#vintage armenia
Text

Armenian woman and a girl, 1890s, Yerevan. State Historical Museum, Moscow.
59 notes
·
View notes
Text

Medieval Armenian Gospel.
#beautiful books#book blog#books books books#book cover#books#vintage books#armenia#book design#book binding#gospel#christian bible#medieval
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo
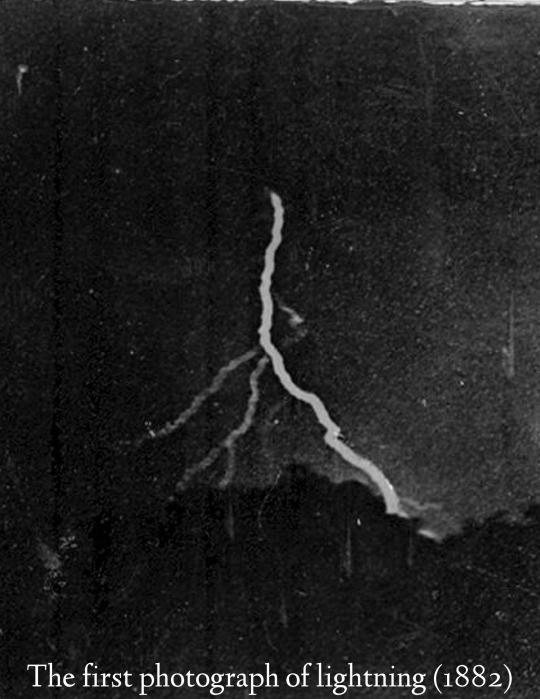
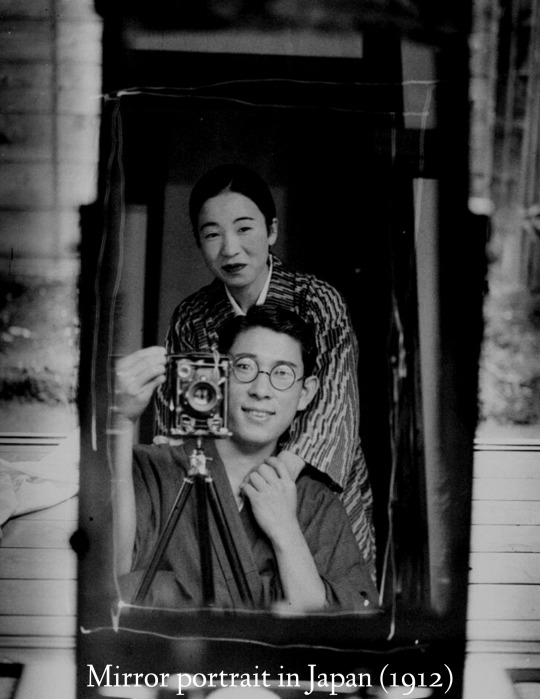
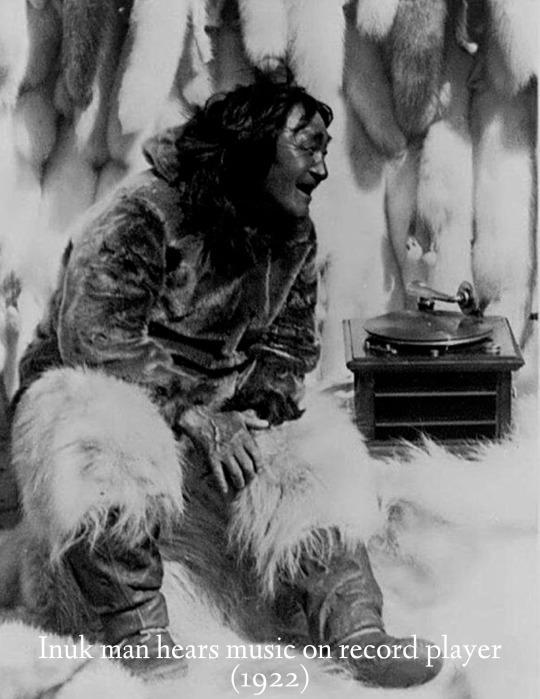
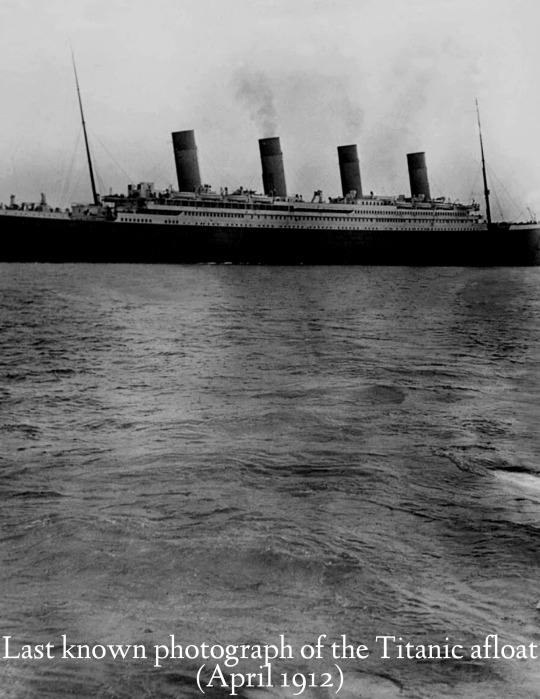
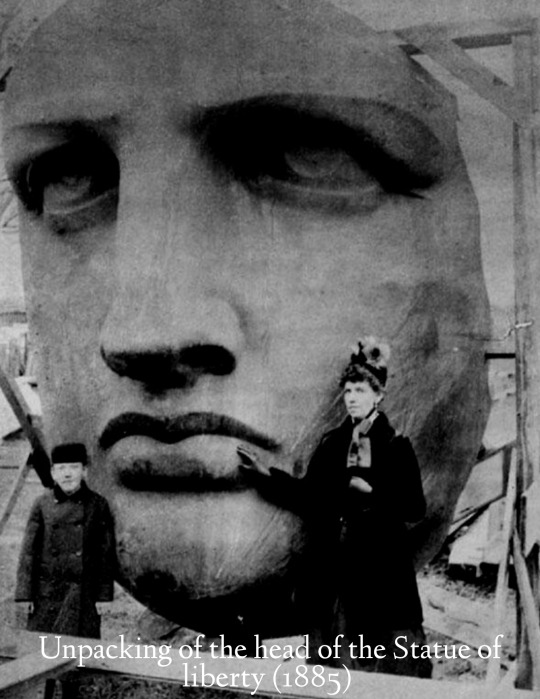
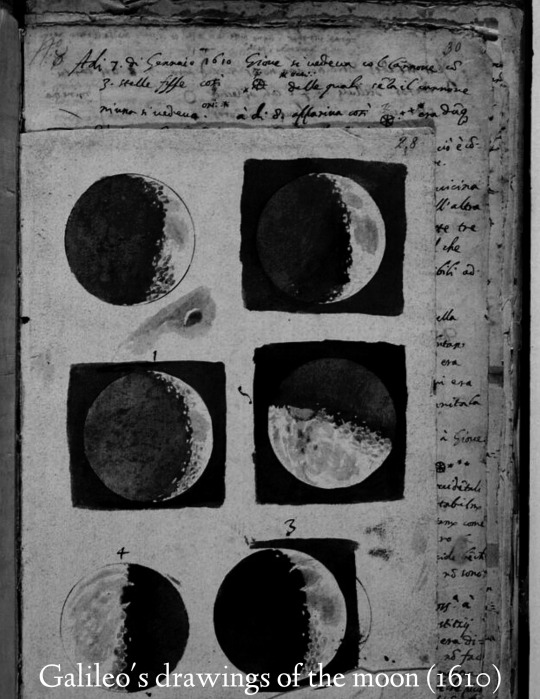








