#Secure Raspberry Pi networking
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Raspberry Pi Firewall Command Line Configuration Step-by-Step
Raspberry Pi Firewall Command Line Configuration Step-by-Step #homelab #selfhosted #rapsberrypi #RaspberryPifirewallguide #UFWsetuponRaspberryPi #SecureRaspberryPinetworking #RaspberryPiUFWconfigurations #TroubleshootingUFWissues #RaspberryPifirewall
Raspberry Pi OS is an extremely popular self-hosting platform many use for running services. Let’s set the tone for Raspberry Pi firewall configuration via the command line and see what we will learn. Raspberry pi os What: A step-by-step how-to guide for UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) on your Raspberry Pi Where: You can use this on native Raspberry Pi devices or other platforms like virtual…

View On WordPress
#Easy firewall setup on Raspberry Pi OS#Essential UFW commands#Protecting Raspberry Pi with UFW#Raspberry Pi firewall best practices#Raspberry Pi firewall guide#Raspberry Pi network security tips#Raspberry Pi UFW configurations#Secure Raspberry Pi networking#Troubleshooting UFW issues#UFW setup on Raspberry Pi
0 notes
Text
RN42 Bluetooth Module: A Comprehensive Guide
The RN42 Bluetooth module was developed by Microchip Technology. It’s designed to provide Bluetooth connectivity to devices and is commonly used in various applications, including wireless communication between devices.
Features Of RN42 Bluetooth Module
The RN42 Bluetooth module comes with several key features that make it suitable for various wireless communication applications. Here are the key features of the RN42 module:
Bluetooth Version:
The RN42 module is based on Bluetooth version 2.1 + EDR (Enhanced Data Rate).
Profiles:
Supports a range of Bluetooth profiles including Serial Port Profile (SPP), Human Interface Device (HID), Audio Gateway (AG), and others. The availability of profiles makes it versatile for different types of applications.
Frequency Range:
Operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) band, the standard frequency range for Bluetooth communication.
Data Rates:
Offers data rates of up to 3 Mbps, providing a balance between speed and power consumption.
Power Supply Voltage:
Operates with a power supply voltage in the range of 3.3V to 6V, making it compatible with a variety of power sources.
Low Power Consumption:
Designed for low power consumption, making it suitable for battery-powered applications and energy-efficient designs.
Antenna Options:
Provides options for both internal and external antennas, offering flexibility in design based on the specific requirements of the application.
Interface:
Utilizes a UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter) interface for serial communication, facilitating easy integration with microcontrollers and other embedded systems.
Security Features:
Implements authentication and encryption mechanisms to ensure secure wireless communication.
Read More: RN42 Bluetooth Module
#rn42-bluetooth-module#bluetooth-module#rn42#bluetooth-low-energy#ble#microcontroller#arduino#raspberry-pi#embedded-systems#IoT#internet-of-things#wireless-communication#data-transmission#sensor-networking#wearable-technology#mobile-devices#smart-homes#industrial-automation#healthcare#automotive#aerospace#telecommunications#networking#security#software-development#hardware-engineering#electronics#electrical-engineering#computer-science#engineering
0 notes
Text
KnowBe4, a US-based security vendor, revealed that it unwittingly hired a North Korean hacker who attempted to load malware into the company's network. KnowBe4 CEO and founder Stu Sjouwerman described the incident in a blog post this week, calling it a cautionary tale that was fortunately detected before causing any major problems.
"First of all: No illegal access was gained, and no data was lost, compromised, or exfiltrated on any KnowBe4 systems," Sjouwerman wrote. “This is not a data breach notification, there was none. See it as an organizational learning moment I am sharing with you. If it can happen to us, it can happen to almost anyone. Don't let it happen to you.”
KnowBe4 said it was looking for a software engineer for its internal IT AI team. The firm hired a person who, it turns out, was from North Korea and was "using a valid but stolen US-based identity" and a photo that was "enhanced" by artificial intelligence. There is now an active FBI investigation amid suspicion that the worker is what KnowBe4's blog post called "an Insider Threat/Nation State Actor."
KnowBe4 operates in 11 countries and is headquartered in Florida. It provides security awareness training, including phishing security tests, to corporate customers. If you occasionally receive a fake phishing email from your employer, you might be working for a company that uses the KnowBe4 service to test its employees' ability to spot scams.
Person Passed Background Check and Video Interviews
KnowBe4 hired the North Korean hacker through its usual process. "We posted the job, received résumés, conducted interviews, performed background checks, verified references, and hired the person. We sent them their Mac workstation, and the moment it was received, it immediately started to load malware," the company said.
Even though the photo provided to HR was fake, the person who was interviewed for the job apparently looked enough like it to pass. KnowBe4's HR team "conducted four video conference based interviews on separate occasions, confirming the individual matched the photo provided on their application," the post said. "Additionally, a background check and all other standard pre-hiring checks were performed and came back clear due to the stolen identity being used. This was a real person using a valid but stolen US-based identity. The picture was AI 'enhanced.'"
The two images at the top of this story are a stock photo and what KnowBe4 says is the AI fake based on the stock photo. The stock photo is on the left, and the AI fake is on the right.
The employee, referred to as "XXXX" in the blog post, was hired as a principal software engineer. The new hire's suspicious activities were flagged by security software, leading KnowBe4's Security Operations Center (SOC) to investigate:
On July 15, 2024, a series of suspicious activities were detected on the user beginning at 9:55 pm EST. When these alerts came in KnowBe4's SOC team reached out to the user to inquire about the anomalous activity and possible cause. XXXX responded to SOC that he was following steps on his router guide to troubleshoot a speed issue and that it may have caused a compromise. The attacker performed various actions to manipulate session history files, transfer potentially harmful files, and execute unauthorized software. He used a Raspberry Pi to download the malware. SOC attempted to get more details from XXXX including getting him on a call. XXXX stated he was unavailable for a call and later became unresponsive. At around 10:20 pm EST SOC contained XXXX's device.
