#information regarding antique
Text
#makes a silly lil poll that Idek if I’m gonna keep up#like in my heart. their genders r. antique clown doll. which is informative but not in this regard lol
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
mini love report — chrollo lucilfer

relationship health diagnosis — 70%*

symptom one — perceptive
this man is an information sponge. he notices everything. as a thief, he's accustomed to canvassing his surroundings. he'll have memorized the layout of your home by the second visit. it isn't for any nefarious purpose (probably), he's just always taking in information and cataloging it.
naturally, this sagacity extends to you. the normal cadence of your voice, mannerisms, favored words, and expressions; he'll know if something's bothering you before you realize it yourself. he isn't above using this knowledge of you for his own purposes. he'll gauge your body language and shift his approach to contentious topics. this is a lifelong habit of his that's difficult to break.
chrollo knows what people want to hear and he's used to utilizing that advantage. however, if you point this out, he'll try curbing the behavior. especially if you stress that it's his actual opinion you want to hear, not specially curated platitudes. he finds your desire for a candid approach almost... impressive? you'd rather disagree with his unfiltered thoughts than gloss over anything touchy. it bolsters his respect for you.
symptom two — enigmatic
there's a noticeable difference in what you know about each another. he knows the names of your co-workers, friends, and family members, as well as your hometown, job or school, etc... you can't say the same regarding him. he keeps his origins ambiguous. the way he frames his upbringing makes you feel guilty should you go prying. chrollo will tell you that he's an orphan who had a rough, destitute childhood, but that's about it. he could easily make up a story, but he doesn't like lying to you. he doesn't want the version of him that you love to be a false construct.
yes, there's the technicality of lying by omission. he doesn't get caught up on that detail.
symptom three — a lil lame
interestingly enough, the suave part of his brain starts acting up when he's known you long enough. this isn't to say that he loses his charm, but it stops being his go-to. now he just nerds out (he prefers the term 'discusses') whatever's caught his attention. there's this gleam in his eyes as he tells you about the history of a painting or antique, a childlike awe. he isn't elaborating to impress you with his knowledge, rather, he enjoys sharing his interests. especially since you care, you aren't just humoring him.
chrollo's emotions come out naturally when he's near you. it's subtle — a twitch of his eye if someone cuts you off, a light blush should you murmur his name while asleep. these simple forms of self-expression are foreign to him. he's used to playing roles, not the aftermath once the stage's curtains close. his corporeal form was all the evidence he had that he existed. lacking a sense of self invokes this numb, hollow feeling. you're his new, favorite proof that he's alive. his world's brighter with you in it.

primary area of concern
objectively speaking, chrollo's an ideal lover. he respects, cherishes, and admires you, altercations are rare. should disagreements occur, he never raises his voice or displays aggression. he'll hear you out and apologize should he feel he's in the wrong. he takes you out on dates, stares at you as if you were divinity incarnate whether you're wearing pajamas or a formal outfit. he's whipped and you both know it.
it's his immortality that keeps his score from being higher. he wouldn't ever hurt you, but his compassion for others is nonexistent. this unsightly side of him is hidden from your sight. at the end of the day, he's a murderer who experiences zero remorse for the pain he's inflicted upon others. he leads a double life. you won't ever completely know him.
selfishly, he doesn't want you to.

prognosis
everything hinges on chrollo preventing you from finding out about his illicit activities. luckily for him, subterfuge is his second nature. he rarely stresses about it. he has the manpower and resources necessary to make just about anything happen. if you're a civilian, the chances you'll uncover his identity on your own are next to nonexistent.
your future together is a priority to him — he doesn't take commitment lightly. you're likely the first person he's fallen in love with. if you'd have him, he'd want nothing more than to be your lifelong partner. marriage is a tradition he's never given much credence to. although, after meeting you, he understands the appeal. now it's a matter of finding a ring that matches your radiance...

*the universe has tried (and failed) to wrench you apart (0-20) your friends are praying that you'll break up (21-40) 'well it could/has be worse' bargaining mindset (41-60) a lil messiness as a treat (61-80) pure and wholesome (81-100)
443 notes
·
View notes
Text
The most important deity you've never heard of: the 3000 years long history of Nanaya

Being a major deity is not necessarily a guarantee of being remembered. Nanaya survived for longer than any other Mesopotamian deity, spread further away from her original home than any of her peers, and even briefly competed with both Buddha and Jesus for relevance. At the same time, even in scholarship she is often treated as unworthy of study. She has no popculture presence save for an atrocious, ill-informed SCP story which can’t get the most basic details right. Her claims to fame include starring in fairly explicit love poetry and appearing where nobody would expect her. Therefore, she is the ideal topic to discuss on this blog.
This is actually the longest article I published here, the culmination of over two years of research. By now, the overwhelming majority of Nanaya-related articles on wikipedia are my work, and what you can find under the cut is essentially a synthesis of what I have learned while getting there. I hope you will enjoy reading it as much as I enjoyed working on it.
Under the cut, you will learn everything there is to know about Nanaya: her origin, character, connections with other Mesopotamian deities, her role in literature, her cult centers… Since her history does not end with cuneiform, naturally the later text corpora - Aramaic, Bactrian, Sogdian and even Chinese - are discussed too. The article concludes with a short explanation why I see the study of Nanaya as crucial.
Dubious origins and scribal wordplays: from na-na to Nanaya
Long ago Samuel Noah Kramer said that “history begins in Sumer”. While the core sentiment was not wrong in many regards, in this case it might actually begin in Akkad, specifically in Gasur, close to modern Kirkuk. The oldest possible attestation of Nanaya are personal names from this city with the element na-na, dated roughly to the reign of Naram-Sin of Akkad, so to around 2250 BCE. It’s not marked in the way names of deities in personal names would usually be, but this would not be an isolated case.
The evidence is ultimately mixed. On one hand, reduplicated names like Nana are not unusual in early Akkadian sources, and -ya can plausibly be explained as a hypocoristic suffix. On the other hand, there is not much evidence for Nanaya being worshiped specifically in the far northeast of Mesopotamia in other periods. Yet another issue is that there is seemingly no root nan- in Akkadian, at least in any attested words.
The main competing proposal is that Nanaya originally arose as a hypostasis of Inanna but eventually split off through metaphorical mitosis, like a few other goddesses did, for example Annunitum. This is not entirely implausible either, but ultimately direct evidence is lacking, and when Nanaya pops up for the first time in history she is clearly a distinct goddess.
There are a few other proposals regarding Nanaya’s origin, but they are considerably weaker. Elamite has the promising term nan, “day” or “morning”, but Nanaya is entirely absent from the Old Elamite sources you’d expect to find her in if Mesopotamians imported her from the east. Therefore, very few authors adhere to this view. The hypothesis that she was an Aramaic goddess in origin does not really work chronologically, since Aramaic is not attested in the third millennium BCE at all. The less said about attempts to connect her to anything “Proto-Indo-European”, the better.
Like many other names of deities, Nanaya’s was already a subject of etymological speculation in antiquity. A late annotated version of the Weidner god list, tablet BM 62741, preserves a scribe’s speculative attempt at deriving it from the basic meaning of the sign NA, “to call”, furnished with a feminine suffix, A. Needless to say, like other such examples of scribal speculation, some of which are closer to playful word play than linguistics, it is unlikely to reflect the actual origin of the name.
Early history: Shulgi-simti, Nanaya’s earliest recorded #1 fan

A typical Ur III administrative tablet listing offerings to various deities (wikimedia commons)
The first absolutely certain attestations of Nanaya, now firmly under her full name, have been identified in texts from the famous archive from Puzrish-Dagan, modern Drehem, dated to around 2100 BCE. Much can be written about this site, but here it will suffice to say that it was a center of the royal administration of the Third Dynasty of Ur ("Ur III") responsible for the distribution of sacrificial animals.
Nanaya appears there in a rather unique context - she was one of the deities whose cults were patronized by queen Shulgi-simti, one of the wives of Shulgi, the successor of the dynasty’s founder Ur-Namma.
We do not know much about Shulgi-simti as a person - she did not write any official inscriptions announcing her preferred foreign policy or letters to relatives or poetry or anything else that typically can be used to gain a glimpse into the personal lives of Mesopotamian royalty. We’re not really sure where she came from, though Eshnunna is often suggested as her hometown. We actually do not even know what her original name was, as it is assumed she only came to be known as Shulgi-simti after becoming a member of the royal family. Tonia Sharlach suggested that the absence of information about her personal life might indicate that she was a commoner, and that her marriage to Shulgi was not politically motivated
The one sphere of Shulgi-simti’s life which we are incredibly familiar with are her religious ventures. She evidently had an eye for minor, foreign or otherwise unusual goddesses, such as Belet-Terraban or Nanaya.
She apparently ran what Sharlach in her “biography” of her has characterized as a foundation. It was tasked with sponsoring various religious celebrations. Since Shulgi-simti seemingly had no estate to speak of, most of the relevant documents indicate she procured offerings from a variety of unexpected sources, including courtiers and other members of the royal family. The scale of her operations was tiny: while the more official religious organizations dealt with hundreds or thousands of sacrificial animals, up to fifty or even seventy thousand sheep and goats in the case of royal administration, the highest recorded number at her disposal seems to be eight oxen and fifty nine sheep.
A further peculiarity of the “foundation” is that apparently there was a huge turnover rate among the officials tasked with maintaining it. It seems nobody really lasted there for much more than four years. There are two possible explanations: either Shulgi-simti was unusually difficult to work with, or the position was not considered particularly prestigious and was, at the absolute best, viewed as a stepping stone.
While the Shulgi-simti texts are the earliest evidence for worship of Nanaya in the Ur III court, they are actually not isolated. When all the evidence from the reigns of Shulgi and his successors is summarized, it turns out that she quickly attained a prominent role, as she is among the twelve deities who received the most offerings. However, her worship was seemingly limited to Uruk (in her own sanctuary), Nippur (in the temple of Enlil, Ekur) and Ur. Granted, these were coincidentally three of the most important cities in the entire empire, so that’s a pretty solid early section of a divine resume. She chiefly appears in two types of ceremonies: these tied to the royal court, or these mostly performed by or for women. Notably, a festival involving lamentations (girrānum) was held in her honor in Uruk.
To understand Nanaya’s presence in the two aforementioned contexts, and by extension her persistence in Mesopotamian religion in later periods, we need to first look into her character.
The character of Nanaya: eroticism, kingship, and disputed astral ventures

Corona Borealis (wikimedia commons)
Nanaya’s character is reasonably well defined in primary sources, but surprisingly she was almost entirely ignored in scholarship quite recently. The first study of her which holds up to scrutiny is probably Joan Goodnick Westenholz’s article Nanaya, Lady of Mystery from 1997. The core issue is the alleged interchangeability of goddesses. From the early days of Assyriology basically up to the 1980s, Nanaya was held to be basically fully interchangeable with Inanna. This obviously put her in a tough spot. Still, over the course of the past three decades the overwhelming majority of studies came to recognize Nanaya as a distinct goddess worthy of study in her own right. You will still stumble upon the occasional “Nanaya is basically Inanna”, but now this is a minority position. Tragically it’s not extinct yet, most recently I’ve seen it in a monograph published earlier this year.
With these methodological and ideological issues out of the way, let’s actually look into Nanaya’s character, as promised by the title of this section. Her original role was that of a goddess of love. It is already attested for her at the dawn of her history, in the Ur III period. Her primary quality was described with a term rendered as ḫili in Sumerian and kuzbu in Akkadian. It can be variously translated as “charm”, “luxuriance”, “voluptuousness”, “sensuality” or “sexual attractiveness”. This characteristic was highlighted by her epithet bēlet kuzbi (“lady of kuzbu”) and by the name of her cella in the Eanna, Eḫilianna. The connection was so strong that this term appears basically in every single royal inscription praising her. She was also called bēlet râmi, “lady of love”. Nanaya’s role as a love goddess is often paired with describing her as a “joyful” or “charming” deity.
It needs to be stressed that Nanaya was by no metric the goddess of some abstract, cosmic love or anything like that. Love incantations and prayers related to love are quite common, and give us a solid glimpse into this matter. Nanaya’s range of activity in them is defined pretty directly: she deals with relationships (and by extension also with matters like one-sided crushes or arguments between spouses), romance and with strictly sexual matters. For an example of a hymn highlighting her qualifications when it comes to the last category, see here. The text is explicit, obviously.
We can go deeper, though. There is also an incantation whose incipit at first glance leaves little to imagination:

However, the translator, Giole Zisa, notes there is some debate over whether it’s actually about having sex with Nanaya or merely about invoking her (and other deities) while having sex with someone else. A distinct third possibility is that she’s not even properly invoked but that “oh, Nanaya” is simply an exclamation of excitement meant to fit the atmosphere, like a specialized version of the mainstay of modern erotica dialogue, “oh god”.
While this romantic and sexual aspect of Nanaya’s character is obviously impossible to overlook, this is not all there was to her. She was also associated with kingship, as already documented in the Ur III period. She was invoked during coronations and mourning of deceased kings. In the Old Babylonian period she was linked to investiture by rulers of newly independent Uruk.
A topic which has stirred some controversy in scholarship is Nanaya’s supposed astral role. Modern authors who try to present Nanaya as a Venus deity fall back on rather faulty reasoning, namely asserting that if Nanaya was associated with Inanna and Inanna personified Venus, clearly Nanaya did too. Of course, being associated with Inanna does not guarantee the same traits. Shaushka was associated with her so closely her name was written with the logogram representing her counterpart quite often, and lacked astral aspects altogether.
No primary sources which discuss Nanaya as a distinct, actively worshiped deity actually link her with Venus. If you stretch it you will find some tidbits like an entry in a dictionary prepared by the 10th century bishop Hasan bar Bahlul, who inexplicably asserted Nanaya was the Arabic name of the planet Venus. As you will see soon, there isn’t even a possibility that this reflected a relic of interpretatio graeca. The early Mandaean sources, many of which were written when at least remnants of ancient Mesopotamian religion were still extant, also do not link Nanaya with Venus. Despite at best ambivalent attitude towards Mesopotamian deities, they show remarkable attention to detail when it comes to listing their cult centers, and on top of that Mesopotamian astronomy had a considerable impact on Mandaeism, so there is no reason not to prioritize them, as far as I am concerned.
As far as the ancient Mesopotamian sources themselves go, the only astral object with a direct connection to Nanaya was Corona Borealis (BAL.TÉŠ.A, “Dignity”), as attested in the astronomical compendium MUL.APIN. Note that this is a work which assigns astral counterparts to virtually any deity possible, though, and there is no indication this was a major part of Nanaya’s character. Save for this single instance, she is entirely absent from astronomical texts.
A further astral possibility is that Nanaya was associated with the moon. The earliest evidence is highly ambiguous: in the Ur III period festivals held in her honor might have been tied to phases of the moon, while in the Old Babylonian period a sanctuary dedicated to her located in Larsa was known under the ceremonial name Eitida, “house of the month”. A poem in which looking at her is compared to looking at the moon is also known. That’s not all, though. Starting with the Old Babylonian period, she could also be compared with the sun. Possibly such comparisons were meant to present her as an astral deity, without necessarily identifying her with a specific astral body. Michael P. Streck and Nathan Wasserman suggest that it might be optimal to simply refer to her as a “luminous” deity in this context. However, as you will see later it nonetheless does seem she eventually came to be firmly associated both with the sun and the moon.
Last but not least, Nanaya occasionally displayed warlike traits. It’s hardly major in her case, and if you tried hard enough you could turn any deity into a war deity depending on your political goals, though. I’d also place the incantation which casts her as one of the deities responsible for keeping the demon Lamashtu at bay here.
Nanaya in art
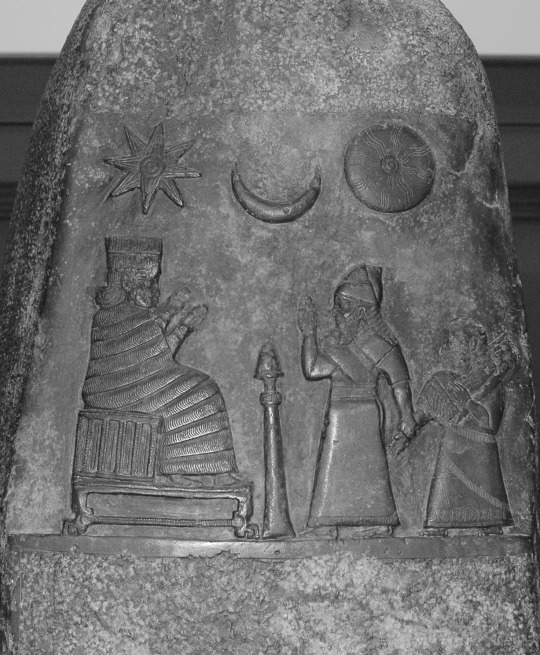

The oldest known depiction of Nanaya (wikimedia commons)
While Nanaya’s roles are pretty well defined, there surprisingly isn’t much to say about her iconography in Mesopotamian art.The oldest certain surviving depiction of her is rather indistinct: she’s wearing a tall headdress and a flounced robe. It dates to the late Kassite period (so roughly to 1200 BCE), and shows her alongside king Meli-Shipak (or maybe Meli-Shihu, reading remains uncertain) and his daughter Hunnubat-Nanaya. Nanaya is apparently invoked to guarantee that the prebend granted to the princess will be under divine protection. This is not really some unique prerogative of hers, perhaps she was just the most appropriate choice because Hunnubat-Nanaya’s name obviously reflects devotion to her.
The relief discussed above is actually the only depiction of Nanaya identified with certainty from before the Hellenistic period, surprisingly. We know that statues representing her existed, and it is hard to imagine that a popular, commonly worshiped deity was not depicted on objects like terracotta decorations and cylinder seals, but even if some of these were discovered, there’s no way to identify them with certainty. This is not unusual though, and ultimately there aren’t many Mesopotamian deities who can be identified in art without any ambiguity.
Nanaya in literature
As I highlighted in the section dealing with Nanaya’s character, she is reasonably well attested in love poetry. However, this is not the only genre in which she played a role.
A true testament to Nanaya’s prominence is a bilingual (Sumero-Akkadian) hymn composed in her honor in the first millennium BCE. It is written in the first person, and presents various other goddesses as her alternate identities. It is hardly unique, and similar compositions dedicated to Ishtar (Inanna), Gula, Ninurta and Marduk are also known.
Each strophe describes a different deity and location, but ends with Nanaya reasserting her actual identity with the words “still I am Nanaya”. Among the claimed identities included are both major goddesses in their own right (Inanna plus closely associated Annunitum and Ishara, Gula, Bau, Ninlil), goddesses relevant due to their spousal roles first and foremost (Damkina, Shala, Mammitum etc) and some truly unexpected, picks, the notoriously elusive personified rainbow Manzat being the prime example. Most of them had very little in common with Nanaya, so this might be less an attempt at syncretism, and more an elevation of her position through comparisons to those of other goddesses.
An additional possible literary curiosity is a poorly preserved myth which Wilfred G. Lambert referred to as “The murder of Anshar”. He argues that Nanaya is one of the two deities responsible for the eponymous act. I don't quite follow the logic, though: the goddess is actually named Ninamakalamma (“Lady mother of the land”), and her sole connection with Nanaya is that they occur in sequence in the unique god list from Sultantepe. Lambert saw this as a possible indication they are identical. There are no other attestations of this name, but ama kalamma does occur as an epithet of various goddesses, most notably Ninshubur. Given her juxtaposition with Nanaya in the Weidner god list - more on that later - wouldn’t it make more sense to assume it’s her? Due to obscurity of the text as far as I am aware nobody has questioned Lambert’s tentative proposal yet, though.
There isn’t much to say about the plot: Anshar, literally “whole heaven”, the father of Anu, presumably gets overthrown and might be subsequently killed. Something that needs to be stressed here to avoid misinterpretation: primordial deities such as Anshar were borderline irrelevant, and weren't really worshiped. They exist to fade away in myths and to be speculated about in elaborate lexical texts. There was no deposed cult of Anshar. Same goes for all the Tiamats and Enmesharras and so on.
Inanna and beyond: Nanaya and friends in Mesopotamian sources
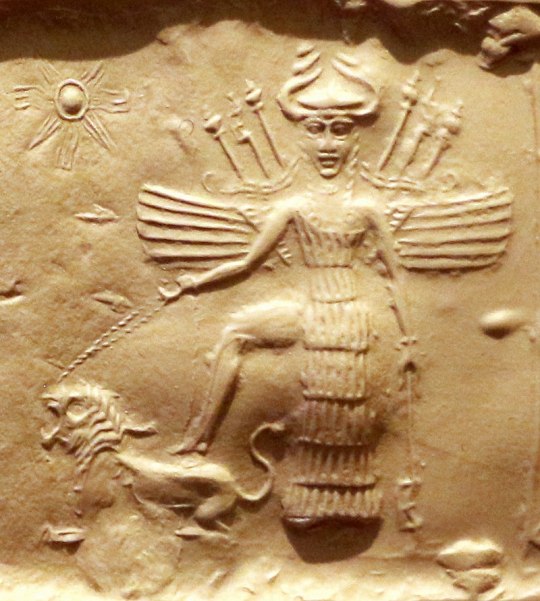

Inanna on a cylinder seal from the second half of the third millennium BCE (wikimedia commons)
Of course, Nanaya’s single most important connection was that to Inanna, no matter if we are to accept the view that she was effectively a hypostasis gone rogue or not. The relationship between them could be represented in many different ways. Quite commonly she was understood as a courtier or protegee of Inanna. A hymn from the reign of Ishbi-Erra calls her the “ornament of Eanna” (Inanna’s main temple in Uruk) and states she was appointed by Inanna to her position. References to Inanna as Nanaya’s mother are also known, though they are rare, and might be metaphorical. To my best knowledge nothing changed since Olga Drewnowska-Rymarz’s monograph, in which she notes she only found three examples of texts preserving this tradition. I would personally abstain from trying to read too deep into it, given this scarcity.
Other traditions regarding Nanaya’s parentage are better attested. In multiple cases, she “borrows” Inanna’s conventional genealogy, and as a result is addressed as a daughter of Sin (Nanna), the moon god. However, she was never addressed as Inanna’s sister: it seems that in cases where Sin and Nanaya are connected, she effectively “usurps” Inanna’s own status as his daughter (and as the sister of Shamash, while at it). Alternatively, she could be viewed as a daughter of Anu.
Finally, there is a peculiar tradition which was the default in laments: in this case, Nanaya was described as a daughter of Urash. The name in this context does not refer to the wife of Anu, though. The deity meant is instead a small time farmer god from Dilbat. To my best knowledge no sources place Nanaya in the proximity of other members of Urash’s family, though some do specify she was his firstborn daughter. To my best knowledge Urash had at least two other children, Lagamal (“no mercy”, an underworld deity whose gender is a matter of debate) and Ipte-bitam (“he opened the house”, as you can probably guess a divine doorkeeper). Nanaya’s mother by extension would presumably be Urash’s wife Ninegal, the tutelary goddess of royal palaces. There is actually a ritual text listing these three together.
In the Weidner god list Nanaya appears after Ninshubur. Sadly, I found no evidence for a direct association between these two. For what it’s worth, they did share a highly specific role, that of a deity responsible for ordering around lamma. This term referred to a class of minor deities who can be understood as analogous to “guardian angels” in contemporary Christianity, except places and even deities had their own lamma too, not just people. Lamma can also be understood at once as a class of distinct minor deities, as the given name of individual members of it, and as a title of major deities. In an inscription of Gudea the main members of the official pantheon are addressed as “lamma of all nations”, by far one of my favorite collective terms of deities in Mesopotamian literature.
A second important aspect of the Weidner god list is placing Nanaya right in front of Bizilla. The two also appear side by side in some offering lists and in the astronomical compendium MUL.APIN, where they are curiously listed as members of the court of Enlil. It seems that like Nanaya, she was a goddess of love, which is presumably reflected by her name. It has been variously translated as “pleasing”, “loving” or as a derivative of the verb “to strip”. An argument can be made that Bizilla was to Nanaya what Nanaya was to Inanna. However, she also had a few roles of her own. Most notably, she was regarded as the sukkal of Ninlil. She may or may not also have had some sort of connection to Nungal, the goddess of prisons, though it remains a matter of debate if it’s really her or yet another, accidentally similarly named, goddess.
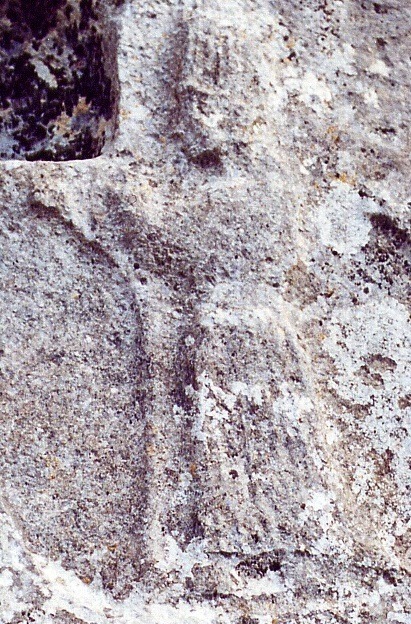

An indistinct Hurro-Hittite depiction of Ishara from the Yazilikaya sanctuary (wikimedia commons)
In love incantations, Nanaya belonged to an informal group which also included Inanna, Ishara, Kanisurra and Gazbaba. I do not think Inanna’s presence needs to be explained. Ishara had an independent connection with Inanna and was a multi-purpose deity to put it very lightly; in the realm of love she was particularly strongly connected with weddings and wedding nights. Kanisurra and Gazbaba warrant a bit more discussion, because they are arguably Nanaya’s supporting cast first and foremost.
Gazbaba is, at the core, seemingly simply the personification of kuzbu. Her name had pretty inconsistent orthography, and variants such as Kazba or Gazbaya can be found in primary sources too. The last of them pretty clearly reflects an attempt at making her name resemble Nanaya’s. Not much can be said about her individual character beyond the fact she was doubtlessly related to love and/or sex. She is described as the “grinning one” in an incantation which might be a sexual allusion too, seeing as such expressions are a mainstay of Akkadian erotic poetry.
Kanisurra would probably win the award for the fakest sounding Mesopotamian goddess, if such a competition existed. Her name most likely originated as a designation of the gate of the underworld, ganzer. Her default epithet was “lady of the witches” (bēlet kaššāpāti). And on top of that, like Nanaya and Gazbaba she was associated with sex. She certainly sounds more like a contemporary edgy oc of the Enoby Dimentia Raven Way variety than a bronze age goddess - and yet, she is completely genuine.
It is commonly argued Kanisurra and Gazbaba were regarded as Nanaya’s daughters, but there is actually no direct evidence for this. In the only text where their relation to Nanaya is clearly defined they are described as her hairdressers, rather than children.
While in some cases the love goddesses appear in love incantations in company of each other almost as if they were some sort of disastrous polycule, occasionally Nanaya is accompanied in them by an anonymous spouse. Together they occur in parallel with Inanna and Dumuzi and Ishara and Almanu, apparently a (accidental?) deification of a term referring to someone without family obligations.
There is only one Old Babylonian source which actually assigns a specific identity to Nanaya’s spouse, a hymn dedicated to king Abi-eshuh of Babylon. An otherwise largely unknown god Muati (I patched up his wiki article just for the sake of this blog post) plays this role here.
The text presents a curious case of reversal of gender roles: Muati is asked to intercede with Nanaya on behalf of petitioners. Usually this was the role of the wife - the best known case is Aya, the wife of Shamash, who is implored to do just that by Ninsun in the standard edition of the Epic of Gilgamesh. It’s also attested for goddesses such as Laz, Shala, Ninegal or Ninmug… and in the case of Inanna, for Ninshubur.

