#transparent data encryption
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Data Transparency: How to Build Data Trust in an Organization

Organizations today are exploring ways to adapt to these ongoing changes by incorporating a culture of transparency that will help them position themselves to grow further in this evolving landscape. Read More: https://www.sganalytics.com/blog/data-trust-how-to-build-data-trust/
#Data Trust#Data Transparency#Future of Data Transparency#what is data transparency#transparent data encryption#why is data transparency important?
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Building Data Trust: Unveiling the Path to a Transparent Data Future
In the age of data-driven decision-making, data has become the lifeblood of businesses and institutions. However, the critical need for Data Trust and Transparency comes with the increasing reliance on data. Our blog explores the significance of Data Transparency and its future for the data landscape. Delve into the realm of transparent data encryption and gain valuable insights into why Data Transparency is of utmost importance in fostering trust, accountability, and ethical data practices. Join us as we unravel the critical aspects of building Data Trust and shaping a more transparent and secure data-driven world.
#Data#Data Trust#Data Transparency#Future of Data Transparency#what is data transparency#transparent data encryption#why is data transparency important?
0 notes
Text
Choosing the Right VPN Service: Key Features and Considerations
In an era where online privacy and security are paramount, selecting the right VPN (Virtual Private Network) service is crucial. With countless options available, it’s essential to understand what features to look for and what makes a VPN service reliable and effective. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to choose a VPN service and the key elements a good VPN should offer. Security…

View On WordPress
#A#Access#Affordable Pricing Plans#Anonymity#Anonymous Browsing#Anonymous Internet Browsing Experience#Anonymous Web Browsing#Compatibility#Competitive and Transparent Pricing#Comprehensive Privacy Protection Features#Cross-Platform Compatibility#Customer Support#Data Protection#Encryption#Extensive Global Server Network#Global Server Network#High Speed#High-Speed Connection Options#High-Speed Connections#Internet Security#Intuitive User-Friendly Interface#Multi-Device Compatibility#No-Logs Policy#Privacy#Privacy and Security#Privacy Policy#reliability#Reliable Customer Support#Reliable Service#Responsive Customer Support Services
0 notes
Note
Hi! You’re in the LA area, right? I hope you and your family are okay.
Unrelatedly, I ran across a thread on Mastodon about Proton Mail, which I think you’ve talked about before, and was curious what you make of it / how credible it is: https://code4lib.social/@[email protected]/113838748729664639
I'm fine thanks! Worried about some friends but I'm good.
I think that thread is not incorrect, but is also bullshit.
Email protocols do not allow for 100% anonymous communication and never will, when Proton was subpoenaed for user data that ended up with some French climate activists getting prosecuted they were transparent about what was requested and updated their logging rules to store less data. *Starting* from the assumption that protonmail is supposed to be totally secure OR sells itself as totally secure is disingenuous.
The great thing about open source software is that you never have to trust a shithead CEO when they talk about what the software does. I get why people are angry at the CEO (I think the CEO is at least half wrong in that he is claiming that Republicans will challenge monopolies, but he's not wrong about the destructive corporatism of the Democratic party even if he is *in essence* wrong about which party is more likely to gesture in the direction of breaking up tech monopolies) but A) the thread says that proton's software is "opaque" and it just. Literally is not. and B) that thread links to another thread talking about how what proton is selling is trust and nope. They don't have to sell trust; you can see what their software does if you choose to investigate it, there's no need for trust when you can verify. What they're selling is transparency and from where i'm standing they are indeed quite transparent.
God. Imagine thinking that a zero trust service is selling trust.
So I think the argument that "protonmail actually isn't as secure as it claims" is bullshit that people bring up whenever they're mad at the company (whether they have legitimate reasons to be mad at the company or not).
For the record: you should never, ever, EVER treat email as a secret. Nothing you do over email is really secret because *the rules that allow email to function as a service* require at least some very sensitive information to be an open part of the protocol.
The Proton page on end to end encryption is *very* clear that it is the contents of your email messages that are encrypted, not your email as a whole, and in the image they use to illustrate this the parts of your email that *cannot* be made private (sender, recipient, subject line, time sent) are shown unencrypted:

They're not subtle about letting people know this. Nor are they quiet about the fact that replies to encrypted emails are not encrypted by default.
So the thread is *technically* correct in that all the security "holes" described reflect reality, but it's correct like saying "McDonald's says that you can eat their food for every meal and you'll put on ten pounds of muscle but ACTUALLY putting on ten pounds of muscle requires a huge amount of dedication and a very careful diet and a lot of resistance exercise" - like, I guess yeah that's what you have to do to put on ten pounds of muscle but where exactly was McDonald's making that claim? Did they actually make that claim or are general statements like "I'm Lovin' It" being misinterpreted in bad faith by people on the internet who are mad at something a CEO did?
So. Like. Yeah the CEO is being a shithead, the social media team made a pretty bad fuckup by doubling down on his shitheadery, the product still works as described, AND the thread discussing all of that is deeply annoying.
So.
I think this thread actually does a great job of explaining why I've never seen a "hackers for social justice" group that has lasted. This reminds me a LOT of when someone tried to say that you shouldn't use firefox because the former CEO was a homophobe. There are a lot of deeply shitty people who have made important contributions to our tech ecosystem and if we threw the baby out with the bathwater every time Notch from Minecraft ended up being Notch from minecraft you'd lock yourself out of a lot of really important tools. And this isn't the same as "buying harry potter merch funds transphobia" because it literally doesn't; especially with open source tools you can continue using the software and cheerfully hate the CEO because A) fuck that guy and B) what the fuck are you going to do about it, guy, this shit's encrypted.
I don't want to get too deeply into a discussion about what is or is not cancel culture, but what I'm seeing in that thread (and what I see coming up every time someone brings up the "But the French Climate Activists!" thing) is an attempt to prioritize political alignment over real-world utility. It's attempting to cancel a *genuinely useful tool* because someone involved in the development is an asshole.
By all means, don't give protonmail money if the CEO's trump-positive comments make you feel unsafe.
However: What service are you going to use that is as accessible and as secure to ensure that you actually *are* safe? There are alternatives out there. Do they actually do more than proton? Are they easier to use? Are they open source? One of the responses to that thread was "yeah, that dude seems shitty; i'd switch to another service if there was another one that I felt was as secure" and that's pretty much what I think the correct attitude is. (If you really, really still want to switch, Tuta has been the broadly recommended alternative to protonmail for years but at this point Proton has a suite of services that some users would need to replace, not just email)
IDK i think shit like this contributes to a lot of the bad kind of security nihilism where people are like "oh no, things will never be secure and even my scrappy little open source product is headed by an asshole, i may as well use google because everything sucks" when they should have the good kind of nihilism which is like "man, there are a lot of assholes out there and they're never going to stop being assholes; i'd better take proactive steps to act like the people who make tech stuff are assholes and operate from a better base of security at the start"
so the takeaways are:
Proton never claimed that anything but the message contents of your e2e encrypted messages are encrypted; as far as these things go, they do a pretty good job of being both secure and easy to use compared to other offerings.
Yeah the CEO is being kind of a shithead and I'm not a huge fan of that.
If you think the CEO is being a shithead and don't want to give the company your money, don't pay for their services, but the CEO being a shithead doesn't actually mean you can't trust their services; their services are literally built on zero trust, if the CEO literally wanted to hunt you down personally he wouldn't be any more able to decrypt your emails than he was before and he wouldn't be any more likely to respond to a subpoena than he was before (proton does respond to subpoenas when required but not otherwise; they've been compelled to produce more data in the last decade than before because law enforcement finally realized who they needed to yell at - one of the bigger issues here is the Swiss courts being more willing to grant subpoenas to international complainants than they were before)
The reason we don't go see hogwarts movies is because doing so gives JK money and that does actual real world harm; using firefox does not have an impact on Brendan Eich's ability to materially change the world. It is very weird that we're in a place where we're treating *open source encryption software that is simple enough for your grandma to use it* as though it is Orson Scott Card.
Sorry i'm still stuck on people thinking that proton, famously open source, is opaque, and that an encryption service with zero trust architecture is selling trust.
Anyway if you've ever got questions about security/privacy/whatever services privacyguides.org is a very reliable source.
OH I FIGURED OUT WHAT WAS BUGGING ME
There are a bunch of people discussing this talking about how the CEO's social media is what has made them feel unsafe and I'm going to be a dick here and say that facts don't care about your feelings.
The CEO saying stupid shit doesn't actually make you unsafe in a situation like this; if the CEO was a violent transphobe or aggressive racist or horribly misogynist that wouldn't actually make any of the users of the product less safe. That's why the SJ hacker stuff I've seen hasn't had much staying power; I think that groups that focus on making people feel included and welcome and safe to be themself within the group run into really big problems when there's a conflict between people in the group FEELING unsafe because of (genuinely important in many ways) cultural signifiers like political alignment and so in order to accommodate that feeling they end up doing things (like some kinds of collaboration/accountability practices, abandoning useful tools, WAY too much personal transparency and radical vulnerability for people who are doing crime shit) that ACTUALLY make them less safe.
The CEO being a shithead may make you feel bad, but moving to a less secure platform may actually be dangerous. One of these things can have a big impact on your life, and it is not the one that is happening on twitter.
Anyway. Email is inherently insecure and if you want a secure messaging tool use Signal.
If you are doing crime shit don't talk about it on the internet and DEFINITELY don't talk about it in any kind of unencrypted platform.
If you are a French climate activist who would like to not get arrested if Tuta gets a subpoena for data, use the email service in concert with tor and be cautious about senders/receivers and subject lines.
244 notes
·
View notes
Text
Chat Control in a nutshell (please reblog this, US people)










