#Industrial Control & Factory Automation Market
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Industrial Automation Software Market is expected to reach a value of $59.5 billion by 2029, at a CAGR of 7.4% during the forecast period 2022–2029
#Industrial Automation Software Market#Factory Automation Software#Industrial Automation Software#Industrial Process Control#Industrial Automation
0 notes
Text
DAY 6274
Jalsa, Mumbai Aopr 20, 2025 Sun 11:17 pm
🪔 ,
April 21 .. birthday greetings and happiness to Ef Mousumi Biswas .. and Ef Arijit Bhattacharya from Kolkata .. 🙏🏽❤️🚩.. the wishes from the Ef family continue with warmth .. and love 🌺
The AI debate became the topic of discussion on the dining table ad there were many potent points raised - bith positive and a little indifferent ..
The young acknowledged it with reason and able argument .. some of the mid elders disagreed mildly .. and the end was kind of neutral ..
Blessed be they of the next GEN .. their minds are sorted out well in advance .. and why not .. we shall not be around till time in advance , but they and their progeny shall .. as has been the norm through generations ...
The IPL is now the greatest attraction throughout the day .. particularly on the Sunday, for the two on the day .. and there is never a debate on that ..
🤣
.. and I am most appreciative to read the comments from the Ef on the topic of the day - AI .. appreciative because some of the reactions and texts are valid and interesting to know .. the aspect expressed in all has a legitimate argument and that is most healthy ..
I am happy that we could all react to the Blog contents in the manner they have done .. my gratitude .. such a joy to get different views , valid and meaningful ..
And it is not the end of the day or the debate .. some impressions of the Gen X and some from the just passed Gen .. and some that were never ever the Gen are interesting as well :
The Printing Press (15th Century)
Fear: Scribes, monks, and elites thought it would destroy the value of knowledge, lead to mass misinformation, and eliminate jobs. Reality: It democratized knowledge, spurred the Renaissance and Reformation, and created entirely new industries—publishing, journalism, and education.
⸻
Industrial Revolution (18th–19th Century)
Fear: Machines would replace all human labor. The Luddites famously destroyed machinery in protest. Reality: Some manual labor jobs were displaced, but the economy exploded with new roles in manufacturing, logistics, engineering, and management. Overall employment and productivity soared.
⸻
Automobiles (Early 20th Century)
Fear: People feared job losses for carriage makers, stable hands, and horseshoe smiths. Cities worried about traffic, accidents, and social decay. Reality: The car industry became one of the largest employers in the world. It reshaped economies, enabled suburbia, and created new sectors like travel, road infrastructure, and auto repair.
⸻
Personal Computers (1980s)
Fear: Office workers would be replaced by machines; people worried about becoming obsolete. Reality: Computers made work faster and created entire industries: IT, software development, cybersecurity, and tech support. It transformed how we live and work.
⸻
The Internet (1990s)
Fear: It would destroy jobs in retail, publishing, and communication. Some thought it would unravel social order. Reality: E-commerce, digital marketing, remote work, and the creator economy now thrive. It connected the world and opened new opportunities.
⸻
ATMs (1970s–80s)
Fear: Bank tellers would lose their jobs en masse. Reality: ATMs handled routine tasks, but banks actually hired more tellers for customer service roles as they opened more branches thanks to reduced transaction costs.
⸻
Robotics & Automation (Factory work, 20th century–today)
Fear: Mass unemployment in factories. Reality: While some jobs shifted or ended, others evolved—robot maintenance, programming, design. Productivity gains created new jobs elsewhere.
The fear is not for losing jobs. It is the compromise of intellectual property and use without compensation. This case is slightly different.
I think AI will only make humans smarter. If we use it to our advantage.
That’s been happening for the last 10 years anyway
Not something new
You can’t control that in this day and age
YouTube & User-Generated Content (mid-2000s onward)
Initial Fear: When YouTube exploded, many in the entertainment industry panicked. The fear was that copyrighted material—music, TV clips, movies—would be shared freely without compensation. Creators and rights holders worried their content would be pirated, devalued, and that they’d lose control over distribution.
What Actually Happened: YouTube evolved to protect IP and monetize it through systems like Content ID, which allows rights holders to:
Automatically detect when their content is used
Choose to block, track, or monetize that usage
Earn revenue from ads run on videos using their IP (even when others post it)
Instead of wiping out creators or studios, it became a massive revenue stream—especially for musicians, media companies, and creators. Entire business models emerged around fair use, remixes, and reactions—with compensation built in.
Key Shift: The system went from “piracy risk” to “profit partner,” by embracing tech that recognized and enforced IP rights at scale.
This lead to higher profits and more money for owners and content btw
You just have to restructure the compensation laws and rewrite contracts
It’s only going to benefit artists in the long run
Yes
They can IP it
That is the hope
It’s the spread of your content and material without you putting a penny towards it
Cannot blindly sign off everything in contracts anymore. Has to be a lot more specific.
Yes that’s for sure
“Automation hasn’t erased jobs—it’s changed where human effort goes.”
Another good one is “hard work beats talent when talent stops working hard”
Which has absolutely nothing to with AI right now but 🤣
