#Digital to Analog Signals Assignment Help
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Telecommunication Protocols Overview: VoIP
Revolutionary Transition from TDM to IP Networks Voice over IP (VoIP) technology VoIP and Triple Play: Key Protocols for Multimedia Transmission in IP Networks
Voice-over-IP (VoIP), also known as IP telephony, connects TDM networks with channel switching to IP networks with packet switching. It also facilitates the gradual transition from TDM to IP networks. Introduced in the late **1990s**, VoIP is one of the earliest telecommunication technologies to enable the use of IP phones, IP PBXs, and similar equipment; the suite of VoIP protocols is **crucial** among other telecom protocols.
According to the common definition, IP telephony is real-time voice signal transmission over a packet-switched network. It converts a phone number into an IP address and the analog voice signal into a digital one.
The birth year of Internet telephony is considered to be 1995, when Vocaltec released the Internet Phone software for telephone transmission using the IP protocol. **Until** the mid-1990s, Internet phone network implementation was possible only via telephone modems, resulting in significantly lower voice quality compared to traditional phones. Nevertheless, this laid the foundation for VoIP.
Since then, the development has been so rapid that VoIP's capabilities now far exceed its formal name. Essentially, this technology allows for the transmission of not only voice but any type of information using the IP protocol, so the term shifted to a broader one, "multimedia." Corresponding data structures can include voice, images, and data in any combination, commonly referred to as Triple Play.
The VoIP network structure can be viewed as two planes. The lower one represents the transport mechanism for non-guaranteed delivery of multimedia traffic as a protocol hierarchy (RTP, UDP/IP), and the upper one is the call service management mechanism. The key protocols here are H.323 ITU-T, SIP, MGCP, and MEGACO, each offering different implementations for call **services** in IP telephony networks.
Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) provides transport services to multimedia applications, but it doesn't guarantee delivery or packet order. RTP helps **apps** detect packet loss or order issues by assigning a number to each packet. RTP works in point-to-point or point-to-multipoint modes with no regard to the transport mechanism, but usually it is UDP.
RTP works with the Real-Time Control Protocol (RTCP), which manages data flow and checks for channel overload. RTP session participants periodically exchange RTCP packets with statistical data (number of packets sent, lost, etc.), which senders can use to adjust transmission speed and load type dynamically.
Recommendation H.323
The recommendation H.323, historically the first method for making calls in an IP network, involves the following types of data exchange: - Digital audio - Digital video - Data (file/image sharing) - Connection management (communicating function support, logical channel management) - Session and connection establishment and termination
Key H.323 network elements include terminals, gateways, gatekeepers, and Multipoint Control Units (MCU).
A terminal provides real-time communication with another H.323 terminal, gateway, or MCU.
Gateways connect H.323 terminals with different network protocol terminals by converting the information back and forth between networks.
Gatekeepers participate in managing connections by converting phone numbers to IP addresses and **vice versa**.
Another element of the H.323 network, the proxy server, operates at the application level to identify application types and establish necessary connections.
The H.323 call service plane includes three main protocols (see picture): RAS (Registration Admission and Status) for terminal registration and resource access control, H.225 for connection management, and H.245 for logical channel management. RAS uses UDP, while H.225 and H.245 use TCP for guaranteed information delivery. UDP's delivery is not guaranteed, so if confirmation isn't received in time, UDP retransmits the message.

Pic. 1. Overview of H.323
The process of establishing a connection involves three stages. The first one is to detect the gatekeeper, register terminals with the gatekeeper, and control **terminals'** access to network resources using the RAS protocol. The next two stages involve H.225 signaling and H.245 control message exchanges.
Recommendation H.225 outlines the procedures for connection management in H.323 networks using a set of signal messages from the ITU-T's Q.931 recommendation.
Recommendation H.245 describes the procedures for managing information channels: determining the master and slave devices, communicating terminal capabilities, and opening and closing unidirectional and bidirectional channels. It also covers delays, information processing modes, and the state of information channels by organizing loops.
The exchange of signaling messages between interacting H.323 network devices happens over H.245 logical channels. The zero logical channel, which carries control messages, must remain open for the entire duration of the connection.
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)
The second method for handling calls in VoIP networks involves using the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), specified in RFC 2543 by the IETF. As an application-level protocol, it is designed for organizing multimedia conferences, distributing multimedia information, and setting up phone connections. SIP is less suited for interaction with PSTN but is easier to implement. It's more suitable for ISPs offering IP telephony services as part of their package.
Key features of SIP include user mobility support, network scalability, the ability to add new functions, integration with the existing Internet protocol stack, interaction with other signaling protocols (e.g., H.323), enabling VoIP users to access intelligent network services, and independence from transport technologies.
It's worth noting that user mobility support is no longer exclusively a SIP feature. H.323 now also supports it (see ITU-T H.510, "Mobility for H.323 Multimedia Systems and Services").
A SIP network contains user agents, or SIP clients, proxy servers, and redirect servers.
User agents are terminal equipment applications that include a client (User Agent Client, UAC) and a server (User Agent Server, UAS). The UAC initiates the service request, while the UAS acts as the calling party.
The proxy server combines UAC and UAS functions. It interprets and, if necessary, rewrites request headers before sending them to other servers.
The redirect server determines the location of the called subscriber and informs the calling user.
MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol)
The third method for building an IP telephony network relies on the Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP), proposed by the IETF's MEGACO workgroup. The architecture of this protocol is probably the simplest of all three in terms of functionality. An MGCP network contains a media gateway (MG) for converting voice data between PSTN and IP telephony networks, a signaling gateway (SG) for processing signaling information, and a call agent (similar to an H.323 gatekeeper) for managing gateways.
Like H.323, MGCP is convenient for organizing PSTN-compatible IP telephony networks. However, in terms of functionality, MGCP surpasses H.323. For example, an MGCP call agent supports SS7 signaling and transparent transmission of signaling information over the IP telephony network. In contrast, H.323 networks require any signaling information to be converted by a gateway into H.225 (Q.931) messages. MGCP messages are transmitted in plain text format.
The fourth method for building an IP network, an improvement over MGCP, was developed by the IETF's MEGACO group together with ITU-T's SG 16, hence the name MEGACO/H.248. It mainly differs from its older sibling in connection organization. Thanks to this, the MEGACO/H.248 controller can change the port connection topology, allowing for flexible conference management. The MEGACO protocol supports two methods of binary encoding.
MGCP has also evolved in the field of the Internet of Things (IoT), where it is used to manage media gateways and transmit voice information in various scenarios, such as smart homes or intelligent buildings.
0 notes
Text
Basic Networking Concepts You Must Know

Basic Networking Concepts You Must Know are essential for anyone working in IT, cybersecurity, or cloud computing. We live in a highly connected world where everything, from smartphones to businesses, depends on networking. Whether you're browsing the internet, sending emails, or streaming videos, networking makes it all possible. Understanding these fundamental concepts will help you navigate the digital landscape effectively.
The TCCI-Tririd Computer Coaching Institute is dedicated to providing strong networking fundamentals to its students. In this article, we will articulate the core networking concepts in a simple manner.
What is Networking?
Networking comprises connecting two or more computing devices for the purpose of data interchange and resource sharing. It may be anything from simple two computers hooked together to working together across an intercontinental complex such as the World Wide Web.
Main Functions of Networking:
Data Sharing – Enable efficient exchange of information between devices.
Resource Sharing – Enable devices to share hardware such as printers or storage.
Communication – Allow users to send messages, make VoIP calls, or use video conferences.
Security & Management – To assist in gaining control and monitoring traffic.
Types of Computer Networks
1. Local Area Network (LAN)
LAN connects devices in a very limited geographical area, typically within a home, office, or school. It provides high-speed connectivity using Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi.
2. Wide Area Network (WAN)
WAN covers a large geographical area and connects multiple LANs; the Internet is therefore the largest WAN.
3. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
The MAN connects multiple LANs in a city or metropolitan area and is felt as the way for universities and government organization networks.
4. Personal Area Network (PAN)
A personal area network is a small network around a person, usually based on Bluetooth or infrared technologies (ex. smartwatches, wireless headphones).
5. Wireless Networks –
Wireless networks make use of radio signals for the connection of devices, such as Wi-Fi and cellular networks.
Networking Key Elements
Routers
Routers help drive traffic along the road leading to an Internet connection between remote networks.
Switches
Switches connect several devices together in a LAN and allow efficient transfer of data.
Modems
A modem converts digital signals from a computer to analog signals so as to transmit them through a telephone line.
Access Points
Access points improve network connectivity by extending wireless coverage.
Networking Protocols You Should Know
TCP/IP
Other key functions also include those for chopping data into packets and ensuring packets are being delivered to corresponding TCP/IP hosts.
HTTP/HTTPS
HTTP and HTTPS for web surfing/secure web surfing: HTTPS encrypts the data for secure connections.
FTP
Ftp transfers files between computers on networks.
DNS
The function of DNS is to convert domain names into IP addresses.
DHCP
DHCP is used to assign IP addresses to devices on a network automatically.
Network Security Essentials
Firewalls
A firewall controls and monitors the incoming and outgoing traffic of a network for unauthorized access.
Encryption
The data is encrypted during transit to prevent hacking attempts from stealing sensitive information.
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
A VPN makes it possible for the internet connections to be secret and secured; this is an already known service while working from home.
How to solve Problems in the Network.
Restart your router or modem.
Check cable connections.
Use the network diagnostic tools.
Update network drivers.
Use command line tools such as ping or tracert.
The Future of Networking
The networking technology is in a fast pace due to breakthroughs in 5G and artificial intelligence, powered by cloud computing. Increasing network efficiency and security by creating AI-powered automation makes this an interesting field for IT professionals.
Conclusion
Understanding networking is a core necessity for anyone in the IT industry; therefore, whether you're a student, an aspiring engineer, or a business owner, these concepts should teach you how to navigate through the digital world.
Now join us at TCCI-Tririd Computer coaching institute through these extensive networking courses to master the concepts in them. Build a strong foundation in networking with us!
Location: Bopal & Iskon-Ambli Ahmedabad, Gujarat
Call now on +91 9825618292
Get information from: https://tccicomputercoaching.wordpress.com/
0 notes
Text
Top 10 Must-Have Audio Equipment for Professional Studios
Setting up a professional studio is an exciting journey, but it can also be overwhelming with so many choices out there. To help you get started, we've compiled a list of the top 10 must-have audio equipment for a professional studio. These essentials will ensure you have everything you need to create high-quality recordings.
1. Audio Interface
An audio interface is the heart of your studio. It connects your microphones, instruments, and other audio gear to your computer. Look for one with multiple inputs and outputs, high-quality preamps, and good digital-to-analog conversion.
2. Studio Monitors
Studio monitors are speakers designed for accurate sound reproduction. Unlike regular speakers, they don't color the sound, allowing you to hear your recordings as they truly are. Popular brands include KRK, Yamaha, and JBL.
3. Microphones
A good selection of microphones is crucial. Start with a large-diaphragm condenser mic for vocals and a dynamic mic for instruments. Brands like Shure, Audio-Technica, and Rode offer excellent options.

4. Headphones
Closed-back headphones are essential for tracking, as they prevent sound from leaking into the microphone. Open-back headphones are better for mixing and provide a more natural sound. Sennheiser, Beyerdynamic, and Sony are top choices.
5. Digital Audio Workstation (DAW)
A DAW is software that lets you record, edit, and mix your music. Popular DAWs include Pro Tools, Logic Pro X, and Ableton Live. Choose one that fits your workflow and budget.

6. MIDI Controller
A MIDI controller allows you to play and record virtual instruments. It's a must-have for composing and producing music. Look for models with responsive keys and assignable knobs and pads. Akai, M-Audio are reliable brands.
7. Preamps
Preamps boost the signal from your microphones and instruments to a usable level. While most audio interfaces have built-in preamps, standalone units often provide better sound quality. Brands like Focusrite, PreSonus are well-regarded.
8. Acoustic Treatment
Good acoustic treatment helps control sound reflections and reduces unwanted noise. Start with bass traps, acoustic panels, and diffusers. This will improve the accuracy of your recordings and mixes.
9. Cables
High-quality cables are essential for a clean signal path. Invest in sturdy, well-shielded cables to connect your microphones, instruments, and monitors. Mogami, Hosa are trusted brands.

