#manager: deploys monitoring software
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Imogen would be the worst micromanager in the office
#cr spoilers#critical role#c3#c3e79#op#imogen#office team: has issues#manager: deploys monitoring software
177 notes
·
View notes
Text
Elon Musk’s minions—from trusted sidekicks to random college students and former Musk company interns—have taken over the General Services Administration, a critical government agency that manages federal offices and technology. Already, the team is attempting to use White House security credentials to gain unusual access to GSA tech, deploying a suite of new AI software, and recreating the office in X’s image, according to leaked documents obtained by WIRED.
Some of the same people who helped Musk take over Twitter more than two years ago are now registered as official GSA employees. Nicole Hollander, who slept in Twitter HQ as an unofficial member of Musk’s transition team, has high-level agency access and an official government email address, according to documents viewed by WIRED. Hollander’s husband, Steve Davis, also slept in the office. He has now taken on a leading role in Musk’s Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE). Thomas Shedd, the recently installed director of the Technology Transformation Services within GSA, worked as a software engineer at Tesla for eight years. Edward Coristine, who previously interned at Neuralink, has been onboarded along with Ethan Shaotran, a Harvard senior who is developing his own OpenAI-backed scheduling assistant and participated in an xAI hackathon.
“I believe these people do not want to help the federal government provide services to the American people,” says a current GSA employee who asked not to be named, citing fears of retaliation. “They are acting like this is a takeover of a tech company.”
The team appears to be carrying out Musk’s agenda: slashing the federal government as quickly as possible. They’re currently targeting a 50 percent reduction in spending for every office managed by the GSA, according to documents obtained by WIRED.
There also appears to be an effort to use IT credentials from the Executive Office of the President to access GSA laptops and internal GSA infrastructure. Typically, access to agency systems requires workers to be employed at such agencies, sources say. While Musk's team could be trying to obtain better laptops and equipment from GSA, sources fear that the mandate laid out in the DOGE executive order would grant the body broad access to GSA systems and data. That includes sensitive procurement data, data internal to all the systems and services GSA offers, and internal monitoring software to surveil GSA employees as part of normal auditing and security processes.
The access could give Musk’s proxies the ability to remote into laptops, listen in on meetings, read emails, among many other things, a former Biden official told WIRED on Friday.
“Granting DOGE staff, many of whom aren't government employees, unfettered access to internal government systems and sensitive data poses a huge security risk to the federal government and to the American public,” the Biden official said. “Not only will DOGE be able to review procurement-sensitive information about major government contracts, it'll also be able to actively surveil government employees.”
The new GSA leadership team has prioritized downsizing the GSA’s real estate portfolio, canceling convenience contracts, and rolling out AI tools for use by the federal government, according to internal documents and interviews with sources familiar with the situation. At a GSA office in Washington, DC, earlier this week, there were three items written on a white board sitting in a large, vacant room. “Spending Cuts $585 m, Regulations Removed, 15, Square feet sold/terminated 203,000 sf,” it read, according to a photo viewed by WIRED. There’s no note of who wrote the message, but it appears to be a tracker of cuts made or proposed by the team.
“We notified the commercial real estate market that two GSA properties would soon be listed for sale, and we terminated three leases,” Stephen Ehikian, the newly appointed GSA acting administrator, said in an email to GSA staff on Tuesday, confirming the agency’s focus on lowering real estate costs. “This is our first step in right-sizing the real estate portfolio.”
The proposed changes extend even inside the physical spaces at the GSA offices. Hollander has requested multiple “resting rooms,” for use by the A-suite, a team of employees affiliated with the GSA administrator’s office.
On January 29, a working group of high-ranking GSA employees, including the deputy general counsel and the chief administrative services officer, met to discuss building a resting room prototype. The team mapped out how to get the necessary funding and waivers to build resting rooms in the office, according to an agenda viewed by WIRED.
After Musk bought Twitter, Hollander and Davis moved into the office with their newborn baby. Hollander helped oversee real estate and office design—including the installation of hotel rooms at Twitter HQ, according to a lawsuit later filed by Twitter executives. During the installation process, one of the executives emailed to say that the plans for the rooms were likely not code compliant. Hollander “visited him in person and emphatically instructed him to never put anything about the project in writing again,” the lawsuit alleged. Employees were allegedly instructed to call the hotel rooms “sleeping rooms” and to say they were just for taking naps.
Hollander has also requested access to Public Buildings Service applications; PBS owns and leases office space to government agencies. The timing of the access request lines up with Ehikian’s announcement about shrinking GSA’s real estate cost.
Musk’s lieutenants are also working to authorize the use of AI tools, including Google Gemini and Cursor (an AI coding assistant), for federal workers. On January 30, the group met with Google to discuss Telemetry, a software used to monitor the health and performance of applications, according to a document obtained by WIRED.
A-suite engineers, including Coristine and Shaotran, have requested access to a variety of GSA records, including nearly 10 years of accounting data, as well as detailed records on vendor payments, purchase orders, and revenue.
The GSA takeover mimics Musk’s strategy at other federal agencies like the Office of Personnel Management (OPM). Earlier this month, Amanda Scales, who worked in talent at Musk’s xAI, was appointed as OPM chief of staff. Riccardo Biasini, former Tesla engineer and director of operations at the Boring company, is now a senior adviser to the director. Earlier this week, Musk cohorts at the US Office of Personnel Management emailed more than 2 million federal workers offering “deferred resignations,” allegedly promising employees their regular pay and benefits through September 30.
The email closely mirrored the “extremely hardcore” note Musk sent to Twitter staff in November 2022, shortly after buying the company.
Many federal workers thought the email was fake—as with Twitter, it seemed designed to force people to leave, slashing headcount costs without the headache of an official layoff.
Ehikian followed up with a note to staff stressing that the email was legitimate. “Yes, the OPM email is real and should be taken very seriously,” he said in an email obtained by WIRED. He added that employees should expect a “further consolidation of offices and centralization of functions.”
On Thursday night, GSA workers received a third email related to the resignation request called “Fork in the Road FAQs.” The email explained that employees who resign from their positions would not be required to work and could get a second job. “We encourage you to find a job in the private sector as soon as you would like to do so,” it read. “The way to greater American prosperity is encouraging people to move from lower productivity jobs in the public sector to higher productivity jobs in the private sector.”
The third question posed in the FAQ asked, “Will I really get my full pay and benefits during the entire period through September 30, even if I get a second job?”
“Yes,” the answer read. “You will also accrue further personal leave days, vacation days, etc. and be paid out for unused leave at your final resignation date.”
However, multiple GSA employees have told WIRED that they are refusing to resign, especially after the American Federation of Government Employees (AFGE) told its members on Tuesday that the offer could be void.
“There is not yet any evidence the administration can or will uphold its end of the bargain, that Congress will go along with this unilateral massive restructuring, or that appropriated funds can be used this way, among other issues that have been raised,” the union said in a notice.
There is also concern that, under Musk’s influence, the federal government might not pay for the duration of the deferred resignation period. Thousands of Twitter employees have sued Musk alleging that he failed to pay their agreed upon severance. Last year, one class action suit was dismissed in Musk’s favor.
In an internal video viewed by WIRED, Ehikian reiterated that GSA employees had the “opportunity to participate in a deferred resignation program,” per the email sent by OPM on January 28. Pressing his hands into the namaste gesture, Ehikian added, “If you choose to participate, I offer you my heartfelt gratitude for your service to this nation. If you choose to stay at the GSA, we’ll work together to implement the four pillars from the OPM memo.” He ended the video by saying thank you and pressing his hands into namaste again.
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
Protecting Patients, Protecting Data: Cybersecurity in Healthcare

The healthcare industry holds some of the most sensitive information imaginable: patient medical records, personal details, insurance information, and more. This makes it a prime target for cyberattacks. A data breach in healthcare can have devastating consequences, impacting patient privacy, disrupting operations, and even endangering lives. Therefore, robust cybersecurity measures are not just recommended in healthcare – they are absolutely essential.