These ladies and Gentlemen of the Ef jury are various conversational opinions on AI .. I am merely pasting them for a view and an opinion ..
And among all the brouhaha about AI .. we simply forgot the Sunday well wishers .. and so ..
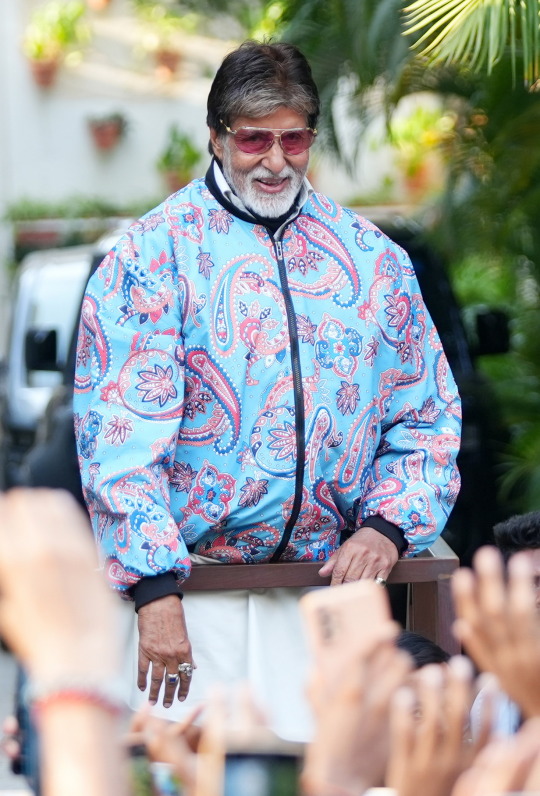
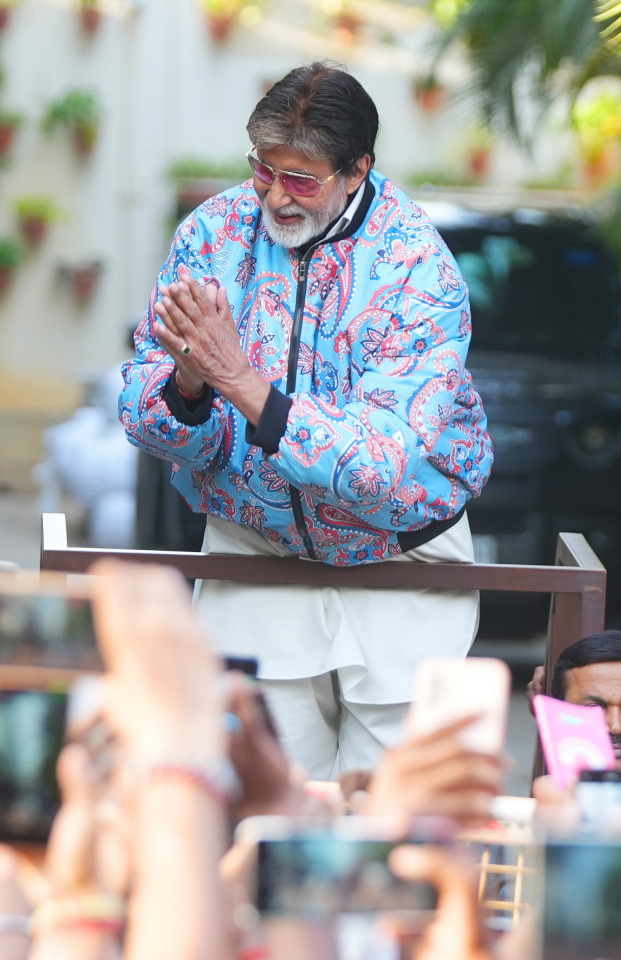
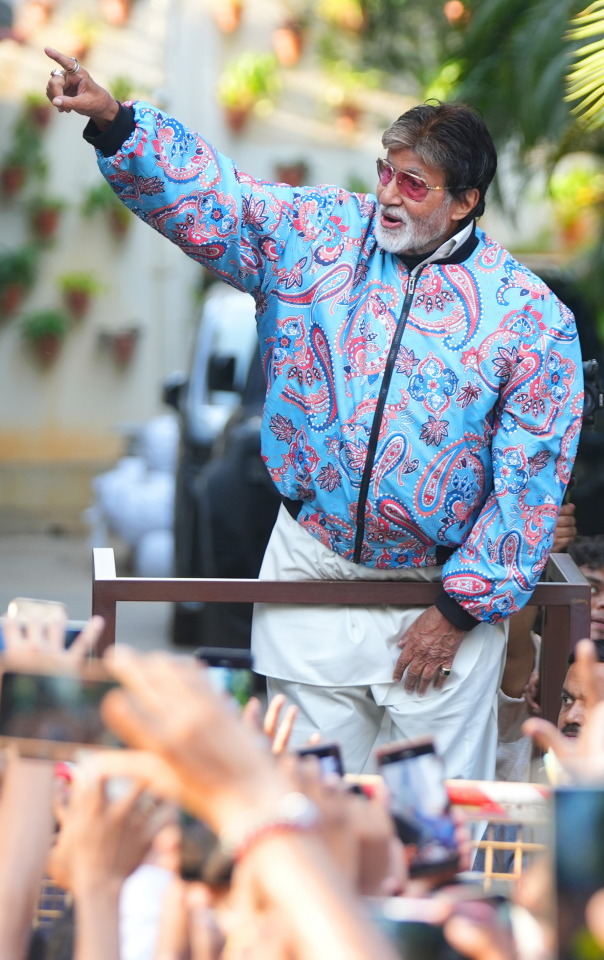














my love and the length be of immense .. pardon

Amitabh Bachchan
107 notes
·
View notes
Text
There are situations in which tariffs are a useful tool to address a trade deficit, or to protect key sectors of a country’s economy. Then there are situations where you accuse a bunch of penguins on an uninhabited island of currency manipulation. Guess which one we’re living in?
This is the takeaway of the manifold tariffs announced by President Donald Trump on Wednesday afternoon. In addition to the penguin-occupied Heard and McDonald Islands, the tariffs target the British Indian Ocean Territory, whose sole occupants live on a joint US-UK military base on Diego Garcia island. Yes, the United States is levying reciprocal tariffs against its own troops.
And then there are the tariffs against countries that have actual goods and services on which US consumers depend. China: 54 percent. Vietnam: 46 percent. Cambodia: 49 percent. South Korea: 25 percent. No corner of the US consumer economy will go untouched. Prices will rise. The stock market is spiraling. A recession looms. The tech industry will be turned upside down. Mark Cuban, noted billionaire, is encouraging people to stockpile consumables before it’s too late.
It’s reckless, it’s absurd, and it’s also everything Donald Trump said plainly he would do on the campaign trail. True, he didn’t telegraph how misguided the methodology would be—you can read about it more here, but suffice to say it’s thoroughly detached from the realities of international trade—but he loudly, repeatedly promised to tariff his way to glory.
The stated goal is to return manufacturing jobs to the United States, which is a bit like resurrecting the dodo. The US still manufactures plenty of goods; it’s second only to China in annual output, according to the World Bank. But many of the industry’s jobs have been replaced by automation, a bottle you can’t re-cork. And higher domestic labor costs mean US-made products will inherently be more expensive, a trade-off American consumers have consistently rejected. All of this was already true in Trump’s first term. It’s even more so now.
And let’s say a plurality of companies did decide to reshore or set up factories in the United States. The timeline for those decisions and implementation is measured in years, if not decades, and follow-through can be spotty. (Just ask Foxconn.) So what happens in the meantime?
The rationale has all the weight of a soap bubble. There isn’t a world where the US suddenly manufactures all the items the country has decided to target. There’s a 47 percent tariff on Madagascar now. Do you know why the US has a trade deficit with Madagascar? They produce vanilla; we don’t. Unless we’re suddenly setting up vanilla assembly lines in Ohio, that’s not changing.
But maybe Trump’s so-called Liberation Day is all just a master negotiating ploy. “Everybody sit back, take a deep breath. Don’t immediately retaliate. Let’s see where this goes,” said Treasury secretary Scott Bessent on CNN Wednesday. “Because if you retaliate, that’s how we get escalation.”
It’s an interesting tactic, to start a bar brawl and ask everyone not to punch back in case someone gets hurt. It’s not working. China has already vowed to retaliate; the EU suggested that it could as well. (New Zealand is officially chill.)
Set the economics of this aside for a moment, though. The insult on top of that looming injury is how sloppy this all is. It’s the same blunt-force destruction that DOGE has implemented within the US government, that Robert F. Kennedy Jr. has imposed on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, now projected on a global scale. Yes, Elon Musk and DOGE have taken a blowtorch to federal agencies. But the tariffs are a helpful reminder that it's Trump who's fiddling while it all burns.
It’s the instinct to measure wins in units of pain and suffering. It’s an assumption that the only way to help yourself is to hurt other people. This is just what America is now.
The optimist’s case is that this is all a feint, that other countries will capitulate or at least make enough of a show of it that things will go back to normal. Seems unlikely. First of all, they’re already doing the opposite, all apologies to Bessent. But even if they weren’t, even if this is just posturing from the US, that posturing has consequences. Whatever equity the US has built up over the last century as a reputable trade partner has been largely wiped out by a businessman-president best known for his bankruptcies.
And then there’s the pessimist’s case, which also seems increasingly like the realist’s. The US is barreling toward a recession for no good reason, and dragging the world—and a few thousand penguins on remote Antarctic islands—down with it.
91 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mmmmm thinking about mafiafell…. Writing chapter 7….. thinking about names….Don fell… mob fell and mafiafell r pretty basic so that’s why….
Hm, I love getting inspired and analyzing characters. DF! Sans is just Red, DF! Papyrus is just Papyrus, DF! Gaster is only Wings to his grandchildren…. Oh yes, we’re using that theory here, I enjoy the dynamic seeing as to how the timeline played out. Really young Papyrus is a bit manipulated by Gaster, when Sans pushed his brother away Wings took it as an advantage…. when Papyrus was cripped and seemingly perma-disabled only then did Sans began to care. So Gaster mentored Sans in welding to makeshift him a proper jaw and took Paps another year before he could speak properly...
