#gridlayout
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Checkmate
🧩 Author: ChiiAka 🔗 Code Link: 52. || Checkmate on Toyhouse 💠 Use Type: Free to Use (F2U) 📄 Purpose: Character Profile 📝 Description: A sleek, modern character profile code that uses smooth animated buttons to swap between detailed panel sections like Likes, Trivia, and Story. The interface is structured with clear segmented areas for personality sliders, relationship blurbs, and profile stats. Its dark background and amber-gold accents create an elegant, tactical vibe—perfect for characters with a regal, strategic, or high-intellect theme. The layout is both visually rich and compact, with multi-tab efficiency and strong aesthetic cohesion.
📷 Previews:

#toyhouse#toyhou.se#html#code#charactercodes#f2u#multi-tab#gridlayout#personalityslider#statbars#quotehighlight#profilebuttons#traitlists#boldcontrast#monochrome#colorpalette#chiiaka
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
CSS Grid Layout by Abdelfattah Ragab
CSS Grid Layout by Abdelfattah Ragab
Welcome to "CSS Grid Layout". In this book you will learn all about the CSS grid layout model and how to create complex and responsive grid-based designs. You will learn about all the properties of grid containers and grid elements. By the end of this book, you will be able to use the grid layout to create responsive layouts and handle all kinds of scenarios. Let’s get started.
Available on https://shop.tredition.com and https://www.amazon.com

0 notes
Text
Introducción a CSS: Estilizando la Web
Introducción
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) es el lenguaje que se utiliza para describir la presentación de un documento escrito en HTML o XML. Mientras que HTML estructura el contenido de la web, CSS se encarga de darle estilo, desde la disposición de los elementos hasta los colores y las fuentes. Si estás empezando en el mundo del desarrollo web, aprender CSS es esencial para crear sitios atractivos y funcionales. En este blog, te proporcionaré una introducción a CSS, cubriendo sus conceptos básicos y algunas prácticas recomendadas para que puedas comenzar a diseñar páginas web impresionantes.
1. ¿Qué es CSS?
CSS es un lenguaje de hojas de estilo que permite definir cómo se muestran los elementos de un documento HTML en la pantalla, en papel o en otros medios. Gracias a CSS, puedes separar la estructura de un sitio web de su presentación, lo que facilita el mantenimiento y la escalabilidad del diseño.
a) Características Principales de CSS:
Selección de Elementos: CSS te permite seleccionar y aplicar estilos a elementos HTML específicos o a grupos de elementos.
Diseño Responsivo: CSS facilita la creación de diseños que se adaptan a diferentes tamaños de pantalla, desde dispositivos móviles hasta monitores de escritorio.
Control de Estilos Visuales: Con CSS, puedes controlar el color, el tamaño, la fuente, el espacio entre elementos, y mucho más.
2. Cómo Empezar con CSS
Para comenzar a usar CSS, puedes incluir las reglas de estilo directamente en un archivo HTML o en un archivo CSS separado. A continuación te muestro cómo hacerlo:
a) CSS en Línea:
Puedes aplicar estilos directamente en los elementos HTML utilizando el atributo style.

b) CSS Interno:
Puedes definir un bloque de CSS dentro de la etiqueta <style> en el <head> de tu documento HTML.

c) CSS Externo:
La mejor práctica es usar un archivo CSS separado para mantener el estilo y el contenido por separado.

Contenido de styles.css:

3. Conceptos Básicos de CSS
CSS se basa en reglas que constan de selectores y declaraciones. A continuación te explico los conceptos más importantes:
a) Selectores:
Los selectores indican qué elementos HTML deben ser estilizados.
Selector de Elemento:

Selector de Clase:

Selector de ID:

b) Propiedades y Valores:
Las propiedades son aspectos específicos del estilo que se aplican a los elementos, como color, fuente, y margen.
Propiedad color: Cambia el color del texto.

Propiedad font-size: Cambia el tamaño de la fuente.

Propiedad margin: Define el espacio exterior alrededor de un elemento.

c) Especificidad y Herencia:
La especificidad determina qué reglas CSS se aplican cuando hay conflictos, y la herencia permite que ciertos estilos se transmitan a los elementos hijos.
Especificidad:

Herencia:

4. Diseño de Páginas Web con CSS
CSS permite controlar el diseño y la disposición de los elementos en una página web, facilitando la creación de sitios visualmente atractivos y organizados.
a) Modelos de Caja (Box Model):
Cada elemento en CSS se representa como una caja que comprende márgenes, bordes, rellenos y el contenido.

b) Layouts (Diseños):
CSS proporciona varias técnicas para organizar elementos en una página, incluyendo Flexbox y Grid.
Flexbox:

Grid Layout:

c) Media Queries y Diseño Responsivo:
Las media queries permiten que los diseños se adapten a diferentes tamaños de pantalla, lo que es fundamental para crear sitios web responsivos.

