#salmon’s river
Text
So I saved a Butters from a claw machine and made him a removable Professor Chaos outfit out of foil and some random t shirt


And extra is him with a knife just for fun,

#south park#professor chaos#mwahahaha#knife#salmon’s river#butters leopold stotch#crafts#silly#aluminum foil#plushie#plush
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you aren't following the news here in the Pacific Northwest, this is a very, very big deal. Our native salmon numbers have been plummeting over the past century and change. First it was due to overfishing by commercial canneries, then the dams went in and slowed the rivers down and blocked the salmons' migratory paths. More recently climate change is warming the water even more than the slower river flows have, and salmon can easily die of overheating in temperatures we would consider comfortable.
Removing the dams will allow the Klamath River and its tributaries to return to their natural states, making them more hospitable to salmon and other native wildlife (the reservoirs created by the dams were full of non-native fish stocked there over the years.) Not only will this help the salmon thrive, but it makes the entire ecosystem in the region more resilient. The nutrients that salmon bring back from their years in the ocean, stored within their flesh and bones, works its way through the surrounding forest and can be traced in plants several miles from the river.
This is also a victory for the Yurok, Karuk, and other indigenous people who have relied on the Klamath for many generations. The salmon aren't just a crucial source of food, but also deeply ingrained in indigenous cultures. It's a small step toward righting one of the many wrongs that indigenous people in the Americas have suffered for centuries.
#salmon#dam removal#fish#animals#wildlife#dams#Klamath River#Klamath dams#restoration ecology#indigenous rights#Yurok Tribe#Karuk Tribe#nature#ecology#environment#conservation#PNW#Pacific Northwest
13K notes
·
View notes
Text

Chinook Salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha)
#salmon#fish#chinook salmon#king salmon#hi im posting some fish pics because i think fish are beautiful#our rivers are full of fascinating elusive lil guys#or in this case fairly large guys
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Klamath River’s salmon population has declined due to myriad factors, but the biggest culprit is believed to be a series of dams built along the river from 1918 to 1962, cutting off fish migration routes.
Now, after decades of Indigenous advocacy, four of the structures are being demolished as part of the largest dam removal project in United States history. In November, crews finished removing the first of the four dams as part of a push to restore 644 kilometres (400 miles) of fish habitat.
“Dam removal is the largest single step that we can take to restore the Klamath River ecosystem,” [Barry McCovey, a member of the Yurok Tribe and director of tribal fisheries,] told Al Jazeera. “We’re going to see benefits to the ecosystem and then, in turn, to the fishery for decades and decades to come.” ...
A ‘watershed moment’
Four years later, [after a catastrophic fish die-off in 2002,] in 2006, the licence for the hydroelectric dams expired. That created an opportunity, according to Mark Bransom, CEO of the Klamath River Renewal Corporation (KRRC), a nonprofit founded to oversee the dam removals.
Standards for protecting fisheries had increased since the initial license was issued, and the utility company responsible for the dams faced a choice. It could either upgrade the dams at an economic loss or enter into a settlement agreement that would allow it to operate the dams until they could be demolished.
