#american unitarian
Text
Thanks to a wonderful outside donation, the utilities bill has been paid!!! Now we just have the car bill which is due by the end of the month, and the car insurance which we would like to pay ASAP. We are hoping to get enough donations to cover those two expenses ($557 together) so that our paychecks can go straight to rent (which is $1420). Our hope is that once this month passes, as long as we are caught up on all bills by the time the month is done, we can move on to allowing this gofundme to go mostly to the debt! Thank you all who have donated, and keep us in your hearts. Here's hoping.
#gofundme#please donate#if you can#transgender#queer#unitarian universalism#the local UU church has been the majority of the help#im so glad we joined#but we cant keep going if theyre the only ones donating#give until it feels good#rent help#donation post#american capitalism
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
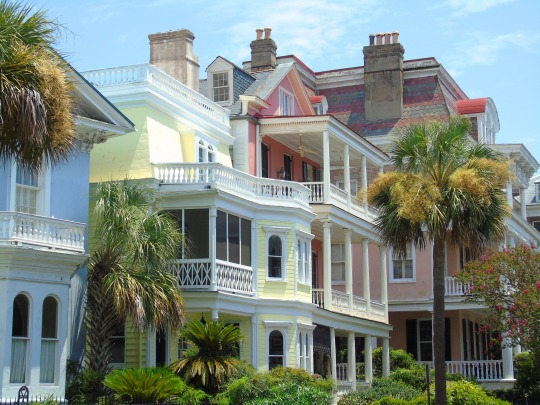
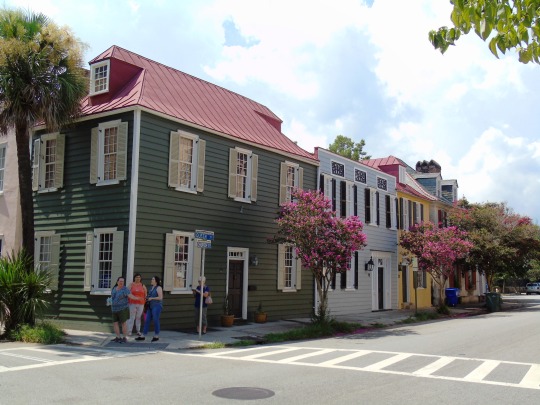
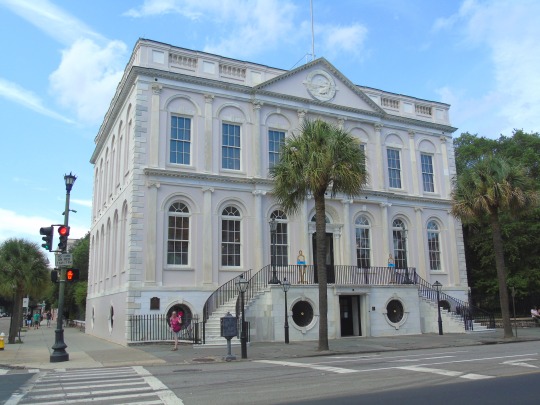
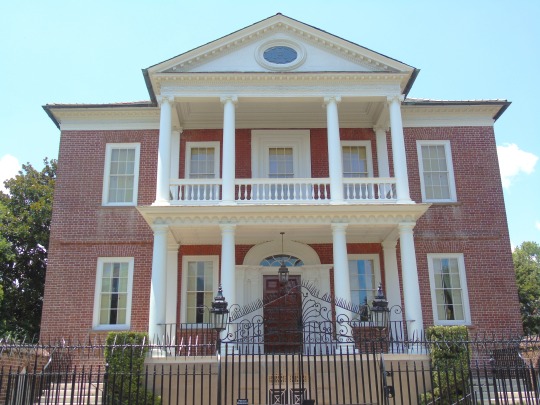
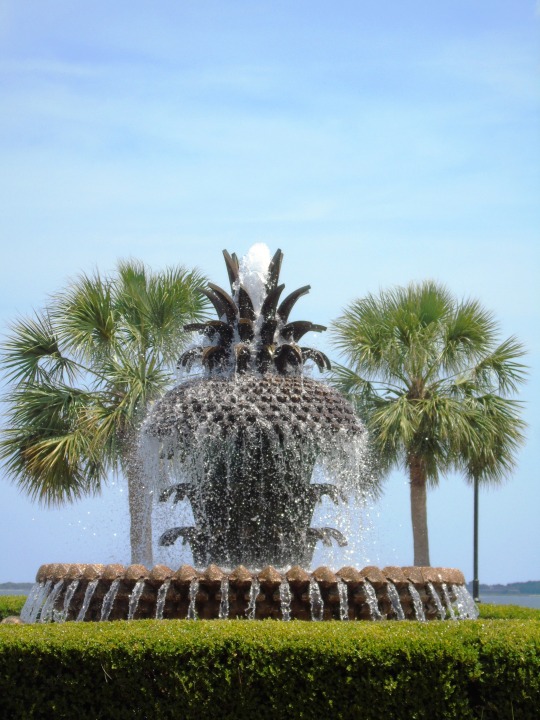
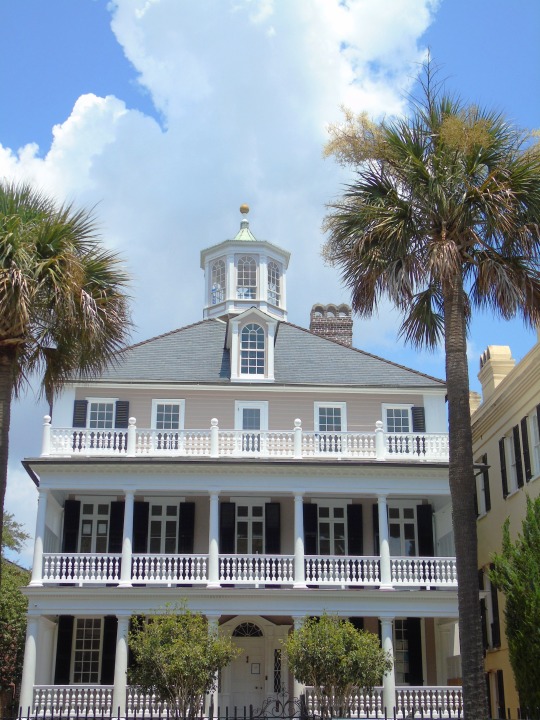
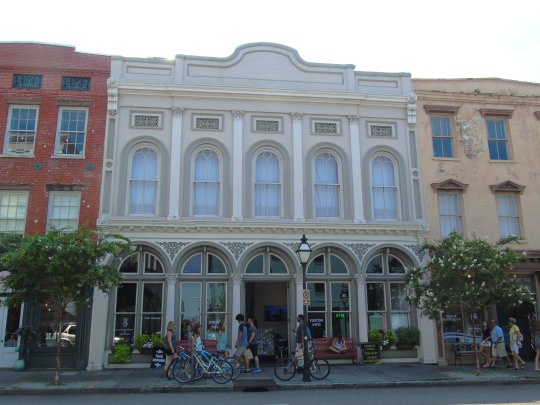
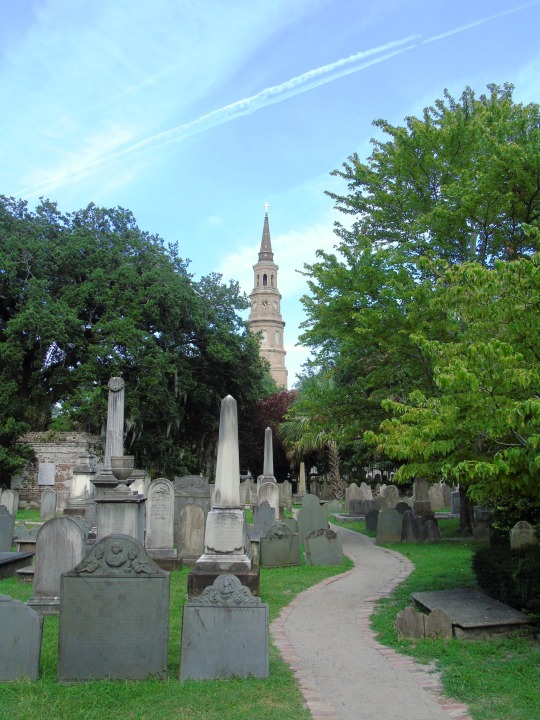
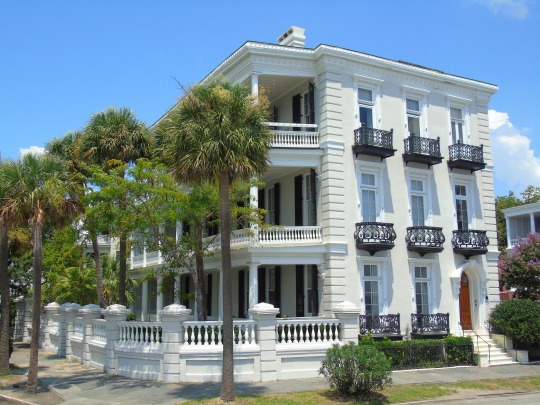
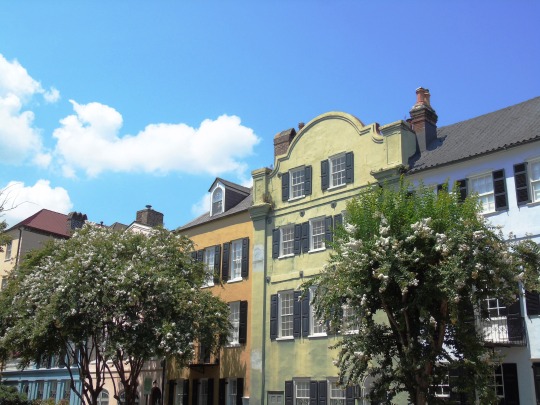
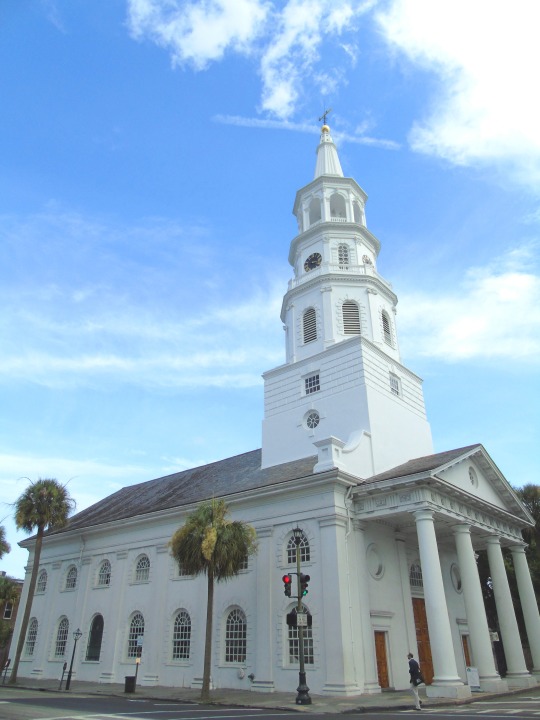
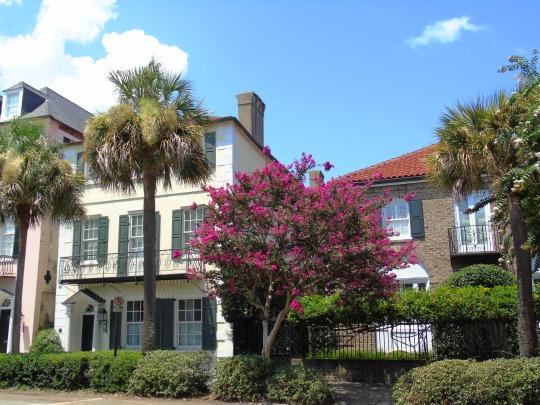
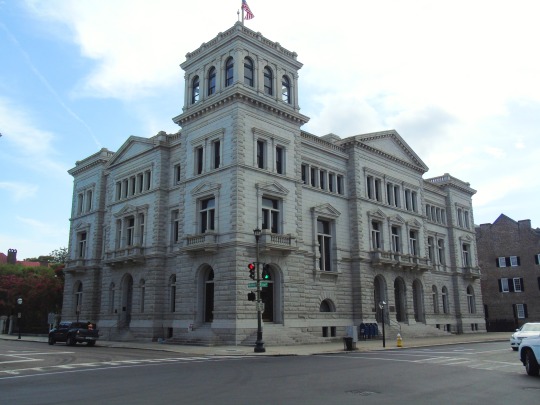
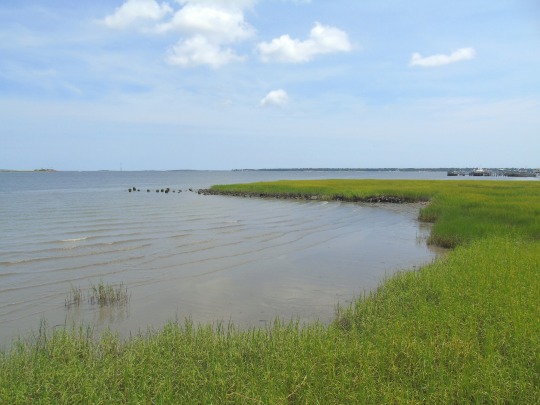
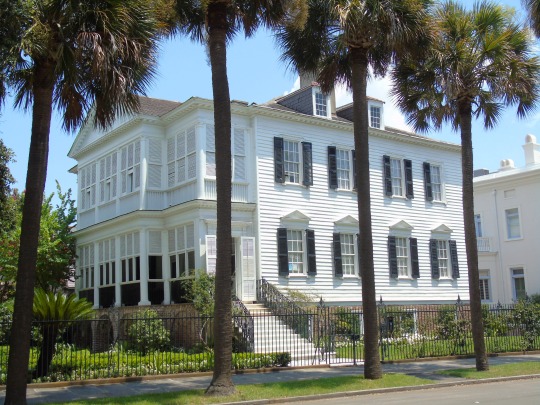
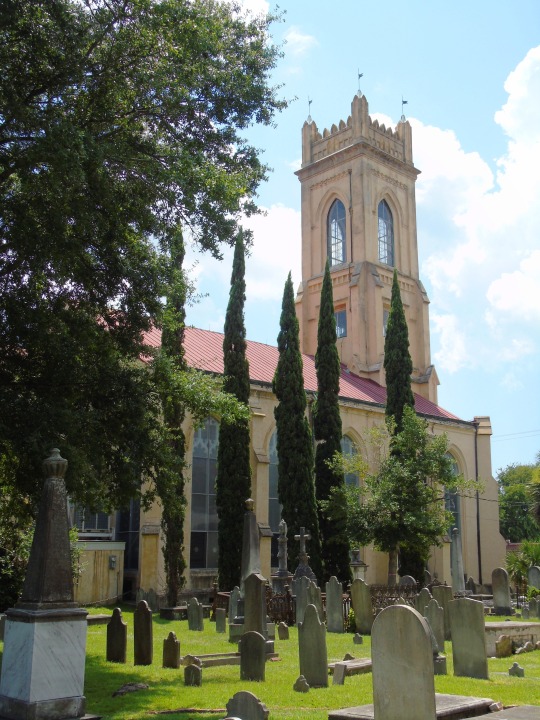
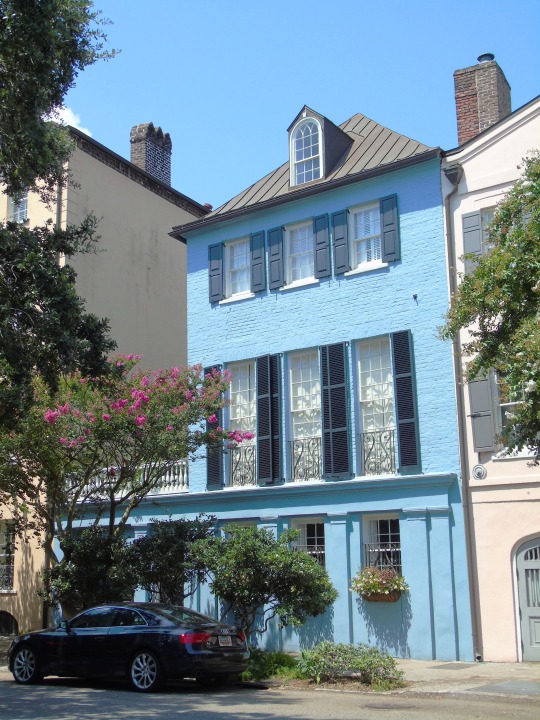
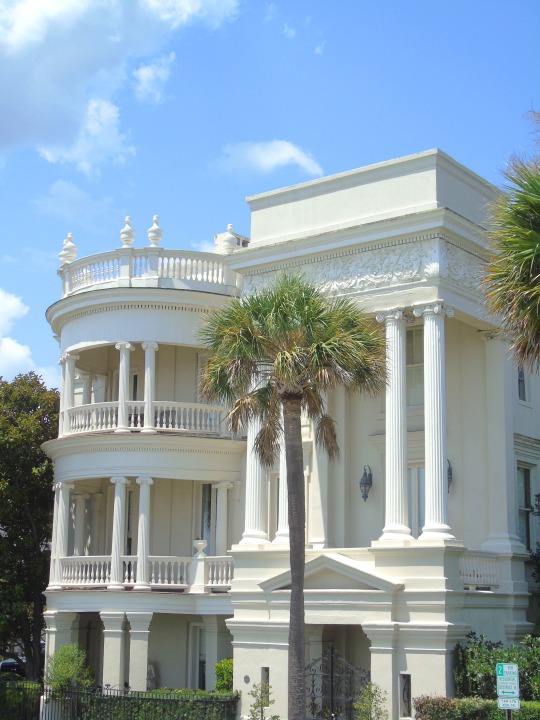
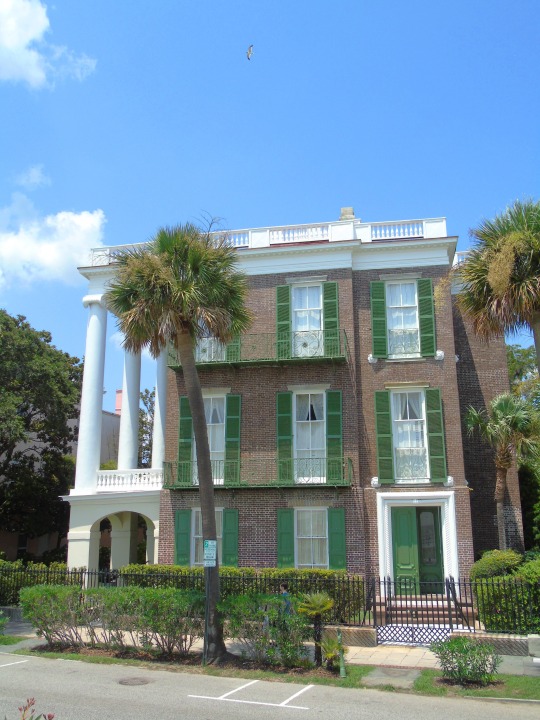
