#Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
TrueNAS SCALE Network Configuration Tips for Home Server
TrueNAS SCALE Network Configuration Deep Dive for Home Server #homeserver #TrueNASScaleNetworkConfiguration #FailoverSetupGuide #LoadbalancingOnTrueNAS #VLANConfigurationTrueNAS #BridgeInterfaceGuide #TrueNASStaticIPAddressSetup #TrueNASSystemSettings
When you set up a TrueNAS SCALE server, one of the first configuration items you will want to tackle is the network configuration. This helps make sure you achieve optimal performance and security. If you are struggling to configure your TrueNAS SCALE home server networking, this post will help you configure a static IP address, Link Aggregation (Failover, LoadBalance, LACP), VLAN, and Bridge…

View On WordPress
#Bridge interface guide#Configure static routes#Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol#Failover setup guide#Loadbalancing on TrueNAS#Network interface configuration#Static IP address setup#TrueNAS Scale network configuration#TrueNAS system settings#VLAN configuration tutorial
0 notes
Text
Alien Romulus & how (not) to optimize your slasher cast dynamics
Much as I enjoyed Alien: Romulus it made the cardinal horror movie sin of killing off the cast in the wrong order for maximum interpersonal carnage.
If your established cast is the hero, the villain, the villain's partner, the hero's partner, and the woobie, killing off the villain's partner and then the villain, leaving only the characters who know and like each other to work together has much lower peak potential for dramatic tension among all possible configurations.
Firstly, there should have been more panic when Navarro died. She was the pilot. How are they meant to get off the ship without their pilot? (Yes, the autopilot exists, but that's a plot contrivance they could find out about later - or they might have to scavenge a new part from the ship to add to their damaged smaller vessel to add autopilot functionality to it. Or, perhaps, Andy can be the autopilot - but that requires Andy getting off the ship which requires convincing the AI upgrade within him to do so - which would be another layer of complication.)
But anyway the ideal next candidate to die is Tyler. Tyler is the peacekeeper between Bjorn and Andy, and the link between Rain and the rest of the remaining crew, who are all family members. (Even before we get to Kay and Bjorn being exes or ex hookups)
Remove Tyler from the remaining cast and Bjorn and Rain immediately have a power struggle. Bjorn hates androids, but they need the android to escape the ship. Neither Andy or Rain like Bjorn, but he is an extra person to use as defence in a situation where they can't afford to make their party any smaller. Bjorn also has immediate personal beef with the aliens as they killed his partner, Navarro - so will be a loose cannon if they ever come across aliens. But, he also has Kay to protect now - the mother of his unborn child.
And, sorry to be gross, but it is the horror genre - imagine the magnification of the horror element if, at the end, when the alien-baby hybrid is born, if not just it's mother but it's father is also still alive there. Or if Bjorn has been hurt by the acid blood still and he and Kay have to choose between them which of them they will use the black goo to save, not knowing that whoever takes it is damning themself to become the next alien host. Or if Kay and Bjorn think they are safe and have escaped, and Bjorn, who has now bonded with and come to respect Andy through their adventure together now calls out to Andy for help against the alien as they are escaping in their escape ship, because he trusts him now and thinks he will save him - but Andy's protocols to do what's best for Rain have at that point been turned back on and so Andy cannot put Rain at risk even to save Bjorn and Kay after all they've been through together.
Now that's how to write a real horror on all levels.
#alien romulus#alien romulus review#alien: romulus#fede alvarez#writers on tumblr#horror#horror writing#2024#text post#bjorn#kay#rain carradine#xenomorph
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mastering the Art of Virtual Presence: Unveiling the Best VPS Hosting Services
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, where the success of an online presence hinges on performance and reliability, mastering the art of virtual presence becomes paramount. For businesses and individuals alike, investing in the right Virtual Private Server (VPS) hosting service is the key to unlocking a seamless and powerful online experience. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of VPS hosting, unraveling the nuances that set the best providers apart.
Understanding the Essence of VPS Hosting
Virtual Presence Redefined
VPS hosting, a revolutionary leap from traditional shared hosting, epitomizes the epitome of virtual presence. Unlike shared hosting where resources are divided among multiple users, a VPS offers a dedicated virtual space within a larger server. This ensures enhanced performance, greater control, and improved security, making it an ideal choice for those seeking a robust online presence.
Unveiling the Top Features of Leading VPS Hosting Services
Scalability: Elevate Your Presence Seamlessly
The best VPS hosting services boast unparalleled scalability, allowing your virtual presence to grow effortlessly. Whether you're running a dynamic business website or managing a high-traffic blog, the ability to scale resources ensures optimal performance at all times.
Performance Optimization: Powering Your Virtual Identity
Performance is the heartbeat of online success. Leading VPS hosting providers leverage cutting-edge technology to optimize server performance. With high-speed SSD storage, advanced caching mechanisms, and top-tier processors, your virtual presence is bound to outshine the competition.
Enhanced Security Protocols: Guardians of Your Digital Fortress
Security is non-negotiable in the digital realm. The best VPS hosting services prioritize security with robust measures such as regular security audits, firewalls, DDoS protection, and malware scans. Your virtual presence remains shielded against potential threats, ensuring a trustworthy and secure online environment.
Dedicated Resources: Your Virtual Sanctuary
Unlike shared hosting, where resources are shared, top-notch VPS hosting allocates dedicated resources to each user. This translates to consistent performance, even during peak traffic periods, providing visitors with a seamless and responsive virtual experience.
User-Friendly Control Panels: Navigate with Ease
The best VPS hosting services understand the importance of user-friendly interfaces. With intuitive control panels, managing your virtual presence becomes a breeze. From server configurations to resource allocation, you're in complete control, empowering you to tailor your hosting environment to suit your specific needs.
Choosing the Best VPS Hosting Service: A Strategic Decision
L3WebHosting.com: Redefining Virtual Presence
Amidst the plethora of VPS hosting providers, L3WebHosting.com stands out as a beacon of excellence. With a commitment to unparalleled performance, security, and customer satisfaction, they redefine the landscape of virtual presence.
Key Advantages of L3WebHosting.com
Reliability: Ensuring 99.9% Uptime
Reliability is the cornerstone of L3WebHosting.com. With a robust infrastructure and proactive monitoring, they guarantee an impressive 99.9% uptime. Your virtual presence remains consistently accessible, fostering trust among your audience.
Customer Support: A Partner in Your Virtual Journey
Exceptional customer support sets L3WebHosting.com apart. Their dedicated support team, available 24/7, ensures that any concerns or queries are addressed promptly. This commitment to customer satisfaction makes them an ideal partner in your virtual journey.
Cutting-Edge Technology: Staying Ahead of the Curve
L3WebHosting.com invests in the latest technology to keep your virtual presence ahead of the curve. From high-performance servers to advanced security protocols, they prioritize staying at the forefront of technological advancements.
Elevate Your Virtual Presence Today!
In conclusion, mastering the art of virtual presence begins with choosing the right VPS hosting service. L3WebHosting.com emerges as a trailblazer in this realm, offering a perfect blend of reliability, performance, and customer-centricity. Elevate your online presence today with a VPS hosting provider that understands and anticipates your digital needs.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Types and 5 Most Popular for 2023