5. Recursos para Aprender Más CSS
Documentación Oficial:
MDN Web Docs: Una guía completa que cubre todo lo que necesitas saber sobre CSS.
Tutoriales en Línea:
CSS-Tricks: Un sitio repleto de tutoriales, ejemplos y trucos para mejorar tu uso de CSS.
W3Schools: Un recurso fácil de seguir para aprender los fundamentos de CSS con ejemplos prácticos.
Libros Recomendados:
“CSS: The Definitive Guide” de Eric A. Meyer: Un recurso profundo para desarrolladores que quieren dominar CSS.
“CSS Secrets” de Lea Verou: Este libro revela técnicas avanzadas para crear efectos y diseños sorprendentes con CSS.
Conclusión
CSS es una herramienta poderosa para cualquier desarrollador web. Desde controlar la apariencia básica de los elementos hasta diseñar sitios complejos y responsivos, el dominio de CSS te permitirá crear experiencias web atractivas y profesionales. Comienza practicando con los conceptos básicos, y poco a poco, profundiza en las técnicas más avanzadas para llevar tus diseños al siguiente nivel.
#CSS#diseñoweb#desarrolloweb#estiloweb#frontenddevelopment#aprendeCSS#webdesign#cssbasics#webdevelopment#responsiveweb#flexbox#gridlayout#webstyling#tutorialesCSS#cssdesign#cssgrid#htmlandcss#webdev#cssforbeginners#diseñoresponsivo#coding#webcoding#frontend#webcss#estilosweb
0 notes
Photo