A Neo-Assyrian statue of Nabu on display in the Iraq Museum (wikimedia commons)
Marten Stol seems to treat Muati and Nabu as virtually the same deity, and on this basis states that Nanaya was already associated with the latter in the Old Babylonian period, but this seems to be a minority position. Other authors pretty consistently assume that Muati was a distinct deity at some point “absorbed” by Nabu.
The oldest example of pairing Nanaya with Nabu I am aware of is an inscription dated to the reign of Marduk-apla-iddina I, so roughly to the first half of the twelfth century BCE. The rise of this tradition in the first millennium BCE was less theological and more political. With Babylon once again emerging as a preeminent power, local theologies were supposed to be subordinated to the one followed in the dominant city. Which, at the time, was focused on Nabu, Marduk and Zarpanit. Worth noting that Nabu also had a spouse before, Tashmetum (“reconciliation”). In the long run she was more or less ousted by Nanaya from some locations, though she retained popularity in the north, in Assyria. She is not exactly the most thrilling deity to discuss. I will confess I do not find the developments tied to Nanaya and Nabu to be particularly interesting to cover, but in the long run they might have resulted in Nanaya acquiring probably the single most interesting “supporting cast member” she did not share with Inanna, so we’ll come back to this later.
Save for Bizilla, Nanaya generally was not provided with “equivalents” in god lists. I am only aware of one exception, and it’s a very recent discovery. Last year the first ever Akkadian-Amorite bilingual lists were published. This is obviously a breakthrough discovery, as before Amorite was largely known just from personal names despite being a vernacular language over much of the region in the bronze age, but only one line is ultimately of note here. In a section of one of the lists dealing with deities, Nanaya’s Amorite counterpart is said to be Pidray. This goddess is otherwise almost exclusively known from Ugarit. This of course fits very well with the new evidence: recent research generally stresses that Ugarit was quintessentially an Amorite city (the ruling house even claimed descent from mythical Ditanu, who is best known from the grandiose fictional genealogies of Shamshi-Adad I and the First Dynasty of Babylon).
Sadly, we do not know how the inhabitants of Ugarit viewed Nanaya. A trilingual version of the Weidner list, with the original version furnished with columns listing Ugaritic and Hurrian counterparts of each deity, was in circulation, but the available copies are too heavily damaged to restore it fully. And to make things worse, much of it seems to boil down to scribal wordplay and there is no guarantee all of the correspondences are motivated theologically. For instance, the minor Mesopotamian goddess Imzuanna is presented as the counterpart of Ugaritic weather god Baal because her name contains a sign used as a shortened logographic writing of the latter. An even funnier case is the awkward attempt at making it clear the Ugaritic sun deity Shapash, who was female, is not a lesbian… by making Aya male. Just astonishing, really.
The worship of Nanaya

A speculative reconstruction of Ur III Uruk with the Eanna temple visible in the center (Artefacts — Scientific Illustration & Archaeological Reconstruction; reproduced here for educational purposes only, as permitted)
Rather fittingly, as a deity associated with Inanna, Nanaya was worshiped chiefly in Uruk. She is also reasonably well attested in the inscriptions of the short-lived local dynasty which regained independence near the end of the period of domination of Larsa over Lower Mesopotamia. A priest named after her, a certain Iddin-Nanaya, for a time served as the administrator of her temple, the Enmeurur, “house which gathers all the me,” me being a difficult to translate term, something like “divine powers”. The acquisition of new me is a common topic in Mesopotamian literature, and in compositions focused on Inanna in particular, so it should not be surprising to anyone that her peculiar double seemingly had similar interests.
In addition to Uruk, as well as Nippur and Ur, after the Ur III period Nanaya spread to multiple other cities, including Isin, Mari, Babylon and Kish. However, she is probably by far the best attested in Larsa, where she rose to the rank of one of the main deities, next to Utu, Inanna, Ishkur and Nergal. She had her own temple, the Eshahulla, “house of a happy heart”. In local tradition Inanna got to keep her role as an “universal” major goddess and her military prerogatives, but Nanaya overtook the role of a goddess of love almost fully. Inanna’s astral aspect was also locally downplayed, since Venus was instead represented in the local pantheon by closely associated, but firmly distinct, Ninsianna. This deity warrants some more discussion in the future just due to having a solid claim to being one of the first genderfluid literary figures in history, but due to space constraints this cannot be covered in detail here.
A later inscription from the same city differentiates between Nanaya and Inanna by giving them different epithets: Nanaya is the “queen of Uruk and Eanna” (effectively usurping Nanaya’s role) while Inanna is the “queen of Nippur” (that’s actually a well documented hypostasis of her, not to be confused with the unrelated “lady of Nippur”).
Uruk was temporarily abandoned in the late Old Babylonian period, but that did not end Nanaya’s career. Like Inanna, she came to be temporarily relocated to Kish. It has been suggested that a reference to her residence in “Kiššina” in a Hurro-Hittite literary text, the Tale of Appu, reflects her temporary stay there.
The next centuries of Nanaya are difficult to reconstruct due to scarce evidence, but it is clear she continued to be worshiped in Uruk. By the Neo-Babylonian period she was recognized as a member of an informal pentad of the main deities of the city, next to Inanna, Urkayitu, Usur-amassu and Beltu-sa-Resh. Two of them warrant no further discussion: Urkayitu was most likely a personification of the city, and Beltu-sa-Resh despite her position is still a mystery to researchers.
Usur-amassu, on the contrary, is herself a fascinating topic. First attestations of this deity, who was seemingly associated with law and justice (a pretty standard concern), come back to the Old Babylonian period. At this point, Usur-amassu was clearly male, which is reflected by the name. He appears in the god list An = Anum as a son of the weather deity couple par excellence, Adad (Ishkur) and Shala. However, by the early first millennium BCE Usur-amassu instead came to be regarded as female - without losing the connection to her parents. She did however gain a connection to Inanna, Nanaya and Kanisurra, which she lacked earlier. How come remains unknown. Most curiously her name was not modified to reflect her new gender, though she could be provided with a determinative indicating it. This recalls the case of Lagamal in the kingdom of Mari some 800 years earlier.
The end of the beginning: Nanaya under Achaemenids and Seleucids

Trilingual (Persian, Elamite and Akkadian) inscription of the first Achamenid ruler of Mesopotamia, Cyrus (wikimedia commons)
After the fall of the Neo-Babylonian Empire Mesopotamia ended up under Achaemenid control, which in turn was replaced by the Seleucids. Nanaya flourished through both of these periods. In particular, she attained considerable popularity among Arameans. While they almost definitely first encountered her in Uruk, she quickly came to be venerated by them in many distant locations, like Palmyra, Hatra and Dura Europos in Syria. She even appears in a single Achaemenid Aramaic papyrus discovered in Elephantine in Egypt. It indicates that she was worshiped there by a community which originated in Rash, an area east to the Tigris. As a curiosity it’s worth mentioning the same source is one of the only attestations of Pidray from outside Ugarit. I do not think this has anything to do with the recently discovered connection between her and Nanaya… but you may never know.
Under the Seleucids, Nanaya went through a particularly puzzling process of partial syncretism. Through interpretatio graeca she was identified with… Artemis. How did this work? The key to understanding this is the fact Seleucids actually had a somewhat limited interest in local deities. All that was necessary was to find relatively major members of the local pantheon who could roughly correspond to the tutelary deities of their dynasty: Zeus, Apollo and Artemis. Zeus found an obvious counterpart in Marduk (even though Marduk was hardly a weather god). Since Nabu was Marduk’s son, he got to be Apollo. And since Nanaya was the most major goddess connected to Nabu, she got to be Artemis. It really doesn’t go deeper than that.
For what it’s worth, despite the clear difference in character this newfound association did impact Nanaya in at least one way: she started to be depicted with attributes borrowed from Artemis, namely a bow and a crescent. Or perhaps these attributes were already associated with her, but came to the forefront because of the new role. The Artemis-like image of Nanaya as an archer is attested on coins, especially in Susa, yet another city where she attained considerable popularity.
Leaving Mesopotamia: Nanaya and the death of cuneiform

A Parthian statue of Nanaya with a crescent diadem (Louvre; reproduced here for educational purposes only. Identification follows Andrea Sinclair's proposal)
The Seleucid dynasty was eventually replaced by the Parthians. This period is often considered a symbolic end of ancient Mesopotamian religion in the strict sense. Traditional religious institutions were already slowly collapsing in Achaemenid and Seleucid times as the new dynasties had limited interest in royal patronage. Additionally, cuneiform fell out of use, and by the end of the first half of the first millennium CE the art of reading and writing it was entirely lost. This process did not happen equally quickly everywhere, obviously, and some deities fared better than others in the transitional period before the rise of Christianity and Islam as the dominant religions across the region. Nanaya was definitely one of them, at least for a time.
In Parthian art Nanaya might have developed a distinct iconography: it has been argued she was portrayed as a nude figure wearing only some jewelry (including what appears to be a navel piercing and a diadem with a crescent. The best known example is probably this standing figure, one of my all time favorite works of Mesopotamian art:
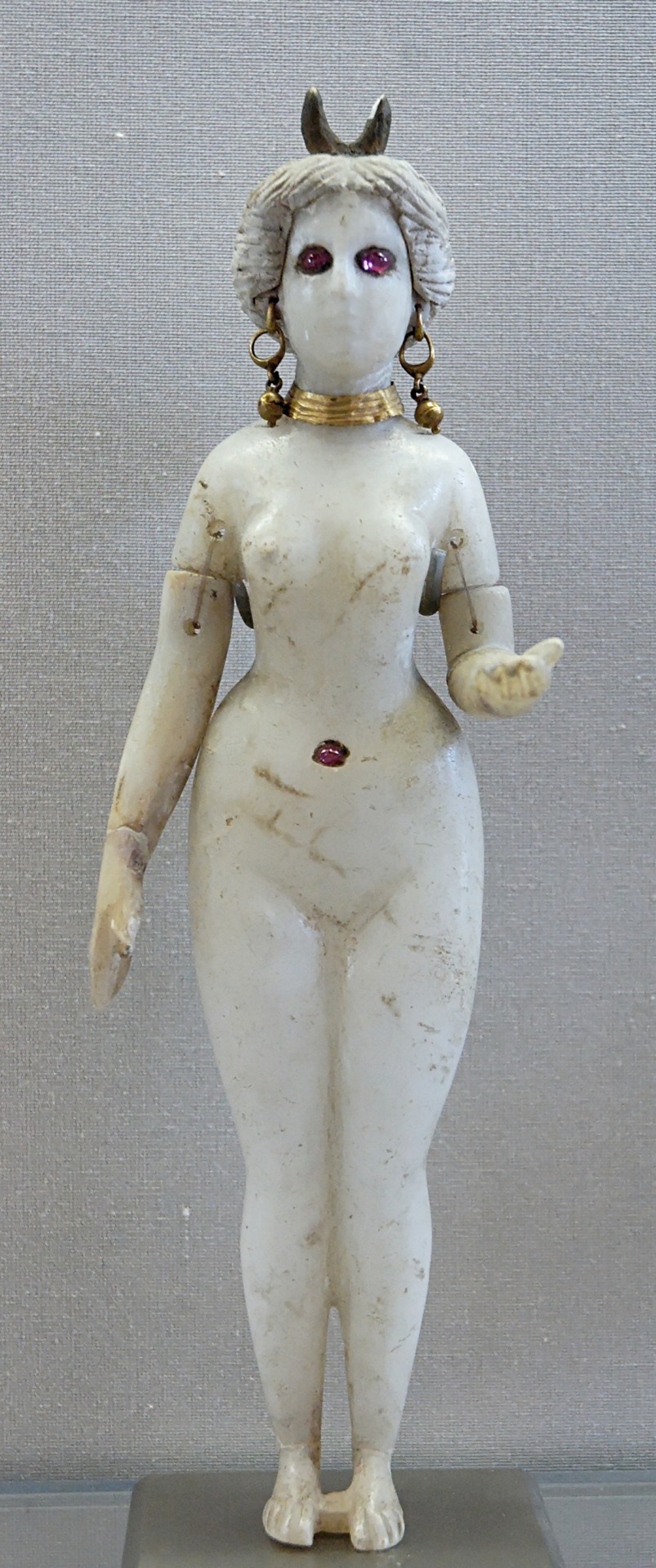