“A big driver was the economics — knowing that they would have to modify these facilities to bring them up to modern environmental standards,” Bransom explained. “And the economics just didn’t pencil out.”
The utility company chose the settlement. In 2016, the KRRC was created to work with the state governments of California and Oregon to demolish the dams.
Final approval for the deal came in 2022, in what Bransom remembers as a “watershed moment”.
Regulators at the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) voted unanimously to tear down the dams, citing the benefit to the environment as well as to Indigenous tribes...
Tears of joy
Destruction of the first dam — the smallest, known as Copco 2 — began in June, with heavy machinery like excavators tearing down its concrete walls.
[Amy Cordalis, a Yurok Tribe member, fisherwoman and lawyer for the tribe,] was present for the start of the destruction. Bransom had invited her and fellow KRRC board members to visit the bend in the Klamath River where Copco 2 was being removed. She remembers taking his hand as they walked along a gravel ridge towards the water, a vein of blue nestled amid rolling hills.
“And then, there it was,” Cordalis said. “Or there it wasn’t. The dam was gone.”
For the first time in a century, water flowed freely through that area of the river. Cordalis felt like she was seeing her homelands restored.
Tears of joy began to roll down her cheeks. “I just cried so hard because it was so beautiful.”
The experience was also “profound” for Bransom. “It really was literally a jolt of energy that flowed through us,” he said, calling the visit “perhaps one of the most touching, most moving moments in my entire life”.
Demolition on Copco 2 was completed in November, with work starting on the other three dams. The entire project is scheduled to wrap in late 2024.
[A resilient river]
But experts like McCovey say major hurdles remain to restoring the river’s historic salmon population.
Climate change is warming the water. Wildfires and flash floods are contaminating the river with debris. And tiny particles from rubber vehicle tires are washing off roadways and into waterways, where their chemicals can kill fish within hours.
McCovey, however, is optimistic that the dam demolitions will help the river become more resilient.
“Dam removal is one of the best things we can do to help the Klamath basin be ready to handle climate change,” McCovey explained. He added that the river’s uninterrupted flow will also help flush out sediment and improve water quality.
The removal project is not the solution to all the river’s woes, but McCovey believes it’s a start — a step towards rebuilding the reciprocal relationship between the waterway and the Indigenous people who rely on it.
“We do a little bit of work, and then we start to see more salmon, and then maybe we get to eat more salmon, and that starts to help our people heal a little bit,” McCovey said. “And once we start healing, then we’re in a place where we can start to help the ecosystem a little bit more.”"
-via Al Jazeera, December 4, 2023
#indigenous#river#riverine#ecosystem#ecosystem restoration#klamath#klamath river#oregon#california#yurok#fishing#fisheries#nature is healing#literally this time lol#united states#dam removal#climate change#conservation#sustainability#salmon#salmon run#water quality#good news#hope#rewilding#ecology#environment
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
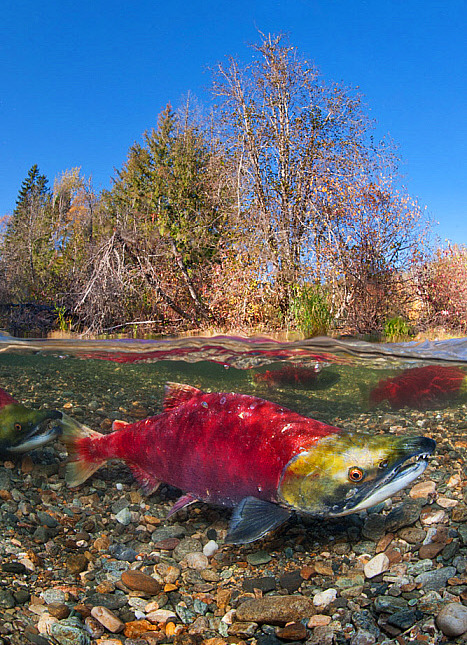