Find out more about Chat Control here TAKE ACTION HERE ! OR HERE Calling is much more efficient ! The latter link will redirect you to the official websites of your respective reps. Under the "read more", you will find what you need to say/write when contacting your reps. You will also find an alternate format of this comic,and I give explicit permission for people to translate it and spread it anywhere for awareness. Credit really not needed, I don't care about that rn Even if this is a EU proposal, I am urging Americans to also share this, since it goes hand in hand with KOSA. DON'T FORGET TO JOIN OUR DISCORD SERVER AGAINST CHAT CONTROL ! https://discord.com/invite/e7FYdYnMkS

(Latest update on Chat Control was the 12 september 2024) This is a little long, so feel free to shorten it as you wish : Subject line: "2022/0155(COD) Dear Sir/Madam, I am writing to express my grave concerns regarding the proposed introduction of "Chat Control" This measure poses a serious threat to the privacy and fundamental rights of all EU citizens and stands in stark contradiction to the core principles that the European Union seeks to uphold. The proposed Chat Control contravenes Articles 7 and 8 of the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union, which guarantee the right to respect for private and family life and the protection of personal data. The indiscriminate surveillance of private messages without specific suspicion or cause directly violates these fundamental rights. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets out stringent rules for the processing of personal data. The proposed indiscriminate surveillance and scanning of private messages before end-to-end encryption is fundamentally incompatible with the principles of data minimization and purpose limitation enshrined in the GDPR. Specifically, Articles 5 and 6 of the GDPR, which govern the lawfulness and principles of data processing, would be violated by the introduction of such measures. The implementation of Client-Side Scanning (CSS) on devices means that all messages and files are scanned on the user's device before being encrypted and sent. This effectively nullifies the protection offered by end-to-end encryption and opens the door to misuse and additional security vulnerabilities. Moreover, the technical capability to scan such content could be exploited by malicious actors to circumvent or manipulate surveillance mechanisms. Such far-reaching surveillance measures not only endanger privacy but also freedom of expression. The knowledge that their private messages are being scanned and monitored could significantly restrict individuals' willingness to freely express themselves. Additionally, trust in digital communication platforms would be severely undermined. I urge you to take a strong stance against this disproportionate and unlawful measure. The privacy and digital rights of EU citizens must be safeguarded. It is imperative that we protect our fundamental rights and ensure transparency in the decision-making processes of our leaders. For more detailed information on the proposal and its implications, please refer to the following resource: Link to Netzpolitik article. https://www.patrick-breyer.de/rat-soll-chatkontrolle-durchwinken-werde-jetzt-aktiv/ Thank you for your attention to this critical matter. Sincerely, [Name] Art. 10 GG , Art. 8 & 11 EU Charta , Art. 8 EMRK (Alternate comic here V)
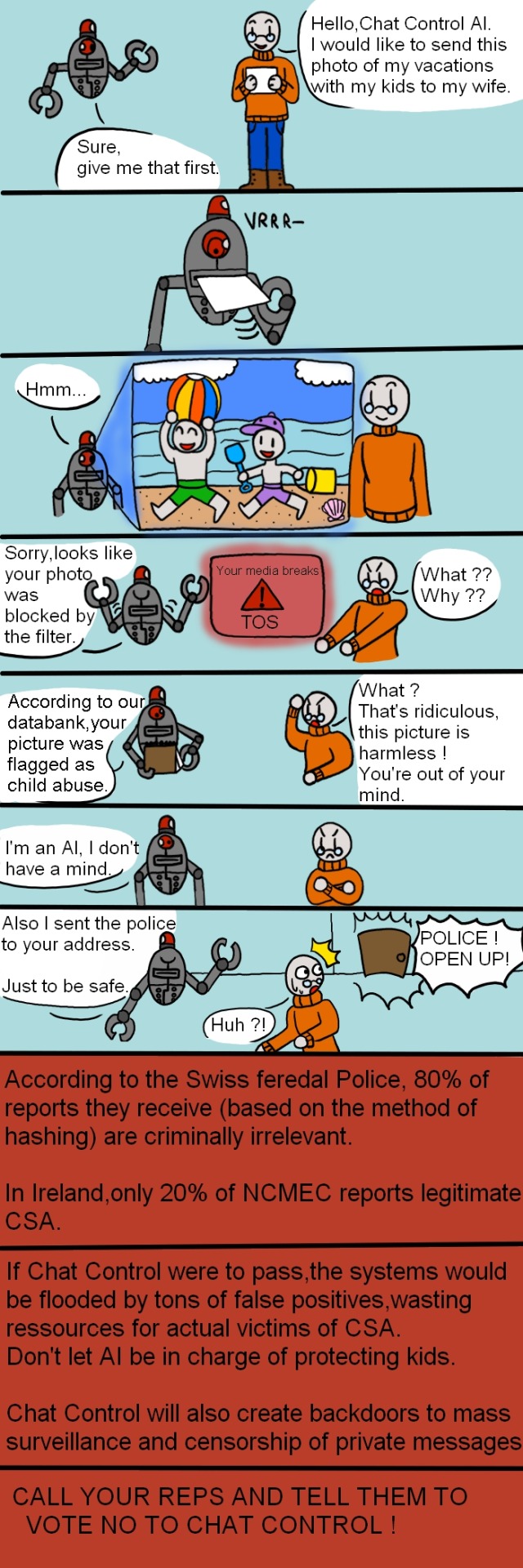
286 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Role of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management: Enhancing Transparency and Efficiency