historical pictures
#just thought these were cool to show#history#photography#vintage photography#armenia#vintage#historical
377 notes
·
View notes
Text
Member of the armenian militia Bourj Hammoud, 1976

21 notes
·
View notes
Text

Jean-Baptiste Delacour - Di ritorno dall'aldilà - Armenia - 1976 (cover photo by M. Zanet)
#witches#stimmen#occult#vintage#di ritorno dall'aldilà#ritorno#aldilà#glimpses of the beyond#glimpses#beyond#the beyond#armenia editore#jean-baptiste delacour#jean baptiste delacour#stimmen aus dem jenseits zurück#jenseits#1976#1973#hanns kurth
7 notes
·
View notes
Text




The Color of Pomegranates
Directed by Sergei Parajanov
1969
Armenia
#The Color of Pomegranates#sergei parajanov#1969#Armenia#vintage poster#graphic poster#vintage posters#poster art#poster design#film poster#movie posters
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
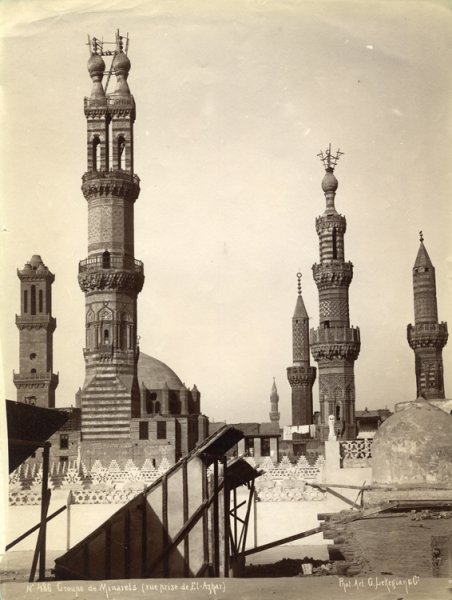

#egypt #photography #art
Group of minarets. View from El-Azhar
by Lekegian, Gabriel 1890s
Gabriel Lekegian (Armenian, 1853–1920)
#1890s#egypt#photojournalism#Gabriel Lekegian#armenien#armenia#azhar#minaret#cairo#vintage#dimension 20 fantasy high fantasy high junior year fhjy d20#fhjy#d20#FANTASY#DIMENSION#ART#ARTISTS#UPDATE#TRAN#translation#fantasy high#dimension 20#ceasefire#BDS#boycott#EUROVISION#SONG#NEWS#CURRENT#music
6 notes
·
View notes
Photo
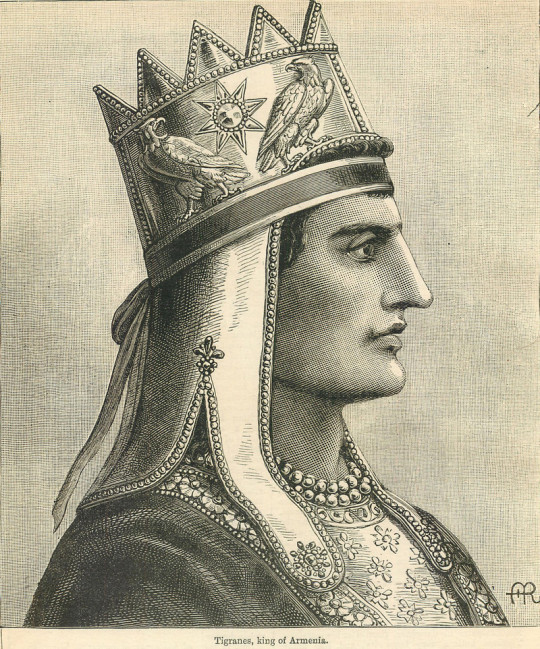

Source details and larger version.
Some true gems in my collection of vintage vintage crowns.
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
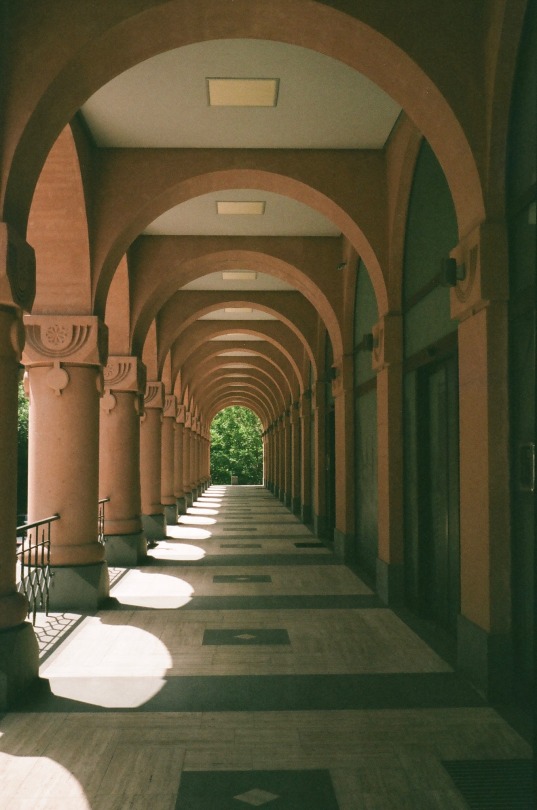