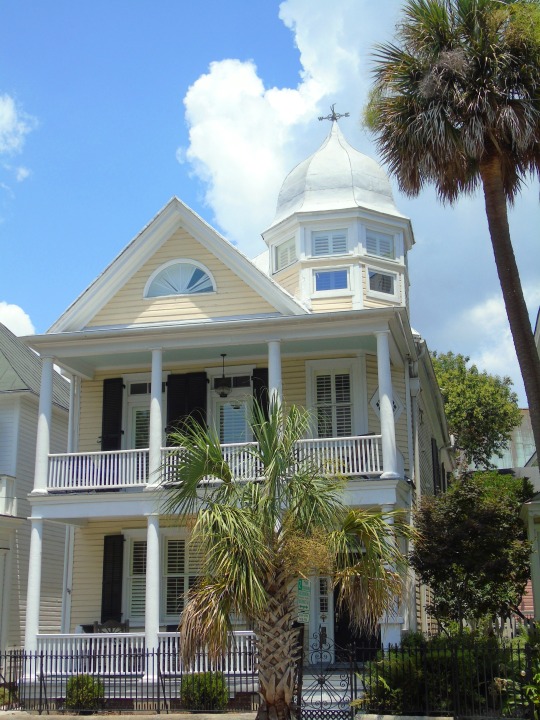
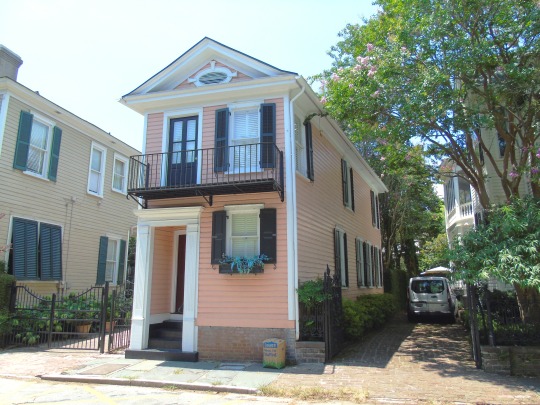
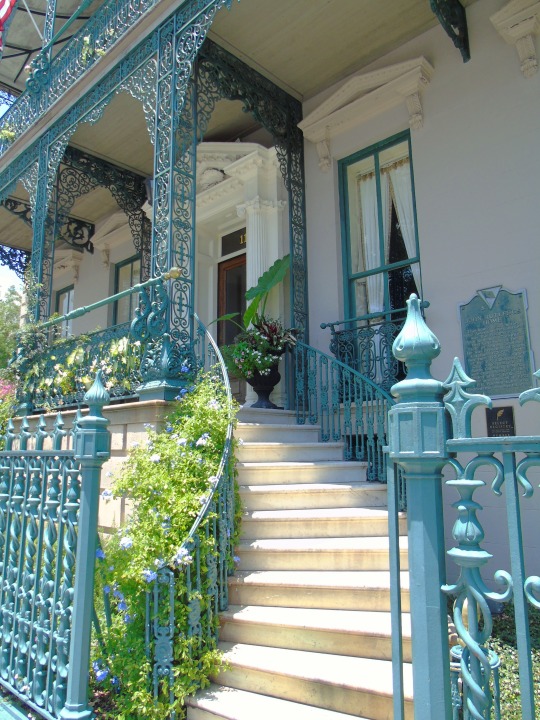
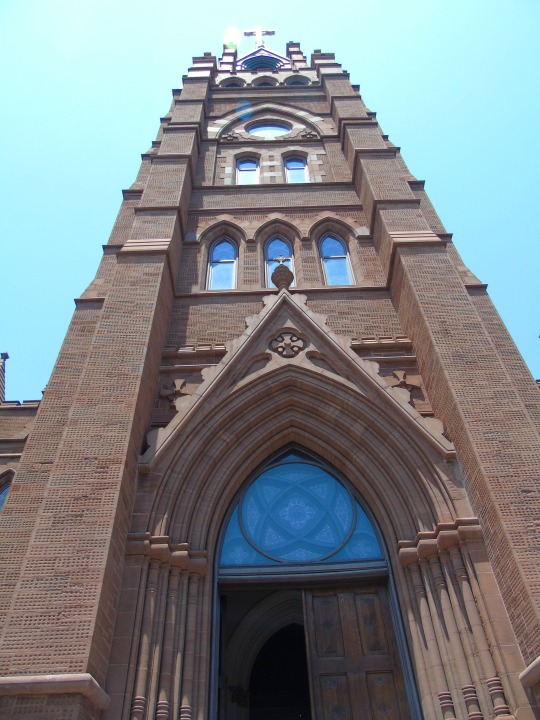

























Charleston surrendered on February 18, 1865.
#18 February 1865#Charleston#surrendered#anniversary#USA#city hall#architecture#US Civil War#American Civil War#US history#travel#summer 2016#original photography#South Carolina#tourist attraction#St. Philips Church Episcopal West Cemetery#Unitarian Church#landmark#Louis DeSaussure House#Cathedral of St John the Baptist#Miles Brewton House#Cooper River#nature#water#reed#vacation#cityscape
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
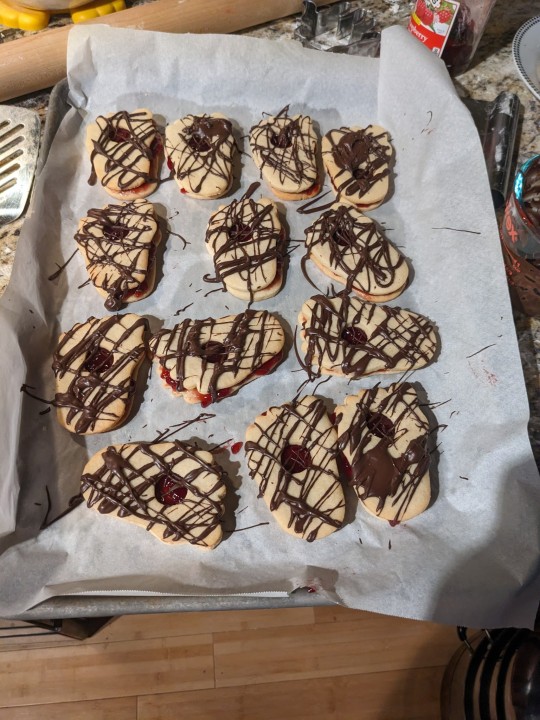
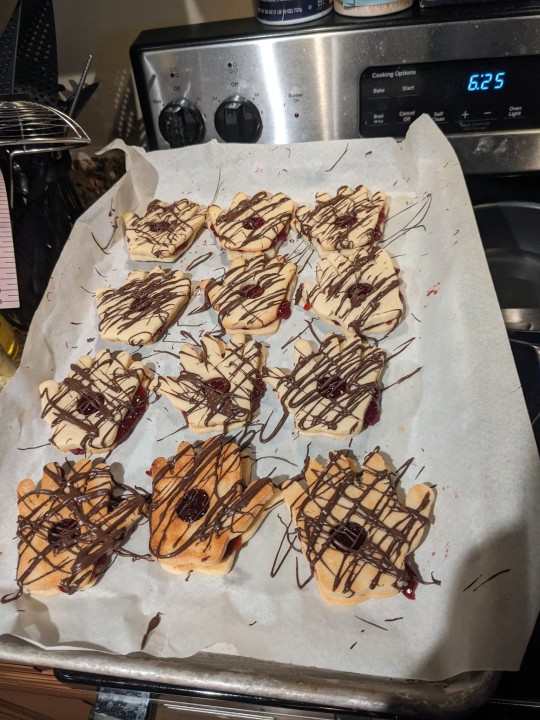


when the catholics eat the body of christ it's fine but when i bring stigmata cookies to easter dinner it's weird?
