#sanctuary at delphi
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Charioteer of Delphi
* 478/474 BCE
* Bronze
* Height: 1,8 m
* Delphi Archaeological Museum
Delphi, October 2008
#Charioteer of Delphi#5th century BCE#Delphi#Pythian Games#Sanctuary of Apollo#Polyzalus#Pythagoras of Rhegion#ancient#art#Greek#bronze#statue#sports#Delphi Museum#my photo
76 notes
·
View notes
Text

#acodyssey#assassin's creed#assassin's creed odyssey#phokis#sanctuary of delphi#ubisoft#gamingedit#virtual photography#photomode#video games#pc gaming#pc share#in game photography#camera tools
20 notes
·
View notes
Text










greece on camera, part six: delphi (sanctuary of apollon and sanctuary of athena pronaia)
#i was BUZZING all the way up#this place is so dear to me it's the main reason i started studying archaeology#AND i picked my thesis topic here. just strolling with my prof <3#paiawon.txt#tagamemnon#archaeoblr#archaeology#studyblr#art history#archaeology tag#delphi#sanctuary of apollon#sanctuary of athena
1 note
·
View note
Text

In ancient Greek religion, an empty throne often signified the possible presence of a god, even in the absence of an image or statue. These thrones were placed during rituals and festivals, such as Theophania at Delphi, as a sign that a deity might arrive.
At times, they were reserved for gods beyond the local pantheon. In intercultural sanctuaries like Delos or Piraeus, divine visitors from other cultures were honoured with these sacred seats. Foreign deities, such as Isis (Auset), were welcomed through processions and offerings. Their presence was acknowledged by the throne left waiting.
This practice was deeply tied to the Greek value of xenia, or sacred hospitality. Welcoming the unknown god mirrored the ethical imperative to welcome the stranger. The Greeks didn't always know who would come, but they made room nonetheless. The empty throne stood as a symbol of respect, openness, and readiness.
For modern Hellenic Polytheists, this symbolism carries real ethical weight. Xenia is not optional; it’s a central religious duty. Refugees, migrants, strangers, and newcomers deserve the same care once offered to unknown gods.
As a divine law protected by Zeus Xenios, xenia calls us to wait with hope, to receive with kindness, and to respond with generosity. The empty throne is a reminder that hospitality is a virtue, custom, and sacred practice in the religion of Hellenic Polytheism.
Hail the deathless gods; Hail Zeus Xenios
My 2min 20s video on this topic Instagram, TikTok, YouTube
#hellenic polytheism#hellenic polythiest#helpol#zeus#zeus xenios#xenia#ancient greece#ancient greek religion
320 notes
·
View notes
Text
Words related to Mythology
to include in your next story/poem
Ambrosia - the food eaten by Greek and Roman gods; a very pleasant food
Chthonic - relating to or living in the underworld (i.e., the place in ancient stories where the spirits of the dead go)
Chimera - in Greek mythology, a creature with a lion's head, a goat's body, and a snake's tail
Delphi - an ancient Greek sanctuary (i.e., a holy place) on Mount Parnassus, where an oracle (i.e., a female priest) was believed to be able to answer questions with advice from the god Apollo
Fate - what happens to a particular person or thing, especially something final or negative, such as death or defeat
Gorgon - one of three sisters in ancient Greek stories who had snakes on their heads instead of hair, and who turned anyone who looked at them into stone
Harpy - in Greek mythology, a creature with the head of a woman and the body of a bird
Hydra - in ancient Greek stories, a creature with many heads that grew again when cut off; also, a difficult problem that keeps returning
Ichor - in Greek mythology, the liquid that flows in the bodies of the gods instead of blood
Muse - in ancient Greek and Roman stories, one of the nine goddesses who were believed to give encouragement in different areas of literature, art, and music
Nectar - in ancient Greek and Roman stories, the drink of the gods; also, a sweet liquid produced by flowers and collected by bees and other insects
Satyr - a god in Greek literature who is half man and half goat
Siren - in ancient Greek literature, one of the creatures who were half woman and half bird, whose beautiful singing encouraged sailors to sail into dangerous waters where they died
Sphinx - an imaginary creature with a lion's body and a person's or animal's head, usually with wings; in ancient Greek stories, a creature at Thebes with the body of a lion, the head and breasts of a woman, and wings. She asked people who passed by a riddle (i.e., a difficult question) and if they could not answer correctly, she killed them
Underworld - in mythology, a place under the earth where the spirits of the dead go
If any of these words make it into your next poem/story, please tag me. Or leave a link in the replies. I’d love to read them!