His speech pattern still remains disjointed so many times he’s removed from the front lines and Sans reserves all the temper of the 3.
And to think Maria is what catches the attention of the most angry skeleton! She and him both die, hm. Say 1950. I do so enjoy torturing them mwah ahaha.
1890-1950 MAFIAFELL TIMELINE
1890: First minster emergence from barrier, remain complacent in scattered regions across Canada
1896: Monster General takes first human soul on surface, first evidence of monsterkinds presence found in Canada. Stories and “myths�� of creatures circulate. Thanks a lot Jeff.
1898: Increased tensions lead to monster communities forming isolated settlements near major trade centers (like [REDACTED]). Government begins recognizing monster populations.
1901: Monsters establish borders as recognition grows. American industrialists exploit monster labor for dangerous factory work, deepening resentment.
1908: Monsters migrate closer to cities and soon forms disrupt. Humans are viewed as economic competition.
1912: Monster raids on human lands increase hostility. In retaliation, the United States military experiments with living monster magic to counteract monster defenses.
1914: Tensions reach a boiling point, IB by real life European imperialism U.S. wages war against the monster kingdom under ideal of protecting American interests.
1916: The Siege of Underground occurs. Monster military collapses, King Asgore killed, and monster communities forcibly relocated to reserves for human study.
1917: Monsters granted “limited citizenship,” through heavily restricted rights. Former monster territories are absorbed into U.S. industrial zones and monsters begin to assimilate to human culture.
1920: President Kempt Warren promises normalcy but fails to resolve monster inequality. Magical weaponry development surges as corporations recognize its profit potential and smuggling of monsterkind begins in urban areas.
1922: Prohibition begins. Black markets thrive, selling magics, consumer goods, fleshtrade, and new monster alcohol. Organized crime explodes, involving human and monster gangs.
1924: Anti-monster sentiment fuels the rise of extremist political groups, demanding segregation and tighter restrictions. Monsters form their own unions and underground communities for protection.
1925: Early television prototypes powered by magical energy appear, revolutionizing entertainment and news. This blending of magic and technology creates a unique cultural identity.
1926: President William Cull focuses on economic growth, ignoring societal unrest. The divide between humans and monsters widens as monsters face violence, exclusion, and job discrimination.
1929: Stock Market Crash leads to the Great Depression. Monsters are scapegoated as job thieves and blamed for economic collapse.
1930: Magical weaponry and machinery technologies reach new heights, giving rise to armored cars, magic-powered aircraft, and industrial automation. Wealthy elites control most of this innovation.
1931: Prohibition ends. Human-run mafia families dominate trade in cities in exploiting magic services. Monsters partake with protection and roles of defense for human mafias.
1933: Fiere D. Roster becomes president, introducing “New Deal” to restore the economy. Monsters are largely excluded from government relief programs save for MLA(Monster Liberation Act- allows designated magic users government funding in independent merchant market.
1934(CURRENT): Monsters remain second-class citizens, confined to slums and ghettos. Cities like [REDACTED] form melting pots for poverty, crime, and societal divide. Progress in technology like magic radio, early television, and mechanized transport contrasts moral and social regression. Extremist human groups clash with monster rights activists.
1935: Monsters gain limited inclusion in labor unions, increasing political tension. Roster struggles to manage both economic recovery and societal divisions.
1936: Advances in magical medicine revolutionize healthcare but remain inaccessible to most monsters.
1938: Political radicals push for harsher policies against monsters, fueling riots in major cities. The military continues testing magic-infused weaponry, preparing for potential global conflict.
1939: With tensions escalating an arms race begins between the U.S. and other nations seeking to harness magical technologies. Canada and European powers grow wary of America.
1940: Monster-rights movements gain traction, demanding full citizenship and equal treatment. Whispers of a new global war loom as technological advancements make conflict inevitable.
1945: Supreme Court case “Arlow Trials” highlight case study of monster laborer accused of murdering human factor overseer. Explores dynamic of labor exploitation and systemic discrimination and opens perspectives for monster rights onpar with African-Americans.
1947: In the preparation for war, the HME(Human Monster Equals) act is formed giving monster same rights as humans. In the same situation as African+Americans John Crow laws are passed.
1950: WW2 erupts with America already a world power fueled by magic weaponry and advanced machinery. Monsters are drafted into the military further complicating societal role.
1950-1970: Post-war America emerges as a global superpower with magic-infused technology dominating industries. As result Canada is formed into America and no longer exists. Cultural divide shows signs of healing.
1970/Beyond: Magic becomes commercialized integrated into everyday life like television, transportation, and weapons. Monsters gradually gain equality but carry generations of discrimination and resentment.
#Donfell#mafiafell#mobfell#underfell au#undertale au#undertale fanfiction#mafiafell papyrus#mafiafell sans#lore#spoiler#story#timeline#Sovls Unrelated🩶#autism#selfship#selfshipper#also kinda used this as lore posting my bad#uf sans#sans#novice writer#writer#ao3 writer#writers on tumblr#history#decade: 1930s#1930s#1940#1940s#1950s#1960s
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
The more I read economics literature about automation trends and globalization trends (the actual economics term, not the rabid racist term) and their economic impacts on developed economies, the more I realize that the fundamental picture we have been sold these things is a lie.
The general picture of automation revolutions is that they present some way of doing work more efficiently and/or to create a better product, and so market forces simply demand it. And we have to figure out how to deal with all of the lost jobs which are resulting from this. Because even in a socialist utopia, surely it would be absurd to continue forcing people to use old and outdated technology to do work less efficiently just so they could have work to do, right? Maybe the socialist utopia will take care of people displaced by this work better, but the displacement will still happen.
Except then I start reading about the actual history in the actual economics of automation revolutions (I recommend Blood In The Machine for a history of the Luddites and the automated textile revolution in Britain). And that's not what happens even a single time. These automated revolutions increase the cost per unit to create a good! They make the quality worse! And the existing workers get displaced, and replaced with oppressed or even outright enslaved labors who make nothing in worse conditions! They didn't even actually reduce the amount of labor involved significantly, they just started working orphan slaves 80-90 hours a week rather than artisan workers doing 30-35, to "reduce" the labor involved by reducing the number of laborers. It seems like no one benefits from this. So why is it happening!?
Well the answer is simple. The machine looms were less efficient, created lower quality products, and were worse for every single person in every sector of the economy ... except insofar as that they enabled a more unequal economy. The textile industry itself made less profit. The world itself had worse and less textiles. But the machine loom owners specifically made more money, because machine rooms enabled more control over workers in ways which could be used to relegate them to an even smaller share of the smaller profits. And they didn't outcompete others by being better, they did it through regulatory capture, illegal business practices, outright fraud, and by having a pre-existing place of power in their society.
The same applies to the classic story of Ford and his great automobile factory model. Sure it produced a lot of cars at low prices, but what the history doesn't tell you is that a bunch of other automobile companies which weren't using the factory model were putting out their own cars similar cost. Sure they weren't scaling up as fast, but everyone involved was making good money and the market kept on producing more companies to fill the gap. Ford made the decision to sell to a new lower cost car market sure, but he did not make a better profit margin per dollar of car purchases than his competitors did. He made significantly worse actually because he had such hideous turnover at his factories, and his cars were of lower quality than non-factory line cars aimed at the same market could be.
So why the hell did the entire automobile industry follow in his wake? Well, because he personally was making an insane amount of money. The factory line model let him simplify the production chain in a way which cut out a lot of people who previously been making good salaries, and it let him replace well paid laborers with dirt cheap labor. (Despite the hubbub about how good Ford's factory jobs paid, they only paid well relative to other no skill no training work available. They paid much worse than the skilled laborers he fired had made.)