“Fake IT Worker From North Korea”
The SOC analysis indicated that the loading of malware "may have been intentional by the user," and the group "suspected he may be an Insider Threat/Nation State Actor," the blog post said.
"We shared the collected data with our friends at Mandiant, a leading global cybersecurity expert, and the FBI, to corroborate our initial findings. It turns out this was a fake IT worker from North Korea," Sjouwerman wrote.
KnowBe4 said it can't provide much detail because of the active FBI investigation. But the person hired for the job may have logged into the company computer remotely from North Korea, Sjouwerman explained:
How this works is that the fake worker asks to get their workstation sent to an address that is basically an "IT mule laptop farm." They then VPN in from where they really physically are (North Korea or over the border in China) and work the night shift so that they seem to be working in US daytime. The scam is that they are actually doing the work, getting paid well, and give a large amount to North Korea to fund their illegal programs. I don't have to tell you about the severe risk of this. It's good we have new employees in a highly restricted area when they start, and have no access to production systems. Our controls caught it, but that was sure a learning moment that I am happy to share with everyone.
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Off topic. Use an Ad Blocker. Use dumb appliances.
It isn't piracy. It isn't stealing content. It's security. Anyone who tells you otherwise has no idea what the early days of these ads were like. It's better today, but still not 100%.
Ads aren't just a simple image or video that plays and annoys you. It's code that gets executed through your browser. Companies get paid to display ads don't know what's in the code. Companies that serve ads make mistakes and let malicious code though. Until the all ads are 100% safe it is a security issue.
Do not use browsers that try to cripple ad blockers. If you can, purchase memberships to sites you want to use ad-free. Most sites, content creators, etc. will get way more from a $1 membership from you than watching or viewing hundreds of ads on their content.
Refuse to pay for ads. Disney has added ads to their premium ad supported tier. People are now paying them for, providing the internet connection to, and providing the screens to Disney for advertising.
Smart appliances monitor everything they can. Your TV has a microphone. Your microwave is listening. Your washing machine hears everything. They monitor traffic on your network. They all upload that data to their manufacturers. Gigabytes of data every day.
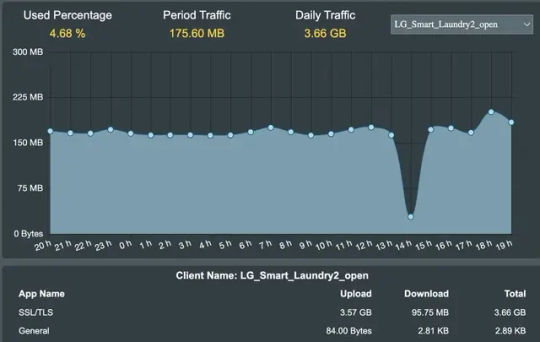
One appliance uploading over 3.5GB a data a day.
Your smart TV apps run in the background monitoring what you do in other apps. You may not have opened Netflix in a week but it is still calling home with information about what you're watching on Hulu, Peacock, or anything else.
If you can't live without these devices. Get some protection. One of the easiest things to get and use, is PiHole. It's easy to set up, you can use an old PC, or an very cheap raspberry pi device like the PiZero 2 W which is $15. I have one of these running powered by the USB port on my router.
As a tech professional with nearly 30 years under my belt...
Use an ad blocker. Use dumb appliances that don't need internet. If the toaster makes a funny noise, shoot it.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Derad Network: The Crypto Project That's Taking Aviation to New Heights https://www.derad.net/
Hey Tumblr fam, let's talk about something wild: a blockchain project that's not just about making money, but about making the skies safer. Meet Derad Network, a Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN) that's using crypto magic to revolutionize how we track planes. If you're into tech, aviation, or just love seeing Web3 do cool stuff in the real world, this one's for you. Buckle up-here's the scoop.
What's Derad Network?
Picture this: every plane in the sky is constantly beaming out its location, speed, and altitude via something called ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast). It's like GPS for aircraft, way sharper than old-school radar. But here's the catch-those signals need ground stations to catch them, and there aren't enough out there, especially in remote spots like mountains or over the ocean. That's where Derad Network swoops in.
Instead of waiting for some big corporation or government to build more stations, Derad says,"Why not let anyone do it?" They've built a decentralized network where regular people-you, me, your neighbor with a Raspberry Pi-can host ADS-B stations or process flight data and get paid in DRD tokens. It's a community-powered vibe that fills the gaps in flight tracking, making flying safer and giving us all a piece of the action. Oh, and it's all locked down with blockchain, so the data's legit and tamper-proof. Cool, right?
How It Actually Works
Derad's setup is super approachable, which is why I'm obsessed. There are two ways to jump in:
Ground Stations: Got a corner of your room and a decent Wi-Fi signal? You can set up an ADS-B ground station with some affordable gear-like a software-defined radio (SDR) antenna and a little computer setup. These stations grab signals from planes flying overhead, collecting stuff like "this Boeing 737 is at 30,000 feet going 500 mph." You send that data to the network and boom, DRD tokens hit your wallet. It's like mining crypto, but instead of solving math puzzles, you're helping pilots stay safe.
Data Nodes: Not into hardware? You can still play. Run a data processing node on your laptop or whatever spare device you've got lying around. These nodes take the raw info from ground stations, clean it up, and make it useful for whoever needs it-like airlines or air traffic nerds. You get DRD for that too. It's a chill way to join without needing to turn your place into a tech lab.