Types of IoT
Networking, communication, and connectivity systems depend on the specific IoT application being deployed. Just as there are many different IoT devices, there are many types of IoT applications depending on their use. Here are some of the more common ones:
• IoT client – intended for everyday use. Examples: home appliances, voice assistants and lighting.
• Business IoT – commonly used in the healthcare and travel industries. Examples: smart pacemakers and monitoring systems.
• Military Matters (IoMT) - Commonly used for the application of IoT technology in the military sector. Examples: surveillance robots and attack-capable objects.
• Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) - commonly used in industrial applications, such as in manufacturing and the energy sector. Ex: Digital control systems, smart agriculture and big data industries.
• IoT Infrastructure – It is widely used for connectivity in smart cities. Example: equipment sensors and control systems.
Why is IoT important? IoT has enabled the physical world to meet the digital world in collaboration. It provides benefits to organizations by allowing them to work and simplify their work. As IoT grows exponentially year on year, businesses are taking advantage of the incredible business benefits it can deliver. Here are some of the most important benefits of IoT:
• Create new business models and revenue streams
• Improve business decisions and insights based on IoT data.
• To increase productivity and efficiency of business operations
• To improve customer experience
Although global IoT spending has been affected by the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, IDC's analysis shows that it will reach a CAGR of 11.3% over the forecast period 2020-2024.
What are IoT devices?
IoT devices are hardware devices, such as sensors, appliances, devices and other machines that collect and exchange data over the Internet. They are designed for certain applications that can be connected to other IoT devices. For example, an IoT device in your car can detect oncoming traffic and send an instant message to the person you're about to see about an upcoming delay.click amazon market place.
How do IoT devices work?
Different IoT devices have different functions, but they all have similarities in terms of how they work. First, IoT devices are physical objects that see what is happening in the physical world. They have integrated processors, network cards, and hardware, and are often connected to Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol servers. It also requires an IP address to work on the network.
Many IoT devices are programmed and controlled through software. For example, an app on your smartphone to control the lights in your home. Some tools are also built into the web server, eliminating the need for external applications. For example, the light turns on immediately when you enter the room.
1 note
·
View note
Text
ok time for wifi troubleshooting dump (for Windows but the concepts are true for any device)
First, how this happens. Imagine you had a router that wasn't plugged into anything but power, and a laptop with an ethernet port. If you plugged the laptop into the router, you would get a similar message of "connected without internet" but it would show an ethernet icon with instead of wifi icon.
What that error means is that you did, in fact, connect to the wifi. That's layers 1 and 2 of the internet. Trouble is, there's more layers, and you need all the layers to use the internet.
Layer 3 of the internet is the Routing layer. Yes, this is where the name "router" actually comes from, but I digress. This is the layer of the internet that deals with "IP addresses". Where your computer or your phone or TV or whatever normally gets an IP address from is something called "DHCP". Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.
You don't need to memorize that. Just know that after you connect to a network with wifi or ethernet cable, one of the first things device will do by default is send a broadcast on the network asking "Hey! Is anyone here a DHCP server?" This works because certain sorts of broadcasts don't need your computer to know how to use the network more than just being connected to it.
The addresses used when asking this are actually 0.0.0.0 and 255.255.255.255. If those sound like special addresses, that's cuz they are. "no address" and "everyone who can hear this". Anyways...
Your home router by default is running a dhcp server on it, so it SHOULD hear this broadcast and it SHOULD respond and your computer SHOULD negotiate whats called a "DHCP lease". This basically is just a bit of information saying "ok so here's your address and subnet size, here's your default gateway, here's some DNS servers, it's good for [LENGTH OF TIME HERE]."
The first thing to check is, did DHCP work? Right-click the network icon, whether ethernet or wifi, and chose "Open Network and Internet Settings".

Then go to the network properties of either the ethernet or the wifi, whichever one you're connected to.

Yours won't say "connected" cuz yall internet is broken but the buttons are still there.

The big thing you're looking for is the "IPv4 address". IPv6 is different don't worry about it right now and usually if IPv4 is broken then IPv6 is broken anyways, if your internet provider even serves you IPv6... ANYWAYS.
If you have an address like 192.168.something.something or 10.something.something.something you probably got a DHCP lease so that's not the issue.
If you have an address like 169.254.something.something then that means that either the DHCP server didn't respond, or it did respond but your wifi signal is so bad that your computer didn't hear the response.
Restart your router, look into changing the wifi channel settings on the router to a less occupied channel, try using 5ghz wifi if possible though not everyone's computer or router supports that, sometimes restart your computer cuz sometimes Windows' networking software does stupid thing.

Also, unless you KNOW you're supposed to be using Static addressing, make sure you're set to Automatic. Someone may have turned off Automatic addressing cuz they're a prankster. Or they don't know what they're doing. Or both.
Well, if you got to this point because you aren't having a DHCP issue, then things get a little tougher cuz the "internet is out and you should call your ISP to find out if it's a wider outage that they're already working on fixing or if it's just you" possibilities start to show up now.
Time for Command Prompt. I promise it's not nearly as scary as you might think.


Alright, time for our first command. Type in "ipconfig" without the quotes, and hit enter. It'll spew out a bunch of text at you, but it's not as complicated as it looks.

I crossed the things in thick red out cuz I don't trust tumblr to not pull some shit, and the one thing in thin orange because it's fine if people see that but it's in the middle of some stuff we want.

Yall have used Discord at some point, right? You see that Default Gateway? We're gonna ping it. "ping 192.168.1.1" or put whatever your gateway is instead.

I'm on ethernet with properly functioning equipment, so my ping delay is <1ms (less than 1 millisecond). Wifi is gonna be higher, anywhere from 10 to 200 milliseconds, depending on your wifi quality.
Also, if your wifi connection is really bad, you may see "Request Timed Out".
If you're having trouble pinging the gateway, you may want to do a ping test. Adding a -w 50 (wait 50 milliseconds) will make the computer not wait long for failed pings, and -n 40 will make it try 40 times instead of just 4 times, cuz we need more data than just 4 tries.

This'll take a while to run (about 40 seconds to be exact). If you get tired of it running or just everything is timing out constantly then you can press Control C (like copying something in a text editor) to interrupt the program.

