#Semantic Tags in HTML
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo

(via Semantic HTML | Navigating the Digital Realm)
0 notes
Note
Hi, Mr Prokopetz, I'm a big fan. Apologies if you've answered this before, but I was wondering what software you use to create the pdf and epub layouts of your ttrpgs, and whether you'd recommend it to a hobbyist who wants to try putting together something more professional than a gdoc for their own ttrpg?
My workflow is unfortunately not terribly accessible unless you have a fair amount of technical know-how.
In brief, I write all of my games in Notepad++ as HTML documents, taking care to use only the subset of HTML5 tags which are supported by most popular EPUB readers. I then use Calibre (or, more, precisely, the command-line utility that comes with Calibre, though you can get mostly the same results via the GUI) to bundle the HTML document as an EPUB3 file. I typically distribute both the HTML and EPUB versions (the former in a zipfile with all of the fonts and images and such) because web browsers tend to have much better screen-reader support than EPUB apps do.
The PDF, meanwhile, is generated from the same master HTML document using CSS paged media extensions – the layout is all generated automatically based on rules specified in a big, gnarly CSS file, and is never touched by human hands. There are a number of software packages which can do this sort of CSS-driven HTML-to-PDF conversion, some of them free or open source; I use a commercial product called Prince because, to the best of my knowledge, it's the only such software which has out-of-the-box support for PDF/UA semantic tagging (i.e., the stuff you need to do in order to make your PDFs screen-reader friendly), but you have more options if you're willing to tag your PDFs manually. (I am not.)
As for whether I'd recommend doing it this way? Like I said, unless you're a proper gearhead, not really; it's super efficient once you get it all set up – the only version of the game I actually maintain is the master HTML document, and generating updated versions of all the other formats is a one-click affair – but it's really only feasible for me because I already knew how to all that workflow automation stuff for unrelated reasons. I can't imagine teaching yourself all that from scratch just to write elfgames!
349 notes
·
View notes
Text
Day 7 [Semantics In HTML]
Introduction To HTML
Day 2 [Multimedia Elements In HTML]
Day 3 [Table in HTML]
Day 4 [Link Tag In HTML]
Day 5 [Lists In HTML]
Day 6 [Forms In HTML]
Code:

Line By Line Explanation:
Semantic Tags in HTML give clear meaning to the code. These are tags like:
<header>: Used for the title of the page.
<nav>: Contains navigation links of the website.
<main>: The main part of the page.
<section>: A group of content that is similar.
<article>: A group of content that is an independent piece.
<aside>: Extra info, like side notes.
<footer>: The bottom of the page that contains the copy rights and additional info.
Navigation Tag:
The navigation tag must be within an unordered list tag. And each item of that list must contain the link tag that should have the URL of that specific page.
Comments In HTML:
It is a note in your code that the browser ignores.
It’s just for you to read.
You can use it to explain your code or temporarily hide some code.
Syntax Of A Comment:
<!-- This Is A Comment -- >
Output Of The Code:

Notes: The arrows and the words in red are something I included. It is not included in the code!
______________
Hope This Helps :)
#code#codeblr#css#html#javascript#python#studyblr#progblr#programming#comp sci#web design#web developers#web development#website design#webdev#website#tech#html css#learn to code#school#study motivation#study aesthetic#study blog#student#high school#studying#study tips#studyspo#website development#coding
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Since the release of HTML5 in 2008, tags such as <b> (bold), <i> (italic) have been softly deprecated for the benefit of users of screenreaders*; instead, it is preferable to use the semantic tags <strong> and <em> (emphasis) respectively, with style defined in CSS. If for some reason they aren't appropriate, it's still preferable to use CSS style attributes within a <span> container to ensure that your text will be interpreted correctly in modern (and future) browsers.
That's why the only tone tag I accept is '/span'. /span
* also to clarify the division between content (HTML) and style (CSS)
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Monday 26th February 2024
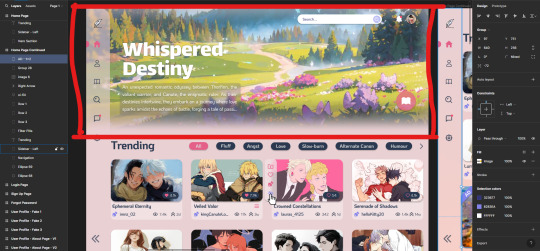
Created the row of fanfic cards! All I had to do was adjust the sizing for the card template because the first one was huge compared to what I wanted! But I am now happy with the results!