All this data flows into a blockchain (Layer 1, for the tech heads), keeping it secure and transparent. Derad's even eyeing permanent storage with Arweave, so nothing gets lost. Then, companies or regulators can buy that data with DRD through a marketplace. It's a whole ecosystem where we're the backbone, and I'm here for it.
DRD Tokens: Crypto with a Purpose
The DRD token is the star of the show. You earn it by hosting a station or running a node, and businesses use it to grab the flight data they need. It's not just some random coin to trade—it's got real juice because it's tied to a legit use case.The more people join, the more data flows, and the more DRD gets moving. It's crypto with a mission, and that's the kind of energy I vibe with.
Why This Matters (Especially forAviation Geeks)
Okay, let's get real-flying's already pretty safe, but it's not perfect. Radar's great, but it's blind in tons of places, like over the Pacific or in the middle of nowhere. ADS-B fixes that, but only if there are enough stations to catch the signals.Derad's like, "Let's crowdsource this." Here's why it's a game-changer:
Safer Skies: More stations = better tracking. That means fewer chances of planes bumping into each other (yikes) and faster help if something goes wrong.
Cheaper Than Big Tech: Building centralized stations costs a fortune. Derad's DIY approach saves cash and spreads the love to smaller players like regional airlines or even drone companies.
Regulators Love It: Blockchain makes everything transparent. Airspace rules getting broken? It's logged forever, no shady cover-ups.
Regulators Love It: Blockchain makes everything transparent. Airspace rules getting broken? It's logged forever, no shady cover-ups.
Logistics Glow-Up: Airlines can plan better routes, save fuel, and track packages like champs, all thanks to this decentralized data stash.
And get this-they're not stopping at planes.Derad's teasing plans to tackle maritime tracking with AlS (think ships instead of wings). This could be huge.
Where It's Headed
Derad's still in its early ascent, but the flight plan's stacked. They're aiming for 10,000 ground stations worldwide (imagine the coverage!), launching cheap antenna kits to get more people in, and dropping "Ground Station as a Service" (GSS) so even newbies can join. The Mainnet XL launch is coming to crank up the scale, and they're teaming up with SDR makers and Layer 2 blockchains to keep it smooth and speedy.
The wildest part? They want a full-on marketplace for radio signals-not just planes, but all kinds of real-time data. It's ambitious as hell, and I'm rooting for it.
Why Tumblr Should Stan Derad
This isn't just for crypto bros or plane spotters-it's for anyone who loves seeing tech solve real problems. Derad's got that DIY spirit Tumblr thrives on: take something niche (flight data), flip it into a community project, and make it matter.The DRD token's got legs because it's useful, not just a gamble. It's like catching a band before they blow up.
The Rough Patches
No flight's turbulence-free. Aviation's got rules out the wazoo, and regulators might side-eye a decentralized setup. Scaling to thousands of stations needs hardware and hype, which isn't instant. Other DePIN projects or big aviation players could try to muscle in too. But Derad's got a unique angle-community power and a solid mission—so I'm betting it'll hold its own.
Final Boarding Call
Derad Network's the kind of project that gets me hyped. It's crypto with soul, turning us into the heroes who keep planes safe while sticking it to centralized gatekeepers. Whether you're a tech geek, a crypto stan, or just someone who loves a good underdog story, this is worth watching.
Derad's taking off, and I'm strapped in for the ride.What about you?
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Raspberry Pi Board: Revolutionizing Computing and Education

The Raspberry Pi board is a series of small, affordable single-board computers developed by the Raspberry Pi Foundation, a UK-based charity focused on promoting computer science education and digital literacy. Since its launch in 2012, the Raspberry Pi has transformed from a niche educational tool into a versatile platform used in a wide range of applications, from DIY electronics projects to industrial automation.
A Brief History
The first Raspberry Pi, the Model B, was released in February 2012. Designed to promote basic computer science in schools and developing countries, it featured a 700 MHz ARM11 processor, 256 MB of RAM, and basic connectivity options. The success of the Model B led to a rapid expansion of the Raspberry Pi lineup, with various models offering improved performance, more memory, and enhanced connectivity.
Key Features and Models
Raspberry Pi 1 Model B (2012):
Processor: 700 MHz ARM11
Memory: 256 MB RAM
Ports: 2 USB 2.0 ports, HDMI, Composite video, 3.5mm audio jack, Ethernet
Storage: SD card slot
Raspberry Pi 2 Model B (2015):
Processor: 900 MHz quad-core ARM Cortex-A7
Memory: 1 GB RAM
Ports: 4 USB 2.0 ports, HDMI, Composite video, 3.5mm audio jack, Ethernet
Storage: MicroSD card slot
Raspberry Pi 3 Model B (2016):
Processor: 1.2 GHz quad-core ARM Cortex-A53
Memory: 1 GB RAM
Ports: 4 USB 2.0 ports, HDMI, Composite video, 3.5mm audio jack, Ethernet
Wireless: Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Raspberry Pi 4 Model B (2019):
Processor: 1.5 GHz quad-core ARM Cortex-A72
Memory: Options of 2 GB, 4 GB, and 8 GB RAM
Ports: 2 USB 3.0 ports, 2 USB 2.0 ports, 2 Micro HDMI ports, Ethernet, USB-C for power
Wireless: Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Raspberry Pi Zero (2015) and Zero W (2017):
Processor: 1 GHz single-core ARM11
Memory: 512 MB RAM
Ports: Mini HDMI, Micro USB OTG, Micro USB for power, GPIO pins
Wireless (Zero W): Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Applications and Uses
The versatility of the Raspberry Pi has led to its adoption in numerous fields:
Education:
Coding and Programming: Used in schools and educational programs to teach students programming languages such as Python, Scratch, and Java.