Yerevan, Armenia
#a e s t h e t i c#aestheitcs#35mm#35mm film#35mm color film#35mm photography#olympustrip35#olympus35mm#armenia#yerevan#vintage photography
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
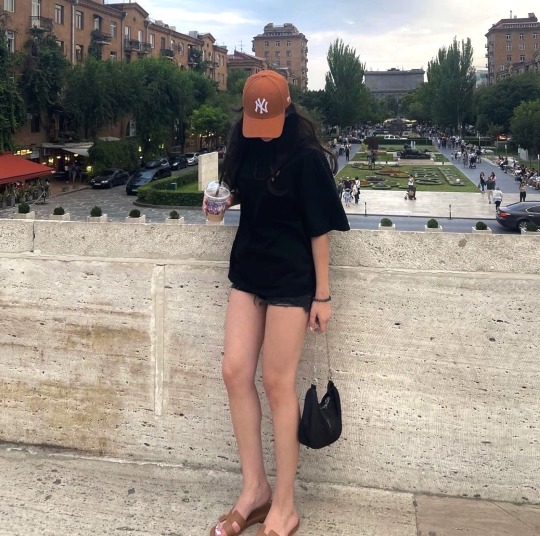

#erevan#armenia#beautiful#beauty#cascade#love#aesthetic#vintage#sunset#flowers#ереван#армения#красиво#эстетика#удовольствие#вау#красотка
1 note
·
View note
Text


Yerevan. Armenian family making sujukh/sharots, 1900-1917.
Hussenig. An Armenian family preparing rodjig (sharots, cevizli sucuk; grape juice and nut roll) and basdegh (pestil; fruit leather).
91 notes
·
View notes
Text

THE GOSPEL OF PARTSERPENT scribed by Kirakos (Armenia: Hromkla (Cilicia) by the order of Catholicos Costantin Partserpertsi, 1248)
After the Armenian genocide of 1915, the manuscript was carried, together with the right hand of St. Gregory the Illuminator and other relics and ancient manuscripts, to Aleppo (Syria) and then to Antelias (Lebanon).
Most pages of the 700 page manuscript contain miniatures of biblical narratives, and a miniature of each Evangelist appears on the first page of his Gospel.
The front and back covers are made of silver.
source
#beautiful books#book blog#books books books#book cover#books#vintage books#illustrated book#christian bible#gospel#armenia#treasure binding#silver#gem stones#book design#book binding
66 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Ախթամար / Akhtamar / Ахтамар
Armenian short film, 1969
Actors: Irina Baghramyan, Vladimir Episkoposyan.
Directors: Ernest Martirosyan, Sebouh Sargsyan
#akhtamar#Sebouh Sargsyan#ernest Martirosyan#irina Baghramyan#Vladimir Episkoposyan#armenia#film#cinema#style#video#vintage#drowning#sea#water#coast#shore#love#couples#lovers#death#religion#church#cathedral#island#van#armenian#art film#short film#violence#tragedy
0 notes
Photo
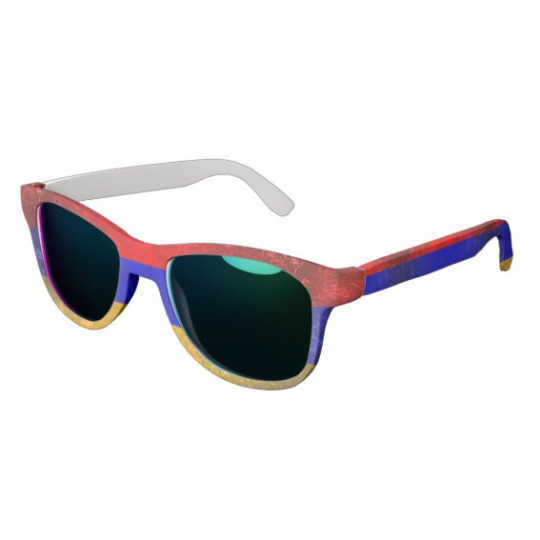

Happy Independence Day, Armenia!
#Armenia#Հայաստան#Hayastan#sunglasses#glasses#shades#party time#party#party shades#vintage flag#vintage#retro#stylish#on sale#shopping day
0 notes
Text
An Introduction To Wine for Dionysians