🎯 Next up: (1) do a side-quest and make an interactive HTML semantic tags webpage for people learning HTML then (2) the hero section:
🎵 song: Rave Angel - Blusher
#quillfic#codeblr#coding#studyblr#programming#studying#comp sci#progblr#tech#programmer#figma#web design#girlhood#cute#oxford#light academia#studyinspo
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Learn HTML and CSS: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
Introduction to HTML and CSS
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) and CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) are the core technologies for creating web pages. HTML provides the structure of the page, while CSS defines its style and layout. This guide aims to equip beginners with the essential knowledge to start building and designing web pages.
Why Learn HTML and CSS?
HTML and CSS are fundamental skills for web development. Whether you're looking to create personal websites, start a career in web development, or enhance your current skill set, understanding these technologies is crucial. They form the basis for more advanced languages and frameworks like JavaScript, React, and Angular.
Getting Started with HTML and CSS
To get started, you need a text editor and a web browser. Popular text editors include Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, and Atom. Browsers like Google Chrome, Firefox, and Safari are excellent for viewing and testing your web pages.
Basic HTML Structure
HTML documents have a basic structure composed of various elements and tags. Here’s a simple example:
html
Copy code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First Web Page</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to My Web Page</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph of text on my web page.</p>
</body>
</html>
: Declares the document type and HTML version.
: The root element of an HTML page.
: Contains meta-information about the document.
: Connects the HTML to an external CSS file.
: Contains the content of the web page.
Essential HTML Tags
HTML uses various tags to define different parts of a web page:
to : Headings of different levels.
: Paragraph of text.
: Anchor tag for hyperlinks.
: Embeds images.
: Defines divisions or sections.
: Inline container for text.
Creating Your First HTML Page
Follow these steps to create a simple HTML page:
Open your text editor.
Write the basic HTML structure as shown above.
Add a heading with the tag.
Add a paragraph with the tag.
Save the file with a .html extension (e.g., index.html).
Open the file in your web browser to view your web page.
Introduction to CSS
CSS is used to style and layout HTML elements. It can be included within the HTML file using the <style> tag or in a separate .css file linked with the <link> tag.
Basic CSS Syntax
CSS consists of selectors and declarations. Here’s an example:
css
Copy code
h1 {
color: blue;
font-size: 24px;
}
Selector (h1): Specifies the HTML element to be styled.
Declaration Block: Contains one or more declarations, each consisting of a property and a value.
Styling HTML with CSS
To style your HTML elements, you can use different selectors:
Element Selector: Styles all instances of an element.
Class Selector: Styles elements with a specific class.
ID Selector: Styles a single element with a specific ID.
Example:
html
Copy code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Styled Page</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="main-heading">Hello, World!</h1>
<p id="intro">This is an introduction paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
In the styles.css file:
css
Copy code
.main-heading {
color: green;
text-align: center;
}
#intro {
font-size: 18px;
color: grey;
}
CSS Layout Techniques
CSS provides several layout techniques to design complex web pages:
Box Model: Defines the structure of an element’s content, padding, border, and margin.
Flexbox: A layout model for arranging items within a container, making it easier to design flexible responsive layouts.
Grid Layout: A two-dimensional layout system for more complex layouts.
Example of Flexbox:
css
Copy code
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
.item {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightblue;
}
Best Practices for Writing HTML and CSS
Semantic HTML: Use HTML tags that describe their meaning clearly (e.g., , , ).
Clean Code: Indent nested elements and use comments for better readability.
Validation: Use tools like the W3C Markup Validation Service to ensure your HTML and CSS are error-free and standards-compliant.
Accessibility: Make sure your website is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, by using proper HTML tags and attributes.
Free Resources to Learn HTML and CSS
W3Schools: Comprehensive tutorials and references.
MDN Web Docs: Detailed documentation and guides for HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Codecademy: Interactive courses on web development.
FreeCodeCamp: Extensive curriculum covering HTML, CSS, and more.
Khan Academy: Lessons on computer programming and web development.
FAQs about Learning HTML and CSS
Q: What is HTML and CSS? A: HTML (HyperText Markup Language) structures web pages, while CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) styles and layouts the web pages.