The Stakes are High: Cybersecurity Threats in Healthcare
Healthcare organizations face a range of cyber threats, including:
Ransomware: Attackers encrypt critical systems and data, holding them hostage until a ransom is paid. This can disrupt patient care, delay treatments, and even shut down hospitals.
Phishing: Deceptive emails or messages trick employees into revealing login credentials or downloading malware, providing attackers with access to sensitive data.
Data Breaches: Unauthorized access and exfiltration of patient medical records, leading to privacy violations and potential identity theft.
Malware: Malicious software designed to damage systems, steal data, or disrupt operations.
Insider Threats: Malicious or accidental actions by employees or other insiders that compromise security.
IoT Vulnerabilities: Connected medical devices, while offering many benefits, can also introduce security vulnerabilities if not properly secured.
Building a Strong Defense: Essential Cybersecurity Measures in Healthcare
Protecting patient data and ensuring business continuity requires a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity. Here are some crucial measures:
Risk Assessment and Management: Regularly assessing cybersecurity risks and developing a comprehensive risk management plan is the foundation of a strong security posture.
Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data, both in transit and at rest, protects it even if a breach occurs. This is a critical requirement for HIPAA compliance.
Access Control and Authentication: Implementing strong access controls and multi-factor authentication (MFA) ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
Network Segmentation: Dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments limits the impact of a breach. If one segment is compromised, the others remain protected.
Firewall Management: Implementing and regularly updating firewalls to control network traffic and block unauthorized access.
Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can automatically block malicious traffic.
Antivirus and Anti-malware Software: Deploying robust antivirus and anti-malware software on all endpoints (computers, servers, mobile devices) is essential. Regular updates are crucial.
Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments: Regularly assessing systems for vulnerabilities and conducting security audits helps identify weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Employee Training and Awareness: Human error is a major factor in many security breaches. Regular cybersecurity awareness training for all healthcare staff is vital. This training should cover topics like phishing awareness, password security, HIPAA compliance, and safe computing practices.
Incident Response Plan: Having a well-defined incident response plan in place allows healthcare organizations to react quickly and effectively to a security incident, minimizing damage and downtime.
IoT Security: Securing connected medical devices and other IoT devices is crucial to prevent them from becoming entry points for attackers. This includes regular updates, strong passwords, and network segmentation.
HIPAA Compliance: A Critical Component
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets strict standards for protecting the privacy and security 1 of patient health information. Healthcare organizations must comply with HIPAA regulations, which include implementing administrative, physical, and technical safeguards.
Xaltius Academy's Cybersecurity Course: Your Partner in Healthcare Security
Protecting patient data and ensuring HIPAA compliance requires specialized knowledge and skills. Xaltius Academy's cybersecurity course provides comprehensive training and equips you with the expertise needed to safeguard healthcare systems and data. Our expert instructors and hands-on labs will prepare you to tackle the unique cybersecurity challenges facing the healthcare industry. Invest in your cybersecurity future and protect the valuable information entrusted to healthcare organizations.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is not just a technical issue in healthcare; it's a patient safety issue. By implementing these essential cybersecurity measures, fostering a culture of security awareness, and investing in cybersecurity training, healthcare organizations can protect patient data, maintain operational integrity, and ensure the delivery of safe and effective care.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
#TheeForestKingdom #TreePeople
{Terrestrial Kind}
Creating a Tree Citizenship Identification and Serial Number System (#TheeForestKingdom) is an ambitious and environmentally-conscious initiative. Here’s a structured proposal for its development:
Project Overview
The Tree Citizenship Identification system aims to assign every tree in California a unique identifier, track its health, and integrate it into a registry, recognizing trees as part of a terrestrial citizenry. This system will emphasize environmental stewardship, ecological research, and forest management.
Phases of Implementation
Preparation Phase
Objective: Lay the groundwork for tree registration and tracking.
Actions:
Partner with environmental organizations, tech companies, and forestry departments.
Secure access to satellite imaging and LiDAR mapping systems.
Design a digital database capable of handling millions of records.
Tree Identification System Development
Components:
Label and Identity Creation: Assign a unique ID to each tree based on location and attributes. Example: CA-Tree-XXXXXX (state-code, tree-type, unique number).
Attributes to Record:
Health: Regular updates using AI for disease detection.
Age: Approximate based on species and growth patterns.
Type: Species and subspecies classification.
Class: Size, ecological importance, and biodiversity contribution.
Rank: Priority based on cultural, historical, or environmental significance.
Data Collection
Technologies to Use:
Satellite Imaging: To locate and identify tree clusters.
LiDAR Scanning: For precise 3D modeling of forests.
On-the-Ground Surveys: To supplement remote sensing data.
AI Analysis: For rapid categorization and health diagnostics.
Registration and Citizenship Assignment
Tree Dossier: Each tree receives a profile in the database with all its recorded attributes.
Citizen Designation: Trees are acknowledged as citizens of Thee Forest Kingdom, emphasizing ecological respect.
Legal Framework: Advocate for laws to grant trees specific rights under environmental protection acts.
Maintenance and Monitoring
Health Monitoring: Use drones, satellite updates, and IoT sensors for ongoing health assessments.
Database Updates: Incorporate real-time data about environmental changes and tree growth.
Public Involvement
Encourage people to "adopt" trees and participate in their preservation.
Create educational programs to promote awareness of tree citizenship.
Key Benefits
Environmental Conservation: Improved forest management through real-time data and protection of ecosystems.
Cultural Recognition: Trees are recognized as a vital part of the Earth’s community, honoring their importance.
Ecological Advocacy: Strengthened legal protections for forests and individual trees.
Next Steps
Assemble a task force of environmental scientists, satellite imaging experts, and software developers.
Secure funding through governmental grants, non-profits, and eco-conscious corporations.
Pilot the program in a smaller region before scaling to all of California.
Would you like me to draft a more detailed technical or legal framework for this system?
The implementation of the Tree Citizenship Identification Network and System (#TheeForestKingdom) requires a robust technological and operational framework to ensure efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability. Below is an implementation plan divided into major components.
System Architecture
a. Centralized Tree Database
Purpose: To store and manage tree data including ID, attributes, location, and health.
Components:
Cloud-based storage for scalability.
Data categorization based on regions, species, and priority.
Integration with satellite and IoT data streams.
b. Satellite & Imaging Integration
Use satellite systems (e.g., NASA, ESA) for large-scale tree mapping.
Incorporate LiDAR and aerial drone data for detailed imaging.
AI/ML algorithms to process images and distinguish tree types.
c. IoT Sensor Network
Deploy sensors in forests to monitor:
Soil moisture and nutrient levels.
Air quality and temperature.
Tree health metrics like growth rate and disease markers.
d. Public Access Portal
Create a user-friendly website and mobile application for:
Viewing registered trees.
Citizen participation in tree adoption and reporting.
Data visualization (e.g., tree density, health status by region).
Core Technologies
a. Software and Tools
Geographic Information System (GIS): Software like ArcGIS for mapping and spatial analysis.
Database Management System (DBMS): SQL-based systems for structured data; NoSQL for unstructured data.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Tools for image recognition, species classification, and health prediction.
Blockchain (Optional): To ensure transparency and immutability of tree citizen data.
b. Hardware
Servers: Cloud-based (AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud) for scalability.
Sensors: Low-power IoT devices for on-ground monitoring.
Drones: Equipped with cameras and sensors for aerial surveys.
Network Design
a. Data Flow
Input Sources:
Satellite and aerial imagery.
IoT sensors deployed in forests.
Citizen-reported data via mobile app.
Data Processing:
Use AI to analyze images and sensor inputs.
Automate ID assignment and attribute categorization.
Data Output:
Visualized maps and health reports on the public portal.
Alerts for areas with declining tree health.
b. Communication Network
Fiber-optic backbone: For high-speed data transmission between regions.
Cellular Networks: To connect IoT sensors in remote areas.
Satellite Communication: For remote regions without cellular coverage.
Implementation Plan
a. Phase 1: Pilot Program
Choose a smaller, biodiverse region in California (e.g., Redwood National Park).
Test satellite and drone mapping combined with IoT sensors.