Start slowly. Artifact Uprising VSCO Grid Take your time to discover the magic of Artifact Uprising and unleash your creativity on the captivating VSCO Grid. Let the process unfold at its own pace.
0 notes
Text
j
Swing is not thread-safe. Updating UI components from background threads (not the Event Dispatch Thread) causes race conditions, freezes, or crashes.
Use SwingUtilities.invokeLater() or SwingWorker to handle background tasks safely.
Component Overlap or Z-order Issues Components might overlap or not render correctly if layout and repainting aren’t managed properly.
revalidate() and repaint() are often needed after dynamic UI changes.
Scaling and DPI Conflicts On high-DPI displays, Swing apps can look blurry or improperly scaled if not configured.
Java 9+ supports HiDPI better, but older setups require workarounds.
Architecture Conflicts Mixing UI logic with business logic leads to spaghetti code and maintenance problems.
Not following patterns like MVC or separating concerns can make the design fragile.
Event Handling Conflicts Multiple listeners acting on the same component or event can cause logic errors.
Improper handling of key bindings or focus can result in unresponsive controls. // Updating a JTable in Java Swing can be done in a few different ways Using a DefaultTableModel (most common way)
Access the model:DefaultTableModel model = (DefaultTableModel) table.getModel(); Refreshing the UI If you're updating the model directly, the JTable usually updates automatically. But if needed:
java model.fireTableDataChanged();
// If you update the JTable (or any Swing component) from a non-EDT thread, you risk:
UI glitches
Random exceptions
Unpredictable behavior
The Fix: Use SwingUtilities.invokeLater() // Always wrap the JTable in a JScrollPane to handle large datasets.
Use BorderLayout.CENTER to make it fill the frame.
This design makes JTable the main UI element—perfect for apps like:
Inventory systems
Admin dashboards
// Custom Cell Rendering (How Data is Displayed) To change how a cell looks, implement a custom TableCellRenderer.
// Make Only Certain Columns Editable Override isCellEditable() in your model:
java Copy Edit DefaultTableModel model = new DefaultTableModel(data, columnNames) { @Override public boolean isCellEditable(int row, int column) {
//
Custom Cell Editors (How Data is Edited) To control how a user edits a cell, use a TableCellEditor.
Example: Use a combo box editor for a column java
String[] roles = {"Developer", "Designer", "Manager"}; JComboBox comboBox = new JComboBox<>(roles);
table.getColumnModel().getColumn(2).setCellEditor(new DefaultCellEditor // Format Displayed Values You can convert raw data (like timestamps, enums, booleans) into human-readable text using renderers or by overriding getValueAt() in a custom TableModel.
//
GridLayout Divides space into equal-sized rows and columns.
java
BoxLayout Aligns components vertically or horizontally.
GridBagLayout Most flexible, but also the most complex.
Allows fine-grained control over row/column span, alignment, padding. //
Optimized event-driven programming for efficient user interactions and system performance.
Implemented MVC architecture to ensure scalability and maintainability of Java Swing applications.
Enhanced multithreading in Swing applications to improve responsiveness using SwingWorker.
Debugged and resolved UI rendering issues, ensuring cross-platform compatibility.
Worked with Look and Feel (LAF) customization for a modern and branded UI experience.
//
ava Swing Application Works JFrame (Main Window) – The base container that holds all UI components.
JPanel (Layout Container) – Used to organize components inside the frame.
Swing Components – Buttons (JButton), labels (JLabel), text fields (JTextField), tables (JTable), etc.
Event Handling – Listeners (like ActionListener) handle user interactions.
Threading (SwingWorker) – Ensures UI remains responsive during background tasks.
Example Use Cases Point of Sale (POS) Systems – Cashier interfaces for processing transactions.
Inventory Management – Applications for tracking stock levels.
Data Entry Forms – GUI forms for database input and management.
Media Players – Applications for playing audio/video with Swing UI.\
JFrame Main application window JPanel Container for organizing UI elements JButton Clickable button JLabel Display text or images JTextField Single-line input field JTextArea Multi-line text input JTable Displays tabular data JMenuBar Menu bar with dropdown menus JList List of selectable items
.. //
Use of Modern Look and Feel (LAF) FlatLaf – A modern, flat UI theme for Swing that provides a better-looking UI.
Improved Concurrency with CompletableFuture Handles long-running tasks without freezing the UI.
Example:
java
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> fetchData()) .thenAccept(data -> SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> label.setText(data)));
// Use a Layout Manager Java Swing provides various layout managers like:
BorderLayout – Divides the window into 5 regions (North, South, East, West, Center).
GridBagLayout – Flexible and customizable grid-based layout.
BoxLayout – Arranges components in a single row or column.
GroupLayout – Best for complex resizable designs (used in NetBeans GUI Builder).
Use JScrollPane to make JTable scrollable ✔ Use DefaultTableModel for editing rows ✔ Add event listeners to detect row selection ✔ Integrate with a database using JDBC
Performance Issues in JTable & How to Optimize When dealing with large datasets in JTable, performance can degrade due to factors like slow rendering, inefficient data models, excessive event handling, Large Dataset Causes UI Lag Issue: If the table has thousands of rows, JTable may slow down because it loads all rows at once.
Solution: Use pagination or lazy loading instead of loading everything upfront.
✅ Example: Paginated JTable (Loading 100 Rows at a Time)
java Copy Edit int pageSize = 100; // Load 100 rows at a time int currentPage = 0; List data = fetchDataFromDatabase(currentPage * pageSize, pageSize); // Load only a subset
DefaultTableModel model = (DefaultTableModel) table.getModel(); for (Object[] row : data) {
//
Slow Rendering Due to Default Renderer Issue: The default cell renderer calls Component.setOpaque(false), causing unnecessary painting.
Solution: Use a custom renderer with setOpaque(true).
✅ Example: Custom Fast Renderer
java Copy Edit class FastRenderer extends DefaultTableCellRenderer { @Override public Component getTableCellRendererComponent(JTable table, Object value, boolean isSelected, boolean hasFocus, int row, int column) { JLabel label = (JLabel) super.getTableCellRendererComponent(table, value, isSelected, hasFocus, row, column); label.setOpaque(true); // Prevents repainting issues
;;
Frequent Repainting & Event Listeners Cause Overhead Issue: JTable repaints everything after every update, even when unnecessary.
Solution: Temporarily disable auto updates, batch updates, then re-enable.