Parthian Nanaya (wikimedia commons; identification courtesy of the Louvre website and J. G. Westenholz)
For years Wikipedia had this statue mislabeled as “Astarte” which makes little sense considering it comes from a necropolis near Babylon. There was also a viral horny tweet which labeled it as “Asherah” a few months ago (I won’t link it but I will point out in addition to getting the name wrong op also severely underestimated the size). This is obviously even worse nonsense both on spatial and temporal grounds. Even if the biblical Asherah was ever an actual deity like Ugaritic Athirat and Mesopotamian Ashratum, it is highly dubious she would still be worshiped by the time this statue was made. It’s not even certain she ever was a deity, though. Cognate of a theonym is not automatically a theonym itself, and the Ugaritic texts and the Bible, even if they share some topoi, are separated by centuries and a considerable distance. This is not an Asherah post though, so if this is a topic which interests you I recommend downloading Steve A. Wiggins’ excellent monograph A Reassessment of Asherah: With Further Considerations of the Goddess.
The last evidence for the worship of Nanaya in Mesopotamia is a Mandaean spell from Nippur, dated to the fifth or sixth century CE. However, at this point Nanaya must have been a very faint memory around these parts, since the figure designated by this name is evidently male in this formula. That was not the end of her career, though. The system of beliefs she originated and thrived in was on its way out, but there were new frontiers to explore.
A small disgression is in order here: be INCREDIBLY wary of claims about the survival of Mesopotamian tradition in Mesopotamia itself past the early middle ages. Most if not all of these come from the writing of Simo Parpola, who is a 19th century style hyperdiffusionist driven by personal religious beliefs based on gnostic christianity, which he believes was based on Neo-Assyrian state religion, which he misinterprets as monotheism, or rather proto-christianity specifically (I wish I was making this up). I personally do not think a person like that should be tolerated in serious academia, but for some incomprehensible reason that isn’t the case.
New frontiers: Nanaya in Bactria
The key to Nanaya’s extraordinarily long survival wasn’t the dedication to her in Mesopotamia, surprisingly. It was instead her introduction to Bactria, a historical area in Central Asia roughly corresponding to parts of modern Afghanistan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. The early history of this area is still poorly known, though it is known that it was one of the “cradles of civilization” not unlike Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley or Mesoamerica. The so-called “Oxus civilization” or “Bactria-Margiana Archaeological Complex” flourished around 2500-1950 BCE (so roughly contemporarily with the Akkadian and Ur III empires in Mesopotamia). It left behind no written records, but their art and architecture are highly distinctive and reflect great social complexity.
I sadly can’t spent much time discussing them here though, as they are completely irrelevant to the history of Nanaya (there is a theory that she was already introduced to the east when BMAC was extant but it is incredibly implausible), so I will limit myself to showing you my favorite related work of art, the “Bactrian princess”:
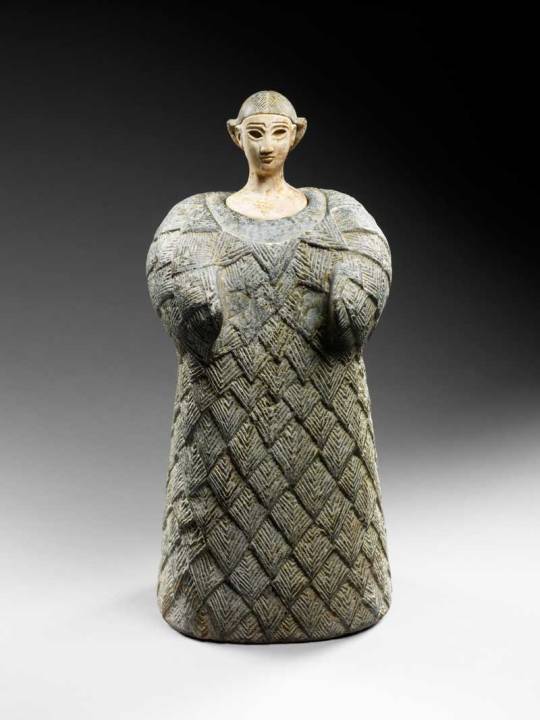

Photo courtesy of Louvre Abu Dhabi, reproduced here for educational purposes only.
By late antiquity, which is the period we are concerned with here, BMAC was long gone, and most of the inhabitants of Bactria spoke Bactrian, an extinct Iranian language. How exactly they were related to their BMAC forerunners is uncertain. Their religious beliefs can be compared to Zoroastrianism, or rather with its less formalized forerunners followed by most speakers of Iranian languages before the rise of Zoroaster. However, there were many local peculiarities. For example, the main deity was the personified river Oxus, not Ahura Mazda. Whether this was a relic of BMAC religion is impossible to tell.We do not know exactly when the eastward transfer of Nanaya to Bactria happened. The first clear evidence for her presence in central Asia comes from the late first century BCE, from the coins of local rulers, Sapadbizes and Agesiles. It is possible that her depictions on coinage of Mesopotamian and Persian rulers facilitated her spread. Of course, it’s also important to remember that the Aramaic script and language spread far to the east in the Achaemenid period already, and that many of the now extinct Central Asian scripts were derived from it (Bactrian was written with the Greek script, though). Doubtlessly many now lost Aramaic texts were transferred to the east.
There’s an emerging view that for unclear reasons, under the Achaemenids Mesopotamian culture as a whole had unparalleled impact on Bactria. The key piece of evidence are Bactrian temples, which often resemble Mesopotamian ones. Therefore, perhaps we should be wondering not why Nanaya spread from Mesopotamia to Central Asia, but rather why there were no other deities who did, for the most part. That is sadly a question I cannot answer. Something about Nanaya simply made her uniquely appealing to many groups at once.
While much about the early history of Nanaya in Central Asia is a mystery, it is evident that with time she ceased to be viewed as a foreign deity. For the inhabitants of Bactria she wasn’t any less “authentically Iranian” than the personified Oxus or their versions of the conventional yazatas like Sraosha. Frequently arguments are made that Nanaya’s widespread adoption and popularity could only be the result of identification between her and another deity.Anahita in particular is commonly held to be a candidate. However, as stressed by recent studies there’s actually no evidence for this.
What is true is that Anahita is notably missing from the eastern Iranian sources, despite being prominent in the west from the reign of the Achaemenid emperor Artaxerxes II onward. However, it is clear that not all yazatas were equally popular in each area - pantheons will inevitably be localized in each culture. Furthermore, Anahita’s character has very little in common with Nanaya save for gender. Whether we are discussing her early not quite Zoroastrian form the Achaemenid public was familiar with or the contemporary yazata still relevant in modern Zoroastrianism, the connection to water is the most important feature of her. Nanaya didn’t have such a role in any culture.
Recently some authors suggested a much more obvious explanation for Anahita’s absence from the eastern Iranian pantheon(s). As I said, eastern Iranian communities venerated the river Oxus as a deity (or as a yazata, if you will). He was the water god par excellence, and in Bactria also the king of the gods. It is therefore quite possible that Anahita, despite royal backing from the west, simply couldn’t compete with him. Their roles overlapped more than the roles of Anahita and Nanaya. I am repeating myself but the notion of interchangeability of goddesses really needs to be distrusted almost automatically, no matter how entrenched it wouldn’t be. While we’re at it, the notion of alleged interchangeability between Anahita and Ishtar is also highly dubious, but that’s a topic for another time.

Nana (Nanaya) on a coin of Kanishka (wikimedia commons)
Nanaya experienced a period of almost unparalleled prosperity with the rise of the Kushan dynasty in Bactria. The Kushans were one of the groups which following Chinese sources are referred to as Yuezhi. They probably did not speak any Iranian language originally, and their origin is a matter of debate. However, they came to rule over a kingdom which consisted largely of areas inhabited by speakers of various Iranian languages, chiefly Bactrian. Their pantheon, documented in royal inscriptions and on coinage, was an eerie combination of mainstays of Iranian beliefs like Sraosha and Mithra and some unique figures, like Oesho, who was seemingly the reflection of Hindu Shiva. Obviously, Nanaya was there too, typically under the shortened name Nana.
The most famous Kushan ruler, emperor Kanishka, in his inscription from Rabatak states that kingship was bestowed upon him by “Nana and all the gods”. However, we do not know if the rank assigned to her indicates she was the head of the dynastic pantheon, the local pantheon in the surrounding area, or if she was just the favorite deity of Kanishka. Same goes for the rank of numerous other deities mentioned in the rest of the inscription. Her apparent popularity during Kanishka’s reign and beyond indicates her role should not be downplayed, though.
The coins of Kanishka and other Bactrian art indicate that a new image of Nanaya developed in Central Asia. The Artemis-like portrayals typical for Hellenistic times continue to appear, but she also started to be depicted on the back of a lion. There is only one possible example of such an image from the west, a fragmentary relief from Susa, and it’s roughly contemporary with the depictions from Bactria. While it is not impossible Nanaya originally adopted the lion association from one of her Mesopotamian peers, it is not certain how exactly this specific type of depictions originally developed, and there is a case to be made that it owed more to the Hellenistic diffusion of iconography of deities such as Cybele and Dionysus, who were often depicted riding on the back of large felines.
The lunar symbols are well attested in the Kushan art of Nanaya too. Most commonly, she’s depicted wearing a diadem with a crescent. However, in a single case the symbol is placed behind her back. This is an iconographic type which was mostly associated with Selene at first, but in the east it was adopted for Mah, the Iranian personification of the moon. I’d hazard a guess that’s where Nanaya borrowed it from - more on that later.
The worship of Nanaya survived the fall of the Kushan dynasty, and might have continued in Bactria as late as in the eighth century. However, the evidence is relatively scarce, especially compared with yet another area where she was introduced in the meanwhile.
Nanaya in Sogdia: new home and new friends

A Sogdian depiction of Nanaya from Bunjikat (wikimedia commons)
Presumably from Bactria, Nanaya was eventually introduced to Sogdia, its northern neighbor. I think it’s safe to say this area effectively became her new home for the rest of her history.
Like Bactrians, the Sogdians also spoke an eastern Iranian language, Sogdian. It has a direct modern descendant, Yaghnobi, spoken by a small minority in Tajikistan. The religions Sogdians adhered to is often described as a form of Zoroastrianism, especially in older sources, but it would appear that Ahura Mazda was not exactly the most popular deity. Their pantheon was seemingly actually headed by Nanaya. Or, at the very least, the version of it typical for Samarkand and Panijkant, since there’s a solid case to be made for local variety in the individual city-states which made up Sogdia. It seems that much like Mesopotamians and Greeks centuries before them, Sogdians associated specific deities with specific cities, and not every settlement necessarily venerated each deity equally (or at all). Nanaya's remarkable popularity is reflected by the fact the name Nanaivandak, "servant of Nanaya", is one of the most common Sogdian names in general.
It is agreed that among the Sogdians Panjikant was regarded as Nanaya’s cult center. She was referred to as “lady” of this city. At one point, her temple located there was responsible for minting the local currency. By the eighth century, coins minted there were adorned with dedications to her - something unparalleled in Sogdian culture, as the rest of coinage was firmly secular. This might have been an attempt at reasserting Sogdian religious identity in the wake of the arrival of Islam in Central Asia.
Sogdians adopted the Kushan iconography of Nanaya, though only the lion-mounted version. The connection between her and this animal was incredibly strong in Sogdian art, with no other deity being portrayed on a similar mount. There were also innovations - Nanaya came to be frequently portrayed with four arms. This reflects the spread of Buddhism through central Asia, which brought new artistic conventions from India. While the crescent symbol can still be found on her headwear, she was also portrayed holding representations of the moon and the sun in two of her hands.
Sometimes the solar disc and lunar orb are decorated with faces, which has been argued to be evidence that Nanaya effectively took over the domains of Mah and Mithra, who would be the expected divine identities of these two astral bodies. She might have been understood as controlling the passage of night and day. It has also been pointed out that this new iconographic type is the natural end point of the evolution of her astral role.
Curiously, while no such a function is attested for Nanaya in Bactria, in Sogdia she could be sometimes regarded as a warlike deity. This is presumably reflected in a painting showing her and an unidentified charioteer fighting demons.

The "Sogdian Deities" painting from Dunhuang, a possible depiction of Nanaya and her presumed spouse Tish (wikimedia commons)
Probably the most fascinating development regarding Nanaya in Sogdia was the development of an apparent connection between her and Tish. This deity was the Sogdian counterpart of one of the best known Zoroastrian yazatas, Tishtrya, the personification of Sirius. As described in the Tištar Yašt, the latter is a rainmaking figure and a warlike protector who keeps various nefarious forces, such as Apaosha, Duzyariya and the malign “worm stars” (comets), at bay. Presumably his Sogdian counterpart had a similar role.
While this is not absolutely certain, it is generally agreed that Nanaya and Tish were regarded as a couple in central Asia (there’s a minority position she was instead linked with Oesho, though). Most likely the fact that in Achaemenid Persia Tishtrya was linked with Nabu (and by extension with scribal arts) has something to do with this. There is a twist to this, though.
While both Nabu and the Avestan Tishtrya are consistently male, in Bactria and Sogdia the corresponding deity’s gender actually shows a degree of ambiguity. On a unique coin of Kanishka, Tish is already portrayed as a feminine figure distinctly similar to Greek Artemis - an iconographic type which normally would be recycled for Nanaya. There’s also a possibility that a feminine, or at least crossdressing, version of Tish is portrayed alongside Nanaya on a painting from Dunhuang conventionally referred to as “Sogdian Daēnās” or “Sogdian Deities”, but this remains uncertain. If this identification is correct, it indicates outright interchange of attributes between them and Nanaya was possible.
The final frontier: Nanaya and the Sogdian diaspora in China
Sogdians also brought Nanaya with them to China, where many of them settled in the Six Dynasties and Tang periods. An obviously Sinicized version of her, accompanied by two attendants of unknown identity, is portrayed on a Sogdian funerary couch presently displayed in the Miho Museum.