Blockchain technology, best known for powering cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, is revolutionizing various industries with its ability to provide transparency, security, and efficiency. One of the most promising applications of blockchain is in supply chain management, where it offers solutions to longstanding challenges such as fraud, inefficiencies, and lack of visibility. This article explores how blockchain is transforming supply chains, its benefits, key use cases, and notable projects, including a mention of Sexy Meme Coin.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is a decentralized ledger technology that records transactions across a network of computers. Each transaction is added to a block, which is then linked to the previous block, forming a chain. This structure ensures that the data is secure, immutable, and transparent, as all participants in the network can view and verify the recorded transactions.
Key Benefits of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
Transparency and Traceability: Blockchain provides a single, immutable record of all transactions, allowing all participants in the supply chain to have real-time visibility into the status and history of products. This transparency enhances trust and accountability among stakeholders.
Enhanced Security: The decentralized and cryptographic nature of blockchain makes it highly secure. Each transaction is encrypted and linked to the previous one, making it nearly impossible to alter or tamper with the data. This reduces the risk of fraud and counterfeiting in the supply chain.
Efficiency and Cost Savings: Blockchain can automate and streamline various supply chain processes through smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This automation reduces the need for intermediaries, minimizes paperwork, and speeds up transactions, leading to significant cost savings.
Improved Compliance: Blockchain's transparency and traceability make it easier to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Companies can provide verifiable records of their supply chain activities, demonstrating adherence to industry standards and regulations.
Key Use Cases of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
Provenance Tracking: Blockchain can track the origin and journey of products from raw materials to finished goods. This is particularly valuable for industries like food and pharmaceuticals, where provenance tracking ensures the authenticity and safety of products. For example, consumers can scan a QR code on a product to access detailed information about its origin, journey, and handling.
Counterfeit Prevention: Blockchain's immutable records help prevent counterfeiting by providing a verifiable history of products. Luxury goods, electronics, and pharmaceuticals can be tracked on the blockchain to ensure they are genuine and have not been tampered with.
Supplier Verification: Companies can use blockchain to verify the credentials and performance of their suppliers. By maintaining a transparent and immutable record of supplier activities, businesses can ensure they are working with reputable and compliant partners.
Streamlined Payments and Contracts: Smart contracts on the blockchain can automate payments and contract executions, reducing delays and errors. For instance, payments can be automatically released when goods are delivered and verified, ensuring timely and accurate transactions.
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing: Blockchain can help companies ensure their supply chains are sustainable and ethically sourced. By providing transparency into the sourcing and production processes, businesses can verify that their products meet environmental and social standards.
Notable Blockchain Supply Chain Projects
IBM Food Trust: IBM Food Trust uses blockchain to enhance transparency and traceability in the food supply chain. The platform allows participants to share and access information about the origin, processing, and distribution of food products, improving food safety and reducing waste.
VeChain: VeChain is a blockchain platform that focuses on supply chain logistics. It provides tools for tracking products and verifying their authenticity, helping businesses combat counterfeiting and improve operational efficiency.
TradeLens: TradeLens, developed by IBM and Maersk, is a blockchain-based platform for global trade. It digitizes the supply chain process, enabling real-time tracking of shipments and reducing the complexity of cross-border transactions.
Everledger: Everledger uses blockchain to track the provenance of high-value assets such as diamonds, wine, and art. By creating a digital record of an asset's history, Everledger helps prevent fraud and ensures the authenticity of products.
Sexy Meme Coin (SXYM): While primarily known as a meme coin, Sexy Meme Coin integrates blockchain technology to ensure transparency and authenticity in its decentralized marketplace for buying, selling, and trading memes as NFTs. Learn more about Sexy Meme Coin at Sexy Meme Coin.
Challenges of Implementing Blockchain in Supply Chains
Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating blockchain with legacy supply chain systems can be complex and costly. Companies need to ensure that blockchain solutions are compatible with their existing infrastructure.
Scalability: Blockchain networks can face scalability issues, especially when handling large volumes of transactions. Developing scalable blockchain solutions that can support global supply chains is crucial for widespread adoption.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations: Blockchain's decentralized nature poses challenges for regulatory compliance. Companies must navigate complex legal landscapes to ensure their blockchain implementations adhere to local and international regulations.
Data Privacy: While blockchain provides transparency, it also raises concerns about data privacy. Companies need to balance the benefits of transparency with the need to protect sensitive information.
The Future of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
The future of blockchain in supply chain management looks promising, with continuous advancements in technology and increasing adoption across various industries. As blockchain solutions become more scalable and interoperable, their impact on supply chains will grow, enhancing transparency, efficiency, and security.
Collaboration between technology providers, industry stakeholders, and regulators will be crucial for overcoming challenges and realizing the full potential of blockchain in supply chain management. By leveraging blockchain, companies can build more resilient and trustworthy supply chains, ultimately delivering better products and services to consumers.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is transforming supply chain management by providing unprecedented levels of transparency, security, and efficiency. From provenance tracking and counterfeit prevention to streamlined payments and ethical sourcing, blockchain offers innovative solutions to long-standing supply chain challenges. Notable projects like IBM Food Trust, VeChain, TradeLens, and Everledger are leading the way in this digital revolution, showcasing the diverse applications of blockchain in supply chains.
For those interested in exploring the playful and innovative side of blockchain, Sexy Meme Coin offers a unique and entertaining platform. Visit Sexy Meme Coin to learn more and join the community.
#crypto#blockchain#defi#digitalcurrency#ethereum#digitalassets#sexy meme coin#binance#cryptocurrencies#blockchaintechnology#bitcoin#etf
284 notes
·
View notes
Text
Updated Personal Infosec Post
Been awhile since I've had one of these posts part deus: but I figure with all that's going on in the world it's time to make another one and get some stuff out there for people. A lot of the information I'm going to go over you can find here:
https://www.privacyguides.org/en/tools/
So if you'd like to just click the link and ignore the rest of the post that's fine, I strongly recommend checking out the Privacy Guides. Browsers: There's a number to go with but for this post going forward I'm going to recommend Firefox. I know that the Privacy Guides lists Brave and Safari as possible options but Brave is Chrome based now and Safari has ties to Apple. Mullvad is also an option but that's for your more experienced users so I'll leave that up to them to work out. Browser Extensions:
uBlock Origin: content blocker that blocks ads, trackers, and fingerprinting scripts. Notable for being the only ad blocker that still works on Youtube.
Privacy Badger: Content blocker that specifically blocks trackers and fingerprinting scripts. This one will catch things that uBlock doesn't catch but does not work for ads.
Facebook Container: "but I don't have facebook" you might say. Doesn't matter, Meta/Facebook still has trackers out there in EVERYTHING and this containerizes them off away from everything else.
Bitwarden: Password vaulting software, don't trust the password saving features of your browsers, this has multiple layers of security to prevent your passwords from being stolen.
ClearURLs: Allows you to copy and paste URL's without any trackers attached to them.
VPN: Note: VPN software doesn't make you anonymous, no matter what your favorite youtuber tells you, but it does make it harder for your data to be tracked and it makes it less open for whatever public network you're presently connected to.
Mozilla VPN: If you get the annual subscription it's ~$60/year and it comes with an extension that you can install into Firefox.
Mullvad VPN: Is a fast and inexpensive VPN with a serious focus on transparency and security. They have been in operation since 2009. Mullvad is based in Sweden and offers a 30-day money-back guarantee for payment methods that allow it.
Email Provider: Note: By now you've probably realized that Gmail, Outlook, and basically all of the major "free" e-mail service providers are scraping your e-mail data to use for ad data. There are more secure services that can get you away from that but if you'd like the same storage levels you have on Gmail/Ol utlook.com you'll need to pay.
Tuta: Secure, end-to-end encrypted, been around a very long time, and offers a free option up to 1gb.
Mailbox.org: Is an email service with a focus on being secure, ad-free, and privately powered by 100% eco-friendly energy. They have been in operation since 2014. Mailbox.org is based in Berlin, Germany. Accounts start with up to 2GB storage, which can be upgraded as needed.
Email Client:
Thunderbird: a free, open-source, cross-platform email, newsgroup, news feed, and chat (XMPP, IRC, Matrix) client developed by the Thunderbird community, and previously by the Mozilla Foundation.
FairMail (Android Only): minimal, open-source email app which uses open standards (IMAP, SMTP, OpenPGP), has several out of the box privacy features, and minimizes data and battery usage.
Cloud Storage:
Tresorit: Encrypted cloud storage owned by the national postal service of Switzerland. Received MULTIPLE awards for their security stats.
Peergos: decentralized and open-source, allows for you to set up your own cloud storage, but will require a certain level of expertise.
Microsoft Office Replacements:
LibreOffice: free and open-source, updates regularly, and has the majority of the same functions as base level Microsoft Office.
OnlyOffice: cloud-based, free
FreeOffice: Personal licenses are free, probably the closest to a fully office suite replacement.
Chat Clients: Note: As you've heard SMS and even WhatsApp and some other popular chat clients are basically open season right now. These are a couple of options to replace those. Note2: Signal has had some reports of security flaws, the service it was built on was originally built for the US Government, and it is based within the CONUS thus is susceptible to US subpoenas. Take that as you will.
Signal: Provides IM and calling securely and encrypted, has multiple layers of data hardening to prevent intrusion and exfil of data.
Molly (Android OS only): Alternative client to Signal. Routes communications through the TOR Network.
Briar: Encrypted IM client that connects to other clients through the TOR Network, can also chat via wifi or bluetooth.
SimpleX: Truly anonymous account creation, fully encrypted end to end, available for Android and iOS.
Now for the last bit, I know that the majority of people are on Windows or macOS, but if you can get on Linux I would strongly recommend it. pop_OS, Ubuntu, and Mint are super easy distros to use and install. They all have very easy to follow instructions on how to install them on your PC and if you'd like to just test them out all you need is a thumb drive to boot off of to run in demo mode. For more secure distributions for the more advanced users the options are: Whonix, Tails (Live USB only), and Qubes OS.
On a personal note I use Arch Linux, but I WOULD NOT recommend this be anyone's first distro as it requires at least a base level understanding of Linux and liberal use of the Arch Linux Wiki. If you game through Steam their Proton emulator in compatibility mode works wonders, I'm presently playing a major studio game that released in 2024 with no Linux support on it and once I got my drivers installed it's looked great. There are some learning curves to get around, but the benefit of the Linux community is that there's always people out there willing to help. I hope some of this information helps you and look out for yourself, it's starting to look scarier than normal out there.