More: Word Lists ⚜ Writing Resources PDFs
#mythology#greek mythology#roman mythology#writeblr#writing prompt#words#linguistics#langblr#studyblr#literature#myth list#writers on tumblr#poetry#poets on tumblr#dark academia#writing resources#writing reference#word list
982 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ἀπόλλων Φοῖβος, Θεὸς τοῦ Ἡλίου
Apollon, Bright One, God of the Sun
He is associated with Sunlight and the Sun, Music and Poetry, Prophecy and Oracles, Healing and Medicine, Plague and Disease, Archery, Knowledge and Wisdom, Purification and Cleansing, Order and Civilization, Protection of Herds and Flocks, Seafarers, Masculine Beauty, Music Theory and Harmony, Time and Seasons.
His symbols are the Lyre, Bows and Arrows, the Laurel Wreath, Ravens, Serpents, the Sun/Chariot of the Sun, Palm Trees, Bay/Laurel Trees, Wolves, Cypress Trees, Tripod, Lyric Poetry Scrolls, Golden Hair and Swans.
Major Sanctuaries and Temples
Delphi was the most famous sanctuary of Apollon, home to the Oracle of Delphi and the Pythian Games.
Delos was Apollon’s birthplace and celebrated Him with grand festivals like the Delia.
Didyma was known for its oracle and the Temple of Apollon, featuring massive columns.
Claros was another major oracle site, with its temple and priesthood.
Thermopylae was sacred to Apollon during the Amphictyonic League meetings.
Bassae was home to the Temple of Apollon Epikourios, renowned for its architectural innovation.
Aegina featured a Doric temple dedicated to Apollon.
Patara was an ancient Lycian city with ties to Apollon and prophecy.
Miletus’ citizens worshipped Apollon as their protector.
Rhodes revered Apollon as part of the island’s patron deities.
Athens worshipped Apollon in several roles, including Apollo Patroos (Protector of Families).
Sparta honoured Apollon as a god of order and harmony.
In Rome, Imperātor Gāius Iūlius Caesar Augustus constructed the Temple of Apollo Palatinus, aligning Apollo with imperial propaganda.
Mt. Parnassus, near Delphi, was regarded as sacred to Apollon and the Muses.
The island of Crete celebrated Apollon in various cities, such as Gortyna and Dreros.
General Epithets
Apollon (Bright, Radiant), associated with His solar and light-bearing qualities.
Delphinios (Of Delphi), linked to His sanctuary and oracle at Delphi.
Mousagetēs (Leader of Muses), celebrating His patronage of the arts and inspiration.
Loxias (Oblique, Mysterious), reflecting His cryptic oracular messages.
Pythios (Of Pythia), commemorating His victory over Python at Delphi.
Alexikakos (Averter of Evil), worshipped as a protector from harm and calamity.
Medicus (Healer), honouring His medical and healing powers, especially in Roman worship.
Catharsius (Purifier), invoked in cleansing rituals.
Smintheus (Mouse God), protector from plague and agricultural pests.
Lykeios (Wolf God), linked to His protective and wild nature.
Nomios (Pastoral), celebrating His guardianship over herds and flocks.
Karneios (Of Flocks), worshipped in rural Spartan traditions as a regional variation of Nomios.
Helios (Sun God), representing His solar connections in later traditions.
Agyieus (Of the Streets), protector of pathways and travelers.
Delios (Of Delos), celebrating His birthplace.
Didymaeus (Of Didyma), connected to His oracle in Ionia.
Festivals
The Pythian Games were held every four years at Delphi, including musical and athletic competitions in Apollon's honour.
Thargelia was an Athenian festival honoring Apollon and Artemis, featuring purification rituals and offerings of first fruits.
Delia, on Delos, was a festival that included musical contests, dances, and sacrifices sacred to Apollon.
Worship Practices
Sacrifices were often of animals such as bulls and goats, symbolic of his divine strength.
