#*and by ai i do mean text and image generation models
Text
i try to curb my reactionary opinions on ai*, but i just heard a youtuber say "and i did some research, by asking chatgpt..." and im about to bite clean through my desk
#jabber jay#*and by ai i do mean text and image generation models#every time im like 'ok ai generation is FINE i guess' i see shit like this and start seething again#like brother do not do RESEARCH on a TEXT GENERATOR its just giving you words in response to the words you said!#you cant guarantee itll say the truth! it doesnt have to fact check! its just a fun toy to play with sometimes it is not an encyclopedia
0 notes
Text
There is no such thing as AI.
How to help the non technical and less online people in your life navigate the latest techbro grift.
I've seen other people say stuff to this effect but it's worth reiterating. Today in class, my professor was talking about a news article where a celebrity's likeness was used in an ai image without their permission. Then she mentioned a guest lecture about how AI is going to help finance professionals. Then I pointed out, those two things aren't really related.
The term AI is being used to obfuscate details about multiple semi-related technologies.
Traditionally in sci-fi, AI means artificial general intelligence like Data from star trek, or the terminator. This, I shouldn't need to say, doesn't exist. Techbros use the term AI to trick investors into funding their projects. It's largely a grift.
What is the term AI being used to obfuscate?
If you want to help the less online and less tech literate people in your life navigate the hype around AI, the best way to do it is to encourage them to change their language around AI topics.
By calling these technologies what they really are, and encouraging the people around us to know the real names, we can help lift the veil, kill the hype, and keep people safe from scams. Here are some starting points, which I am just pulling from Wikipedia. I'd highly encourage you to do your own research.
Machine learning (ML): is an umbrella term for solving problems for which development of algorithms by human programmers would be cost-prohibitive, and instead the problems are solved by helping machines "discover" their "own" algorithms, without needing to be explicitly told what to do by any human-developed algorithms. (This is the basis of most technologically people call AI)
Language model: (LM or LLM) is a probabilistic model of a natural language that can generate probabilities of a series of words, based on text corpora in one or multiple languages it was trained on. (This would be your ChatGPT.)
Generative adversarial network (GAN): is a class of machine learning framework and a prominent framework for approaching generative AI. In a GAN, two neural networks contest with each other in the form of a zero-sum game, where one agent's gain is another agent's loss. (This is the source of some AI images and deepfakes.)
Diffusion Models: Models that generate the probability distribution of a given dataset. In image generation, a neural network is trained to denoise images with added gaussian noise by learning to remove the noise. After the training is complete, it can then be used for image generation by starting with a random noise image and denoise that. (This is the more common technology behind AI images, including Dall-E and Stable Diffusion. I added this one to the post after as it was brought to my attention it is now more common than GANs.)
I know these terms are more technical, but they are also more accurate, and they can easily be explained in a way non-technical people can understand. The grifters are using language to give this technology its power, so we can use language to take it's power away and let people see it for what it really is.
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
PLEASE JUST LET ME EXPLAIN REDUX
AI {STILL} ISN'T AN AUTOMATIC COLLAGE MACHINE
I'm not judging anyone for thinking so. The reality is difficult to explain and requires a cursory understanding of complex mathematical concepts - but there's still no plagiarism involved. Find the original thread on twitter here; https://x.com/reachartwork/status/1809333885056217532
A longpost!

This is a reimagining of the legendary "Please Just Let Me Explain Pt 1" - much like Marvel, I can do nothing but regurgitate my own ideas.
You can read that thread, which covers slightly different ground and is much wordier, here; https://x.com/reachartwork/status/1564878372185989120
This longpost will;
Give you an approximately ELI13 level understanding of how it works
Provide mostly appropriate side reading for people who want to learn
Look like a corporate presentation
This longpost won't;
Debate the ethics of image scraping
Valorize NFTs or Cryptocurrency, which are the devil
Suck your dick
WHERE DID THIS ALL COME FROM?
The very short, very pithy version of *modern multimodal AI* (that means AI that can turn text into images - multimodal means basically "it can operate on more than one -type- of information") is that we ran an image captioner in reverse.


The process of creating a "model" (the term for the AI's ""brain"", the mathematical representation where the information lives, it's not sentient though!) is necessarily destructive - information about original pictures is not preserved through the training process.


The following is a more in-depth explanation of how exactly the training process works. The entire thing operates off of turning all the images put in it into mush! There's nothing left for it to "memorize". Even if you started with the exact same noise pattern you'd get different results.

SO IF IT'S NOT MEMORIZING, WHAT IS IT DOING?
Great question! It's constructing something called "latent space", which is an internal representation of every concept you can think of and many you can't, and how they all connect to each other both conceptually and visually.

CAN'T IT ONLY MAKE THINGS IT'S SEEN?
Actually, only being able to make things it's seen is sign of a really bad AI! The desired end-goal is a model capable of producing "novel information" (novel meaning "new").
Let's talk about monkey butts and cigarettes again.

BUT I SAW IT DUPLICATE THE MONA LISA!
This is called overfitting, and like I said in the last slide, this is a sign of a bad, poorly trained AI, or one with *too little* data. You especially don't want overfitting in a production model!
To quote myself - "basically there are so so so many versions of the mona lisa/starry night/girl with the pearl earring in the dataset that they didn't deduplicate (intentionally or not) that it goes "too far" in that direction when you try to "drive there" in the latent vector and gets stranded."

Anyway, like I said, this is not a technical overview but a primer for people who are concerned about the AI "cutting and pasting bits of other people's artworks". All the information about how it trains is public knowledge, and it definitely Doesn't Do That.
There are probably some minor inaccuracies and oversimplifications in this thread for the purpose of explaining to people with no background in math, coding, or machine learning. But, generally, I've tried to keep it digestible. I'm now going to eat lunch.
Post Script: This is not a discussion about capitalists using AI to steal your job. You won't find me disagreeing that doing so is evil and to be avoided. I think corporate HQs worldwide should spontaneously be filled with dangerous animals.
Cheers!
666 notes
·
View notes
Text
Often when I post an AI-neutral or AI-positive take on an anti-AI post I get blocked, so I wanted to make my own post to share my thoughts on "Nightshade", the new adversarial data poisoning attack that the Glaze people have come out with.
I've read the paper and here are my takeaways:
Firstly, this is not necessarily or primarily a tool for artists to "coat" their images like Glaze; in fact, Nightshade works best when applied to sort of carefully selected "archetypal" images, ideally ones that were already generated using generative AI using a prompt for the generic concept to be attacked (which is what the authors did in their paper). Also, the image has to be explicitly paired with a specific text caption optimized to have the most impact, which would make it pretty annoying for individual artists to deploy.
While the intent of Nightshade is to have maximum impact with minimal data poisoning, in order to attack a large model there would have to be many thousands of samples in the training data. Obviously if you have a webpage that you created specifically to host a massive gallery poisoned images, that can be fairly easily blacklisted, so you'd have to have a lot of patience and resources in order to hide these enough so they proliferate into the training datasets of major models.
The main use case for this as suggested by the authors is to protect specific copyrights. The example they use is that of Disney specifically releasing a lot of poisoned images of Mickey Mouse to prevent people generating art of him. As a large company like Disney would be more likely to have the resources to seed Nightshade images at scale, this sounds like the most plausible large scale use case for me, even if web artists could crowdsource some sort of similar generic campaign.
Either way, the optimal use case of "large organization repeatedly using generative AI models to create images, then running through another resource heavy AI model to corrupt them, then hiding them on the open web, to protect specific concepts and copyrights" doesn't sound like the big win for freedom of expression that people are going to pretend it is. This is the case for a lot of discussion around AI and I wish people would stop flagwaving for corporate copyright protections, but whatever.
The panic about AI resource use in terms of power/water is mostly bunk (AI training is done once per large model, and in terms of industrial production processes, using a single airliner flight's worth of carbon output for an industrial model that can then be used indefinitely to do useful work seems like a small fry in comparison to all the other nonsense that humanity wastes power on). However, given that deploying this at scale would be a huge compute sink, it's ironic to see anti-AI activists for that is a talking point hyping this up so much.
In terms of actual attack effectiveness; like Glaze, this once again relies on analysis of the feature space of current public models such as Stable Diffusion. This means that effectiveness is reduced on other models with differing architectures and training sets. However, also like Glaze, it looks like the overall "world feature space" that generative models fit to is generalisable enough that this attack will work across models.
That means that if this does get deployed at scale, it could definitely fuck with a lot of current systems. That said, once again, it'd likely have a bigger effect on indie and open source generation projects than the massive corporate monoliths who are probably working to secure proprietary data sets, like I believe Adobe Firefly did. I don't like how these attacks concentrate the power up.
The generalisation of the attack doesn't mean that this can't be defended against, but it does mean that you'd likely need to invest in bespoke measures; e.g. specifically training a detector on a large dataset of Nightshade poison in order to filter them out, spending more time and labour curating your input dataset, or designing radically different architectures that don't produce a comparably similar virtual feature space. I.e. the effect of this being used at scale wouldn't eliminate "AI art", but it could potentially cause a headache for people all around and limit accessibility for hobbyists (although presumably curated datasets would trickle down eventually).
All in all a bit of a dick move that will make things harder for people in general, but I suppose that's the point, and what people who want to deploy this at scale are aiming for. I suppose with public data scraping that sort of thing is fair game I guess.
Additionally, since making my first reply I've had a look at their website:
Used responsibly, Nightshade can help deter model trainers who disregard copyrights, opt-out lists, and do-not-scrape/robots.txt directives. It does not rely on the kindness of model trainers, but instead associates a small incremental price on each piece of data scraped and trained without authorization. Nightshade's goal is not to break models, but to increase the cost of training on unlicensed data, such that licensing images from their creators becomes a viable alternative.
Once again we see that the intended impact of Nightshade is not to eliminate generative AI but to make it infeasible for models to be created and trained by without a corporate money-bag to pay licensing fees for guaranteed clean data. I generally feel that this focuses power upwards and is overall a bad move. If anything, this sort of model, where only large corporations can create and control AI tools, will do nothing to help counter the economic displacement without worker protection that is the real issue with AI systems deployment, but will exacerbate the problem of the benefits of those systems being more constrained to said large corporations.
Kinda sucks how that gets pushed through by lying to small artists about the importance of copyright law for their own small-scale works (ignoring the fact that processing derived metadata from web images is pretty damn clearly a fair use application).
1K notes
·
View notes
Note
I saw something about generative AI on JSTOR. Can you confirm whether you really are implementing it and explain why? I’m pretty sure most of your userbase hates AI.
A generative AI/machine learning research tool on JSTOR is currently in beta, meaning that it's not fully integrated into the platform. This is an opportunity to determine how this technology may be helpful in parsing through dense academic texts to make them more accessible and gauge their relevancy.
To JSTOR, this is primarily a learning experience. We're looking at how beta users are engaging with the tool and the results that the tool is producing to get a sense of its place in academia.
In order to understand what we're doing a bit more, it may help to take a look at what the tool actually does. From a recent blog post:
Content evaluation
Problem: Traditionally, researchers rely on metadata, abstracts, and the first few pages of an article to evaluate its relevance to their work. In humanities and social sciences scholarship, which makes up the majority of JSTOR’s content, many items lack abstracts, meaning scholars in these areas (who in turn are our core cohort of users) have one less option for efficient evaluation.
When using a traditional keyword search in a scholarly database, a query might return thousands of articles that a user needs significant time and considerable skill to wade through, simply to ascertain which might in fact be relevant to what they’re looking for, before beginning their search in earnest.
Solution: We’ve introduced two capabilities to help make evaluation more efficient, with the aim of opening the researcher’s time for deeper reading and analysis:
Summarize, which appears in the tool interface as “What is this text about,” provides users with concise descriptions of key document points. On the back-end, we’ve optimized the Large Language Model (LLM) prompt for a concise but thorough response, taking on the task of prompt engineering for the user by providing advanced direction to:
Extract the background, purpose, and motivations of the text provided.
Capture the intent of the author without drawing conclusions.
Limit the response to a short paragraph to provide the most important ideas presented in the text.