Male sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) in Adams River, British Columbia
Photos by Alex Mustard
#Oncorhynchus nerka#Oncorhynchus#salmon#sockeye salmon#red#fish#red fish#male salmon#salmon river#adams river#river#river fish#british columbia#animals#wildlife#nature#breeding season
5K notes
·
View notes
Text










#plushie#cute#agere#age dreaming#age regression#agedre#system little#little#stuffie#stuffed animal#fish#lake#river#bass#largemouth bass#salmon#trout#rainbow trout#sockeye salmon#png#transparent
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
#art#animal#baby animals#animals#bears#big bears#grizzly bear#brown bear#salmon#eating#fishing#waterfall#river#mountains#trees#pond#lake#fyp#tumblr fyp#foryoupage#fyp2023#foryou#fypage#fypツ#fypシ
949 notes
·
View notes
Text

#art#california#nature#bay area#mendocino#sonoma#printmaking#ink#illustration#mokuhanga#linocut#linoleum#coho#salmon#Salmonids#fish#fishing#spawning#blue#traditional art#reliefprint#river#ocean
512 notes
·
View notes
Text



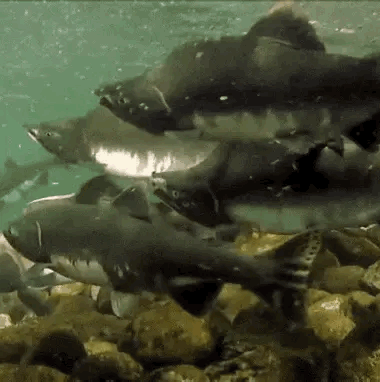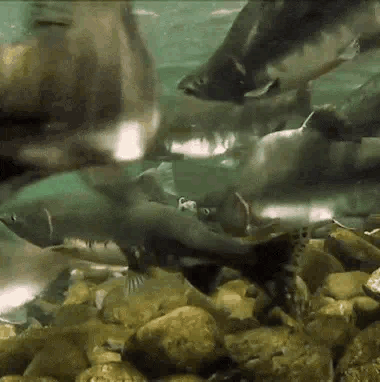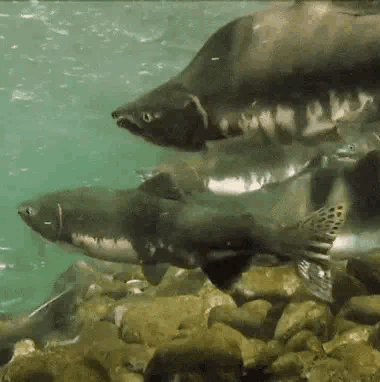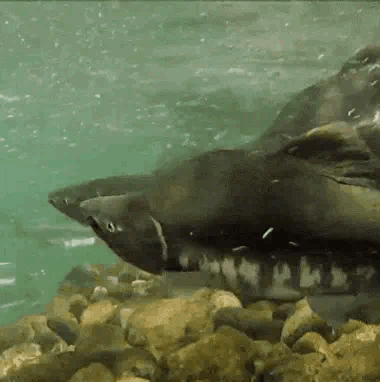

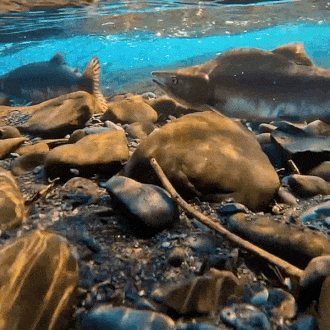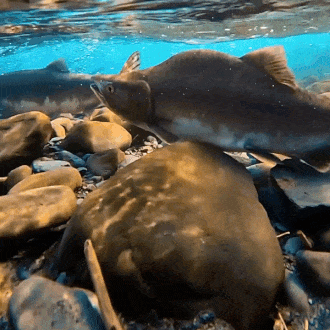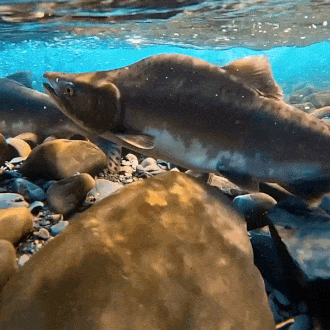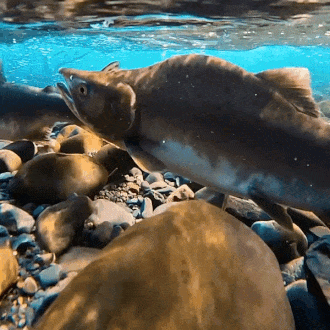



salmon for anon!
🐟-🌊-🐟 / 🌊-🐟-🌊 / 🐟-🌊-🐟
#stim#stimboard#salmon#fish#sfw#nature#red#gray#grey#blue#green#underwater#animals#water#sockeye salmon#freshwater fish#salmon run#rocks#euryhaline ray-finned fish#rivers#requests
900 notes
·
View notes
Text
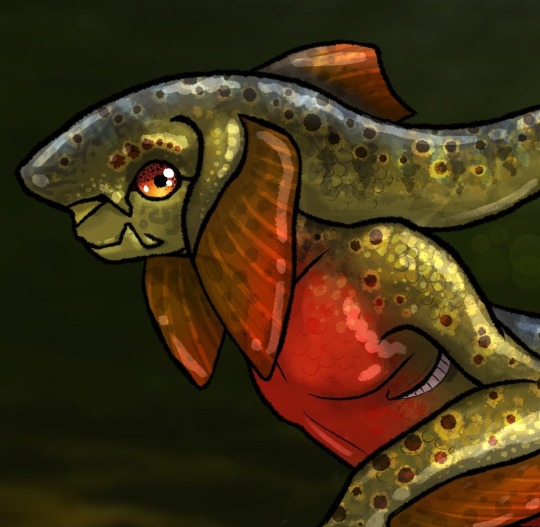