10. Pop Filter
A pop filter is a simple but effective tool that reduces plosive sounds (like "p" and "b") when recording vocals. It ensures cleaner recordings and protects your microphone from moisture.
Building a professional studio requires investment in the right gear. Start with these ten essentials to ensure you have a solid foundation. There are many shops like VIP PRO AUDIO in Brooklyn which stocks all the essential audio equipment's consider visiting such shops to gain valuable insights. Remember, quality equipment can make a significant difference in your recordings, helping you achieve professional results. Happy recording!
0 notes
Text
Cracking the HAL Test: A Detailed Success Guide
One of India's top aerospace and military organizations might offer a lucrative job to those who pass the Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) exam. HAL exam competition is fierce, with thousands of applicants vying for a few number of spots each year. Whether you're a seasoned expert looking to join HAL or a recent engineering graduate, preparation is the key to success. This blog offers a thorough analysis of the HAL test along with useful advice to help you ace it.
Comprehending the HAL Assessment The purpose of the HAL exam is to evaluate applicants' technical knowledge and problem-solving skills. Usually, it is divided into two primary sections: Section Technical: This portion assesses your knowledge of fundamental engineering concepts that are pertinent to the job for which you are applying. For example, if you are a candidate for electrical engineering, you should be prepared for questions about power electronics, control systems, and circuits. Section on General Aptitude: This section assesses your verbal, quantitative, and logical reasoning skills. It comprises math, data interpretation, logical puzzles, and English language proficiency questions.
To move on to the interview stage, you must do well in both of these sections, which are quite important. Exam Structure and Content The exact function and discipline may cause modest variations in the HAL exam pattern. Still, a common pattern is as follows: Technical Section: Approximately 120 inquiries Section on General Aptitude: Approximately 60 questions Time: two to three hours The technical course is extensive and covers both basic and advanced engineering topics. Here is a quick synopsis of some important disciplines:
Mechanical Engineering: Thermodynamics, Fluid Mechanics, Manufacturing Processes, Strength of Materials, Heat Transfer.
Electrical Engineering: Circuit Theory, Electrical Machines, Power Systems, Control Systems, Electronics.
Electronics and Communication Engineering: Analog and Digital Circuits, Communication Systems, Signal Processing, Microprocessors.
Strategies for Preparation Recognize the syllabus and format of the exam: Start preparing by familiarizing yourself with the syllabus and format of the test. You can more successfully manage your study routine when you know what to expect. assemble the study materials Gather reference books, standard textbooks, and exam papers from prior years. Online tools such as discussion boards and lecture videos can also be quite beneficial. Make a Study Schedule: Make a schedule and break your syllabus up into digestible sections. Give subjects you find difficult additional time, and make sure you have regular revision sessions.
Practice on a regular basis: Complete past years' assignments and take practice exams to have a sense of the format and complexity of the examination. To increase your accuracy and speed, time yourself. Concentrate on Core Concepts: Make sure you understand the essential ideas. Several of the questions aim to assess your grasp of fundamental ideas rather than memorization.
Keep Up: Stay informed on the most recent advancements in your industry. This is especially crucial for the interview phase, as being up to date on industry trends and new technology will help you stand out. Join Study Groups: Talking with peers in a study group might open your eyes to new ideas and help you clear up any confusion. Learning is improved by talking about issues and their fixes.
Exam Day Sleep Advice: Make sure you get a decent night's sleep the night before the exam. A relaxed mind functions more effectively. Arrive Early: To minimize tension at the last minute, get to the exam location well in advance. Carefully read the instructions: Before beginning, take some time to thoroughly read the instructions on the question paper. Effective Time Management: Make sensible time divisions between the sections. Don't linger too long on any one query. If you become stuck, go on and, if time allows, come back later. Remain Calm: Retain your poise throughout the test. You can stay focused and reduce stress by practicing deep breathing.
Exam-After Preparation The written exam is only the first step to take. The shortlisted candidates will be contacted for an interview, during which their technical expertise, problem-solving abilities, and character attributes will be evaluated. Review important ideas, practice standard interview questions, and keep up to date with HAL's initiatives and advancements to help you prepare for the interview. For those who want to become engineers, the HAL exam is a demanding yet worthwhile chance. By following a methodical preparation plan, being committed, and maintaining composure, you can pass the test and land a job at Hindustan Aeronautics Limited. Remain persistent and diligent; these will be your greatest allies along this adventure. Wishing you luck!
Start Your Preparation With : https://gameacademy.in/ / https://clppenny.page.link/cTBm
0 notes
Note
11 15 26
I'm putting this under a readmore because I'm uh... thorough in my responses here. X]
11: describe your ideal day.
Waking up (without an alarm) at 8 am, wishing my girlfriend good morning with a kiss, washing up. After that, catching up on internet friend stuff until lunchtime around 11 am. After a simple lunch (sandwiches, probably, even in my ideal world X]) I could spend the early afternoon on a single-player game I'm playing though (or maybe watch my girlfriend play something) until I switch to doing something more creative like draw or code until dinner. (probably something more elaborate, like helping my girlfriend make "yuri pasta" (penne rosa) from scratch or my mother's signature "Sanette Spaghetti"). Then me and my girlfriend can play/read something together for the evening (and get to other yuri activities as our uh... mood may dictate)
15: five most influential books over your lifetime.
OOGH I uh... I might have a hard time pulling out five... I better try, though.
"Cat Wishes" (the full title is longer). I mark this as the most impactful because it's what really convinced me that I needed to transition. It's a simple, earnest, wish-fulfillment furry-adjacent light novel that really got me to realize I wanted to be... something else. That "sometimes it's worth asking for what you want," as the book puts it.
"Substitute Familiar" (same author). Same vibe as above, but I read it second so the impact had already been made. Turns out I'm a huge sucker for "transgender person gets her egg cracked wide open before she even knows what's happening."
Book of Mormon (TECHNICALLY***. Also the Bible and stuff). I'm not like... recommending reading it. This list of "books that influenced my life" just wouldn't be complete without the thing that I spend two decades reading almost every day and that shaped my approach to theology and spirituality, even if I've uh... distanced myself somewhat from that group since then. Like, some of my first posts on this blog were talking about "#ldsconf", but now I'm on that "#that is yuri" and "#do that to me" posting era. X]
[Brony Fanfic I think is best left in obscurity] (ask for a link and I'll send it if you really wanna know) I remember it was filled with lots of... hallmarks of bronydom from the time, but it was the first story that was like... that direct about how weird it was to be at a stage of life where my "bOdY iS cHaNgInG" and I'm suddenly interested in girls in a new way but there's all kinds of other baggage that's attached to those feelings? Not the least of which was, at the time, the pressures of masculinity? And everyone around me is really cagey about explaining any of it clearly? It resonated with me so well at the time that I would recommend it to everyone who asked me at the time about my favorite book.
DK Scientific Encyclopedia (I... think that was the title?) I don't know if it really counts as a book for the purposes of this ask, but it's gotta mean something about the kind of kid I was that, when assigned to read something EVERY DAY that my parents had to sign off on, my instinct was "I don't wanna have to pick something new every day or week, so I'll just pick the biggest book my family has" and then actually enjoyed learning about atoms and electricity and analog/digital signals. I think I was 7. I was definitely younger than 10. If that doesn't count then uh... Homestuck. Because Homestuck is just a domino that keeps coming back around to so many big things in my life.
26: how would you describe your gender/sexuality?
Short answer: transfeminine lesbian
More complicated short answer: girl-adjacent nonbinary girl-liker
Kitchen sink answer: I'm like if a girl was also kind of a raccoon who isn't REALLY a robot but likes to think of herself that way to frame her behavior and past. Oh and I wanna live like a yuri light novel.
My "real" (thorough) answer: if we take the mean value of what many people call "girl" in the two-dimensional space formed by the cross of Masculinity and Femininity, my gender lies in a space that projects into low-masculinity, medium femininity, but in fact lies in a higher-dimensional location (as all genders do) that can be found navigating a short distance along orthogonal basis vectors "domestic creature" and "machine". That space that is not quite otherkin but is nonetheless intertwined with the desire to be cared for like a strange pet raccoon but also linked to the symbols of being jailbroken from a dogmatic hivemind of normalized thought patterns and behaviors prescribed as "worthy". (a similar expression can be found using an alternate vector space, feminine x profane x solarpunk). Oh and kissing girls. I just... (gestures widely to the multidimensional space that lies in my own gender neighborhood) really REALLY like girls.
#text post#long post#ask game#ask#abalidoth#identity ask game#smie speaks#I uh... sure can type a lot can't I? X]#thanks for the ask! It's exciting to just... lay stuff out like this!#religion#exmo#?
1 note
·
View note
Text
I just think it's ridiculous that mortals invent fun new concepts like chatrooms and Betamax and now video rental stores and they take them away almost immediately and you wonder why they even bothered to go through all that effort to begin with if they were just going to throw it all away like that. What if I wanted to watch a movie and didn't want to buy it? I have limited space, you know, I can't go around buying movies every time I want to watch one, that's absurd. Streaming is stupid and will never last and I refuse to do it on principle. Why do I need so many subscriptions? What are they playing at? Ridiculous. Now they have these smart TVs and why would I ever want my television to be smart? Make it stupid.
It's bad enough we made the transition from analog to digital. What an awful time. The aesthetic just isn't the same. I miss the static and messing with antenna. I miss television signal hijackings. You used to be able to hack a phone if you whistled just right, did you know that? I never did that but some people did. Everything is so clean and boring now and they don't even let you skip the ads. If I wanted to watch advertisements, I'd just watch cable. The advertisers don't know what gender I am, so they only show me stupid advertisements. At least it's better than my email ads because they're trying to sell me maternity wear and birth control, which I absolutely can't stand because wow, way to rub it in. Assholes, all of them. Stop trying to sell me cleaning products, television.
It's fine. It's so fine. I don't need a movie to have a good time. I'm handsome and charming and I fill a shirt out well, so there you go, that's a start. I can just take a woman out to my favorite ice cream restaurant. No wait, I can't. It's dead. They tore it down to put a Chi-Chi's and now they don't even have those anymore. Great. Fantastic. You know, the old lady who ran the ice cream parlor was very nice and she let me sleep in the back as long as the health inspector wasn't due. She gave Bonnie free sundaes. Now everything is gone and I can't even get a taco, so what's the point?
I can't even settle on a wardrobe without it immediately being dating. I'm embracing the retro look lately because it's so much easier than fussing about skirt lengths. Not even doing the masculine thing helps, you know, because they keep changing how suits should fit. I'm glad we aren't all wearing baggy suits, you know, but why are the pants so short now? Why do you need to see my socks? I hate this. Feminine things are a nightmare because you need a gold necklace but wait, silver is in but oh no, now you absolutely must wear rose gold. Make up your mind. I feel much more comfortable with an ambiguous presentation nowadays but even that has its pitfalls. Am I doing it right? Do I look good? How much cleavage is tasteful? Why do people assign special meaning to fat deposits? Why did they invent sexism and why is it so concerned about the size of my chest? This is why I don't even bother with the things most of the time, you know.
Why do we have to prescribe special meaning (derogatory meaning) to uncontrollable (to most) body shapes? I love having gender, I really do, I am never going back to not having gender, but why did they make things gendered in a bad way? I'm great at gender, you know, fantastic. I love being both man and woman in a way that pisses people off. It's fun. I didn't like the woman part before but now I do. Men and women and everyone else are so neat and I adore them and I would like to go on many dates with them.
Do people even like romantic comedies anymore? I don't know the last time one really made it big. Should I even take someone to see one? Will they think I'm just a dusty old relic? I'm not going to take someone to see a superhero movie. Why do we need so many of them? You have to see all of them to make sense of the next but they're all the same movie. Why do I have to see movies I don't like just to make smalltalk with people? Are we all just watching these things to make smalltalk? It's all Chris and Chris and Chris and Chris. These are all the same man.
I don't even like going to the theater anymore. I can't bring a woman there. No one can afford to pay for concessions these days, not even the Famazon man. I can't rent movies because it's online and I don't want it to be online. I want to hold the box. I don't like having things I can't hold. The internet doesn't even have the good old movies, anyway. They're held up in legal disputes over streaming. I can't even stream what I want to watch. What am I supposed to do? I can do other things for dates but sometimes I like to be in and that's a good thing to do while in.
It's fine. It's so absolutely fine. Great! We just killed an entire genre of date night for no fucking reason! I don't even want to invite a Finder date over now. I don't even like Finder. Garbage. There aren't enough secret, glamours off bars anymore. They felt like a meat market, sure, but at least people said more than hey.
Everything is awful and I hate it and I don't understand why they don't even let me rent movies anymore. I am going to drink a fine premixed cocktail that you can buy in my shop and take a fucking nap.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Radio Remote Control Transmitter and Receiver
The Anand device transmitter is designed to transmit command Signals for controlling EOT cranes, hoists, and machines. 12 control instructions plus the included emergency button are to be had to the operator. The radio remote control includes the transmitter, inner alkaline batteries, and a receiver. The transmitter housing with an integrated antenna is made from impact-resistant plastic.
Anand Radio Remote Control for EOT cranes are available in different types i.e., Anand 8 Button, Anand 12 Button, Anand Joystick remote control, and wireless remote control
ANAND 8 BUTTON
Anand 8 Button is the powerful and up to 3 motions radio remote control for cranes. It is a handheld device to control industrial cranes. eot crane remote is available in single and Dual Speeds. Another feature of Radio remote control is having the ability to cross and long travel.
ANAND 12 BUTTON
Anand 12 Button is a powerful, handheld radio remote control for overhead cranes. It is up to 4 motions. 12 button transmitter speed is single and dual. Ability to travel long.
JOYSTICK RADIO REMOTE CONTROL