And the people who controlled how the car manufacturing process worked were the people who would stand to make money by switching over.
The same is true for globalization. When a berry monopoly which controls 60% of all berry sales in the US does so by importing berries from South America, from varieties optimized for durability rather than flavor, that isn't cheaper than growing them at home. Not even with the higher cost of labor in the US. Not even if you actually paid farm hands a good wage rather than by abusing undocumented workers who can't fight back as effectively. The transport costs are too high.
All across the US food sector we have examples of food monopolies exporting produce production overseas in ways that make the final product more expensive for the customer, and lower quality at the same time. Why!?
Well because it allows them to access even more vulnerable labor markets. So even though the whole pie shrinks, the company owners get a bigger enough cut of the pie to make up for it.
The lie of automation and globalization of work and the damage it does to developed economies is just that, a lie. It is not economically predestined for this stuff to happen. Alternatives are not predestined to be competed out of the market. Unless, of course, ownership of profits is concentrated in only a few hands. Unless what's being competed for isn't net profit or net service provided or net quality of goods, but how much profit you can localize in capital owners.
If that's the actual competition, and of course it is because the people making decisions for companies also own those companies, only then does job automation and the presence of exploitable overseas labor devastate economies.
If laborers actually owned their places of business piecemeal, the motivation for these kinds of economic shocks would largely dry up. Like, sure, labor saving devices get invented sometimes and you need less people to do the same work. And sure, sometimes work can be done overseas for cheaper because standards of living at lower or because there's some comparative economic advantage. But that is not actually what is happening most of the time this stuff occurs.
If there's one thing I've learned studying this stuff, it's that genuine examples of net gain automation are less common than we think, and tend to be implemented on fairly slower timelines. Same for globalization of work. What is very common is ways in which already unequal systems of ownership and decision making and profit can be made more unequal. And the only fix I can imagine is fundamentally changing and democratizing how businesses operate, and how we handle concepts of ownership.
#also I know this can read as dismissive of the impacts#of this stuff on the labor forces most exploited by it#especially in South America#it's just that I'm trying to come at this from the perspective of#the justification of the existing system uses#which do not care about that kind of suffering#and trying to point out how they don't even do the things they claim to do
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
CNC Press Brake Machine in India: Shaping the Future of Metal Bending
In the dynamic world of metal fabrication, CNC Press Brake Machines have become indispensable. These machines are critical in industries that demand precision bending and forming of sheet metal components. In India, the rising focus on infrastructure development, automotive manufacturing, and localized production has driven the adoption of CNC press brake technology across various sectors.
From small workshops to large-scale factories, CNC press brakes are revolutionizing how Indian manufacturers handle metal forming—efficiently, accurately, and consistently.
What is a CNC Press Brake Machine?
A CNC (Computer Numerical Control) Press Brake Machine is used to bend and shape metal sheets with precision. It uses a punch and die to perform various bends, guided by a CNC system that ensures exact specifications for angle, length, and repetition.
Modern CNC press brakes are far more advanced than traditional mechanical or hydraulic versions. They come with programmable controls, automated back gauges, and advanced sensors to deliver high-speed and high-precision bending.
Why CNC Press Brakes are Gaining Popularity in India
1. Precision and Consistency
In sectors like automotive, aerospace, and electronics, even minor deviations in part dimensions can lead to quality issues. CNC press brakes eliminate human error and ensure consistent output across batches.
2. Growing Industrialization
India’s expanding industrial base, especially in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities, is fueling demand for reliable fabrication equipment. CNC press brakes allow businesses to scale up production without compromising on accuracy.
3. Labour Efficiency
With a skilled labor shortage and rising wages, automation is becoming more attractive. CNC press brakes require minimal human intervention, reducing labor costs and dependency on manual operators.
4. Government Incentives
Government initiatives like Make in India and Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes are encouraging manufacturers to invest in advanced machinery, including CNC press brakes, for higher productivity.
Key Features of CNC Press Brake Machines in the Indian Market
High-Tonnage Capability: Machines ranging from 30 to 1000+ tons to suit various applications.
CNC Control Systems: Brands like Delem, ESA, and Cybelec offer intuitive interfaces for programming and automation.
Servo-Electric or Hydraulic Drive Systems: Depending on precision, energy efficiency, and speed requirements.
Multi-Axis Back Gauge: Enables complex bends and reduces setup time.
Automatic Tool Changers (ATC): For higher production environments.
Leading Indian and International Brands
India has a strong presence of both domestic and international CNC press brake manufacturers. Some notable names include:
Hindustan Hydraulics
Electropneumatics
Energy Mission
LVD India
Amada (Japan)
Durma (Turkey)
Yawei (China)
These companies offer machines tailored to the needs and budget of Indian manufacturers.
Applications in India
Automobile Body & Chassis Manufacturing
Kitchen Equipment Fabrication
Electrical Enclosures & Cabinets
Elevator and Escalator Components
Construction and Infrastructure Products
Railways and Defence Equipment
Challenges for Indian Buyers
High Initial Investment: CNC press brakes can be capital intensive, though the ROI is excellent over time.
Skill Development: Operators need training to use CNC systems effectively.
After-Sales Service: Choosing a vendor with reliable local support is crucial for maintenance and uptime.
The Road Ahead: Smart Factories & Industry 4.0
India is steadily moving towards smart manufacturing. CNC press brakes are now integrating with IoT, ERP systems, and robotic automation, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and remote troubleshooting. This evolution is making Indian factories more agile and globally competitive.
Conclusion
The CNC Press Brake Machine is no longer a luxury—it's a necessity in modern Indian manufacturing. With its unmatched accuracy, efficiency, and automation capabilities, it empowers businesses to meet rising customer expectations while optimizing operational costs.
As India continues to climb the global manufacturing ladder, CNC press brake machines will play a pivotal role in shaping the future—quite literally.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Top 10 Pneumatic Actuator Brands In 2025
The pneumatic actuator market continues to thrive in 2025, driven by advancements in automation and industrial efficiency. Based on comprehensive evaluations by CN10/CNPP research departments, which integrate big data analytics, AI-driven insights, and market performance metrics, here are the leading brands shaping the industry.
1. SMC (SMC Corporation)
Performance & Reliability: As a global leader since 1959, SMC delivers over 10,000 pneumatic components, including high-precision cylinders, valves, and F.R.L. units. Its products are renowned for durability, energy efficiency, and adaptability to extreme industrial conditions. Industry Applications: Widely used in automotive manufacturing, semiconductor production, and robotics, SMC’s actuators ensure seamless automation across 80+ countries. Its China-based facilities, established in 1994, serve as a primary global production hub.
2. FESTO (Festo AG & Co. KG)
Performance & Reliability: With nearly a century of expertise, Festo combines innovative engineering with IoT-enabled solutions. Its actuators emphasize precision control, low maintenance, and compatibility with smart factory ecosystems. Industry Applications: Festo dominates sectors like pharmaceuticals, food processing, and renewable energy, offering customized automation systems that enhance productivity and sustainability.
Other Notable Brands In The 2025 Rankings
While SMC and Festo lead the list, the following brands also excel in specific niches:
Brand A: Specializes in compact actuators for medical devices.
Brand B: Focuses on heavy-duty applications in construction machinery.
Brand C: Pioneers eco-friendly designs with reduced carbon footprints.
Key Trends Driving Market Growth
Smart Automation: Integration of AI and real-time monitoring in actuator systems.
Sustainability: Energy-efficient designs aligned with global decarbonization goals.
