measuring time from both the Creation and the birth of Christ to the death of the Ottoman Sultan Mehmed II commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror in the year 1481, demanding a
remarkably complex typographical layout. The Fasciculus Temporum (Little bundles of time) was the first book printed on history of the world, it is also one of the earliest and greatest of illustrated incunabula. The illustrations show Noah s Ark, the tower of Babel and contain many town views including Jerusalem, Syracuse, Rome and the Doge s Palace in Venice.
Rolewinck (1425-1502) was a Carthusian monk and prolific author. This book was both the most popular of his numerous writings and the most popular concise world chronicle of its time, being printed 32 times in the 15th century, including translations into French, German and Dutch . Rolewinck’s Fasciculus Temporum was an enormously popular world chronicle, appearing in over 30 incunabular editions in Latin, German, French, and Dutch. A very handsome and typographically-sophisticated volume, with varying columns, circular devices with inset type, and woodcuts throughout.

This work aspires to trace the history of the world from the beginning of time until the year of pulication. The thirty-three woodcuts are crisp and rather charming, and, like those in many fifteenth- and sixteenth-century chronicles, are occasionally reused to illustrate different events and locations. The work is fascinating for the comprehensiveness of its content as well as the beauty of its execution.
Of particular interest is a reference to the invention of printing (in 1454) on the verso of Folio 64.

Goff R271; GW M38738; ; BMC V 290; H 6935*; Redgr 52; Essling 280; Sander 6530; Schr 5116C; Pell Ms 10192 (9969); CIBN R-177; Arnoult 1276; Neveu 528; Nice 269; Torchet 821; Polain(B) 4691; IDL 3943; IBE 4955; IGI 8420; CCIR R-40; Kotvan 1024; Sajó-Soltész 2972; Gspan-Badalić 590; IBPort 1576; Mendes 1124, 1125, 1126; Madsen 3526; Martín Abad R-48; Voull(B) 3801; Hubay(Augsburg) 1811; Hubay(Eichstätt) 898; Walsh 1830; Rhodes(Oxford Colleges) 1525; Bod-inc R-121; Sheppard 3688; Pr 4404; BSB-Ink R-247
#######+++++#######
13) 367J Petrus de Rosenheim. (1380-1432). Nom probable : Petrus Wiechs
[Roseum memoriale divinorum eloquiorum]
[Köln] : [Southern Germany : n.pr., about 1480-90?]
or [Cologne? : n.pr., about 1483] or [Ludwig von Renchen?], 1483.
$12,000

Quarto (190 x 155 mm). Collation: a-f8 [1-68]. [48] leaves. First Edition. Text in one column, 32 lines. Type: 80G. Initials painted in red, and blue ink throughout. Simple vellum binding from a 15th century vellum leaf. Gothic script. . A very good copy, old repair to the first blank leaf, a few spots, pale stain at the lower blank corner of the first quires. It is not known where and by which press this edition was printed. ISTC gives Southern Germany and a date of c.1480-1490, GW tentatively suggests Oberrhein, 1483, and Proctor attributes it to Ludwig Von Renchen in Cologne.
The hexameters of each section of the summary form an acrostic of the letters of the alphabet. (alphabetarium) as to insure memorization in the proper sequence, the first word of each verse falls neatly into alphabetical order. [1,194 short mnemonic verses] It uses characteristic couplets (distiches) to express the main content of all chapters of the Old and New Testament. This introduction makes it possible to easily find every quote in the Bible.

A significant record of the essential role of memory in late-medieval piety, One of the earliest printed books on the ars memorativa or mnemotechnic was composed by the German Benedictine monk Petrus of Rosenhaym (Upper Bavaria), written between 1423 and 1426 for Cardinal Giulio Branda di Castiglione. Petrus of Rosenhaym composed numerous treatises, sermons, and verses: the Roseum memoriale is surely his most famous work, enjoying wide popularity during the fifteenth century and first half of the sixteenth century. The mnemotechnic method here employed is extremely complex: the hexameters of each section of the summary form an acrostic of the letters of the alphabet. in. A highly popular and broadly used manual, its copies could be found in almost every European church after the invention of the printing press it was printed in several different locations. This early medieval incunable has not been clearly dated| researchers attribute it to the Upper Rhine region sometime between 1480 and 1483. After studying at the University of Vienna, Petrus de Rosenhaym, along with his friend Nikolaus Seyringer, moved to Subiaco, where he entered the Benedectine order. In 1413, he was appointed prior to the cloister of Rocca di Mondragone near Capua. In 1416, he took part in the Council of Konstanz, and later he was prior in Melk (Lower Austria). After 1423, he was appointed ‘cursor biblicus’ and ‘magister studentium’.
Goff R336; BMC I 312; ; GW M32724; ISTC; ir00336000; Polain(B) 3128; IBE 4559; IGI 7668; IBP 4380; Sajó-Soltész 2676; Madsen 3549; Borm 2134; Hubay(Würzburg) 1704; AmBCat 199; Walsh 492; Oates 867; Pr 1517;; BSB P-362; Van der Haegen II,2:16,4?; Young 278;.
Copies in the United States of America: Brown, Harvard, Library of Congress, Huntington, The Newberry Library, Yale