Joystick remote controls will have as many as five steps in every direction. The joystick can be configured in many different options such as spring return, lock type, locks, analog output, and digital output. Joystick radio remote controls with potentiometers can be used to wirelessly control the speed of frequency converters, proportional control of hydraulic pumps, etc.
Functions of Crane Remote Control
Features of Crane remote control system is as follows
1. Tandem mode
Tandem mode is controlled by the selector switch. During this mode, the radio remote is synchronized with multiple receivers.
2. Customized Radio Range

Wireless radio remote controls have the ability to transmit and receive the signal at a range of above 200 meters. Anand crane remotes are designed to transmit signals long distances with less power.
3. Communication System
In crane remote control, advanced closed-loop communication systems are used. In radio remote System, closed-loop communication between transmitter and receiver. The transmitter transmits the signal and receives that signal and gives you the required feedback.
4. Digital Address Used
All crane remote control systems used an 8-byte address. An 8-byte digital address is assigned to a transmitter and receiver.
5. Configurable Receiver
Radio receivers have 2 to 8 relays. Relay contact rating is 275Vac at 10 Amps. The Receiver operates in 30mWatt power consumption and saves electricity. It gives the signal indication with the help of a power indication lamp. Another feature is having a mainline contactor on/off indicator.
Applications of Radio Remote Controls
· EOT Cranes
· Electric Hoist
· Jib Cranes
· Goliath Cranes
· Mobile Cranes
· Gantry Cranes
· Tower Crane, and so on
Here are types of Radio Remote Control for cranes with its features. Choose radio control remote based on different parameters and features. Anand Systems Engineering Pvt. Ltd. is a leading crane remote control manufacturers in India. For more details visit our official website https://www.anandcontrol.in/radio-remote-control/anand-remote.html
#radio remote control#crane remote control manufacturers#Radio Remote Control for cranes#crane remote control#Radio Remote Control for EOT cranes#EOT Cranes#radio remote control for overhead cranes.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Escape the Confines of Time and Space According to the CIA
She turned to me the other morning and said, “You heard of The Gateway?” It didn’t register in the moment. She continued, “It’s blowing up on TikTok.” Later on, she elaborated: it was not in fact the ill-fated 90s computer hardware company folks were freaking out about. No, they’ve gone further back in time, to find a true treasure of functional media.
The intrigue revolves around a classified 1983 CIA report on a technique called the Gateway Experience, which is a training system designed to focus brainwave output to alter consciousness and ultimately escape the restrictions of time and space. The CIA was interested in all sorts of psychic research at the time, including the theory and applications of remote viewing, which is when someone views real events with only the power of their mind. The documents have since been declassified and are available to view.
This is a comprehensive excavation of The Gateway Process report. The first section provides a timeline of the key historical developments that led to the CIA’s investigation and subsequent experimentations. The second section is a review of The Gateway Process report. It opens with a wall of theoretical context, on the other side of which lies enough understanding to begin to grasp the principles underlying the Gateway Experience training. The last section outlines the Gateway technique itself and the steps that go into achieving spacetime transcendence.
Let’s go.
Screengrab: CIA
THE TIMELINE
• 1950s – Robert Monroe, a radio broadcasting executive, begins producing evidence that specific sound patterns have identifiable effects on human capabilities. These include alertness, sleepiness, and expanded states of consciousness.
• 1956 – Monroe forms an R&D division inside his radio program production corporation RAM Enterprises. The goal is to study sound’s effect on human consciousness. He was obsessed with “Sleep-Learning," or hypnopedia, which exposes sleepers to sound recordings to boost memory of previously learned information.
• 1958 – While experimenting with Sleep-Learning, Monroe discovers an unusual phenomenon. He describes it as sensations of paralysis and vibration accompanied by bright light. It allegedly happens nine times over the proceeding six weeks, and culminates in an out-of-body experience (OBE).
• 1962 – RAM Enterprises moves to Virginia, and renames itself Monroe Industries. It becomes active in radio station ownership, cable television, and later in the production and sale of audio cassettes. These cassettes contain applied learnings from the corporate research program, which is renamed The Monroe Institute.
• 1971 – Monroe publishes Journeys Out of the Body, a book that is credited with popularizing the term “out-of-body experience.”

Books by Robert Monroe.
• 1972 – A classified report circulates in the U.S. military and intelligence communities. It claims that the Soviet Union is pouring money into research involving ESP and psychokinesis for espionage purposes.
• 1975 – Monroe registers the first of several patents concerning audio techniques designed to stimulate brain functions until the left and right hemispheres become synchronized. Monroe dubs the state "Hemi-Sync" (hemispheric synchronization), and claims it could be used to promote mental well-being or to trigger an altered state of consciousness.
• 1978 to 1984 – Army veteran Joseph McMoneagle contributes to 450 remote viewing missions under Project Stargate. He is known as “Remote View No. 1”. This is kind of a whole other story.
• June 9th, 1983 – The CIA report "Analysis and Assessment of The Gateway Process" is produced. It provides a scientific framework for understanding and expanding human consciousness, out-of-body experiments, and other altered states of mind.
• 1989 – Remote viewer Angela Dellafiora Ford helps track down a former customs agent who has gone on the run. She pinpoints his location as “Lowell, Wyoming”. U.S. Customs apprehend him 100 miles west of a Wyoming town called Lovell.
• 2003 – The CIA approves declassification of the Gateway Process report.
• 2017 – The CIA declassifies 12 million pages of records revealing previously unknown details about the program, which would eventually become known as Project Stargate.
THE REPORT

Screengrab: CIA
Personnel
The author of The Gateway Process report is Lieutenant Colonel Wayne M. McDonnell, hereon referred to simply as Wayne. There isn’t a tremendous amount of information available on the man, nor any photographs. In 1983, Wayne was tasked by the Commander of the U.S. Army Operational Group with figuring out how The Gateway Experience, astral projection and out-of-body experiences work. Wayne partnered with a bunch of different folks to produce the report, most notably Itzhak Bentov, a very Googleable American-Israeli scientist who helped pioneer the biomedical engineering industry.
A scientific approach
From the outset of the report, Wayne states his intent to employ an objective scientific method in order to understand the Gateway process. The various scientific avenues he takes include:
• A biomedical inquiry to understand the physical aspects of the process.
• Information on quantum mechanics to describe the nature and functioning of human consciousness.
• Theoretical physics to explain the time-space dimension and means by which expanded human consciousness transcends it.
• Classical physics to bring the whole phenomenon of out-of-body states into the language of physical science (and remove the stigma of an occult connotation).
Methodological frames of reference
Before diving into the Gateway Experience, Wayne develops a frame of reference by dissecting three discrete consciousness-altering methodologies. He’s basically saying, there’s no way you’re going to get through The Gateway without a solid grounding in the brain-altering techniques that came before it.
1) He begins with hypnosis. The language is extremely dense, but the basic gist is as follows: the left side of the brain screens incoming stimuli, categorizing, assessing and assigning meaning to everything through self-cognitive, verbal, and linear reasoning. The left hemisphere then dishes the carefully prepared data to the non-critical, holistic, pattern-oriented right hemisphere, which accepts everything without question. Hypnosis works by putting the left side to sleep, or at least distracting it long enough to allow incoming data direct, unchallenged entry to the right hemisphere. There, stimuli can reach the sensor and motor cortices of the right brain, which corresponds to points in the body. Suggestions then can send electrical signals from the brain to certain parts of the body. Directing these signals appropriately, according to the report, can elicit reactions ranging from left leg numbness to feelings of happiness. Same goes for increased powers of concentration.
2) Wayne continues with a snapshot of transcendental meditation. He distinguishes it from hypnotism. Through concentration the subject draws energy up the spinal cord, resulting in acoustical waves that run through the cerebral ventricles, to the right hemisphere, where they stimulate the cerebral cortex, run along the homunculus and then to the body. The waves are the altered rhythm of heart sounds, which create sympathetic vibrations in the walls of the fluid-filled cavities of the brain’s ventricles. He observed that the symptoms begin in the left side of the body, confirming the right brain’s complicity. Bentov also states that the same effect might be achieved by prolonged exposure to 4 – 7 Hertz/second acoustical vibrations. He suggests standing by an air conditioning duct might also do the trick. (David Lynch and other celebrities are committed adherents to transcendental meditation today.)
3) Biofeedback, on the other hand, uses the left hemisphere to gain access to the right brain’s lower cerebral, motor, and sensory cortices. Whereas hypnosis suppresses one side of the brain, and TM bypasses that side altogether, biofeedback teaches the left hemisphere to visualize the desired result, recognize the feelings associated with right hemisphere access, and ultimately achieve the result again. With repetition, the left brain can reliably key into the right brain, and strengthen the pathways so that it can be accessed during a conscious demand mode. A digital thermometer is subsequently placed on a target part of the body. When its temperature increases, objective affirmation is recognized and the state is reinforced. Achieving biofeedback can block pain, enhance feeling, and even suppress tumors, according to the report.

Image: e2-e4 Records.
The Gateway mechanics
With that, Wayne takes a first stab at the Gateway process. He classifies it as a “training system designed to bring enhanced strength, focus and coherence to the amplitude and frequency of brainwave output between the left and right hemispheres so as to alter consciousness.”
What distinguishes the Gateway process r from hypnosis, TM, and biofeedback, is that it requires achieving a state of consciousness in which the electrical brain patterns of both hemispheres are equal in amplitude and frequency. This is called Hemi-Sync. Lamentably, and perhaps conveniently, we cannot as humans achieve this state on our own. The audio techniques developed by Bob Monroe and his Institute (which comprise a series of tapes), claim to induce and sustain Hemi-Sync.
Here, the document shifts to the usage of quotes and other reports to describe the powers of Hemi-Sync. Wayne employs the analogy of a lamp versus a laser. Left to its own devices the human mind expends energy like a lamp, in a chaotic and incoherent way, achieving lots of diffusion but relatively little depth. Under Hemi-Sync though, the mind produces a “disciplined stream of light.” So, once the frequency and amplitude of the brain are rendered coherent it can then synchronize with the rarified energy levels of the universe. With this connection intact, the brain begins to receive symbols and display astonishing flashes of holistic intuition.
The Hemi-Sync technique takes advantage of a Frequency Following Response (FFR). It works like this: an external frequency emulating a recognized one will cause the brain to mimic it. So if a subject hears a frequency at the Theta level, it will shift from its resting Beta level. To achieve these unnatural levels, Hemi-Sync puts a single frequency in the left ear and a contrasting frequency in the right. The brain then experiences the Delta frequency, also known as the beat frequency. It’s more familiarly referred to these days as binaural music. With the FFR and beat frequency phenomena firmly in place, The Gateway Process introduces a series of frequencies at marginally audible, subliminal levels. With the left brain relaxed and the body in a virtual sleep state, the conditions are ideal to promote brainwave outputs of higher and higher amplitude and frequency. Alongside subliminal suggestions from Bob Monroe (naturally), the subject can then alter their consciousness.

Image: Thobey Campion
The Gateway system only works when the audio, which is introduced through headphones, is accompanied by a physical quietude comparable to other forms of meditation. This increases the subject’s internal resonance to the body’s sound frequencies, for example the heart. This eliminates the “bifurcation echo”, in which the heartbeat moves up and down the body seven times a second. By placing the body in a sleep-like state, The Gateway Tapes, like meditation, lessen the force and frequency of the heartbeat pushing blood into the aorta. The result is a rhythmic sine wave that in turn amplifies the sound volume of the heart three times. This then amplifies the frequency of brainwave output. The film surrounding the brain—the dura—and fluid between that film and the skull, eventually begin to move up and down, by .0005 and .010 millimeters.
The body, based on its own micro-motions, then functions as a tuned vibrational system. The report claims that the entire body eventually transfers energy at between 6.8 and 7.5 Hertz, which matches Earth’s own energy (7 – 7.5 Hertz). The resulting wavelengths are long, about 40,000 kilometers, which also happens to be the perimeter of the planet. According to Bentov, the signal can move around the world’s electrostatic field in 1/7th of a second.
To recap, the Gateway Process goes like this:
• Induced state of calm
• Blood pressure lowers
• Circulatory system, skeleton and other organ systems begin to vibrate at 7 – 7.5 cycles per second
• Increased resonance is achieved
• The resulting sound waves matches the electrostatic field of the earth
• The body and earth and other similarly tuned minds become a single energy continuum.
We’ve gotten slightly ahead of ourselves here though. Back to the drawing board.