Customization: Tailored solutions for niche industries like aerospace and biotechnology.
This ranking underscores the critical role of innovation and adaptability in maintaining competitive advantage. Brands that prioritize R&D and cross-industry collaboration are poised to lead the next decade of pneumatic automation.
If you want to learn more about low-priced products, please visit the following website: www.xm-valveactuator.com
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
AI & IT'S IMPACT
Unleashing the Power: The Impact of AI Across Industries and Future Frontiers
Artificial Intelligence (AI), once confined to the realm of science fiction, has rapidly become a transformative force across diverse industries. Its influence is reshaping the landscape of how businesses operate, innovate, and interact with their stakeholders. As we navigate the current impact of AI and peer into the future, it's evident that the capabilities of this technology are poised to reach unprecedented heights.
1. Healthcare:
In the healthcare sector, AI is a game-changer, revolutionizing diagnostics, treatment plans, and patient care. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets to identify patterns, aiding in early disease detection. AI-driven robotic surgery is enhancing precision, reducing recovery times, and minimizing risks. Personalized medicine, powered by AI, tailors treatments based on an individual's genetic makeup, optimizing therapeutic outcomes.
2. Finance:
AI is reshaping the financial industry by enhancing efficiency, risk management, and customer experiences. Algorithms analyze market trends, enabling quicker and more accurate investment decisions. Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by AI streamline customer interactions, providing real-time assistance. Fraud detection algorithms work tirelessly to identify suspicious activities, bolstering security measures in online transactions.
3. Manufacturing:
In manufacturing, AI is optimizing production processes through predictive maintenance and quality control. Smart factories leverage AI to monitor equipment health, reducing downtime by predicting potential failures. Robots and autonomous systems, guided by AI, enhance precision and efficiency in tasks ranging from assembly lines to logistics. This not only increases productivity but also contributes to safer working environments.
4. Education:
AI is reshaping the educational landscape by personalizing learning experiences. Adaptive learning platforms use AI algorithms to tailor educational content to individual student needs, fostering better comprehension and engagement. AI-driven tools also assist educators in grading, administrative tasks, and provide insights into student performance, allowing for more effective teaching strategies.
5. Retail:
In the retail sector, AI is transforming customer experiences through personalized recommendations and efficient supply chain management. Recommendation engines analyze customer preferences, providing targeted product suggestions. AI-powered chatbots handle customer queries, offering real-time assistance. Inventory management is optimized through predictive analytics, reducing waste and ensuring products are readily available.
6. Future Frontiers:
A. Autonomous Vehicles: The future of transportation lies in AI-driven autonomous vehicles. From self-driving cars to automated drones, AI algorithms navigate and respond to dynamic environments, ensuring safer and more efficient transportation. This technology holds the promise of reducing accidents, alleviating traffic congestion, and redefining mobility.
B. Quantum Computing: As AI algorithms become more complex, the need for advanced computing capabilities grows. Quantucm omputing, with its ability to process vast amounts of data at unprecedented speeds, holds the potential to revolutionize AI. This synergy could unlock new possibilities in solving complex problems, ranging from drug discovery to climate modeling.
C. AI in Creativity: AI is not limited to data-driven tasks; it's also making inroads into the realm of creativity. AI-generated art, music, and content are gaining recognition. Future developments may see AI collaborating with human creators, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in fields traditionally associated with human ingenuity.
In conclusion, the impact of AI across industries is profound and multifaceted. From enhancing efficiency and precision to revolutionizing how we approach complex challenges, AI is at the forefront of innovation. The future capabilities of AI hold the promise of even greater advancements, ushering in an era where the boundaries of what is achievable continue to expand. As businesses and industries continue to embrace and adapt to these transformative technologies, the synergy between human intelligence and artificial intelligence will undoubtedly shape a future defined by unprecedented possibilities.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Basis of the Environmental Crisis
There is a fundamental problem here: The dynamics of capitalism have an inherent tendency towards ecological devastation. To understand why this is so, we need to look at how firms are constantly searching for ways to minimize their expenses. This is how they ensure the firm can make the maximum in profits. Because capitalism is made up of relatively autonomous firms, they are in competition. If a firm doesn’t continuously seek ways to make profits, they won’t be able to expand their business, move into new markets, invest in new technology. Other firms will out-compete them. And minimizing expenses is central to the pursuit of profits. Thus minimizing expenses is central to survival for the capitalist firms. And to do this, firms do cost-shifting at the expense of both workers and the environment.
First, companies try to keep compensation to workers as low as they can get away with. They may look to cut taxes that support services working class people rely on. They try to find new forms of technology or new ways to organize the work that reduces the number of worker hours it takes to produce a unit of output. They might automate a production operation with robots, or they will seek ways to intensify work through “lean production” methods. For example, they’ll use computer tracking of a warehouse worker picking items for an order so that they have no rest time after finishing an order but are pushed to a new task through computer control. Work intensification and computer monitoring puts workers under more stress which can have damaging health effects over time. This means the employers are imposing a human cost on workers. If workers in a furniture factory are constantly breathing in finishes or paints being sprayed on furniture in the open, or electronics assemblers are breathing in solder fumes, these are also cases where capital is shifting costs onto workers. And these are cases where the costs could be avoided. For example, there are soldering tools that have a vacuum to suck off solder fumes so workers don’t breath it, but a firm may not want to pay the expense of installing that equipment. These are examples of how the capitalist mode of production tends to shift costs onto workers.
Second, emissions into the air and water are another form of cost-shifting. A utility firm may burn coal to generate electricity. This creates emissions that damage the respiratory systems of people in the region and also contributes to global warming. But the power firm is not required to pay anything for these damages. These costs to others from emissions are “external” to the market transaction between the power firm and its customers who pay for electricity. This is an example of a “negative externality.” Externalities are a pervasive feature of the capitalist mode of production. The fossil fuel industry generates many “negative externalities.” Fracking operations insert chemicals underground which can pollute the underground water sources. A large gas field or leaky oil refinery will generate large amounts of volatile organic compounds — including carcinogens and endocrine disruptors. Studies of gas fields show effects in the surrounding area such as goat herds and barn cats losing the ability to have viable offspring, due to the endocrine disruptors. Gas fields also contribute to global warming by leaking large amounts of methane. Contrary to gas industry claims, gas power plants contribute as much as coal-fired power plants to global warming due to all the methane leaks.
You’ll notice here that I’m focusing on how environmental devastation is rooted in production — not consumption. Some environmentalists try to suggest that we should understand the global warming problem by looking at consumption practices, and they use ideas like a person’s “carbon footprint” to focus on personal consumption. But consumers of electric power don’t have control over the decisions of power firms on the methods of electricity generation, or what technology firms rely on to move cargo around in the global supply chains.
Another useful concept here is throughput. The throughput of production consists of two things: (1) All the material extracted from nature for the production process, and (2) all the damaging emissions (“negative externalities”) from the production process. In addition to the damaging emissions into the air and water, capitalism is an extractivist regime with a long history of land-grabbing to minimize expenses — as in the US government handing over mineral wealth to mining companies, lands for commercial ranching and extraction of logs and wood debris from forests for the lumber and paper industries. The search for short-term profits can lead to unsustainable practices such as clear-cutting of forests or use of huge nets to scarf up all the fish in a coastal region without regard to the future of that fishery.
With the concept of throughput, we can define a concept of ecological efficiency. If a production process is changed in ways that reduce the amount of damage from emissions (or amount of extracted resource) per unit of human benefit, then that change improves ecological efficiency. And here is a basic structural problem of capitalism: It has no inherent tendency towards ecological efficiency. If nature is treated as a free dumping ground for wastes, there will be no tendency to minimize damaging emissions per unit of human benefit from production. Also, there will be no tendency to minimize materials extracted from nature except to the extent firms have pay for these resources.