Q: Why should I learn HTML and CSS? A: Learning HTML and CSS is essential for creating websites, understanding web development frameworks, and progressing to more advanced programming languages.
Q: Do I need prior experience to learn HTML and CSS? A: No prior experience is required. HTML and CSS are beginner-friendly and easy to learn.
Q: How long does it take to learn HTML and CSS? A: The time varies depending on your learning pace. With consistent practice, you can grasp the basics in a few weeks.
Q: Can I create a website using only HTML and CSS? A: Yes, you can create a basic website. For more complex functionality, you'll need to learn JavaScript.
Q: What tools do I need to start learning HTML and CSS? A: You need a text editor (e.g., Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text) and a web browser (e.g., Google Chrome, Firefox).
Q: Are there free resources available to learn HTML and CSS? A: Yes, there are many free resources available online, including W3Schools, MDN Web Docs, Codecademy, FreeCodeCamp, and Khan Academy.
#how to learn html and css#html & css course#html & css tutorial#html and css#html course#html css tutorial#html learn#html learn website#learn html#learn html and css#html and css course#html and css full course#html and css online course#how to learn html and css for beginners
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
HTML Tutorial: A Quick Overview
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) forms the backbone of web development, enabling the structure and presentation of content on the web. It’s a markup language that defines elements like headings, paragraphs, links, images, lists, and more, providing a standardized way to format and display information in browsers.
HTML uses tags, enclosed in angle brackets, to represent different types of content. Each tag typically comes in pairs, an opening tag and a closing tag, to wrap and describe the content in between. HTML is fundamental for building web pages, allowing developers to create structured documents with defined sections and multimedia elements.
One of HTML’s key features is its ability to create links, connecting different parts of the web. This hyperlinking capability is what makes HTML unique, forming the web as we know it today. Additionally, HTML supports embedding multimedia like images, videos, and audio, which brings pages to life.
As web standards evolve, HTML has grown, too, with the latest version being HTML5. This version introduced new elements that provide semantic meaning to the structure of web documents, ensuring that content is more accessible and well-organized.
fro more:https://quipoin.com/tutorial/HTML-tutorial
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Let's understand HTML

Cover these topics to complete your HTML journey.
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the standard language used to create web pages. Here's a comprehensive list of key topics in HTML:
1. Basics of HTML
Introduction to HTML
HTML Document Structure
HTML Tags and Elements
HTML Attributes
HTML Comments
HTML Doctype
2. HTML Text Formatting
Headings (<h1> to <h6>)
Paragraphs (<p>)
Line Breaks (<br>)
Horizontal Lines (<hr>)
Bold Text (<b>, <strong>)
Italic Text (<i>, <em>)
Underlined Text (<u>)
Superscript (<sup>) and Subscript (<sub>)
3. HTML Links
Hyperlinks (<a>)
Target Attribute
Creating Email Links
4. HTML Lists
Ordered Lists (<ol>)
Unordered Lists (<ul>)
Description Lists (<dl>)
Nesting Lists
5. HTML Tables
Table (<table>)
Table Rows (<tr>)
Table Data (<td>)
Table Headings (<th>)
Table Caption (<caption>)
Merging Cells (rowspan, colspan)
Table Borders and Styling
6. HTML Forms
Form (<form>)
Input Types (<input>)
Text Fields (<input type="text">)
Password Fields (<input type="password">)
Radio Buttons (<input type="radio">)
Checkboxes (<input type="checkbox">)
Drop-down Lists (<select>)
Textarea (<textarea>)
Buttons (<button>, <input type="submit">)
Labels (<label>)
Form Action and Method Attributes
7. HTML Media
Images (<img>)
Image Maps
Audio (<audio>)
Video (<video>)
Embedding Media (<embed>)
Object Element (<object>)
Iframes (<iframe>)
8. HTML Semantic Elements
Header (<header>)
Footer (<footer>)
Article (<article>)
Section (<section>)
Aside (<aside>)
Nav (<nav>)
Main (<main>)
Figure (<figure>), Figcaption (<figcaption>)
9. HTML5 New Elements
Canvas (<canvas>)
SVG (<svg>)
Data Attributes
Output Element (<output>)
Progress (<progress>)
Meter (<meter>)
Details (<details>)
Summary (<summary>)
10. HTML Graphics
Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG)
Canvas
Inline SVG
Path Element
11. HTML APIs
Geolocation API
Drag and Drop API
Web Storage API (localStorage and sessionStorage)
Web Workers
History API
12. HTML Entities
Character Entities
Symbol Entities
13. HTML Meta Information
Meta Tags (<meta>)
Setting Character Set (<meta charset="UTF-8">)
Responsive Web Design Meta Tag
SEO-related Meta Tags
14. HTML Best Practices
Accessibility (ARIA roles and attributes)
Semantic HTML
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) Basics
Mobile-Friendly HTML
15. HTML Integration with CSS and JavaScript
Linking CSS (<link>, <style>)
Adding JavaScript (<script>)
Inline CSS and JavaScript
External CSS and JavaScript Files
16. Advanced HTML Concepts
HTML Templates (<template>)
Custom Data Attributes (data-*)
HTML Imports (Deprecated in favor of JavaScript modules)
Web Components
These topics cover the breadth of HTML and will give you a strong foundation for web development.