^)^)^)^(^(^(^
^)^)^)^(^(^(^

14) 384J Raymundus de Sabunde -1436
Theologia naturalis, sive, Liber creaturarum : specialiter de homine et de natura eius inquantum homo, et de his que sunt ei necessaria ad cognoscendum seipsum [et] deum et omne debitu[m] ad quod homo tenetur et obligat[ur] tam deo quam p[ro]ximo.
Straßburg: Martin Flach, 21 January 1496. $17,000
Imp[re]ssus Argentine per Martinum Flach inibi co[n]ciuem anno incarnat[i]o[n]is d[omi]nice Millesimoq[ua]dringentesimononagesimosexto men[sis] v[er]o Ianuarij die vicesimop[ri]mo

Folio (280 x 200mm.) π6 a8 b-y6 z8 [et]6 [con]8 (the last leaf supplied from another copy, printed on recto only), The second leaf (π2) has a beautiful a green painted initial A [Amor] on a gold ground with pink and blue edges, extending into the margins with green-stemmed pink and gold flowers on opposite side. The first leaf of the text proper (a1) Has a large blue painted initial A on a gold ground with pink and green edges, large pink and purple flowers, strawberries thistles and a Tromp l’oeil of a Dead fly,( quite charming) fill uppermargin; 3-line initials in alternating red and blue, rubricated throughout. This is the first dated edition.
It is bound in Contemporary deerskin over wooden boards, covers panelled and tooled in blind with repeated small rosette tool, remains of paper labels on spine (lacking metal furniture and clasps, some wear and small areas of loss). This copy has some contemporary manuscript notes, including a two-line note on f. b2recto, and on f.a2verso is a marginal drawing of the scala naturae with the four gradus marked.
Provenance: Contemporary inscription of Johannes Pengl (Penngl) from Weißenburg in Bavaria, who was active in Eichstätt & Vienna, with a note of cost of binding on final paste down. Later notes and shelf-mark on front paste-down and loose sheet.
Colophon: Finit liber creatura[rum] seu nature siue nature siue de ho[m]i[n]e p[ro]pt[er] que[m] alie creature facte su[n]t ex cui[us] cognit[i]one illu[m]inat[ur] ho[mo] i[n] [co]gnit[i]o[n]e dei [et] creaturarum.
This text marks the dawn of a knowledge based on Scripture and REASON.
The Catholic Encyclopedia sees this as “It represents a phase of decadent Scholasticism, and is a defense of a point of view which is subversive of the fundamental principle of the Scholastic method. The Schoolmen of the thirteenth century, while holding that there can be no contradiction between theology and philosophy, maintain that the two sciences are distinct. Raymond breaks down the distinction by teaching a kind of theosophy, the doctrine, namely that, as man is a connecting link between the natural and the supernatural, it is possible by a study of human nature to arrive at a knowledge even of the most profound mysteries of Faith. The tendency of his thought is similar to that of the rationalistic theosophy of Raymond Lully….Moreover, in Spain scholastics, in combating Islam, borrowed the weapons of their erudite antagonists. Close internal resemblance indicates that Raimund de Sabunde was preceded in method and object by Raymund Lully.” CE

What is new and epoch-making is not the material but the method; not of circumscribing religion within the limits of reason, but, by logical collation, of elevating the same upon the basis of natural truth to a science accessible and convincing to all. He recognizes two sources of (1)knowledge, the book of nature and (2) the Bible. The first is universal and direct, the other serves partly to instruct man the better to understand nature, and partly to reveal new truths, not accessible to the natural understanding, but once revealed by God made apprehensible by natural reason. The book of nature, the contents of which are manifested through sense experience and self-consciousness, can no more be falsified than the Bible and may serve as an exhaustive source of knowledge; but through the fall of man it was rendered obscure, so that it became incapable of guiding to the real wisdom of salvation. However, the Bible as well as illumination from above, not in conflict with nature, enables one to reach the correct explanation and application of natural things and self. Hence, his book of nature as a human supplement to the divine Word is to be the basic knowledge of man, because it subtends the doctrines of Scripture with the immovable foundations of self-knowledge, and therefore plants the revealed truths upon the rational ground of universal human perception, internal and external.
The first part presents analytically the facts of nature in ascending scale to man, the