A photo from my wine class, the pink being my Chambourcin and Sangiovese rosés.
[ID: An image of two wine glasses on a stainless steel table. The first glass, closer to the observer, is bright pink. The second glass, to the right of the pink one is a salmon colour and slightly blurry.]
THIS POST IS SLIGHTLY BASIC, IN MY OPINION. It’s not exactly hard to research wine, especially now that the industry is beginning to have new winemakers such as myself. But this is my job and passion, so I thought it may be useful in the end. Especially for us Dionysians, most who never engage in the winemaking process—which is fine, but it does offer a more intimate knowledge of his realms. So as a winemaker myself, I want to share the wonders of winemaking with others. This post is meant to be a quick introduction to wine from a viticulturist and enologist.
SOME TERMINOLOGY
Entering the world of wine does require a basic understanding of some jargon. To make it easy, I have listed some common terms:
Anthocyanins — the red-purple colour compound in red grapes
Bret — short for Bretannomyces, this is an endemic yeast to Europe and often a pest in wineries. This yeast creates leather, hide, barnyard, etc., flavours and aromas in wine. This is often desirable in small amounts in certain styles, but can quickly overpower a wine.
Fault — an issue with the wine, typically in flavour, aroma, colour, or taste. Faults are subjective and sometimes may be beneficial. A key part of wine sensory analysis is tasting faults.
Macerate — a process in which colour and flavour is leached from the skins of the grape. This is most common in reds and is aided by ethanol.
Noble Rot — a form of Botrytis Cinerea that is beneficial within the wine process to make sweet wines.
Press — a winemaking device that extracts juices from grapes to make wine
Terroir — the characteristic taste and flavor imparted to a wine by the environment in which it is produced.
Vintage — the year the grapes were harvested and are typically fermented in the same year, however, this is not always the case.
ANCIENT, OLD WORLD, AND NEW WORLD
The wine world has often been divided into “old world” and “new world”, but I have personally taken a liking to the classification of some wine regions as ancient world wine regions. These regions would be Georgia, Armenia, Assyrian lands, Greece, some parts of Italy, and more. Ancient winemaking is well, winemaking in regions that have continuously made wine with the same or similar techniques over thousands of years. An ancient wine that I always recommend to Dionysians is Retsina.
Old world wine is essentially European wine. While this term has its issues, it is the one that the wine industry understands. Europe has been making wine for hundreds of years, thousands in some regions. Old world wine is known for the less fruity, more aged styles, along with producing table wine. These wines also tend to be oaked, in which the wood imparts flavours into the wine which is dependent on the type of wood used. Bret is also common in the old world, which is often a hit or miss with consumers.
New world wine is wine made in wine regions that are relatively new, associated with more scientific approaches to wine. Another way to look at it is wine regions that are or were colonies of Europe, though a few new world wine regions do not have this history. New world wine is often associated with brightness, fruity flavours, higher alcohol levels, etc.
Simply put:
Ancient — regions such as the Fertile Crescent, Palestine, Assyrian lands, Greece, parts of Italy, etc.,
Old — Europe, including wine regions more similar to the new world such as Slovakia
New — Generally colonised countries, the largest example being the United States.
TYPES OF WINE
Most people grasp the basics: white wine comes from white grapes and red wine comes from red grapes. However, of course, it gets more complicated from here. To list it simply:
White wine is wine made from white grapes that are removed from the skins.
Red wine is made from red grapes left to macerate on the skins.
Orange wine is made from white grapes left to macerate on the skins.
Rose is made from red wines removed from the skins.
Pink wines are wines made through blending white and red wine, considered of lesser craftsmanship than a rose by most winemakers
Commercial wines are typically whites, reds, and rose/pink. Orange wines are seldom found outside of Slovenia and Georgia due to tradition. Overall, the wine world considers orange wine strange, however the market has been increasing in recent years.
Wine is also a term applied to fruit wines (fruit other than grapes). Legally in most regions, wine can only be applied to fermented grapes—though of course, nobody listens to that. Essentially, I like to phrase wine as anything made from fermented fruits, roots, and tree-sugars. Cider is technically wine, but this is defined in the USA by tax brackets—below 8% ABV is a cider, over is an apple fermented product/wine.