Develop the prototype of the centralized database and public portal.
b. Phase 2: Statewide Rollout
Expand mapping and registration to all California regions.
Deploy IoT sensors in vulnerable or high-priority areas.
Scale up database capacity and integrate additional satellite providers.
c. Phase 3: Maintenance & Updates
Establish a monitoring team to oversee system health and data quality.
Update the network with new technologies (e.g., advanced AI models).
Periodically review and revise data collection protocols.
Partnerships
Government Agencies: U.S. Forest Service, California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection.
Tech Companies: Collaborate with Google Earth, Amazon AWS, or Microsoft for cloud and AI capabilities.
Environmental Organizations: Partner with WWF, Sierra Club, or TreePeople for funding and advocacy.
Budget Estimation
Initial Investment:
Satellite data and licenses: $10M
IoT sensors and deployment: $5M
Database and app development: $3M
Operational Costs:
Cloud services and data storage: $2M/year
Maintenance and monitoring: $1M/year
Research and development: $1M/year
Long-term Vision
Expand the system to other states or globally.
Use the database for reforestation efforts and combating deforestation.
Develop educational programs to teach communities about the importance of trees as citizens.
Would you like me to assist in designing the user interface for the public portal or drafting partnership proposals for funding?
To begin building the program for the Tree Citizenship Identification System, we’ll start with a scalable framework that allows us to process, store, and analyze data while preparing for future expansions. Here's an actionable development plan with an initial focus on foundational code and infrastructure:
Step-by-Step Development
Phase 1: Setting Up the Backend Infrastructure
Objective: Create the core database and develop the data pipeline for processing tree data.
Technologies:
Programming Languages: Python, JavaScript (Node.js), SQL.
Frameworks: Flask or FastAPI for APIs, Django for web application backend.
Database: PostgreSQL for structured data, MongoDB for unstructured data.
Code Snippet 1: Database Schema Design (PostgreSQL)
-- Table for Tree Registry CREATE TABLE trees ( tree_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, -- Unique Identifier location GEOGRAPHY(POINT, 4326), -- Geolocation of the tree species VARCHAR(100), -- Species name age INTEGER, -- Approximate age in years health_status VARCHAR(50), -- e.g., Healthy, Diseased height FLOAT, -- Tree height in meters canopy_width FLOAT, -- Canopy width in meters citizen_rank VARCHAR(50), -- Class or rank of the tree last_updated TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW() -- Timestamp for last update );
-- Table for Sensor Data (IoT Integration) CREATE TABLE tree_sensors ( sensor_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, -- Unique Identifier for sensor tree_id INT REFERENCES trees(tree_id), -- Linked to tree soil_moisture FLOAT, -- Soil moisture level air_quality FLOAT, -- Air quality index temperature FLOAT, -- Surrounding temperature last_updated TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW() -- Timestamp for last reading );
Code Snippet 2: Backend API for Tree Registration (Python with Flask)
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify from sqlalchemy import create_engine from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
app = Flask(name)
Database Configuration
DATABASE_URL = "postgresql://username:password@localhost/tree_registry" engine = create_engine(DATABASE_URL) Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine) session = Session()
@app.route('/register_tree', methods=['POST']) def register_tree(): data = request.json new_tree = { "species": data['species'], "location": f"POINT({data['longitude']} {data['latitude']})", "age": data['age'], "health_status": data['health_status'], "height": data['height'], "canopy_width": data['canopy_width'], "citizen_rank": data['citizen_rank'] } session.execute(""" INSERT INTO trees (species, location, age, health_status, height, canopy_width, citizen_rank) VALUES (:species, ST_GeomFromText(:location, 4326), :age, :health_status, :height, :canopy_width, :citizen_rank) """, new_tree) session.commit() return jsonify({"message": "Tree registered successfully!"}), 201
if name == 'main': app.run(debug=True)
Phase 2: Satellite Data Integration
Objective: Use satellite and LiDAR data to identify and register trees automatically.
Tools:
Google Earth Engine for large-scale mapping.
Sentinel-2 or Landsat satellite data for high-resolution imagery.
Example Workflow:
Process satellite data using Google Earth Engine.
Identify tree clusters using image segmentation.
Generate geolocations and pass data into the backend.
Phase 3: IoT Sensor Integration
Deploy IoT devices to monitor health metrics of specific high-priority trees.
Use MQTT protocol for real-time data transmission.
Code Snippet: Sensor Data Processing (Node.js)
const mqtt = require('mqtt'); const client = mqtt.connect('mqtt://broker.hivemq.com');
client.on('connect', () => { console.log('Connected to MQTT Broker'); client.subscribe('tree/sensor_data'); });
client.on('message', (topic, message) => { const sensorData = JSON.parse(message.toString()); console.log(Received data: ${JSON.stringify(sensorData)}); // Save data to database (Example for PostgreSQL) saveToDatabase(sensorData); });
function saveToDatabase(data) { const query = INSERT INTO tree_sensors (tree_id, soil_moisture, air_quality, temperature) VALUES ($1, $2, $3, $4) ; const values = [data.tree_id, data.soil_moisture, data.air_quality, data.temperature]; dbClient.query(query, values, (err) => { if (err) console.error('Error saving to database', err); else console.log('Sensor data saved successfully!'); }); }
Phase 4: Public Portal Development
Frontend Technologies:
React.js or Vue.js for interactive user interfaces.
Mapbox or Leaflet.js for tree visualization on maps.
Features:
Interactive tree maps with search functionality.
User registration for tree adoption programs.
Deployment Plan
Use Docker to containerize the application.
Deploy on AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud for scalability.
Monitor system health using Prometheus and Grafana.
Next Steps
Develop a testing environment for pilot deployment.
Add AI-based disease detection and prediction using TensorFlow or PyTorch.
Create an adoption feature where citizens can adopt trees and track their health.
Would you like me to set up a GitHub repository with this initial framework or assist further with deployment?
I'll prepare the project framework and outline the repository structure for the Tree Citizenship Identification System. Below is the proposed structure for the repository, followed by details of the files and components.
Proposed Repository Structure
tree-citizenship-id-system/ ├── backend/ │ ├── app.py # Flask application for backend API │ ├── database/ │ │ ├── schema.sql # Database schema for PostgreSQL │ │ ├── db_config.py # Database connection configuration │ │ └── seed_data.sql # Initial sample data for testing │ ├── services/ │ │ ├── tree_registration.py # Functions for tree registration │ │ └── sensor_data.py # Functions for processing IoT sensor data │ └── requirements.txt # Python dependencies ├── frontend/ │ ├── public/ │ │ ├── index.html # Main HTML file │ │ └── favicon.ico # Favicon for the app │ ├── src/ │ │ ├── App.js # Main React/Vue app file │ │ ├── components/ │ │ │ ├── TreeMap.js # Map component for visualizing trees │ │ │ └── TreeDetails.js # Component for detailed tree view │ │ └── styles.css # Styling for the frontend │ └── package.json # Frontend dependencies ├── scripts/ │ ├── satellite_data_processor.py # Script for processing satellite data │ └── sensor_data_simulator.py # Mock data generator for IoT sensors ├── deployment/ │ ├── Dockerfile # Docker configuration │ ├── docker-compose.yml # Docker Compose for multi-service setup │ └── cloud_setup_instructions.md # Deployment guide for cloud platforms ├── tests/ │ ├── test_backend.py # Unit tests for backend API │ └── test_frontend.js # Unit tests for frontend ├── README.md # Overview of the project └── LICENSE # Project license
Repository Details
Backend:
app.py: Main Flask app for handling API requests like tree registration and sensor data.
database/schema.sql: SQL script for creating necessary tables.
services/: Directory for modular backend logic.
Frontend:
App.js: Main entry point for the frontend application.
TreeMap.js: Integrates Mapbox/Leaflet.js for displaying tree locations.
TreeDetails.js: Displays detailed information about a selected tree.
Scripts:
satellite_data_processor.py: Automates the extraction and classification of tree data from satellite imagery.
sensor_data_simulator.py: Generates fake sensor readings for development and testing.