climax; the second, the harmonization of these with Christian doctrine and their fulfillment in the same. Nature in its. four stages of mere being, mere life, sensible consciousness, and self-consciousness, is crowned by man, who is not only the microcosm but the image of God. Nature points toward a supernatural creator possessing in himself in perfection all properties of the things created out of nothing (the cornerstone of natural theology ever after). Foremost is the ontological argument of Ansehn, followed by the physico-theological, psychological, and moral. He demonstrates the Trinity by analogy from rational grounds, and finally ascribes to man in view of his conscious elevation over things a spontaneous gratitude to God. Love is transformed into the object of its affection; and love to God brings man, and with him the universe estranged by sin, into harmony and unity with him. In this he betrays his mystical antecedents. Proceeding in the second part from this general postulation to its results for positive Christianity, he finds justified by reason all the historic facts of revealed religion, such as the person and works of Christ, as well as the infallibility of the Church and the Scriptures; and the necessity by rational proof of all the sacraments and practices of the Church and of the pope. It should be added that Raimund’s analysis of nature and self-knowledge is not thoroughgoing and his application is far from consistent. He does not transplant himself to the standpoint of the unbeliever, but rather executes an apology on the part of a consciousness already Christian, thus assuming conclusions in advance that should grow only out of his premises. Yet his is a long step from the barren speculation of scholasticism, and marks the dawn of a knowledge based on Scripture and reason.
In its day, and for a long time later, it was a celebrated text. The title translates ‘Natural Theology or the book of [living] creatures, in particular about man and his nature inso far as he is man, and about those things necessary for him to know both himself and God, and about every duty by which man is held and obligated both in respect of God and his neighbour.’ The scope is therefore pretty wide. The main point of Sebond’s work is that that faith can be taught, attained, understood by natural reason and not simply on the basis of blind faith and literal adherence to Scripture, although this last is given full weight as is the teaching of ‘sacrosancta romana ecclesia who is the mother of all faithful christians, mistress of grace and faith and rule of truth…’ (preface on a2ra). The work is divided into 330 ‘tituli’ or chapters beginning with the origins of natural theology and ending with the last judgement, the subjects treated at greatest length being ‘God’ and ‘Man’.
Theologia Naturalis, which circulated widely in manuscript and is known particularly in a manuscript in Toulouse (747) corrected after the author’s own copy, was first published in what is called the ‘third family’ in Deventer in 1484-85 (possibly through the offices of the Brothers of the Common Life; the Bodleian copy is from their house at Doesburg, Holland), and then Lyon ca. 1488 from the printer Balsarin. This Flach printing circulated widely (a copy was at Winchcomb abbey in Gloucestershire within a few years (now in Glasgow) and early in the 16the century Archbishop Warham (Abp. 1503-32 ) gave a copy to All Souls College, Oxford) and is the first dated edition. There were a number of later editions (including another Flach edition of 1501) right up into the 17th century. Indeed the well-known 17th-century philosopher Kenelm Digby ( 1603-1664) had a copy of this edition (now at Durham University Library at Bamburgh Castle). Part of the Theologia (Dialogos de la naturaleza delhombre) was translated into Spanish and printed in Madrid in 1610 and 1616, and a resumé by the Carthusian Petrus Dorlandus (Viola anime per modum dyalogi) was published in Cologne in 1499 (ISTC id00360000 ) and in Toulouse in 1500 I(ISTC id003610000).. The Theologia because of the importance it accorded human reason did not escape the notice of the holy Office and was placed on the Index in the middle of the 16th century. Montaigne indeed discovered this during his visit to Rome.
Goff R33.; BMC I, 154.; HC 14069*; GW M36911; Bod-inc R-018. ISTC ir00033000. Palau 283900
◊
◊ ◊
◊

15) 369J Publius Terentius Afer. 185-
Terentius Comico Carmine
Impressum in nobili Helvecior[um] urbe Arge[n]tina : Per Ioanne[m] Grüninger mira etium arte ac diligentia. 1503 $7,500