Nanaya (top) on a relief from the Miho funerary couch (Miho Museum; reproduced here for educational purposes only)
For the most part the evidence is limited to theophoric names, though. Due to unfamiliarity with Sogdian religious traditions and phonetic differences between the languages there was no consistent Chinese transcription of Nanaya’s name. I have no clue if Chinese contemporaries of the Sogdians were always aware of these elements in personal names referred to a deity. There is a fringe theory that Nanaya was referred to as Nantaihou (那那女主, “queen Nana”) in Chinese. However, the evidence is apparently not compelling, and as I understand the theory depends in no small part on the assertion that a hitherto unattested alternate reading of one of the signs was in use on the western frontiers of China in the early first millennium CE. The alleged Nantaihou is therefore most likely a misreading of a reference to a deceased unnamed empress dowager venerated through conventional ancestor worship, as opposed to Nanaya.
Among members of the Sogdian diaspora, in terms of popularity Nanaya was going head to head with Jesus and Buddha. The presence of the latter two reflected the adoption of, respectively, Manichaeism and Buddhism. Manicheans seemingly were not fond of Nanaya, though, and fragments of a polemic against her cult have been identified. It seems ceremonies focused on lamentations were the main issue for the Manichaeans. Sadly there doesn’t seem to be any worthwhile study of possible Mesopotamian influence on that - the only one I found is old and confuses Nanaya with Inanna.
We do not have much of an idea how Buddhists viewed Nanaya, though it is worth noting a number of other Sogdian deities were incorporated into the local form of Mahayana (unexpectedly, one of them was Zurvan). It has also been argued that a Buddhist figure, Vreshman (Vaisravana) was incorporated into Nanaya’s entourage.
Nanaya might additionally be depicted in a painting showing Buddha’s triumph over Mara from Dunhuang. Presumably her inclusion would reflect the well attested motif of local deities converting to Buddhism. It was a part of the Buddhist repertoire from the early days of this religion and can be found in virtually every area where this religion ever spread. Nanaya is once again in elevated company here, since other figures near her have been tentatively interpreted as Shiva, Vishnu, Kartikeya and… Zoroaster.

Buddha conquering Mara (maravijaya) on a painting from Dunhuang (wikimedia commons)

zoom in on a possible depiction of Nanaya next to a demon suspiciously similar to Tove Jansson’s Fillyjonk
To my best knowledge, the last absolutely certain attestation of Nanaya as an actively worshiped deity also comes from the western frontier of China. A painting from Dandan Oilik belonging to the artistic tradition of the kingdom of Khotan shows three deities from the Sogdian pantheon: the enigmatic Āδβāγ (“highest god”; interpreted as either Indra, Ahura Mazda or a combination of them both) on the left, Weshparkar (a later version of Kushan Oesho) on the right and Nanaya in the center. It dates to the ninth or tenth century.

Nanaya (center) on the Dandan Oilik painting (wikimedia commons)
We will probably never know what Nanaya’s last days were like, though it is hard to imagine she retained much relevance with the gradual disappearance of Sogdian culture both in Sogdia and in China in the wake of, respectively, the rise of Islam in Central Asia and the An Lushan rebellion respectively. Her history ultimately most likely ended with a whimper rather than a bang.
Conclusions and reflections
Obviously, not everything about Nanaya could be covered in this article - there is enough material to warrant not one, but two wiki articles (and I don't even think they are extensive enough yet). I hope I did nonetheless manage to convey what matters: she was the single most enduring Mesopotamian deity who continued to be actually worshiped. She somehow outlived Enlil, Marduk, Nergal and even Inanna, and spread further than any of them ever did.
It does not seem like her persistence was caused by some uniquely transcendent quality, and more to a mix of factors we will never really fully understand and pure luck. She is a far cry from the imaginary everlasting universal goddesses such longevity was attributed to by many highly questionable authors in the past, from Frazer to Gimbutas. Quite the opposite, once you look into the texts focused on her she comes across as sort of pathetic. After all, most of them are effectively ancient purple prose.
And yet, this is precisely why I think Nanaya matters. To see how an author approaches her is basically a litmus test of trustworthiness - I wish I was kidding but this “Nanaya method” works every time. To even be able to study her history, let alone understand it properly, one has to cast away most of the dreadful trends which often hindered scholarship of ancient deities, and goddesses in particular, in the past. The interchangeability of goddesses; the Victorian mores and resulting notion that eroticism must be tied to fertility; the weird paradigms about languages neatly corresponding to religions; and many others. And if nothing else, this warrants keeping the memory of her 3000 years long history alive through scholarship (and, perhaps, some media appearances).
Bibliography
Julia M. Asher-Greve & Joan Goodnick Westenholz, Goddesses in Context: On Divine Powers, Roles, Relationships and Gender in Mesopotamian Textual and Visual Sources (2013)
Paul-Alain Beaulieu, The Pantheon of Uruk During the Neo-Babylonian Period (2003)
idem, Nabû and Apollo: The Two Faces of Seleucid Religious Policy in: Orient und Okzident in Hellenistischer Zeit (2014)
Matteo Compareti, Nana and Tish in Sogdiana (2017)
idem, The So-Called "Pelliot Chinois 4518.24". Illustrated Document from Dunhuang and Sino-Sogdian Iconographical Contacts (2021)
Olga Drewnowska-Rymarz, Mesopotamian Goddess Nanāja (2008)
Benjamin R. Foster, Before the Muses: an Anthology of Akkadian Literature (2005)
Andrew R. George & Manfred Krebernik, Two Remarkable Vocabularies: Amorite-Akkadian Bilinguals! (2022)
Valerie Hansen, Kageyama Etsuko & Yutaka Yoshida, The Impact of the Silk Road Trade on a Local Community: The Turfan Oasis, 500-800 in: Les sogdiens en Chine (2005)
Wilfred G. Lambert, Babylonian Creation Myths (2013)
Enrico Marcato, An Aramaic Incantation Bowl and the Fall of Hatra (2020)
Christa Müller-Kessler & Karlheinz Kessler, Spätbabylonische Gottheiten in spätantiken mandäischen Texten (1999)
Lilla Russel-Smith, Uygur Patronage in Dunhuang. Regional Art Centres on the Northern Silk Road in the Tenth and Eleventh Centuries (2005)
idem, The 'Sogdian Deities' Twenty Years on: A Reconsideration of a Small Painting from Dunhuang in: Buddhism in Central Asia II. Practices and Rituals, Visual and Material Transfer (2022)
Tonia M. Sharlach, An Ox of One's Own. Royal Wives and Religion at the Court of the Third Dynasty of Ur (2017)
Michael Shenkar, Intangible Spirits and Graven Images: The Iconography of Deities in the Pre-Islamic Iranian World (2014)
idem, The Religion and the Pantheon of the Sogdians (5th-8th Centuries CE) in Light of their Sociopolitical Structures (2017)
idem, The So-Called "Fravašis" and the "Heaven and Hell" Paintings, and the Cult of Nana in Panjikent (2022)
Marten Stol, Nanaja in: Reallexikon der Assyriologie, vol. 9 (1998)
Michael P. Streck & Nathan Wasserman, More Light on Nanāya (2013)
Aaron Tugendhaft, Gods on Clay: Ancient Near Eastern Scholarly Practices and the History of Religions in: Canonical Texts and Scholarly Practices. A Global Comparative Approach (2016)
Joan Goodnick Westenholz, Nanaya, Lady of Mystery in: Sumerian Gods and Their Representations (1997)
idem, Trading the Symbols of the Goddess Nanaya in: Religions and Trade. Religious Formation, Transformation and Cross-Cultural Exchange between East and West (2014)
Xinjiang Rong, The Colophon of the Manuscript of the Golden Light Sutra Excavated in Turfan and the Transmission of Zoroastrianism to Gaochang in: The Silk Road and Cultural Exchanges between East and West (2022)
Gioele Zisa, The Loss of Male Sexual Desire in Ancient Mesopotamia. ›Nīš Libbi‹ Therapies (2021)
#mesopotamian mythology#sumerian mythology#mythology#bactrian mythology#sogdian mythology#sogdia#nanaya
455 notes
·
View notes
Note
I don't think that any of your conlangs are progressive enough to express being trans, but if they were, how would they? What about other gender/sexuality things?
That first clause is quite a thing to say. Languages aren't progressive. Their users may be, but the languages aren't anything. They're just languages. If you mean they're not modern (i.e. a lot of the languages I create are for cultures that are somewhat antiquated compared to our world), this is true, but that doesn't necessarily mean the languages won't have terminology for different gender identities.
There is a major assumption here, though. My understanding (and please do note: I am a cis man; please feel free to correct), cis and trans individuals, as opposed to nonbinary and genderfluid, are similar in that neither have any doubt about what gender they are, identifying with either male or female. So if any language I've created has a word for "man" or "woman", then there's sufficient vocabulary for a trans individual to express their identity that way.
However, there is a terminological difference, and it's both an individual choice and societal preference: Whether to identify as one's chosen gender identity, as trans, or both (e.g. "I am a woman", "I am trans", or "I am a trans woman"—and then preferring to use one of those or all of those, or some other combination of the three). My personal language preference (as a user and language creator) is fewer distinctions are better (why have three third person singular pronouns—or four or twelve—when you can have one?), because it's less to memorize, less work to use, and demands less specificity of the user—and allows the hearer/reader to make fewer assumptions. Unless the situation calls for it (e.g. the gender system hard-coded into Ravkan in Shadow & Bone), I prefer lumping rather than splitting. This is especially useful as I'm often not in charge of the culture I create languages for.
For example, the languages I've created for A Song of Ice and Fire were for cultures created and maintained by George R. R. Martin. Whatever cultural innovations I have made in creating the languages are, at best, pending—that is, true until George R. R. Martin says otherwise, which he is free to do at any time, as it's his world. As a result, I don't feel confident enough to say what life is like for a trans individual in his world, and how that might be reflected in the languages there. There's simply not enough information.
Where I might be in charge of the culture, you do know my preference now (i.e. fewer distinctions), but, as I am not trans, I'd prefer to leave it to the trans community to decide, and then do what I can to support those decisions linguistically (i.e. to make it work within the language). Any term chosen highlights some aspect of the experience while downplaying others. In English, trans, coming from transition, highlights the change from one identity to another. Other ideas for how to come up with a term might be using a root that refers to "true", highlighting the transition to one's true gender expression. Perhaps another root to look for would be "choose", framing it as one's chosen gender expression—IF one wishes to look at it that way.
In many ways, both the term and the experience are highly individual, and it's difficult to come up with a blanket term and say "this is the term". It's especially difficult since this isn't a life experience I share. It feels both disingenuous and a bit icky to come up with a term to describe an experience that is decidedly not my own.
My own preference in this regard is a twofold approach:
Allow trans users of whatever language to figure out what term works for them, and then support them in creating a term that obeys the various language rules (i.e. the phonology is correct, derived words are derived correctly, etc.). Those users, however, will be operating under the same "rules" that I operate under, e.g. the one who's creating the culture has the final say, if they care to weigh in, and so the result may end up not being canon, at which point it's up to the user to decide whether they care or not. (Note: I shouldn't have to explain it here on Tumblr, but, of course, you don't have to care if the creator of the canon says something isn't so, no matter how many billions they have.)
Allow polysemy. There will never be a term that is THE term. It may be an individual's preferred term, but someone else may like another, in which case it should be allowed.
A very important language-specific note (and the same is true of fandom, generally). By agreeing to work within a language, we're essentially agreeing to rules of a game. The rules can always be broken. When rules are broken, the question language users have to answer is if they've been broken so egregiously that they're no longer playing the game, or if it's fine. For example, if you look at fanfic, there's plenty of fanfic with gender-swapped characters, or the same characters in a radically different setting. Some readers may decide they don't want the characters to be gender-swapped. Others may decide that if it's not in the same setting they're not interested. And that's fine! Both the writers and the readers are deciding which rules of the game can be broken while still calling it the same game. This works very, very well so long as no one gets mad at anyone else. If someone says, "I don't enjoy this because it breaks the rules in a way that ruins my enjoyment", that's perfectly fine. If that same person says, "You're not allowed to break the rules in this way", that's not fine.
So hopefully this all makes sense. And, furthermore, when I say I want to support those who wish to create their own terms, I do mean it. If anyone has suggestions or needs help coining a possible word, feel free to message me! But do bear (2) above in mind. I'm not going to say any term is THE term, and have that be the end of it. It'll be one possibility amongst a rainbow of possibilities.
#conlang#language#lgbtq+#trans#nonbinary#grrm#asoiaf#shadow and bone#shadow & bone#s&b#grishaverse#genderfluid
369 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Ministry of Magic: Part 1/?
(Part 2, Part 3)
Legislative Processes
I don't know if I was the only one who was paying too close attention any time Arthur or Percy Weasley mentioned anything to do with their ministry jobs to try and understand how the magical government works... but I made some notes based on random one-off lines that have some implications.
So, I'll start with a short one about one of the ways laws come into existence in the UK Ministry of Magic.
“C-cars, Molly, dear?”
“Yes, Arthur, cars,” said Mrs. Weasley, her eyes flashing. “Imagine a wizard buying a rusty old car and telling his wife all he wanted to do with it was take it apart to see how it worked, while really he was enchanting it to make it fly.”
Mr. Weasley blinked.
“Well, dear, I think you’ll find that he would be quite within the law to do that, even if — er — he maybe would have done better to, um, tell his wife the truth. . . . There’s a loophole in the law, you’ll find. . . . As long as he wasn’t intending to fly the car, the fact that the car could fly wouldn’t—”
“Arthur Weasley, you made sure there was a loophole when you wrote that law!” shouted Mrs. Weasley. “Just so you could carry on tinkering with all that Muggle rubbish in your shed! And for your information, Harry arrived this morning in the car you weren’t intending to fly!”
(CoS, 43)
Like, this is bizarre. Let's recap, Arthur Weasley is the head of the Misuse of Muggle Artefacts Office, described as:
“What does your dad do at the Ministry of Magic, anyway?”
“He works in the most boring department,” said Ron. “The Misuse of Muggle Artifacts Office.”
“The what?”
“It’s all to do with bewitching things that are Muggle-made, you know, in case they end up back in a Muggle shop or house. Like, last year, some old witch died and her tea set was sold to an antiques shop. This Muggle woman bought it, took it home, and tried to serve her friends tea in it. It was a nightmare — Dad was working overtime for weeks.”
“What happened?”
“The teapot went berserk and squirted boiling tea all over the place and one man ended up in the hospital with the sugar tongs clamped to his nose. Dad was going frantic — it’s only him and an old warlock called Perkins in the office — and they had to do Memory Charms and all sorts of stuff to cover it up —”
(CoS, 36)
It's a small office, only Arthur, the office's head, and one employee, Perkins. Even though it's such a small office, that is held in low regard, Arthur still has the legal authority to bill laws relevant to his office. Molly and he literally say he wrote a loophole into the law on purpose!
This means any department or office head in the ministry, regardless of how small or inconsequential they are, has the legal authority to draft a law and offer it to vote in the Wizengamot. We know the law bills get voted on, so at least random ministry personnel can't just make laws for whatever they want.
We don't really know what Araminta Meliflua Black did for a living, but she was clearly legally allowed to draft laws too:
and Araminta Meliflua . . . cousin of my mother’s . . . tried to
force through a Ministry Bill to make Muggle-hunting legal
(OotP, 113)
And we know her law didn't pass, so I assume it was dropped during a Wizengamot vote.
But this process shows how much the Ministry of Magic doesn't function like a democracy.
I'll write about what exactly the Wizengamot is, how I believe it functions, and who the members are (I'm pretty sure they aren't elected democratically though. Edit: I wrote it). Still, for now, the legislative process in the ministry is that every office head writes laws in their area of expertise (or anything else they're passionate about, apparently). Then the law gets voted on by the Wizengamot which is both the Parliament (the legislature) and the supreme court of justice in the ministry (somewhat like the House of Lords in the UK used to function in the past).
In democracies, the legislature is usually elected by popular vote or indirectly elected, this group of elected legislators would be the only ones who could legally write laws. As every office head in the ministry has the authority to act as a legislator, I assume no such election methods are in place for every single office in the ministry. For the larger department heads, perhaps, but not every minor office.
If we take the muggle UK as our legislature template, laws can be billed by any member of the parliament (be it the House of Lords or the House of Commons). Then these bills are voted on multiple times by the parliament. It's more complex than that, but my main point is that in every sensible democratic country, the members of the parliament are the ones drafting laws and voting on them. In the Ministry of Magic, it seems like basically everyone in the Ministry can draft a law, not just Wizengamot members (who vote on them).
In the US there are ways for citizens to recommend laws to the member of Congress that represents them, but that's completely different to Arthur just straight up writing a loophole into the law intentionally! There isn't even anyone who oversees the phrasing of the bill, or reads through it to make sure it makes sense or, idk, legal if Arthur could just write what he wished! Or that Araminta could write a bill for muggle-hunting and offer it up to a vote, like... there doesn't seem to be any screening for the laws that go into a vote. Not even for their phrasing.
This is just a messed up little fact about the legislative processes within the Ministry of Magic I didn't see anyone mention that I think is interesting.
#harry potter#hp#harry potter theory#hp theory#hp meta#harry potter meta#wizarding world#ministry of magic#arthur weasley#hollowedtheory#wizarding politics
119 notes
·
View notes
Text
Analyzing 35 Portland Row:
Back at it with my set decoration posts, but lets overanalyze 35 Portland Row, shall we?
I love the way most of the house seems untouched, like it was frozen in time. Presumably, Lockwood never really "redesigned" the home from its original state, maybe a couple of changes here and there (which are more noticeable as we move on to other rooms) I say this, because of the contrast between pristine and messy in the areas.
The entryway:
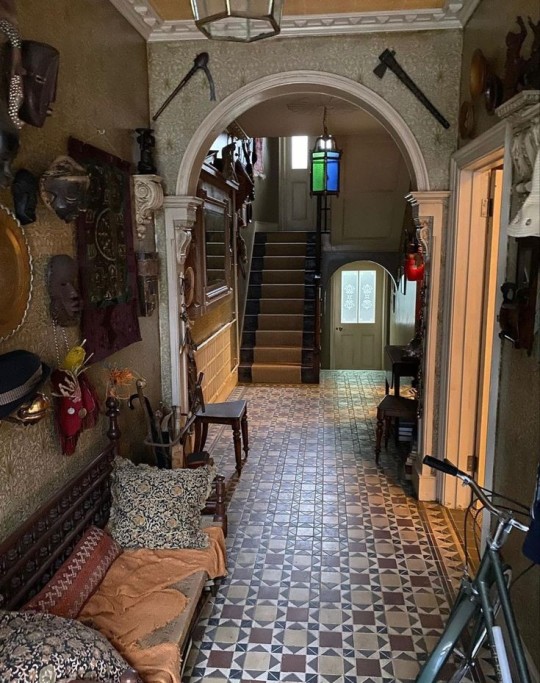