✅ Example: Batch Update with Table Locking
java Copy Edit DefaultTableModel model = (DefaultTableModel) table.getModel(); model.setRowCount(0); // Clear table without repainting table.setAutoCreateColumnsFromModel(false); // Avoid unnecessary updates
// Batch insert rows for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { model.addRow(new Object[]{"ID " + i, "Name " + i, i + 20}); }
table.setAutoCreateColumnsFromModel(true); //
Using DefaultTableModel for Large Data Handling Issue: DefaultTableModel is inefficient for large datasets because it stores all data in memory.
Solution: Use a custom TableModel that fetches data dynamically.
✅ Example: Custom Lazy Loading Table Model
java Copy Edit class CustomTableModel extends AbstractTableModel { private final int rowCount = 1000000; // Simulating large dataset@Override public int getRowCount() { return rowCount;
Slow Sorting & Filtering Issue: Default sorting can be slow for large datasets.
Solution: Use RowSorter with custom sorting instead of sorting all rows at once.
✅ Example: Optimized Sorting
java Copy Edit TableRowSorter sorter = new TableRowSorter<>(table.getModel()); table.setRowSorter(sorter);
Use pagination or lazy loading for large datasets. ✅ Optimize cell rendering with setOpaque(true). ✅ Batch updates & disable auto updates temporarily. ✅ Use a custom TableModel instead of DefaultTableModel. ✅ Implement RowSorter for efficient sorting.
0 notes
Text
Debugging Your Kivy App with MD Python Designer: Common Pitfalls and Solutions
The creation of applications with the Kivy UI Designer is, indeed, an exciting journey. One can create truly fantastic, cross-platform interfaces without any problems. Even the best designs, however, may become a problem when one starts coding. So, effective debugging of your Kivy app is a critical step to achieving a good user experience. In this post, we will go over common pitfalls developers encounter while using the Kivy UI Designer and how to resolve them.
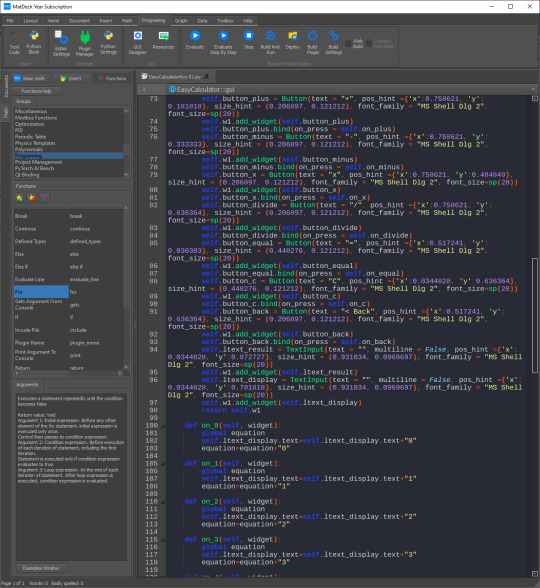
The Kivy Event System Kivy applications suffer mainly from a lack of understanding of the Kivy event system. Kivy is an event-driven architecture where several functions are exposed to user actions or system events.
Solution: Make sure you understand how the event flow works in Kivy. Print statements or logging can show you when and where events are triggered in your application, so you can trace the problem back to its source and easily identify and solve it.
Widget Sizing and Positioning Another problem developers often encounter is that the widgets are not sized or placed correctly. Sometimes, the widgets overlap or do not appear as intended because of the wrong layout properties.
Solution: Use Kivy's layout classes, like BoxLayout, GridLayout, etc., to control the placement of widgets dynamically. These classes maintain the integrity of the layout regardless of screen size and orientation. You can preview these layouts directly in the Kivy UI Designer, making it easier to change widget properties.
Resource Management Applications that support images or fonts will hang or crash if resource management is missing. Often, programmers forget to include the needed files as part of a package and errors are triggered at runtime.
Solution: Check your project setting every time when you go back to Kivy UI Designer, referenced, and included every necessary resource when you go through with creating your APK, used relative paths and avoid using an absolute path that makes it run whichever the environment it is placed into.
Wrong Data Validation The most common mistake is binding events to the wrong functions. This might lead to unexpected behavior, like not being able to use some buttons or triggering something inappropriate.
Solution: Check your event bindings with Kivy UI Designer. Using the properties panel, it's easy to see what functions are bound to the events. Ensure each button or interactive element is properly assigned to its respective callback function.
Debugging Code with Integrated Tools Kivy UI Designer has integrated debugging tools that are going to be a savior when it comes to debugging; however, most of the developers forget about them and use only manual debugging techniques.
Solution: Use the Kivy UI Designer's internal debugger. This will allow you to set breakpoints and debug variables, and step line by line through your code so you can clearly observe how the application is going to behave at run-time. Learning how to leverage these features will sharply diminish debugging time.
Layouts and responsiveness Since Kivy is designed for various devices, it may be hard to ensure that your app is responsive. A layout that works fine on one device does not necessarily display correctly on another.
Solution: Test your app on different devices and orientations. The Kivy UI Designer will let you simulate different screen sizes, which will help identify layout issues. In general, always use a flexible design approach and make use of relative sizes, such as percentages, when designing widgets.
Documentation and Community Documentation and community forums will be Kivy's most valuable assets. In a way, one could say that most of the time, it's not very different when the problem developers face often looks very familiar, and the solution is documented by others.
Solution: The Kivy documentation is what needs to be consulted if unclear issues arise to find out how a specific function or feature works. In some cases, discussion of your debugging problem in the community on Stack Overflow or Kivy Google Group will get you through the situation. Conclusion Kivy application debugging is pretty daunting. Yet, once you are cognizant of common traps and leverage the Kivy UI Designer features, things could become quite smooth and relatively easy. Once you find a way to remain organized with all the tools and resources accessible to you and your community, then your process is easier, and the end result - polished applications on the part of your end users - will not seem as challenging. Keep in mind that every bug might provide you with an opportunity for learning and improving in regards to coding skills. Stop running away from debugging procedures; push your projects along!
0 notes
Video
youtube
free premium html and css template with javascript | free template #htm...
#HTML, #CSS, #JavaScript, #WebDevelopment, #FrontendDevelopment, #Coding, #WebDesign, #ResponsiveDesign, #DynamicWeb, #UserInterface, #UIUX, #Website, #HTML5, #CSS3, #WebDev, #InteractiveWeb, #MobileFirst, #GridLayout, #Flexbox, #Bootstrap, #WebAnimation, #AJAX, #DOMManipulation, #APIs, #FrontEndCoding, #FullStack, #Scripting, #SEO, #WebPerformance, #CrossBrowser
4o
1 note
·
View note
Text
5-2-24: Day 76
Day 76 consisted of
Accessibility review
Challenge 1: The check out view in Cupcake Corner uses an image and loading spinner that don’t add anything to the UI, so find a way to make the screenreader not read them out:

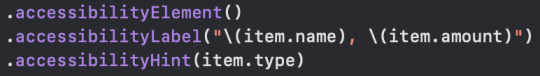
Challenge 2: Fix the list rows in iExpense so they read out the name and value in one single VoiceOver label, and their type in a hint:
Challenge 3: Do a full accessibility review of Moonshot—what changes do you need to make so that it’s fully accessible?
I could picture this in my head and decided not to write the code, but the changes would include: using .accessibilityElement(children: .combine), .accessibilityRemoveTraits(.isImage), and .accessibilityAddTraits(.isButton) on each of the mission buttons (images) that navigate to a detail view, as well as on a few of the Text views and stacks in ContentView, GridLayout, ListLayout, MissionView, and AstronautView. I would also create a constant to store the labels for each of the crew members’ names and mission badges to be read correctly by VoiceOver using .accessibilityLabel(), instead of reading the image file names which are currently only a crew members’ last name and "apollo" with the number beside it.
Day 76 quote: "Accessible design is good design—it benefits people who don’t have disabilities as well as people who do." - Steve Ballmer
#day 76#100 days of swiftui#ios#ios development#software development#software engineering#programming#coding#codeblr
0 notes
Text
android has so many fucked-up little elements it’s ridiculous. it starts off normal (you want to make a set of linear visual elements? oh use LinearLayout! you want to make a grid of stuff? use GridLayout!) but then it gets to be so specific like why does some of this stuff even exist. if you want to make a page-style UI, you can’t just make a set of views and a swipe listener and swipe between them, you have to use a ViewPager with a PagerAdapter. if you want to make a list of stuff, you can use ListView (normal) or you can use RecyclerView and make a RecyclerViewAdapter and then a ViewHolder to go along with it (why are there three different things? because android). im going to lose my fuckign mind
1 note
·
View note
Photo