WINE STYLES
To put it simply: there are thousands of wine styles. I cannot summarise them here, however I will try to summarise some of the common styles I know of.. ‘Old world’ and ‘new world’ are also considered broad styles.
Dessert Wines
Dessert wine as a term is dependent on location, as in the USA it is any wine over 14% ABV. In the UK, it is often classified as a sweet wine drunk before a meal. It is also usd colloquially for sweet, high-alcohol wines that are drunk with dessert. A bit of a meaningless term, but it is used regardless.
Sweet Wines
Sweet wines are wines that have residual sugar from fermentation. Most wines are finished dry, which is when the yeast consumes most to all available sugars and converts them into ethanol. This can be intentional or the result of a stuck or dead fermentation. Sweet wines are known for getting people drunk quickly and giving a particularly nasty headache.
Table Wine
Table wine is perfectly named, as these are common wines that are meant to appear at the dinner table and be paired with food. Italy is famous for creating popular table wines such as Chianti and Prosecco. The table wine market is however slowly dying. I personally liken table wines to Dionysus Hestios.
Straw wine
Straw wine is wine made from grapes that have been dried. This makes very sweet wines due to the lack of water.
Rot wines
Rot wines, also called Noble Rot wines, are a unique form of sweet wines created by noble rot. In viticulture, botrytis is a fungus that often ruins clusters by mummifying grape clusters. In the right conditions however, it instead only takes the water content in a grape berry over a series of days before perishing. Rot wines often occur near rivers, lakes, and other regions with mist and then scorching sun. This fascinating process creates natural sweet wines—many of which demand high price points, such as sauternes that are priced at over one thousand euros. Another form of rot wine I enjoy is Slovak tokaji.
In my personal practice, these wines hold a special spot due to my focus on divine rot. Dionysus wise, I think these wines possess such a unique quality of him—they are dead yet not, and Dionysus may be found in the marshes where rot blooms.
Sparkling Wine
Often known as champagne, sparkling wine is wine that when opened/poured will fizz with carbon dioxide bubbles. This is usually due to secondary fermentation, in which yeast are inoculated to ferment trace amounts of sugar to create the carbonation that appears when you open the bottle. Sparkling wine can only be labelled champagne if it is from Champagne, France. With the climate crisis however, champagne may disappear and Southern England has been contending to become the next major sparkling wine region.
There are lesser quality sparkling wines made by injecting carbonation into the metal wine vats. This is common with sparkling juices that are not fermented.
Fortified Wines
When you think of Port, that is a fortified wine. These wines are mixed in with ethanol, typically spirits, to increase the alcohol content of the wines. This makes them less likely to spoil and creates a unique flavour profile.
Some traditional fortified wines are Port, Sherry,
Cooking Wines
These are wines that are not typically used for drinking, but rather feature as a culinary ingredient. This does not mean low quality however, as some cooking wines such madeira can fetch a very high price point.
BARRELS
Barrels are enchanting. Even if I see them daily, there is a bit of romance to working with them. Wines are put in barrels for storage and for flavour. The most common wood used in wine are oaks, with French oak (Quercus robur) and American oak (Quercus alba) being the most common and stylistic. Barrels are a core aspect of traditionally ageing wine, as the barrel allows enough oxygen into the liquid to be beneficial. For those who do not know, oxygen degrades wine over time. This is why cheaper wines quickly turn bad, as they were not designed to age.
The flavour-changing profile of wood-contact on wine works through phenols and other compounds interacting with the oak, creating vanilla flavours. For other woods, a similar process occurs, such as Pine creating a pinewood taste, chestnut increasing the perception of sweetness, etc. Research is being continued on alternative woods in winemaking.
Barreling is not the only source of flavour profile in wine. Wines gain their flavour from three sources. This is simply:
Primary: flavours derived from the grape
Secondary: flavours derived from yeast. Yeast often create secondary flavour compounds, such as floral, herbal, spicy, etc notes.
Tertiary: barrel and ageing flavour.
When doing wine tastings, these are excellent factors to begin wine analysis. Deciphering these notes allows one to build a palette and understand more of the expanses of vinification.
GRAPE CULTIVARS