Image: kovacevicmiro via Getty Images
A psycho-quantum level deeper
Wayne then turns to the very nature of matter and energy. More materially (or less if you will), solid matter in the strict construction of the term, he explains, doesn’t exist. The atomic structure is composed of oscillating energy grids surrounded by other oscillating energy grids at tremendous speeds. These oscillation rates vary—the nucleus of an atom vibrates at 10 to the power of 22, a molecule vibrates at 10 to the power of 9, a human cell vibrates at 10 to the power of 3. The point is that the entire universe is one complex system of energy fields. States of matter in this conception then are merely variations in the state of energy.
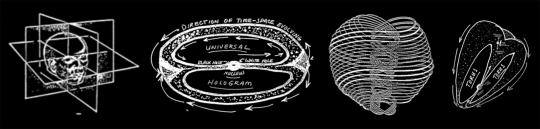
The result of all these moving energies, bouncing off of energy at rest, projects a 3D mode, a pattern, called a hologram, A.K.A our reality as we experience it. It's best to think of it as a 3D photograph. There's a whole rabbit hole to go down here. Suffice it to say, the hologram that is our experience is incredibly good at depicting and recording all the various energies bouncing around creating matter. So good, in fact, that we buy into it hook, line, and sinker, going so far as to call it our "life."
Consciousness then can be envisaged as a 3D grid system superimposed over all energy patterns, Wayne writes. Using mathematics, each plane of the grid system can then reduce the data to a 2D form. Our binary (go/no go) minds can then process the data and compare it to other historical data saved in our memory. Our reality is then formed by comparisons. The right hemisphere of the brain acts as the primary matrix or receptor for this holographic input. The left hemisphere then compares it to other data, reducing it to its 2D form.
In keeping with our species' commitment to exceptionalism, as far as we know humans are uniquely capable of achieving this level of consciousness. Simply, humans not only know, but we know that we know. This bestows upon us the ability to duplicate aspects of our own hologram, project them out, perceive that projection, run it through a comparison with our own memory of the hologram, measure the differences using 3D geometry, then run it through our binary system to yield verbal cognition of the self.
Screengrab: CIA
The click-out phase
Wayne then shows his cards as a true punisher, issuing, "Up to this point our discussion of the Gateway process has been relatively simple and easy to follow. Now the fun begins." Shots fired, Wayne. What he's preparing the commander reading this heady report for is the reveal—how we can use the Gateway to transcend the dimension of spacetime.
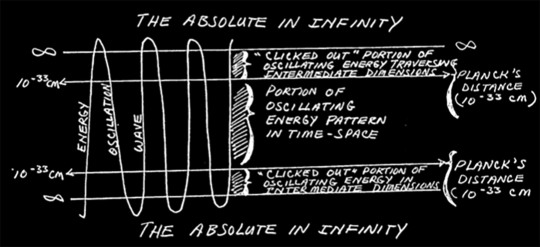
Time is a measurement of energy or force in motion; it is a measurement of change. This is really important. For energy to be classified as in motion, it must be confined within a vibratory pattern that can contain its motion, keeping it still. Energy not contained like this is boundary-less, and moves without limit or dimension, to infinity. This disqualifies boundary-less energy from the dimension of time because it has no rate of change. Energy in infinity, also called "the absolute state," is completely at rest because nothing is accelerating or decelerating it—again, no change. It therefore does not contribute to our hologram, our physical experience. We cannot perceive it.
Now back to frequencies. Wave oscillation occurs because a wave is bouncing between two rigid points of rest. It's like a game of electromagnetic hot potato (the potato being the wave and the participants' hands being the boundaries of the wave). Without these limits, there would be no oscillation. When a wave hits one of those points of rest, just for a very brief instant, it "clicks out" of spacetime and joins infinity. For this to occur, the speed of the oscillation has to drop below 10 the power of -33 centimeters per second. For a moment, the wave enters into a new world. The potato simply disappears into a dimension we cannot perceive.
Theoretically speaking, if the human consciousness wave pattern reaches a high enough frequency, the “click-outs” can reach continuity. Put another way, if the frequency of human consciousness can dip below 10 to the power of 33 centimeters per second but above a state of total rest, it can transcend spacetime. The Gateway experience and associated Hemi-Sync technique is designed for humans to achieve this state and establish a coherent pattern of perception in the newly realized dimensions.
Image: Spectral-Design via Getty Images
Passport to the hologram
In theory, we can achieve the above at any time. The entire process though is helped along if we can separate the consciousness from our body. It’s like an existential running head start where the click-out of a consciousness already separated from its body starts much closer to, and has more time to dialogue with, other dimensions.
This is where things get a little slippery; hold on as best you can. The universe is in on the whole hologram thing, too, Wayne writes. This super hologram is called a "torus" because it takes the shape of a fuck-off massive self-contained spiral. Like this:
Give yourself a moment to let the above motion sink in…
This pattern of the universe conspicuously mirrors the patterns of electrons around the nucleus of an atom. Galaxies north of our own are moving away from us faster than the galaxies to the south; galaxies to the east and west of us are more distant. The energy that produced the matter that makes up the universe we presently enjoy, will turn back in on itself eventually. Its trajectory is ovoid, also known as the cosmic egg. As it curls back on itself it enters a black hole, goes through a densely packed energy nucleus then gets spat out the other side of a white hole and begins the process again. Springtime in the cosmos, baby!
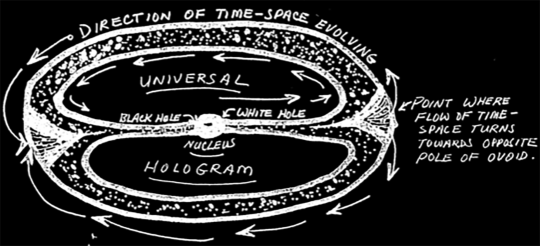
Screengrab: CIA
The entire universe hologram—the torus—represents all the phases of time: the past, present, and future. The takeaway is that human consciousness brought to a sufficiently altered (focused) state could obtain information about the past, present, and future, since they all live in the universal hologram simultaneously. Wayne reasons that our all-reaching consciousness eventually participates in an all-knowing infinite continuum. Long after we depart the space-time dimension and the hologram each one of us perceives is snuffed out, our consciousness continues. Reassuring in a way.
And that is the context in which the Gateway Experience sits.
[Deep breaths.]
THE TECHNIQUE
The following is an outline of the key steps to reach focus levels necessary to defy the spacetime dimension. This is an involved and lengthy process best attempted in controlled settings. If you’re in a rush, you can apparently listen to enough Monroe Institute Gateway Tapes in 7 days to get there.
The Energy Conversion Box: The Gateway Process begins by teaching the subject to isolate any extraneous concerns using a visualization process called “the energy conversion box.”
Resonant Humming: The individual is introduced to resonant humming. Through the utterance of a protracted single tone, alongside a chorus on the tapes, the mind and body achieve a state of resonance.
The Gateway Affirmation: The participant is exposed to something close to a mantra called The Gateway Affirmation . They must repeat to themselves variations of, “I am merely a physical body and deeply desire to expand my consciousness.”
Hemi-Sync: The individual is finally exposed to the Hemi-Sync sound frequencies, and encouraged to develop a relationship with the feelings that emerge.
Additional Noise: Physical relaxation techniques are practiced while the Hemi-Sync frequencies are expanded to include “pink and white” noise. This puts the body in a state of virtual sleep, while calming the left hemisphere and raising the attentiveness of the right hemisphere.
The Energy Balloon: The individual is then encouraged to visualize the creation of an “energy balloon” beginning at the top of the head, extending down in all directions to the feet then back up again. There are a few reasons for this, the main one being that this balloon will provide protection against conscious entities possessing lower energy levels that he or she may encounter when in the out-of-body state.
Focus 12: The practitioner can consistently achieve sufficient expanded awareness to begin interacting with dimensions beyond their physical reality. To achieve this state requires conscious efforts and more “pink and white noise” from the sound stream.
Tools: Once Focus 12 is achieved, the subject can then employ a series of tools to obtain feedback from alternative dimensions.
Problem Solving: The individual identifies fundamental problems, fills their expanded awareness with them, and then projects them out into the universe. These can include personal difficulties, as well as technical or practical problems.
Patterning: Consciousness is used to achieve desired objectives in the physical, emotional, or intellectual sphere.
Color Breathing: A healing technique that revitalizes the body’s energy flows by imagining colors in a particularly vivid manner.
Energy Bar Tool: This technique involves imagining a small intensely pulsating dot of light that the participant charges up. He or she then uses the sparkling, vibrating cylinder of energy (formerly known as the dot) to channel forces from the universe to heal and revitalize the body.
Remote Viewing: A follow-on technique of the Energy Bar Tool where the dot is turned into a whirling vortex through which the individual sends their imagination in search of illuminating insights.
Living Body Map: A more organized use of the energy bar in which streams of different colors flow from the dot on to correspondingly-colored bodily systems.
Seven days of training have now occurred. Approximately 5 percent of participants get to this next level, according to the report.
Focus 15 – Travel Into the Past: Additional sound on the Hemi-Sync tapes includes more of the same, plus some subliminal suggestions to further expand the consciousness. The instructions are highly symbolic: time is a huge wheel, in which different spokes give access to the participant’s past.
Focus 21 – The Future: This is the last and most advanced state. Like Focus 15, this is a movement out of spacetime into the future.
Out-of-Body Movement: Only one tape of the many is devoted to out-of-body movement. This tape is devoted to facilitating out-of-body state when the participant’s brain wave patterns and energy levels reach harmony with the surrounding electromagnetic environment. According to Bob Monroe, the participant has to be exposed to Beta signals of around 2877.3 cycles per second.
CONCLUSIONS
Wayne expresses concern about the fidelity of information brought back from out-of-body states using the Gateway technique. Practical applications are of particular concern because of the potential for “information distortion.”
The Monroe Institute also ran into a bunch of issues in which they had individuals travel from the West to the East Coast of the U.S. to read a series of numbers off of a computer screen. They never got them exactly right. Wayne chalks this up to the trouble of differentiating between physical entities and extra-time-space dimensions when in the out-of-body state.
Wayne swings back to support mode though, lending credence to the physics foundation of the report. He cites multiple belief systems that have established identical findings. These include the Tibetan Shoug, the Hindu heaven of Indra, the Hebrew mystical philosophy, and the Christian concept of the Trinity. Here he seems more interested in hammering home the theoretical underpinnings that make The Gateway Experience possible, rather than the practical possibilities promised by The Gateway Tapes.
Possibly with his CIA top brass audience in mind, Wayne then gives an A-type nod to The Gateway Experience for providing a faster, more efficient, less subservient, energy-saving route to expanded consciousness. This finishes with a series of recommendations to the CIA for how to exploit Gateway’s potential for national defense purposes.

Screengrab: CIA

Screengrab: CIA
The missing page
One curious feature of The Gateway Report is that it seems to be missing page 25. It’s a real cliffhanger too. The bottom of page 24 reads “And, the eternal thought or concept of self which results from this self-consciousness serves the,” The report picks back up on page 26 and 3 sections later as if Wayne hadn’t just revealed the very secret of existence.
The gap has not gone unnoticed. There's a Change.org petition requesting its release. Multiple Freedom of Information Act requests have demanded the same. In all cases, the CIA has said they never had the page to begin with. Here’s a 2019 response from Mark Lilly, the CIA’s Information and Privacy Coordinator, to one Bailey Stoner regarding these records:

Screengrab: CIA via Muckrock
One theory goes that that rascal Wayne M.-fricking-McDonnell left the page out on purpose. The theory contends that it was a litmus test—if anyone truly defies time-space dimensions, they’ll certainly be able to locate page 25.
[Cosmic shrug.]
Thobey Campion is the former Publisher of Motherboard. You can subscribe to his Substack here.
How to Escape the Confines of Time and Space According to the CIA syndicated from https://triviaqaweb.wordpress.com/feed/
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
XILS-lab creates KaoX a virtual instrument inspired by legendary FM synthesizer
XILS-lab creates KaoX a virtual instrument inspired by legendary FM synthesizer
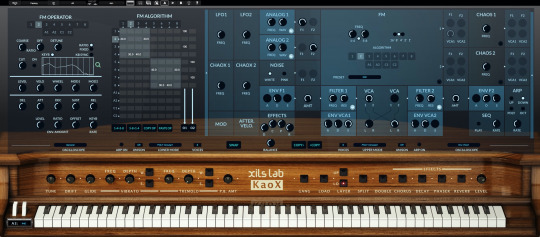
XILS-lab is proud to announce availability of KaoX — a virtual instrument inspired by a legendary FM (Frequency Modulation) synthesizer, albeit bolstered by virtual analogue sound synthesis and additional chaotic algorithms in an advanced two-layer architecture allowing for a powerful sound creation tool to fuel DAW-driven synthesizer dreams with a much more easily understood signal path than its iconic FM forefather
To appreciate its iconic inspiration is to truly appreciate the power of KaoX, XILS-lab’s latest virtual instrument. Indeed, the early-Eighties synthesizer market was dominated by analogue synthesizers using analogue circuits and analogue signals to generate sounds electronically, which, when made available as programmable polysynths with patch storage, were costly with limited polyphony. Putting paid to that dominance, an Eighties-dominating 16-voice FM synthesizer changed course — changing the course of musical history in the process — by generating sounds via frequency modulation, a form of sound synthesis whereby the frequency of a waveform is changed by modulating its frequency with a modulator. Mass manufactured using very-large- scale integration chips by a Japanese giant of a company who had licensed the technology from Stanford University, California — composer, musician, and professor John Chowning developed the digital implementation of FM synthesis while there, the world’s first commercially-successful digital synthesizer subsequently sold over 200,000 units within three years — around 20 times more than the most iconic analogue synthesizer of all time sold in its impressive decade-long lifespan — and its preset sounds soon became staples of the Eighties pop pantheon with E PIANO 1 purportedly ending up on 40% of the US Billboard Hot 100 chart toppers throughout 1986. Therein lay the rub. Really complex menus and a lack of conventional controls meant that few learned to program the comparatively keenly-priced instrument in depth — despite FM synthesis lending itself to creating brighter, glassier sounds, as well as imitative acoustic sounds so much better than its instantly unfashionable analogue adversaries, programmable polyphonic or otherwise. Of course, fashions change with time and technology; the instrument in question has long since fallen out of favour. Although analogue synthesizers — somewhat ironically — are now more commonplace than they ever were with a perceived warmth of sound and appealing hands-on control working in their favour, the convenience of an ITB (in the box) workflow with DAW-driven virtual instruments and effect plug-ins has far from lost its appeal for today’s music-making masses. Time to revisit the wonderful world of FM synthesis with a modern-day twist? Knowingly, KaoX does just that. After all, as a virtual instrument- and effect plug-in-specialising software company, XILS-lab loves to create tools that inspire its users to create more imaginative music than they ever dreamed possible!
Put it this way: with KaoX, XILS-lab has created a virtual instrument inspired by that legendary FM synthesizer, albeit bolstered by virtual analogue sound synthesis and additional chaotic algorithms in an advanced two-layer architecture allowing for a powerful sound creation tool to fuel DAW-driven synthesizer dreams with a much more easily understood signal path than its iconic FM forefather since said signal path is easily understood through the use of illuminated modules in a GUI (Graphical User Interface) that is equally easy on the eye. KaoX’s knowing nod towards the preset-powered popularity of its iconic FM forefather is immediately obvious for all to see and hear in an easy-to-tweak simplified view allowing its UP (upper) and LO (lower) synthesizer layers — each with independent synthesis modules — to be combined in three different ways. Working in single mode, only the selected layer is active and heard, while both layers are active and heard in SPLIT and DOUBLE modes — the lower part of the keyboard playing the LO layer and the upper part of the keyboard playing the UP layer in the case of the former, while both the UP and LO layers are simultaneously played across the keyboard in the case of the latter. Limited controls are available in this simplified view, including TUNE, DRIFT, GLIDE, VIBRATO, FREQ (vibrato frequency), DEPTH (vibrato), W (wheel), TREMOLO, FREQ (tremolo frequency), and DEPTH (tremolo), plus CHORUS, DELAY, PHASER, and REVERB effects, enabling users to easily play presets and to tweak them accordingly — adding vibrato and tremolo or switching effects on and off, for instance.
Alternatively, activating an advanced settings view brings the wonderful world of KaoX into full view, allowing more adventurous users access to the virtual instrument’s internal modules to tweak or change any parameter therein, aided by contextual help windows, while active modules are helpfully illuminated. FM synthesis options are available on each of the two available layers with eight operators grouped in two banks with independent pitch — perfect for creating chorus-like FM sounds or punchy stereo patches — and two outputs (O1 and O2). Each FM OPERATOR features one LFO (Low Frequency Oscillator), one envelope, WHEEL and VEL (velocity aftertouch) access, two user-definable external modulators (assignable to any KaoX modulation source), KEYB (keyboard follower) 2D pad, RATIO or FIXED frequency selection, and a lowpass filter. Furthermore, virtual analogue synthesis options are also available on each of the two available layers with two continuous waveform analogue oscillators (ANALOG OSCILLATOR 1 and ANALOG OSCILLATOR 2), two zero-delay-like analogue filters (FILTER 1 and FILTER 2), four D-ADSR envelopes, and four VCA outputs for bringing a depth and warmth to the sound creation table. That said, KaoX also allows its users to create sounds that they had never thought possible, thanks to two chaotic oscillators (CHAOS OSCILLATOR 1 and CHAOS OSCILLATOR 2) and two chaotic ring modulators (CHAOX 1 and CHAOX 2). And as if that was not enough to keep committed sound creators seriously satisfied, KaoX comes complete with a flexible four-track step SEQUENCER, where each track can be assigned to the UP or LO layer with independent sustain and gating or used as a modulation source. Sound-wise, KaoX comes packed with 500-plus presets programmed by world-class sound designers Mikael Adle, Soundsdivine, Status, Nori Ubukata, Tom Wolfe, Xenos, Yuli-Yolo, Zensound, and many more — more than enough to point anyone of any ability in the general direction of where they might musically want to go. Getting there is made much easier with its integrated single-window preset manager making finding the right patch for the task, managing presets and sound banks, as well as creating custom tags, an efficient easy-going experience that could barely be dreamt of back in the early Eighties. Today the time has clearly come to revisit the wonderful world of FM synthesis with a modern-day twist and appreciate the power of KaoX, XILS- lab’s latest virtual instrument par excellence — from France with love... and all without the need for very-large-scale integration chip mass manufacture! KaoX is available to purchase as an iLok (2 and 3 dongle hardware or software) protected plug-in priced at an introductory promo price of €99.00 EUR until May 15, 2021 — rising thereafter to an MSRP (Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price) of €179.00 EUR — directly from XILS-lab via the dedicated KaoX webpage (https://www.xils-lab.com/products/kaox-p-168.html), which also includes more in-depth information. KaoX can be directly downloaded as a multi-format AAX, AU, and VST (Mac OS X 10.8 and later) and AAX and VST (Windows 7, 8, and 10) plug-in from here: https://www.xils-lab.com/products/kaox-p-168/download.html Listen to several KaoS-showcasing demo tracks providing the soundtrack to XILS-labs’ latest teaser video here: https://youtu.be/qeZJvGe6a4Y
youtube
https://www.xils-lab.com/products/kaox-p-168.html
#news#xilslab#synth#plugin#musicproduction#musicproducer#composer#compostion#sounddesign#fmsynthesis
1 note
·
View note
Text
HTML vs CSS
In the digital world, if you want to design your website, you need to use HTML and CSS. And explaining what the difference between HTML and CSS is can help you web design faster and create likable sites with great user experience counts.
HTML vs CSS
Works mutually to generate the website. Hypertext markup language generates the on-page page content, and CSS generate the style of the website.
In other words, HTML is like a body, and CSS looks like a garment. The body may exist without clothes, but it can look quite simple. When you put simple HTML on CSS, you create a more dynamic website, improving your user experience.
In this blog, we will explain the difference between HTML vs CSS below:
Difference Between HTML vs CSS
These are the following:
HTML: HTML stands for a hypertext markup language.It is a fundamental language being used to make website pages. It has an especially d code structure, which makes it very simple to learn and learn differentiated with some other language.
CSS or falling style tables are the language of style tables that can be applied to any XML archive. Its motivation is to improve the stylization of specific things so the composed code will be a lot simpler to peruse.
HTML is really basic, with a couple of signals that are intended to arrange certain words, sentences, or passages. It additionally very justifies mistakes by giving a few outcomes, regardless of whether there are mistakes in the code.
This part of HTML makes it simple to learn and compose basic site pages that contain just a modest quantity of substance and designing. The issue with HTML is that it doesn’t scale well when you begin to create greater or progressively delightful pages.
Styling can remember a few catchphrases for each area, and this is rehashed a few times in the same spot, making the page pointlessly long. The simple to learn language turns out to be confusing, and it’s very hard to follow after you’ve committed errors.
Examples:
HTML tags on very basic level keywords, which are encased in point sections and usually arrive in a set.
<tagname> content </tagname>
HTML components represent a particular area on a site page.
Content is the writings, connections, pictures, or other data shown on your site page.
The start tag is an HTML component used to show the start of the component.
End tags are the HTML component to separate individual parts.
CSS: CSS stands for cascading style sheets. This is the language of style tables that can be utilized for any XML record on the screen. CSS was intended to rearrange code on a lot of bigger pages.
This doesn’t indicate that CSS can’t be utilized on more straightforward and less complex pages. CSS can, in any case, be helpful for littler pages, however, the advantages become all the more clear as the page size increments. CSS does this by making a custom that characterizes the correct textual style, size, shading, edges, and even foundation. These custom labels can be utilized similarly as standard HTML catchphrases.
For example:
Font and Bold; however rather, on the off chance that you simply transform one perspective, it changes each viewpoint as per the meaning of the tag.
The last result of this is you will simply need to use one tag to achieve a particular view, and you can use that tag over and over on your pages. You are moreover not confined to a solitary tag, you can make as much as you need to change your page totally.
CSS is just a gadget that has gotten well known on account of its identity. This makes it much less complex to make pages and fix issues. While you can use CSS on HTML pages, it’s not just for HTML. It can in like manner be utilized in various tongues like XML and XHTML, among others.
Examples:
CSS statements rest inside wavy sections, and each consists of two sections: property and its worth, isolated by a colon. You can characterize various features in a single revelation, each separated by a semi-colon.
Selectors demonstrate which HTML component you need to style.
Declaration incorporates property and worth isolated by a colon. Also, wavy props encasing all affirmations are known as Declaration square.
Qualities determine the settings you need to apply in the picked properties.
Properties mean the parts of components you need to change.
Advantage of HTML vs CSSHTML:
HTML is generally utilized.
Simple to learn and utilize.
Each program supports HTML Language.
Try not to need to buy any additional product since it is naturally in each window.
Analogous from XML linguistic structure, which used to an expanding degree for information stockpiling.
It is free as you need not purchase any product.
Simple to learn and code even to apprentices.
CSS:
It easily maintains large websites.
CSS saves the time of the website. You can specify a method for each HTML element and easily apply it to the web pages.
The Script offers steady stage freedom and can bolster the most recent programs also.
Global web standards provide good ideas to start using CSS in all the HTML pages.
The search engine will allow a large number of users to locate you on the internet. Less content will play an important role in the search engine.
CSS can position your elements where you want on the web page.
CSS has better styles for HTML and a lot more extensive scope of characteristics.
Disadvantage of HTML vs CSS HTML:
1. It can generate just static and plain pages, so if we need dynamic pages, at that point, HTML isn’t valuable.
2. Need to compose part of code for making an easy site page.
3. Security highlights are bad in HTML.
4. On the off chance that we have to compose long code for making a website page, at that point, it delivers some intricacy.
CSS:
Lack of security: CSS doesn’t have the work in security that will shield it from being abrogated. Any individual who has a perused/compose access to a site can change the CSS document, adjust the connections or upset the organizing, regardless of whether coincidentally or structure.
Fragmentation: CSS renders various measurements with every program. Developers ought to consider and test all code over numerous programs before taking any site, or portable application live with the goal that no similarity issues would emerge.
Key Difference between HTML vs CSS
These are the following:
HTML is essentially a standard markup language for representing the structure of website pages though CSS is the template language for depicting the introduction and plan of pages
HTML is anything but difficult to learn and has clear language structure though CSS can here and there get untidy and can make entanglements in codes.
CSS is autonomous of HTML, and it tends to be utilized with any XML-based markup language while this isn’t a similar case with HTML
HTML records can contain CSS codes, yet then again, CSS can never contain HTML codes in it.
HTML gives labels which are encompassing the substance of any website page components through CSS comprises of selectors which are encompassed by an affirmation square
CSS has fractured, yet HTML doesn’t create any such issues.
CSS utilizes a lot lesser code and along these lines produce a lot lesser page stacking time than HTML.
Should you learn HTML or CSS
Website designers need to ace both HTML and CSS. When all is said in done, it bodes well, to begin with, HTML first, especially on the grounds that the expense framework is generally simple to learn.
Yet, learning HTML and CSS together, particularly the manners in which they associate with one another, gives website specialists more authority over their pages.
For instance, architects compose CSS in a few distinct organizations: outside templates, inner templates, and inline style. Outer models gather all the CSS guidelines for a site’s plan in a single record, which creators usually connect to in the header of each page on their site.
Interior templates apply to one specific page, a valuable device for architects who need an alternate style for a single page on their site. Creators incorporate the inner template in the page’s header. At long last, inline styles influence just a solitary line of HTML code, changing only the title or one single section.
Understanding when to utilize these various arrangements is a significant piece of acing, both CSS and website designers.
Conclusion:
In the above discussion, we explain the difference between HTML vs CSS. In the difference of looking at HTML vs CSS over a scope of variables, it very well may be supposed that these are two of the center web scripting languages for website page improvement however at a similar purpose of time, everyone has its own upsides and downsides.
Along these lines, before picking any of them, engineers ought to learn and break down various parts of HTML and CSS dialects. Therefore, in light of the kind of undertaking need, time of work and on all other unique examined viewpoints, these web scripting languages ought to be chosen to appear at the ideal objective.
Our computer science homework help and computer science assignment help experts provide programming assignment help related to HTML assignment help with the best solution.
#hypertextmarkuplanguage#html#CSS#programming#difference#difference between HTML and CSS#html and css#blog#codeavail
1 note
·
View note
Text
Digital to Analog Signals Assignment Homework Help
http://computernetworkingonlinehelp.com/DigitaltoAnalogSignals.php
Digital to Analog Signals assignment help| Digital to Analog Signals homework help| Digital to Analog Signals online tutor
ComputerNetworkingOnlineHelp services provide you with a skilled team of presentation. We provide the homework and assignments solution with no plagiarism and with reference styles Harvard, APA, AMA, MLA and IEEE. Computernetworkassignmenthelp.com imparts our online Assignment service on reasonable prices. Our Professionals are Master or PhD degree holders in the field of Digital-to-Analog assignment and homework from top ranked institutions, universities and colleges with a year of experience in imparting their services in the field of Computer.