Full course link for free: https://shorturl.at/igVyr
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Round 3 of the Regular WIPBB art claims is live! You may claim as many fics as you want, just fill out a separate form for each and give each claim a different username.
Art claims for this round will be open until August 7th!
This is just one of the stories still available for claiming...
Semantic Error #091 Title: Pairing/Characters: Choi Yuna/Ryu Jihye Rating: General | G Warnings/Tags: No Warnings apply Summary: Yuna is supposed to be living the good life. She landed a great job after college, and she's invited to the best parties. But as she gets to know Jihye -- who she only used to know as "that girl who liked Sangwoo" -- she realizes that there's way more to happiness than being cool.
And here are the links to the claims list and the form to claim fics:
#semantic error#choi yuna#ryu jihye#yuna x jihye#jihye x yuna#wip big bang#signal boost#looking for an artist
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mastering Web Development: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
In the vast landscape of technology, web development stands as a crucial cornerstone. It encompasses the art and science of building websites, ranging from simple static pages to complex web applications. Whether you're aiming to pursue a career in software development or seeking to enhance your digital presence, understanding web development is essential.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll take you through the fundamental concepts and practical skills needed to master web development from scratch. Let's dive in!
1. Understanding HTML (Hypertext Markup Language)
HTML serves as the backbone of every web page, providing the structure and content. It uses tags to define different elements such as headings, paragraphs, images, and links. By mastering HTML, you'll be able to create well-structured and semantically meaningful web documents.
2. Exploring CSS (Cascading Style Sheets)
CSS is the language used to style HTML elements, enhancing their appearance and layout. With CSS, you can customize colors, fonts, spacing, and more, giving your website a polished and professional look. Understanding CSS selectors and properties is essential for effective styling.
3. Introduction to JavaScript
JavaScript is a versatile programming language that adds interactivity and dynamic behavior to web pages. From simple animations to complex web applications, JavaScript powers a wide range of functionalities. Learning JavaScript fundamentals such as variables, functions, and events is crucial for web development.
4. Building Responsive Websites
In today's mobile-centric world, it's essential to create websites that adapt seamlessly to various screen sizes and devices. Responsive web design achieves this by using fluid grids, flexible images, and media queries. Mastering responsive design principles ensures that your websites look great on desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
5. Introduction to Version Control with Git
Git is a powerful tool for tracking changes in your codebase and collaborating with other developers. By learning Git basics such as branching, merging, and committing, you can streamline your development workflow and effectively manage project versions.
6. Introduction to Front-End Frameworks
Front-end frameworks like Bootstrap, Foundation, and Materialise provide pre-designed components and stylesheets to expedite web development. By leveraging these frameworks, you can create responsive and visually appealing websites with less effort and code.
7. Introduction to Back-End Development
While front-end development focuses on the user interface, back-end development deals with server-side logic and database management. Learning back-end languages such as Node.js, Python, or PHP enables you to build dynamic web applications and handle user interactions efficiently.
8. Deploying Your Website
Once you've developed your website, it's time to make it accessible to the world. Deploying a website involves selecting a web hosting provider, uploading your files, and configuring domain settings. Understanding the deployment process ensures that your website goes live smoothly.
9. Conclusion and Next Steps
Congratulations on completing this comprehensive guide to mastering web development! By now, you've gained a solid understanding of HTML, CSS, JavaScript, version control, frameworks, and deployment. As you continue your journey in web development, remember to stay curious, practice regularly, and explore advanced topics to further refine your skills.