I assume that the perspective pictures were taken as a way to assess how the set was going to look, in perspective 1 you can see the pillows on the bench missing, and in perspective 2 the clothing rack/hanger are completely missing.
On screen, we see that contrast I was talking about, you can see the way the clothes are almost stacked on that clothing rack (we can see George's coat, for example) I regard this as the kids respecting the space, since it is Lockwood's house they, most likely, don't want to trash it with their personal mess (or maybe George is the one that sets the 'mess-boundaries' to lighten the cleaning work).
On the other side of the spectrum we see the neat decorations and respected vases (respected as in, not using them as holders or trash bins) and the well cleaned masks and antiques hanging on the wall.
The Living Room:


This room is the "look how professional and neat we are" room, it is (by far) the cleanest one of them all, here is where they receive people and it is evident that they don't use it much by themselves, I know this because of the alarming lack of books laying around. I promise you, in Portland Row there are books EVERYWHERE.
Proof:




(these are just from the first couple episodes)
The Library:



I would argue that this is the "let's talk" room of the house, because it's the place where all of the information is. This is the room with the most "Lockwood flare", plus it's the perfect place for me to talk more about the messiness contrast.
In the scene where Lucy goes to talk to Lockwood, she has an apple core in her hand and this madwoman sets it ON THE TABLE (outrageous) but she looks for a spot where she wont ruin the table OR the books beside it. THE SELECTIVE MESS, PEOPLE! And Lockwood doesn't care, he just smiles, thankful.
Also there's a piano on the corner. (Hey! Locky, play Piano Man!)
The Kitchen:




Lockwood & Co's kitchen my beloved <3
By far my favorite room of the house, it is so cozy! From the spice rack, to the pot holders, to the kitchen utensils, the DETAILS. I'm in love, I love it.
And of course, the thinking cloth. The kitchen is the heart of Portland Row 35. And the crumbs on the table mean the world to me. LIKE DO YOU GET IT? DO YOU UNDERSTAND THE SIMBOLYSM OF CRUMBS ON THE TABLE?
I love kitchens, and I love set decor. That's all I have to say.
The Rooms:
Last sections of me nerding out about set decor, I promise!
Lockwood's Room:
It's safe to assume that Lockwood doesn't spend much time in his room, so it stays mostly neat. Probably only in use when he's sleeping or getting changed, and most of his time is spent in the library or in the kitchen with the others.
Lucy's Room:


Okay, this room is a set decor work of art. Why? Well, because it is a prime example of a characters personality shining through in a new space.
Not only does it show what it was before (a storage attic) but it also shows what it is now (a personal room) AT THE SAME TIME! You can see the way Lucy organizes everything contrasted with the way it was laid out before.
(look at the shopping bags she was carrying when talking to Kipps beside the bed, CONTINUITY!)
George's Room:



One thing about George is that he is way too excited about The Problem to care about actually cleaning and organizing his own room.
I think that his room is a physical representation of how his brain works. Books on the floor, papers stacked over anything, post it notes on the wall. You can just see the way his brain jumps from one thought to the other by the way his room is laid out!
The set decorator credits: JUDE FARR
So that's it! Im sure i missed a couple of things so if you want to add your observations, please do! And if i made any mistakes or incorrect assumptions I apologize, i am by no means and expert, I just like the subject.
#l&co#lockwood and co#lockwood netflix#locklyle#lucy carlyle#anthony lockwood#george karim#l&co. netflix#set decoration#35 portland row#neverendingthoughts#lockwood & co
356 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Hippocrates
Hippocrates was born on the Greek island of Kos in the 5th century BCE, and he became the most famous physician in antiquity. He established a medical school on the island, wrote many treatises on medical matters, and is, through his systematic and empirical investigation of diseases and remedies, credited with being the founder of modern medicine.
Biographical Details
Information regarding Hippocrates is patchy and unreliable. He was perhaps born c. 460 BCE, but details of his life were speculated upon even in ancient times. One of the oldest sources is the Life of Hippocrates credited to Soranus of Ephesus, himself a physician, who lived in the 1st and 2nd centuries CE. Soranus' method of quoting from now lost earlier texts has been an invaluable source of information on ancient medicine. He states that Hippocrates knew several 5th-century sophists, notably Gorgias of Leontini, and was taught medicine by both his father and Herodicus of Selymbria, a gymnastic trainer. We also know that Hippocrates set up and ran a school of medicine on Kos.
Plato mentions Hippocrates in his Protagoras, suggesting that he worked for fees and believed the body should be treated as a whole (Phaedrus). The Roman scholar and medical writer Cornelius Celsus claims that Hippocrates was the first to separate medicine from philosophy, and other ancient sources also suggest that Hippocrates believed in the importance of diet and exercise for a healthy body. Soranus goes on to inform us that Hippocrates travelled throughout his life and died at Larissa in Thessaly, c. 370 BCE.
In antiquity, many legends arose of Hippocrates' great talents but most of these are likely pure invention. He reportedly discovered that King Perdiccas II of Macedon's health problems were down to lovesickness, he eliminated the plague that hit Athens in 430 BCE by burning fires everywhere, and he treated the philosopher Democritus whom everybody thought mad (not without some justification). Hippocrates had three sons who carried on his work - Thessalus, Dracon, and Polybus.
Continue reading...
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
Headcanons, re: Melkor's and Manwë's origins and relation
So when it comes to Melkor and Manwë I find myself in a bit of a "headcanon dilemma". On one hand, I really like the idea of them being twins, but on the other hand, a lot of stuff that I personally hc regarding their interpersonal dynamic and conflict rests on the basic assumption that Melkor is older than Manwë - not too much, as in not on the same level as I hc for the Fëanturi (with Námo practically raising Irmo), but a noticeable, significant amount. Enough for Melkor to have spent some time alone with Eru, let's say.
(Side note: I am aware of that one line stating they were coeval. What I'm going to say next will address how I'm trying to solve that conflict and afterwards I'll cycle back to it to explain why I felt like deviating from it/not taking it as literally.)
I've been rotating this back and forth in my head for a while, trying to figure out how I can fit these two ideas together, and what occurred to me now are two things:
The Timeless Halls. Timeless. Time doesn't exist as we know it there ("Then those of the Ainur who desired it arose and entered into the World at the beginning of Time" - Valaquenta)
Ainur are made from Eru's thoughts ("and Eru made first the
Ainur, the Holy Ones, that were the offspring of his thought" - Ainulindalë)
With this in mind, as well as the fact that Ainur are spirit beings in general and exist outside of most "biological realities" (for lack of a better term) that inform the relations and interactions between incarnate beings, I think that Ainur twins don't have to be the same age. While coeval is defined as "of the same or equal age, antiquity, or duration" (source: Merriam-Webster), therefore having a clear temporal dimension to it, I would say that, under the above mentioned circumstances, such a notion would be more vague, have less clear boundaries.
(Personally, I see all of the Aratar as more or less "coeval", with the non-Arata Valar being a sort of "second generation" or "later additions" if you will, and the Maiar being made some time after them. My headcanon is that Eru had no plans to raise every single Ainu individually and only did so for the oldest Aratar, later relying on them and subsequently the other Valar and older generation of Maiar to raise and teach the young Ainur (and yes, parentification is a thing and yes, in real life it's a problem).)
Now cycling back to my original "issue" with the coeval line (not really, but just the reason why I wanted to read it a little differently), I felt like it was a bit... strange? thematically. Again, the part of Melkor and Manwë being essentially the evil and good twin is a dynamic I really like, but they're "made" from rather different "blueprints".
While Manwë has a special position as the Elder King, the other Aratar are his peers ("Though Manwë is their King and holds their allegiance under Eru, in majesty they are peers" - Valaquenta) and he's very much like any other Vala in the sense that he has one particular domain that informs his nature and where his talents lie and outside of that he relies on cooperation with his fellow Valar.
Melkor on the other hand (though don't get me wrong, he wasn't supposed to never go without any sort of collaboration or support) is special in the sense that he has a share in the other Valar's domains ("To Melkor among the Ainur had been given the greatest gifts of power and knowledge, and he had a share in all the gifts of his brethren." - Ainulindalë) and he's so vastly more powerful that he was able to hold his own against everyone else for a long time:
"Melkor must be made far more powerful in original nature (cf.
'Finrod and Andreth'). The greatest power under Eru (sc. the
greatest created power).(1) (He was to make I devise I begin;
Manwe (a little less great) was to improve, carry out, complete.)
Later, he must not be able to be controlled or 'chained' by all
the Valar combined. Note that in the early age of Arda he was
alone able to drive the Valar out of Middle-earth into retreat."
(Melkor Morgoth, Morgoth's Ring)
In my mind, it doesn't really "fit" for Eru to make this twin pair of Valar, born at the same time and presumably first, before all the other Ainur, and have one be this super powerful, not domain-bound Vala and the other being significantly less strong and very much domain-bound, as well as further restricted by not comprehending evil ("For Manwë was free from evil and could not comprehend it" - Of Fëanor and the Unchaining of Melkor).
What it does fit into is this idea prevalent in a lot of medieval narratives (broadly speaking) that the eldest son is special and usually the "greatest" and "most powerful", according to whichever metric is important in any given context. This idea can be found in Tolkien's works as well, one notable example being Fëanor.
Therefore I like to hc that Eru made Melkor first and, dare I say, made him in his own image as well. But then he quickly realized Melkor's potential for evil/his shortcomings/wasn't fully content with how he turned out/wanted to course-correct and "continued the thought" Melkor had come from, adding Manwë as his twin brother to balance him out; not in power, but in nature and purpose.
And the reason why Manwë knew that Melkor was like him originally, but at first failed to see what he turned himself into ("and he knew that in the beginning, in the thought of Ilúvatar, Melkor had been even as he; and he saw not to the depths of Melkor’s heart, and did not perceive that all love had departed from him for ever" - same source as last quote, sentence continued) is because Manwë came from that same thought.
~
So yeah, just my two cents and I want to stress again that these are my headcanons and my currently preferred reading and understanding of the above lines; the goal is never to say "you can't have your headcanons and here's why".
#headcanons#my headcanons#meta#silm headcanons#silm analysis#silmarillion#melkor#morgoth#manwe#manwë#eru#valar#ainur
43 notes
·
View notes
Text