A ray-finned (actinopterygian) River Zora.
Unlike his cartilaginous (chondrichthyan) relatives, he and the other males turn red in the spring. They also gets very aggressive.
#I saw that one post with those gorgeous trout skin patterns and i needed to draw it so here you go#my art#zora#Zora oc#fish#salmon#trout#botw#breath of the wild#botw zora#tloz#loz#the legend of zelda#legend of zelda#speculative biology#spec evo#speculative evolution#speculative zoology#river zora#digital art
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
#good news#dams#dam removal#environmentalism#science#environment#nature#salmon#endangered#endangered species#fish#streams and rivers#puyallup river
215 notes
·
View notes
Text
Okay so I drew Jimmy from South Park because I love him dearly




I apologize for the hands I suck at drawing hands!
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

URGENT! DO YOU WANT TO HELP THE SOUTHERN RESIDENTS? PLEASE HELP US WRITE, CALL AND TEXT!
A lawsuit, National Wildlife Federation vs National Marine Fisheries Service, may finally determine the fate of the 4 Lower Snake River Dams, the salmon who spawn there and the remaining 75 Southern Resident Orca who desperately need salmon to survive.
Biden needs to know that we want those dams breached. He's broken enough of his climate promises - let him know that, and the extinction of these amazing animals, isn't an option!
Public comment is also being sought on the matter. Please visit our page, BidenBreachNow, for talking points, social media shareables, and extensive information about why the dams need to go.
This is a critical time. Please call, text, write or email, every day if you can, until August 31st. Even if you already have acted and/or shared, please do it again. Please keep sharing because every voice counts!
The Snake River was once one of the top salmon rivers in the world. That is sadly no longer the case. Four deadbeat dams on the Lower Snake River have cost an estimated 8 to 9 billion dollars in failed salmon recovery attempts - taxpayer money! - and they lose millions more every year generating unstorable surplus energy. What they do sell is often sold at a loss.
The dams continue to get older and costlier to maintain, while solar and wind energy have replaced their power output; energy efficiency alone has done the same seven times over.
These dams aren't even clean energy! Their reservoirs emit huge amounts of methane, which contributes to the climate crisis.
Please help spread this if you can, and join in. We have a real chance here to get this done - so let's do it.
As the late and great Ken Balcomb said: "We're at a point in history where we need to wake up to what we have to consider: do we want whales, or not?"
He never stopped fighting for the Southern Residents, and neither should we.
#srkw#bidenbreachnow#orca#salmon#orcanize#southern residents#snake river dams#killer whale#conservation
662 notes
·
View notes
Text

Tongass National Forest
#Tongass National Forest#alaska#photography#nature#plants#green#trees#water#landscape#blue#salmon#river#moss#forest#woods#rocks#fish
759 notes
·
View notes
Link
“Famous more as a cultural feature than as a natural one, the pace at which the River Mersey is recovering to a fishy wonderland has ecologists stunned.
Splitting The Beatles’ home city of Liverpool in two, a recent survey found 37 different species of fish, more than two-and-a-half-times as many as were found in the previous survey 20 years ago.
Five different species of sharks were also found, along with huge eels and sea scorpions. ‘Holiday species’ as one local fishermen called them, like turbot, smelt, and cod, have also been caught.
Scientists at the Mersey Rivers Trust, a public/private charity-driven partnership for nature in the area believe that these species are breeding in the 3 mile-wide estuary.
The Liverpool Docks—the largest enclosed dock system in the world, were described by Herman Melville as comparable to the Pyramids in size and construction. As a result, industrialization heavily polluted the river. In 2009 however it was announced that the river was “cleaner than at any time since the industrial revolution” and is “now considered one of the cleanest [rivers] in the UK.”
“Over the last 30 years, there’s been this tremendous regeneration, this renewal of the River Mersey that started slowly but is now picking up pace. I still think we’re right at the beginning of something special,” said Mike Duddy at the Mersey Rivers Trust, who spoke to the Wirral Globe about the restoration...
Humpback whales were recently seen in Liverpool Bay for the first time since 1938, while the Mersey itself has also welcomed back otters, salmon, octopus, porpoises, and seals.
The Trust is currently compiling a species list, and is holding a competition with local fishermen to see how many can be recorded. Duddy expects to raise the count of 37 fish species to 50 next year.”
-via Good News Network, 1/23/23
#england#uk#liverpool#conservation#water pollution#biodiversity#ecosystem restoration#fish#sharks#eels#humpback whale#otter#salmon#octopus#porpoise#seal#rivers#good news#hope
3K notes
·
View notes
Text





Chum salmon run in Juneau— faces left downstream
Taken August 2023
278 notes
·
View notes