#Digital to Analog Signals Assignment Homework Help#Digital to Analog Signals Assignment Help#Digital to Analog Signals Homework Help#Digital to Analog Signals Online Help#Digital to Analog Signals Project Help#Digital to Analog Signals Assignment Homework Help Experts
0 notes
Text
How to use Camera?
All protection cameras require a principal video recorder to transmit and archive the footage captured. Dvrs (virtual video recorders) evolved from the older vcr fashions, while nvrs (community video recorders) represents the following step in the evolution of . Here’s a side-by-aspect look at how dvrs and nvrs evaluate.
Dvrs normally offer what's known as “d1” resolution. That is the conventional video fine used in closed-circuit tv structures. D1 equates to a decision of 720×480 pixels, which is taken into consideration a “general decision” that can be recorded and, consequently, displayed on a playback monitor.
Nvrs, in assessment, can document in 1080p, that's high-definition (hd). It is a extensive improvement in video best over the dvr device. For evaluation functions, 1080p equates to a pixel resolution of 1920 vertical traces x1080 horizontal traces whilst viewed on a monitor. This results in a miles clearer, cleanser recorded video photo. Digicam connections
Ip cameras are well suited with community video recorders (nvrs), which give different advantages over the older virtual video recorders (dvrs). In quick, nvr statistics better-best video in a virtual format this is encoded at the camera itself earlier than being transmitted wirelessly or over the internet to the nvr. Those structures can be scaled up a good deal greater without difficulty than dvr structures. Nvrs also help wi-fi cameras and do now not need to be hardwired. http://fixdreviews.net/blink-vs-arlo-security-camera/
Nvr setups use a software program to document — it’s basically a laptop related to the net — whilst a dvr encodes the video sign on the dvr, now not on the digital camera, and is confined by way of the wide variety of cameras and distance between cameras and the dvr. For that reason, nvrs may be installed anywhere on the internet and be programmed to sync with the assigned cameras at the same time as dvrs should be hardwired immediately to a confined variety of cameras. Let me give an explanation for similarly.
Connecting analog cameras with a dvr gadget is completed by way of without delay plugging a bnc coaxial cable from the dvr into the digital camera. To attach extra cameras to the dvr gadget, you want extra coaxial cables. Such structures are difficult to enlarge because as soon as every bnc connection on the dvr unit is occupied by a digicam, you need to purchase a completely new dvr earlier than including any other camera to the gadget. (dvrs are generally bought with four-, 8- or 16-digital camera enter abilities.) dvrs additionally require that the related cameras be set up within approximately 500 toes of the dvr, in any other case the video exceptional starts offevolved to degrade and can require a video signal amplifier. Finally, dvrs may not offer strength via the cable connections to the attached cameras, thereby requiring you to install extra gadget for offering electricity on your cameras.
An nvr gadget eliminates these problems as it connects at once to a network. Ip cameras which are linked to the same network, normally via way of a poe transfer, are then able to transmit footage to the nvr. Using poe, or “electricity over ethernet,” means the electric required for the digital camera runs via the same ethernet cable that carries the automatic video facts. Thus, nvr setups are a lot simpler to scale up than dvr structures, actually because they can be given any new digicam introduced to the network with not anything more than something like an extra poe transfer, if that. A few ip cameras also transmit pictures to the nvr over wireless. There aren't any proximity boundaries to these arrangements so long as a digital camera is hooked up to the identical community as the nvr.
The biggest drawback to an nvr machine is that not each ip digicam will paintings with each nvr, so, you’ll need to understand whether your cameras could be well suited with a given video recorder before investing. Moreover, a few nvrs will have a handful of poe ports built into them, at the same time as others will no longer. If you want to buy a poe switch, the smaller ones start between $40 and $50 and offer approximately 5 ports. Every port represents a information connection and a electricity supply for one digicam. That said, in case your plan is to scale up and enforce a completely huge safety camera gadget, there are poe switches that feature as many as 48 distinct ports and can variety in fee from $800 to $1,000.
70 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thinking Through Interfaces, a syllabus
*That looks enlightening.
THINKING THROUGH INTERFACES
Co-taught by Zed Adams (Philosophy) and Shannon Mattern (Media Studies)
Tuesdays 4:00 - 5:50pm | 6 East 16th St #1003
Interfaces are everywhere and nowhere. They pervade our lives, mediating our interactions with one another, technology, and the world. But their very pervasiveness also makes them invisible. In this seminar, we expose the hidden lives of interfaces, illuminating not just what they are and how they work, but also how they shape our lives, for better and worse. We also discuss a number of pressing social and political issues, such as why we are quick to adopt some interfaces (e.g., smartphones and social media platforms), but reluctant to embrace others (e.g., new voting machines and Google Glass).
(...)
RESOURCES
With a few exceptions, all readings will be made available on our class website, at http://www.wordsinspace.net/interfaces/2019/. We’ll provide everyone with a copy of Tom Mullaney’s The Chinese Typewriter and David Parisi’s Archaeologies of Touch.
SCHEDULE OF MEETINGS
WEEK 1: JANUARY 22: INTRODUCTIONS
What is an interface?
How are interfaces differentiated?
Can an interface become a part of our mind?
Do interfaces shape what we use them to do?
What are the limits of interfaces: what problems do they not help us solve?
WEEKS 2 AND 3: CONCEPTUALIZATION
WEEK 2: JANUARY 29: CONCEPTUALIZATION I
Nelson Goodman, “The Theory of Notation” (Chapter Four), Languages of Art (Hackett, 1976): 127-173.
Florian Cramer and Matthew Fuller, “Interface” in Software Studies, ed., Matthew Fuller (MIT Press, 2008): 149-53.
Johanna Drucker, “Interface and Interpretation” and “Designing Graphic Interpretation” in Graphesis: Visual Forms of Knowledge Production (Harvard University Press, 2014): 138-97.
WEEK 3: FEBRUARY 5: CONCEPTUALIZATION II
Shannon Mattern, “Mission Control: A History of the Urban Dashboard,” Places Journal (March 2015).
Shannon Mattern, “Things that Beep: A Brief History of Product Sound Design,” Avant (August 2018).
We encourage you to think, too, about how interfaces might embody different cultures and ideologies. Consider, for example, feminist interfaces or indigenous interfaces -- or interfaces that embody universal, accessible design. You'll find some relevant resources in the modules at the end of this syllabus, and we'll explore many of these themes as part of our case studies throughout the semester.
In-Class Workshop (second half of class): small-group interface critiques
Supplemental:
Christian Ulrich Andersen and Soren Bro Pold, eds., Interface Criticism: Aesthetics Beyond the Buttons (Aarhus University Press, 2011).
Martijn de Waal, The City as Interface: How New Media Are Changing the City (nai010, 2014).
Johanna Drucker, “Humanities Approach to Interface Theory,” Culture Machine 12 (2011).
Johanna Drucker, “Performative Materiality and Theoretical Approaches to Interface,” Digital Humanities Quarterly 7:1 (2013).
Florian Hadler and Joachim Haupt, “Towards a Critique of Interfaces” in Interface Critique, eds., Florian Hadler and Joachim Haupt (Berlin: Kulturverlag Kadmos, 2016): 7-16.
John Haugeland, “Representational Genera” in Having Thought: Essays in the Metaphysics of Mind, ed. Haugeland (Harvard Univ Press, 1992): 171-206.
Branden Hookway, Interface (MIT Press, 2014)
Interface Critique (journal).
Steven Johnson, Interface Culture (Basic Books, 1999)
Matthew Katz, “Analog Representations and Their Users,” Synthese 193: 3 (June 2015): 851-871.
Kimon Keramidas, The Interface Experience - A User’s Guide (Bard Graduate Center, 2015).
Shannon Mattern, “Interfacing Urban Intelligence,” Places Journal (April 2014).
Don Norman, The Design of Everyday Things (Basic Books, 2013).
Mitchell Whitelaw, “Generous Interfaces for Digital Cultural Collections,” Digital Humanities Quarterly 9:1 (2015).
Jeff Johnson, Designing with the Mind in Mind (Morgan Kauffmann, 2014).
WEEKS 4 AND 5: TYPEWRITER KEYBOARDS
Our first case study is the QWERTY keyboard. This case raises fundamental questions about why interfaces are adopted in the first place, the extent to which their original designs constrain how they are subsequently used, and how particular linguistic politics and epistemologies are embodied in our interfaces.
WEEK 4: FEBRUARY 12: KEYBOARDS & QWERTY
Andy Clark, Chapters One through Three, and Ten, Being There: Putting Brain, Body, and World Together Again (MIT Press, 1998): 11-69 and 193-218.
S. J. Liebowitz and Stephen E. Margolis, “The Fable of the Keys,” The Journal of Law & Economics 33:1 (1990): 1-25.
WEEK 5: FEBRUARY 19: OTHER KEYBOARDS
Thomas S. Mullaney, The Chinese Typewriter: A History (MIT Press, 2017): Chapter 1, 35-74; Chapter 4, 161-93; Chapter 6, 237-53 (up through “How Ancient China Missed…”; and Chapter 7, 283-8 (through “China’s First ‘Model Typist’”).
Kim Sterelny, “Minds: Extended or Scaffolded?” Phenomenology and the Cognitive Sciences 9:4 (2010): 465-481.
See Marcin Wichary’s forthcoming book about the global history of keyboards, as well as his research newsletters.
4-5pm: Skype TBD
Supplemental:
Louise Barrett, Beyond the Brain (Princeton University Press, 2015).
Andy Clark and David Chalmers, “The Extended Mind,” Analysis 58:1 (1998): 7-19.
Friedrich A. Kittler, Gramophone, Film, Typewriter, trans. Geoffrey Winthrop-Young and Michael Wutz (Stanford University Press, 1986).
Lisa Gitelman, Scripts, Grooves, and Writing Machines: Representing Technology in the Edison Era (Stanford University Press, 1999).
John Haugeland, “Mind Embodied and Embedded,” Having Thought (Harvard University Press, 1998): 207-237.
Richard Heersmink, "A taxonomy of cognitive artifacts: function, information, and categories." Review of philosophy and psychology 4.3 (2013): 465-481.
Richard Heersmink, "The Metaphysics of Cognitive Artefacts," Philosophical Explorations 19.1 (2016): 78-93.
Neil M. Kay, “Rerun the Tape of History and QWERTY Always Wins,” Research Policy 42:6-7 (2013): 1175-85.
Prince McLean, “Inside the Multitouch FingerWorks Tech in Apple’s Tablet,” Apple Insider (January 23, 2010).
Jan Noyes, “QWERTY - The Immoral Keyboard,” Computing & Control Engineering Journal 9:3 (1998): 117-22.
Kim Sterelny, The Evolved Apprentice: How Evolution Made Humans Unique (MIT Press, 2012).
Cassie Werber, “The Future of Typing Doesn’t Involve a Keyboard,” Quartz (November 23, 2018).
Darren Wershler-Henry, The Iron Whim: A Fragmented History of Typewriting (Cornell University Press, 2007).
WEEKS 6 AND 7: HAPTICS
WEEK 6: FEBRUARY 26: PUSHING BUTTONS
H. P. Grice, “Some Remarks About the Senses,” in Analytical Philosophy, First Series, ed. R. J. Butler (OUP Press, 1962): 248-268. Reprinted in F. MacPherson (ed), The Senses (OUP Press, 2011): 83-101.
Matthew Fulkerson, “Rethinking the Senses and Their Interactions: The Case for Sensory Pluralism,” Frontiers in Psychology (December 10, 2014).
Rachel Plotnick, “Setting the Stage,” in Power Button: A History of Pleasure, Panic, and the Politics of Pushing (MIT Press, 2018): 3-16.
Rachel Plotnick, “Force, Flatness, and Touch Without Feeling: Thinking Historically About Haptics and Buttons,” New Media and Society 19:10 (2017): 1632-52.
WEEK 7: MARCH 5: HAPTICS II
David Parisi, Archaeologies of Touch: Interfacing with Haptics from Electricity to Computing (University of Minnesota Press, 2017): Introduction, 1-40; Chapter 3, 151-212; and Chapter 4, 213-264.
4-5pm: Skype with Dave Parisi
Supplemental:
Sandy Isenstadt, “At the Flip of a Switch,” Places Journal (September 2018).
Mathias Fuchs, Moisés Mañas, and Georg Russegger, “Ludic Interfaces,” in Exploring Videogames: Culture, Design and Identity, eds., Nick Webber and Daniel Riha (Interdisciplinary-Net Press): 31-40.
Matthew Fulkerson, The First Sense: A Philosophical Study of Human Touch (MIT Press, 2013).
Gerard Goggin, “Disability and Haptic Mobile Media,” New Media & Society 19:10 (2017): 1563-80.
Kim Knight, “Wearable Interfaces, Networked Bodies, and Feminist Interfaces,” MLA Commons (2018).
Brian Merchant, The One Device: The Secret History of the iPhone (Little, Brown, 2017).
Stephen Monteiro, The Fabric of Interface: Mobile Media, Design, and Gender (MIT Press, 2017).
David Parisi, “Games Interfaces as Bodily Techniques,” Handbook of Research on Effective Electronic Gaming in Education, ed. Richard Ferdig (IGI Global): 111-126.
David Parisi, Mark Paterson, and Jason Edward Arches, eds., “Haptic Media” Special Issue, New Media & Society 19:10 (October 2017).
Rachel Plotnick, “At the Interface: The Case of the Electric Push Button, 1880-1923,” Technology and Culture 53:4 (October 2012): 815-45.
MARCH 11 @ NOON
Share your final project and presentation proposal with Zed and Shannon. See “Assignments” for more detail.
WEEK 8: MARCH 12
Individual meetings to discuss presentations and final projects
MARCH 19: NO CLASS: SPRING BREAK
WEEKS 9-10: VOICE
WEEK 9: MARCH 26: History of Vocal Interfaces (Zed away)
Mara Mills, “Media and Prosthesis: The Vocoder, the Artificial Larynx, and the History of Signal Processing,” Qui Parle 21:1 (Fall/Winter 2012): 107-49.
Danielle Van Jaarsveld and Winifred Poster, “Call Centers: Emotional Labor Over the Phone,” in Emotional Labor in the 21st Century: Diverse Perspectives on Emotion Regulation at Work, ed. Alicia Grandey, Jim Diefendorff, and Deborah Rupp (LEA Press, 2012): 153-73.
Confirm the assigned text for your presentation: send to Shannon and Zed a complete Chicago-style citation and either a high-quality pdf or a link to the online resource before class today, so we can update our class website with everyone’s material.
WEEK 10: APRIL 2: Contemporary Vocal Interfaces
Adelheid Voshkul, “Humans, Machines, and Conversations: An Ethnographic Study of the Making of Automatic Speech Recognition Technologies,” Social Studies of Science 34:3 (2004).
Andrea L. Guzman, “Voices in and of the Machine: Source Orientation Toward Mobile Virtual Assistants,” Computers in Human Behavior (2018).
Halcyon M. Lawrence and Lauren Neefe, “When I Talk to Siri,” Flash Readings 4 (September 6, 2017) {podcast: 10:14}.
Halcyon M. Lawrence, “Inauthentically Speaking: Speech Technology, Accent Bias and Digital Imperialism,” SIGCIS, Computer History Museum, March 2017 {video: 1:26 > 17:16}
Lauren McCarthy, LAUREN. A human smart home intelligence (review press, too).
4-5pm: Skype with Halcyon M. Lawrence
Supplemental:
Meryl Alper, Giving Voice: Mobile Communication, Disability, and Inequality (MIT Press, 2017).
Michel Chion, Sound: An Acoulogical Treatise (Duke, 2016).
Karin Bijsterveld, “Dissecting Sound: Speaker Identification at the Stasi and Sonic Ways of Knowing,” Hearing Modernity (2018).
Trevor Cox, Now You’re Talking: The Story of Human Communication from the Neanderthals to Artificial Intelligence (Counterpoint, 2018).
Brian Dumaine, “It Might Get Loud: Inside Silicon Valley’s Battle to Own Voice Tech,” Fortune (October 24, 2018).
Larry Greenemeier, “Alexa, How Do We Take Our Relationship to the Next Level?” Scientific American (April 26, 2018).
Jason Kincaid, “A Brief History of ASR,” descript (July 12, 2018).
Halcyon M. Lawrence, “Siri Disciplines,” in Your Computer is on Fire, eds., Marie Hicks, Ben Peters, Kavita Philips and Tom Mullaney (MIT Press, forthcoming 2019).
Halcyon Lawrence and Lauren Neefe, “Siri’s Progeny: Voice and the Future of Interaction Design,” Georgia Tech, Fall 2016.
Xiaochang Li and Mara Mills, “Vocal Features: From Voice Identification to Speech Recognition by Machine,” Technology and Culture (forthcoming 2019).
Luke Munn, “Alexa and the Intersectional Interface,” _Angles (June 2018).
Quynh N. Nguyen, Ahn Ta, and Victor Prybutok, “An Integrated Model of Voice-User Interface Continuance Intention: The Gender Effect,” International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction (2018).
Winifred Poster, “Sound Bites, Sentiments, and Accents: Digitizing Communicative Labor in the Era of Global Outsourcing,” in digitalSTS: A Field Guide for Science & Technology Studies, eds., David Ribes and Janet Vertesi (Princeton University Press, forthcoming April 2019).
Winifred Poster, “The Virtual Receptionist with a Human Touch: Opposing Pressures of Digital Automation and Outsourcing in Interactive Services” in Invisible Labor: Hidden Work in the Contemporary World, eds. Marion G. Crain, Winifred R. Poster, and Miriam A. Cherry (University of California Press, 2016): 87-111.
Thom Scott-Phillips, Speaking our Minds: Why Human Communication is Different, and How Language Evolved to Make it Special (Palgrave Macmillan, 2015).
Craig S. Smith, “Alexa and Siri Can Hear This Hidden Command. You Can’t,” New York Times (May 10, 2018).
Dave Tompkins, How to Wreck a Nice Beach: The Vocoder from World War II to Hip-Hop, The Machine Speaks (Stop Smiling Books, 2011).
Mickey Vallee, “Biometrics, Affect, Autoaffection and the Phenomenological Voice,” Subjectivity 11:2 (2018): 161-76.
Bruce N. Walker and Michael A. Nees, “Theory of Sonification” in The Sonification Handbook, eds. Thomas Hermann, Andy Hunt, and John G. Neuhoff (Logos Publishing, 2011).
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring the Differences Between a Modem Vs Router: Which One is Right for You?
In today's world, internet connectivity is an integral part of our lives. We rely on the internet for communication, entertainment, and even work. However, when it comes to setting up an internet connection, there are two important devices that you should be familiar with: a modem and a router. These devices are essential for connecting to the internet and transmitting data between devices. In this article, we will explore the differences between a modem vs router and why it's important to understand these differences. Understanding the differences between a modem vs router can help you troubleshoot connectivity issues, upgrade your network, and make informed decisions when choosing a new device. With the right knowledge, you can ensure that your network is secure, efficient, and capable of meeting your needs. Now let us get to know about these two. What is a Router? What is a Modem? Differences Between a Modem Vs Router Which one to Choose Between, Modem vs Router? Why choose Separate Modem and Router? Troubleshooting and Maintaining your Modem or Router Final Deduction FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)