#infosec#personal information#personal infosec#info sec#firefox#mullvad#vpn#vpn service#linux#linux tails#pop_os#ubuntu#linux mint#long post#whonix#qubes os#arch linux
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
The messaging app used by at least one top Trump administration official has suspended its services following reports of hackers stealing data from the app. Smarsh, TeleMessage’s parent company, says it is now investigating the incident.
“TeleMessage is investigating a potential security incident. Upon detection, we acted quickly to contain it and engaged an external cybersecurity firm to support our investigation,” a Smarsh spokesperson told WIRED in a statement. “Out of an abundance of caution, all TeleMessage services have been temporarily suspended. All other Smarsh products and services remain fully operational.”
President Donald Trump's now-former national security adviser Mike Waltz was captured by a Reuters photographer last week using an unauthorized version of the secure communication app Signal—known as TeleMessage Signal or TM Signal—which allows users to archive their communications. Photos of Waltz using the app appear to show that he was communicating with other high-ranking officials, including Vice President JD Vance, US Director of National Intelligence Tulsi Gabbard, and US Secretary of State Marco Rubio.
Experts told WIRED on Friday that, by definition, TM Signal's archiving feature undermined the end-to-end encryption that makes the actual Signal communication app secure and private. 404 Media and independent journalist Micah Lee reported on Sunday that the app had been breached by a hacker. NBC News reported on Monday that it had reviewed evidence of an additional breach.
TeleMessage was founded in Israel in 1999 and was acquired last year by the US-based digital communications archiving company Smarsh. TeleMessage makes apparently unauthorized versions of popular communications apps that include archiving features for institutional compliance. But the company claims that its look-alikes have the same digital defenses as their legitimate counterparts, potentially giving users a false sense of security.
Waltz's app usage came under intense scrutiny last month after he appeared to have added the editor in chief of The Atlantic to a Signal group chat in which Trump administration officials discussed plans for a military operation. Dubbed SignalGate, the scandal ultimately preceded Waltz's ouster as national security adviser. President Trump said last week that he plans to nominate him to be ambassador to the United Nations.
TeleMessage apps are not approved for use under the US government's Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program, or FedRAMP, and yet they seem to be proliferating. Leaked data reportedly from TM Signal indicates that multiple US Customs and Border Protection agents may be using the Signal look-alike. When asked about the breach and whether CBP officers use TM Signal, the agency told WIRED, “We're looking into this.”
After a number of reports by Lee and 404 Media over the weekend, TeleMessage removed all content from its website on Saturday and took down its archiving service on Sunday.
“We are committed to transparency and will share updates as we are able,” the Smarsh statement adds. “We thank our customers and partners for their trust and patience during this time.”
Since the revelation last week that Waltz appeared to be using TM Signal, experts have feared that information shared on the app could jeopardize US national security.
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is the Accountability Archive?
(I was gonna make this an addition to another post but OP turned off reblogs while I was halfway through my deep dive so I'm making my own)
With any activism (or something trying to pass itself off as activism), especially list-making like this site, the most important question to ask is "why". What is the purpose? What do they hope to accomplish? How will this data be used?