“Space-Ship” and “Fun In The Sun”
Tetradic-color-harmony Project for Color Theory class!
Kelsey Spring 2020
#myart#abstract#geometric#gridformat#gridlayout#ACRYLIC#liquitexheavybodyacrylic#neon#rainbow#tetrad
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to make your HTML responsive using display grid. 💯✅
To make your HTML responsive using display grid, you can follow these steps:
#beginners#css#html#web#responsiveDesign#webDesign#gridLayout#mediaQueries#webDevelopment#frontEndDevelopment#codeSnippet#programmingTips
1 note
·
View note
Text
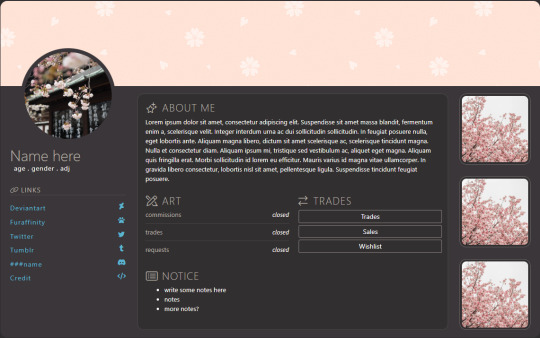
User Axis
🧩 Author: Pinky 🔗 Code Link: [Freebie] User Axis on Toyhouse 💠 Use Type: Free to Use (F2U) 📄 Purpose: User Card 📝 Description: A soft, elegant user profile layout with a cherry blossom theme. Features a sidebar for avatar, social links, and basic info, alongside a main panel for about text, art/trade info, and customizable notices. Includes buttons for Trades, Sales, and Wishlist, plus a vertical image gallery for showcasing favorites, art, or characters. Great for users looking for a clean, organized front page with gentle aesthetic flair.
📷 Previews:
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo

🐶💞🐶 2️⃣ / 3️⃣ 🐶💞🐶 ⭐️Favorite past time, sploot’n⭐️ . . . . . #grid #gridview #gridlayout #tile #papillon #daschund #pdxpup #portlandpup #papillonmix #spreadeagle #dogsofinstagram #cute #furry #fluffy #blackandwhite #puppy #dog #dogs #mixed #obsessed #パピヨン #papillonsofinstagram #portlanddogs #portland #pdxpups (at Portland, Oregon)
#obsessed#portlandpup#papillonmix#dogs#pdxpup#cute#fluffy#daschund#gridview#portlanddogs#papillon#dogsofinstagram#puppy#gridlayout#portland#papillonsofinstagram#furry#blackandwhite#pdxpups#パピヨン#spreadeagle#mixed#dog#tile#grid
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
hi
Scrollbar ScrollPane Type Component (a widget) Container (a container that can hold components)Scrollbar: Just the scroll bar, standalone.
ScrollPane: A container that can show scrollbars when needed for its content.
Java Swing, a Container is a component that can hold and organize other components (like buttons, text fields, etc.). It is part of the AWT hierarchy but is also used in Swing through classes like JPanel, JFrame, and JDialog, which are all containers.
Here's a simple Swing layout design using a JFrame with a combination of BorderLayout and FlowLayout. It includes a header, footer, center area, and side panel.
FlowLayout Default for: JPanel
Arranges: Left to right, wraps to next line.
BorderLayout Default for: JFrame
Divides into 5 regions: North, South, East, West, Center
GridLayout Arranges: Components in a rectangular grid.
All cells are equal in size.
BoxLayout Arranges: Components either vertically (Y_AXIS) or horizontally (X_AXIS).
Usage:
GridBagLayout Most flexible, but complex.
Allows components to span multiple rows/columns and align precisely.
FlowLayout Simple row layout Low Low BorderLayout App-like UI with sections Medium Low GridLayout Equal-sized grid Medium Low BoxLayout List-like vertical/horizontal stack Medium Medium GridBagLayout Complex form-like layout High High CardLayout Switching panels (tabs/wizards)
Using layout managers provides flexibility, portability, and maintainability when building GUIs. Here's a breakdown of their key advantages:
Platform Independence Layout managers adapt to different screen sizes and resolutions automatically.
You don't need to manually set pixel positions for components.
Without Layout Manager (using null layout): You're responsible for absolute positioning and sizing (setBounds()).
Not responsive or portable.
Breaks with different screen DPI or user settings.
Scrollbar vs ScrollPane Scrollbar:
A standalone component (widget).
Just the scroll bar itself; does not contain other components.
ScrollPane:
A container that can hold another component and adds scrollbars as needed.
Manages content overflow automatically.
Container in Java Swing A Container can hold and organize other components like buttons, text fields, panels, etc.
Examples of Containers in Swing:
JPanel
JFrame
JDialog
Containers come from the AWT hierarchy, but are heavily used in Swing as well.
Why Use Layout Managers? Platform Independence:
Layout managers automatically adjust to different screen sizes and resolutions.
Avoids Manual Positioning:
No need to manually set x, y, width, height via setBounds().
Responsiveness:
UIs adapt to font changes, screen DPI settings, window resizing, etc.
Maintainability:
Easier to modify layouts without breaking the UI across different devices.
Drawback of NOT Using Layout Managers Using null layout (no layout manager):
You must manually set component positions and sizes.
Non-responsive: Breaks on different screen sizes and settings.
Not portable: UI may look fine on one machine, but terrible on another.
FlowLayout
Arranges: Left to right, wraps to next line.
Notes: Default for JPanel.
BorderLayout
Arranges: Divides into 5 regions — North, South, East, West, Center.
Notes: Default for JFrame.
GridLayout
Arranges: Components in a rectangular grid with equal-sized cells.
Notes: Simple and uniform layout.
BoxLayout
Arranges: Components stacked vertically (Y_AXIS) or horizontally (X_AXIS).
Notes: Good for list-like or linear layouts.
GridBagLayout
Arranges: Highly flexible, components can span multiple rows/columns.
Notes: Complex but powerful for fine-tuned layouts.
CardLayout
Arranges: Allows switching between multiple panels (like cards).
Notes: Useful for building tabbed panels, step-by-step wizards.
Quick Comparison of Layout Managers FlowLayout
Use Case: Simple row layout.
Flexibility: Low.
Complexity: Low.
BorderLayout
Use Case: Application-like UI with structured sections.
Flexibility: Medium.
Complexity: Low.
GridLayout
Use Case: Uniform grid with equal-sized components.
Flexibility: Medium.
Complexity: Low.
BoxLayout
Use Case: Vertical or horizontal stacking of components.
Flexibility: Medium.
Complexity: Medium.
GridBagLayout
Use Case: Complex, form-like layouts with precise control.
Flexibility: High.
Complexity: High.
CardLayout
Use Case: Switching between multiple panels (like tabs).
Flexibility: Medium.
Complexity: Medium.
Event Dispatch Thread (EDT) in Java Swing is the special thread responsible for handling all GUI events — like button clicks, screen repaints, key presses, and mouse movements. Swing is not thread-safe — meaning you should only update the UI from one thread, and that thread is the EDT.
Key Rules: Create and update GUI components on the EDT.
Never do long-running tasks (like file or network access) on the EDT — it freezes the UI.
Creating GUI on EDT (best practice): java Copy Edit SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> { // Safe to create GUI components here JFrame frame = new JFrame("EDT Example"); frame.setSize(300, 200); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); });
EDT handles all UI updates and events.
Always use invokeLater() or SwingWorker to interact with the UI safely.
Never block the EDT — it makes your GUI unresponsive.
Using SwingWorker The built-in SwingWorker handles threading and result-passing for you.
// 1) Define a SwingWorker that returns your data type SwingWorker, Void> worker = new SwingWorker<>() { @Override protected List doInBackground() throws Exception {
Using ExecutorService + invokeLater If you need a pool of threads or more control:
ExecutorService dbPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Use background threads (SwingWorker, ExecutorService, CompletableFuture).
Update Swing components only on the EDT (invokeLater(), done(), or thenAcceptAsync).
Java Swing, a component's preferred size determines how much space it wants to occupy, and layout managers usually respect this when arranging components.
MVC (Model-View-Controller) – Primary Swing Pattern Swing uses a lightweight version of MVC.
Model – Holds data (e.g., TableModel, ListModel)
View – The UI component (e.g., JTable, JList)
Controller – Often combined into the View via event listeners
Observer Pattern Used in event handling — listeners observe changes and respond.
Example: ActionListener, ChangeListener, PropertyChangeListener
Composite Pattern UI components and containers follow this pattern.
JPanel can contain JButton, JLabel, etc., and be treated as a single component.
Singleton Pattern Often used for a central app window or config manager.
develop a JTable in Java Swing, you can either use:
Simple data + column arrays (quick setup), or
Custom TableModel (for more control, e.g., editable cells, dynamic data).
JTable with DefaultTableModel (editable & dynamic)
. Custom TableModel (for full control) If you want non-editable columns or custom data source (like a database), extend AbstractTableModel. Use a Custom TableModel (AbstractTableModel) This gives you full control over:
Data source (could be a list, database, etc.)
Column behavior (e.g., types, editable columns) if your table data changes frequently (like from a database, real-time updates, or user interaction), you should use a custom AbstractTableModel with a List-based backend. This approach gives you:
Clean separation of data and UI
Easy updates (add, remove, modify rows)
Fine control over column behavior (e.g., editable or read-only)
create a JTable with dynamic columns at runtime — meaning the columns can change while the application is running (e.g., based on user action or data changes).
Custom TableModel for Dynamic Columns
You can call setColumns(…) at any time to dynamically change column headers and structure.
Rows can be added using addRow(…) with values matching the new column layout.
The table refreshes itself with fireTableStructureChanged().
Cell Click / Selection Event Use a ListSelectionListener to detect row selection:
To handle mouse clicks in a JTable, such as detecting double-clicks, right-clicks, or clicks on specific cells, use a MouseListener or MouseAdapter.
display different cells in different colors based on data, you can override the prepareRenderer() method in JTable. This lets you customize cell background and foreground colors dynamically depending on the cell's content or row/column inde
What You Can Customize: c.setBackground(Color.X) – change background
c.setForeground(Color.Y) – change text color
You can also change font, borders, tooltips, etc.
Steps to Update Cell Background Based on Data and Repaint Assuming you're customizing cell colors with prepareRenderer():
Change the underlying data in your TableModel
model.setValueAt("Failed", rowIndex, colIndex);
Then trigger a repaint of the table
table.repaint();
Ensure the TableModel supports editing If you're using DefaultTableModel, editing is enabled by default.
If you're using a custom AbstractTableModel, override: Implement setValueAt() in Custom TableModel If you're using a custom model, this method must actually update the data:
sort data in a JTable, you can use the built-in TableRowSorter, which works with any TableModel (like DefaultTableModel or AbstractTableModel).
Features of TableRowSorter Click on a column header to sort ascending/descending
Can sort numerically or alphabetically
You can programmatically control sorting:
Sorting for Custom TableModel Works the same way as long as your getValueAt() returns proper data types (Integer, String, etc.) — not Strings for everything.
To implement flushing (auto-refresh) every 3 seconds in a JTable, you can use a javax.swing.Timer. This is Swing-safe and fires events on the Event Dispatch Thread (EDT).
Flush from a database query
Flush based on web API call
Conditional flushing (if flag is dirty)
0 notes
Photo
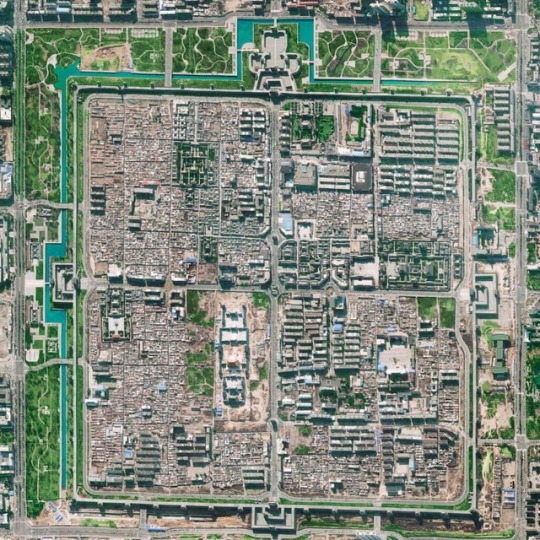