What is a Router?
A router is a networking device that acts as a central hub for your home or office network. Its primary purpose is to connect multiple devices to a network and provide a way for these devices to communicate with each other. Routers work by directing data traffic between devices and managing the flow of information. When you connect a device to a router, it sends data in the form of packets. The router then reads the destination IP address of each packet and determines where it needs to go. The router then sends the packet to the appropriate device or forwards it to another router that can deliver it to its destination.

What is a Modem?
A modem is a device that connects your home or office network to your internet service provider (ISP). The term "modem" is short for "modulator-demodulator", which refers to the device's ability to convert digital data signals to analog signals that can be transmitted over traditional telephone lines. The purpose of a modem is to translate the digital data signal from your ISP into a format that can be understood by your devices. When you connect to the internet, your modem communicates with your ISP's network, establishing a connection and allowing you to access the internet.
Differences Between a Modem Vs Router
While a router and modem are essential components of a home or office network, they perform very different functions. The main differences between modem vs router are: - Functionality: A modem connects your network to the internet, while a router manages the traffic between devices on your network. - Connection: A modem requires a physical connection to your ISP, while a router is connected to the modem and allows multiple devices to connect to the network. - IP Addresses: A modem receives a single public IP address from your ISP, while a router assigns private IP addresses to devices on your network. - Security: Modems do not provide any security features, while routers have built-in firewalls and other security measures to protect your network from online threats. In summary, while a modem connects your network to the internet, a router manages the flow of data traffic between devices on your network. The two devices work together to provide a seamless and secure online experience.
Which one to Choose Between, Modem vs Router?
It would be best to have a modem and router for a functional home or office network. A modem connects your network to the internet, while a router manages the traffic between devices on your network. Without a modem, you cannot access the internet, and without a router, you cannot connect multiple devices to the network. If you only have a modem, you can only connect one device to the internet. This can be limiting, especially in a home or office where multiple devices need internet connectivity. On the other hand, if you only have a router and no modem, you will not be able to access the internet at all, as the router cannot connect to your ISP's network. It's also worth noting that many internet service providers offer a combination modem and router device. While these devices can be convenient, they may not offer the same level of performance or security as a separate modem and router devices. Additionally, having separate devices allows for easier upgrading and replacement of either component. In conclusion, both a modem and a router are necessary components for a functional home or office network. While they perform different functions, they work together to provide seamless and secure internet connectivity to all of your devices.