The big things to pay attention to are the "round trip times" and the % loss.
If your % loss to the gateway is 100% then either your computer is configured wrong and you should check that you're using the right addressing, or your wifi is extremely bad, or extremely rarely your router doesn't respond to pings on its local network. This is almost never the case. Your router probably doesn't respond to pings from the internet for security reasons, but pings from the inside are good for troubleshooting.
If your % loss to the gateway is over 10%, and/or your times are consistently very high (over 100ms or so) then your wifi conditions are extremely bad. Either you don't have enough signal strength, or there's heavy interference and basically your computer and router are effectively trying to have a conversation while at a loud metal concert. Neither of them can hear eachother very well.
There might be something wrong with your internet service provider still; but if you were wondering why using your wifi is suffering even when the internet isn't out, that's a hint.
If your % loss to the gateway is over 1% but under 10% then that's Not Great and you should still look into wifi channelization but it wouldn't stop you from being able to use the internet entirely.
Under 1% is okay, that means it's not a wifi issue.
The next thing to try is to ping a well-known usually-up service, such as Cloudflare Public DNS (1.1.1.1) or Google Public DNS (8.8.8.8) or Quad9 (9.9.9.9)


My internet is working fine, so I have 0 loss and while there is some variance (one got 34ms instead of 11) everything looks peachy.
If your pings to one of these public services all fail, then either your router needs to be configured because either 1. it wasn't set up in the first place (you would not believe how many people I take calls from that have this issue) or 2. it factory reset itself for some reason (some people think that rebooting the router means use the reset button. IT DOES NOT MEAN THAT.) and you need to pay attention cuz if it happens again that may mean ur router is screwed.
Or, there's an actual service outage, and you should call your ISP to find out if it's just you, or if it's a general outage and they're already working on it and all you can do is hurry up and wait.
And... that's it. There are other weirder issues that you can have, sure. As long as this post is, explaining some of those issues would take even longer. And I would LOVE to explain some of them. But this post is already more than long enough, and it covers the vast majority of cases.
Thank you for reading and good luck!
when the wifi says "connected without internet" how about i fucking kill you
#long post#come get yalls juice#i promise promise promise that the first 90% of the troubleshooting i do in my irl job is not hard#i also promise that the remaining 10% of the troubleshooting i do in my irl job IS that hard but that's why i get paid to do it#seriously i have handheld 70 year olds through the process please im begging u learning this one thing will make ur life so much better#please dont let the powers that be gatekeep you from learning how to fix stuff
41K notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding 10.24.1.53: A Deep Dive

In the digital world, IP addresses play a crucial role in how devices communicate with each other. One such IP address, 10.24.1.53, often appears in private networks—but what exactly does it mean, and why is it important? This blog breaks it down for beginners and tech enthusiasts alike.
What is 10.24.1.53? The IP address 10.24.1.53 falls under the private IP range (10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255) as defined by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). This means it’s not routable on the public internet and is typically used for internal networking within homes, businesses, or organizations.
Why is it Used? Private IP addresses like 10.24.1.53 are used for devices within a local area network (LAN) to communicate with each other securely without accessing the internet. Routers assign these IPs through DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) to enable seamless connectivity.
Benefits of Private IPs
Enhanced network security
Conserves public IP address space
Simplifies internal communications
Cost-effective networking
Common Uses of 10.24.1.53 You might find 10.24.1.53 in use for:
Office printers
Internal servers
Smart devices in homes
Admin consoles for routers and switches
Conclusion Understanding IP addresses like 10.24.1.53 is essential for managing secure and efficient local networks. Whether you're a system admin or a curious user, knowing how these addresses function can enhance your grasp of networking fundamentals.
0 notes
Text
How LiteSpeed Improves Loading Speed
Website speed is a critical factor in user experience, SEO performance, and conversion rates. Faster-loading websites engage visitors better, reduce bounce rates, and rank higher in search results. LiteSpeed Web Server (LSWS) is engineered to optimize website speed with powerful technologies built into its core. This article provides a technical and practical look at how LiteSpeed improves website performance, its architectural strengths, and comparisons with other web servers like Apache and NGINX.
What Is LiteSpeed?
LiteSpeed is a high-performance web server software developed by LiteSpeed Technologies. It serves as a drop-in replacement for Apache, meaning it can use Apache configurations such as .htaccess and mod_rewrite while offering far superior performance.

Unlike traditional web servers that rely on process-based or thread-based architectures, LiteSpeed uses an event-driven approach. This enables it to handle thousands of simultaneous connections efficiently without consuming excessive resources. It’s widely used in shared, VPS, and dedicated hosting environments due to its scalability and speed.
LiteSpeed is compatible with major web hosting control panels like cPanel, Plesk, and DirectAdmin. It also integrates seamlessly with WordPress, Magento, Joomla, and other popular CMS platforms.
How LiteSpeed Improves Loading Speed
LiteSpeed's performance is not just theoretical. Numerous benchmarks and case studies show significant improvements in load time, server response, and concurrent user handling. Its technical foundation plays a pivotal role in enabling these advantages.

Event-Driven Architecture
Most traditional web servers like Apache use a process-based or threaded architecture. Each connection requires a dedicated process or thread, which leads to high memory usage under load.
LiteSpeed uses an event-driven, asynchronous model. It processes multiple connections within a single thread, significantly reducing memory consumption and CPU load.
For example, benchmarks by LiteSpeed Technologies show that LSWS handles over 2x more concurrent connections than Apache with the same hardware configuration [1]. This architecture is especially beneficial during traffic spikes, such as flash sales or viral content events.
Built-In Caching (LSCache)
LiteSpeed’s caching engine, LSCache, is built directly into the server core. Unlike third-party caching plugins that operate at the application level, LSCache works at the server level, making it faster and more efficient.
With LSCache enabled on WordPress, testing from WPPerformanceTester shows up to 75% reduction in page load times compared to uncached sites. This is because LSCache delivers prebuilt HTML pages directly to users, bypassing PHP execution and database queries.
LSCache also supports advanced features such as:
ESI (Edge Side Includes) for partial page caching
Smart purging rules
Private cache for logged-in users
Image optimization and critical CSS generation
These features make it suitable not only for static pages but also for dynamic, eCommerce-heavy platforms like WooCommerce or Magento.
Compression and Optimization
LiteSpeed supports GZIP and Brotli compression out of the box. These technologies reduce the size of files transmitted over the network, such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
According to Google PageSpeed Insights, compressing assets can reduce page size by up to 70%, which directly improves load time. Brotli, developed by Google, provides even better compression rates than GZIP in many cases, and LiteSpeed uses it efficiently.
Additionally, LiteSpeed can minify JavaScript, CSS, and HTML, combine files to reduce HTTP requests, and enable lazy loading for images—all directly from the server level.
QUIC and HTTP/3 Support
LiteSpeed is one of the earliest web servers to fully support QUIC and HTTP/3, protocols developed by Google and later adopted by IETF.
QUIC is built on UDP instead of TCP, which reduces handshake latency and improves performance over poor network conditions. HTTP/3 inherits QUIC’s benefits and introduces faster parallel requests and better encryption handling.
When HTTP/3 is enabled, page loads feel snappier, especially on mobile devices and in regions with weaker connectivity. Cloudflare reported up to 29% faster page loads using HTTP/3 versus HTTP/2 [2].
LiteSpeed’s implementation ensures that your site is future-ready and delivers optimal performance even under challenging network environments.
LiteSpeed vs Apache and NGINX
Performance benchmarks consistently show that LiteSpeed outperforms both Apache and NGINX in various scenarios, especially under high traffic and dynamic content conditions.