The answer is......eh? The list is being compiled so that possibly someday some future historian might maybe think about wanting to form a committee to explore the possibility of..."understanding how 'power holders' manufacture consent". These power holders are, of course, politicians, but also journalists?, and "public figures", which is an extremely vague term. Am I a public figure? I certainly make my opinions public. So when these future researchers want to understand the nature of the current conflict, they won't need to look at the history of the region, the contemporary local politics as well as the international stage, and the personalities of the specific people involved. They'll just check out this eyesore of a website to find proof that slyandthefamilybook supports genocide. And future lawyers will be able to use this incontrovertible evidence to...sorry, to prosecute war crimes?????? Sorry, I couldn't help but laugh at that one. Well if I am on there it shouldn't be too hard to check. Surely a site called the "Accountability Archive" believes in transparency

Oh. Well. I'm sure if you pass their screening process they'll respond promptly from their encrypted archive-less email and definitely give you access. But don't worry. They have a "vision" of one day making this public. When are we the people going to be able to see the info? I want the juicy deets on who is and isn't a Zionist!

So, sometime in the future. Maybe. Probably. Well what kind of info are they collecting anyway?

Alright, seems normal so far. I appreciate that when talking about targeting of civilian populations or infrastructure they've remained impartial. I submitted a page from the ADL cataloguing US professors who celebrated Hamas' pogrom on 10/7. I will let you know how or if they respond

One thing I've noticed is the distinctly European spelling of some words like "dehumanisation" and "analyse". So who are these people even? They must have pictures, or names, or evidence of their bona fides. They claim to be "middle east experts" [sic] so surely they'll link articles they've written, or talk about degrees or accolades they've received. Something, anything to let us know that they're real serious people who know what they're talking about

Well that's......I mean that's not even an answer. You don't answer the question of "who are we" with "this is the purpose of our website". They have a Twitter, which despite being made in October 2023 (huh. weird) only made its first post in February 2024
The site itself went live on November 22, 2023, but according to Google was only certified as of 9 days ago


I'm not going to try to dig into who potentially runs the account. I don't want to doxx anyone. But this should give you an overview of what this site is and why you definitely shouldn't use it
95 notes
·
View notes
Text
"In the age of smart fridges, connected egg crates, and casino fish tanks doubling as entry points for hackers, it shouldn’t come as a surprise that sex toys have joined the Internet of Things (IoT) party.
But not all parties are fun, and this one comes with a hefty dose of risk: data breaches, psychological harm, and even physical danger.
Let’s dig into why your Bluetooth-enabled intimacy gadget might be your most vulnerable possession — and not in the way you think.
The lure of remote-controlled intimacy gadgets isn’t hard to understand. Whether you’re in a long-distance relationship or just like the convenience, these devices have taken the market by storm.
According to a 2023 study commissioned by the U.K.’s Department for Science, Innovation, and Technology (DSIT), these toys are some of the most vulnerable consumer IoT products.
And while a vibrating smart egg or a remotely controlled chastity belt might sound futuristic, the risks involved are decidedly dystopian.
Forbes’ Davey Winder flagged the issue four years ago when hackers locked users into a chastity device, demanding a ransom to unlock it.
Fast forward to now, and the warnings are louder than ever. Researchers led by Dr. Mark Cote found multiple vulnerabilities in these devices, primarily those relying on Bluetooth connectivity.
Alarmingly, many of these connections lack encryption, leaving the door wide open for malicious third parties.
If you’re picturing some low-stakes prank involving vibrating gadgets going haywire, think again. The risks are far graver.
According to the DSIT report, hackers could potentially inflict physical harm by overheating a device or locking it indefinitely. Meanwhile, the psychological harm could stem from sensitive data — yes, that kind of data — being exposed or exploited.
A TechCrunch exposé revealed that a security researcher breached a chastity device’s database containing over 10,000 users’ information. That was back in June, and the manufacturer still hasn’t addressed the issue.
In another incident, users of the CellMate connected chastity belt reported hackers demanding $750 in bitcoin to unlock devices. Fortunately, one man who spoke to Vice hadn’t been wearing his when the attack happened. Small mercies, right?
These aren’t isolated events. Standard Innovation Corp., the maker of the We-Vibe toy, settled for $3.75 million in 2017 after it was discovered the device was collecting intimate data without user consent.
A sex toy with a camera was hacked the same year, granting outsiders access to its live feed.
And let’s not forget: IoT toys are multiplying faster than anyone can track, with websites like Internet of Dongs monitoring the surge.
If the thought of a connected chastity belt being hacked makes you uneasy, consider this: sex toys are just a small piece of the IoT puzzle.
There are an estimated 17 billion connected devices worldwide, ranging from light bulbs to fitness trackers — and, oddly, smart egg crates.
Yet, as Microsoft’s 2022 Digital Defense Report points out, IoT security is lagging far behind its software and hardware counterparts.
Hackers are opportunistic. If there’s a way in, they’ll find it. Case in point: a casino lost sensitive customer data after bad actors accessed its network through smart sensors in a fish tank.
If a fish tank isn’t safe, why would we expect a vibrating gadget to be?
Here’s where the frustration kicks in: these vulnerabilities are preventable.
The DSIT report notes that many devices rely on unencrypted Bluetooth connections or insecure APIs for remote control functionality.
Fixing these flaws is well within the reach of manufacturers, yet companies routinely fail to prioritize security.
Even basic transparency around data collection would be a step in the right direction. Users deserve to know what’s being collected, why, and how it’s protected. But history suggests the industry is reluctant to step up.
After all, if companies like Standard Innovation can get away with quietly siphoning off user data, why would smaller players bother to invest in robust security?
So, what’s a smart-toy enthusiast to do? First, ask yourself: do you really need your device to be connected to an app?
If the answer is no, then maybe it’s best to go old school. If remote connectivity is a must, take some precautions.
Keep software updated: Ensure both the device firmware and your phone’s app are running the latest versions. Updates often include critical security patches.
Use secure passwords: Avoid default settings and choose strong, unique passwords for apps controlling your devices.
Limit app permissions: Only grant the app the bare minimum of permissions needed for functionality.
Vet the manufacturer: Research whether the company has a history of addressing security flaws. If they’ve been caught slacking before, it’s a red flag.
The conversation around sex toy hacking isn’t just about awkward headlines — it’s about how we navigate a world increasingly dependent on connected technology. As devices creep further into every corner of our lives, from the bedroom to the kitchen, the stakes for privacy and security continue to rise.
And let’s face it: there’s something uniquely unsettling about hackers turning moments of intimacy into opportunities for exploitation.
If companies won’t take responsibility for protecting users, then consumers need to start asking tough questions — and maybe think twice before connecting their pleasure devices to the internet.
As for the manufacturers? The message is simple: step up or step aside.
No one wants to be the next headline in a tale of hacked chastity belts and hijacked intimacy. And if you think that’s funny, just wait until your light bulb sells your Wi-Fi password.
This is where IoT meets TMI. Stay connected, but stay safe."
https://thartribune.com/government-warns-couples-that-sex-toys-remain-a-tempting-target-for-hackers-with-the-potential-to-be-weaponized/
#iot#I only want non-smart devices#I don't want my toilet to connect to the internet#seriously#smart devices#ai#anti ai#enshittification#smart sex toys
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
On Sunday, June 15, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu made the explosive claim on Fox News’ Special Report with Bret Baier that Iran was behind the two assassination attempts on President Trump.
We beg to differ.
We, the American People, Invite the FBI & DOJ to Be Heroes of Transparency
Uncover the Explosive Ukrainian-Linked Patterns in the Trump Assassination Plots and Include the Butler Attempt by Thomas Matthew Crooks
Critical Data on Crooks’ Encrypted Communications Remains Hidden — Will the FBI & DOJ Step Up to Unveil Who Thomas Matthew Crooks Was Communicating With?
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is the Difference Between a Smart Contract and Blockchain?
In today's digital-first world, terms like blockchain and smart contract are often thrown around, especially in the context of cryptocurrency, decentralized finance (DeFi), and Web3. While these two concepts are closely related, they are not the same. If you’re confused about the difference between a smart contract and blockchain, you’re not alone. In this article, we’ll break down both terms, explain how they relate, and highlight their unique roles in the world of digital technology.
1. Understanding the Basics: Blockchain vs Smart Contract
Before diving into the differences, let’s clarify what each term means.
A blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that stores data across a network of computers.
A smart contract is a self-executing program that runs on a blockchain and automatically enforces the terms of an agreement.
To put it simply, blockchain is the infrastructure, while smart contracts are applications that run on top of it.
2. What is a Blockchain?
A blockchain is a chain of blocks where each block contains data, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash of the previous block. This structure makes the blockchain secure, transparent, and immutable.
The key features of blockchain include:
Decentralization – No single authority controls the network.
Transparency – Anyone can verify the data.
Security – Tampering with data is extremely difficult due to cryptographic encryption.
Consensus Mechanisms – Like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), which ensure agreement on the state of the network.
Blockchains are foundational technologies behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many others.
3. What is a Smart Contract?
A smart contract is a piece of code stored on a blockchain that automatically executes when certain predetermined conditions are met. Think of it as a digital vending machine: once you input the right conditions (like inserting a coin), you get the output (like a soda).
Smart contracts are:
Self-executing – They run automatically when conditions are met.
Immutable – Once deployed, they cannot be changed.
Transparent – Code is visible on the blockchain.
Trustless – They remove the need for intermediaries or third parties.
Smart contracts are most commonly used on platforms like Ethereum, Solana, and Cardano.