Grape cultivars, also called varietals, are what impart unique flavours into a wine at the primary level. Each cultivar gives its own unique flavour profile. The most commonly planted grapes are the noble varieties, which were prized by French nobility—these being grapes such as Chardonnay and Sauvignon blanc.
Grape cultivars can change their profile depending on where they are grown, called terroir. As an example, a French Cabernet Sauvignon is completely different from a Napa Valley Cabernet Sauvignon. Terroir encompasses soil, weather patterns, climate, etc. Another example is that wines made in years of heavy wildfires often taste smoky and Australian wines taste burnt due to the extreme sun exposure.
Profit and market trends have caused lesser known and cultural grapes in many places to become extinct or endangered. There are movements and efforts to preserve these cultural vines and many wine drinkers are interested in the unique experiences rare cultivars can provide.
Cultivars also often have regional and cultural significance. The Bacchus grape has been found to grow excellently in southern England, Agiorgitiko is the most common Greek red grape, Sangiovese is the grape for Tuscan Chianti, etc. In the new world, Grape cultivars often take on new significance, such as Sauvignon Blanc in New Zealand. As obscure grapevines become more popular, regional and forgotten grape varieties have been reappearing.
Hybrid vines, which are some of my favourite, are the result of viticultural science. These are vines bred to exhibit certain traits, whether as a ‘find out’ project or specially designed for certain wine regions. These are often called French-American hybrids, however hybrids are also being produced in Korea, Slovakia, and other countries. One of the most commonly planted hybrids is Chambourcin, called ‘king of the hybrid reds’, due to its striking fuschia red or barbie pink rose and desirable flavour profile. I have made a post over these hybrids before and they are readily searchable for anyone interested.
There are thousands of cultivars and new cultivars are created each year. The world of wine is ever expansive when it comes to grapevines, just as Dionysus always brings something new. There is always something new to try, or a new spin on something familiar. Yet when we crave a taste of something familiar, traditional varieties and vintages are around to return to. Wine is both new and old, alive and dead, familiar and yet ever-changing.
HOW TO BEGIN IN WINE
Beginning in wine is as simple as buying wine. Advancing understanding then comes through sensory analysis, experimentation, trying new and different wines, historical research, and much more. I doubt most people will be like myself, who decided to get an associates degree in winemaking and make it my secondary career. Honestly, it’s much more fun as a hobby than a job.
I recommend experiencing the differences between reds and whites, along with sampling table wines with and without food. Picking out grape varietals is also fun, but may be subtle. As an example, a sauvignon blanc is immediately recognisable for its bellpepper note, but I have developed the skill to taste the general region where sauvignon blanc was grown (it is my favourite white wine grape).
I have touched upon sensory analysis and terminology with it, such as palette and body, but I will reserve that for another post. Trying wine and research is the best way to begin—and there is no such thing as beginner wine in my opinion. There are wines that are harsh, different, and likely undesirable to someone who is used to sweet juice and unchallenging sweet drinks, however I believe it limits a wine explorer when you limit yourself to “beginner wines”. Finding that brings you joy matters most, whether that is a classic sweet wine or mouth-punching red. And pour some out for Dionysus, the sweet lord of the eternal winepress.
view this post on wordpress
References
Bird, D. (2011). Understanding Wine Technology, 3rd Edition: The Science of Wine Explained. Board and Bench Publishing.
Puckette, M., & Hammack, J. (2018). Wine Folly: Magnum Edition: The Master Guide. Penguin UK.
Wilson, J. (2019). Godforsaken grapes: A slightly tipsy journey through the world of strange, obscure, and ... underappreciated wine. HARRY N ABRAMS.
Wine microbiology. (2007). In Springer eBooks. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-33349-6
#vīnum#dragonis.txt#witchcraft#paganism#hellenic polytheism#witchblr#dionysus deity#pagan#dionysus worship#hellenic polytheist#helpol#hellenic paganism
197 notes
·
View notes
Photo
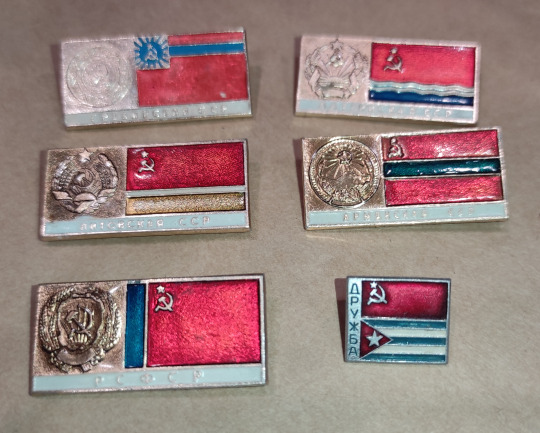


Vintage pins - flags of Soviet republics. Available: Armenia, Georgia, Latvia, Lithuania, Russia, Uzbekistan
$6/ea + $5 shipping
Cuba is also available (it reads “Friendship”) / $5
Message me!
How to buy. Other items in my shop. I combine shipping if you buy more than one item.
63 notes
·
View notes