Apache Comparison
Apache is widely used but is resource-heavy under load. When serving PHP applications like WordPress, Apache relies on external modules (e.g., mod_php) or handlers like PHP-FPM, which increase overhead.
LiteSpeed replaces these with LiteSpeed SAPI, a more efficient PHP handler. Benchmarks show that LiteSpeed can process 3x more PHP requests per second compared to Apache [3].
NGINX Comparison
NGINX is known for its speed with static files, but it lacks full .htaccess compatibility and requires more manual tuning for dynamic sites.
LiteSpeed combines Apache’s ease of configuration with NGINX’s speed and goes further by offering built-in caching and QUIC support. This makes it a more all-in-one solution for both static and dynamic content delivery.
Real-World Results
A hosting provider, NameHero, migrated over 50,000 sites from Apache to LiteSpeed. The result was an average decrease in load time by 40%, with no change in hardware configuration [4].
Another example is a WooCommerce store that used LiteSpeed Cache. Load times dropped from 4.2s to 1.2s after activation, significantly improving Core Web Vitals and user retention.
Website owners consistently report faster Time to First Byte (TTFB), better PageSpeed scores, and fewer server crashes during traffic peaks when using LiteSpeed.
Who Should Use LiteSpeed?
LiteSpeed is ideal for:
WordPress users who want faster page loads without complex configurations.
WooCommerce and Magento store owners needing efficient dynamic caching.
Web hosting providers looking to reduce server load and increase client satisfaction.
SEO-focused marketers who want better Core Web Vitals.
Developers who want Apache compatibility with modern performance.
LiteSpeed is available in both open-source (OpenLiteSpeed) and commercial versions. While OpenLiteSpeed is suitable for smaller projects, the enterprise version offers advanced features and full control panel integration.
Final Thoughts
LiteSpeed offers a clear performance advantage due to its architecture, built-in caching, modern protocol support, and optimization features. It helps websites load faster by minimizing server load, reducing latency, and delivering content more efficiently.
Whether you're a developer, site owner, or hosting provider, switching to LiteSpeed can result in measurable improvements in speed, stability, and scalability. In today’s performance-driven web ecosystem, LiteSpeed is a practical solution backed by real results and advanced engineering.
1 note
·
View note
Text
YI Cam Remote Access: Your Guide to Self-Hosted Surveillance

Want to have complete control over your YI Cam and go beyond its default cloud? For more privacy and customization, many users prefer YI Cam Remote Access, rather than using the manufacturer's cloud. Therefore, this post explores how to accomplish this sophisticated configuration, assisting you in navigating the frequently challenging process of self-hosting your camera's feed. Walk through this post to learn more details!
Understanding the YI Cam Remote Access
Generally, you need to install a custom firewall on your device if you want to access the YI camera remotely and connect it to your server. Additionally, it allows leveraging the benefits of the RTSP (real-time streaming protocol) streaming as well as FTP access. Moreover, it eliminates the need for third-party platforms and for configuring cameras to the self-hosted servers.
However, it acts as a “Network Remote Controller,” especially for the multimedia servers. It allows users to control media playback remotely. But it does not deliver audio or video streams continuously; instead, it communicates with the servers streaming the multimedia content. Hence, for the YI Cam Remote Access, users must connect their security cameras to the server through RTSP.
How to Connect Camera To Server for YI Remote Access?
Moreover, enabling the YI Cam Remote Access opens up several possibilities and advanced functionalities. So, let’s begin with the essential steps to Connect Camera To Server for managing and monitoring your YI camera remotely.
Initially, confirm your YI Cam supports the RTSP or streaming compatibility, as some models may require custom firmware.
Subsequently, set up your chosen server device, such as a computer, NAS, or Raspberry Pi, with a suitable operating system.
Next, install essential software like Blue Iris, MotionEye, FFmpeg, or Home Assistant to manage the video feed.
Finally, configure secure remote access using methods such as port forwarding, VPN, or Dynamic DNS for external viewing.
Now, you can view, configure, and control your YI camera remotely.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, YI Cam Remote Access empowers you with full control over your camera's feed through self-hosting, prioritizing privacy & customization. Additionally, this advanced setup typically requires RTSP compatibility, a dedicated server, and management software. With secure remote access methods such as VPN or port forwarding, you can ensure seamless monitoring from anywhere.
#YICameraSetup#YICamRemoteAccess#SelfHostedCamera#IPCameraSetup#RemoteCameraAccess#YICamOnServer#RTSPStream#ONVIFCamera#YICamRTSP
1 note
·
View note
Text