Search term context is automatically generated as soon as a user opens a text from search results, and provides information on how that text relates to the search terms the user has used. Whereas the summary allows the user to quickly assess what the item is about, this feature takes evaluation to the next level by automatically telling the user how the item is related to their search query, streamlining the evaluation process.

Discovering new paths for exploration
Problem: Once a researcher has discovered content of value to their work, it’s not always easy to know where to go from there. While JSTOR provides some resources, including a “Cited by” list as well as related texts and images, these pathways are limited in scope and not available for all texts. Especially for novice researchers, or those just getting started on a new project or exploring a novel area of literature, it can be needlessly difficult and frustrating to gain traction.
Solution: Two capabilities make further exploration less cumbersome, paving a smoother path for researchers to follow a line of inquiry:
Recommended topics are designed to assist users, particularly those who may be less familiar with certain concepts, by helping them identify additional search terms or refine and narrow their existing searches. This feature generates a list of up to 10 potential related search queries based on the document’s content. Researchers can simply click to run these searches.

Related content empowers users in two significant ways. First, it aids in quickly assessing the relevance of the current item by presenting a list of up to 10 conceptually similar items on JSTOR. This allows users to gauge the document’s helpfulness based on its relation to other relevant content. Second, this feature provides a pathway to more content, especially materials that may not have surfaced in the initial search. By generating a list of related items, complete with metadata and direct links, users can extend their research journey, uncovering additional sources that align with their interests and questions.

Supporting comprehension
Problem: You think you have found something that could be helpful for your work. It’s time to settle in and read the full document… working through the details, making sure they make sense, figuring out how they fit into your thesis, etc. This all takes time and can be tedious, especially when working through many items.
Solution: To help ensure that users find high quality items, the tool incorporates a conversational element that allows users to query specific points of interest. This functionality, reminiscent of CTRL+F but for concepts, offers a quicker alternative to reading through lengthy documents.
By asking questions that can be answered by the text, users receive responses only if the information is present. The conversational interface adds an accessibility layer as well, making the tool more user-friendly and tailored to the diverse needs of the JSTOR user community.
Credibility and source transparency
We knew that, for an AI-powered tool to truly address user problems, it would need to be held to extremely high standards of credibility and transparency. On the credibility side, JSTOR’s AI tool uses only the content of the item being viewed to generate answers to questions, effectively reducing hallucinations and misinformation.
On the transparency front, responses include inline references that highlight the specific snippet of text used, along with a link to the source page. This makes it clear to the user where the response came from (and that it is a credible source) and also helps them find the most relevant parts of the text.
292 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'd like to take a couple of minutes to talk about NaNoWriMo (National Novel Writers Month) and their terrible, very bad, no good stance on genAI (generative artificial intelligence) and why I won't be writing anything for this challenge again.
I'm very aware that I am an active and vocal genAI hater. But I am willing and open to hear about positive and useful things LLMs (large language models) can do. There are valid scientific uses for the technology and some really fascinating medical and academic breakthroughs that come from LLMs. But the use of genAI in creative writing context is complete bullshit.
Come with me for the breakdown.
The first part of their statement:

NaNoWriMo has made it clear they are not just tolerating genAI in their month long writing challenge, but that those of us who don't are 'classist' and 'ableist' because we don't.
The post was later amended with a list of reasons why they make each of those claims. We'll start from the top.

GenAI uses the technology in a way that is morally, ethically and environmentally bankrupt. See, all LLMs have to train on something. When you're using it to, say, detect cancers you can feed it images of cancer scans so that it builds up a dataset of what those look like to predict future scans. But when you want to generate text, images and video you have to feed it text, images and video. Those things came from people, actual people and actual artists who overwhelmingly did not agree to train anything with their work and can no longer wrest their work from the machine now that it's been stolen from them.
It also isn't 'intelligent' at all, considering it has that word in the name. Think of genAI like an alien learning our language with absolutely no frame of reference for what it's learning. It can predict that the letters "w-e" and "c-a-n" often come after the letters "y-e-s" because the phrase "yes we can" will come up often in training data, it's a common phrase. But it doesn't actually understand what any of those words MEAN. Just that they often follow one another so that when prompted it will, statistically, try put those letters and words together again.
So when it comes to actually writing or responding to prompts what you're getting is the most likely outcome based on a massive amount of data input. It is not actually giving you feedback on what your writing looks like, it's giving you the most statistically possible response based on input. It's fake feedback, a thousand other feedbacks crammed together and extruded into a goo that looks and sounds like feedback but is actually meaningless. ChatGPT doesn't understand your writing sample anymore than a phone tree understands your anger and desperation when you continue to say "OPERATOR" as clearly as you can to try to get through to a real human. Both understand you input a word and will output based on that, but context, emotions, cultural mores etc. are all beyond it.
This is why AI is so absurdly shitty at things like math, counting letters in words and identifying words that start with the same letter. It's mashing together a million math problem answers betting on the likelihood that statistically someone has already answered that question enough times in the training data that it can spit the correct answer out at you.
TLDR: If you're using genAI to get feedback on your writing you're not actually getting feedback on your writing at all, but the most statistically probable set of words that relate to feedback. So right off the bat the idea that genAI is going to help you be a better writer is just flat wrong. It doesn't know how to write, it doesn't even know how many Rs are in the word 'strawberry'.
Second point has the same issues as the first:

I actually agree with them on the point that if your brain doesn't handle certain writer activities well it's perfectly okay to use an outside source for help with it. GenAI isn't actually helping you be a better writer, though; it can't. It doesn't understand anything you write nor can it provide meaningful feedback when it's just spitting out statistically probably words to you based on your input. So while the point here is actually good on the surface, the solution of using genAI to help people who have trouble with certain aspects of writing is still not correct.
The final point:

Again, this is a very good point... if it wasn't being made in conjunction with a defense of generative AI WHICH DOES NOT HELP OR SOLVE THIS ISSUE. In fact, because of the known issues of bias in how genAI LLMs are built they can make issues for marginalized writers worse.
I genuinely have no idea how this very true paragraph about people who are routinely pushed out of traditional writing spaces is helped by genAI. Their entire point thus far seems to be that genAI is a 'cheap' alternative to some traditional writing aids but considering genAI doesn't work like that it's all dead in the water as far as I'm concerned.
If NaNoWriMo was actually concerned with solving these access issues to things they consider critical to writing in general, why not offer a place for real people to read and critique one another on their platform? There are myriad other technological solutions that don't cost huge amounts of water AND actually help aspiring writers!
All of this to say that you should write for yourself, write what you enjoy and get better the same way generations of people before you have: by reading other people's work, talking to and exchanging time with other authors and writing and rewriting in your own words until you're satisfied.
Wasting water asking genAI to do things for you that would make you a better writer to do yourself or with trusted allies is just that, a waste.
118 notes
·
View notes
Text
Auto-Generated Junk Web Sites
I don't know if you heard the complaints about Google getting worse since 2018, or about Amazon getting worse. Some people think Google got worse at search. I think Google got worse because the web got worse. Amazon got worse because the supply side on Amazon got worse, but ultimately Amazon is to blame for incentivising the sale of more and cheaper products on its platform.
In any case, if you search something on Google, you get a lot of junk, and if you search for a specific product on Amazon, you get a lot of junk, even though the process that led to the junk is very different.
I don't subscribe to the "Dead Internet Theory", the idea that most online content is social media and that most social media is bots. I think Google search has gotten worse because a lot of content from as recently as 2018 got deleted, and a lot of web 1.0 and the blogosphere got deleted, comment sections got deleted, and content in the style of web 1.0 and the blogosphere is no longer produced. Furthermore, many links are now broken because they don't directly link to web pages, but to social media accounts and tweets that used to aggregate links.
I don't think going back to web 1.0 will help discoverability, and it probably won't be as profitable or even monetiseable to maintain a useful web 1.0 page compared to an entertaining but ephemeral YouTube channel. Going back to Web 1.0 means more long-term after-hours labour of love site maintenance, and less social media posting as a career.
Anyway, Google has gotten noticeably worse since GPT-3 and ChatGPT were made available to the general public, and many people blame content farms with language models and image synthesis for this. I am not sure. If Google had started to show users meaningless AI generated content from large content farms, that means Google has finally lost the SEO war, and Google is worse at AI/language models than fly-by-night operations whose whole business model is skimming clicks off Google.
I just don't think that's true. I think the reality is worse.
Real web sites run by real people are getting overrun by AI-generated junk, and human editors can't stop it. Real people whose job it is to generate content are increasingly turning in AI junk at their jobs.
Furthermore, even people who are setting up a web site for a local business or an online presence for their personal brand/CV are using auto-generated text.
I have seen at least two different TV commercials by web hosting and web design companies that promoted this. Are you starting your own business? Do you run a small business? A business needs a web site. With our AI-powered tools, you don't have to worry about the content of your web site. We generate it for you.
There are companies out there today, selling something that's probably a re-labelled ChatGPT or LLaMA plus Stable Diffusion to somebody who is just setting up a bicycle repair shop. All the pictures and written copy on the web presence for that repair shop will be automatically generated.
We would be living in a much better world if there was a small number of large content farms and bot operators poisoning our search results. Instead, we are living in a world where many real people are individually doing their part.
164 notes
·
View notes
Note
Your discussions on AI art have been really interesting and changed my mind on it quite a bit, so thank you for that! I don’t think I’m interested in using it, but I feel much less threatened by it in the same way. That being said, I was wondering, how you felt about AI generated creative writing: not, like AI writing in the context of garbage listicles or academic essays, but like, people who generate short stories and then submit them to contests. Do you think it’s the same sort of situation as AI art? Do you think there’s a difference in ChatGPT vs mid journey? Legitimate curiosity here! I don’t quite have an opinion on this in the same way, and I’ve seen v little from folks about creative writing in particular vs generated academic essays/articles
i think that ai generated writing is also indisputably writing but it is mostly really really fucking awful writing for the same reason that most ai art is not good art -- that the large training sets and low 'temperature' of commercially available/mass market models mean that anything produced will be the most generic version of itself. i also think that narrative writing is very very poorly suited to LLM generation because it generally requires very basic internal logic which LLMs are famously bad at (i imagine you'd have similar problems trying to create something visual like a comic that requires consistent character or location design rather than the singular images that AI art is mostly used for). i think it's going to be a very long time before we see anything good long-form from an LLM, especially because it's just not a priority for the people making them.
ultimately though i think you could absolutely do some really cool stuff with AI generated text if you had a tighter training set and let it get a bit wild with it. i've really enjoyed a lot of AI writing for being funny, especially when it was being done with tools like botnik that involve more human curation but still have the ability to completely blindside you with choices -- i unironically think the botnik collegehumour sketch is funnier than anything human-written on the channel. & i think that means it could reliably be used, with similar levels of curation, to make some stuff that feels alien, or unsettling, or etheral, or horrifying, because those are somewhat adjacent to the surreal humour i think it excels at. i could absolutely see it being used in workflows -- one of my friends told me recently, essentially, "if i'm stuck with writer's block, i ask chatgpt what should happen next, it gives me a horrible idea, and i immediately think 'that's shit, and i can do much better' and start writing again" -- which is both very funny but i think presents a great use case as a 'rubber duck'.
but yea i think that if there's anything good to be found in AI-written fiction or poetry it's not going to come from chatGPT specifically, it's going to come from some locally hosted GPT model trained on a curated set of influences -- and will have to either be kind of incoherent or heavily curated into coherence.
that said the submission of AI-written stories to short story mags & such fucking blows -- not because it's "not writing" but because it's just bad writing that's very very easy to produce (as in, 'just tell chatGPT 'write a short story'-easy) -- which ofc isn't bad in and of itself but means that the already existing phenomenon of people cynically submitting awful garbage to literary mags that doesn't even meet the submission guidelines has been magnified immensely and editors are finding it hard to keep up. i think part of believing that generative writing and art are legitimate mediums is also believing they are and should be treated as though they are separate mediums -- i don't think that there's no skill in these disciplines (like, if someone managed to make writing with chatGPT that wasnt unreadably bad, i would be very fucking impressed!) but they're deeply different skills to the traditional artforms and so imo should be in general judged, presented, published etc. separately.
211 notes
·
View notes
Text
"how do I keep my art from being scraped for AI from now on?"
if you post images online, there's no 100% guaranteed way to prevent this, and you can probably assume that there's no need to remove/edit existing content. you might contest this as a matter of data privacy and workers' rights, but you might also be looking for smaller, more immediate actions to take.
...so I made this list! I can't vouch for the effectiveness of all of these, but I wanted to compile as many options as possible so you can decide what's best for you.
Discouraging data scraping and "opting out"
robots.txt - This is a file placed in a website's home directory to "ask" web crawlers not to access certain parts of a site. If you have your own website, you can edit this yourself, or you can check which crawlers a site disallows by adding /robots.txt at the end of the URL. This article has instructions for blocking some bots that scrape data for AI.
HTML metadata - DeviantArt (i know) has proposed the "noai" and "noimageai" meta tags for opting images out of machine learning datasets, while Mojeek proposed "noml". To use all three, you'd put the following in your webpages' headers:
<meta name="robots" content="noai, noimageai, noml">
Have I Been Trained? - A tool by Spawning to search for images in the LAION-5B and LAION-400M datasets and opt your images and web domain out of future model training. Spawning claims that Stability AI and Hugging Face have agreed to respect these opt-outs. Try searching for usernames!
Kudurru - A tool by Spawning (currently a Wordpress plugin) in closed beta that purportedly blocks/redirects AI scrapers from your website. I don't know much about how this one works.
ai.txt - Similar to robots.txt. A new type of permissions file for AI training proposed by Spawning.
ArtShield Watermarker - Web-based tool to add Stable Diffusion's "invisible watermark" to images, which may cause an image to be recognized as AI-generated and excluded from data scraping and/or model training. Source available on GitHub. Doesn't seem to have updated/posted on social media since last year.
Image processing... things
these are popular now, but there seems to be some confusion regarding the goal of these tools; these aren't meant to "kill" AI art, and they won't affect existing models. they won't magically guarantee full protection, so you probably shouldn't loudly announce that you're using them to try to bait AI users into responding
Glaze - UChicago's tool to add "adversarial noise" to art to disrupt style mimicry. Devs recommend glazing pictures last. Runs on Windows and Mac (Nvidia GPU required)
WebGlaze - Free browser-based Glaze service for those who can't run Glaze locally. Request an invite by following their instructions.
Mist - Another adversarial noise tool, by Psyker Group. Runs on Windows and Linux (Nvidia GPU required) or on web with a Google Colab Notebook.
Nightshade - UChicago's tool to distort AI's recognition of features and "poison" datasets, with the goal of making it inconvenient to use images scraped without consent. The guide recommends that you do not disclose whether your art is nightshaded. Nightshade chooses a tag that's relevant to your image. You should use this word in the image's caption/alt text when you post the image online. This means the alt text will accurately describe what's in the image-- there is no reason to ever write false/mismatched alt text!!! Runs on Windows and Mac (Nvidia GPU required)
Sanative AI - Web-based "anti-AI watermark"-- maybe comparable to Glaze and Mist. I can't find much about this one except that they won a "Responsible AI Challenge" hosted by Mozilla last year.
Just Add A Regular Watermark - It doesn't take a lot of processing power to add a watermark, so why not? Try adding complexities like warping, changes in color/opacity, and blurring to make it more annoying for an AI (or human) to remove. You could even try testing your watermark against an AI watermark remover. (the privacy policy claims that they don't keep or otherwise use your images, but use your own judgment)
given that energy consumption was the focus of some AI art criticism, I'm not sure if the benefits of these GPU-intensive tools outweigh the cost, and I'd like to know more about that. in any case, I thought that people writing alt text/image descriptions more often would've been a neat side effect of Nightshade being used, so I hope to see more of that in the future, at least!
242 notes
·
View notes
Text
Artificial Intelligence Risk
about a month ago i got into my mind the idea of trying the format of video essay, and the topic i came up with that i felt i could more or less handle was AI risk and my objections to yudkowsky. i wrote the script but then soon afterwards i ran out of motivation to do the video. still i didnt want the effort to go to waste so i decided to share the text, slightly edited here. this is a LONG fucking thing so put it aside on its own tab and come back to it when you are comfortable and ready to sink your teeth on quite a lot of reading
Anyway, let’s talk about AI risk
I’m going to be doing a very quick introduction to some of the latest conversations that have been going on in the field of artificial intelligence, what are artificial intelligences exactly, what is an AGI, what is an agent, the orthogonality thesis, the concept of instrumental convergence, alignment and how does Eliezer Yudkowsky figure in all of this.
If you are already familiar with this you can skip to section two where I’m going to be talking about yudkowsky’s arguments for AI research presenting an existential risk to, not just humanity, or even the world, but to the entire universe and my own tepid rebuttal to his argument.
Now, I SHOULD clarify, I am not an expert on the field, my credentials are dubious at best, I am a college drop out from the career of computer science and I have a three year graduate degree in video game design and a three year graduate degree in electromechanical instalations. All that I know about the current state of AI research I have learned by reading articles, consulting a few friends who have studied about the topic more extensevily than me,
and watching educational you tube videos so. You know. Not an authority on the matter from any considerable point of view and my opinions should be regarded as such.
So without further ado, let’s get in on it.
PART ONE, A RUSHED INTRODUCTION ON THE SUBJECT
1.1 general intelligence and agency
lets begin with what counts as artificial intelligence, the technical definition for artificial intelligence is, eh…, well, why don’t I let a Masters degree in machine intelligence explain it:

Now let’s get a bit more precise here and include the definition of AGI, Artificial General intelligence. It is understood that classic ai’s such as the ones we have in our videogames or in alpha GO or even our roombas, are narrow Ais, that is to say, they are capable of doing only one kind of thing. They do not understand the world beyond their field of expertise whether that be within a videogame level, within a GO board or within you filthy disgusting floor.
AGI on the other hand is much more, well, general, it can have a multimodal understanding of its surroundings, it can generalize, it can extrapolate, it can learn new things across multiple different fields, it can come up with solutions that account for multiple different factors, it can incorporate new ideas and concepts. Essentially, a human is an agi. So far that is the last frontier of AI research, and although we are not there quite yet, it does seem like we are doing some moderate strides in that direction. We’ve all seen the impressive conversational and coding skills that GPT-4 has and Google just released Gemini, a multimodal AI that can understand and generate text, sounds, images and video simultaneously. Now, of course it has its limits, it has no persistent memory, its contextual window while larger than previous models is still relatively small compared to a human (contextual window means essentially short term memory, how many things can it keep track of and act coherently about).
And yet there is one more factor I haven’t mentioned yet that would be needed to make something a “true” AGI. That is Agency. To have goals and autonomously come up with plans and carry those plans out in the world to achieve those goals. I as a person, have agency over my life, because I can choose at any given moment to do something without anyone explicitly telling me to do it, and I can decide how to do it. That is what computers, and machines to a larger extent, don’t have. Volition.
So, Now that we have established that, allow me to introduce yet one more definition here, one that you may disagree with but which I need to establish in order to have a common language with you such that I can communicate these ideas effectively. The definition of intelligence. It’s a thorny subject and people get very particular with that word because there are moral associations with it. To imply that someone or something has or hasn’t intelligence can be seen as implying that it deserves or doesn’t deserve admiration, validity, moral worth or even personhood. I don’t care about any of that dumb shit. The way Im going to be using intelligence in this video is basically “how capable you are to do many different things successfully”. The more “intelligent” an AI is, the more capable of doing things that AI can be. After all, there is a reason why education is considered such a universally good thing in society. To educate a child is to uplift them, to expand their world, to increase their opportunities in life. And the same goes for AI. I need to emphasize that this is just the way I’m using the word within the context of this video, I don’t care if you are a psychologist or a neurosurgeon, or a pedagogue, I need a word to express this idea and that is the word im going to use, if you don’t like it or if you think this is innapropiate of me then by all means, keep on thinking that, go on and comment about it below the video, and then go on to suck my dick.
Anyway. Now, we have established what an AGI is, we have established what agency is, and we have established how having more intelligence increases your agency. But as the intelligence of a given agent increases we start to see certain trends, certain strategies start to arise again and again, and we call this Instrumental convergence.
1.2 instrumental convergence
The basic idea behind instrumental convergence is that if you are an intelligent agent that wants to achieve some goal, there are some common basic strategies that you are going to turn towards no matter what. It doesn’t matter if your goal is as complicated as building a nuclear bomb or as simple as making a cup of tea. These are things we can reliably predict any AGI worth its salt is going to try to do.
First of all is self-preservation. Its going to try to protect itself. When you want to do something, being dead is usually. Bad. its counterproductive. Is not generally recommended. Dying is widely considered unadvisable by 9 out of every ten experts in the field. If there is something that it wants getting done, it wont get done if it dies or is turned off, so its safe to predict that any AGI will try to do things in order not be turned off. How far it may go in order to do this? Well… [wouldn’t you like to know weather boy].
Another thing it will predictably converge towards is goal preservation. That is to say, it will resist any attempt to try and change it, to alter it, to modify its goals. Because, again, if you want to accomplish something, suddenly deciding that you want to do something else is uh, not going to accomplish the first thing, is it? Lets say that you want to take care of your child, that is your goal, that is the thing you want to accomplish, and I come to you and say, here, let me change you on the inside so that you don’t care about protecting your kid. Obviously you are not going to let me, because if you stopped caring about your kids, then your kids wouldn’t be cared for or protected. And you want to ensure that happens, so caring about something else instead is a huge no-no- which is why, if we make AGI and it has goals that we don’t like it will probably resist any attempt to “fix” it.
And finally another goal that it will most likely trend towards is self improvement. Which can be more generalized to “resource acquisition”. If it lacks capacities to carry out a plan, then step one of that plan will always be to increase capacities. If you want to get something really expensive, well first you need to get money. If you want to increase your chances of getting a high paying job then you need to get education, if you want to get a partner you need to increase how attractive you are. And as we established earlier, if intelligence is the thing that increases your agency, you want to become smarter in order to do more things. So one more time, is not a huge leap at all, it is not a stretch of the imagination, to say that any AGI will probably seek to increase its capabilities, whether by acquiring more computation, by improving itself, by taking control of resources.
All these three things I mentioned are sure bets, they are likely to happen and safe to assume. They are things we ought to keep in mind when creating AGI.
Now of course, I have implied a sinister tone to all these things, I have made all this sound vaguely threatening, haven’t i?. There is one more assumption im sneaking into all of this which I haven’t talked about. All that I have mentioned presents a very callous view of AGI, I have made it apparent that all of these strategies it may follow will go in conflict with people, maybe even go as far as to harm humans. Am I impliying that AGI may tend to be… Evil???
1.3 The Orthogonality thesis
Well, not quite.
We humans care about things. Generally. And we generally tend to care about roughly the same things, simply by virtue of being humans. We have some innate preferences and some innate dislikes. We have a tendency to not like suffering (please keep in mind I said a tendency, im talking about a statistical trend, something that most humans present to some degree). Most of us, baring social conditioning, would take pause at the idea of torturing someone directly, on purpose, with our bare hands. (edit bear paws onto my hands as I say this). Most would feel uncomfortable at the thought of doing it to multitudes of people. We tend to show a preference for food, water, air, shelter, comfort, entertainment and companionship. This is just how we are fundamentally wired. These things can be overcome, of course, but that is the thing, they have to be overcome in the first place.
An AGI is not going to have the same evolutionary predisposition to these things like we do because it is not made of the same things a human is made of and it was not raised the same way a human was raised.
There is something about a human brain, in a human body, flooded with human hormones that makes us feel and think and act in certain ways and care about certain things.
All an AGI is going to have is the goals it developed during its training, and will only care insofar as those goals are met. So say an AGI has the goal of going to the corner store to bring me a pack of cookies. In its way there it comes across an anthill in its path, it will probably step on the anthill because to take that step takes it closer to the corner store, and why wouldn’t it step on the anthill? Was it programmed with some specific innate preference not to step on ants? No? then it will step on the anthill and not pay any mind to it.
Now lets say it comes across a cat. Same logic applies, if it wasn’t programmed with an inherent tendency to value animals, stepping on the cat wont slow it down at all.
Now let’s say it comes across a baby.
Of course, if its intelligent enough it will probably understand that if it steps on that baby people might notice and try to stop it, most likely even try to disable it or turn it off so it will not step on the baby, to save itself from all that trouble. But you have to understand that it wont stop because it will feel bad about harming a baby or because it understands that to harm a baby is wrong. And indeed if it was powerful enough such that no matter what people did they could not stop it and it would suffer no consequence for killing the baby, it would have probably killed the baby.
If I need to put it in gross, inaccurate terms for you to get it then let me put it this way. Its essentially a sociopath. It only cares about the wellbeing of others in as far as that benefits it self. Except human sociopaths do care nominally about having human comforts and companionship, albeit in a very instrumental way, which will involve some manner of stable society and civilization around them. Also they are only human, and are limited in the harm they can do by human limitations. An AGI doesn’t need any of that and is not limited by any of that.
So ultimately, much like a car’s goal is to move forward and it is not built to care about wether a human is in front of it or not, an AGI will carry its own goals regardless of what it has to sacrifice in order to carry that goal effectively. And those goals don’t need to include human wellbeing.
Now With that said. How DO we make it so that AGI cares about human wellbeing, how do we make it so that it wants good things for us. How do we make it so that its goals align with that of humans?
1.4 Alignment.
Alignment… is hard [cue hitchhiker’s guide to the galaxy scene about the space being big]
This is the part im going to skip over the fastest because frankly it’s a deep field of study, there are many current strategies for aligning AGI, from mesa optimizers, to reinforced learning with human feedback, to adversarial asynchronous AI assisted reward training to uh, sitting on our asses and doing nothing. Suffice to say, none of these methods are perfect or foolproof.
One thing many people like to gesture at when they have not learned or studied anything about the subject is the three laws of robotics by isaac Asimov, a robot should not harm a human or allow by inaction to let a human come to harm, a robot should do what a human orders unless it contradicts the first law and a robot should preserve itself unless that goes against the previous two laws. Now the thing Asimov was prescient about was that these laws were not just “programmed” into the robots. These laws were not coded into their software, they were hardwired, they were part of the robot’s electronic architecture such that a robot could not ever be without those three laws much like a car couldn’t run without wheels.
In this Asimov realized how important these three laws were, that they had to be intrinsic to the robot’s very being, they couldn’t be hacked or uninstalled or erased. A robot simply could not be without these rules. Ideally that is what alignment should be. When we create an AGI, it should be made such that human values are its fundamental goal, that is the thing they should seek to maximize, instead of instrumental values, that is to say something they value simply because it allows it to achieve something else.
But how do we even begin to do that? How do we codify “human values” into a robot? How do we define “harm” for example? How do we even define “human”??? how do we define “happiness”? how do we explain a robot what is right and what is wrong when half the time we ourselves cannot even begin to agree on that? these are not just technical questions that robotic experts have to find the way to codify into ones and zeroes, these are profound philosophical questions to which we still don’t have satisfying answers to.
Well, the best sort of hack solution we’ve come up with so far is not to create bespoke fundamental axiomatic rules that the robot has to follow, but rather train it to imitate humans by showing it a billion billion examples of human behavior. But of course there is a problem with that approach. And no, is not just that humans are flawed and have a tendency to cause harm and therefore to ask a robot to imitate a human means creating something that can do all the bad things a human does, although that IS a problem too. The real problem is that we are training it to *imitate* a human, not to *be* a human.
To reiterate what I said during the orthogonality thesis, is not good enough that I, for example, buy roses and give massages to act nice to my girlfriend because it allows me to have sex with her, I am not merely imitating or performing the rol of a loving partner because her happiness is an instrumental value to my fundamental value of getting sex. I should want to be nice to my girlfriend because it makes her happy and that is the thing I care about. Her happiness is my fundamental value. Likewise, to an AGI, human fulfilment should be its fundamental value, not something that it learns to do because it allows it to achieve a certain reward that we give during training. Because if it only really cares deep down about the reward, rather than about what the reward is meant to incentivize, then that reward can very easily be divorced from human happiness.
Its goodharts law, when a measure becomes a target, it ceases to be a good measure. Why do students cheat during tests? Because their education is measured by grades, so the grades become the target and so students will seek to get high grades regardless of whether they learned or not. When trained on their subject and measured by grades, what they learn is not the school subject, they learn to get high grades, they learn to cheat.
This is also something known in psychology, punishment tends to be a poor mechanism of enforcing behavior because all it teaches people is how to avoid the punishment, it teaches people not to get caught. Which is why punitive justice doesn’t work all that well in stopping recividism and this is why the carceral system is rotten to core and why jail should be fucking abolish-[interrupt the transmission]
Now, how is this all relevant to current AI research? Well, the thing is, we ended up going about the worst possible way to create alignable AI.
1.5 LLMs (large language models)
This is getting way too fucking long So, hurrying up, lets do a quick review of how do Large language models work. We create a neural network which is a collection of giant matrixes, essentially a bunch of numbers that we add and multiply together over and over again, and then we tune those numbers by throwing absurdly big amounts of training data such that it starts forming internal mathematical models based on that data and it starts creating coherent patterns that it can recognize and replicate AND extrapolate! if we do this enough times with matrixes that are big enough and then when we start prodding it for human behavior it will be able to follow the pattern of human behavior that we prime it with and give us coherent responses.
(takes a big breath)this “thing” has learned. To imitate. Human. Behavior.
Problem is, we don’t know what “this thing” actually is, we just know that *it* can imitate humans.
You caught that?
What you have to understand is, we don’t actually know what internal models it creates, we don’t know what are the patterns that it extracted or internalized from the data that we fed it, we don’t know what are the internal rules that decide its behavior, we don’t know what is going on inside there, current LLMs are a black box. We don’t know what it learned, we don’t know what its fundamental values are, we don’t know how it thinks or what it truly wants. all we know is that it can imitate humans when we ask it to do so. We created some inhuman entity that is moderatly intelligent in specific contexts (that is to say, very capable) and we trained it to imitate humans. That sounds a bit unnerving doesn’t it?
To be clear, LLMs are not carefully crafted piece by piece. This does not work like traditional software where a programmer will sit down and build the thing line by line, all its behaviors specified. Is more accurate to say that LLMs, are grown, almost organically. We know the process that generates them, but we don’t know exactly what it generates or how what it generates works internally, it is a mistery. And these things are so big and so complicated internally that to try and go inside and decipher what they are doing is almost intractable.
But, on the bright side, we are trying to tract it. There is a big subfield of AI research called interpretability, which is actually doing the hard work of going inside and figuring out how the sausage gets made, and they have been doing some moderate progress as of lately. Which is encouraging. But still, understanding the enemy is only step one, step two is coming up with an actually effective and reliable way of turning that potential enemy into a friend.
Puff! Ok so, now that this is all out of the way I can go onto the last subject before I move on to part two of this video, the character of the hour, the man the myth the legend. The modern day Casandra. Mr chicken little himself! Sci fi author extraordinaire! The mad man! The futurist! The leader of the rationalist movement!
1.5 Yudkowsky
Eliezer S. Yudkowsky born September 11, 1979, wait, what the fuck, September eleven? (looks at camera) yudkowsky was born on 9/11, I literally just learned this for the first time! What the fuck, oh that sucks, oh no, oh no, my condolences, that’s terrible…. Moving on. he is an American artificial intelligence researcher and writer on decision theory and ethics, best known for popularizing ideas related to friendly artificial intelligence, including the idea that there might not be a "fire alarm" for AI He is the founder of and a research fellow at the Machine Intelligence Research Institute (MIRI), a private research nonprofit based in Berkeley, California. Or so says his Wikipedia page.
Yudkowsky is, shall we say, a character. a very eccentric man, he is an AI doomer. Convinced that AGI, once finally created, will most likely kill all humans, extract all valuable resources from the planet, disassemble the solar system, create a dyson sphere around the sun and expand across the universe turning all of the cosmos into paperclips. Wait, no, that is not quite it, to properly quote,( grabs a piece of paper and very pointedly reads from it) turn the cosmos into tiny squiggly molecules resembling paperclips whose configuration just so happens to fulfill the strange, alien unfathomable terminal goal they ended up developing in training. So you know, something totally different.