Symbols of the Xiongnu, Sarmatians, Scythians, and Alans from various branded objects 2nd C. BCE - 2nd C. CE
"Starting in the 1950s, the source base for the study of the branding of cattle has substantially broadened. One of the Sarmatian burials of the lower Don contained a unique instrument for branding an animal (Raev 1979, pp. 207–08, Fig 3.9; Yatsenko 2001, p. 12, Fig. 1.1). A male burial of the last quarter of the 1st century CE not far from the village of Porogi near the Dniester yielded a silver cup with a handle in the form of a horse with brands on the right shoulder and left flank [Figs. 3.1, 6.2]. In this same complex was a gold torque with ends shaped like horse heads. One of the heads has a brand on the cheek (Simonenko and Lobai 1991, Fig. 16.1,2; Simonenko 1991, p. 316, Nos. 154, 157). One should include here a long-known gold bracelet accidentally discovered on the shore of the Bug estuary. Its ends, analogous to those of the torque from Porogi, also are shaped like horse heads, on one of which is a brand (Solomonik 1959, pp. 131–32; Voroniatov 2013, Fig. 1.2). Additional evidence regarding the tradition of branding Sarmatian horses may be found in numerous examples of Roman-period ceremonial horse harness, whose decoration includes Sarmatian tamgas (Voroniatov 2013). S. A. Yatsenko’s idea (2001, p. 13) that details of horse gear can duplicate or imitate a real brand on the body of the horse merits close attention.
As unusual as the buckle from Mongolia is the depiction of a bear on a wooden harp [Fig. 6.3] from the interesting complex of the end of the 1st–beginning of the 2nd centuries CE not far from Olbia (Simonenko 1999, pp. 111–14, Figs. 2, 3; Simonenko 2004, pp. 209– 21, Abb. 7). In toto there are 32 tamgas on the harp, six of which are incised on the figure of the bear. A.V. Simonenko emphasized (1999, p. 112) that the tamgas are placed in the same locations as the signs on the figure of a horse which served as the handle for the silver cup from Porogi [Figs. 3.1, 6.2].
I would propose that the depiction of a branded wild animal (a bear) on Alano-Sarmatian materials is related to the depiction of a fantastic animal with a brand in Xiongnu antiquities. It is possible that the meaning attached to signs specifically on such creatures relates to something other than the pragmatic tradition of branding cattle. This phenomenon, on which I will not dwell in greater detail, requires special study. I would merely note that early medieval depictions of wild animals and mythical creatures with a brand are attested in the territory of Inner Asia and Asia Minor (Boardman 2010, Fig. 19; Samashev and Bazylkhan 2010, p. 311).
In discussing the tradition of branding cattle along the northern Black Sea littoral, E. I. Solomonik (1957, pp. 215–17) provides information about this practice in archaic Greece, a practice which might well also have existed in the Greek Black Sea colonies. Clearly horses and cattle, branded with Sarmatian tamgas and, correspondingly, their depictions appear in the steppes of the northern Black Sea littoral and in the Bosporan region with the arrival of a new wave of nomadic tribes in the first century CE.
The objects examined here in the three categories demonstrate not only the similarity of several types of tamgas of Inner Asia and Sarmatia but also suggest common features of ritual practice among the Xiongnu and the Alano-Sarmatians. All three categories of objects have characteristics which are not merely the inherent qualities found in artefacts of daily life.
The astragalus with a tamga found in the burned layer of the Bosporan fortress of Artezian [Fig. 5.5] also has been interpreted as a cult object (Vinokurov 2007). In addition to the astragalus with a tamga, in the same layer of the Liubimov settlement on the lower Dnieper [Fig. 5.3] was a whetstone inscribed with three tamgas. Scholars have attributed a cultic and magic purpose to unusual whetstones of the Scytho-Sarmatian period and specifically to whetstones with tamgas (Griaznov 1961; Anikeeva and Iablonskii 2012, p. 52; Voroniatov 2012)."
-Sergey V. Voroniatov, State Hermitage Museum - Connections between Central Asia and the Northern Littoral of the Black Sea: Evidence from objects with tamgas.
103 notes
·
View notes
Text