ARMxy Based SBC Cortex-A53 BL340 optimizes Smart Building HVAC Systems
Case Details
In modern building management, Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems are critical for ensuring indoor comfort and energy efficiency. With the rapid development of the Internet of Things (IoT) and industrial automation, the ARMxy BL340 series embedded industrial computer stands out as an ideal solution for optimizing HVAC system performance, thanks to its powerful processing capabilities, flexible I/O configurations, and high reliability. This article explores the specific applications of the BL340 series in building HVAC systems and the significant benefits it delivers.
Data Acquisition and Real-Time Monitoring
The core of an HVAC system lies in real-time data acquisition for precise control. The ARMxy BL340 series, powered by the Allwinner T507-H quad-core Cortex-A53 processor (up to 1.4GHz), supports a wide range of I/O interfaces, including RS485, CAN, analog inputs (AI), and digital inputs/outputs (DI/DO). Through Y-series I/O boards (e.g., Y31 for 4-20mA analog inputs and Y51 for PT100 temperature sensors), the BL340 can effortlessly collect critical data such as temperature, humidity, pressure, and flow.
For instance, the BL340 can acquire data from sensors#> sensors via the Modbus protocol and, using the pre-installed BLloTLink software, convert it into MQTT protocol for upload to cloud platforms like AWS IoT Core or Thingsboard. This enables building managers to monitor HVAC system performance in real time, promptly identify anomalies, and take corrective actions. Accurate data acquisition also allows dynamic adjustments to heating or cooling outputs, reducing energy waste.
Edge Computing and Intelligent Control
Traditional HVAC systems often rely on cloud-based processing, which introduces latency and network dependency. The BL340 supports edge computing, equipped with 1/2GB DDR4 memory and 8/16GB eMMC storage, enabling complex control logic execution locally. Developers can use Node-Red or Qt-5.12.5 to rapidly develop applications, such as automatically adjusting damper positions or compressor frequencies based on indoor-outdoor temperature differences.
With the PWM output capabilities of the Y95/Y96 modules, the BL340 can precisely control variable-frequency fans or pumps, achieving on-demand ventilation or flow regulation. This intelligent control not only improves system responsiveness but also significantly reduces energy consumption. For example, during low-occupancy periods, the BL340 can automatically reduce ventilation frequency, optimizing energy use.
Multi-Protocol Communication and System Integration
Building HVAC systems need seamless integration with Building Management Systems (BMS) and other devices. The BL340 offers three 10/100M Ethernet ports, two USB 2.0 interfaces, and Mini PCIe-supported 4G/WiFi/Bluetooth modules, supporting multiple industrial protocols (e.g., Modbus, BACnet, OPC UA). This ensures easy connectivity with sensors, actuators, and host systems.
Additionally, the BLRAT remote access tool allows maintenance personnel to adjust HVAC parameters or diagnose issues over the internet in real time. For example, the BL340 can upload operational data to SCADA systems via Ethernet or integrate with smart building platforms like IgnitionSCADA for centralized monitoring and management. The inclusion of a 4G module further enhances communication capabilities in remote locations.
Energy Optimization and Intelligent Management
Energy management is a key focus for HVAC system optimization. The BL340 supports Docker containers and Node-Red, enabling developers to quickly deploy IoT applications and optimize operational strategies by analyzing historical and real-time data. For instance, by developing control logic based on schedules or occupancy sensors in Node-Red, the BL340 can reduce heating/cooling intensity during off-peak hours, minimizing unnecessary energy consumption.
Moreover, the BL340’s cloud integration capabilities allow energy consumption data to be uploaded to platforms like Thingsboard for visualization and analysis. Managers can adjust operational strategies based on these insights to further improve energy efficiency. For example, during peak summer heat, the BL340 can initiate pre-cooling based on forecasted outdoor temperatures, reducing peak electricity demand.
High Reliability and Environmental Adaptability
Building HVAC systems are often deployed in machine rooms or outdoor environments, requiring high equipment reliability. The BL340 has undergone rigorous Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) and environmental adaptability testing, supporting a wide operating temperature range of -40°C to 85°C and meeting IP30 protection standards, ensuring resistance to dust and vibration. Its aluminum alloy casing and DIN35 rail mounting design further enhance stability in harsh environments.
The BL340 also features a wide-range power supply (9-36VDC) with reverse polarity and overcurrent protection, ensuring reliable operation in complex electrical environments. For instance, in high-humidity underground machine rooms, the BL340’s compliance with constant damp heat testing (+40°C, 85% relative humidity, 48 hours) validates its stable performance.
Development and Maintenance Convenience
The BL340 provides extensive development resources, including Linux, Qt, and Node-Red development examples, as well as the BLRAT remote maintenance tool, significantly reducing development and maintenance costs. Engineers can quickly customize HVAC control applications, such as developing PID control algorithms to optimize temperature regulation accuracy. The BLRAT tool supports remote firmware upgrades and fault diagnosis, minimizing the need for on-site maintenance.
Additionally, the pre-installed BLloTLink and BLRAT software simplifies protocol conversion and remote access configuration. For example, maintenance personnel can remotely adjust fan speeds or check sensor statuses via BLRAT, greatly improving operational efficiency.
Typical Application Case Study
Consider a commercial building’s HVAC system using the BL340-SOM340-X10-Y63 configuration, featuring one Ethernet port, 8GB eMMC storage, two RS485 ports, and four RS485/232 interfaces. The system collects PT100 temperature sensor data via the Y51 module, uses Node-Red to develop ventilation control logic based on occupancy sensors, and uploads operational data to a cloud platform via a 4G module. The results show a 15% reduction in energy consumption, a 30% improvement in response time, and a 20% decrease in maintenance costs.
Conclusion
The ARMxy based SBC BL340 series, with its robust data acquisition capabilities, edge computing performance, multi-protocol communication support, and high reliability, provides a comprehensive solution for optimizing building HVAC systems. It not only enhances the operational efficiency of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems but also significantly reduces energy consumption and operational costs through intelligent management and remote maintenance. Whether for new constructions or retrofitting existing systems, the BL340 is an ideal choice.
0 notes
Text
Alltick API: Real-Time Data Solutions from Quantitative Trading Primer to Professional Strategies
Why You Need to Eliminate 15-Minute Delayed Market Data?
In fast-paced financial markets, a 15-minute data delay can mean massive opportunity costs. While retail investors rely on outdated prices to formulate strategies, institutional traders have already executed multiple trades using real-time data. This information asymmetry exists not only in stock markets but also in forex, futures, and cryptocurrencies—delayed data essentially provides historical, not actionable insights for live trading.
Alltick API’s Competitive Edge
1. Millisecond-Level Real-Time Global Coverage
Unlike traditional minute-delayed feeds, Alltick API delivers:
Equities: Real-time quotes from 50+ exchanges (NYSE, Nasdaq, HKEX, etc.)
Crypto: Full-coverage pricing from Binance, Coinbase, and other top platforms
Forex & Futures: CME/ICE derivatives market depth data
Unique Tick-Level Streams: Granular order-by-order execution records
2. Quant-Optimized Infrastructure
Architected for algorithmic trading:
99.99% Uptime SLA with 24/7 monitoring
Smart Bandwidth Compression for cost-efficient high-frequency data
Dynamic Load Balancing for scalable request handling
Unified Historical + Real-Time APIs for seamless backtesting
3. Frictionless Developer Experience
Designed for quant newcomers and pros alike:
Multi-Language SDKs (Python/Java/C++)
Plug-and-Play Code Templates
Interactive API Debug Console
Comprehensive English/Chinese Documentation
7×12 Technical Support via Slack & Email
Real-World Use Cases
Case 1: Rapid Strategy Validation
Case 2: Cross-Market Arbitrage Monitoring
Multi-Asset Capabilities Enable:
Stock vs ETF price divergence alerts
Crypto cross-exchange arbitrage detection
Forex spot-futures basis analysis
Case 3: HFT System Deployment
Institutional-Grade Features:
Co-located server hosting
Custom binary protocols
Microsecond-precision timestamps
Order flow analytics toolkit
Choosing Your API Tier
FeatureFree FeedsLegacy VendorsAlltick ProLatency15+ minutes1-5 seconds<100msHistorical DepthEOD Only1 Year10+ YearsConcurrent ConnectionsSingle Thread10-50UnlimitedData FieldsBasic OHLCStandardImplied Volatility, GreeksSupportNoneEmail (Weekdays)Dedicated Engineer
Start Your Quant Journey Today
Whether You Are:
A developer building your first SMA strategy
A quant team stress-testing models
An institution managing multi-strategy portfolios
Alltick offers tailored solutions from free trials to enterprise-grade deployments. Sign Up Now to Get: ✅ 30-Day Full-Feature Trial ✅ Exclusive Quant Strategy Playbook ✅ $500 Cloud Computing Credits
Visit Alltick Official Site to Experience Market Pulse in Real Time. Transform Every Decision with Data That Beats the Speed of Markets.
(CTA: Click "Developer Hub" to configure SDK in 5 mins and claim your API key.)
Technical Highlights
WebSocket/ REST API Hybrid Architecture: Balance speed with flexibility
Regulatory-Compliant Data: FINRA/SEC-reviewed market feeds
Zero Data Gaps: Guaranteed 100% tick reconstruction accuracy
Smart Retry Mechanisms: Auto-reconnect during network instability
Why 2,300+ Hedge Funds Choose Alltick? *"Alltick's unified API eliminated our multi-vendor integration headaches. We achieved 37% faster strategy iteration cycles."* — Head of Quant Trading, Top 50 Crypto Fund
Upgrade Your Edge. Trade at the Speed of Now.