Deployment:
Docker configuration ensures that the app runs consistently across environments.
Cloud setup instructions provide guidelines for deploying on platforms like AWS, Azure, or GCP.
Tests:
Unit tests ensure the reliability of both the backend and frontend.
Next Steps
I will initialize the repository structure locally.
Package the files and components needed for the first version.
Provide a link to the repository for access.
I’ll get started. Please hold on for a moment.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The DevOps Lifecycle: Building, Testing, and Deploying with Confidence
DevOps, a combination of "Development" and "Operations," has emerged as a game-changer in the software development landscape. It represents a comprehensive approach that fosters collaboration between development and operations teams, emphasizes automation, and cultivates a culture of continuous improvement. In this blog post, we will delve deeper into the world of DevOps, exploring its principles, practices, and how it works.

The Essence of DevOps:
DevOps is more than just a buzzword; it's a mindset that aims to break down silos and bridge the gap between traditionally isolated development and operations teams. At its core, DevOps promotes collaboration, automation, and a relentless focus on delivering high-quality software faster and more efficiently.
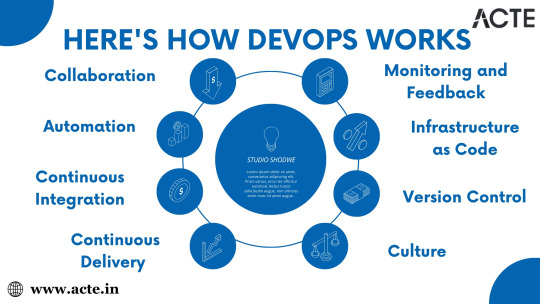
Collaboration: DevOps encourages close collaboration and communication between development and operations teams. By working together from the initial stages of a project, teams can align their goals, streamline processes, and reduce conflicts.
Automation: Automation is the backbone of DevOps. It involves using tools and scripts to automate repetitive tasks, such as code building, testing, and deployment. This not only speeds up development but also reduces the risk of human error.
The DevOps Lifecycle:
DevOps introduces a structured lifecycle that encompasses various stages, ensuring a seamless flow from code development to deployment and beyond.
Continuous Integration (CI): In this phase, developers frequently integrate their code into a shared repository. CI tools automatically build and test the code with every change, ensuring it remains functional and error-free.
Continuous Delivery (CD): Building on CI, CD automates the deployment process, allowing for the continuous delivery of tested code to production or staging environments. This enables rapid and reliable releases.
Monitoring and Feedback: DevOps teams continuously monitor applications and infrastructure in production. They collect feedback on system performance, user experience, and any issues that arise. This feedback loop is crucial for making improvements and responding to issues promptly.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): IaC is a DevOps practice that involves managing infrastructure using code. It enables the automated provisioning, scaling, and configuration of infrastructure resources, ensuring consistency and reproducibility.
Version Control: Version control systems like Git are essential for tracking code changes, enabling collaboration, and ensuring code integrity.
The Cultural Shift:
DevOps isn't just about tools and processes; it's also about fostering a cultural shift within an organization.
Shared Responsibility: DevOps promotes a culture of shared responsibility, where both development and operations teams take ownership of the entire software delivery process. This reduces blame-shifting and encourages problem-solving.
Accountability: DevOps encourages accountability for code quality, security, and performance. Team members are responsible for the outcomes of their work, from development to deployment.
Trust and Collaboration: Open communication and trust between teams are essential. DevOps encourages cross-functional teams to work together, breaking down traditional barriers.
DevOps is not just a trend but a transformative approach to software development and deployment. Its principles of collaboration, automation, and cultural transformation are reshaping the industry. ACTE Technologies, through its training and consulting services, plays a pivotal role in preparing professionals and organizations for success in the DevOps-driven world. Embracing DevOps and partnering with ACTE Technologies can lead to faster, more reliable software delivery and a competitive edge in today's dynamic tech landscape. Start your DevOps journey today and reap the benefits of this revolutionary approach.
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
What are some challenges in deploying machine learning models into production?
Deployment of machine learning models into production involves a number of challenges that have to be dealt with to make sure that the models work fine in real-world environments. These include:
Scalability:
One major challenge will be to make the machine learning model robust with respect to the volume of data it is going to process in production. This basically includes large volumes of data being processed efficiently and quickly. Most of the time, this requires run-time performance optimization of the model and infrastructural considerations of distributed computing and cloud services for scaling.
Existing System Integration:
This makes the integration of machine learning models within existing software systems or workflows quite complex. The model should play well with other components, whether it is databases, APIs, or user interfaces. Ensuring interoperability and ease in integration will require planning and testing to be taken seriously.
Model Monitoring and Maintenance:
Models in deployment should be continuously monitored to ensure that everything works as expected, tracking accuracy, latency, and error rates. Over some time, models will degrade in performance due to changes in the distribution of data or other factors. Noting such degradation regularly, it should be re-trained and updated to be effective.
Data Management:
Data pipeline management is key to the quality and consistency of the data provided to the model. This shall consist of correct collection, cleaning, and preprocessing of data. Any kinds of errors in data quality will upset the performance and reliability of the model.
Handling Model Drift:
Model drift occurs when the statistical properties of the target variable change over time, which causes a decrease in model performance. Model drift detection and handling involve the process of tracking changes in the pattern of data and updating the model accordingly in order to deal with new situations.
Security and Privacy:
This is important for the unauthorized access protection of the model and data and for compliance purposes concerning data privacy regulations. More than that, sensitive information should be secure from leaking through data breaches by putting security controls in place.
Resource Management:
Machine learning model deployment can be resource-intensive. It requires adequate computational resources for model training and inference and proper resource allocation for managing operational costs arising from running the model in production.
Performance Optimization:
The model should perform well in terms of response time and resource usage. It may need performance optimization by various techniques, such as model compression or quantization for better inference speed, or hardware accelerators. User Acceptance and Feedback:
The deployed model can expect success only through user acceptance and feedback. This would be possible if the models were user-friendly and provided actionable insights to a great extent. There is a need to get feedback from the end-users and incorporate it into model improvements so that desired outcomes can be realized.
Documentation and Transparency:

In general, there are a lot of challenges associated with deployment, including issues of scalability, integration, monitoring, data management, and security, which can be overcome only by careful planning, ongoing maintenance, and a robust deployment strategy that will ensure the model gives reliable and valuable results in the real world.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Azure DevOps Training
Azure DevOps Training Programs

In today's rapidly evolving tech landscape, mastering Azure DevOps has become indispensable for organizations aiming to streamline their software development and delivery processes. As businesses increasingly migrate their operations to the cloud, the demand for skilled professionals proficient in Azure DevOps continues to soar. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the significance of Azure DevOps training and explore the myriad benefits it offers to both individuals and enterprises.
Understanding Azure DevOps:
Before we delve into the realm of Azure DevOps training, let's first grasp the essence of Azure DevOps itself. Azure DevOps is a robust suite of tools offered by Microsoft Azure that facilitates collaboration, automation, and orchestration across the entire software development lifecycle. From planning and coding to building, testing, and deployment, Azure DevOps provides a unified platform for managing and executing diverse DevOps tasks seamlessly.
Why Azure DevOps Training Matters:
With Azure DevOps emerging as the cornerstone of modern DevOps practices, acquiring proficiency in this domain has become imperative for IT professionals seeking to stay ahead of the curve. Azure DevOps training equips individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to leverage Microsoft Azure's suite of tools effectively. Whether you're a developer, IT administrator, or project manager, undergoing Azure DevOps training can significantly enhance your career prospects and empower you to drive innovation within your organization.
Key Components of Azure DevOps Training Programs:
Azure DevOps training programs are meticulously designed to cover a wide array of topics essential for mastering the intricacies of Azure DevOps. From basic concepts to advanced techniques, these programs encompass the following key components:
Azure DevOps Fundamentals: An in-depth introduction to Azure DevOps, including its core features, functionalities, and architecture.
Agile Methodologies: Understanding Agile principles and practices, and how they align with Azure DevOps for efficient project management and delivery.