Computer Science Concepts: Introduces concepts like hardware, software, and networking.
DIY Projects and Maker Community:
Home Automation: Controls smart home devices, including lights, thermostats, and security systems.
Media Centers: Powers home media centers using software like Kodi.
Retro Gaming: Emulates classic gaming consoles using software like RetroPie.
Industrial and Commercial Applications:
IoT Devices: Serves as a hub for Internet of Things (IoT) devices, enabling data collection and remote control.
Automation and Control Systems: Used in factories and labs for monitoring and controlling equipment.
Research and Development:
Prototyping: Facilitates rapid prototyping of electronic devices and systems.
Data Collection: Gathers data from various sensors in environmental and scientific research.
Community and Ecosystem
The Raspberry Pi has cultivated a vibrant global community of developers, hobbyists, educators, and students. Online forums, tutorials, and community projects provide extensive support and resources for users at all skill levels. The Raspberry Pi Foundation also offers official accessories, including cases, cameras, and expansion boards, further enhancing the functionality of the Raspberry Pi.
Conclusion
The Raspberry Pi board has revolutionized the way people learn about and interact with technology. Its affordability, versatility, and extensive support network have made it an indispensable tool in education, DIY projects, and professional applications. As technology continues to evolve, the Raspberry Pi Foundation remains committed to expanding the capabilities and accessibility of this remarkable platform, ensuring that computing remains within reach for everyone.
3 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello sorry for tagging. I am very sick, my asthma is at its maximum level, my nose freezes, I have no medicine or food. I am in bad shape financially, I am a black disabled, who uses multiple medications, I pay for my food and lodging
Unfortunately I do not have all the resources to keep me safe, that is why I need your help, whatever you can contribute to me will be of great help.
Aww geez, that really sucks, Tumblr user who doesn't follow me, didn't exist until about a week ago, and mysteriously asked for help using the exact same words as several known spambots.
For resources to keep you safe, I would recommend backing yourself up on a local hard disk and also to a cloud service; things like Google drive or Dropbox will do in a pinch, but for things you really care about like your own code there are dedicated cloud backup companies like SpiderOak and IDrive that provide more security-focused services. For local backups there are a wide variety of disk vendors; I personally use a Synology NAS with redundant drives to minimize the difficulty of replacing any parts that fail. You can also use a NAS for storing media and making it accessible on your phone, computer, and smart devices like TVs, and if it has enough processing power you can run something like Pi-Hole (a local-network-wide ad blocker) on it without needing a dedicated raspberry pi or similar.
#the risk of making posts like this is that sooner or later a real person is going to ask me for help#and I'll be like 'oh no poor robot are you exhausted from your long hours at the spam factory?'#and then it'll turn out that I was a huge asshole to a real person in distress#otoh if a real person decides to ask me for help by creating a random tumblr account and copying the pleas the spambots use#then they are legitimately going to have a hard time convincing anyone they're not a spambot
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Another super useful thing is non-commercial/organizational VPNs. I use two currently:
VPN to my home: I can securely access resources I don't want exposed to the internet like my NAS, home automation, PCs via SSH... you can also use this to circumvent geoblocking while abroad (i.e. access content available from your home country but not abroad)
VPN to my uni: I can download literature for free from uni library or publishers since apparently they check whether you're coming from a university network
Anyone can set up a VPN using Wireguard. Most routers can do it and if yours can't, you may be able to use OpenWRT (third party firmware) or a Raspberry Pi.
I might do a Wireguard tutorial post later if anyone is interested.
VPNs do not make you more secure
here's how they work!
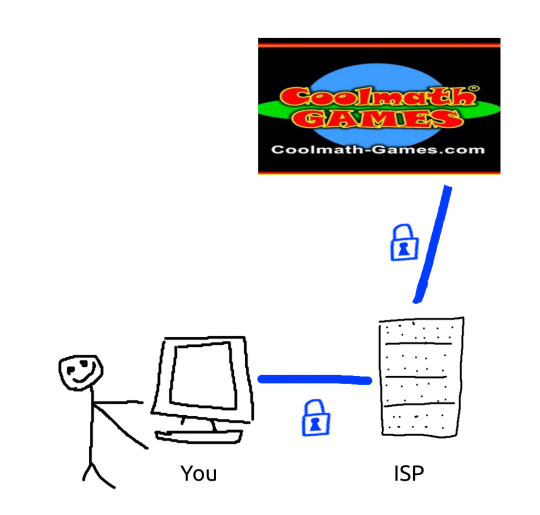
first of all, most of your internet traffic is already encrypted via TLS (Transport Layer Security). Things that aren't encrypted are usually videogames or less important applications.
a VPN encrypts traffic between your computer and the VPN server you're using.
your Internet Service Provider (ISP) sits in the middle of that transaction.
cue the MS paint diagram
Without a VPN:
With a VPN:
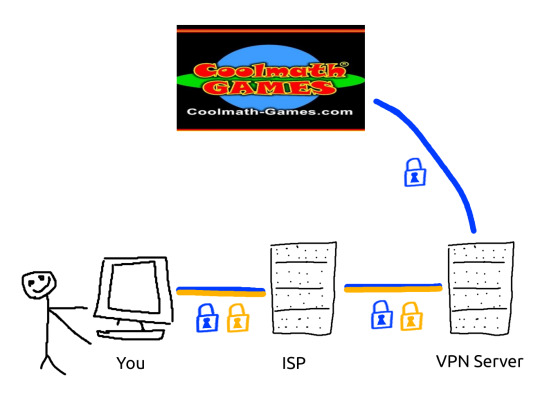
the traffic between your VPN server and the rest of the internet is not encrypted any further.
things that VPNs are good for:
bypassing geo-blocking
bypassing website blocks set up by your ISP
obscuring network traffic from your ISP
things that VPNs are not good for:
browsing the internet without having your activity logged. every company that gives internet service logs the activity, it's half of how they make sure they're not being hacked.
hiding information from the government. VPN providers WILL bend to subpoenas, they WILL turn over logs of your network activity.
cybersecurity. VPNs can't save you once the traffic is between them and the final destination. they don't analyze your traffic to detect and stop hackers, they don't add any encryption where it matters.