Prophecy played a central role in his worship, with priestesses and the Oracle at Delphi channeling his divine wisdom.
Apollon was invoked in rituals of cleansing and renewal, often symbolized by water.
Roman Veneration
Apollo Medicus was venerated as a god of healing during plagues.
Imperātor Gāius Iūlius Caesar Augustus claimed Apollo as his divine patron, constructing the Temple of Apollo on the Palatine Hill of Rome.
Altars and Sacred Spaces
Altars dedicated to Apollon are typically adorned with symbols like the lyre, laurel leaves, sun motifs and representations of His sacred animals (e.g., swans, wolves, or ravens), often altars placed in sunlit areas to honor His solar aspects.
Altars are frequently decorated with golden or yellow fabrics, sun-shaped decorations, and natural materials like wood or stone are common.
Offerings
Traditional Offerings are laurel leaves, honey, olives, figs, and wine.
Music, poetry, and other creative expressions are also considered as offerings due to Apollon's role as a patron of the arts.
Frankincense and bay laurel oil are burned, while crystals like sunstone and pyrite are used to symbolize His solar and abundant aspects.
Rituals and Practices
Devotees skilled in the arts often recite prayers or compose hymns in His honor, often inspired by ancient texts, while others prefer to stay with the ancient texts themselves. Both choices are equally valid.
Practices like meditating on Apollon's attributes or using divination tools to seek His guidance are common.
The creation of or recitation of music and poetry are also acts of worship. From humming a tune to singing along to your favourite songs, it counts as an offering and is just as valid.
Apollon's teachings on balance and enlightenment inspire personal growth and artistic pursuits, often being blended with the pursuit of philosophical and sometimes even spiritual enlightenment.
Rituals for spiritual or physical healing often invoke Apollon's aid, emphasizing His role as a healer.
Devotees seek His guidance in intellectual and intuitive endeavors, reflecting His association with wisdom and oracles.
Seasonal Celebrations:
Some practitioners observe festivals inspired by ancient traditions, such as the Thargelia or Delia, adapting them to modern contexts. I have yet to find a universally agreed upon date, but April 6th or the Spring Equinox are common due to Apollon's purifying and cleansing epithets, as well as His light and solar epithets.
Personal Notes
Apollon is a deity who only very recently called to me, which is amusing to me since I would have been under His protection. It speaks to me of His integrity that rather than reach out to me then, He has waited nearly seventeen years to do so. I think that perhaps is to do with two things which actually blend hand in hand; the first being that I have a strong suspicion that when He reached out to me, it was not as His Greek self nor even His Roman self; rather, it was as Paean (𐀞𐀊𐀺𐀚, Pajawone) that He reached out.
While I try to keep the history out of the religion in these posts, I feel it is best to explain fully in the case of Hellenic deities whose Mycenaean forms call to me most (of which there is a surprising number). Apollon, as Paean, is chiefly a god of medicine and healing. However, in Troy he was a god of hunting and protection, defending the early Trojans from the beasts of the forest. It is this Trojan Apollon, whom they called Paeiōn (𐀞𐀊𐀩𐀍, Pajerone) that called to me and is still known to this day as Apollon Lykeios. For those wondering why the names changed so much, the evolution from Pajerone to Apollon is due to the language changing and evolving during the Greek Dark Ages; the earliest known midway point is Apeljōn, so the linguistic evolution would be Pajerone -> Apeljōn -> Apollon.
With the mini history lesson out of the way, apologies for boring any of you, now to explain the significance of Pajerone/Apollon Lykeios as main epithet I worship. The Wolf God, Apollon Lykeios, is very different from the other representations of Apollon and is quite, shall we say, wild by comparison. He is still a healer, still knowledgeable in philosophy and music, but He is much more akin to His Sister Artemis and Her preference of the forest and the hunt. He is the Wolf, the hunter who struck down the Python and gained prophetic insight, the friend of Hyperborea whose bow can bring any prey low. To me, as Lykeios, he is still a God of Light, but his light is not simply the gold of the sun. It is the green of the field, the red and pink of blood on his skin. It is the purple of his robe and the blue of his eyes, dancing in the sky as the Aurora Borealis. He is the light that dances with the moon and stars, the Hunter who no prey escapes, the Wanderer who heals all with his herbs.