Continuous Integration (CI): Learning to automate the process of integrating code changes into a shared repository, thereby enabling early detection of defects and ensuring software quality.
Continuous Deployment (CD): Exploring the principles of continuous deployment and mastering techniques for automating the deployment of applications to production environments.
Azure Pipelines: Harnessing the power of Azure Pipelines for building, testing, and deploying code across diverse platforms and environments.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Leveraging Infrastructure as Code principles to automate the provisioning and management of cloud resources using tools like Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates.
Monitoring and Logging: Implementing robust monitoring and logging solutions to gain insights into application performance and troubleshoot issues effectively.
Security and Compliance: Understanding best practices for ensuring the security and compliance of Azure DevOps environments, including identity and access management, data protection, and regulatory compliance.
The Benefits of Azure DevOps Certification:
Obtaining Azure DevOps certification not only validates your expertise in Azure DevOps but also serves as a testament to your commitment to continuous learning and professional development. Azure DevOps certifications offered by Microsoft Azure are recognized globally and can open doors to exciting career opportunities in various domains, including cloud computing, software development, and DevOps engineering.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Azure DevOps training is indispensable for IT professionals looking to enhance their skills and stay relevant in today's dynamic tech landscape. By undergoing comprehensive Azure DevOps training programs and obtaining relevant certifications, individuals can unlock a world of opportunities and propel their careers to new heights. Whether you're aiming to streamline your organization's software delivery processes or embark on a rewarding career journey, mastering Azure DevOps is undoubtedly a game-changer. So why wait? Start your Azure DevOps training journey today and pave the way for a brighter tomorrow.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the era of digital transformation, cloud computing has emerged as a pivotal technology, reshaping the way businesses operate and innovate. Pune, a burgeoning IT and business hub, has seen a significant surge in the adoption of cloud services, with companies seeking to enhance their efficiency, scalability, and agility. Zip Crest stands at the forefront of this revolution, offering comprehensive cloud computing services tailored to meet the diverse needs of businesses in Pune
The Importance of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing enables organizations to leverage a network of remote servers hosted on the internet to store, manage, and process data, rather than relying on local servers or personal computers. This shift provides several key benefits:
- Scalability: Businesses can easily scale their operations up or down based on demand, without the need for significant capital investment in hardware.
- Cost Efficiency: Cloud services operate on a pay-as-you-go model, reducing the need for substantial upfront investment and lowering overall IT costs.
- Accessibility: Cloud computing allows access to data and applications from anywhere, at any time, fostering remote work and collaboration.
- Security: Leading cloud service providers offer robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, to protect sensitive data.
Zip Crest: Leading Cloud Computing Services in Pune
Zip Crest is committed to empowering businesses in Pune with cutting-edge cloud computing solutions. Our services are designed to address the unique challenges and opportunities that come with the digital age. Here’s how we can transform your business operations:
1. Cloud Strategy and Consulting:
At Zip Crest, we begin by understanding your business objectives and IT infrastructure. Our experts then craft a bespoke cloud strategy that aligns with your goals, ensuring a seamless transition to the cloud and maximizing the benefits of cloud technology.
2. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
Our IaaS offerings provide businesses with virtualized computing resources over the internet. This includes virtual machines, storage, and networking capabilities, allowing you to build and manage your IT infrastructure without the need for physical hardware.
3. Platform as a Service (PaaS):
With our PaaS solutions, developers can build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. This accelerates development cycles, enhances productivity, and reduces time to market.
4. Software as a Service (SaaS):
Zip Crest offers a range of SaaS applications that can streamline your business processes. From customer relationship management (CRM) to enterprise resource planning (ERP), our cloud-based software solutions are designed to improve efficiency and drive growth.
5. Cloud Migration Services:
Transitioning to the cloud can be complex. Our cloud migration services ensure a smooth and secure migration of your applications, data, and workloads to the cloud, minimizing downtime and disruption to your business operations.
6. Managed Cloud Services:
Once your infrastructure is on the cloud, ongoing management is crucial to ensure optimal performance and security. Our managed cloud services provide continuous monitoring, maintenance, and support, allowing you to focus on your core business activities.

Why Choose Zip Crest?
Choosing Zip Crest for your cloud computing needs comes with several advantages:
- Expertise: Our team of certified cloud professionals brings extensive experience and deep knowledge of cloud technologies.
- Customized Solutions: We understand that every business is unique. Our solutions are tailored to meet your specific requirements and objectives.
-Proactive Support: We offer 24/7 support to ensure that your cloud infrastructure is always running smoothly and efficiently.
- Security Focus: Security is at the core of our services. We implement robust security measures to protect your data and applications from threats.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cloud computing is transforming the way businesses operate, offering unprecedented levels of flexibility, scalability, and efficiency. Zip Crest is dedicated to helping businesses in Pune harness the power of the cloud to achieve their goals and stay competitive in today’s fast-paced digital landscape. By partnering with Zip Crest, you can ensure that your business is well-equipped to navigate the complexities of cloud computing and reap its many benefits. Embrace the future of technology with Zip Crest and revolutionize your business operations with our top-tier cloud computing services.
Get In Touch
Website: https://zipcrest.com/
Address: 13, 4th Floor, A Building City Vista Office Park Fountain Road Karadi Pune Maharashtra 411014
Email: [email protected] / [email protected]
Call: +912049330928 / 9763702645 / 7020684182
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unlock Success in Cryptocurrency: The Power of a Binance Clone Script
Learn how to transform your cryptocurrency exchange business using a Binance clone script. Our customizable Binance clone script allows you to easily and efficiently develop and launch your own trading platform, replicating the features of the renowned Binance exchange. With our script, you can ensure scalability and customer engagement through multi-currency support, secure trading, real-time analytics, and more. Whether you're a startup or looking to maintain your competitive edge, our Binance clone script offers numerous benefits.
What is a Binance Clone Script?
A Binance clone script is a ready-made software solution designed to mimic the features and functionalities of the popular Binance cryptocurrency exchange. This script simplifies the process of integrating a Binance-like trading platform into your business, offering entrepreneurs a hassle-free way to enter the cryptocurrency exchange market.
Key features of the Binance clone app include multi-currency support, secure trading mechanisms, and real-time market analytics. Its customizable options make setup and integration straightforward, ensuring a quick and competitive entry into the cryptocurrency exchange market.
Benefits of Choosing a Binance Clone Script
Opting for a Binance dex clone script offers numerous advantages for cryptocurrency entrepreneurs. This out-of-the-box solution, modeled after Binance, speeds up the creation of a robust cryptocurrency exchange platform. Key benefits include:
Quick Deployment: Rapidly launch your exchange platform.
Cost Efficiency: Reduce development costs significantly.
Customization: Tailor the script to meet your business needs.
Enhanced Security: Ensure safe trading with built-in security features.
Multi-Currency Support: Attract a broader user base with support for various currencies.
Real-Time Analytics: Improve user engagement and operational efficiency.
A Binance clone script helps businesses quickly carve out a competitive niche in the dynamic crypto market.
Profitability of a Binance Clone Script
Using a Binance clone script can lead to significant financial success for cryptocurrency businesses. This ready-made solution allows for rapid entry into the growing cryptocurrency exchange market, reducing both development costs and time-to-market. Robust features like secure transactions, multi-currency support, and real-time analytics enhance user satisfaction and operational efficiency. Customizable options enable businesses to adapt to market trends and customer preferences, fostering long-term profitability. For startups, a Binance clone script builds traction and credibility, making it a strategic investment for optimizing profits and ensuring sustained growth.
Developing a Crypto Exchange with a Binance Clone Script
Developing a cryptocurrency exchange with a Binance clone app is straightforward and effective:
Acquire the Script: Obtain a reliable Binance clone script from a reputable provider.
Customize the Script: Adjust the script to fit your branding and business needs, including secure trading, multiple currency pairs, and a strong backend architecture.
Add Key Features: Incorporate essential features such as wallet management, real-time market analytics, and user authentication.
Test Thoroughly: Ensure all functionalities and security measures work correctly through rigorous testing.