1 note
·
View note
Text
What is CCNA Certification?
The CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate) certification is one of the most popular entry-level IT certifications globally, designed and offered by Cisco Systems, a leading company in networking and telecommunications. This credential validates a professional's ability to install, configure, operate, and troubleshoot medium-size routed and switched networks. It also includes the verification and implementation of connections to remote sites in a WAN.
For individuals starting a career in IT, especially in networking, the CCNA acts as a solid foundation. It covers fundamental concepts that help in building a long-term career in computer networking, cybersecurity, and other related domains.
Background of CCNA
Cisco introduced the CCNA certification in 1998, aiming to standardize the foundational networking knowledge required for entry-level network engineers. Since its inception, the certification has undergone numerous updates to keep pace with evolving technologies, such as cloud computing, automation, and cybersecurity.
As of 2020, Cisco streamlined its certification process, consolidating multiple CCNA specializations (e.g., CCNA Security, CCNA Wireless) into a single, comprehensive CCNA exam that covers a broader range of networking fundamentals.
Who Should Take the CCNA?
The CCNA is best suited for:
Entry-level IT professionals
Network support engineers
Network administrators
Help desk engineers
Aspiring network engineers
Computer science or IT students
Even professionals in non-networking IT roles often pursue the CCNA to broaden their understanding of how networks function.
Topics Covered in CCNA
The CCNA 200-301 exam, which is the current version as of 2025, tests a candidate’s knowledge in several areas, including:
1. Network Fundamentals
OSI and TCP/IP models
IP addressing (IPv4 and IPv6)
Subnetting
Ethernet and data encapsulation
Cables, switches, routers, and other hardware
2. Network Access
VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks)
Inter-switch communication
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
Wireless networking basics
3. IP Connectivity
Static and dynamic routing (RIP, OSPF)
Default routing
Troubleshooting routing issues
4. IP Services
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
NAT (Network Address Translation)
DNS (Domain Name System)
QoS (Quality of Service)
5. Security Fundamentals
Firewall basics
VPNs
Access Control Lists (ACLs)
Device security using passwords and SSH
6. Automation and Programmability
Introduction to network automation tools
APIs and Cisco DNA Center
JSON, REST, and basic Python scripting (awareness level)
Benefits of CCNA Certification
1. Globally Recognized Credential
CCNA is one of the most respected certifications in the IT industry. It’s recognized by employers around the world, opening doors to jobs in both local and international markets.
2. Stronger Networking Knowledge
Whether you're new to networking or already working in IT, preparing for the CCNA gives you a solid grounding in networking principles, device configuration, and troubleshooting.
3. Better Job Opportunities
CCNA-certified professionals are eligible for roles such as:
Network Technician
Network Administrator
Systems Engineer
IT Support Specialist
4. Higher Salary Potential
According to industry surveys, CCNA-certified individuals earn significantly more than their non-certified peers. In India, for example, entry-level salaries for CCNA-certified professionals typically range from ₹3 to ₹6 lakhs per annum, depending on experience and location.
5. Foundation for Higher Certifications
CCNA is a stepping stone to more advanced Cisco certifications like:
CCNP (Cisco Certified Network Professional)
CCIE (Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert)
It also lays the groundwork for other vendor certifications in networking and security.
CCNA Exam Details
As of now, Cisco’s CCNA certification is awarded after passing a single exam:
Exam Code: 200-301 CCNA
Duration: 120 minutes
Format: Multiple-choice, drag-and-drop, simulation-based questions
Languages: English and Japanese
Cost: Approximately $300 USD (price may vary by country)
Prerequisites: None officially, but basic IT and networking knowledge is recommended
Candidates can take the exam at a Pearson VUE test center or online through proctored delivery.
How to Prepare for the CCNA Exam
1. Official Cisco Training
Cisco offers instructor-led training known as “Implementing and Administering Cisco Solutions (CCNA)”, which is a comprehensive course aligned with the exam.
2. Self-Study Resources
Cisco Press books like “CCNA 200-301 Official Cert Guide”
Video courses on platforms like Udemy, LinkedIn Learning, and Coursera
Cisco Packet Tracer (a free network simulation tool)
Lab practice with real or virtual equipment (e.g., GNS3, Cisco VIRL)
3. Practice Tests
Mock exams help assess readiness and simulate the actual exam environment. Many websites offer free and paid CCNA practice questions.
4. Join Study Groups
Networking with others preparing for the exam helps with knowledge exchange and staying motivated.
Is the CCNA Worth It in 2025?
Yes, the CCNA remains highly relevant and valuable in 2025, especially with the growing need for secure, reliable, and high-speed networking infrastructure. As organizations increasingly move toward hybrid cloud and remote work setups, network engineers and IT professionals play a more critical role.
Despite newer technologies and evolving job roles, the fundamentals of networking still serve as the bedrock for IT systems. Cisco has also modernized the CCNA to include topics like automation and programmability, ensuring that candidates are prepared for today’s IT environment.
Challenges in Earning CCNA
While the CCNA is considered an entry-level certification, it is not necessarily easy. Candidates often face challenges such as:
Understanding subnetting and IP addressing
Learning command-line configurations using Cisco IOS
Grasping routing protocols like OSPF
Staying current with evolving exam topics
However, with dedicated study and consistent practice, most candidates can pass the exam in 2 to 4 months.
Recertification and Validity
The CCNA certification is valid for 3 years from the date of passing the exam. To recertify, candidates can:
Retake the CCNA exam
Pass any higher-level Cisco certification (e.g., CCNP)
Earn Continuing Education (CE) credits via Cisco’s CE program
This ensures professionals remain current with industry standards and technological advancements.
Alternatives and Complementary Certifications
While CCNA is an excellent start, other certifications may be pursued alongside or after it:
Alternatives:
CompTIA Network+ – more vendor-neutral but less advanced
Juniper JNCIA – for networks using Juniper devices
Complementary:
Cisco DevNet Associate – focuses on network automation and software skills
CompTIA Security+ – covers cybersecurity fundamentals
Microsoft Certified: Azure Fundamentals – useful for cloud integration
Conclusion
The CCNA certification is a powerful credential for anyone seeking a career in networking and IT infrastructure. It provides a strong technical foundation, industry recognition, and opportunities for professional growth. Whether you’re a student, a recent graduate, or someone switching careers, earning the CCNA can open numerous doors in the tech industry.
As technology evolves, so does the role of the network engineer. The CCNA ensures you're not only equipped to handle today’s networking challenges but also prepared for tomorrow’s innovations.
0 notes
Text
10 Tips to Maximize SAN Storage Performance
Storage Area Networks (SANs) remain the backbone of enterprise data infrastructure. As workloads grow increasingly complex, extracting optimal performance from your SAN architecture will be essential in 2025. This guide shares expert-driven strategies for IT professionals, helping you unlock higher throughput, lower latency, and superior reliability in your next-gen storage environment.
Why Focus on SAN Storage Performance?
Enterprise SAN storage delivers high availability, seamless scalability, and robust performance for mission-critical applications. Maximizing these core benefits ensures organizations can support databases, virtualization, disaster recovery, and analytics workloads without compromise. By implementing the right practices and leveraging the latest advancements, you’ll secure measurable improvements in speed, efficiency, and resilience.
Core Benefits of Optimized SAN Storage
A high-performing SAN infrastructure goes beyond raw storage capacity. Consider these critical advantages:
High Performance
Reduced Latency: SANs support rapid data access via high-speed fabric protocols like Fibre Channel and NVMe over Fabrics, minimizing wait times for demanding applications.
Consistent Throughput: Optimized SANs handle simultaneous workloads, ensuring stable performance even under peak demand.
Scalability
Linear Growth: Add new disks, controllers, or switches with minimal disruption, scaling alongside business requirements.
Flexible Tiering: Automated storage tiering lets you align workloads with the right media type, from SSDs for speed to HDDs for cost efficiency.
Reliability
Redundancy Built-In: Multipathing, failover, and RAID configurations maintain uptime during hardware failures or maintenance.
Data Protection: Integration with enterprise backup, snapshots, and replication secures critical assets.