While far from the first Hellenic deity to call to me, He is perhaps the most important one for bridging the gap between the two main pantheons I worship, an ancient link between the northern hunters and the cradle of the West. It is through this link, through His wandering path from Hellas and Hyperborea all the way to Middungeard and beyond, that I can best reconcile worshipping two pantheons without Syncretism. He is a bridge between worlds, a fierce protector and a noble friend to all.
Orphic Hymn to Apollon
Blest Pæan, come, propitious to my pray'r,
illustrious pow'r, whom Memphian tribes revere,
Slayer of Tityus, and the God of health,
Lycorian Phœbus, fruitful source of wealth.
Spermatic, golden-lyr'd, the field from thee
receives it's constant, rich fertility.
Titanic, Grunian, Smynthian, thee I sing,
Python-destroying, hallow'd,
Delphian king:
Rural, light-bearer, and the Muse's head,
noble and lovely, arm'd with arrows dread:
Far-darting, Bacchian, two-fold, and divine,
pow'r far diffused, and course oblique is thine.
O, Delian king, whose light-producing eye views all within,
and all beneath the sky:
Whose locks are gold, whose oracles are sure,
who, omens good reveal'st, and precepts pure:
Hear me entreating for the human kind, hear,
and be present with benignant mind;
For thou survey'st this boundless æther all,
and ev'ry part of this terrestrial ball
Abundant, blessed; and thy piercing sight,
extends beneath the gloomy, silent night;
Beyond the darkness, starry-ey'd, profound,
the stable roots, deep fix'd by thee are found.
The world's wide bounds, all-flourishing are thine,
thyself all the source and end divine:
'Tis thine all Nature's music to inspire, with various-sounding, harmonising lyre;
Now the last string thou tun'ft to sweet accord,
divinely warbling now the highest chord;
Th' immortal golden lyre, now touch'd by thee,
responsive yields a Dorian melody.
All Nature's tribes to thee their diff'rence owe,
and changing seasons from thy music flow
Hence, mix'd by thee in equal parts, advance
Summer and Winter in alternate dance;
This claims the highest, that the lowest string,
the Dorian measure tunes the lovely spring.
Hence by mankind, Pan-royal, two-horn'd nam'd,
emitting whistling winds thro' Syrinx fam'd;
Since to thy care, the figur'd seal's consign'd,
which stamps the world with forms of ev'ry kind.
Hear me, blest pow'r, and in these rites rejoice,
and save thy mystics with a suppliant voice.










#hellenic deities#hellenic pagan#hellenism#hellenic polytheism#hellenic worship#hellenic gods#helpol#hellenic polythiest#greek gods#greek mythology#apollo
195 notes
·
View notes
Text


The 'Carnyx' Nightmare of the Roman Soldiers
The Carnyx was a brass musical instrument used as a psychological weapon of war by the ancient Celts between 300 BC and 200AD in western and central Europe and beyond.
The carnyx was once widespread throughout much of Europe, although only a dozen or so fragments are known to us.
It was carried by bands of Celtic mercenaries; it was present at the attack on the Greek sanctuary at Delphi in 279 BC; it defied Julius Caesar in Gaul; and it faced Claudius when he invaded Britain. They are even shown on a Buddhist sculpture in India, proof of the far-flung connections of the Iron Age world.
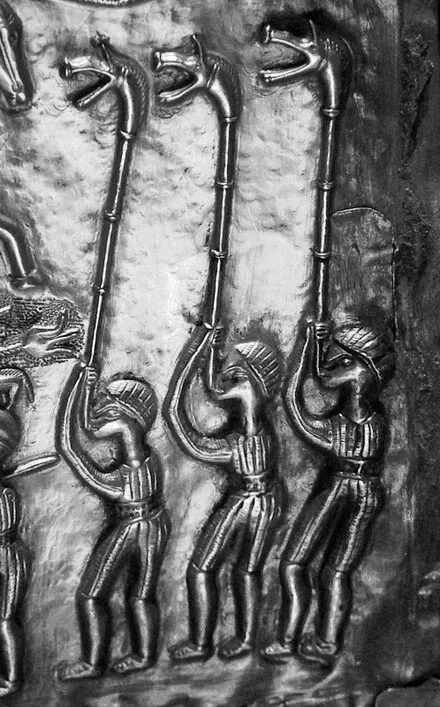

However, they were not only used by the Celts; they were also used by the Dacians in modern Romania. The term “Celtic” is a complicated one. The concept of a pan-European Celtic culture is a myth; rather, aspects of art and technology were shared across vast distances by diverse cultures. The carnyx was one example of this.