A production system that could generate increasing ecological efficiency would tend towards reductions in pollution and resource extraction. This would require a non-profit, non-market type of eco-socialist economy where production organizations are held socially accountable — required to systematically internalize their ecological costs. Capitalism’s tendency to ever greater environmental devastation happens because firms have an incentive to not internalize their costs, but dump them on others.
The devastation wrought by the cost-shifting dynamic of capitalism is not limited to global warming. Capitalism has favored the evolution of agricultural practices that aim at highest output at lowest financial cost to the firm. Intense competition has led to ever-greater concentration in ownership of farm land. The capitalist setup allows the growers to rely on labor contractors to pay laborers as little as possible and get rid of workers who try to organize. Growers often own lands in various locations and pursue different crops to minimize their risks. With encouragement from the chemical industry, growers have adopted industrial production of a single crop in a large field with increasing usage of pesticides and inorganic fertilizer over time. Inorganic fertilizers typically provide some mix of nitrogen, phosphorus and calcium. Over-use of these fertilizers has led to excessive runoff, polluting water courses and leading to ocean “dead spots” around the mouths of rivers. Destructive effects on fisheries is thus one of the negative externalities from capitalist agriculture.
Since World War 2 chemical pesticide production world-wide grew from 0.1 ton to 52 million tons in 1976 and 300 million tons in 2015. Pesticides produced by the chemical industry are damaging to the health of farm workers, and pollutes water courses, and leaves residues on food. Pesticide overuse also destroys the natural predators of insects and breeds pesticide-resistant pests. This leads a kind of agricultural arms race as more and more pesticide is needed. As Fred Magdoff and Chris Williams report in Creating an Ecological Society, pesticides also reduce “presence in the soil of organisms that stimulate plants to produce chemicals to defend themselves.”
As with pesticides the chemical industry has also vastly pumped up the production of petroleum-based plastics which do not biodegrade but end up as vast scourge of pollution in the oceans. Plastic bags have grown in use because they take a lot less energy to produce than paper bags, and thus cost less. Production has increased from less than 5 tons in 1950 to over 340 million tons by 2014, according to the Plastics Europe trade association. At least a third of all plastic produced is not recaptured, but mostly ends up in the ocean where it is destructive to living organisms. The plastics industry does not have to pay for the negative effects on living things in the oceans.
If we bring in our definition of throughput, pollution and dumping of wastes are one aspect, but we need to also look at the destructive extractivist tendencies in capitalism, such as clear-cutting of forests or over-fishing. According to a 2003 study, “90 percent of all large fishes have disappeared from the world’s oceans in the past half century,” since the onset of industrial fishing with huge nets in the 1950s. “”Whether it is yellowfin tuna in the tropics, bluefin in cold waters, or albacore tuna in between, the pattern is always the same. There is a rapid decline of fish numbers,” according to Ransom Myers, a fisheries biologist at Dalhousie University in Halifax. To address the problem, many countries have banned long drift nets and untended longlines, and have instituted elaborate systems of licensing, and have instituted quotas and third party observers working on boats. Nonetheless, capitalist fishing outfits frequently ignore or evade these rules.
#climate crisis#Working Class#autonomous zones#autonomy#anarchism#revolution#ecology#climate change#resistance#community building#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#anarchist society#practical#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#anarchy works#environmentalism
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
U.S. Industrial Control and Factory Automation Market: Transforming Manufacturing with Smart Technologies
The U.S. Industrial Control and Factory Automation market is experiencing a significant transformation, driven by advancements in smart technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, and advanced sensors. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for smarter, more efficient, and more reliable manufacturing solutions has never been greater. The infusion of digital technologies into manufacturing processes is not only enhancing productivity but is also enabling the U.S. to maintain its competitive edge in the global market. From the rise of smart factories to the integration of machine learning in production lines, the U.S. industrial control and automation market is poised for robust growth.
0 notes
Text
#Industrial Automation Software Market#Factory Automation Software#Industrial Automation Software#Industrial Process Control#Industrial Automation
0 notes
Text
About socoje.com
SOCOJE is a factory direct sales company integrating production and sales that was re-established in order to expand production and scale. socoje was established in 2023. Its address is Room 1, 8th Floor, Building 513, Mingdu Garden South District Phase 1, Zhuodaoquan Village, Hongshan Township, Hongshan District, Wuhan City, Hubei Province,China. Its production bases are located in Dongguan and Ningbo . We are committed to designing, developing and manufacturing high-quality and innovative products to meet our customers' needs. As a leading Factory direct sales company, we possess advanced production facilities, technologies, and an experienced team. Our goal is to maintain a leading position in the market of intelligent mechanical equipment and accessories by providing reliable, durable, and competitive products. Our product range covers a variety of intelligent mechanical equipment and accessories, including but not limited to automation equipment, robots, control systems, metal machining category, plastic machining category, wood machining category, laser category, various tools, and components. We prioritize product quality and performance, ensuring that each product meets customer requirements and provides exceptional performance and reliability. As a Factory direct sales company, we have established long-term and stable partnerships with global collaborators. We work closely with suppliers, partners, and customers, actively listening to their feedback and needs. We believe that collaboration is key to achieving mutual success, and we strive to develop and succeed together with our partners. We always adhere to the principle of putting quality first. Through strict quality control processes and testing procedures, we ensure that each product meets high standards. We also prioritize environmental sustainability and take measures to reduce the environmental impact of our production processes. On socoje.com, you can learn about our product line, technical capabilities, and manufacturing processes. We welcome potential customers, partners, and suppliers to reach out to us to explore collaboration opportunities. If you have any questions or requirements regarding our products or services, our team is dedicated to providing support and assistance. Thank you for your interest and support in socoje! We look forward to working with you to create a better future for the intelligent mechanical equipment and accessories industry!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
5 Unique Benefits of ERP for Manufacturers
STERP (Shanti Technology) is one of the leading ERP software companies in India, offering comprehensive solutions for businesses in the manufacturing sector. Among the top ERP software providers in India, STERP has emerged as a frontrunner thanks to its dedication to serving manufacturers.

The STERP ERP software has helped Indian manufacturers become more productive, automate processes that formerly required human labour, and foster a culture of collaboration. Production scheduling, inventory management, quality control, and material need planning are just some of the ways in which this software may help businesses better meet customer needs and deliver superior products. Researching aggregate statistics may tell you a lot about the spread of enterprise resource planning software around the world.
General worldwide statistics for ERP Software:
The worldwide enterprise resource planning (ERP) software market is valued at over $25 billion, with yearly growth of 10%–20%.
More than half (53%) of all businesses agree that ERP is a promising sector in which to invest.
From 2019 to 2026, the worldwide market for ERP software is projected to expand to $78.40 billion, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.2%.
The defence and aerospace sectors will have the highest ERP software adoption rates by 2026.
88% of organisations say that ERP has helped their chances of success.
Among all enterprises, 62.7% favour cloud-based ERP solutions over locally hosted ones.
When it comes to using an ERP solution, about 27% of firms worry that their data would be jeopardised.
Half of all companies will soon install an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system or enhance their current one.
5 Advantages of ERP for manufacturing company in India:
1. Streamlined Operations and Increased Efficiency:
Manufacturing enterprises in India need streamlined processes and enhanced efficiency to survive in today's competitive business environment. One of the most important tools for accomplishing these objectives is ERP software, and STERP - an excellent ERP software company in India is the most successful.
Manufacturing companies in India need to improve their productivity and efficiency to compete in the global manufacturing market. ERP software is a key component in achieving these goals, and STERP is the leading ERP software provider in India.