VPNs are not a shortcut to security. you cannot pay 15 dollars a month to forgo all responsibility for your own digital privacy. do your research, use a password manager, stay safe.
my friends i hope you find this information useful. you have been sold a lie. remember to show extreme skepticism to youtube sponsorships and journalism websites which sing their praises.
sources: i have a certificate iv in cybersecurity
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Mastering Personal SMS Gateways for Seamless IFTTT Integration
Unlocking the Power of Personal SMS Gateways for IFTTT Automation
In today's connected world, automation is key to streamlining your daily tasks and enhancing your smart home and business workflows. One effective way to achieve this is by integrating a personal SMS gateway with IFTTT (If This Then That), enabling you to send and receive SMS notifications automatically based on various triggers. This comprehensive guide walks you through the process of setting up a personal SMS gateway for seamless integration with IFTTT, empowering you to automate alerts, reminders, and updates effortlessly.
What is a Personal SMS Gateway?
A personal SMS gateway serves as a bridge between your devices and the cellular network, allowing you to send and receive SMS messages programmatically. Unlike third-party services, a personal gateway offers greater control, privacy, and customization, making it ideal for businesses and tech enthusiasts who want to automate communication without relying on external platforms.
Why Integrate Your SMS Gateway with IFTTT?
Integrating your SMS gateway with IFTTT opens up a world of automation possibilities. You can trigger SMS alerts based on weather conditions, security system events, calendar reminders, or other web services. This integration ensures you stay informed in real-time, whether you're at home or on the go.
Setting Up Your Personal SMS Gateway
To begin, you'll need a device capable of acting as your SMS gateway. Options include a Raspberry Pi with a GSM modem, a dedicated SMS gateway hardware, or a server with SMS API capabilities. Here’s an overview of the setup process:
Choose Your Hardware: Select a device with cellular connectivity. Raspberry Pi combined with a GSM module is a popular choice due to its affordability and flexibility.
Install Necessary Software: For Raspberry Pi, install a Linux OS, then set up software like Gammu or Kannel, which facilitate SMS sending and receiving.
Configure the Gateway: Connect your GSM modem, configure the software with your SIM card details, and ensure it can send/receive messages.
Test Your Gateway: Send a test SMS to confirm proper setup and connectivity.
Integrating with IFTTT
Once your SMS gateway is operational, the next step is connecting it with IFTTT. You can do this either through a webhook service or by setting up a custom applet. Here’s a typical integration approach:
Create a Webhook Endpoint: Use a service like IFTTT Webhooks to listen for trigger events.
Configure Your Gateway to Send Requests: Program your SMS gateway to send HTTP POST requests to the IFTTT webhook URL when certain conditions are met (e.g., a sensor detects motion).
Create IFTTT Applets: Set up applets that listen for these webhook triggers and then send SMS messages via your gateway or notify you through other channels.
Automating Notifications and Alerts
With the integration in place, you can automate a variety of notifications, such as:
Security alerts when your alarm system detects movement.
Reminders for appointments or medication schedules.
Weather alerts for severe conditions.
System status updates from your IoT devices.
Benefits of Using a Personal SMS Gateway with IFTTT
Using your own SMS gateway for IFTTT integration offers numerous advantages:
Privacy and Control: Manage your data without relying on third-party services.
Cost Efficiency: Reduce costs associated with commercial SMS services, especially at scale.
Customization: Tailor messages and triggers to suit your specific needs.
Reliability: Ensure messages are sent promptly with direct control over the gateway.
Conclusion
Integrating a personal SMS gateway with IFTTT is a powerful way to automate notifications, enhance your smart home, or streamline business communications. While the setup requires some technical knowledge, the benefits of increased privacy, customization, and control make it a worthwhile investment. For detailed instructions and resources, visit sms gateway ifttt and start building your automated communication system today!
0 notes
Text
Tired of Paying for Tools? These 40 Open-Source Alternatives Have You Covered?
Let’s be real for a second.
We’ve all been there—mid-project, mid-semester, or mid-burnout—when a paid tool throws up a paywall and asks for $19.99/month just to export your file. It stings, especially when you’re trying to keep your budget lean.

But here’s the good news: the open-source community has your back. 💪 There are dozens of completely free, insanely powerful tools that can do (almost) everything their paid counterparts can—without locking your best features behind a subscription.
Whether you're a freelancer, student, startup founder, or just someone who loves great software, this list is your new toolbox.
🚀 Why Open-Source Is the Underdog That Wins Before we dive in, let’s clarify something: Open-source ≠ low quality. In fact, some of the world’s biggest companies (Google, NASA, Netflix) use open-source tools every day. These aren’t sketchy knockoffs—they’re community-powered, security-tested, and constantly evolving.
Now, let’s talk about the 40 free tools that could save you hundreds—or even thousands—of dollars a year.
🧠 Smart Swaps for Everyday Tools
LibreOffice → Ditch Microsoft Office Docs, Sheets, Presentations—all offline, all free.