#is this offensive to christians#to be fair i think my partner's family are protestants and not the eucharist kind#and i don't think they understood the reference#not sure how#they're the like....ambiguous american christian type#which ends up being super regional in my experience#like my hometown most were presbyterian or episcopalian#then elsewhere they were like...majorly lutheran or unitarian or congregationalist#then there's my friend who is like....fundamentalist non denominational which seems like a weird cult denomination#i tell him this and he laughs and says yeah I'm keeping an eye on it which is why we're still friends#hey ct is this anything#cryptotheism#stigmata#cookies#baking#it me#easter
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Christopher Mathias at HuffPost:
A coalition of 185 social justice and religious groups published an open letter Monday expressing support for the campus protest encampments sweeping the country in opposition to Israel’s siege of Gaza, and calling on university administrators to end the brutal crackdowns of the student-led demonstrations.
“We commend the students who are exercising their right to protest peacefully despite an overwhelming atmosphere of pressure, intimidation and retaliation, to raise awareness about Israel’s assault on Gaza — with U.S. weapons and funding,” the letter states. “These students have come forth with clear demands that their universities divest from corporations profiting from Israeli occupation, and demanding safe environments for Palestinians across their campuses. ”
Groups that signed the letter include Gen-Z for Change, Working Families Party, IfNotNow Movement, Young Democrats of America Black Caucus, Movement for Black Lives, Sunrise Movement, MPower Change, Jewish Voice for Peace, Palestine Legal, and the Unitarian Universalist Association.
Some 900 students have been arrested during anti-war encampments and demonstrations at American universities in the last 10 days, per a tally from Al Jazeera — a tumultuous period that mirrors volatile demonstrations against the Vietnam War in 1968, when police arrested at least 700 students.
The open letter Monday represents one of the largest shows of support among progressive groups for the burgeoning student protests, and makes clear the divide between establishment Democratic figures and social justice groups when it comes to U.S. support for Israel. President Joe Biden has refused so far to condition the sale of weapons to Israel.
“Our communities have been horrified to see the militarized and violent response to students protesting an ongoing genocide funded and supported by our government, and our coalition of organizations join millions of our members across the country in standing in solidarity with the students’ efforts in support of the people of Gaza,” Yasmine Taeb, one of the main organizers of the letter, told HuffPost. Taeb is a human rights lawyer and political director at MPower Change, a Muslim social justice group.
“Instead of attacking young people mobilizing for Palestinian human rights, President Biden needs to listen to the majority of Americans who have been calling on him to stop funding and supporting the atrocities committed against the people of Gaza,” Taeb said.
[...]
Israel has killed over 33,000 Palestinians since Oct. 7, when the Gaza-based militant group Hamas launched an attack in which nearly 1,200 Israelis were killed. In January, the International Court of Justice ruled that Israel’s siege of Gaza — which has displaced 85% of the population and put the occupied territory on the cusp of famine — left Palestinians at risk of experiencing a genocide. Last week, health officials in Gaza said medics had discovered mass graves at hospitals raided by Israeli troops.
“We join [the students] in calling for an immediate and lasting ceasefire and an end to the U.S. government’s and institutions’ role in the ongoing genocide of Palestinians in Gaza,” Monday’s letter states.
“As we stand in solidarity with the students protesting in encampments across the country, we reaffirm our commitment to amplifying their voices, condemn the university administration officials’ violent response to their activism, and demand that universities remove the presence of police and other militarized forces from their campuses,” it continues.
[...]
Meanwhile, Republican Party officials and right-wing media figures have accused the demonstrations of antisemitism, falsely equating criticism of Israel with bigotry towards Jews. Although there have been scattered reports of actual antisemitic incidents at or near the encampments, many were not perpetrated by students but by interlopers. Many of the student protesters across the country are Jewish.
Far-right agitators, including Christian nationalist activists, have also targeted the encampments, with MAGA pastor Sean Feucht leading hundreds of Christian and Jewish Zionists on a march around the Columbia campus on Thursday. The rally ended with pro-Israel demonstrators yelling through the gate at pro-Palestinian Columbia students. “Go back to Gaza!” they screamed.
More than 185 groups, including IfNotNow, Jewish Voice For Peace, MPower Change, and Working Families Party, signed a letter in support of the campus protests against Israel Apartheid State's genocide against Palestinians in Gaza.
#Gaza Genocide#Israel Apartheid#Israel/Hamas War#Ceasefire NOW Protests#Protests#Columbia University#Israel Apartheid State#Palestine#Gaza#IfNotNow#Jewish Voice For Peace#MPower Change#Working Families Party#Sunrise Movement#Gen Z For Change#Campus Protests
748 notes
·
View notes
Text
I decided to make this its own post for two reasons: one, I didn't want to derail a post that is about Judaism with a discussion of a different faith and two, it was really only one of several posts I've seen recently that stuck out to me as being "man, this is way off-base."
This is not so much about "people are saying mean things about this religion and it hurts my feelings!" but it is definitely about "people are making statements that represent a wildly skewed and inaccurate picture of the reality, and I can't tell whether they're being hyperbolic on purpose or think they're genuinely telling the truth." This is not a question of whether any given church is good or bad; this is a question of whether there is or can be a distinct entity that serves as a single unified church or faith in American Christian tradition (spoiler: No.)
Here's the basic message: Any discussion of "the Christian god" or "the Christian faith" or "American Christianity" needs to be taken with a big honking asterisk that there is no single portrayal of God, or Christianity, or spirituality and faith that conveys accurate information about the entire breadth of American Christianity.
There is no single American Christian Church. None. The single biggest branch of American Christianity, Southern Evangelical Baptist, makes up at its broadest 30% of all American Christians (12% of the overall population.) The rest are split between Catholic, Methodist, Episcopalian, Presbyterian, Lutheran, Pentecostal, Adventist, Congregationalist, and a dozen other even tinier branches, before you even get into the more far-out variants that people have ongoing arguments as to whether they even really count as "Christian." (LDS, Unitarians, and possibly Mennonites fall into this category.) Most of the major branches share a lot of common ground, but there's an enormous amount of variation -- they disagree widely on concepts such as the existence or nonexistence of Hell; the mechanics of conversion or salvation; the requirements of baptism or confirmation; whether prostylezation is required, encouraged or even permitted; what kind of sexualities are or are not accepted; God as an active or non-active role in the world; how 'sin' works or if it's even a thing; the existence or not of saints; the divinity or not of Christ; or even the idea of an anthropomorphic God at all. Some are progressive, some are fundamentalist, some are fundamentalist in ways that are completely at odds with the popular perception of what those fundaments are. I personally know one Methodist pastor who also believes and teaches about God as a "oneness of the universe" and have met others who conceive of God as "that which spans the space between the limits of our understanding and the limits of our universe." You cannot categorically state that all American Christians share a common notion on any of these topics.
Other statements I've seen recently that just made me go "what? no?"
That the USA was founded by religious extremists and That's Why America is Like That. Only one or two of the original settlements were founded for this purpose. Some were founded with an explicit purpose of total freedom of (or from) religion; others were entrepreneurial ventures with nothing to say on the topic of religion at all. When the guiding documents of the American state were put together the clause of freedom of religion was included front and center precisely because they didn't want religious extremists to be steering the ship.
That the majority of USAmericans are in cults and don't even realize they're in cults. This requires both an extremely broad definition of “cult” (to encompass pretty much any branch of Christianity, not only the more extremely evangelical ones) and severely over-estimates how many people in the US are practicing Christians (less than half.)
That the "Christian God" is intended to function as a "Great Uniter" into which other faiths can be folded; This is not a Protestant thing. Most Protestant faiths are not syncretic to the degree Catholicism is (or at all,) since there wasn't a motivating political entity backing their creeds to make them so. Again: Not all branches of American Protestantism require, encourage, or even permit prostylezation.