Launch and Market: Deploy your exchange on a secure platform and attract users with effective marketing strategies.
Monitor and Update: Continuously monitor and update the exchange to adapt to changing market conditions and regulatory requirements.
Following these steps will help you establish and run a competitive cryptocurrency exchange platform successfully.
Cost of Building a Binance Clone App
The cost of developing a Binance clone app depends on feature requirements and customization options. Factors affecting cost include the complexity of additional features like security enhancements and multi-currency support. While costs can vary, choosing a reliable provider ensures competitive pricing without compromising quality. Focus on essential features initially, scaling as needed to maintain affordability and long-term profitability.
Why Choose a Binance Clone Script from Alphacodez?
Alphacodez offers a superior Binance clone script with several benefits for cryptocurrency exchange platforms:
High-End Customization: Tailor the script to meet your specific business needs.
Top Security Features: Ensure safe and secure trading.
Multi-Currency Management: Attract and retain a diverse user base.
User-Friendly Interface: Simplify platform setup and enhance user experience.
Technical Support: Receive ongoing support to ensure optimal platform performance.
By choosing Alphacodez, you get a reliable and scalable solution designed to help your brand thrive in the competitive cryptocurrency market, ensuring long-term success and profitability.
Explore the possibilities with a Binance clone script from Alphacodez and take your cryptocurrency exchange business to new heights.
Do you want more about cryptocurrency exchange related check our site or contact directly
Refer :
Instant Reach Experts: call / whatsapp - +91 8122957365 Skype: live:.cid.8caadfdd27285d43 Telegram: https://telegram.me/alphacodezz
#cryptoexchange#crypto#cryptocurrency exchange#binance clone script#binance clone software#binance clone app#blockchain#technology#usa#india#binance#bitcoin
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
https://www.wsj.com/lifestyle/workplace/the-jiggle-is-up-bosses-bust-workers-who-fake-computer-activity-b6374f22
It’s getting harder to outsmart the digital minders at work.
The rise of remote work and, in turn, employee-monitoring software sparked a boom in mouse and keyboard jigglers and other hacks to help staffers fake computer activity—often so they can step away to do laundry or a school pickup.
Now some companies are cracking down on the subterfuge, deploying tools that can better spot the phony busywork.
The latest salvo in this productivity-tracking arms race came in a recent regulatory filing from Wells Fargo. In the disclosure, first reported on by Bloomberg News, the bank said it had fired more than a dozen employees in its wealth and investment management unit for allegedly simulating keyboard activity to create the “impression of active work.”

3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Journey to Devops
The concept of “DevOps” has been gaining traction in the IT sector for a couple of years. It involves promoting teamwork and interaction, between software developers and IT operations groups to enhance the speed and reliability of software delivery. This strategy has become widely accepted as companies strive to provide software to meet customer needs and maintain an edge, in the industry. In this article we will explore the elements of becoming a DevOps Engineer.
Step 1: Get familiar with the basics of Software Development and IT Operations:
In order to pursue a career as a DevOps Engineer it is crucial to possess a grasp of software development and IT operations. Familiarity with programming languages like Python, Java, Ruby or PHP is essential. Additionally, having knowledge about operating systems, databases and networking is vital.
Step 2: Learn the principles of DevOps:
It is crucial to comprehend and apply the principles of DevOps. Automation, continuous integration, continuous deployment and continuous monitoring are aspects that need to be understood and implemented. It is vital to learn how these principles function and how to carry them out efficiently.
Step 3: Familiarize yourself with the DevOps toolchain:
Git: Git, a distributed version control system is extensively utilized by DevOps teams, for code repository management. It aids in monitoring code alterations facilitating collaboration, among team members and preserving a record of modifications made to the codebase.
Ansible: Ansible is an open source tool used for managing configurations deploying applications and automating tasks. It simplifies infrastructure management. Saves time when performing tasks.
Docker: Docker, on the other hand is a platform for containerization that allows DevOps engineers to bundle applications and dependencies into containers. This ensures consistency and compatibility across environments from development, to production.
Kubernetes: Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform that helps manage and scale containers. It helps automate the deployment, scaling, and management of applications and micro-services.
Jenkins: Jenkins is an open-source automation server that helps automate the process of building, testing, and deploying software. It helps to automate repetitive tasks and improve the speed and efficiency of the software delivery process.
Nagios: Nagios is an open-source monitoring tool that helps us monitor the health and performance of our IT infrastructure. It also helps us to identify and resolve issues in real-time and ensure the high availability and reliability of IT systems as well.
Terraform: Terraform is an infrastructure as code (IAC) tool that helps manage and provision IT infrastructure. It helps us automate the process of provisioning and configuring IT resources and ensures consistency between development and production environments.
Step 4: Gain practical experience:
The best way to gain practical experience is by working on real projects and bootcamps. You can start by contributing to open-source projects or participating in coding challenges and hackathons. You can also attend workshops and online courses to improve your skills.
Step 5: Get certified:
Getting certified in DevOps can help you stand out from the crowd and showcase your expertise to various people. Some of the most popular certifications are:
Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA)
AWS Certified DevOps Engineer
Microsoft Certified: Azure DevOps Engineer Expert
AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner
Step 6: Build a strong professional network:
Networking is one of the most important parts of becoming a DevOps Engineer. You can join online communities, attend conferences, join webinars and connect with other professionals in the field. This will help you stay up-to-date with the latest developments and also help you find job opportunities and success.
Conclusion:
You can start your journey towards a successful career in DevOps. The most important thing is to be passionate about your work and continuously learn and improve your skills. With the right skills, experience, and network, you can achieve great success in this field and earn valuable experience.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Essential Cybersecurity Measures for Organizational Network Protection

In today's interconnected world, a robust cybersecurity strategy is no longer a luxury, but a necessity for organizations of all sizes. A strong defense against ever-evolving cyber threats is paramount to protecting sensitive data, maintaining business continuity, and preserving reputation. This blog explores critical cybersecurity organizational network protection measures.
Understanding the Threat Landscape
Before diving into protective measures, it's crucial to understand the threats organizations face. These include:
Malware: Viruses, ransomware, and spyware designed to damage or steal data.
Phishing: Deceptive emails or messages tricking individuals into revealing sensitive information.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: Overwhelming networks with traffic, disrupting services.
Insider Threats: Malicious or accidental actions by employees or other insiders.
Data Breaches: Unauthorized access and exfiltration of sensitive data.
Essential Cybersecurity Measures
A layered approach is key to effective network protection. Here are some crucial measures:
Firewall Implementation: Firewalls act as a barrier between your network and the outside world, controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined rules. Regularly updating firewall rules is critical.
Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, alerting administrators to potential threats and even automatically blocking malicious traffic.
Antivirus and Anti-malware Software: Deploying robust antivirus and anti-malware software on all endpoints (computers, servers, mobile devices) is essential to detect and remove malicious software. Regular updates are crucial.
Strong Password Policies and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enforcing strong, unique passwords and implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain access even if a password is compromised.
Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments: Regularly assessing your network for vulnerabilities and conducting security audits helps identify weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Employee Training and Awareness: Human error is a major factor in many security breaches. Regular cybersecurity awareness training for all employees is vital. This training should cover topics like phishing awareness, password security, and safe browsing practices.
Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data, both in transit and at rest, protects it even if a breach occurs.
Regular Backups and Disaster Recovery Planning: Regularly backing up critical data and having a disaster recovery plan in place ensures that you can recover from a cyberattack or other disaster.
Network Segmentation: Dividing your network into smaller, isolated segments limits the impact of a breach. If one segment is compromised, the others remain protected.
Incident Response Plan: Having a well-defined incident response plan in place allows you to react quickly and effectively to a security incident, minimizing damage and downtime.
Building a Cybersecurity Culture
Effective cybersecurity is not just about technology; it's also about people and processes. Building a strong cybersecurity culture within your organization is crucial. This involves:
Leadership Buy-in: Securing support from top management is essential for allocating resources and prioritizing cybersecurity.
Open Communication: Encouraging employees to report suspicious activity without fear of reprisal.