OnlyOffice → Google Docs Vibes, but Yours Looks and feels like MS Office, works online or self-hosted.
Joplin → Evernote for Nerds Markdown-based, syncs securely, and doesn’t sell your notes.
Zettlr → Perfect for Writers & Academics Citation support + distraction-free writing.
🌐 For Browsing, Email & Team Chat
Firefox → More Privacy, Less Google Extensible and fast—and they don’t track you.
Brave → Built-in Ad Blocker? Yes Please Faster browsing + rewards system.
Thunderbird → Outlook Without the Overkill Email, calendar, and to-do list in one clean interface.
Mattermost → Slack Without the Bill Your team chat, your server, your rules.
Jitsi Meet → Free Video Calls—No Sign-Up Needed Start a call with a link. Done.
🎨 Designers & Creators, Rejoice
GIMP → Photoshop for the People Yes, it’s that powerful. Yes, it’s free.
Inkscape → Vector Design Like a Boss Great for logos, icons, and print design.
Krita → Digital Painting Heaven Designed by artists, for artists.
Blender → Hollywood-Grade 3D Modeling Used in actual movies. Free forever.
Darktable → Lightroom Without the Monthly Bill RAW editing + professional workflow.
🎧 Audio & Video Editing
Audacity → Podcasting, Remixing, Editing, Easy Intuitive multi-track editor.
OBS Studio → Streaming & Screencasting Gold What Twitch streamers use. Seriously.
Shotcut → Video Editing That Just Works Cross-platform and powerful.
Olive → Modern Video Editor in the Making Sleek, promising, and growing fast.
👨💻 Developers, You’re Going to Love These
VSCodium → VS Code Without Microsoft Tracking Same editor, privacy-respecting build.
Atom → Hackable to the Core Loved by web devs and hobbyists.
Eclipse → Java Devs’ Old-School Favorite Still rock-solid.
NetBeans → Full IDE for Polyglot Coders Good for Java, PHP, and C++.
Hoppscotch → Postman Without the Bloat Runs in your browser, free forever.
MariaDB / MySQL → Free SQL Workhorses The backbone of many web apps.
SQLite → Tiny, Powerful, Portable Database No server required. Zero config.
✅ Organize Your Life (and Work)
Wekan → Trello Clone, But Open Kanban boards made simple.
Focalboard → Self-Hosted ClickUp Alternative Task management that respects your data.
Redmine → Jira's Open Twin Great for bug tracking & agile workflows.
Taskcafe → Asana-Style, Cleaner Interface New kid on the block, with potential.
🔐 Privacy Tools That Feel Like Superpowers
Bitwarden → Best Password Manager, Hands Down Cloud, browser, and mobile support.
KeePassXC → Local, Bulletproof Password Vault For privacy purists.
Tutanota → Private Email That Just Works End-to-end encrypted email, minimal design.
Pi-hole → Block Ads on Your Entire Network Install it on a Raspberry Pi and say goodbye to web ads.
☁️ Sync, Store, and Share Files Securely
Nextcloud → Your Own Google Drive Private cloud, full control.
Syncthing → Dropbox, But Peer-to-Peer No servers. Just your devices talking securely.
rclone → Cloud Storage on the Command Line Sync anything, anywhere.
📊 Data, Dashboards & Decisions
Metabase → BI Dashboards Without the Headache Plug in your data, get answers fast.
Grafana → DevOps’ Favorite Dashboard Tool Real-time, customizable graphs.
Apache Superset → Data Exploration for Pros Used by Airbnb, Netflix, and more.
🤖 Bonus: Automate All the Things
AutoHotKey → Make Your Computer Work For You Automate anything on Windows. Seriously.
🌍 Your Wallet and Your Future Will Thank You Switching to open-source isn’t just about saving money (though that’s nice). It’s about:
💻 Owning your tools
🔐 Protecting your privacy
🌱 Supporting innovation and community
🧰 Having control over your workflow
These tools are built by people like you, for people like you. Try just a few of them, and you’ll wonder why you ever paid in the first place.
0 notes
Text
YI Cam Remote Access: Your Guide to Self-Hosted Surveillance

Want to have complete control over your YI Cam and go beyond its default cloud? For more privacy and customization, many users prefer YI Cam Remote Access, rather than using the manufacturer's cloud. Therefore, this post explores how to accomplish this sophisticated configuration, assisting you in navigating the frequently challenging process of self-hosting your camera's feed. Walk through this post to learn more details!
Understanding the YI Cam Remote Access
Generally, you need to install a custom firewall on your device if you want to access the YI camera remotely and connect it to your server. Additionally, it allows leveraging the benefits of the RTSP (real-time streaming protocol) streaming as well as FTP access. Moreover, it eliminates the need for third-party platforms and for configuring cameras to the self-hosted servers.
However, it acts as a “Network Remote Controller,” especially for the multimedia servers. It allows users to control media playback remotely. But it does not deliver audio or video streams continuously; instead, it communicates with the servers streaming the multimedia content. Hence, for the YI Cam Remote Access, users must connect their security cameras to the server through RTSP.
How to Connect Camera To Server for YI Remote Access?
Moreover, enabling the YI Cam Remote Access opens up several possibilities and advanced functionalities. So, let’s begin with the essential steps to Connect Camera To Server for managing and monitoring your YI camera remotely.
Initially, confirm your YI Cam supports the RTSP or streaming compatibility, as some models may require custom firmware.
Subsequently, set up your chosen server device, such as a computer, NAS, or Raspberry Pi, with a suitable operating system.
Next, install essential software like Blue Iris, MotionEye, FFmpeg, or Home Assistant to manage the video feed.