On that note: Not all Christians are Catholic. This isn't news, right? People know this, right? This is one of those things that I always assumed was very common knowledge, and was very surprised to run into people who were not aware of this (who either think that all Christians or Catholic, or else that Catholics are not Christian at all, depending on which side of the equation they're approaching from.) Protestant and Catholic Christianity are very very distinct entities both spiritually and politically, and in the USA, Catholic Christianity is a minority religion and is mostly (though not exclusively) practiced in minority demographic communities. Of 46 presidents so far only one has been Catholic, and a lot of the opposition to JFK's appointment was people being suspicious of his Catholicism since it was thought that his loyalty to the Church might supersede his loyalty to the US. American Christianity is mostly Protestant, not Catholic, and Protestant Christianity does not function at all the way Catholicism does. We had a whole Reformation about this. Any take that refers to "The Church" in America as a single united entity that dictates theology to its outreaching branches is... off-base.
What certainly is true is that a number of individual churches in the US have organized around the aim of consolidating social and political power, have worked at advancing their members to positions of power in order to protect and promote their interests, and thus are over-represented and have outsized influence on the political sphere. The ones that do this, as well as the ones that put emphasis on proselytizing and on money-making, tend to self-select for being the most visible and infamous because their business model is expansive by nature. That's certainly the case for the SEB in the American South, or the LDS in Utah. I really get the feeling when people use these broad terms that they are thinking either of the SEB (again, not even a majority among American Protestants!) or of the Catholic church (even less so!) But not only do not all Americans agree with those beliefs, they don't even agree with each other.
1K notes
·
View notes
Photo

Henry David Thoreau
Henry David Thoreau (1817-1862) was an American philosopher, writer, naturalist, and political activist. He is best known for his book Walden, published in 1854, which recounts his two-year experiment living alone in a small cottage at Walden Pond two miles outside Concord, Massachusetts, and his essay On the Duty of Civil Disobedience written in 1849 shortly after his release from a Concord jail for non-payment of a poll tax.
Early Life & Transcendentalism
Thoreau was born in Concord, Massachusetts, on 12 July 1817. He studied at Harvard College and his worldview was shaped by transcendentalism, a belief in the divinity of human nature, which was not a coherent philosophy but an attitude or state of mind that inspired many American intellectuals who flourished between 1820 and 1860. The movement's foremost representative, Ralph Waldo Emerson (1803-1882) had given the Phi Beta Kappa commencement address at Harvard with Thoreau in attendance. Other notable transcendentalists were Margaret Fuller, Louisa May Alcott, Walt Whitman, and Bronson Alcott. They were young Americans who had been born into the Unitarianism of New England. According to Perry Miller in his American Transcendentalists, they responded to the new literature of England and the continent "revolting" against the rationalism of Harvard College. Although Protestant, they turned against the Protestant ethic, choosing instead to cultivate the arts of leisure to avoid making money. To some, it was intense individualism, but to others, it was sympathy for the poor and oppressed. Morris wrote: "…the self-reliance and self-determination exalted by the transcendentalists gave to American writers a freedom that vitalized the first period of national letters." (600)
Thoreau graduated in 1837 without distinction and returned to Concord; he viewed Concord as a microcosm of the world. Instead of seeking employment like his fellow graduates, he chose instead to become an observer and interpreter, a "thinker of thoughts, a student of nature and of literature – half-scientist and half-poet" (Mead, 112) He tried teaching for a while and even land surveying. In Walden he wrote, "I did not teach for the good of my fellow man but simply for a livelihood, this was a failure" (65). He even worked for a time in his family's pencil factory. An occasional odd job provided him with enough money to be clothed and fed. He became friends with Emerson, who took him into his home (1841-43) and offered him advice on the craft of poetry and writing. Thoreau moved briefly to New York, living with Emerson's brother, to try to sell some of his essays and poems, but he was unsuccessful.
Continue reading...
38 notes
·
View notes
Note
i’ve been feeling compelled to plan a protest for Palestine in my small texas hometown. i haven’t made any posts about it yet, but i’m anxious about being the only one to show up. there have been protests in my town before in the same area and people had nasty reactions. do you have any advice for doing something like this solo?
You shouldn't do a thing like this solo. You should partner with local groups like Students for Justice in Palestine (check all your local college/university campuses), the US Palestinian Community Network, American Muslims for Palestine, various anti-racist and abolitionist groups within your community, other leftist organizing groups (but NOT the PSL or RCP), etc.
If your town is tiny tiny and not plugged into the existing infrastructure for these groups, you should still reach out to them and see how these orgs would prefer for engaged comrades to make a positive impact. They might have strong reasons to prefer that you invest your energy into another activity. Our energies should be coordinated and strategic here, and we should take our lead from the movement leaders who have been doing this work for decades and have the existing connections and know-how.
If these groups are supportive of the idea of you holding a protest but cannot offer the resources to support it, then you want to tap into local groups that might be able to generate a turnout: your local Mosques and Islamic community centers, Unitarian Universalist Churches, Society of Friends groups, pro-Palestinian Jewish groups, etc.
You want to make sure you are including the Palestinian liberation community directly in all things that you are doing here, and handing off the mic to them, if you are not Palestinian, or do not have extensive experience doing this work.
If there aren't large enough numbers of folks with close ties to this kind of activist work within your community, you can still make a big showing of solidarity with a small symbolic protest, but you want to exhaust all other options first, because it is far more useful for you to get organized alongside other people who have been doing this work than to launch an event yourself that potentially no one might go to. It might very well be the case that you have a lot more growing in your connections and activist experience that you need to do first and as your primary act of service to the cause at this time.
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
Revs. Jan Barnes and Krista Taves have logged hundreds of hours standing outside abortion clinics across Missouri and Illinois, going back to the mid-1980s. But unlike other clergy members around the country, they never pleaded with patients to turn back.
The sight of the two women in clerical collars holding up messages of love and support for people terminating a pregnancy “so infuriated the anti-abortion protesters that they would heap abuse on us and it drew the abuse away from the women,” recalled Taves, a minister at Eliot Unitarian Chapel in Kirkwood, Missouri, as she sat on a couch at Barnes’ stately church in this quiet suburb of St. Louis.
“I thought: ‘Whoa, these people really are not messing around.’ But then I thought, ‘Well, I’m not messing around either.’”
So when Missouri’s abortion ban took effect after the Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade last year, Barnes and Taves decided to fight back. Along with rabbis and ministers across several denominations, they joined a first-of-its-kind lawsuit arguing Missouri blurred the line between church and state, imposed a particular Christian idea of when life begins over the beliefs of other denominations, and threatened their ability to practice their religions.
As the nation nears the one year anniversary of the fall of Roe, the Missouri case is one of nearly a dozen challenges to abortion restrictions filed by clergy members and practitioners of everything from Judaism to Satanism that are now making their way through state and federal courts — a strategy that aims to restore access to the procedure and chip away at the assumption that all religious people oppose abortion.
In fact, many of the lawsuits are wielding religious protection laws enacted by anti-abortion state officials to target those officials’ own restrictions on the procedure.
In Indiana, a group of Jewish, Muslim and other religious plaintiffs sued over the state’s near-total abortion ban. Their argument: that it violates the Religious Freedom Restoration Act signed into law in 2015 by then-Gov. Mike Pence. A lower court judge sided with them in December and blocked the state’s ban from taking effect — the most significant win the religious challengers have notched so far.
Then, earlier this month, the Indiana judge granted the challengers class action status, meaning a win for them could apply to anyone in the state whose religion supports abortion access in cases prohibited by state law.
“Even if the Religious Freedom law was intended by Mike Pence to discriminate against people, we thought: ‘Let’s use this for good instead,’” said Amalia Shifriss, a leader of Hoosier Jews for Choice, one of the Indiana plaintiffs. “It brings me joy to think how much this must upset him.”
A Pence spokesperson characterized the lawsuit as a “pursuit to legalize abortion up to and even after birth.” They added: “It will probably strike Americans as pretty tasteless to call the latest iteration of their abortion crusade as a cause ‘for good’ and a source of ‘joy.’”
Conservatives with a history of mounting their own religious challenges to state laws dismiss the effort as doomed to fail, arguing that even if people can prove the abortion bans violate their beliefs, it won’t be enough to halt enforcement.
“As Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg explained in one Free Exercise case, the right to swing your arm ends just where the other man’s nose begins,” said Denise Harle, senior counsel with Alliance Defending Freedom, a conservative legal group that has filed briefs defending state abortion restrictions, including from faith-based challenges in Wyoming and Florida. “Even if you have religious freedom, there is a line at which you are doing actual deadly harm and destroying human life, so it’s appropriate to limit what can be done in the name of religion.”