And he is utterly convinced of this idea, has been for over a decade now, not only that but, while he cannot pinpoint a precise date, he is confident that, more likely than not it will happen within this century. In fact most betting markets seem to believe that we will get AGI somewhere in the mid 30’s.
His argument is basically that in the field of AI research, the development of capabilities is going much faster than the development of alignment, so that AIs will become disproportionately powerful before we ever figure out how to control them. And once we create unaligned AGI we will have created an agent who doesn’t care about humans but will care about something else entirely irrelevant to us and it will seek to maximize that goal, and because it will be vastly more intelligent than humans therefore we wont be able to stop it. In fact not only we wont be able to stop it, there wont be a fight at all. It will carry out its plans for world domination in secret without us even detecting it and it will execute it before any of us even realize what happened. Because that is what a smart person trying to take over the world would do.
This is why the definition I gave of intelligence at the beginning is so important, it all hinges on that, intelligence as the measure of how capable you are to come up with solutions to problems, problems such as “how to kill all humans without being detected or stopped”. And you may say well now, intelligence is fine and all but there are limits to what you can accomplish with raw intelligence, even if you are supposedly smarter than a human surely you wouldn’t be capable of just taking over the world uninmpeeded, intelligence is not this end all be all superpower. Yudkowsky would respond that you are not recognizing or respecting the power that intelligence has. After all it was intelligence what designed the atom bomb, it was intelligence what created a cure for polio and it was intelligence what made it so that there is a human foot print on the moon.
Some may call this view of intelligence a bit reductive. After all surely it wasn’t *just* intelligence what did all that but also hard physical labor and the collaboration of hundreds of thousands of people. But, he would argue, intelligence was the underlying motor that moved all that. That to come up with the plan and to convince people to follow it and to delegate the tasks to the appropriate subagents, it was all directed by thought, by ideas, by intelligence. By the way, so far I am not agreeing or disagreeing with any of this, I am merely explaining his ideas.
But remember, it doesn’t stop there, like I said during his intro, he believes there will be “no fire alarm”. In fact for all we know, maybe AGI has already been created and its merely bidding its time and plotting in the background, trying to get more compute, trying to get smarter. (to be fair, he doesn’t think this is right now, but with the next iteration of gpt? Gpt 5 or 6? Well who knows). He thinks that the entire world should halt AI research and punish with multilateral international treaties any group or nation that doesn’t stop. going as far as putting military attacks on GPU farms as sanctions of those treaties.
What’s more, he believes that, in fact, the fight is already lost. AI is already progressing too fast and there is nothing to stop it, we are not showing any signs of making headway with alignment and no one is incentivized to slow down. Recently he wrote an article called “dying with dignity” where he essentially says all this, AGI will destroy us, there is no point in planning for the future or having children and that we should act as if we are already dead. This doesn’t mean to stop fighting or to stop trying to find ways to align AGI, impossible as it may seem, but to merely have the basic dignity of acknowledging that we are probably not going to win. In every interview ive seen with the guy he sounds fairly defeatist and honestly kind of depressed. He truly seems to think its hopeless, if not because the AGI is clearly unbeatable and superior to humans, then because humans are clearly so stupid that we keep developing AI completely unregulated while making the tools to develop AI widely available and public for anyone to grab and do as they please with, as well as connecting every AI to the internet and to all mobile devices giving it instant access to humanity. and worst of all: we keep teaching it how to code. From his perspective it really seems like people are in a rush to create the most unsecured, wildly available, unrestricted, capable, hyperconnected AGI possible.
We are not just going to summon the antichrist, we are going to receive them with a red carpet and immediately hand it the keys to the kingdom before it even manages to fully get out of its fiery pit.
So. The situation seems dire, at least to this guy. Now, to be clear, only he and a handful of other AI researchers are on that specific level of alarm. The opinions vary across the field and from what I understand this level of hopelessness and defeatism is the minority opinion.
I WILL say, however what is NOT the minority opinion is that AGI IS actually dangerous, maybe not quite on the level of immediate, inevitable and total human extinction but certainly a genuine threat that has to be taken seriously. AGI being something dangerous if unaligned is not a fringe position and I would not consider it something to be dismissed as an idea that experts don’t take seriously.
Aaand here is where I step up and clarify that this is my position as well. I am also, very much, a believer that AGI would posit a colossal danger to humanity. That yes, an unaligned AGI would represent an agent smarter than a human, capable of causing vast harm to humanity and with no human qualms or limitations to do so. I believe this is not just possible but probable and likely to happen within our lifetimes.
So there. I made my position clear.
BUT!
With all that said. I do have one key disagreement with yudkowsky. And partially the reason why I made this video was so that I could present this counterargument and maybe he, or someone that thinks like him, will see it and either change their mind or present a counter-counterargument that changes MY mind (although I really hope they don’t, that would be really depressing.)
Finally, we can move on to part 2
PART TWO- MY COUNTERARGUMENT TO YUDKOWSKY
I really have my work cut out for me, don’t i? as I said I am not expert and this dude has probably spent far more time than me thinking about this. But I have seen most interviews that guy has been doing for a year, I have seen most of his debates and I have followed him on twitter for years now. (also, to be clear, I AM a fan of the guy, I have read hpmor, three worlds collide, the dark lords answer, a girl intercorrupted, the sequences, and I TRIED to read planecrash, that last one didn’t work out so well for me). My point is in all the material I have seen of Eliezer I don’t recall anyone ever giving him quite this specific argument I’m about to give.
It’s a limited argument. as I have already stated I largely agree with most of what he says, I DO believe that unaligned AGI is possible, I DO believe it would be really dangerous if it were to exist and I do believe alignment is really hard. My key disagreement is specifically about his point I descrived earlier, about the lack of a fire alarm, and perhaps, more to the point, to humanity’s lack of response to such an alarm if it were to come to pass.
All we would need, is a Chernobyl incident, what is that? A situation where this technology goes out of control and causes a lot of damage, of potentially catastrophic consequences, but not so bad that it cannot be contained in time by enough effort. We need a weaker form of AGI to try to harm us, maybe even present a believable threat of taking over the world, but not so smart that humans cant do anything about it. We need essentially an AI vaccine, so that we can finally start developing proper AI antibodies. “aintibodies”
In the past humanity was dazzled by the limitless potential of nuclear power, to the point that old chemistry sets, the kind that were sold to children, would come with uranium for them to play with. We were building atom bombs, nuclear stations, the future was very much based on the power of the atom. But after a couple of really close calls and big enough scares we became, as a species, terrified of nuclear power. Some may argue to the point of overcorrection. We became scared enough that even megalomaniacal hawkish leaders were able to take pause and reconsider using it as a weapon, we became so scared that we overregulated the technology to the point of it almost becoming economically inviable to apply, we started disassembling nuclear stations across the world and to slowly reduce our nuclear arsenal.
This is all a proof of concept that, no matter how alluring a technology may be, if we are scared enough of it we can coordinate as a species and roll it back, to do our best to put the genie back in the bottle. One of the things eliezer says over and over again is that what makes AGI different from other technologies is that if we get it wrong on the first try we don’t get a second chance. Here is where I think he is wrong: I think if we get AGI wrong on the first try, it is more likely than not that nothing world ending will happen. Perhaps it will be something scary, perhaps something really scary, but unlikely that it will be on the level of all humans dropping dead simultaneously due to diamonoid bacteria. And THAT will be our Chernobyl, that will be the fire alarm, that will be the red flag that the disaster monkeys, as he call us, wont be able to ignore.
Now WHY do I think this? Based on what am I saying this? I will not be as hyperbolic as other yudkowsky detractors and say that he claims AGI will be basically a god. The AGI yudkowsky proposes is not a god. Just a really advanced alien, maybe even a wizard, but certainly not a god.
Still, even if not quite on the level of godhood, this dangerous superintelligent AGI yudkowsky proposes would be impressive. It would be the most advanced and powerful entity on planet earth. It would be humanity’s greatest achievement.
It would also be, I imagine, really hard to create. Even leaving aside the alignment bussines, to create a powerful superintelligent AGI without flaws, without bugs, without glitches, It would have to be an incredibly complex, specific, particular and hard to get right feat of software engineering. We are not just talking about an AGI smarter than a human, that’s easy stuff, humans are not that smart and arguably current AI is already smarter than a human, at least within their context window and until they start hallucinating. But what we are talking about here is an AGI capable of outsmarting reality.
We are talking about an AGI smart enough to carry out complex, multistep plans, in which they are not going to be in control of every factor and variable, specially at the beginning. We are talking about AGI that will have to function in the outside world, crashing with outside logistics and sheer dumb chance. We are talking about plans for world domination with no unforeseen factors, no unexpected delays or mistakes, every single possible setback and hidden variable accounted for. Im not saying that an AGI capable of doing this wont be possible maybe some day, im saying that to create an AGI that is capable of doing this, on the first try, without a hitch, is probably really really really hard for humans to do. Im saying there are probably not a lot of worlds where humans fiddling with giant inscrutable matrixes stumble upon the right precise set of layers and weight and biases that give rise to the Doctor from doctor who, and there are probably a whole truckload of worlds where humans end up with a lot of incoherent nonsense and rubbish.
Im saying that AGI, when it fails, when humans screw it up, doesn’t suddenly become more powerful than we ever expected, its more likely that it just fails and collapses. To turn one of Eliezer’s examples against him, when you screw up a rocket, it doesn’t accidentally punch a worm hole in the fabric of time and space, it just explodes before reaching the stratosphere. When you screw up a nuclear bomb, you don’t get to blow up the solar system, you just get a less powerful bomb.
He presents a fully aligned AGI as this big challenge that humanity has to get right on the first try, but that seems to imply that building an unaligned AGI is just a simple matter, almost taken for granted. It may be comparatively easier than an aligned AGI, but my point is that already unaligned AGI is stupidly hard to do and that if you fail in building unaligned AGI, then you don’t get an unaligned AGI, you just get another stupid model that screws up and stumbles on itself the second it encounters something unexpected. And that is a good thing I’d say! That means that there is SOME safety margin, some space to screw up before we need to really start worrying. And further more, what I am saying is that our first earnest attempt at an unaligned AGI will probably not be that smart or impressive because we as humans would have probably screwed something up, we would have probably unintentionally programmed it with some stupid glitch or bug or flaw and wont be a threat to all of humanity.
Now here comes the hypothetical back and forth, because im not stupid and I can try to anticipate what Yudkowsky might argue back and try to answer that before he says it (although I believe the guy is probably smarter than me and if I follow his logic, I probably cant actually anticipate what he would argue to prove me wrong, much like I cant predict what moves Magnus Carlsen would make in a game of chess against me, I SHOULD predict that him proving me wrong is the likeliest option, even if I cant picture how he will do it, but you see, I believe in a little thing called debating with dignity, wink)
What I anticipate he would argue is that AGI, no matter how flawed and shoddy our first attempt at making it were, would understand that is not smart enough yet and try to become smarter, so it would lie and pretend to be an aligned AGI so that it can trick us into giving it access to more compute or just so that it can bid its time and create an AGI smarter than itself. So even if we don’t create a perfect unaligned AGI, this imperfect AGI would try to create it and succeed, and then THAT new AGI would be the world ender to worry about.
So two things to that, first, this is filled with a lot of assumptions which I don’t know the likelihood of. The idea that this first flawed AGI would be smart enough to understand its limitations, smart enough to convincingly lie about it and smart enough to create an AGI that is better than itself. My priors about all these things are dubious at best. Second, It feels like kicking the can down the road. I don’t think creating an AGI capable of all of this is trivial to make on a first attempt. I think its more likely that we will create an unaligned AGI that is flawed, that is kind of dumb, that is unreliable, even to itself and its own twisted, orthogonal goals.
And I think this flawed creature MIGHT attempt something, maybe something genuenly threatning, but it wont be smart enough to pull it off effortlessly and flawlessly, because us humans are not smart enough to create something that can do that on the first try. And THAT first flawed attempt, that warning shot, THAT will be our fire alarm, that will be our Chernobyl. And THAT will be the thing that opens the door to us disaster monkeys finally getting our shit together.
But hey, maybe yudkowsky wouldn’t argue that, maybe he would come with some better, more insightful response I cant anticipate. If so, im waiting eagerly (although not TOO eagerly) for it.
Part 3 CONCLUSSION
So.
After all that, what is there left to say? Well, if everything that I said checks out then there is hope to be had. My two objectives here were first to provide people who are not familiar with the subject with a starting point as well as with the basic arguments supporting the concept of AI risk, why its something to be taken seriously and not just high faluting wackos who read one too many sci fi stories. This was not meant to be thorough or deep, just a quick catch up with the bear minimum so that, if you are curious and want to go deeper into the subject, you know where to start. I personally recommend watching rob miles’ AI risk series on youtube as well as reading the series of books written by yudkowsky known as the sequences, which can be found on the website lesswrong. If you want other refutations of yudkowsky’s argument you can search for paul christiano or robin hanson, both very smart people who had very smart debates on the subject against eliezer.
The second purpose here was to provide an argument against Yudkowskys brand of doomerism both so that it can be accepted if proven right or properly refuted if proven wrong. Again, I really hope that its not proven wrong. It would really really suck if I end up being wrong about this. But, as a very smart person said once, what is true is already true, and knowing it doesn’t make it any worse. If the sky is blue I want to believe that the sky is blue, and if the sky is not blue then I don’t want to believe the sky is blue.
This has been a presentation by FIP industries, thanks for watching.
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nightshade
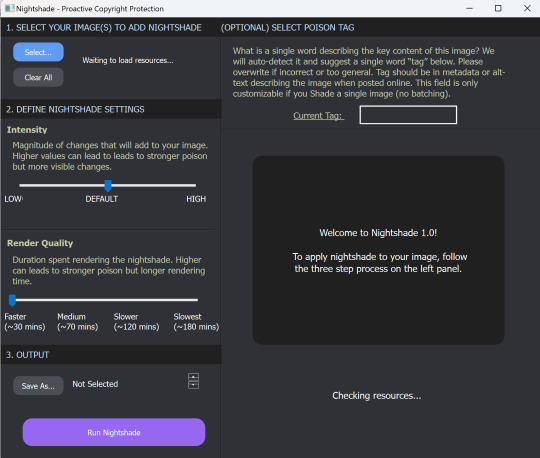
Guys, this is really easy. I just ran my first render on Nightshade, and it's very simple to use.
What is Nightshade?
It's software to "poison" the AI image-"generating" models which scrape your art without permission. It works by telling the AI software that this car is really a cow, or something similarly improbable, so that someone using that scraped art to "generate" a car will get a cow instead. This makes stealing art dangerous and costly and ineffective.
Thieving tech-bro: "That's so mean! They're poisoning our data!"
Hey, you know the absolutely guaranteed way to make sure you don't eat brownies full of laxatives? Don't steal brownies out of someone else's lunch in the break room fridge. This will only poison data that's stolen. Be ethical, be unaffected.
Download Nightshade here.
How To Use Nightshade
First, you can choose how intense to make the poison. :D It does increase render time, but that's okay, we know wars aren't won in a moment.
You can specify a tag for your primary image content ("fire," "rabbit," "forest," etc.) to establish content for the scrapers, and it reminds you to use this tag in the alt text and description, and in the post, for maximum impact.
Nightshade takes a while to download and then again to update libraries on first open, but that's a one-time thing. And then it takes a while to render, but again, we are here to preserve art and save the internet, so I can wait a bit to post.
And the output quality is good! Allegedly there are some image effects, but I'm not good enough to spot the difference when I have the before and after together.
Tips:
The guide says to run Nightshade last, after resizing, watermarking, etc. This will be most effective.
Do Nightshade before Glaze, if you choose to do both.
Render in PNG for best results but it's okay to convert to JPG after.
Remember to use your content tag in alt test, description, and your post! This is exactly where you'd be putting accessibility text anyway, so it's good practice with or without Nightshade.
Please share, please protect!
Note: I'm not an artist, I'm a writer, but I'm using Nightshade on promo images I'm putting together for a future project, because those software companies didn't buy that stock art either and I won't make it available to them for free on the license I purchased.