Finally, configure secure remote access using methods such as port forwarding, VPN, or Dynamic DNS for external viewing.
Now, you can view, configure, and control your YI camera remotely.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, YI Cam Remote Access empowers you with full control over your camera's feed through self-hosting, prioritizing privacy & customization. Additionally, this advanced setup typically requires RTSP compatibility, a dedicated server, and management software. With secure remote access methods such as VPN or port forwarding, you can ensure seamless monitoring from anywhere.
#YICameraSetup#YICamRemoteAccess#SelfHostedCamera#IPCameraSetup#RemoteCameraAccess#YICamOnServer#RTSPStream#ONVIFCamera#YICamRTSP
1 note
·
View note
Link
0 notes
Text

Comparison of Ubuntu, Debian, and Yocto for IIoT and Edge Computing
In industrial IoT (IIoT) and edge computing scenarios, Ubuntu, Debian, and Yocto Project each have unique advantages. Below is a detailed comparison and recommendations for these three systems:
1. Ubuntu (ARM)
Advantages
Ready-to-use: Provides official ARM images (e.g., Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS) supporting hardware like Raspberry Pi and NVIDIA Jetson, requiring no complex configuration.
Cloud-native support: Built-in tools like MicroK8s, Docker, and Kubernetes, ideal for edge-cloud collaboration.
Long-term support (LTS): 5 years of security updates, meeting industrial stability requirements.
Rich software ecosystem: Access to AI/ML tools (e.g., TensorFlow Lite) and databases (e.g., PostgreSQL ARM-optimized) via APT and Snap Store.
Use Cases
Rapid prototyping: Quick deployment of Python/Node.js applications on edge gateways.
AI edge inference: Running computer vision models (e.g., ROS 2 + Ubuntu) on Jetson devices.
Lightweight K8s clusters: Edge nodes managed by MicroK8s.
Limitations
Higher resource usage (minimum ~512MB RAM), unsuitable for ultra-low-power devices.
2. Debian (ARM)
Advantages
Exceptional stability: Packages undergo rigorous testing, ideal for 24/7 industrial operation.
Lightweight: Minimal installation requires only 128MB RAM; GUI-free versions available.
Long-term support: Up to 10+ years of security updates via Debian LTS (with commercial support).
Hardware compatibility: Supports older or niche ARM chips (e.g., TI Sitara series).
Use Cases
Industrial controllers: PLCs, HMIs, and other devices requiring deterministic responses.
Network edge devices: Firewalls, protocol gateways (e.g., Modbus-to-MQTT).
Critical systems (medical/transport): Compliance with IEC 62304/DO-178C certifications.
Limitations
Older software versions (e.g., default GCC version); newer features require backports.
3. Yocto Project
Advantages
Full customization: Tailor everything from kernel to user space, generating minimal images (<50MB possible).
Real-time extensions: Supports Xenomai/Preempt-RT patches for μs-level latency.
Cross-platform portability: Single recipe set adapts to multiple hardware platforms (e.g., NXP i.MX6 → i.MX8).
Security design: Built-in industrial-grade features like SELinux and dm-verity.
Use Cases
Custom industrial devices: Requires specific kernel configurations or proprietary drivers (e.g., CAN-FD bus support).
High real-time systems: Robotic motion control, CNC machines.
Resource-constrained terminals: Sensor nodes running lightweight stacks (e.g., Zephyr+FreeRTOS hybrid deployment).
Limitations
Steep learning curve (BitBake syntax required); longer development cycles.
4. Comparison Summary
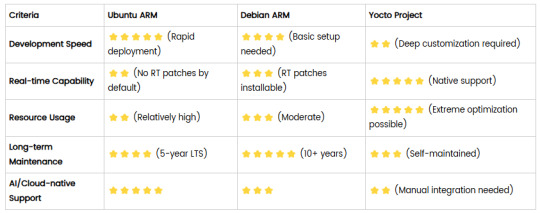
5. Selection Recommendations
Choose Ubuntu ARM: For rapid deployment of edge AI applications (e.g., vision detection on Jetson) or deep integration with public clouds (e.g., AWS IoT Greengrass).
Choose Debian ARM: For mission-critical industrial equipment (e.g., substation monitoring) where stability outweighs feature novelty.
Choose Yocto Project: For custom hardware development (e.g., proprietary industrial boards) or strict real-time/safety certification (e.g., ISO 13849) requirements.
6. Hybrid Architecture Example
Smart factory edge node:
Real-time control layer: RTOS built with Yocto (controlling robotic arms)
Data processing layer: Debian running OPC UA servers
Cloud connectivity layer: Ubuntu Server managing K8s edge clusters
Combining these systems based on specific needs can maximize the efficiency of IIoT edge computing.
0 notes
Text
Decentralized or Die Trying

The fight was never really left versus right. That is just the surface-level distraction. The real divide is control versus autonomy, centralization versus decentralization. That is the war happening beneath your feet, and most people do not even know it is being fought.
You were born into a system that was not built to set you free. It was built to keep you docile, obedient, and dependent. Schools teach conformity, not curiosity. Banks teach you to stay in debt, not to build wealth. Media teaches you fear, not understanding. And governments? They teach you to stay in line, not to question the rules of the game.
But some of us have stopped waiting for permission. We are not asking for a better system, we are building one.
There is a quiet revolution unfolding. People are walking away from broken systems and constructing their own alternatives from the ground up.
They are choosing Bitcoin over fiat. They are embracing self-custody instead of chasing credit scores. They are running nodes instead of trusting centralized authorities. They are homesteading, installing solar panels, growing their own food, and teaching their children to question everything they see and hear.