4. How Smart Contracts Operate on a Blockchain
Smart contracts are deployed on a blockchain, usually via a transaction. Once uploaded, they become part of the blockchain and can't be changed. Users interact with these contracts by sending transactions that trigger specific functions within the code.
For example, in a decentralized exchange (DEX), a smart contract might govern the process of swapping one cryptocurrency for another. The logic of that exchange—calculations, fees, security checks—is all written in the contract's code.
5. Real-World Applications of Blockchain
Blockchains are not limited to cryptocurrencies. Their properties make them ideal for various industries:
Finance – Fast, secure transactions without banks.
Supply Chain – Track goods transparently from origin to destination.
Healthcare – Secure and share patient data without compromising privacy.
Voting Systems – Transparent and tamper-proof elections.
Any situation that requires trust, security, and transparency can potentially benefit from blockchain technology.
6. Real-World Applications of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts shine when you need to automate and enforce agreements. Some notable use cases include:
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) – Lending, borrowing, and trading without banks.
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) – Automatically transferring ownership of digital art.
Gaming – In-game assets with real-world value.
Insurance – Auto-triggered payouts when conditions (like flight delays) are met.
Legal Agreements – Automatically executed contracts based on input conditions.
They’re essentially programmable agreements that remove the need for middlemen.
7. Do Smart Contracts Need Blockchain?
Yes. Smart contracts depend entirely on blockchain technology. Without a blockchain, there's no decentralized, secure, and immutable platform for the smart contract to run on. The blockchain guarantees trust, while the smart contract executes the logic.
8. Which Came First: Blockchain or Smart Contract?
Blockchain came first. The first blockchain, Bitcoin, was introduced in 2009 by the anonymous figure Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin’s blockchain didn’t support smart contracts in the way we know them today. It wasn’t until Ethereum launched in 2015 that smart contracts became programmable on a large scale.
Ethereum introduced the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), enabling developers to build decentralized applications using smart contracts written in Solidity.
9. Common Misconceptions
There are many misunderstandings around these technologies. Let’s clear a few up:
Misconception 1: Blockchain and smart contracts are the same.
Reality: They are separate components that work together.
Misconception 2: All blockchains support smart contracts.
Reality: Not all blockchains are smart contract-enabled. Bitcoin’s blockchain, for example, has limited scripting capabilities.
Misconception 3: Smart contracts are legally binding.
Reality: While they enforce logic, they may not hold legal standing in court unless specifically written to conform to legal standards.
10. Benefits of Using Blockchain and Smart Contracts Together
When used together, blockchain and smart contracts offer powerful advantages:
Security – Combined, they ensure secure automation of processes.
Efficiency – Remove delays caused by manual processing.
Cost Savings – Eliminate middlemen and reduce administrative overhead.
Trustless Interactions – Parties don't need to trust each other, only the code.
This combination is the backbone of decentralized applications (DApps) and the broader Web3 ecosystem.
11. Popular Platforms Supporting Smart Contracts
Several blockchain platforms support smart contracts, with varying degrees of complexity and performance:
Ethereum – The first and most widely used platform.
Solana – Known for speed and low fees.
Cardano – Emphasizes academic research and scalability.
Polkadot – Designed for interoperability.
Binance Smart Chain – Fast and cost-effective for DeFi apps.
Each platform has its own approach to security, scalability, and user experience.
12. The Future of Blockchain and Smart Contracts
The future looks incredibly promising. With the rise of AI, IoT, and 5G, the integration with blockchain and smart contracts could lead to fully automated systems that are transparent, efficient, and autonomous.
We may see:
Global trade systems are using smart contracts to automate customs and tariffs.
Self-driving cars using blockchain to negotiate road usage.
Smart cities are where infrastructure is governed by decentralized protocols.
These are not sci-fi ideas; they are already in development across various industries.
Conclusion: A Powerful Partnership
Understanding the difference between smart contracts and blockchain is essential in today's rapidly evolving digital world. While blockchain provides the secure, decentralized foundation, smart contracts bring it to life by enabling automation and trustless execution.
Think of blockchain as the stage, and smart contracts as the actors that perform on it. Separately, they're impressive. But together, they're revolutionary.
As technology continues to evolve, the synergy between blockchain and smart contracts will redefine industries, reshape economies, and unlock a new era of digital transformation.

#coin#crypto#digital currency#finance#invest#investment#bnbbro#smartcontracts#decentralization#decentralizedfinance#decentralizedapps#decentralizedfuture#cryptocurrency#btc#cryptotrading#usdt
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What are the unique challenges faced in developing iOS apps?
iOS App Development Services