But with oral arguments and rulings in several of the cases expected this summer and fall, other legal experts say there’s a solid chance the challengers can persuade courts to grant religious exemptions to abortion bans if not strike them down altogether.
Shlomo C. Pill, a lecturer at the Emory University School of Law who specializes in religious rights, said the lawsuits have “a strong basis and should be successful,” particularly after a series of COVID-19-related cases paved the way for more religious exemptions. Pill pointed to multiple Supreme Court decisions during the pandemic that said whenever states create secular exemptions to laws — like indoor gathering restrictions or vaccine mandates — they have to justify not offering religious exemptions as well.
“So the fact that secularly-motivated exemptions to abortion bans exist — such as for rape and incest — means the legislature could also have to offer similar exemptions for people with religious objections,” he said.
‘REAL CHUTZPA’
Most of the cases, including those in Indiana, Kentucky, and Texas, are demanding exemptions from the bans for people whose religions support abortion rights. But a few, including the lawsuits in Florida, Missouri and Wyoming, are attempting to have the bans struck down entirely.
In Missouri, the plaintiffs argue that because lawmakers put religious language in the text of the abortion ban itself and made explicit religious appeals when voting on it, they violated the Establishment Clause.
“It took real chutzpah for the legislators to voice their own religious motivations, to wantonly and shamelessly purport to know what God wants or doesn’t want and to enshrine that into law,” said Rabbi James Bennett of Congregation Shaare Emeth in St. Louis, another plaintiff in the Missouri lawsuit. “They’re entitled to their interpretation of when life begins, but they’re not entitled to have the exclusive one.”
Last week, the group faced off in a St. Louis courtroom with state officials who are pushing to have the case thrown out. A ruling could come as soon as this summer.
In Florida, clergy representing Reform Judaism, Buddhism, the Episcopal Church, the United Church of Christ and the Unitarian Universalist Church sued in state court both to overturn the state’s 15-week abortion ban, and — if that fails — to secure religious exemptions. Their case makes free speech arguments as well — claiming that state bans on “aiding and abetting” abortions are muzzling clergy members who want to offer counseling to parishioners grappling with whether to terminate a pregnancy.
In Kentucky, three Jewish women are arguing that the state’s near-total abortion ban violates their belief that life only begins when a baby takes its first breath, saying it’s preventing them from pursuing pregnancy through in-vitro fertilization.
“To have someone else’s religious belief that an embryo is a human being imposed on me in a way that’s so personal, that prevents me from growing my family, is just rude and un-American,” Lisa Berlow, the lead plaintiff in that case, said in an interview. Berlow had one child through IVF and was planning to have another before Dobbs made her and her fellow plaintiffs fear prosecution. “Discarding non-viable embryos could now be criminalized, or I could miscarry and not know what type of medical care I would get or whether I would be investigated for causing the miscarriage,” she said.
The Satanic Temple is in federal court challenging abortion bans in Texas, Idaho and Indiana, arguing that the laws infringe upon their congregants’ belief in bodily autonomy and right to practice abortion as a religious ritual. A Texas District Court ruled against the Satanists last fall, saying they didn’t prove the need for a temporary restraining order blocking enforcement of the ban against its members. The 5th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals is poised to rule on the challenge in the coming weeks.
These cases are unlikely to restore abortion rights at the federal level given the weaker religious rights protections in the U.S. Constitution compared to many state constitutions as well as the federal judiciary’s rightward tilt.
Elizabeth Reiner Platt, director of the Law, Rights, and Religion Project at Columbia Law School, stressed that the Supreme Court has a record of protecting the religious rights of some groups and not others, pointing to its back-to-back decisions in 2017 upholding the right of a Christian baker to refuse to bake a cake for a same-sex wedding and allowing the right of the Trump administration to deny entry to travelers from majority-Muslim countries.
“While I don’t like to read the tea leaves, I don’t have any hope that the current Supreme Court would, after ruling that there was no due process right or privacy right to abortion, would find a right under the Free Exercise Clause or the Establishment Clause,” Platt said.
Still, she and other legal experts see the state-level religious challenges as one of the best chances abortion-rights advocates have to chip away at bans on the procedure.
“The arguments are quite powerful for creating religious exemptions in the reproductive context under First Amendment doctrine and under state laws for Free Exercise,” said Micah Schwartzman, director of the Karsh Center for Law and Democracy at the University of Virginia Law School. “What Judges do with them is another story.”
In order to succeed, these lawsuits must prove: that the right to an abortion is central to the religious practices of the people suing; that they are sincere in their beliefs and have a track record of observing them; and that state abortion bans make it impossible for them to live according to their faith.
The cases challenging abortion restrictions in their entirety face an additional hurdle: proving that state officials stepped over the line separating church and state in crafting the bans.
“We have a really strong Establishment Clause argument because it’s clear that these bills were passed for religious reasons,” said Marci Hamilton, a professor of constitutional law at the University of Pennsylvania who is part of the legal team representing clergy in Florida. “The 15-week bill was signed in a church and members of the state legislature repeatedly referred to God when arguing why this had to be done.”
Other experts are skeptical, however, of the strength of these arguments.
“There are a million-and-one other explanations a state could give for their abortion restrictions,” Pill said. “They could argue it’s a matter of secular conscience, for example. And once you have any kind of secular justification, an Establishment Clause argument becomes more difficult.”
For their part, the states defending their abortion laws and the conservative legal groups supporting them have to prove that they have a compelling interest — unrelated to religion — in protecting fetal life, that they’re using the least restrictive means to protect that interest, and that the challengers’ claims are speculative and premature because none of them have actually sought an abortion or been blocked from obtaining one since the laws took effect.
“I think these are much more like political stunts than they are viable court cases,” said Lori Windham, a vice president and senior counsel at the Becket Fund, the legal firm behind the Hobby Lobby case that secured a Supreme Court ruling allowing many employers to opt out of covering certain forms of birth control for their workers due to a religious objection. “You can have a sincere political belief or policy preference, and it can be passionate and deeply held, but that doesn’t make it a religious practice.”
CITING SCRIPTURE
Judges have historically avoided questioning the sincerity of someone’s religious beliefs, but Becket and other groups have filed amicus briefs that do so.
To combat these accusations, the challengers point to scripture that lays out a case for abortion rights as well as support from religious leaders for their claims.
The Jewish challengers in Kentucky cite religious texts including the Mishnah that say life begins when a baby takes its first breath, not when it is conceived, and if medical issues arise during pregnancy, the pregnant person’s life “comes before the life of [the child].” They also submitted to the court letters from rabbis arguing that current state exemptions for life-threatening medical emergencies aren’t enough, saying Jewish law permits, and in some cases requires, an abortion when there is “a risk of poverty, abuse, addiction, or mental illness.”
The case challenging Missouri’s ban cites the United Church of Christ’s vote in 1971 to acknowledge the right to abortion and members’ “autonomy to determine what happens to their own bodies,” as well as the Episcopal Church’s “long-standing opposition” to any government attempt to infringe on reproductive choices.
“There’s a tendency to see these cases as kind of a clever, legal switcheroo. Like, here’s a way to take these laws that are often thought of as very conservative and use them to protect abortion rights,” Platt said. “But the idea of reproductive rights as a religious liberty issue is absolutely not something that came from lawyers. It’s how faith communities themselves have been talking about their approach to reproductive rights for literally decades.”
#us politics#news#politico#2023#abortions#abortion bans#reproductive rights#reproductive health#Missouri#Indiana#Religious Freedom Restoration Act#mike pence#Hoosier Jews for Choice#Alliance Defending Freedom#free exercise clause#religious exemptions#Kentucky#Texas#Florida#Wyoming#Establishment Clause#us constitution#in-vitro fertilization#Judaism#Episcopal Church#United Church of Christ#Unitarian Universalist Church#organized religion#religious freedom#the satanic temple
100 notes
·
View notes
Audio
Truly He taught us to love one another
His law is love and His gospel is peace
Chains he shall break, for the slave is our brother
And in his name all oppression shall cease
Sweet hymns of joy in grateful chorus raise we
With all our hearts we praise His holy name
Christ is the Lord! Then ever, ever praise we
His power and glory ever more proclaim!