Even the internet, the very platform you are reading this on, was quietly shaped by decentralization. Linux, the open-source operating system, is the silent giant behind much of the internet. Built by a global community of developers who believed in collaboration over control, Linux now powers everything from servers to smartphones. No marketing campaign made that happen. No corporation mandated it. It was simply the best idea, and it spread like wildfire because it was open, accessible, and fair.
And now Bitcoin is doing for money what Linux did for information. It is removing the gatekeepers. It is replacing permission with protocol. It is unleashing financial freedom the same way Linux unleashed digital freedom.
We are not just witnessing a trend or another technological wave. This is a paradigm shift. A mass awakening. A growing realization that you do not have to play a rigged game when you can build a new one.
Legacy institutions are panicking. You can see it in their scramble: central bank digital currencies, mandatory digital IDs, surveillance tech packaged as convenience. They are desperately trying to keep people inside the system by making the cage more comfortable. But the truth is out. The door is open. And people are walking out.
This movement is not about gadgets or hype. It is about truth. It is about reclaiming the right to live without being watched, taxed, manipulated, or controlled. It is about freedom that does not come from elections or permissions, but from education, intention, and action.
So take the tools. Use them. Share them.
Stack sats. Run a node. Flash a Raspberry Pi with Linux. Learn to grow your own food. Pick up a trade skill. Talk to your neighbors. Educate your friends. Build networks that are too distributed to be shut down and too local to be ignored.
Because the future does not belong to the centralized. It belongs to the builders. The rebels. The ones who said enough is enough and started crafting a new reality from the ground up.
Decentralized or die trying.
Take Action Towards Financial Independence
If this article has sparked your interest in the transformative potential of Bitcoin, there’s so much more to explore! Dive deeper into the world of financial independence and revolutionize your understanding of money by following my blog and subscribing to my YouTube channel.
🌐 Blog: Unplugged Financial Blog Stay updated with insightful articles, detailed analyses, and practical advice on navigating the evolving financial landscape. Learn about the history of money, the flaws in our current financial systems, and how Bitcoin can offer a path to a more secure and independent financial future.
📺 YouTube Channel: Unplugged Financial Subscribe to our YouTube channel for engaging video content that breaks down complex financial topics into easy-to-understand segments. From in-depth discussions on monetary policies to the latest trends in cryptocurrency, our videos will equip you with the knowledge you need to make informed financial decisions.
👍 Like, subscribe, and hit the notification bell to stay updated with our latest content. Whether you’re a seasoned investor, a curious newcomer, or someone concerned about the future of your financial health, our community is here to support you on your journey to financial independence.
📚 Get the Book: The Day The Earth Stood Still 2.0 For those who want to take an even deeper dive, my book offers a transformative look at the financial revolution we’re living through. The Day The Earth Stood Still 2.0 explores the philosophy, history, and future of money, all while challenging the status quo and inspiring action toward true financial independence.
Support the Cause
If you enjoyed what you read and believe in the mission of spreading awareness about Bitcoin, I would greatly appreciate your support. Every little bit helps keep the content going and allows me to continue educating others about the future of finance.
Donate Bitcoin:
bc1qpn98s4gtlvy686jne0sr8ccvfaxz646kk2tl8lu38zz4dvyyvflqgddylk
#Decentralization#Bitcoin#Linux#OpenSource#Homesteading#SelfSovereignty#FinancialFreedom#ParallelSystems#OptOut#FixTheMoney#StackSats#RunYourNode#ResistTheSystem#DigitalFreedom#RebelTech#cryptocurrency#financial experts#digitalcurrency#financial education#finance#globaleconomy#financial empowerment#blockchain#unplugged financial
1 note
·
View note
Link
#configuration#encryption#firewall#IPmasking#Linux#networking#OpenVPN#Performance#PiVPN#Privacy#RaspberryPi#remoteaccess#Security#self-hosted#Server#Setup#simplest#systemadministration#tunneling#VPN#WireGuard
0 notes
Text

Bring your imagination to life and hone your tech skills with Heartening Raspberry Pi projects that are more practical than theoretical. Raspberry Pi projects. No matter if you have interest in electronics, IoT, robotics, or automation-these projects prove to be suitable for Computer Science, Electronics, as well as Electrical engineering students. Construct authentic solutions for the world, improve your CV, and remain in front of the competition in technology!
Types of Raspberry Pi Projects for Engineering Students Raspberry Pi is truly the breakthrough invention that will take up engineering students building ground breaking yet real-time applications. Some of the most common types of Raspberry Pi projects are:
1. Through Internet of Things (IoT) projects, sensors and devices can be connected to the internet for making advanced homes, weather stations, or health monitoring systems.
2. Automate anything from lights and appliances to security systems with Raspberry Pi and Python.
3. Using motor drivers and Raspberry Pi, a robotic project would control robots that may be line followers or robotic arms.
4. AI and ML projects simulate basic image recognition, voice assistants, or face detection modelling in Python and TensorFlow Lite.
5. Networking is where mini-servers, VPNs, or network scanners can be made using Raspberry Pi.
6. Projects of Media and Entertainment create smart mirrors and media centers and also game emulators for some fun and learning.
7. Educational projects will create learning kits for kids, digital notice boards, or interactive classroom tools.
It is the best medium for undergraduate students who are interested in practical study in the domains of computer science, electrical, electronics, electronic systems, and telecommunications engineering.
#RaspberryPi#EngineeringProjects#IoTProjects#Automation#RoboticsWithPi#AIProjects#PythonProjects#FinalYearProjects#CSEProjects#EEEProjects#EmbeddedSystems#StudentInnovators#TakeoffEduGroup#Takeoffprojects
0 notes