Optimizing these benefits directly translates into business continuity, compliance, and competitive advantage.
Key Use Cases for SAN Storage
Understanding where SAN shines helps guide optimization efforts. Leading applications include:
Database Management
Databases require sustained, predictable I/O. SANs serve as the foundation for:
High-transaction OLTP workloads
Data warehousing
Real-time analytics
Fast response times prevent bottlenecks and downtime during queries or batch processing.
Virtualization Environments
Storage is the lifeblood of virtualization:
Hypervisors (VMware, Hyper-V) rely on shared SAN storage for VM mobility and fault tolerance.
Dynamic workload balancing, vMotion, and DRS need latency-free storage access for seamless migrations.
Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity
SANs facilitate RPO- and RTO-compliant strategies:
Synchronous/asynchronous replication delivers rapid failover.
Snapshots and clones enable testing without impacting production.
Big Data Analytics
Analytical workloads demand elastic, reliable storage capable of handling petabytes at high throughput. SANs with intelligent caching and parallelism are essential for:
Real-time business intelligence
Machine learning data preparation
Large-scale log and sensor data ingestion
10 Tips to Maximize SAN Storage Performance
The following expert strategies for 2025 help you achieve peak efficiency, longevity, and security from your SAN investments.
1. Align SAN Design with Workload Profiles
Not all workloads require the same storage characteristics. Analyze application requirements to distinguish between throughput, IOPS, and latency needs. Use tools like Iometer or vendor-specific analytics to benchmark.
Transactional Databases: Opt for low-latency, high-IOPS SSD tiers.
Archive Storage: Use high-capacity HDDs or tape for infrequent access.
2. Invest in High-Speed Interconnects
Upgrade to 32Gb/64Gb Fibre Channel, NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF), or high-bandwidth Ethernet (25/40/100GbE) as supported by your SAN and hosts. Reduced bottlenecks at the transport layer are essential for granular performance optimization.
3. Enable and Fine-Tune Multipathing
Multipathing ensures uninterrupted access even if a cable, switch, or HBA fails. It also enables load balancing:
Use native OS multipathing drivers or solutions like VMware NMP or Microsoft MPIO.
Regularly test and validate failover paths.
4. Implement Advanced Storage Tiering
Automated tiering software reallocates data between SSD, SAS, and NL-SAS/HDD based on usage patterns. This maximizes both cost efficiency and speed:
Pin mission-critical VM images or DB files to flash storage.
Move archival or static data to lower tiers automatically.
5. Optimize Fabric Zoning and LUN Masking
Effective zoning reduces unnecessary traffic and enhances security:
Use single-initiator, single-target zones for best isolation.
Apply LUN masking to control device access by host or application.
6. Monitor and Manage Storage Utilization
Leverage SAN management tools for proactive health and capacity tracking:
Monitor IOPS, bandwidth, and latency via vendor dashboards or third-party platforms.
Set threshold alerts for utilization hot spots.
Run periodic health checks and firmware updates.
7. Keep Firmware and Drivers Up-to-Date
Hardware and software teams release updates to address bugs, vulnerabilities, and improve performance:
Periodically audit firmware, HBA drivers, and storage OS versions.
Test new releases in a staging environment before full deployment.
8. Separate Production from Non-Production Traffic
Isolating backup, replication, and management traffic ensures production I/O isn’t impacted during heavy data movement windows:
Use VLANs, separate logical fabrics, or physical ports where possible.
Schedule non-production processes during off-peak hours.
9. Leverage Data Reduction Technologies
Deduplication, compression, and thin provisioning decrease the physical storage demand for the same logical footprint, improving efficiency:
Configure inline deduplication and compression on capable arrays.
Regularly reclaim orphaned space.
10. Regularly Test Disaster Recovery Procedures
No SAN is truly optimized without confirmed recoverability. Conduct periodic “fire drills”:
Simulate failovers to secondary sites or replicated arrays.
Verify RTO and RPO targets.
Update documentation and train staff after each test.
Practical Implementation Strategies
Getting the most from SAN storage isn’t just about hardware choices. Expert planning, setup, and ongoing maintenance are critical.
Planning
Needs Assessment: Document application SLAs and projected growth for five years.
Vendor Comparison: Evaluate not just IOPS and throughput, but total ecosystem costs (support, upgrades, expansion).
Compatibility Checks: Confirm OS, hypervisor, and application support for advanced SAN features.
Setup
Standardized Cabling: Color-code and label all cables for troubleshooting.
Redundant Power and Cooling: Ensure environmental resilience in your data center.
Config Templates: Use vendor best-practice templates for initial device settings (RAID, caching, LUN parameters).
Maintenance
Regular Audits: Schedule quarterly performance reviews and security scans.
Firmware Compliance: Track EOL/EOS for hardware/software lifecycles.
Staff Training: Maintain certifications (e.g., Brocade, Cisco, vendor-specific) and stay updated on storage trends.
SAN Storage in the Roadmap of Enterprise IT
Modern enterprises face relentless IT demands. A well-optimized SAN solution is not just a technical asset but a strategic enabler for digital transformation. Whether you’re supporting mission-critical databases, scaling virtualized environments, or safeguarding petabytes of analytic data, adherence to best practices ensures your storage foundation remains rock-solid and ready for future innovations.
Prioritize ongoing optimization, rigorous planning, and continual education for your team. Robust SAN performance isn’t a one-time achievement but an ongoing commitment to excellence.
0 notes
Text
【step by step】Easyi3C Host I3C adapter (1)
Easyi3C is a leading supplier of embedded system tools that simplify the development and debugging of various communication protocols. The company offers a range of products designed to help engineers and developers use I3C/I2C , USB and MIPI, JEDEC, MCTP and other protocols more efficiently.
1. Basic Introduction
Easyi3C Host I3C adapter is a powerful and easy-to-use I3C and I2C host adapter produced by Easyi3C. It connects the computer to the downstream embedded system environment through the USB interface and adopts the advanced I3C and I2C protocol.
Based on the application programming interface (API) function and the Easyi3C Tower console graphical user interface (GUI) tool, combined with the Python development environment, the Easyi3C Host adapter greatly simplifies the development process of I3C/I2C chip testing and data transmission environment. It provides great convenience for AE engineers, FAE engineers, etc. to verify I3C/I2C chips. Simple verification can be done through the graphical console interface, which is easy to use and easy to learn. If you want to test more complex functions or perform automated testing, you can use the rich API functions provided by the manufacturer to quickly implement automated scripts in the Python development environment.
We know that I2C was invented by Philips Semiconductors in 1981, and its history is a bit old and mature. The I3C protocol I3C specification was originally released by in 2017. I3C is the abbreviation of improved internal integrated circuit, which is a 2-wire digital interface similar to I2C. It improves and optimizes the previously released I2C and SPI interfaces, solves the problem of slow I2C communication speed, and optimizes the shortcomings of SPI through four-wire connection. The I3C specification is managed by MIPI Alliance Inc. I3C also solves the problem of high power consumption of I2C. I3C becomes a low-power, low-cost and fast digital interface. It supports multi-point connection between host MCU and peripheral devices such as sensors and multi-master devices. Because the protocol is still very new, there are not many good tools on the market. The series of products launched by Easyi3C will fill this gap. The same interface supports I3C/I2C protocols at the same time, which is convenient for engineers to write automated scripts for chip protocol testing, shorten the product launch cycle, and help the company’s products win the competition.
2. Key features:
Supports MIPI I3C BASIC v1.1 JEDEC JESD403–1 Specifications (JEDEC DDR5 Sideband Bus Spec) I3C Master in SDR mode Variable Working Frequencies (Open-Drain Mode: 1 kHz to 4 MHz (Default: 1MHz); Push-Pull Mode: 100KHz to 12.5 MHz (Default: 4MHz)) Adjustable SCL Duty Cycle Amplitude Variation: 0.8V to 3.3V in steps of 10mV 5ns resolution Supports 7-Bit Slave Addressing Supports Common Command Code (CCC) transactions Supports flexible payload length’s IBI Supports Hot Plug Supports all Dynamic Address Assignments Supports legacy I2C Master, Software configurable I2C pull-up Error Injection such as parity errors USB Type-C port, Max. Current & Voltage: 500 mA @ 5 V Supports online upgrade API support for automation test in Python Physical Size: 114mm x 81mm x 27mm Operating Temperature From –20°C to +85°C
3. Hardware