“Since that first rendition at a small Christmas mass in 1847, "O Holy Night" has been sung millions of times in churches in every corner of the world. And since the moment a handful of people first heard it played over the radio, the carol has gone on to become one of the entertainment industry's most recorded and played spiritual songs. This incredible work--requested by a forgotten parish priest, written by a poet who would later split from the church, given soaring music by a Jewish composer, and brought to Americans to serve as much as a tool to spotlight the sinful nature of slavery as tell the story of the birth of a Savior--has become one of the most beautiful, inspired pieces of music ever created.” (x)
Learn about the abolitionist history of O Holy Night:
“Things start in 1843 or 1847—there’s some discrepancy about the year—in Roquemaure, a small town in the Rhône valley region. Placide Cappeau, who had followed his father into the wine business, was also known for the poetry he composed. Though a critic of the Catholic church, Cappeau was asked by the local priest to write a few stanzas in celebration of the town cathedral’s newly refurbished organ. He is said to have written the song’s words while in transit to Paris on business, with the biblical Gospel of Luke as inspiration. On the advice of the same clergyman who had commissioned him, Cappeau took his completed work—then titled “Minuit, Chrétiens,” or “Midnight, Christians”—to Adolphe Adams, a composer of some renown. Adams, who was of French-Jewish descent, arranged the music, and the song was newly christened as "Cantique de Noel.” The carol would make its world debut, with opera singer Emily Laurey belting lyrics, during Christmas eve midnight mass at the Roquemaure church...
Though "Cantique de Noel” would quickly become a French Christmas favorite, it was later denounced by the French Catholic church—a reported consequence of Cappeau being an avowed atheist and socialist, along with the discovery that Adams was Jewish, not Christian. One bishop reportedly dismissed the song as having a "lack of musical taste and total absence of the spirit of religion.” There was also some resistance to Cappeau’s overtly anti-slavery lyrics in the third verse, which were perhaps made more glaring by his emergent political outspokenness. In any case, the ban reveals where the French Catholic church stood on matters of abolition...
In any case, "Cantique de Noel” would make its way across the Atlantic to John Sullivan Dwight, a white American abolitionist, Unitarian minister, musician and classical music aficionado who published a magazine called Dwight's Journal of Music...
Dwight gave his translated verse the title “O Holy Night” when he published it in his music periodical in 1855. It apparently became a hit in the U.S., gaining popularity among the abolitionist crowd during the Civil War. Even as the song was being banned in its home country, it was becoming a staple of Christmas, and a song of protest, thousands of miles away, in the U.S. It’s long since become part of the broader American Christmas songbook.”
(x)
353 notes
·
View notes
Text
So um… I don’t see enough people talking about Sophie’s older claim that the Abrahamic God (specifically the Christian version) is a system.
Look, I get it, the whole three people are one person thing? Yes, I get how on the surface that is absolutely a plurality staple. But that’s like… a piss baby understanding of the Trinity.
First of all, not all Christians accept the Trinity in the first place, so if Sophie says the Christian God is a system I’d be asking “which version of the Christian God”.
Certainly not the version of God from the Latter Day Saints, because they believe that the Father, Son, and Holy Ghost are three distinct beings that are united in purpose known as “the Godhead”. And I’m sorry, despite what everyone says, they consider themselves a Christian creed, even if they are not a sect or denomination but a whole different religious group.
Certainly not the version of God observed by Jehovah’s Witnesses, who reject any divine claim of Christ and believe the Holy Spirit is an extension of God rather than any personified entity.
Certainly not Orthodoxy, which does not say that the Spirit proceeds from the Son.
Certainly not Christian Scientists, or Oneness Pentecostals, or La Luz del Mundo Christians, or Unitarian Universalist Christians (in some cases). None of these have Trinitarian beliefs and they’re all Christian.
But sure, tell me how it is that it’s fine to throw a blanket statement over all of the different flavors of Christianity like they’re all the same.
Maybe a non-religious person with no experience outside of American Christendom should NOT be speaking about religious topics.
If you wanna headcanon that for yourself, feel free to remember that you’re making a headcanon on someone else’s firmly and sincerely held beliefs like it’s an AO3 fic.
God, are you fucking 5? You act like you know better than experts and people who live through those experiences. Making a statement like that only serves to do two things: attract religious people who agree with you, and piss off religious people who don’t.
It’s not about research, it’s not about any sort of cultural delicacy, it’s not about genuine curiosity, it’s about numbers for your army of little keyboard goblins.
And you do the same to other religious groups, so I guess you’re an equal-opportunity employer of callous gestures. What gives you the right to discuss religion like that when you claim none and have no insight into the lives of the pious?
Elementary understanding of the Trinity, get that shit outta my sight.
—Jackalope and Proteus
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
jean from american psycho is unitarian (headcanon) and bisexual (headcanon)



submitted by anon
9 notes
·
View notes
Photo
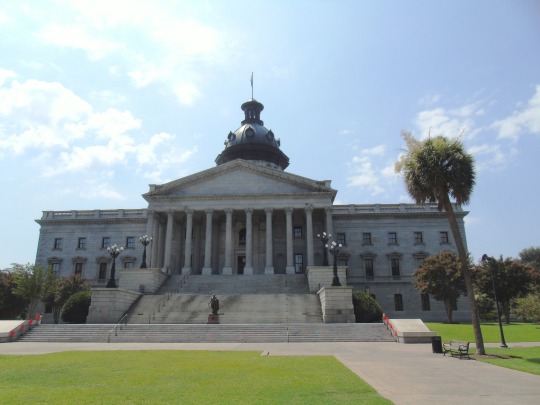
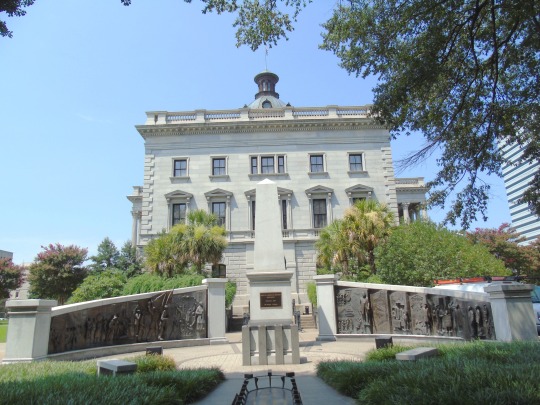
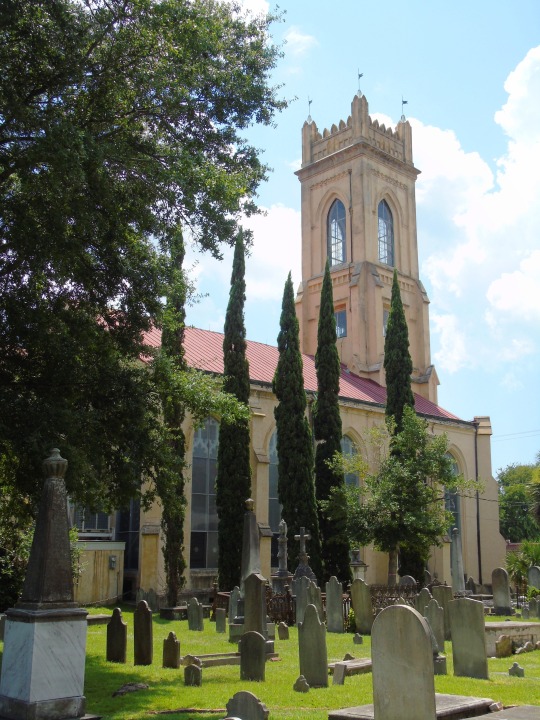
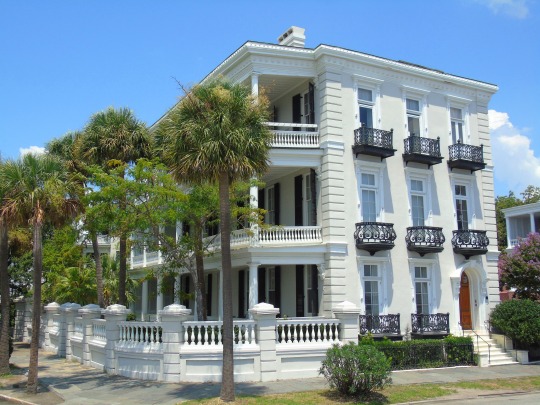










South Carolina ratified the United States Constitution as the eighth American state on May 23, 1788.
#South Carolina State House#Columbia#Charleston#summer 2016#travel#St. Philips Church Episcopal West Cemetery#architecture#public art#USA#African-American History Monument by Ed Dwight#Unitarian Church#Louis DeSaussure House#North Augusta#Savannah River#Miles Brewton House#South Carolina#US Constitution#23 May 1788#8th US State#235th anniversary#US history#tourist attraction#landmark#cityscape
7 notes
·
View notes
Note
The Hightowers ARE like American protestants but specifically New England protestants where the exact same churches and parishes that were super puritan and hanging witches in the 1600s are now all unitarian and congregational churches with pride flags outside and the sermons are all like God loves everyone, if she even exists. Which she may not. Who are we to say.
as a occasional unitarian by obligation i gotta veto this we have NO swag we are the oatmeal raisin cookie of religions. the hightowers are very firmly like renaissance era italian catholics to me they’re in with the church insofar as it grants them political power and they can keep getting one of theirs elected the pope and then they spend their free time on their scheming and on their weird hobbies (wizard shit)
48 notes
·
View notes
Quote
Life seeks life and loves life. The opening of a catkin of a willow, in the flight of the butterfly, in the chirping of a tree-toad or the sweep of an eagle - my life loves to see how others live, exults in their joy, and so far is partner in their great concern.