STERP understands the unique challenges faced by manufacturing facilities. Their ERP software for factories is specifically designed to raise output quality anywhere it's implemented.
By consolidating previously siloed departments and processes, STERP's ERP software makes key business operations transparent in real-time. The ability to step back and look at the larger picture helps manufacturers detect and fix inefficiencies and streamline processes.
2. Enhanced Visibility and Real-time Data Insights:
When it comes to making decisions and propelling corporate success in India's dynamic and ever-expanding industrial industry, increased visibility and real-time data insights are crucial. STERP is a leading service provider of ERP software in India, and its products help industrial companies improve their transparency and access to real-time data.
STERP provides ERP software tailored specifically for the manufacturing industry. Better management is possible with the help of our ERP software for manufacturing company in India by centralising functions like accounting, inventory control, production, and logistics. This connection gets rid of data silos and gives you a bird's eye view of the production process.
3. Improved Quality Control and Compliance:
Production relies heavily on quality control and following procedures. STERP offers exhaustive options for producers to improve quality control and conform to ever-changing regulations.
STERP, a market leader in India's enterprise resource planning software industry, understands the value of quality control. Our manufacturing-specific ERP software features robust quality management components that enable organisations to establish and rigorously adhere to quality control standards. It is now possible for businesses to create quality standards, set up inspection criteria, and track quality parameters continuously throughout the production cycle.
4. Effective Resource Management and Cost Reduction:
Successful manufacturing enterprises rely on STERP's ERP for manufacturing company in India, which was developed with the specific needs of Indian manufacturers in mind. STERP (Shanti Technology) is a well-established ERP software company in India that offers useful solutions for the industrial sector.
The top ERP software in India supplied by STERP (Shanti Technology), streamlines production scheduling, allowing firms to maximise resource utilisation and cut down on downtime. Taking into account factors like machine capacity, workforce availability, and raw materials on hand, the software develops production schedules that optimise output and minimises downtime.
5. Enhanced Customer Relationship Management and Service:
STERP is one of the leading ERP software companies in India because of the quality of the relationships we've built with our clients. The robust CRM features built into STERP's ERP software for manufacturers allow for streamlined management of customer communications, preferences, and historical data.
STERP's enterprise resource planning (ERP) software helps organisations better understand their customers by highlighting their wants, needs, and buying behaviours. With this holistic view, companies may provide customers with individualised solutions, goods, and encounters.
Final Thoughts:
For manufacturing companies in India, ERP software has certain particularly useful features. As the industry standard for enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, STERP creates tailor-made solutions for businesses in the manufacturing sector. ERP software opens the way for the effective administration of resources by optimising stock levels, improving production planning, and cutting costs. Manufacturers can save money by improving their procurement processes, throwing away less, and using their resources more efficiently. STERP is one of the top-ranked ERP software providers in India if you need ERP software for your manufacturing business.
#ERP software Companies in India#ERP software providers in India#ERP for manufacturing company in India#ERP software in India#ERP software company in India#ERP software#technology#ERP system#cloud ERP#ERP solutions#manufacturer#ERP software for engineering
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blockchain in Manufacturing Market Creating Safer, Transparent Production Networks
The Blockchain in the Manufacturing Market was valued at USD 3.9 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 116.9 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 45.93% from 2024-2032.
Blockchain in Manufacturing Market is experiencing transformative growth as industries adopt decentralized technologies to improve transparency, traceability, and operational efficiency. From raw material sourcing to supply chain logistics, blockchain is reshaping how manufacturers manage data integrity and security across global networks.
U.S. manufacturers are rapidly deploying blockchain to enhance product traceability and drive smart factory initiatives
Blockchain in Manufacturing Market continues to expand as companies recognize its potential to eliminate fraud, reduce costs, and ensure compliance in real-time. With its capability to create immutable records, blockchain is gaining traction in critical manufacturing domains such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
Get Sample Copy of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/6681
Market Keyplayers:
IBM Corporation – IBM Blockchain
Microsoft Corporation – Azure Blockchain Service
Amazon Web Services (AWS) – Amazon Managed Blockchain
Oracle Corporation – Oracle Blockchain Platform
SAP SE – SAP Blockchain
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. – Huawei Blockchain Service
Infosys Limited – Infosys Blockchain Suite
Intel Corporation – Intel Sawtooth
Siemens AG – Siemens Blockchain Lab
Wipro Limited – Blockchain as a Service (BaaS)
Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Limited – Deloitte Blockchain Solutions
Accenture Plc – Accenture Blockchain Services
Capgemini SE – Capgemini Blockchain Applications
TIBCO Software Inc. – TIBCO Blockchain Solution
Chainstack – Chainstack Blockchain Platform
Market Analysis
The integration of blockchain in manufacturing is no longer a concept—it's becoming a core operational strategy. Manufacturers are leveraging blockchain for end-to-end supply chain visibility, smart contract automation, and counterfeit mitigation. These benefits are especially valuable in high-risk and highly regulated sectors. In the U.S., early adoption is driven by Industry 4.0 initiatives, while Europe is seeing strong traction through sustainability compliance and digital transformation mandates.
Market Trends
Growing use of blockchain for real-time supply chain transparency
Increased deployment of smart contracts to automate procurement and payments
Adoption of decentralized identity systems for equipment and personnel verification
Integration with IoT and AI for advanced process validation and data logging
Rising focus on carbon tracking and ESG reporting through blockchain ledgers
Use in quality control to ensure product authenticity and batch traceability
Formation of blockchain consortia among leading manufacturers and suppliers
Market Scope
The Blockchain in Manufacturing Market offers vast potential as manufacturers seek greater control, security, and interoperability in increasingly complex production ecosystems.
Immutable data for compliance audits and quality assurance
Enhanced supplier coordination through shared digital ledgers
Fraud and counterfeit reduction via product serialization
Real-time visibility into multi-tier supply chains
Integration with legacy ERP and MES systems
Streamlined documentation and record-keeping
Greater trust among global stakeholders and partners
Forecast Outlook
The outlook for blockchain in manufacturing is highly promising. With increasing regulatory pressure, demand for transparency, and the push toward smarter factories, blockchain adoption is set to accelerate. The U.S. remains a leader in pilot projects and implementation, while European countries are integrating blockchain into sustainability and circular economy frameworks. As manufacturing networks become more digital and global, blockchain’s role in enabling trust, efficiency, and innovation will be central to future growth.
Access Complete Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/blockchain-in-manufacturing-market-6681
Conclusion
Blockchain in manufacturing is no longer an emerging trend—it's a competitive advantage. As industries pivot to digital-first strategies, blockchain offers the trust infrastructure needed for secure, transparent, and agile manufacturing. Businesses in the U.S. and Europe that invest in blockchain today are not just optimizing workflows—they are shaping the foundation of next-generation manufacturing.
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Related Reports:
U.S.A witnesses rapid transformation in the Next-Generation ICT Market driven by digital innovation
U.S.A drives innovation as Smart Port Market reshapes maritime infrastructure
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave - Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
Mail us: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Popular Commercial RO Plant Manufacturers in Delhi

Delhi essentially needs clean and pure water for commercial premises, industries, and commercial houses. Commercial RO plants have emerged as the most popular and successful water purification solution. Most of the leading manufacturer’s design and develop these important water treatment systems in Delhi. It removes dissolved solids, chemicals, and other impurities by making them safe for various uses of water in the respective commercial institutions. Be it a hotel, a hospital, a factory, or any other business, the right RO plant manufacturer is sought for water purification purposes. In this blog we discuss the Commercial RO Plant Manufacturers in Delhi, highlighting their efficiency, products, and services.