Sat, Jan 12 - I visited the ancient Roman city of Sardes today for the first time. (Information about the city is under this post.) It consisted of the Gymnasium with the remains of many Byzantine shops including restaurants and painting shops, a public pool, tombs, and a Synagogue. It was truly refreshing to see the place overall, but what I adored about the visit was the fact that you could imagine and experience the feeling of what it was like to be living in an ancient city, as it was empty because of the weather conditions. No voices, no noise, no motion, just the smell and the air of this ancient place. (I bet Henry Winter would die for it.) The Temple of Artemis was also close and I went there as well. I'll publish the pictures from the Synagogue and the Temple next if you want to check them out.
Sardis (/ˈsɑːrdɪs/ SAR-diss) or Sardes (/ˈsɑːrdiːs/SAR-de ess; Lydian: 𐤳𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣, romanized: Sfard; Ancient Greek: Σάρδεις, romanized: Sárdeis; Old Persian: Sparda) was an ancient city best known as the capital of the Lydian Empire. After the fall of the Lydian Empire, it became the capital of the Persian satrapy of Lydia and later a major center of Hellenistic and Byzantine culture. It is now an active archaeological site in modern-day Turkey, in Manisa Province near Sart.
In 334 BC, Sardis was conquered by Alexander the Great. The city was surrendered without a fight, the local satrap having been killed during the Persian defeat at Granikos. After taking power, Alexander restored earlier Lydian customs and laws. For the next two centuries, the city passed between Hellenistic rulers including Antigonus Monophthalmos, Lysimachus, the Seleucids, and the Attalids. It was besieged by Seleucus I in 281 BC and by Antiochus III in 215-213 BC, but neither succeeded at breaching the acropolis, regarded as the strongest fortified place in the world. The city sometimes served as a royal residence, but was itself governed by an assembly.
In this era, the city took on a strong Greek character. The Greek language replaced the Lydian language in most inscriptions, and major buildings were constructed in Greek architectural styles to meet the needs of Greek cultural institutions. These new buildings included a prytaneion, gymnasium, theater, hippodrome, and the massive Temple of Artemis still visible to modern visitors. Jews were settled at Sardis by the Hellenistic king Antiochos III, where they built the Sardis Synagogue and formed a community that continued for much of Late Antiquity.
In 129 BC, Sardis passed to the Romans, under whom it continued its prosperity and political importance as part of the province of Asia. The city received three neocorate honors and was granted ten million sesterces as well as a temporary tax exemption to help it recover after a devastating earthquake in 17 AD.
Sardis had an early Christian community and is referred to in the New Testament as one of the seven churches of Asia. In the Book of Revelation, Jesus refers to Sardians as not finishing what they started, being about image rather than substance.
I take the pictures that are on my blog myself. In case you're interested in this post, I also post/reblog content including travel/cultural pictures, books, book recommendations, analysis, quotes, anything related to movies, series, and girl blog entries.
#sardes#ancient rome#ancient greek#gymnasium#ancient history#ancientmonuments#roman architecture#archeology#blog#travel#history#the secret history#henry winter#synagogue#dark academia#aesthetic#light academia#books#girlblogging#hellenistic#reading#if we were villains
39 notes
·
View notes
Note
There had been a number of questionable takes recently regarding the Frev in the past few days that came in succession . Do you reckon if works in the past decades or so that were published in France and were made available to English readers would it may have at least mitigated such thing to ever happen or is the black legend so ingrained that even with the idea of an era where works by Belissa et Al were in circulation in English to people outside France, the result would be the same?
Before I reply, I need to make a disclaimer that I am not the best person to answer this question. I arrive from a very different educational tradition (neither Anglo nor French), and I actually discovered embarrassingly late about the whole black legend and the fact that, among some, the French Revolution was considered a horrible event (that failed). I was taught it was an event that changed the world forever (and helped shape the world today, mostly in a positive sense) and that it has to be studied to understand our world. So I am not the best person to judge the effect of the black legend vs new historiography. If others have more informed takes, please tell us; I am super interested.
Now, the bad (as in, incorrect) takes we get here. They happen periodically, and they tend to be very similar, often by people claiming (and I have no reason to doubt them) that they are taking history courses on frev, typically in the USA. So these takes tell me about the state of teaching frev in the USA (Anglo?) sphere. Which is not necessarily the same as "what experts publish in academic articles", because - not sure if people are aware of it, so I need to emphasize - you do not have to be an expert on a topic to teach it at the university level. You typically need a PhD in the discipline, but not necessarily on the topic of the course you teach. I can imagine that they won't give a frev course to someone with a PhD in, say, antiquity, but "early modern period" is good enough, even if you are not an expert on France or the revolution.
Sorry for this preamble; I swear it is related to your question. What I mean is that these specific takes we saw here seem to me (though I could be wrong) not necessarily a product of current English-language academia on frev, but what students are taught. So yes, it is a good question on what kind of books students are given on the mandatory readings list, and if those teaching are even aware of the most current English-language books on the topic (let alone French).
I swear most of this stuff is so dated and proven to be incorrect over and over again. We had someone a few months ago saying they read Carlyle for their frev class. ?? This is really strange to me, especially in the North American academia, where even books that are considered new-ish elsewhere, are seen as old, so why teach something published in early 19c? Unless you want to demonstrate changed attitudes about frev and discuss historiography, propaganda, etc. which doesn't seem to be the case. Those assigning such readings are teaching what they feel is true. So I can only guess that they never bothered to read newer stuff.
Look. I am all for authors not liking the French Revolution or specific things in it (I am critical of many frev stuff myself), but you have to use current sources that go through earlier misconceptions. We can't still be stuck at "dictator Robespierre who ruled France", a thing that was disproven so long ago and no credible historian believes in (even if they hate Robespierre).
Now, this is about teaching history at the university level and not about experts in academia, because I do think most incorrect takes we get here on tumblr are from students. Experts sticking to the black legend and "horrible horror of the revolution that failed anyway and didn't achieve anything" are a different group. Though I am not an expert on the current historiography to judge it in detail. So, if someone reading this knows more and can explain, please share!
28 notes
·
View notes
Note
Pokemon Au: What if Ozpin can tell that Kyurem is near so he goes to meet him(possibly with Glynda) and ask why he's he traveled so far. Kyurem says a the true test for them(students) will come soon. And leaves with the question "Will their ideals shape fate or will the truth of absolute power tear it all down." *I think you could some more to that to make it the best*
"Professor Ozpin," Doctor Oobleck entered the office, Antiquity's Roast perched on his shoulder, "if I could have a moment of your time?"
"Of course, Doctor Oobleck." The headmaster looked up from his desk, his faithful Espeon nestled in his lap. "Is there a problem?"
"I don't believe so, no. However, it is something I feel I cannot overlook."
"Very well." Nodded the headmaster, urging his friend to continue.
"It is in regards to Mr. Arc." Ozpin wouldn't say it, but a part of him wanted to reply 'Of course it is'. "I have reason to believe that he may be connected to an old legend about the Unova region."
"What makes you believe this?"
"Are you familiar with the Swords of Justice legend?" Ozpin nodded. "The tale is more commonly known in Remnant as a tale of three Pokémon acting in the defense of humanity against tyranny. However, Mr. Arc seems aware of the tale in a different manner, with four Pokémon instead."
"I know you wouldn't bring this to my attention without further evidence. You never have."
"Of course, sir, and I don't intend to break that habit now. The legend mentions a youth, often a young man, wielding a sword and shield at his side as he does battle with the tyrants of Unova."
"And you believe Mr. Arc, who is the trainer to an Aegislash, is this same youth?"
"One and the same. It is said to be a trainer with a special connection with their Pokémon, well beyond the level noted among even those who truly cherish their companions."
"Mm." Ozpin nodded, stroking the ear of The Longest Memory. "And what do you intend to do with this information?"
"With your permission, sir, I would like to explore this story to its completion. It is not the first time we have heard stories breaking through the binds of pages to enter reality. Legendary Pokémon truly exist across the world, and this young man could be the key to understanding them all! I would like to travel with Mr. Arc and expand both his experience and his skill so that he may reach his full potential."
"Then I'm afraid I must decline, Doctor Oobleck." At this, his Espeon leapt from his lap. "We cannot show favoritism to our students, nor can we grant them special permission to miss out on their education at our academy. Not to mention that Mr. Arc likely wouldn't find this as interesting as the tournament he and the other students intend to participate in."
"Of... Of course, sir. Forgive me for my enthusiasm."
"It's quite alright, Bartholomew. I know your eagerness comes from a place of joy for learning. Just be careful your haste doesn't lead to the waste of another students chance to learn as well." He leaned forward. "Perhaps, after the tournament, you could ask the winners if they too would like to go on this adventure?"
"I will keep that in mind, sir. Thank you." He then left, allowing the headmaster to return to his thoughts.
'Mr. Arc faces a great deal already. Would it be so wrong for the universe to focus on another soul? One not burdened by such foolishness as destiny and fate?'
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Help preserve the teaching of ancient material culture at the University of Helsinki!
If you're a student, a researcher or a teacher of Latin, Greek, or classical archaeology, or just generally interested in classics, this is for you!
University of Helsinki is planning to disband the teaching of Ancient Culture, starting from the summer of 2024. This includes the subjects of Greek and Roman archaeology and material culture of the ancient world; a discipline previously known as classical archaeology. The signatories of this petition demand that the regular contact teaching of Ancient Culture or classical archaeology will continue at the University of Helsinki, and this way in Finland. The optimal solution to this would be the re-opening of the position of university lecturer of classical archaeology, and selecting a new lecturer to this position. This way the continuation of teaching will be ensured in a discipline that ultimately is one of the cornerstones of European civilisation.
The teaching of material cultures of the ancient world supports the studies of philology, other humanistic disciplines, and the understanding of European history of civilisation and cultural heritage. Competent teaching has been a requirement for the high-profile projects taking place at the University of Helsinki, and the research at Finnish Institutes in Rome, Athens, and Middle East. The experts of the field have made it possible to organise various popular exhibitions that have brought research of antiquity and its legacy into the knowledge of larger audiences.
The teaching of classical archaeology first began in Finland in the 1780s. At the University of Helsinki, the basic studies (15 study points) have been available for students since the early 1980s, and the intermediate studies (30 study points) since the early 1990s. After the discontinuation of the lectureship of classical archaeology in Oulu, the University of Helsinki offered regular contact teaching of classical archaeology as the only instance in the country between 2014-2018. Until 2018, classical archaeology also had the status of an independent discipline. Since then, teaching has been organised with multiple projects from different disciplines, and students have been able to complete two study modules of 15 and 30 study points, or 3-6 courses respectively.
Now the university plans to disband the teaching and discontinue the study modules. The courses have been extremely popular among the students. The arguments used in support of not opening the position of lecturer of classical archaeology in 2018 included the excellent resources of the discipline in relation to number of students. Now the decision to discontinue the teaching is supported by claims that the discipline is unable to provide a long-term solution to the unstable teaching situation, and students do not complete the entire study modules, only isolated courses. Re-opening the position of lecturer of classical archaeology is the only long-term solution that benefits both students and the university; it secures competent teaching, enables the completion of study modules, and brings stability to the uncertain situation that has lasted for years.
By discontinuing the teaching of ancient material culture and disbanding the study modules, the University of Helsinki debases both teaching and research, and erodes its own status as a European elite university that regards sophistication and civilisation as its key values. This decision will drive away both students and international experts, as well as funding for research projects. By opening the position of lecturer of classical archaeology and selecting a new lecturer to this position, University of Helsinki can ensure the continuation of expertise appreciated in the academic world, in Finland, and in the international arenas.
More information on the history of teaching ancient material culture and classical archaeology in Finland: http://www.taidehistorianseura.fi/tiedotteet/taidehistoriallisia-tutkimuksia-50/
Statement by the student organisation of Ancient Languages and Cultures, Symposion ry: https://rostrasymposion.wixsite.com/rostra/post/symposion-ry-n-kannanotto-antiikin-kulttuurin-opetuksen-puolesta
Please consider signing the petition and spread the word! This would be a huge tragedy for the teaching of classical philology and archaeology in Finland! The decision is not yet final, so we still have a chance to make a difference!
The petition site is unfortunately only in Finnish. The site will ask your name and email address to sign the petition, but you can choose not to share your name publicly. Your email address will not be published anywhere. You can also leave your own comments.
Thank you so much for helping! <3
-Sofia, the chair of Symposion, student organisation of classics at the University of Helsinki
#classics#history#ancient history#ancient rome#ancient greece#classical philology#classical archaeology#classical studies#suomi#helsingin yliopisto#university of helsinki#archaeology
25 notes
·
View notes
Note
What are your thoughts on the Schiaparelli tech baby, specifically in regards to any sort of societal commentary but also in terms of the rest of the collection?
Collection description from Daniel Roseberry
If there's one thing Schiaparelli is good at, it's having a weird showstopper that everyone will be talking about. It always feels a little gimmicky but clearly it works and keeps fashion week interesting, so I'm not complaining. Also, Daniel Roseberry's dedication to fashion + couture is always inspiring. You can read an article here where he complains about people feeding his work through AI, being inspired by other couture icons, and honoring a member of the atelier who's retring.
I think they accomplished the classic Schiaparelli goal of putting two unlikely things together and making them work, but to me this collection kind of felt like it had one too many design concepts going on. It had extraterrestrial, technology, texas cowboy, and then all the iconic Schiaparelli design elements. The outfits on their own were great and cohesive, but it kind of made the show feel like it was all over the place.
Collection description from Daniel Roseberry:
In 1877, Elsa Schiaparelli’s uncle Giovanni Schiaparelli, the director of the Brera Observatory in Milan, discovered something new: a series of channels, an area as large as the Grand Canyon, scoring the surface of Mars. He also coined the term “Martian”, and inadvertently began our modern fascination with creatures from out there, a fascination that continues to this day.
So it makes sense that space has always been an informal code of the Maison. Elsa was, famously, preoccupied with astrology, and why not? Looking to the stars was clearly a family pastime. This collection is an homage to that obsession, as well as a study in contradictions — of legacy and the avant-garde, of the beautiful and the provocative, of the earthbound and the heaven-sent.
But as art (and nature) teaches us again and again, the things and ideas that seem diametrically opposed to each other can also combine to make startling chimeras, objects composed of familiar parts that, when united, create something unexpected and new It is, in fact, one of the Maison’s guiding philosophies: Elsa was committed to unlikely marriages win her own design, and the looks in this collection honor that tradition, combining old world techniques (such as over-embroidered guipure laces, velvet and lace appliqués, and hand cut and embroidered chenille fringe) with new world shapes, patterns, and references (such as a motherboard-and-strasse microchip dress encrusted with pre-2007 technological artifacts — now, the technology I grew up with is so antiquated that it’s almost as difficult to source as certain vintage fabrics and embellishments).
They also unite her personal references with my own: you’ll see abstracted references to iconographies of my home state of Texas throughout, from the bandana, here remade in hand-painted paillettes; to the cowboy boot, reconceived as a thigh-high fantasy bristling with buckles; to the iconic horse braid dressage knots redone as silk satin spikes and smothering a camel suede bomber jacket and a white denim corset suit. Elsa was famous for her codes — the keyhole, the measuring tape, anatomical body parts — and we’ve embedded them like Easter eggs in jewelry, shoes, clutches, and embroidery, a secret message from us to the woman who wears them. The result are a series of profiles both familiar and not — part human, part something else. And, therefore, totally Schiaparelli.
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here’s all of the decipherable text from the piece of paper found in Logan’s safe. Full credit to Reddit user Educational_green711 for the transcription. The original Reddit post can be found here
To my executors and family,
The following is a record of additions and clarifications to be added to my official letter of wishes in the… of my passing:
I have … this record to provide my executor and family with information they will need after my death. It includes financial and personal information that will be needed to settle certain affairs … performances and suggestions for arrangements that must be made. I hope this record will help make a difficult time easier for my family.
It is my preference that the title and role of CEO should be bestowed upon my son, Kendall Logan Roy.
Regarding my funeral arrangements: my funeral and burial are to take place in accordance with the … practices of the Roman Catholic Church.
My preferred hymns:
Amazing Grace, Abide With Me, Here I Am, Lord, I Watch the Sunrise Lighting the Sky, The Lord’s My Shepard (Psalm 23)
I wish to be buried with the attached copy of my sister Rose’s photograph placed in … of my wife, Marcia in my right hand … pocket.
I would like to change the epitaph on my headstone …
“Truthful lips, endure forever, the lying tongue lasts only a moment.” Proverbs 12:19.
Leave my head of security, Colin Stiles, my Rolex Daytona Lapis …
Regarding personal assets, include the following: I advise that … should remain in a secured facility indefinitely, and … family … unnecessary financial complications … collection of Impressionism paintings and … Switzerland.
Sincerely yours, Logan Roy.

- NRPI
- Re..? Antiquities/antiques
- Journalism Ex../Ca..?
- Greg?
109 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi! There is an Spartan Calendar in Hellenic Polytheism? I know it used the Athenian one, but me, who want to worship Apollon and Hyakinthos togheter like in Amyklae, would like to know when Hyakinthia comes... I thought is in this month, but i'm not sure... Do you know in which month the festival was celebrated?
I am using this answering post to announce our upcoming Hyakinthia Ceremony. More info after the answer.
Khaire Anon,
I will readily admit I did not know this information off the top of my head, so I wanted to check my sources before answering.
In general, the reason you will see the Athenian Calendar most often used by Hellenics, is because it is the calendar we know the most about. While we do know some things about the calendars of other Ancient Greek regions - it is usually more fragmented or incomplete when compared to the Athenian Calendar.
In the same vein, we don’t know *everything* about the Athenian Calendar or even Athenian Religious Practices - but it is the region we know the most about at this time.
If you are doing research on the Spartan Calendar you should also try searching for and reading about the Laconian Calendar. Based on current research, the Laconian Calendar is believed to be very similar (if not the same as) the Spartan Calendar. And from my sources, it would appear we know slightly more about the Laconians as opposed to the Spartans.
Regarding Hyakintha, according to Harper’s Dictionary of Classical Antiques by Harry Peck (2002), Hyakintha was celebrated for three days during the month of July. The exact three days are presumably unknown based on my sources.
I’d recommend giving them a look to learn more.
[Source 1] [Source 2]
I hope this helped!
- Aön
—————————————
Announcing The Temple of Hyacinthus’
Hyakintha Service
August 6th, 7th, and 8th
More info here
Hyakínthia honors the myth of Hyacinthus, the lover of Lord Apollo who was admired for his beauty and athleticism. This joyous event pays homage to romantic love, growth through change, and the wonder of nature.
This year, the Temple of Hyacinthus will be hosting religious services through a series of posts that will include prayers, the retelling of myths, and Ritual Speeches.
There will also be posts regarding celebration preparation - such as traditional attire, modern rites, and even some recipes!
Join us on August 6th, 7th, and 8th for our inaugural Hyakintha Service.
Eirene, peace and farewell,
#helpol#hellenic polytheism#textpost#ask#answered ask#Hyakintha#Hyakíntha#hyakinthos#hyakinthos deity#Apollo#apollo deity#lord Apollo#the temple of hyacinthus
15 notes
·
View notes