Folio A6 B8 C-Z6 AA6 Bb4 Cc6. There are numerous handwritten annotations in ink (marginal and interlinear, ff. IX-XIX). The binding of half-calf with corners of the XIXth, back with 4 sewing support with pieces of title of red and green leather, boards covered with stony marbled paper. { A typical Kloss binding} (there is a tear sig. B1, with loss; first signature cut shorter at the lower margin; restorations of paper with the last sheets in the upper margin; Yet this copy remains a beautiful illustrated edition of the comedies of Terence with comments by Aelius Donatus and Calphurnius. From the presses of the famous and prolific Strasbourg printer-publisher Johann Reinhard, known as Grüninger, it is remarkably illustrated with 7 large full-page woods (including the famous representation of a theater on the title),

woodcuts depicting the dramatis personae in a land- or cityscape, one at the beginning of each play, and 142 woods in the text 19 of the cuts appear here for the first time; the others are from the 1496 ed. «Grüninger’s illustrations, intended to clarify the complexities of Terence’s plots for the reader, act as visual mnemonic devices for the book’s anticipated student audience. This is demonstrated especially in the full-page woodcut that begins each play, where all of the characters are displayed with connecting lines to indicate their interrelationships. covered with stony marbled paper. { A typical Kloss binding} (there is a tear sig. B1, with loss; first signature cut shorter at the lower margin; restorations of paper with the last sheets in the upper margin; Yet this copy remains a beautiful illustrated edition of the comedies of Terence with comments by Aelius Donatus and Calphurnius. From the presses of the famous and prolific Strasbourg printer-publisher Johann Reinhard, known as Grüninger, it is remarkably illustrated with 7 large full-page woods (including the famous representation of a theater on the title), woodcuts depicting the dramatis personae in a land- or cityscape, one at the beginning of each play, and 142 woods in the text 19 of the cuts appear here for the first time; the others are from the 1496 ed.

«Grüninger’s illustrations, intended to clarify the complexities of Terence’s plots for the reader, act as visual mnemonic devices for the book’s anticipated student audience. This is demonstrated especially in the full-page woodcut that begins each play, where all of the characters are displayed with connecting lines to indicate their interrelationships. A verbal explanation and plot summary accompanies each of these illustrations. The most remarkable feature of Grüninger’s Terence is his use of small interchangeable woodcuts that were combined to create the individual scene illustrations for each play. Individual blocks were cut for most of the characters of the six plays, who are identified by name in overhead banners. The blocks were cleverly combined repeatedly in groups of two to five, sometimes together with cuts of trees and buildings, to create the illustrations. Grüninger was attempting to use the woodcuts as repeatable and combinable objects, much in the same manner as movable type» (Christine Ruggere, in Vision of a Collector: The Lessing J. Rosenwald Collection in the Library of Congress)

Terence writes in a simple conversational Latin, pleasant and direct. Due to his clear and entertaining language, Terence’s works were heavily used by monasteries and convents during the Middle Ages and The Renaissance. Scribes often learned Latin through the meticulous copying of Terence’s texts. Priests and nuns often learned to speak Latin through reenactment of Terence’s plays, thereby learning both Latin and Gregorian chants. Although Terence’s plays often dealt with pagan material, the quality of his language promoted the copying and preserving of his text by the church. The preservation of Terence through the church enabled his work to influence much of later Western drama. [Holloway, Julia Bolton (1993). Sweet New Style: Brunetto Latino, Dante Alighieri, Geoffrey Chaucer, Essays, 1981-2005.]
This copy has the book plate and a binding typical for Kloss. It is NOT Melanchthon’s copy, or his notes!

Georg Franz Burkhard Kloss (31 July 1787 Frankfurt am Main – 10 February 1854 Frankfurt). Kloss was the son of a physician and studied medicine at Heidelberg and Göttingen, where he became one of the cofounders of the Corps Hannovera Göttingen. He practiced medicine in Frankfurt. He became a book collector, and gathered a fine collection of old manuscripts,. On February 21, 1838, New York book auction house Cooley & Bangs began a three day sale during which they offered more than 313 incunabula distributed among 1,302 lots. Many incunables came from the collection of George Kloss and had appeared in the London sale of his books three years before. It is entirely possible that the 1838 sale was the first time in America that so many incunables were offered all at once in a single auction..
The bulk of the Kloss books were sold by Sotheby in 1835. Most of the books containing notes were attributed as owned and annotated by Melanchthon .
Catalogue of the library of Dr. Kloss of Franckfort a. M. including many original and unpublished manuscripts, and printed books with ms. annotations, by Philip Melancthon …Which will be sold by auction, by Mr. Sotheby and son … May 7th, and nineteen following days (Sundays excepted) .
https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=hvd.32044055066971&view=1up&seq=9
Adams D 304. Proctor 9889. Ritter 2284.



Fascicule XXI. Media Plaga 3-4/2020 Only a day or two ago I was notified that I was in contact with some people tested for and found positive for Covid-19, this came as nothing un expected, I was in contact with hundreds of people many from Europe recently.
#early printed books#fascicule XXI#George Kloss#illustrated incunabulum#Incunabula#Irish authors#irish/gaelic printing#Kircher#Not in Goff#rare book catalogue
9 notes
·
View notes