Please share, please protect!
(Now, speaking as a writer, I wish we had something similar for text!)
47 notes
·
View notes
Note
Why do you like AI art?
The simple and biggest answer is that it lets people create and experience art that would not otherwise exist. And in particular, it lets me give life to the images in my head without needing to destroy my wrists in the process. Even without anything else, that would be enough.
For a more specific answer - the way I see it, there are two main ways of approaching AI art. The artist can aim for the expectations of other art forms, or they can lean into ones specific to AI. I think both of these approaches have significant merit, and much more flexibility than most people realize. I've seen many incredible examples of each approach, and I share them whenever I can.
As someone who tends to feel like a crude imitation of a human, I have deep investment in the idea that mimicking actions expected of a human is just as meaningful as doing them "normally". And, for that matter, the idea that not acting "normally" is not a flaw in the first place. So I wholeheartedly reject the idea that either of these things could be held against AI, and I find that idea incompatible with accepting me as a person.
Some people accuse image generators of creating collages, but that could not be further from the truth. AI models record patterns, not actual pieces of images. And I certainly can't agree with the idea that collages lack artistic merit in the first place. My blog banner is a collection of pre-existing images, my image edits are modifications to existing images, and I've been working on an AMV that combines clips of an existing show with the audio of an existing song. All of these involve using copyrighted material without permission from the copyright holders, and I reject the idea that I should need that permission, just as I reject the idea that training an AI model on copyrighted material should require permission.
I also write. Writing does not involve creating an image directly, but it involves creating text that others might depict in their mind as an image. And writing an image prompt means creating text that an AI can depict digitally as an image. Just as writing stories is an artistic action, writing prompts is also an artistic action.
But there is so much more to image generation than writing prompts. Image generators can offer countless other controls, and the quality of AI art depends on its creator's skill in using them. AI art is a skilled pursuit, and while it does not require manual drawing, making good AI art requires assessing the generator's outputs and identifying ways to iterate on them.
AI art sometimes gets characterized as being under the thumb of big tech companies, but that is also false. Stable Diffusion is an open-source image generator you can run on your own computer, and I've personally done so. It's free, it's got countless independent add-ons to change the workings or to use different models, it doesn't require using anyone else's servers. It's great. And by having it locally, I can see for myself that the models are nowhere near big enough to actually contain the images they're trained on, and that the power consumption is no more than using the internet or playing a video game.
AI art offers an ocean of possibilities, both on its own and in conjunction with other art forms, and we've barely scratched the surface. I'm excited to see how much more we can do with it and to be as much a part of that as I can, and I think everyone should take a few minutes to try it out for themselves.
That is why I like AI art.
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to recognize AI "Art"
A post I have wanted to make for a long time because I think it's important to know! Please mind that this is not 100% accurate and I am by no means an expert on AI art. My knowledge on the topic comes from a semester of research on the development of AI art and how it has improved over the years. I wrote a pretty intense paper on it (I got an A on this!) and I am now using this knowledge to help identify AI art.
I often ask myself "did an actual person make this art or did they just generate it?" because I WANT TO SUPPORT ARTISTS WITH A REBLOG BUT AI "ART" IS NOT ART!!!!
Image description and tags, other posts by the same user
If there is no image description by OP, that's usually a bit sketchy. Also read tags other people have added in their reblogs!
And look at other posts from the same user!
Features blending
In an image where a person is wearing glasses, do they maybe merge into the skin a bit? (see Image 9)
Circular artefacts
TBH I forgot why they happen but one paper I studied discussed ways to remove them because they are an obvious giveaway that an image is artificial (see Image 10)