A 12-foot-long, thin bronze tube with right-angle bends on both ends made up the carnyx. The lower end ended in a mouthpiece, and the upper end flared out into a bell that was usually decorated to look like a wild boar’s had. Historians believe it had a tongue that flapped up and down, increasing the noise made by the instrument. The carnyx was played upright so that the boar’s head bell protruded well above the warriors’ heads. Its primary goal was to create more noise and confusion on the battlefield.



The Greek historian Polybius (206-126BC) was so impressed by the clamor of the Gallic army and the sound of the carnyx, he observed that “there were countless trumpeters and horn blowers and since the whole army was shouting its war cries at the same time there was such a confused sound that the noise seemed to come not only from the trumpeters and the soldiers but also from the countryside which was joining in the echo”.
And the Roman historian Diodorus Siculus wrote, “Their trumpets are also of a peculiar and barbaric kind which produce a harsh, reverberating sound suitable to the confusion of battle.”
Archaeologists discovered a hoard of ritually destroyed weapons in 2004, including a dozen swords, scabbards, spearheads, a shield, bronze helmets, an iron helmet shaped like a swan, a cauldron, animal remains, and seven carnyces. Before the Tintignac discovery, the remains of only five actual carnyces had been found.
The finest was unearthed in Deskford, Scotland in 1816. The Deskford carnyx only has the boar’s head bell and is missing the mane, tongue, and tubing. Images of Carnyx players have been found as well. A Roman denarius, dating from 48 BC bears a representation of a Carnyx. Three carnyx players are featured prominently on the Gundestrup Cauldron, which was found in a Danish peat bog.
One of the seven found at Tintignac, on the other hand, was almost entirely complete. The Tintignac Carnyx was broken into 40 pieces. When puzzled back together, it was found to be just an inch short of six feet long with a single missing section of the tube. The bell was a boar’s head with protruding tusks and large pointed ears. Once restored, the Tintignac Carnyx proved to be the first virtually complete carnyx ever found.
By Leman Altuntaş.
Music video by John Kenny.
#The Carnyx#The 'Carnyx' Nightmare of the Roman Soldiers#Iron Age war trumpet#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#celtic mythology#celtic history#roman history#roman empire#roman legion
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
💿Some of life things in astrology💿
✨Venus in cancer - I usually see that these people always include parents in their daily life , in their love life , in their life in general. Also they always include their parents in their vlogs. They will always post their parents on social media or doing videos with them.
🎶People who have aquarius in 2nd house have the best taste in music. They have their own music that they listen to, but people always like it. They just put some song and people will love it.
🍸Mercury is how you express yourself and in which way and also shows how good you are in texting with people and how you are in contact with others.
🦭Mercury in capricorn- they are not such a good texter actually.I would say that they will texting you about: I don't know about time or place you two will meet or practical things. But they will not text you like 24/7 or something they are too busy. And also I feel like capricorn usually think they wasting their time texting someone things that don't usually have any meaning or are not practical.
🦋Mercury in scorpio- dig deep into things. Sometimes even too deep. In the sense that they go so deep into the things they want to find out ,that they hurt them at the end. One thing they have is, that they feel better when they find out things by themselves than when they find out from others. They are very deep thinkers and very deep in conversations they don't like small talks and they will always want to go deep with you in every conversation they will have. When you hurt them they will be harsh and very mean to you because when they speak they speak to their emotions.
❤️🔥Fire signs are confident, driven, lively and full of energy. They like to be mentally and physically active. They are also dreamers who measure their height. Fire signs are competitive.
🖤Earth signs are more in tune with nature and their bodies. They are reliable, tough, practical partners and friends. Earth signs take time to master a skill.
💕Air signs are mental and need a lot of communication. They like to remain objective. They often negotiate for justice. They value freedom and dislike conflict.