. Location | Datong, Shanxi province, China The original city wall in Datong was built in 1372. It was 14 meters high, had 4 main gates, 4 turrets and 46 watch towers. The ancient city used to be one of the nine military towns along the Great Wall of China. The industrialisation however damaged or destroyed some of its old buildings and thus its history. If planners and developers in Datong had been more sensitive and respected its history, then Datong would perhaps still be as beautiful today. . Now, however, the municipality has initiated a restoration plan which has been going on for more several years. The plan has the intention of restoring the city walls similar to how it looked like in its glorious years. Moreover, Datong’s municipal government have started demolishing newer buildings in favor of replicating older ones. The city will thus shift its focus towards a historical tourism. . The formerly disordered urban planning in the city was an important fight for an upcoming Chinese historical revivalist movement. Supporters of urban regeneration have praised the movement for protecting the city’s traditional culture, giving the city a face-lift, and improving the environment and air quality. Critics, however, say that the movement is a waste of money and labor because they claim the restored buildings don’t live up to their former glory, and that the municipal government has failed to properly compensate and relocate displaced residents. . #datong #shanxiprovince #china #worldurbanplanning #urbanplanning #cityplanning #architecture #restoration #urbandesign #gridlayout #cityscape #citywalls #도시 #도시계획 #aerial #aerialview #drone #houses #大同 #다퉁 #중국 #city (at Datong)
#gridlayout#datong#china#도시계획#urbandesign#cityscape#도시#중국#urbanplanning#city#worldurbanplanning#shanxiprovince#citywalls#다퉁#restoration#aerialview#aerial#architecture#drone#houses#大同#cityplanning
24 notes
·
View notes