1. Netsol Water
Netsol Water is a major Delhi-based Commercial RO Plant Manufacturer that has more than 15 years of experience providing water treatment solutions. Netsol Water is known for offering industrial quality water purification systems made in its in-house manufacturing unit at Delhi's industrial area.
The company manufactures commercial RO plants in capacities ranging from 100 LPH to 100,000 LPH that are offered for use by various industries. The plants are made of high-grade stainless steel and other premium components sourced from the best brands available in the market. Each plant undergoes a full-fledged test for quality before it is actually delivered so that it offers prime performance and long use.
What sets Netsol Water apart is their comprehensive approach to customer service. They offer free consultation services, helping businesses choose the right RO plant capacity based on their specific requirements. Their team of experienced engineers provides detailed site surveys and water quality analysis before recommending solutions.
The company's commercial RO plants come with advanced features like automatic operation, digital display panels, and remote monitoring capabilities. They use energy-efficient pumps and motors, helping businesses save on electricity costs. All plants include pre-treatment systems like multimedia filters, activated carbon filters, and antiscalant dosing systems for complete water purification.
Netsol Water's after-sales support is particularly noteworthy. They provide annual maintenance contracts, emergency repair services, and regular performance monitoring. Their spare parts inventory ensures quick replacements when needed, minimizing downtime.
The company has successfully installed RO plants in numerous hotels, hospitals, schools, manufacturing units, and residential complexes across Delhi NCR. Their plants are certified by relevant authorities and come with warranties on major components. They also offer flexible payment options and competitive pricing, making quality water treatment solutions accessible to businesses of all sizes.
For businesses considering a commercial RO plant purchase, Netsol Water offers several advantages:
- Extensive experience in water treatment solutions
- Wide range of plant capacities to suit different needs
- High-quality components and durable construction
- Comprehensive pre and post-sale support
- Energy-efficient designs
- Competitive pricing and flexible payment options
- Quick installation and professional maintenance services
- Proven track record with numerous successful installations
- Advanced monitoring and control systems
- Complete water analysis and customized solutions
2. Pure Aqua Technologies
Pure Aqua Technologies has established itself as a reliable Commercial RO Plant Manufacturer in Delhi. With over a decade of experience, they specialize in medium to large-capacity plants suitable for industrial applications. Their systems feature automated operations and come with comprehensive warranty packages. The company offers installation services and regular maintenance support to ensure optimal plant performance.
3. Waterkraft Systems
Waterkraft Systems rounds out the top three manufacturers, known for their innovative approach to water treatment solutions. They focus on energy-efficient designs and user-friendly interfaces in their RO plants. The company provides customized solutions based on input water quality and client requirements. Their after-sales service includes operator training and quarterly maintenance checks.
Bottom-line
When planning to invest in a commercial RO plant, customers should consider factors like water quality requirements, daily consumption needs, available space, and budget constraints. Netsol Water's expert team can help analyze these factors and recommend the most suitable solution. They also provide detailed project proposals including technical specifications, installation requirements, and maintenance schedules, helping customers make informed decisions.
Contact Netsol Water for a free consultation to discuss your commercial water purification needs and find the perfect RO plant solution for your business in Delhi.
#environment#manufacturer#industries#water#environmental#manufacturers#industrial#netsolwater#purifier#manufacturing#industry#wastewater#filter#delhi
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Choosing the Right Concrete Batching Plant Manufacturers for Your Construction Needs

In today’s fast-paced construction industry the demand for high-quality concrete production has never been greater. Whether it's for large-scale infrastructure projects or residential developments the efficiency and reliability of concrete batching play a crucial role in ensuring successful project completion. This is where the role of Concrete Batching Plant Manufacturers becomes central. Selecting the right manufacturer is vital to meet the specific needs of a project maintain quality standards and ensure cost-effectiveness.
Understanding Concrete Batching Plants
A concrete batching plant is a facility where ingredients like cement water sand and aggregates are combined to form concrete. This equipment ensures that the right quantity and quality of concrete are produced with precision and consistency. Batching plants can be either stationary or mobile depending on the scope and requirements of the construction project.
There are mainly two types of batching plants:
Dry Mix Plants: Here the ingredients are mixed without water. The mixture is then transferred into a mixer truck where water is added.
Wet Mix Plants: All components including water are mixed at the plant itself ensuring a consistent mix ready for immediate use.
The right batching plant helps reduce manual labor enhances productivity and ensures accurate proportioning of materials.
Importance of Reliable Concrete Batching Plant Manufacturers
Choosing from among reputable Concrete Batching Plant Manufacturers is not just a matter of equipment; it's a decision that impacts the long-term success of your construction endeavors. Manufacturers with proven experience and cutting-edge technology offer superior quality equipment after-sales support and custom solutions tailored to specific project demands.
Some key benefits of working with a reliable manufacturer include:
High-Quality Machinery: Durable components and precision engineering ensure low maintenance and long operational life.
Customization Options: Good manufacturers offer solutions that fit your project’s unique capacity and layout needs.
After-Sales Service: Technical support spare parts and maintenance are crucial for uninterrupted operations.
Compliance with Standards: Leading manufacturers ensure their plants meet local and international construction and safety standards.
Key Features to Look for in a Batching Plant Manufacturer
When narrowing down your options among Concrete Batching Plant Manufacturers it's essential to evaluate several aspects:
1. Experience and Reputation
Established manufacturers with a long track record in the industry are often more reliable. Check client testimonials online reviews and case studies of completed projects.
2. Technological Advancements
Modern batching plants come with computerized control systems real-time data tracking and automated batching functions. Choose a manufacturer that incorporates the latest technologies.
3. Production Capacity
Manufacturers should offer a range of plant capacities from small portable units to large-scale industrial models. This allows you to choose one that matches your current and future project demands.
4. Ease of Installation and Operation
Top manufacturers design their plants for easy assembly and user-friendly operation minimizing downtime and labor requirements.
5. Environmental Considerations
Eco-friendly features like dust collection systems and energy-efficient motors should be considered especially for urban or environmentally sensitive areas.
Top Markets Served by Concrete Batching Plant Manufacturers
Concrete Batching Plant Manufacturers cater to various sectors within the construction industry. Their products are commonly used in:
Residential Construction: For houses apartment buildings and gated communities.
Commercial and Industrial Projects: Such as malls factories and office buildings.
Infrastructure Projects: Including highways bridges airports and railways.
Precast Concrete Production: For producing concrete blocks beams and panels.
Different sectors require different batching solutions. For example infrastructure projects often need high-capacity stationary plants while urban projects may benefit from compact mobile units.
Global Trends in the Batching Plant Manufacturing Industry
The market for concrete batching plants is growing rapidly due to increasing infrastructure development in emerging economies. Trends such as automation remote monitorin and sustainable manufacturing practices are shaping the future of the industry.
Some global Concrete Batching Plant Manufacturers are investing heavily in research and development to produce energy-efficient and high-performance plants that reduce waste and carbon emissions.
Another trend is the integration of IoT Internet of Things and AI-based systems which enable operators to control batching operations remotely predict maintenance needs and optimize production efficiency in real time.
Conclusion
The selection of reliable Concrete Batching Plant Manufacturers can significantly influence the success quality and profitability of a construction project. By investing in high-quality equipment from a trusted manufacturer contractors and developers can ensure consistent concrete output reduce operational costs and stay competitive in an increasingly demanding industry.
Whether you are embarking on a small residential project or managing a major infrastructure venture choosing the right batching plant manufacturer is a decision that warrants careful consideration. Look for a manufacturer with a proven track record advanced technology strong customer support and a commitment to quality and sustainability.
0 notes