Resources for Further Learning:
Online tutorials and documentation
Interactive coding platforms
Community forums and discussion groups
Next Steps:
Explore advanced topics such as web performance optimization, server-side rendering, and progressive web apps.
Build real-world projects to apply your skills and showcase your portfolio.
Stay updated with the latest trends and technologies in web development through blogs, podcasts, and conferences.
With dedication and perseverance, you'll continue to evolve as a proficient web developer, creating innovative solutions and contributing to the ever-changing digital landscape . Happy coding!
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding HTML: The Building Blocks of the Web
In the vast landscape of the internet, HTML stands as the foundation upon which the digital world is built. From simple static web pages to dynamic interactive experiences, HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) plays a pivotal role in shaping the online landscape. Let's embark on a journey to demystify HTML and understand its significance in the realm of web development.
What is HTML?
HTML is a markup language used to create the structure and content of web pages. It consists of a series of elements, or tags, that define the various components of a web page, such as headings, paragraphs, images, links, and more. These elements are enclosed within angled brackets (< >) and typically come in pairs, with an opening tag and a closing tag, sandwiching the content they define.
The Anatomy of HTML:
Tags: Tags are the building blocks of HTML and serve as the basic units of structure. They encapsulate content and provide semantic meaning to different parts of a web page. Common tags include <html>, <head>, <title>, <body>, <h1> (heading), <p> (paragraph), <img> (image), <a> (anchor/link), and many more.
Attributes: Tags can also contain attributes, which provide additional information about the element. Attributes are specified within the opening tag and consist of a name and a value. For example, the <img> tag may include attributes such as src (source) to specify the image file and alt (alternative text) for accessibility purposes.
Nesting: HTML elements can be nested within one another to create hierarchical structures. This nesting allows for the organization and hierarchy of content, such as placing lists within paragraphs or dividers within sections.
Document Structure: Every HTML document begins with a <!DOCTYPE> declaration, followed by an <html> element containing <head> and <body> sections. The <head> section typically contains metadata and links to external resources, while the <body> section contains the visible content of the web page.
The Role of HTML in Web Development:
HTML serves as the backbone of web development, providing the structure and semantics necessary for browsers to interpret and render web pages correctly. Combined with CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) for styling and JavaScript for interactivity, HTML forms the core technology stack of the World Wide Web.
Conclusion:
In essence, HTML is the language of the web, enabling the creation of rich and immersive digital experiences. Whether you're a seasoned web developer or a newcomer to the world of coding, understanding HTML is essential for navigating the intricacies of web development. Embrace the power of HTML, and embark on a journey to craft compelling narratives and experiences in the ever-evolving digital realm.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

Basic HTML Interview Questions
Following are the basic interview questions that you must know:
What is HTML?
What are Tags?
Do all HTML tags have an end tag?
What is formatting in HTML?
How many types of heading does an HTML contain?
How to create a hyperlink in HTML?
Which HTML tag is used to display the data in the tabular form?
What are some common lists that are used when designing a page?
What is the difference between HTML elements and tags?
What is semantic HTML?
#besttraininginstitute#online#onlinetraining#traininginstitute#training#education#tutorial#coding#programming#music#html#htmlinterviewquestions#htmlcode#html5#code#trending#technology#tech#engineering#software#development#softwaredevelopment#webdesigning#webdesign
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
How To Boost The Indexability Of A New Website 🔥
🔥 Skyrocket your website's indexability and conquer the search engine rankings! 🌟 Buckle up, folks, because I've got some insider secrets and juicy tips that'll turbocharge your site's visibility. Let's dive in! 💪
1️⃣ Speed is 🔑: Did you know that a slow website can make spiders crawl slo-mo? ⌛ Yup, search engines love speedy sites! Optimize loading times by compressing images, minifying CSS/JavaScript, and leveraging caching techniques. ⚡️ Slow websites ain't got no time for rankings!