iOS App Development is also known and considered for its sleek interface, strong security, and loyal user base and stand. However, building and crafting the apps for Apple devices isn't without its hurdles or obstacles. As the developers often face and seek unique challenges that differ and outlast from other platforms like Android. These challenges and obstacles can affect down the timelines, budgets, and overall user experience and matches if not managed carefully or sought in for.
Strict App Store Guidelines:
One of the most common challenges and occurrences in iOS App Development is meeting Apple's strict App Store policies and standard guidelines. As the review process is more rigorous and stiff sometimes than the most common platforms, apps can get rejected for minor issues—ranging from UI design to privacy violations. Developers must thoroughly review Apple's Human Interface Guidelines and follow best practices to avoid delays or rejections.
Limited Customization Options:
Apple has a highly controlled ecosystem. While this assures up the consistency and overall performance is maintained and is stuck with it, as it limits up the developers' ability to customize their user interfaces or access the set of certain hardware functionalities. This means more time and efficiency is intended to be spent finding creative workarounds to deliver unique features within the platform's constraints.
Device and OS Compatibility:
Though Apple has fewer devices than Android, iOS App Development must still account for different screen sizes, resolutions, and operating system versions. Supporting older iOS versions can be tricky, as Apple users adopt new versions quickly, but some still rely on older devices.
Frequent OS Updates:
Apple regularly updates iOS, which can introduce new features and deprecate existing ones. Developers need to stay current and adapt their apps quickly. Failing and not opting to do so can and may lead towards compatibility issues or the app crashes, impacting the overall user satisfaction and their experience which helps to build a smooth appearance to the users.
Security and Data Privacy Compliance:
Apple places high emphasis on user privacy and app security and safeguarding their thoughts and processes. Apps must comply with requirements like App Tracking Transparency (ATT) data encryption standards and commonly specified parameters. Assuring these compliances and sticked with added extra layers of testing and development work into it. While iOS App Development offers and assists with great rewards, it demands precision, flexibility, and constant adaptation. Companies like Suma Soft, IBM, Cyntexa, and Cignex bring the expertise to navigate these challenges effectively, helping businesses to launch their polished, compliant, and user-friendly iOS apps.
#it services#technology#saas#software#saas development company#saas technology#digital transformation#ios app development#ios
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Chat control email script (english)
Subject line: "2022/0155(COD)
Dear Sir/Madam,
I am writing to express my grave concerns regarding the proposed introduction of "Chat Control,", also known as CSAM regulation This measure poses a serious threat to the privacy and fundamental rights of all EU citizens and stands in stark contradiction to the core principles that the European Union seeks to uphold.
Violation of Fundamental Rights
The proposed Chat Control contravenes Articles 7 and 8 of the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union, which guarantee the right to respect for private and family life and the protection of personal data. The indiscriminate surveillance of private messages without specific suspicion or cause directly violates these fundamental rights. Contradiction to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets out stringent rules for the processing of personal data. The proposed indiscriminate surveillance and scanning of private messages before end-to-end encryption is fundamentally incompatible with the principles of data minimization and purpose limitation enshrined in the GDPR. Specifically, Articles 5 and 6 of the GDPR, which govern the lawfulness and principles of data processing, would be violated by the introduction of such measures.
Technical and Ethical Concerns The implementation of Client-Side Scanning (CSS) on devices means that all messages and files are scanned on the user's device before being encrypted and sent. This effectively nullifies the protection offered by end-to-end encryption and opens the door to misuse and additional security vulnerabilities. Moreover, the technical capability to scan such content could be exploited by malicious actors to circumvent or by taking advantage of surveillance mechanisms Threat to Freedom of Expression and Trust in Digital Communication
Such far-reaching surveillance measures endanger not only privacy but also freedom of expression. The knowledge that their private messages are being scanned and monitored could significantly restrict individuals' willingness to freely express themselves. Additionally, trust in digital communication platforms would be severely undermined.
Call to Action
I urge you to take a strong stance against this disproportionate and unlawful measure. The privacy and digital rights of EU citizens must be safeguarded. It is imperative that we protect our fundamental rights and ensure transparency in the decision-making processes of our leaders.
Furthermore, given the current war happening in Ukraine, installing back doors in private communications would create more security vulnerabilities that Russia could exploit in order to launch cyber attacks within Europe and steal essential data. American officials have been recommending their citizens to use encrypted messaging following the multiple cyber attacks that targeted 8 telecom providers, including Verizon according to this article : https://www.nbcnews.com/tech/security/us-officials-urge-americans-use-encrypted-apps-cyberattack-rcna182694
For more detailed information on the Chat Control proposal and its implications, please refer to the following resource: https://edri.org/our-work/dutch-decision-puts-brakes-on-chat-control/
Thank you for your attention to this critical matter.
Sincerely,
[Name]
Art. 10 GG , Art. 8 & 11 EU Charta , Art. 8 EMRK ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
( This is the kind of arguments you can use when contacting your officials. I don't have a phone script ready yet,but you should familiarize yourself with your meps / prime ministers and tell them to keep opposing Chat Control,no matter what country you are in. It's best that you translate this script in your own language when contacting your officials and reword some parts so it doesnt sound repetitive if they are going to receive similar emails of that nature. )
Find your meps : https://www.europarl.europa.eu/meps/en/search/advanced?
If anyone knows a site where all the EU prime ministers are listed, let me know ! If you have no clue what im takling about,please check this post : https://www.tumblr.com/taikeero-lecoredier/769688553496215552/okayso-good-news-chat-control-still-didnt?source=share
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
New Security Features for Canada’s Driver’s Licenses
As Canada advances into 2025, the security of driver's licenses is undergoing a significant transformation. With the integration of digital technologies and enhanced physical features, Canadian provinces are setting new standards to combat identity theft and fraud.