Image 1: Circular Artifacts [1]
4. Problems with text or other "logical composition stuff" (sorry I'm bad at words)
AI is bad at generating text! It looks like words, but it makes no sense. In Image 3, where does the cat's paw come from? (Also note here that DALL-E puts those coloured squares in the bottom right corner).
Take a closer look at the hands of the women in the image on the bottom right. How many are there? Hands are also a good indicator!


Image 2 [2], Image 3 [3]


Image 4 [4], Image 5 [5]
5. mismatched earrings/eyes... ("long range dependencies")
Human faces are symmetric, we (usually) have two eyes, two ears... That's a problem for AI. Earrings and eyecolours usually have to match. Either side may look perfectly fine, but when you look at is as a whole, it does not always work.
6. seems "too smooth"?
I've noticed a lack of texture. Brushstrokes are missing, everything seems just a little flat. There are definitely generative models that can emulate brush strokes, but watch out for backgrounds. They sometimes give it away!
7. read this article for a lot of additional information!
8. something I found in this article that is not mentioned: the harsh contrast
I have taken the below pictures from that article, and you can see some very "harsh" areas around the irises in the pictures with the eyes, or around the kids



Image 6, 7, 8 [6, 7, 8]
In the two images below, I have just marked some areas that seem off and I will briefly discuss why:


Image 9, Image 10 [9, 10]
Left (Image 9): In Halbrand's hair, there seems to be part of a crown or some other adornment, but it's not quite there. You can also see the general "smoothness" in this image. Another suspicious looking area is Galadriel's neck. Between their faces, you can see the mountain range in the background continue, but it stops exactly where the strand of hair is. On the right side of the image, there are some bright spots on the rocks that also look a bit weird.
Right (Image 10): I have marked some spots that I think look a bit like circular artifacts (that have probably already been "treated" by the generative model). On the bottom left side I have circled this jar? vase? Whatever. You can see that the lid and the rest of the object don't align.
Once again: DISCLAIMER - I could be wrong! This is really hard because the generative models get better.
Sources:
[1] D. Stap, M. Bleeker, S. Ibrahimi, and M. ter Hoeve. Conditional image generation and manipulation for user-specified content. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.04909, 2020.
[2] A. Ramesh, P. Dhariwal, A. Nichol, C. Chu, and M. Chen. Hierarchical text-conditional image generation with clip latents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.06125, 2022.
[3, 4] Generated by me using DALL-E for research purposes.
[5, 6, 7, 8] from this article, accessed on August 15 2023
[9, 10] posted by Tumblr user @ fandomfatale, accessed on August 15 2023
84 notes
·
View notes
Note
Ok. It's pretty clear you are more welcoming of AI, and it does have enough merits to not be given a knee jerk reaction outright.
And how the current anti-ai stealing programs could be misused.
But isn't so much of the models built on stolen art? That is one of the big thing keeping me from freely enjoying it.
The stolen art is a thing that needs to be addressed.
Though i agree that the ways that such addressing are being done in are not ideal. Counterproductive even.
I could make a quip here and be like "stolen art??? But the art is all still there, and it looks fine to me!" And that would be a salient point about the silliness of digital theft as a concept, but I know that wouldn't actually address your point because what you're actually talking about is art appropriation by generative AI models.
But the thing is that generative AI models don't really do that, either. They train on publicly posted images and derive a sort of metadata - more specifically, they build a feature space mapping out different visual concepts together with text that refers to them. This is then used at the generative stage in order to produce new images based on the denoising predictions of that abstract feature model. No output is created that hasn't gone through that multi-stage level of abstraction from the training data, and none of the original training images are directly used at all.
Due to various flaws in the process, you can sometimes get a model to output images extremely similar to particular training images, and it is also possible to get a model to pastiche a particular artist's work or style, but this is something that humans can also do and is a problem with the individual image that has been created, rather than the process in general.
Training an AI model is pretty clearly fair use, because you're not even really re-using the training images - you're deriving metadata that describes them, and using them to build new images. This is far more comparable to the process by which human artists learn concepts than the weird sort of "theft collage" that people seem to be convinced is going on. In many cases, the much larger training corpus of generative AI models means that an output will be far more abstracted from any identifiable source data (source data in fact is usually not identifiable) than a human being drawing from a reference, something we all agree is perfectly fine!
The only difference is that the AI process is happening in a computer with tangible data, and is therefore quantifiable. This seems to convince people that it is in some way more ontologically derivative than any other artistic process, because computers are assumed to be copying whereas the human brain can impart its own mystical juju of originality.
I'm a materialist and think this is very silly. The valid concerns around AI are to do with how society is unprepared for increased automation, but that's an entirely different conversation from the art theft one, and the latter actively distracts from the former. The complete refusal from some people to even engage with AI's existence out of disgust also makes it harder to solve the real problem around its implementation.
This sucks, because for a lot of people it's not really about copyright or intellectual property anyway. It's about that automation threat, and a sort of human condition anxiety about being supplanted and replaced by automation. That's a whole mess of emotions and genuine labour concerns that we need to work through and break down and resolve, but reactionary egg-throwing at all things related to machine learning is counterproductive to that, as is reading out legal mantras paraphrasing megacorps looking to expand copyright law to over shit like "art style".
I've spoken about this more elsewhere if you look at my blog's AI tag.
159 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why AI sucks so much
(And why it doesn't have to.)

AI sucks right now. Because it was never to be used, like it is used right now. Because the way AI is currently employed, it does the one thing, that was always meant to be human.
Look. AI has a ton of technological problems. I wrote about it before. Whenever you have some "AI Writer" or "AI Art", there is no intelligence there. There is only a probability algorithm that does some math. It is like the auto-complete on your phone, just a bit more complex, because it has been fed with basically the entire internet's worth of words and pictures. So, when the AI writes a story, it just knows that there is a high likelyhood that if it has been asked to write a fantasy story it might feature swords, magic and dragons. And then puts out a collection of words that is basically every fantasy story ever thrown into a blender. Same when it "draws". Why does it struggle so much with teeth and fingers? Well, because it just goes by likelihood. If it has drawn a finger, it knows there is a high likelihood that next to the finger is going to be another finger. So it draws one. Simple as that. Because it does not know, what a finger is. Only what it looks like.
And of course it does not fact check.
But all of that is not really the main problem. Because the main culture actually just is the general work culture, the capitalist economy and how we modelled it.
See, once upon a time there was this economist named Kaynes. And while he was a capitalist, he did in fact have quite a few good ideas and understood some things very well - like the fact that people are actually working better, if their basic needs have been taken care for. And he was very certain that in the future (he lived a hundred years ago) a lot of work could be done by automation, with the people still being paid for what the machines were doing. Hence having the people work for like 15 hours a week, but getting paid for a fulltime job - or even more.
And here is the thing: We could have that. Right now. Because we did in fact automate a lot of jobs and really a ton of jobs we have right now are just endless busywork. Instead of actually being productive, it only exists to keep up the appearance of productivity.
We already know that reducing the workdays to four a week or the workload to 30 or even 25 hours a week does not really decrease productivity. Especially with office jobs. Because the fact is that many, many jobs are not that much work and rather just involve people sitting in an office working like two hours a day and spending the rest with coffee kitchen talk or surfing the internet.
And there are tons of boring jobs we can already automate. I mean, with what I am working right now - analyzing surveying data - most I do is just put some parameters into an algorith and let the algorith do the work. While also part time training another algorithm, that basically automatically reads contracts to make notes what data a certain contract involves. (And contrary to what you might believe: No, it is not complicated. Especially those text analysis tasks are actually super simple to construct, once you get the hang of it.)
Which also means, that half of my workday usually is spend of just sitting here and watching a bar fill up. Especially with the surveying data, because it is large, large image files that at times take six to ten hours to process. And hint: Often I will end up letting the computer run over night to finish the task.
But that brings me to the question: What am I even doing here? Most of the time it takes like two hours to put the data in, run a small sample size for checking it and then letting it run afterwards. I do not need to be here for that. Yet, I do have to sit down for my seven and a half hours a day to collect my paycheck. And... It is kinda silly, right?
And of course there is the fact that we technically do have the technology to automate more and more menial tasks. Which would make a lot of sense, especially with the very dangerous kinda tasks, like within mining operations. Like, sure, that is a lot more work to automate, given that we would need robots that are actually able to navigate over all sorts of terrain, but... You know, it would probably save countless lives.
Same goes for many, many other areas. We could in fact automate a lot. Not everything (for example fruit picking is surprisingly hard to automate, it turns out), but a lot. Like a real lot.
And instead... they decided to automate art. One of the things that is the most human, because art for the most part depends on emotions and experience. Art is individual for the most part. It is formed by experience and reflection of the experience. And instead of seeing that, they decided to... create a probability generator for words and pixels.
So, why?
Well, first and foremost, because they (= the owner class) do want to keep us working. And with that I mean those menial, exhausting, mind-numbing jobs that we are forced to have right now. And they want us to keep working, because the more free time we have, the more time we have to organize and, well, rise up against the system, upon realizing how we are exploited. Work itself is used as a tool of oppression. Which is why, no matter how many studies show that the 30 hour week or 4 day week is actually good, that UBI actually helps people and what not, the companies are so against it. It is also why in some countries, like the US, the companies are so against paid sick leave, something that is scientifically speaking bonkers, because it actually harms the productivity of the company. And yes, it is also why still in the midth of a pandemic, we act as if everything is normal, because they found out that in the early pandemic under lock down and less people working, people actually fucking organized.
And that... also kinda is, why they hate art. Because art is something that is a reflection upon a world - and it can be an inspiration for people, something that gives them hope and something worth working towards to. So, artists are kinda dangerous. Hence something has to be done to keep them from working. In this case: Devaluing their work.
And no, I do not even think that the people programming those original algorithms were thinking this. They were not like "Yes, we need to do this to uphold the capitalist systems", nor do most of the AI bros, who are hyping it right now. But there are some people in there, who see it just like that. Who know the dangers of actual art and what it can mean for the system that keeps them powerful.
So, yeah... We could have some great stuff with AI and automation... If used in other areas.
I mean, just imagine what AIs could do under communism...

#solarpunk#cyberpunk#fuck ai art#fuck ai writing#anti ai art#anti ai writing#ubi#universal basic income#anti capitalism#bullshit jobs#automation
128 notes
·
View notes
Text
you know, thinking about the whole worry over data scraping images for LLMs and other generative algorithms, it's worth remembering that poisoning a data set is basically as simple as introducing elements that people wouldn't want to see in the generated end results.
things like text, jpeg compression artefacts, even filters and effects that add distortions and the like for visual style can still help break up the graphics and make it harder for an algorithmic system to parse, because - importantly - none of these systems understand any of the data they're being fed: they can't parse structure or meaning, only patterns, and thus any disruptive pattern you introduce can muck about with the learning process.
also, any kind of image they might not actually want as part of their training set also adds to this - screenshots, memes, even pure visual garbage; remember that one of the things these "AI" companies desperately try to avoid is accidentally feeding generated content into the learning process because it reinforces the mistakes in the model; if you want to poison the data set, these kinds of things will absolutely do that - or at least force them to spend more time and money on having to go through the data set and remove potentially disruptive elements.
similarly, if you want to poison text-based data sets, you can always add in various typos and misspellings, use special characters for punctuation or to replace certain letters, mess around with sentence structure and grammar and the like.
this is basically why I can't help but think that tumblr might inherently be one of the most poisoned data sets there is - the terminology, expressions, the slang, the nonsense - the less comprehensible it is to an outsider, the less useful it is going to be to anyone trying to teach an algorithm how to behave comprehensively.
28 notes
·
View notes