2️⃣ XML Sitemaps for the Win 🗺️: A well-crafted XML sitemap is the magic 🔮 that helps search engines understand your website structure. Create and submit one to Google Search Console, Include all your pages, prioritize 'em, and watch as the bots scuttle through your content. 🕷️
3️⃣ Mobile-Friendly FTW 📱: it's a no-brainer to know that mobile searches surpasses desktop searches. Ensure your site is responsive and looks fab on all devices. Mobile-friendly sites win bonus points with the search bots and get blessed with better indexability. 🙌
4️⃣ Link Juice Matters 💪🧃: Internal linking is like a power-packed energy drink for your SEO efforts. 🥤 Pass that link juice around by interlinking your pages with relevant anchor texts. Search engines adore such connected websites, and it helps them find all your cool content.
5️⃣ Clear the Dead Ends ☠️: Broken links are like ghosts haunting your website. 👻 Sweep 'em away, my friend! Regularly audit your site for 404 errors and redirect 'em to relevant pages. Goodbye dead ends, hello smooth and indexable pathways! 🛠️
6️⃣ Hail the Hierarchy 🏰: A well-structured website hierarchy is a superhero cape for indexability. 🦸♂️ Use clear headings, subheadings, and semantic HTML to organize your content. It helps search engines understand the context better and boost your chances of claiming that top spot. 🥇
7️⃣ Snacks for Spiders 🍴🕷️: Meta tags bring all the spiders to the yard! Craft compelling meta titles and descriptions that entice users and search engines alike. Use relevant keywords, be concise, and ooze that click-worthy appeal. 🤩 Meta tags are the snacks search bots love to munch on!
⚠️ Hold up, folks! This is just a taste of the SEO buffet I've got for you. For a full-on feast of technical SEO expertise, check out my guide, "Unlock the Secrets of Technical SEO" 📚🔓. It's packed with even more insider info to supercharge your website's indexability and beyond! 🚀🎉
#SEO #TechnicalSEO #Indexability #SearchTraffic #WebOptimization #HustleHard #onpageseo #intetnallinks #internallinking #boosttraffic #organictraffic #freetraffic #searchengineoptimization #onpageoptimization #indexability #sitemaps #metatags #websitespeed #seomarketing #seosecrets #seostrategy #makemoneyonline #earnmoneyonline #workfromhome #homebusiness #onlinebusiness #onlinemarketing #internetmarketing #digitalmarketing #contentmarketing #digitalmarketer #affiliatemarketing
#make money online#work from home#affiliate marketing#make money with affiliate marketing#marketing#online business#home business#digital marketing#online marketing#blogger#on page seo#seo tutorial#seo services#seo#seo tips#socialmediamarketing#seo marketing#emailmarketing#on page optimization#technical seo
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
It is possible to employ AI in Search-Engine Optimisation. In my view, good semantic, accessible, validated HTML5 along with the correct meta tags go a very long way to optimising a website, with the goal of improving its ranking when searched for in a search engine such as Google’s. Web designers are very often lazy. Web Designers very often use div tags instead of the numerous semantic tags which proliferated when the HTML5 standard was released, in 2008–2014. “sema” in Greek means “sign”. Thus, “semantic tags” “signify stuff”, whereas div tags do not. Web designers very often do not add an alt description when including images. Very often web designers neglect to include ARIA attributes in their HTML code for the sake of screen-reading devices employed by the visually impaired. Very often web designers fail to validate their HTML. Very often web designers use CSS art instead of inline SVG. In my view, coding good HTML5 is a Search-Engine-Optimisation exercise all in itself.
#html#Google#web#webDesign#SEO#accessibility#code#AI#chatgpt#STEM#greek#classicsforstem#classics#coding#programming
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The semantic-html tag for this is <abbr>! Default AO3 styling will render it as a dashed underline so your readers know that there's a tooltip for that section of the text, and of course you can use workskins to modify its appearance as you see fit.
A Simple Trick for Fic Writers
Hey, if you're a fic writer and a character speaks in a different language, you don't just have to add the translation in the notes. Use the following HTML coding to add 'text on hover' to the word(s). If the reader is on a computer they can hover over the text to see the translation.
<div title="This is the text in the box!">This is the text that shows in your fic!</div>
Here are some examples from a fic on my AO3.
This coding here <div title="a fool, idiot (lit. emptyhead)">Eyn utreekov</div> will show this on hover.

This next example shows that you can add a lot of text. The formatting is the same as above.