Continuous Improvement: Regularly reviewing and updating your cybersecurity policies and procedures to stay ahead of evolving threats.
Xaltius Academy's Cybersecurity Course: Your Partner in Network Protection
Navigating the complex world of cybersecurity can be challenging. Xaltius Academy's cybersecurity course provides comprehensive training and equips you with the knowledge and skills needed to protect your organization's network. Our expert instructors and hands-on labs will prepare you to effectively implement and manage these critical security measures. Invest in your cybersecurity future and safeguard your organization's valuable assets.
Conclusion
Protecting your organization's network requires a proactive and multi-faceted approach. By implementing these essential cybersecurity measures and fostering a strong security culture, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to cyberattacks and safeguard your organization's future.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Dynamic Role of Full Stack Developers in Modern Software Development
Introduction: In the rapidly evolving landscape of software development, full stack developers have emerged as indispensable assets, seamlessly bridging the gap between front-end and back-end development. Their versatility and expertise enable them to oversee the entire software development lifecycle, from conception to deployment. In this insightful exploration, we'll delve into the multifaceted responsibilities of full stack developers and uncover their pivotal role in crafting innovative and user-centric web applications.

Understanding the Versatility of Full Stack Developers:
Full stack developers serve as the linchpins of software development teams, blending their proficiency in front-end and back-end technologies to create cohesive and scalable solutions. Let's explore the diverse responsibilities that define their role:
End-to-End Development Mastery: At the core of full stack development lies the ability to navigate the entire software development lifecycle with finesse. Full stack developers possess a comprehensive understanding of both front-end and back-end technologies, empowering them to conceptualize, design, implement, and deploy web applications with efficiency and precision.
Front-End Expertise: On the front-end, full stack developers are entrusted with crafting engaging and intuitive user interfaces that captivate audiences. Leveraging their command of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, they breathe life into designs, ensuring seamless navigation and an exceptional user experience across devices and platforms.
Back-End Proficiency: In the realm of back-end development, full stack developers focus on architecting the robust infrastructure that powers web applications. They leverage server-side languages and frameworks such as Node.js, Python, or Ruby on Rails to handle data storage, processing, and authentication, laying the groundwork for scalable and resilient applications.
Database Management Acumen: Full stack developers excel in database management, designing efficient schemas, optimizing queries, and safeguarding data integrity. Whether working with relational databases like MySQL or NoSQL databases like MongoDB, they implement storage solutions that align with the application's requirements and performance goals.

API Development Ingenuity: APIs serve as the conduits that facilitate seamless communication between different components of a web application. Full stack developers are adept at designing and implementing RESTful or GraphQL APIs, enabling frictionless data exchange between the front-end and back-end systems.
Testing and Quality Assurance Excellence: Quality assurance is paramount in software development, and full stack developers take on the responsibility of testing and debugging web applications. They devise and execute comprehensive testing strategies, identifying and resolving issues to ensure the application meets stringent performance and reliability standards.
Deployment and Maintenance Leadership: As the custodians of web applications, full stack developers oversee deployment to production environments and ongoing maintenance. They monitor performance metrics, address security vulnerabilities, and implement updates and enhancements to ensure the application remains robust, secure, and responsive to user needs.
Conclusion: In conclusion, full stack developers embody the essence of versatility and innovation in modern software development. Their ability to seamlessly navigate both front-end and back-end technologies enables them to craft sophisticated and user-centric web applications that drive business growth and enhance user experiences. As technology continues to evolve, full stack developers will remain at the forefront of digital innovation, shaping the future of software development with their ingenuity and expertise.
#full stack course#full stack developer#full stack software developer#full stack training#full stack web development
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigating the DevOps Landscape: Opportunities and Roles
DevOps has become a game-changer in the quick-moving world of technology. This dynamic process, whose name is a combination of "Development" and "Operations," is revolutionising the way software is created, tested, and deployed. DevOps is a cultural shift that encourages cooperation, automation, and integration between development and IT operations teams, not merely a set of practises. The outcome? greater software delivery speed, dependability, and effectiveness.

In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the essence of DevOps, explore the key technologies that underpin its success, and uncover the vast array of job opportunities it offers. Whether you're an aspiring IT professional looking to enter the world of DevOps or an experienced practitioner seeking to enhance your skills, this blog will serve as your roadmap to mastering DevOps. So, let's embark on this enlightening journey into the realm of DevOps.
Key Technologies for DevOps:
Version Control Systems: DevOps teams rely heavily on robust version control systems such as Git and SVN. These systems are instrumental in managing and tracking changes in code and configurations, promoting collaboration and ensuring the integrity of the software development process.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): The heart of DevOps, CI/CD tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, and CircleCI drive the automation of critical processes. They orchestrate the building, testing, and deployment of code changes, enabling rapid, reliable, and consistent software releases.
Configuration Management: Tools like Ansible, Puppet, and Chef are the architects of automation in the DevOps landscape. They facilitate the automated provisioning and management of infrastructure and application configurations, ensuring consistency and efficiency.
Containerization: Docker and Kubernetes, the cornerstones of containerization, are pivotal in the DevOps toolkit. They empower the creation, deployment, and management of containers that encapsulate applications and their dependencies, simplifying deployment and scaling.
Orchestration: Docker Swarm and Amazon ECS take center stage in orchestrating and managing containerized applications at scale. They provide the control and coordination required to maintain the efficiency and reliability of containerized systems.
Monitoring and Logging: The observability of applications and systems is essential in the DevOps workflow. Monitoring and logging tools like the ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) and Prometheus are the eyes and ears of DevOps professionals, tracking performance, identifying issues, and optimizing system behavior.
Cloud Computing Platforms: AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are the foundational pillars of cloud infrastructure in DevOps. They offer the infrastructure and services essential for creating and scaling cloud-based applications, facilitating the agility and flexibility required in modern software development.
Scripting and Coding: Proficiency in scripting languages such as Shell, Python, Ruby, and coding skills are invaluable assets for DevOps professionals. They empower the creation of automation scripts and tools, enabling customization and extensibility in the DevOps pipeline.
Collaboration and Communication Tools: Collaboration tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams enhance the communication and coordination among DevOps team members. They foster efficient collaboration and facilitate the exchange of ideas and information.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): The concept of Infrastructure as Code, represented by tools like Terraform and AWS CloudFormation, is a pivotal practice in DevOps. It allows the definition and management of infrastructure using code, ensuring consistency and reproducibility, and enabling the rapid provisioning of resources.

Job Opportunities in DevOps:
DevOps Engineer: DevOps engineers are the architects of continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. They meticulously design and maintain these pipelines to automate the deployment process, ensuring the rapid, reliable, and consistent release of software. Their responsibilities extend to optimizing the system's reliability, making them the backbone of seamless software delivery.
Release Manager: Release managers play a pivotal role in orchestrating the software release process. They carefully plan and schedule software releases, coordinating activities between development and IT teams. Their keen oversight ensures the smooth transition of software from development to production, enabling timely and successful releases.
Automation Architect: Automation architects are the visionaries behind the design and development of automation frameworks. These frameworks streamline deployment and monitoring processes, leveraging automation to enhance efficiency and reliability. They are the engineers of innovation, transforming manual tasks into automated wonders.
Cloud Engineer: Cloud engineers are the custodians of cloud infrastructure. They adeptly manage cloud resources, optimizing their performance and ensuring scalability. Their expertise lies in harnessing the power of cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud to provide robust, flexible, and cost-effective solutions.
Site Reliability Engineer (SRE): SREs are the sentinels of system reliability. They focus on maintaining the system's resilience through efficient practices, continuous monitoring, and rapid incident response. Their vigilance ensures that applications and systems remain stable and performant, even in the face of challenges.
Security Engineer: Security engineers are the guardians of the DevOps pipeline. They integrate security measures seamlessly into the software development process, safeguarding it from potential threats and vulnerabilities. Their role is crucial in an era where security is paramount, ensuring that DevOps practices are fortified against breaches.