Accessories:


4. Interface Introduction 4.1 Front Panel


5. Test chip connection method
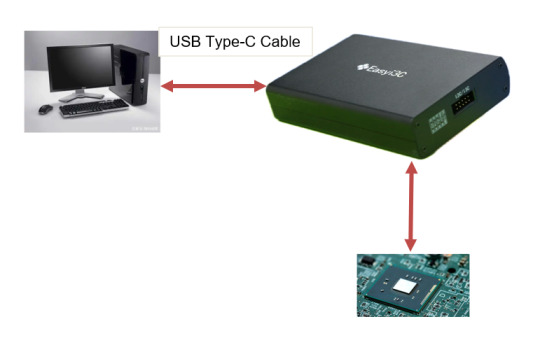
5.1 Connect the Easyi3C adapter to the I2C/I3C device using a 10-pin cable.
5.2 Connect the Easyi3C adapter to the computer with a USB Type-C cable. The adapter is powered by USB Type-C communication, so no separate external power supply is required, which simplifies device connection.
Next, we will continue to introduce the use of the product in depth.
1 note
·
View note
Text
0 notes
Text
Introduction Virtual network is a system that composed of virtual machines that are usually configured to manage or process external or internal network resources. This system is often configured to function with a network adapter especially when using a physical computer or work without adapter when using virtual machines (Lowe, 2011). Different networks often respond to different machines in a specific manner (Simpson, and Novak, 2010). Connecting a network adapter to a physical computer requires a virtual machine to be connected or linked to a virtual network to which the physical adapter is connected. When the adapter is not used, the virtual machine connected to the virtual network forms part of the internal virtual machine (Oppenheimer, 2005). It is worth noting that the internal virtual machine networking usually consists of all other virtual machines connected to the virtual network that is configured to function without network adapter. In this case, every internal virtual machine network is isolated completely from other systems of internal virtual machine network. Fig. 1. An example of a virtual network design (VMnet virtual network design (Lowe, 2011)) It is worth noting that the Virtual Server supports a significant number of virtual networks; therefore, virtual network can serve many or unlimited virtual machines that are connected to it. Using the virtual DHCP Server The virtual Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server is usually part of the virtual network. It provides that IP address that it leases only to the virtual machine. The main advantage of the DHCP is that it can be used instead of configuring the virtual machine to a DHCP server since DHCP usually disable it by default. Therefore, if the virtual network is linked to the adapter of the physical network and the virtual DHCP server is activated, the DHCP server will be expected to isolate from the operating system of the host and all other virtual machines. Despite being isolated, the DHCP server will still assign unique IP addresses to the virtual machines and within a specified range. In the case above, the DHCP server is configured to only use for the IP address of 10.244.0.254 as the range within which the IP address range commences (Simpson, and Novak, 2010). Therefore, the system above is expected to assign the IP addresses ranging from 10.244.0.16 to 10.244.0.254 for all the virtual machines attached to the same DHCP’s network. Configuring Multiple Virtual Networks A single network adapter can be associated with multiple virtual networks. In this case, the created virtual network is associated with the physical network adapter within the virtual network system. This linking mode will enable linking numerous the 75 and 100 virtual machines to a system of virtual network. If the organization will need multiple virtual networks to be connected to its host operating system, then there will be needed to create additional virtual network (Daft, Murphy, and Willmott, 2010). This will be achieved through a repeated procedure (Oppenheimer, 2005). However, if the organization wants to configure the virtual machines without network connectivity, then the virtual machines will not be connected to the virtual network. It should be noted that the creation of the virtual network automatically configures a network file that is stored in the cloud. Moreover, the virtual network configuration automatically allows files, documents and settings, document sharing, and all users to access to share the folders in the virtual network. Therefore, only a few or a single central server will be used by all users who require the same information from the same source or server. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
DVI extender
Find the remotely accessible DVI extender from Beacon functioning over IP technology that delivers increased network scalability while helping the admin to effortlessly debug multiple PCs and servers. Such KVM extenders help to promptly arrange the particular matrix configuration by using the built-in client/server protocol of the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). This DHCP server can be positioned anywhere in the entire network matrices, helping to support the admin to spontaneously install the network IP addresses. Such DVI USB KVMs also assist in integrating several devices and users in the entire single network.
0 notes