PS: When doing this, there may be spacing issues, but you can edit the text through AO3's html or rich text editor. From there you can add italics (like I did), bold, etc, and fix any weird spacing issues. Just be careful not to delete the coding that you worked so hard on 😂
16K notes
·
View notes
Text
SEO-Ready Development: What Agencies Do from Day One
In today’s digital world, your website isn’t just your online storefront—it’s your gateway to organic traffic, leads, and long-term growth. And for that to happen, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) can’t be an afterthought. It needs to be built into the foundation of your website from day one.
That’s why a professional Web Development Company doesn’t just focus on clean code and visual design. They prioritize technical SEO during the development process, ensuring your site is fully optimized before it even goes live. This approach saves time, avoids costly rework, and sets your business up for better visibility from the start.
So what exactly does “SEO-ready development” mean? Let’s dive into what top agencies do right from day one.
1. SEO-Friendly Site Architecture
One of the first things agencies do is map out a logical, crawlable site structure. A well-planned architecture helps both users and search engines navigate your site with ease.
This includes:
Creating a clear hierarchy of pages (homepage > category > product)
Limiting click depth (no important page should be more than 3 clicks away)
Structuring URLs to be clean and keyword-relevant
Planning internal linking to distribute page authority effectively
When your site is structured well, Google bots can crawl and index your content more efficiently—and users can find what they need faster.
2. Clean, Crawlable Code
Web development teams ensure your site is built using clean, semantic HTML. This helps search engines understand your content and rank it appropriately.
Best practices include:
Using proper heading tags (<h1>, <h2>, etc.) to define content hierarchy
Avoiding excessive inline styles or JavaScript that hides content
Using alt tags for images and aria labels for accessibility
Structuring content with schema markup (more on that below)
Clean code reduces rendering issues, supports faster indexing, and improves accessibility—a key ranking factor in modern SEO.
3. Fast Load Times from Day One
Site speed is a critical ranking factor, especially on mobile. SEO-ready development means optimizing performance early—before launch.
Development teams use:
Minified CSS, JavaScript, and HTML
Lazy loading for images and videos
Optimized server configurations and CDN integration
Image compression and next-gen formats (WebP)
These improvements don’t just help SEO—they create better user experiences, reduce bounce rates, and improve conversion.
4. Mobile-First and Responsive Design
With Google’s mobile-first indexing, a mobile-optimized website isn’t optional—it’s essential. Agencies design with responsive frameworks that adapt content across screen sizes, ensuring consistent performance.
This includes:
Scalable typography and flexible grid layouts
Touch-friendly elements and simplified navigation
Responsive media queries and breakpoint testing
Your mobile site needs to be just as fast and user-friendly as your desktop version to maintain rankings and retain visitors.
5. SEO Metadata and Tags Implementation
From the earliest sprints, developers ensure that every page supports the proper:
Title tags
Meta descriptions
Canonical tags
Open Graph tags for social sharing
Robots meta tags for crawl control
These tags are essential for controlling how your site appears in search results and avoiding duplicate content issues.
6. Schema Markup and Structured Data
Structured data helps search engines understand your content in context. Development companies implement schema.org markup to qualify your site for rich snippets—such as:
Product details
FAQs
Reviews and ratings
Events or courses
These enhancements improve click-through rates and boost visibility on the SERP.
7. Optimized URL Structures
A good SEO strategy starts with user-friendly URLs. Agencies create URLs that are:
Short and readable
Contain target keywords
Use hyphens instead of underscores
Avoid unnecessary parameters or IDs
Example: ✅ yoursite.com/seo-services ❌ yoursite.com/index.php?id=123
Clean URLs make it easier for both users and search engines to understand what the page is about.
8. XML Sitemaps and Robots.txt Configuration
At launch, development teams generate and submit a comprehensive XML sitemap to help search engines find and index all your pages. They also configure a robots.txt file to control crawler access and prevent indexing of irrelevant or sensitive areas like admin dashboards or cart pages.
9. Analytics and Tracking Setup
Finally, SEO-ready development includes installing:
Google Analytics
Google Search Console
Tag management tools (like GTM)
Event tracking for key conversions
This ensures your marketing team has the data they need to track organic performance and optimize future content.
Conclusion
An SEO-friendly website isn’t something that happens after launch—it’s something that’s built from the ground up. From architecture and performance to metadata, schema, and mobile design, every decision made during development can either boost or block your visibility in search results.
That’s why partnering with a Web Development Company that understands technical SEO is crucial. When SEO is integrated into every layer of your site from day one, you don’t just launch—you rank, engage, and grow.
0 notes