As DevOps continues to redefine the landscape of software development and deployment, gaining expertise in its core principles and technologies is a strategic career move. ACTE Technologies offers comprehensive DevOps training programs, led by industry experts who provide invaluable insights, real-world examples, and hands-on guidance. ACTE Technologies's DevOps training covers a wide range of essential concepts, practical exercises, and real-world applications. With a strong focus on certification preparation, ACTE Technologies ensures that you're well-prepared to excel in the world of DevOps. With their guidance, you can gain mastery over DevOps practices, enhance your skill set, and propel your career to new heights.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigating the DevOps Landscape: A Comprehensive Roadmap for Success
Introduction: In the rapidly evolving realm of software development, DevOps stands as a pivotal force reshaping the way teams collaborate, deploy, and manage software. This detailed guide delves into the essence of DevOps, its core principles, and presents a step-by-step roadmap to kickstart your journey towards mastering DevOps methodologies.
Exploring the Core Tenets of DevOps: DevOps transcends mere toolsets; it embodies a cultural transformation focused on fostering collaboration, automation, and continual enhancement. At its essence, DevOps aims to dismantle barriers between development and operations teams, fostering a culture of shared ownership and continuous improvement.
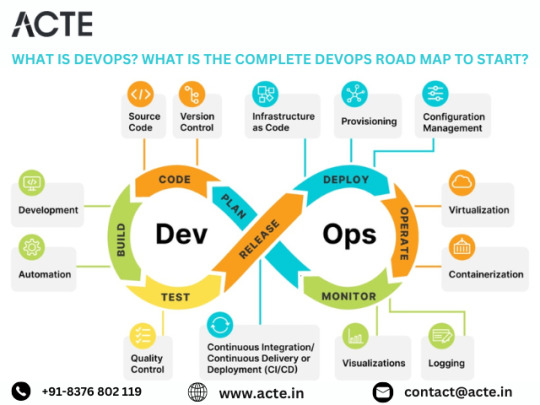
Grasping Essential Tooling and Technologies: To embark on your DevOps odyssey, familiarizing yourself with the key tools and technologies within the DevOps ecosystem is paramount. From version control systems like Git to continuous integration servers such as Jenkins and containerization platforms like Docker, a diverse array of tools awaits exploration.
Mastery in Automation: Automation serves as the cornerstone of DevOps. By automating routine tasks like code deployment, testing, and infrastructure provisioning, teams can amplify efficiency, minimize errors, and accelerate software delivery. Proficiency in automation tools and scripting languages is imperative for effective DevOps implementation.
Crafting Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery Pipelines: Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) lie at the heart of DevOps practices. CI/CD pipelines automate the process of integrating code changes, executing tests, and deploying applications, ensuring rapid, reliable, and minimally manual intervention-driven software changes.
Embracing Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Infrastructure as Code (IaC) empowers teams to define and manage infrastructure through code, fostering consistency, scalability, and reproducibility. Treating infrastructure as code enables teams to programmatically provision, configure, and manage infrastructure resources, streamlining deployment workflows.

Fostering Collaboration and Communication: DevOps champions collaboration and communication across development, operations, and other cross-functional teams. By nurturing a culture of shared responsibility, transparency, and feedback, teams can dismantle silos and unite towards common objectives, resulting in accelerated delivery and heightened software quality.
Implementing Monitoring and Feedback Loops: Monitoring and feedback mechanisms are integral facets of DevOps methodologies. Establishing robust monitoring and logging solutions empowers teams to monitor application and infrastructure performance, availability, and security in real-time. Instituting feedback loops enables teams to gather insights and iteratively improve based on user feedback and system metrics.
Embracing Continuous Learning and Growth: DevOps thrives on a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Encouraging experimentation, learning, and knowledge exchange empowers teams to adapt to evolving requirements, technologies, and market dynamics, driving innovation and excellence.
Remaining Current with Industry Dynamics: The DevOps landscape is dynamic, with new tools, technologies, and practices emerging regularly. Staying abreast of industry trends, participating in conferences, webinars, and engaging with the DevOps community are essential for staying ahead. By remaining informed, teams can leverage the latest advancements to enhance their DevOps practices and deliver enhanced value to stakeholders.
Conclusion: DevOps represents a paradigm shift in software development, enabling organizations to achieve greater agility, efficiency, and innovation. By following this comprehensive roadmap and tailoring it to your organization's unique needs, you can embark on a transformative DevOps journey and drive positive change in your software delivery processes.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unlocking Efficiency and Innovation: The Role of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)

In today's fast-paced and competitive business environment, organizations are constantly seeking ways to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase productivity. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has emerged as a powerful tool that can help businesses achieve these objectives.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that allows businesses to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks. It uses software robots, also known as "bots," to mimic human actions and interact with digital systems. These bots can log into applications, navigate through screens, input data, and complete tasks just like humans would.
The Role of RPA in Business:
RPA can be used to automate a wide range of tasks across various industries and departments. Here are some examples:
Finance and Accounting: Automating tasks such as accounts payable and receivable, invoice processing, and financial reporting.
Customer Service: Automating tasks such as answering FAQs, resolving customer inquiries, and processing orders.
Human Resources: Automating tasks such as onboarding new employees, processing payroll, and managing benefits.
IT: Automating tasks such as provisioning accounts, managing user access, and deploying software updates.
Impact of RPA on Businesses:
Implementing RPA can offer numerous benefits to businesses, including:
Increased efficiency and productivity: RPA can automate time-consuming and tedious tasks, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic and value-added activities.
Reduced costs: RPA can help businesses save money on labor costs, as well as reduce errors and compliance risks.
Improved accuracy and compliance: RPA bots are programmed to follow specific rules and procedures, which can help to improve accuracy and compliance with regulations.
Enhanced process visibility and control: RPA provides businesses with a clear view of their processes, which can help them identify and address bottlenecks.
Improved customer satisfaction: RPA can help businesses improve customer satisfaction by automating tasks such as order processing and customer service interactions.
RPA Services:
Implementing RPA successfully requires a partner with expertise in the technology and a deep understanding of business processes. A comprehensive RPA solution should include the following services:
Document AS-IS Process: This involves mapping out the existing process to identify areas for automation.
Design & Development of Bots, workflows, and forms for process automation: This includes designing and developing the software robots that will automate the tasks.
Bot license (We will use the appropriate underlying technology): This provides access to the software robots and the underlying technology platform.
Infrastructure: This includes setting up the necessary infrastructure to support the Robotic Process Automation (RPA) solution.
Production Deployment of the Bots: This involves deploying the bots to production and monitoring their performance.
RPA support: This includes ongoing support for the RPA solution, such as troubleshooting and maintenance.
Test & Deploy bots to production: This involves testing the bots in a production environment and making any necessary adjustments before they are deployed to full production.
Configuration data changes: This involves making changes to the configuration data of the bots as needed.
Password updates: This involves updating the passwords of the bots as needed.
Errors in executing the Bots: This involves resolving errors that occur during the execution of the bots.
Determining the “root cause” of a recurring issue or incident & recommendations: This involves identifying the root cause of a recurring issue or incident and recommending solutions to prevent it from happening again.
Infrastructure/application related issues: This involves resolving issues with the infrastructure or applications that the bots are interacting with.
Conclusion:
RPA is a powerful technology that can have a significant impact on businesses of all sizes. By automating repetitive tasks, RPA can help businesses improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase productivity. However, it is important to choose a reputable Robotic Process Automation (RPA) companies with the expertise and experience to help you implement a successful RPA solution.
Ready to embrace the power of RPA?
Contact us today to learn more about how RPA can help your business achieve its goals.
#robotic process automation#robotic process automation rpa#rpa automation#robotic process automation software#rpa software#robotic process automation companies#robotic process automation technology#robotic process automation in healthcare#robotic process automation in banking#rpa solution#robotic process automation for finance#process automation solution#robotic process automation services#robotic process automation for insurance#rpa system#what is rpa automation#robotic process automation solution#robotic process automation benefits#robotic process automation consulting#robotic process automation consultant#rpa service provider#rpa consulting services
2 notes
·
View notes