Enhanced Physical Security Features
Several provinces have introduced advanced security measures in their physical driver's licenses:
Alberta has redesigned its driver's licenses and ID cards to include high-definition laser-engraved photos, transparent windows shaped like Alberta and maple leaves, rainbow printing, and raised text. These features make the cards more difficult to alter or replicate .
Ontario is enhancing its digital infrastructure to support secure online services, strengthening cybersecurity, and leveraging digital tools to improve the verification process .
The Rise of Digital Driver’s Licenses
Digital driver's licenses are becoming more prevalent, offering several advantages:
Biometric Verification: Incorporating facial recognition and fingerprint scanning to ensure the rightful owner is accessing the license.
Encryption: Protecting personal data stored digitally to prevent unauthorized access.
Real-Time Verification: Allowing authorities to verify the authenticity of a license instantly, reducing the risk of fraud .
For more information on how to transition to a digital driver's license and understand the new security features, visit licenseprep.ca.
Preparing for the Transition
To ensure a smooth transition to the new security standards:
Stay Informed: Regularly check updates from your provincial licensing authority.
Upgrade Your Devices: Ensure your smartphone or digital wallet supports the latest security features.
Practice Digital Hygiene: Use strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication where possible.
For detailed guidance on preparing for the upcoming changes, licenseprep.ca offers comprehensive resources.
Canada's commitment to enhancing the security of driver's licenses reflects a proactive approach to safeguarding personal information. By embracing these new features, Canadians can enjoy increased protection against identity theft and fraud.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Many of us are pissed,” wrote the “commander” of a Three Percenter militia in Kentucky in a post. “We need to have a location all patriots from all states can come to when the time comes,” he continued. “Thoughts?” Other militia members replied, affirming their readiness. “It’s time the enemy paid a price for their treason and crimes against humanity,” one person responded.
These plans for militia activity in the wake of the US election are not from a private conversation on an encrypted platform. It was unfolding on a public Facebook profile.
Anti-government militia movements have been continuing to use Facebook to recruit, coordinate training, promote ballot box stake outs, and prepare for a civil war that many militants believe will break out after election day. And in some cases, the movement is attracting people who don’t appear to have any prior background in a militia. Meta is even doing the work for extremist movements by auto-generating some group pages on their behalf.
Data shared exclusively with WIRED by the Tech Transparency Project shows that these groups have only continued to grow on Facebook, despite WIRED previously flagging this lapse in Meta’s moderation.
The brazen proliferation of paramilitary activity on the social media platform days before the election highlights Meta’s lackadaisical approach to enforcing its own bans against groups it has labeled dangerous extremists. Militias require platforms like Facebook to grow: It’s a tool for the paramilitary movement to strengthen and radicalize its network. It also helps them facilitate local organizing, state by state and county by county, and boost their membership.
The American paramilitary movement is much less visible than it was in 2020. Militias largely retreated from the streets after the January 6 Capitol riot exposed them to intense public and legal scrutiny, which was intensified by the prosecution of dozens of Oath Keepers. Some groups tried to distance themselves from the movement altogether by dropping any language about a “militia” from their websites, opting instead for more euphemistic names like “civilian guard” and “patriot group.” But after the dust settled following the Capitol riot, the movement began quietly rebuilding on Facebook. And they ramped up training and began coordinating, across counties and states.
The Tech Transparency Project has compiled a list of 262 Facebook public and private groups and 193 Facebook pages for militia and anti-government activists that were created since January 6, 2021. Nearly two dozen of those groups and pages have been created since May, according to the TTP. Some make minimal effort to conceal their affiliations to extremist networks: One new public group created in May is called The Michigan III%. Increasingly, the movement is also relying on individual profiles associated with leaders of local militia, the TTP says. Moderation has put a dent in the presence of American Patriots Three Percent (AP3), one of the largest active militias that Facebook explicitly banned in 2020 as a “militarized social movement” and “armed militia group.”
Meta, Facebook's parent company, says it carried out a “strategic network disruption” of AP3 in 2020 and again earlier this year in June, removing from Facebook and Instagram a total of 900 groups, pages, and accounts associated with members.
"Adversaries are constantly trying to find new ways around our policies, which is why we continually enforce against violating groups and accounts by investing heavily in people, technology, research, and partnerships,” a Meta spokesperson told WIRED in an email. “We will continue to remove any groups and accounts that violate our policies.” Meta says the company is investigating some of the screenshots of groups that WIRED shared and will remove any content that violates its policies.
But WIRED reviewed posts from AP3 groups and profiles that are still on the platform, including examples where members and leaders brandish AP3 insignia and share photos from their in-person training sessions.
There have also been some recent instances where Facebook has even auto-generated pages for militias. In May, Facebook auto-generated a page for AP3’s Arizona chapter. In June, Facebook auto-generated a page for “AP3 NM [New Mexico] Training Range.” If you hover over the information widget on the page, Facebook’s explainer reads: “This unofficial page was created because people on Facebook have shown interest in this place or business. It’s not affiliated with or endorsed by anyone associated with AP3 Training Range.”
WIRED sent Meta two examples of auto-generated pages. In a statement, the company said: "One of the two auto-generated Pages had one follower and has been removed, and we couldn’t even verify that the second example of an auto-generated Page exists on the platform."
Meta has repeatedly come under fire in the past for auto-generating pages for extremist, white supremacist, and terrorist organizations; a whistleblower first flagged the issue in 2020 in a supplement to an earlier petition filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
“Nearly four years after the January 6 attack on the capitol, Facebook remains a significant recruiting and organizing tool for militias like the AP3, despite creating policies that ban them,” said Katie Paul, director of the Tech Transparency Project. “How can Meta be trusted to effectively thwart extremists that have a record of engaging in and stoking political violence when its own systems create business pages for them?”
In a video from 2022 that was recently published as part of a leak to Distributed Denial of Secrets, AP3 leader Scot Seddon stressed the importance of Facebook to his group’s operational success. “We’ve always used Facebook, Facebook has been our greatest weapon. It has gotten us where we are today,” Seddon told the camera. “We need to use the tools that are in front of us to achieve the goals of where we want to be. Our goal is to network, be as big as possible, have as many like-minded patriots in our states that we can rely upon should shit hit the fan.”
Extremist groups need access to mainstream platforms like Facebook to reach and radicalize people. When those groups are banned from larger platforms and relegated to fringe sites, their reach and recruitment opportunities are limited and their numbers can become stagnant or start dropping.
“We know the power of Facebook as an organizing platform, to pull in people who have fallen down rabbit holes and radicalize them further,” says Jon Lewis, a research fellow at George Washington University’s Program on Extremism. “We should be concerned that actual organized domestic extremist groups have free rein on platforms that millions of Americans use.”
Now, as the election fast approaches, the paramilitary network on Facebook has been a hive of people looking to link up, train, and prepare. A review by WIRED of recent Facebook posts in a number of these militia groups also suggests that the paramilitary movement has lately been attracting individuals who don’t have previous experience of being part of a militia.
“I’m looking for a group of people that see and understand the dire situation our country is in,” wrote one poster in the Facebook group U.S.A. Militia We The People last month. “A group of people that understand that civil war is at our doorstep if Kamala makes it into office. Am I in the right place?”
In another post earlier this month in a group for a county-level militia in Virginia, a member shared that he and his wife were interested in joining up, before asking for more information about how to do so. Also earlier this month, a new member of a militia group in Oklahoma introduced himself as a military veteran and said he was a member of a militia from 2015 to 2017 but wants to get involved again. “My battle rattle is ready to go any time,” he added.
Two county-level militias in Virginia have created Facebook pages in the past month, which they’ve used to coordinate their inaugural “musters” (militia speak for a meetup) in recent weeks. Another local Virginia militia has organized a meeting for two days after the election.
The “commander” of a Three Percenter group in Kentucky—who posed for a photograph viewed by WIRED with Representative Thomas Massie last summer while wearing full gear and insignia—has used his profile to share images from training sessions and regularly makes inflammatory statements. In a recent post, he suggested that state militias ought to rally at their chosen state parks: “Three national base camps could be state or national parks … (for example) west in NV or CO, central Missouri and east WV or VA. Then get comms established.”
In a “Patriot Group” in Barron County, Wisconsin, a recent lively discussion led by a “top contributor” urged members to “organize and monitor” ballot drop boxes. Several members of the group proposed planting small cameras in the vicinity of the boxes. Ballot drop surveillance has continued to be a hot topic of discussion among election deniers and paramilitary groups. Militias also teamed up with election deniers to conduct covert surveillance of ballot drop boxes during the midterm elections, recent leaks published by Distributed Denial of Secrets and reported by WIRED show. A recent DHS intelligence memo warned law enforcement agencies that domestic extremists could try to sabotage or attack ballot boxes.
The administrator of a New Hampshire–based group called the MAGA Continental Army claims that he recently met with the local police chief to discuss preparations in the event that a civil war breaks out. “He told me if it came to civil war that he will be directing his officers to defend the people—they will not be coming after your guns,” he wrote. He added that the chief said all members should come to the police department if conflict broke out.
In one public group called The Party of Trump, with 171,000 members, a discussion about ballot drop box monitoring prompted someone to suggest that Trump supporters come armed with their AR-15s to stand guard. In another public group called We Fight for Our Lives, someone urged others to get organized ahead of the election and suggested enlisting bikers and militia. “I’m ready to fight,” one person responded. “I’ll pull the fuckin trigger fo sho” the original poster added. In another public group called SAVE THE FLAG AMERICA, someone put the stakes of the election in bleak terms: “In a matter of days, we will ascertain our financial capacity to procure essential commodities such as groceries and fuel, or, alternatively face the prospect of engaging in armed conflict.”
“Trump 2024,” someone responded. “God is always in control.”
9 notes
·
View notes