Edward Everett Hale was an American author, historian, and Unitarian minister, best known for his writings such as "The Man Without a Country", published in Atlantic Monthly, in support of the Union during the Civil War. He was the grand-nephew of Nathan Hale, the American spy during the Revolutionary War. Wikipedia
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
Yesterday an active-duty Air Force soldier named Aaron Bushnell self-immolated in front of the Israeli Embassy. His last words were “Free Palestine.” Of the cops responding to the scene, some pointed guns at him while others sought to extinguish the flames; the image of a cop pointing a gun at a man on fire is the most American thing I have ever seen.
On June 11th, 1963, a Buddhist monk named Thích Quảng Đức set himself on fire in Ho Chi Minh City (then Saigon). In South Vietnam, Buddhists were an oppressed majority, ruled by a Catholic minority—the Buddhist flag was banned, Catholics were chosen for all the better jobs, and protesting Buddhists were being murdered in the streets or sent to concentration camps.
So Thích set himself on fire and calmly burned in front of hundreds of spectators on a public street. There’s a film of it, and I’m not big into “watch people die on film,” but some moments in history are worth seeing. He didn’t cry out; he just sat in lotus position, engulfed in flames. Afterwards, the cops tried to take his remains, but thousands of angry protestors took him back, and they re-cremated him for a proper funeral. His heart didn’t burn. It solidified in the fire. Today it is today a sacred relic. I have no explanation for this.
Other monks in Vietnam followed his example. By the end of the year, the CIA led a coup and toppled the Catholic dictator of the country. This isn’t “the US being good,” mind you, they’d been propping the asshole up in the first place. Thích’s sacrifice is often credited as what brought down that regime.
Two years later, the first American set herself on fire in protest of the Vietnam war. Alice Herz was a German Jew, 82 years old. She’d seen some shit. She’d fought for feminism in 1910s Germany, helped bring about the Weimar Republic, fled Germany to France only to end up in a Nazi concentration camp. Survived. Made it to the US. Lived in Detroit and became a Unitarian. Then one day she wrote a letter about how horrible the Vietnam war was, went out to the street, and set herself on fire. She wasn’t the last. In South Vietnam and the US alike, Buddhists and Quakers and Catholics set themselves on fire in service of the same cause.
When a 16 year old Catholic named Ronald Brazee set himself on fire in October 1967, a Catholic Worker named Father Daniel Berrigan wrote a poem for him called “In the Land of Burning Children”
He was still living a month later
I was able to gain access to him
I smelled the odor
Of burning flesh
And I understood anew
What I had seen in North Vietnam
I felt that my senses
Had been invaded in a new way
I now understood
the power of death in the modern world
I knew I must speak and act
against death
because this boy’s death
was being multiplied
a thousandfold
The Dutch resistance to the Nazi Occupation was characterized by a unique nonviolence, focusing primarily on hiding Jewish people and acts of sabotage. This wasn’t necessarily an ethical or even strategic decision, but one forced onto them by circumstance—according to one resistance fighter, since the Dutch government maintained a firearms registry before the invasion, the Nazis were able to acquire that list and go door-to-door to disarm the Dutch population.
But what the Dutch resistance lacked in firearms it made up for in mass participation. Roughly a million people were involved in sheltering people, secreting people away, striking, or helping those who were doing such things. The two most active groups were churches and communist organizations.
The Nazis responded with collective punishment. The occupiers cut off food supplies inside the Netherlands, blockading the roads between farms and cities. The entire population of the country went hungry during what’s called the Hunger Winter of 1944-1945. Between 18-22,000 people starved to death. Four-and-a-half million people were living off of something like 600 calories a day each. A whole generation of children born or living at the time suffered lifelong ailments. Audrey Hepburn grew up in Occupied Netherlands (and as a preteen performed ballet to raise money to support the resistance). Her time in the hunger winter left her with lifelong ailments like anemia.
In case the parallel I’m drawing is not obvious, Gaza is currently being starved by the Israeli government.
Quite notably, quite worth understanding in the modern context, the Hunger Winter persisted despite relief efforts until the Allied forces liberated the Netherlands from the fascists in May 1945.
Aaron Bushnell was twenty-five years old when he died. He sent a message to media outlets before his act: “Today, I am planning to engage in an extreme act of protest against the genocide of the Palestinian people.”
He posted on Facebook: “Many of us like to ask ourselves, ‘What would I do if I was alive during slavery? Or the Jim Crow South? Or apartheid? What would I do if my country was committing genocide?’ The answer is, you’re doing it. Right now.”
His last words, engulfed in flames, were “Free Palestine.”
I know that what stopped US involvement in Vietnam was the military victory of the Vietnamese people against US forces, combined with the direct action action efforts of the American Left that made the war harder to execute. I know what ended the Nazi occupation was the Allied invasion. I know what stopped legal chattel slavery in the US was the deadliest war in our country’s history. I also know that what stopped Jim Crow was… nothing. Nothing has stopped it, not completely. The long, hard, thankless work of a combination of reform and direct action has mitigated its effects somewhat.
I can’t say I think others should follow Aaron’s example. I doubt he wanted anyone to. An act like this needs attention, not imitation. What we can follow is the moral courage. What we need to decide for ourselves is how to act, not whether or not to act. I don’t have any answers for me, and I don’t have any answers for you.
I can say that he shouldn’t be forgotten, that he ought to be remembered when we ask ourselves if we have the courage to act.
I can also say that it takes an incredible number of people doing an incredible variety of work to effect change. That poet, Father Daniel Berrigan, did a lot more than write poetry. He and others in the broader Catholic Left raided draft offices and burned records, directly impacting the US’s ability to send young men off to die in an imperialist war. A group of people who came out of their movement (but were primarily Jewish and/or secular) raided an FBI office and uncovered the spying and disruption that was done of the peace movement under the name COINTELPRO.
A vibrant and militant counterculture sprang up, drawing Americans away from the clutches of conservative propaganda. They built nationwide networks of mutual aid and they helped draft dodgers escape the country.
An awful lot of American soldiers in Vietnam directly defected, enough that “fragging” entered the English language as a verb for throwing a grenade at your commanding officer.
As for the Hunger Winter, it was not ended until the Nazi party was ended through force of arms, but its worst effects were alleviated by the bravery and thankless work of uncountable people who cobbled together meals from nothing or who organized to bring food aid in across German lines.
In the US now we’re seeing a growing movement opposed to our country’s collaboration with the genocidal regime in Israel.
It’s impossible to know if it will be enough. When you pile straw onto the proverbial camel, you never know which straw will be the last. We just keep piling.
And in the meantime, we remember names like Aaron Bushnell, Ronald Brazee, Alice Herz, and Thích Quảng Đức.
#gaza#palestine#aaron bushnell#self immolation#child death#tw#death#military#protest#self harm#margaret killjoy#community building#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#anarchist society#practical#revolution#anarchism#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues
7 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo Emerson (1803-1882) was an American essayist as well as the foremost representative of the transcendentalist movement of the early to mid-19th century. Known mostly for his essays Self-Reliance, The American Scholar, and Nature, he was also a major poet, although he did not consider himself one.
His works not only inspired writers of his own generation (e.g. Henry David Thoreau and Nathaniel Hawthorne) but also authors of the 20th century such as Theodore Dreiser, Robert Frost, and Ralph Waldo Ellison. His home in Concord, Massachusetts, became a haven for many young "like-minded New Englanders."
Early Life
Ralph Waldo Emerson was born in Boston, Massachusetts, on 25 May 1803, the second of five surviving sons; three other siblings died in childhood. When he was eight, his father, a Unitarian minister, died, leaving his family in poverty, often on the brink of starvation. These early years of poverty would foster in Emerson a streak of independence visible in his essays and poetry. To survive, his mother ran a boardinghouse but was determined that her sons would receive a good education. At the age of nine, Emerson attended the Boston Public Latin School. His years at Harvard (1817-1821) were seen as frugal, industrious, and undistinguished.
In 1825, he attended the Harvard Divinity School to study theology. The years 1826-1827 were spent outside Boston recovering from tuberculosis. With his health restored, he began preaching, and in 1829, he was ordained a Unitarian minister at Boston Second Church, but he soon realized that church life was not to his liking, especially the daily mundane duties of a minister. His contempt began to grow and become more serious. He became skeptical of Christianity, developing a faith "greater in individual moral sentiment than revealed religion" (Norton, 1104).
Continue reading...
29 notes
·
View notes