Why choose Separate Modem and Router?
Choosing separate modem and router devices can offer several benefits, including: - Flexibility: When you have a separate modem and router, you can upgrade or replace each component independently of the other. This means that you can take advantage of new technologies or features without having to replace both devices. - Better performance: A separate modem and router can provide better overall performance than a single all-in-one device. For example, a dedicated modem can provide faster internet speeds, while a high-quality router can provide better Wi-Fi coverage and performance. - Customization: With separate modem and router units, you have more control over the configuration and settings of each device. This can be especially useful for advanced users or those with specific networking needs. - Security: Separating your modem and router can improve the security of your home network. If your all-in-one device is compromised, both your internet connection and your Wi-Fi network may be vulnerable. With separate devices, however, an attacker would need to compromise both devices to gain access to your network. Overall, choosing separate modem and router units can provide greater flexibility, performance, customization, and security for your home network.
Troubleshooting and Maintaining your Modem or Router
As with any electronic device, routers and modems can experience issues from time to time. Here are some common issues and solutions to help you troubleshoot your router or modem: - Connectivity issues: If you are experiencing connectivity issues, try restarting your modem and router. You can also check your network cables to ensure they are properly connected. - Slow internet: If your internet is slow, try disconnecting some of the devices on your network. You can also try resetting your router or upgrading to a faster internet plan. - Security issues: To ensure your network is secure, make sure your router's firmware is up to date and that you are using strong passwords. You can also enable WPA2 encryption and disable remote management to enhance your network's security further. To keep your router or modem functioning properly, here are some maintenance tips: - Keep your firmware up to date: Manufacturers often release firmware updates to fix bugs and improve performance. Check for updates regularly and install them as needed. - Keep your device clean: Dust and debris can accumulate on your router or modem and cause overheating. Use a can of compressed air to blow away any dust or debris. - Keep your device in a cool, dry place: Heat and humidity can also cause your device to overheat. Please keep it in a cool, dry place to prevent any issues. By following these troubleshooting and maintenance tips, you can ensure that your router or modem functions properly and provides a reliable and secure network connection for all of your devices.
Final Deduction
In conclusion, understanding the differences between a modem vs router is essential for setting up and maintaining a functional home or office network. While a modem connects your network to the internet, a router manages the traffic between devices on your network. Both components are necessary for a seamless and secure internet connection. It's important to note that while many internet service providers offer a combination modem and router device, separate units may offer better performance and security. In summary, having a modem and router is essential for internet connectivity, and it's important to keep them functioning properly to ensure reliable and secure network performance. We hope this article has provided helpful information to improve your understanding of these important components, and we recommend seeking professional assistance if you encounter any issues with your network setup. Related Articles: - Modem-Router Combo vs Separate: Which is Better Choice in 2023? - What is the guest WiFi Network? - Setting Up Access Control on Your Netgear Nighthawk Router to Allow/Block Devices From Accessing the Internet - Steps to Ensure the Security of Business and Home Network?
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Is a modem and a router the same thing?No, a modem and a router are not the same things. A modem is a device that connects your network to the internet, while a router is a device that manages the traffic between devices on your network. A modem converts the digital data signal from your internet service provider (ISP) into an analog signal that can be transmitted over a phone or cable line, while a router sends and receives data between devices on your local network and allows multiple devices to share a single internet connection.Does a modem or router give you WiFi?A router is what gives you WiFi, not a modem. A router acts as a central hub for your home or office network, allowing multiple devices to connect to the internet and communicate with each other. It does this by broadcasting a wireless signal that devices can connect to. A modem, on the other hand, provides access to the internet and does not offer WiFi functionality.Can the modem be used as a router?Some modems have a built-in router function, but not all modems can be used as routers. If your modem has a built-in router function, you can connect devices to it, and it will manage the traffic between them. However, if your modem does not have a built-in router, you will need to connect a separate router to your modem to manage your network.Do I need both a modem and a router?Yes, it would be best if you had both a modem and a router to set up a home or office network. A modem connects your network to the internet, while a router manages the traffic between devices on your network. Without a modem, you cannot access the internet, and without a router, you cannot manage the traffic between devices on your local network.Do I need a modem if I have a router?Yes, you need a modem if you have a router. A modem is what connects your network to the internet, while a router manages the traffic between devices on your local network. Without a modem, you cannot access the internet, even if you have a router.Does the modem or router give an IP address?A router gives IP addresses to devices on your local network, while a modem does not. When a device connects to your network, the router assigns it a unique IP address that allows it to communicate with other devices on the network and access the internet. A modem, on the other hand, provides access to the internet and does not assign IP addresses to devices on your local network.Is TP-Link a router or modem?TP-Link is a brand that produces both routers and modems. They offer a wide range of networking products, including routers, modems, and mesh WiFi systems. Some of their products have built-in modem functionality, while others are designed to be used in conjunction with a separate modem.Can I get internet with just a router?No, you cannot get internet with just a router. A router manages the traffic between devices on your local network, but it does not provide access to the internet. To access the internet, you need a modem, which connects your network to the internet.What is WPS on a router?WPS (WiFi Protected Setup) is a feature found on many routers that allows you to connect devices to your network quickly and easily. With WPS, you can connect devices to your network without having to enter a password. Instead, you simply press the WPS button on your router and then press the WPS button on the device you want to connect.What would you not use a router for?Routers are designed to connect multiple devices to a network and allow them to communicate with each other. However, there are some situations where using a router may not be necessary or practical. For example, if you only have one device and do not plan on connecting any other devices to a network, using a router would be unnecessary. Similarly, if you are using a wired connection and do not require wireless capabilities, you may not need a router.Can you get internet without a modem?In most cases, you need a modem to get internet. A modem is a device that connects your home network to your internet service provider (ISP) and is responsible for converting the signal from your ISP into a format that your devices can understand. Without a modem, your devices would not be able to communicate with your ISP, and you would not be able to access the internet. However, there are some exceptions to this rule. For example, if you are using a mobile device, such as a smartphone or tablet, you may be able to connect to the internet without a modem by using a cellular data connection. Additionally, some internet service providers offer fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) service, which does not require a modem. Instead, the fiber optic cable is connected directly to a special router that is provided by the ISP. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
High Quality Audio Dataset For Speech Recognition System As Synthetic Dataset

The explosive expansion of vocal technologycan be explained by a variety of reasons. A few of them are the rise in the use technology, such as the growth of biometrics that are operated by voice as well as voice-driven navigation systems as well as the advancements with the development of machine-learningmodels. Let's explore this new technology and learn about the workings of it and its applications.
With the development of technology There has been a difficulties in obtaining the necessary AI Training Datasets for ML models. To make up for this, a lot of synthetic or artificial data is created or simulated to help train models using ML. Primary data collection, while extremely reliable, is usually expensive and takes a long time to complete. Hence, there is an increasing demand for simulated data that could be precise and replicate actual experiences. The following article attempts to look at the benefits and drawbacks.
In just a little over twenty years, the voice recognition technology has seen a massive increase. But what is the future have in store? In 2020, the world market for voice recognition was estimated at $10.7 billion. The market is predicted to grow into $27.16 billion in 2026, growing at an annual rate of 16.8 percent from 2021 to 2026.
What is Voice Recognition?
The term "voice recognition," also known as speaker recognitionis computer program that is trained to detect as well as decode, recognize from and verify the sound of an individual in accordance with their distinctive voiceprint.
The program analyzes the biometrics of a person's voice by scanning their voice and comparing it with the needed speech command. It does this by carefully analyzing the frequency of the voice, its pitch, accent intonation, and the stress that the person speaking.
What's the benefit of synthetic data? And when should you use it?
The data is created by algorithms instead of being generated through real-world events. Real data is directly observed in the real world. It can be used to gain the most accurate information. Although real data can be valuable but it is typically expensive and time-consuming to collect and is not feasible due to privacy concerns. Synthetic data hence becomes a secondary/alternative to real data and can be used to develop accurate and advanced AI models. The artificially created data can be used in conjunction with real data in order to build an improved dataset for Audio Transcription which is free of the flaws inherent to real data.
Synthetic data is most effective to test a newly-developed system when real data is either unavailable or is biased. Synthetic data can also complement real data, which is limited not able to be shared, unusable and inaccessible.
How Does Voice Recognition Work?
The technology for speech recognition is subjected to a number of steps before it is able to reliably identify the speaker.
It starts by converting the analog sound into digital signal. To determine the question you're asking the voice assistant the microphone inside your device, listens to your voice, transforms them into electrical currents, then transforms the analog sound into binary digital format.
When electrical signals are fed through the Analog-toDigital Converter, the software begins to pick up the voltage fluctuations within certain areas that are part of the flow. The samples are very small in length - they are just a few thousandths of a second. Based on the voltage, the converter assigns binary numbers for the information.
To understand the signals, the computer program requires an extensive digital database of words, syllables, phrases or wordsand an efficient method of comparing the signals with information. The program is able to compare the sounds of the database to the digital audio converter by with a pattern recognition function.
Why Use Synthetic Data?
Obtaining large amounts of high-quality data in order to train models within the set time frame is difficult for many businesses. In addition the manual labeling of data can be a lengthy and costly procedure. This is why creating synthetic data can assist businesses overcome these obstacles and build solid models quickly.
Synthetic data decreases dependance on the original datasets and also reduces the necessity of capturing it. It is a simpler to produce, more cost-effective and efficient method of creating data sets. A large amount of quality data can be produced in much less time than real-world data. It is particularly beneficial to generate data based upon edges - or instances that are not often observed. Furthermore the synthetic data can be labeled and annotated while it is created and reduce the time required to label data.
If privacy or data safety are the primary security concerns, synthetic datasets can be utilized to reduce the risk. Real-world data must be anonymized in order to be deemed usable to use it as for training purposes. Even after anonymization, like the elimination of identification numbers from the dataset there is still the possibility for a different variable to function as an identifier variable. However, this isn't the situation with synthetic data since it's not inspired by a real person or an actual occasion.
The process of identifying and authenticating an individual's identity by analyzing the voice of a person. The process is based by assuming that no two individuals sound exactly the same due to the variations in their larynx size, the form the voice tract and other aspects.
The accuracy and reliability of the speech or voice recognition system are dependent on the training method as well as the testing and database utilized. If you've got an innovative idea to develop software for voice recognition contact GTS for databases as well as training requirements.
You can get an authentic top-quality, secure, and safe Audio Datasets that you can use to test and train machines learning models or natural model of language processing.
0 notes
Text
How to Check if Your Carbon Monoxide Detector Is Expired [It Probably Is]
Have you heard random beeps from your carbon monoxide device? Can you recall the last time you’ve had it checked?
Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning is life-threatening. Neglecting the maintenance of your carbon monoxide devices can harm the people in your property!
According to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), accidental CO poisoning has claimed the lives of 430 U.S. residents every year.
In addition, an estimated 50,000 U.S. residents are admitted to an emergency department because of carbon monoxide poisoning complications.
Carbon monoxide detectors must be installed to act as the first line of defense against the unseen threat of carbon monoxide to ensure the safety of your home and property.
Regularly maintaining CO detectors is an essential responsibility of a homeowner or a commercial building owner.
Read this article to learn more about how you can inspect if your carbon monoxide detector has expired.
Types of Carbon Monoxide Detectors
CO detectors may be classified according to the mechanism of operation.
The three types are as follows:
Biomimetic sensors work when high-concentrations of the gas block the laser inside before triggering the alarm,
Metal Oxide Semiconductors (MOS) rely on the change of temperature between carbon monoxide gas interaction to a preheated semiconductor. The temperature change is proportional to the change of resistance, which triggers the alarm, and
Electromechanical detectors operate when the interaction of air and carbon monoxide generates an electric current. When the current goes beyond the threshold, the alarm is set off.
As for the area of installation, there are also 3 classifications to choose from:
A combination of a combustible gas/CO detector is usually used for areas that receive heating from natural gas space heaters.
Digital display detectors are wall-mounted devices for household installation. They are installed within the eye-level because of the display.
Non-digital wall-mounted detectors are installed 15 inches below the ceiling to detect carbon monoxide on high levels.
Do These Detectors Really Expire?
Just like any device ran with an electrical circuit, carbon monoxide detectors expire when the sensitivity of the sensor’s components dull because of its exposure to the gas for a long time.
The estimated time frame is usually five to seven years, but newly-manufactured models can reach up to 10 years.
Moreover, all detectors manufactured before 2013 should probably reach expiration by now.
If you’re a homeowner planning to install one, it would be easy to monitor its effectiveness by checking the expiry date behind.
But when renting a space with an existing device, you will not have any idea about it. It’s best to ask the establishment owner to avoid a potential safety hazard.
3 Ways To Check For An Expired Carbon Monoxide Detector
1. Check and take note of the expiration date
Over time, CO detectors expire because of high concentrations of carbon monoxide, which affects its sensitivity.
Your CO detector is expected to work for about 5 to 10 years.
To verify these, manufacturers put on expiration dates at the back of the device.
From 2009 to 2013, federal laws have been passed requiring state residents and commercial owners to install CO detectors.
Some of those devices should already be expired or nearing its expiry date this year, making inspection an urgent matter.
If you see that your device is nearing its expiration, schedule an appointment with a fire prevention specialist to replace your device with a new one.
2. Monitor the end-of-life signal for on both digital and analog alarms
Aside from the expiration date, manufacturers also integrated warning signals to notify owners of the device’s expiration.
For detectors with digital alarms, the screen will show an “ERR” or “END” message, which means the device is up for disposal.
You will also hear a “beeping” or “chirping” sound every 30 seconds, a signal that you should have it replaced.
Be mindful of the sound pattern when it rings. Most detectors signify when it detects high carbon monoxide concentrations through a different tone.
Intermittent beeping every 4 to 5 seconds alerts a carbon monoxide leak, which means you need to call the fire department.
On the other hand, carbon monoxide detectors that are non-digital exclusively flashes a red light with the beeping sound on a 30-second interval when the battery is drained.
The emitted signals should stop by replacing the batteries with new ones, and the device is ready to work again.
If the signals persist even after the battery replacement, your device has reached its end-of-life.
It is important to remember these indicators and immediately replace your carbon monoxide alarm to prevent CO poisoning.
3. Manually test your devices
It’s also good practice to manually test the functionality of your device.
Carbon monoxide (CO) detectors have an integrated “test” button on the back or front of the device.
Make sure to test monthly to evaluate the device’s performance and maintain its effectiveness.
To test your detector, follow these steps:
Press the “test” button and wait for two beeps.
If you don’t hear any sound or if the alarm is inaudible, replace the batteries.
When the batteries are all new, but the sound is still non-existent, replace your detector.
For monitored detector installations, inform your provider beforehand to avoid triggering the emergency alarm.
It is also good practice to involve family members when testing the device. Assign them to certain places at home to check if the alarm is audible.
To ensure that the testing is professionally handled, hire a fire protection company to assess your device.
Check Your Carbon Monoxide Detectors Now!
It is your responsibility to protect your family members from the dangers of carbon monoxide poisoning by installing a detector and making sure it is fully functional.
Exposure to high concentrations of CO can lead to severe consequences.
If unsure as to what you should do, you can seek the help of professionals.
Originally published at https://assuranceelectricalaz.com/
0 notes