🩵Water signs are by nature creative, imaginative, dreamy and often very ignorant. Water is associated with emotions and the unconscious. They can be visionaries and have many ideas clairvoyant abilities. Water signs care about the environment and by nature feel with everyone and everything around them.
🌞God of Sun is Apollo. It is carved in the sanctuary of Apollo in Delphi the ancient saying "Know thyself". Because with the sun we ask ourselves "who am I?" and "why am I here?". Because with the sun we feel that our lives have meaning, that we were born with a mission that we must fulfill, and we want to know what it is supposed to be.
The sun represents its essence and indicates our goal in life. With the sun, we can discover qualities and find ways to use them in our lives. This can mean that we engage in a certain activity or wear colors with a connection to the sun. Just as Apollo rides in his fiery chariot across the sky, so the sun represents a heroic journey through life. Therefore, we can connect it to the work we do or should do performed in the world. The path of the sun is usually not very clear and, just like the heroic myths say, there are many pitfalls to overcome and lessons to be learned. It is these difficult tasks that test our limits, they confront us with loss and sacrifice and force us to become the best we can be. The Sun together with Saturn represent the father principle. The sign in which our sun is describes experiences with the father figure. In childhood, our first hero is the father.
🫧Nobody talks about how lonely you can feel with Uranus in the first house. Because it's the part of your personality and Uranus could make you feel that you don't belong somewhere or you feel some kind of distance in this house. When it's in in your first house you could feel that being around people make you lonely or doing some things alone for ex.: eating alone in the restaurant this could be the problem for you because you could feel very lonely when you do some things in the public alone or I don't know going to the coffee alone.
🌟Planets return show you things that you are not aware of it or you're not expressing them. For example Mercury return can show you the whole new perspective about things and could change your mindset for the better. Venus return can show you the new value about you or what you value about others. You are more aware now what u actually want. Where do you find real love. Mars return it can show you a new way to be brave, fearless and go outside your comfort zone. And where is your energy best expressed and through what. You can show your anger more during this time.
🍿It’s really hard to forget people with whom you share 4th House this is because they make you feel the most familiar and the most comfortable around them. It's like the family kind of vibe.It feels like coming home and being with them it's like being in the safe and secure environment. 4th house represents our home , the people that are closed to us , the space when you feel the most comfortable and people with whom you feel the most comfortable with.
🧜🏼♀️ Venis trine Uranus- I find this aspect so unique because you actually fall in love with the person's uniqueness and differentness they have. You actually love them for it. You love that this person is different and is not the same that anyone else. For ex.: it could be you don't like face tattoos or you don't like someone who dress extra but when you meet this person you actually love this on them. This relationship can be unique and so different than the others.
🧚🏼♀️Uranus in 1st house in synastry- it's kind of the same vibe that with uranus conj venus but it's not because when you first meet this person you feel like this person is different than the others and that they have some unique energy that nobody else has. You feel like this person is special and so unique. That their personality could be so different than the others. It's like you can try to find someone else but you feel like nobody else could compare to this person.
🌙Personal planets appear faster in synastry and the first time you meet the person (especially: sun, moon, mercury). And, of course, rising sign :which indicates the energy of a person when you meet them. But here's the trick with rising sign that many times the true energy of a person can be hidden and only show up after a while when you get to know the person better. 💧The outer planets, however, manifest themselves over the years, when the persons already know each other very well and have a relationship.
🧸3rd house not only represents communication, mind,car ,electronics ,social media ,telephones and any of this stuff. It's also represents your early high school experience and also people who were with you in your high school. Your high school first love and how it feels like. Your high school best friend. So every person you have a 3rd house synastry with is usually a person you met at that time. A lot of people you share third house with or the sign you have in the third house is meant to be for you to meet them actually.
🎸The best time you will have with the person and the best things you will experience with the people are people u share 9th house. This house is ruled by Jupiter the luckiest Planet. This is the house of gifts. The girt from God, so when you meet the people you share this house with it's a gift that actually was brought into your life. All the things you will experience with these people will actually mean something to you. Because 9th house is meaningful house is where you find meaning, where u seek for meaning , when u actually find optimism. The person's u share this house with can actually inspire you the most or give you the most luckiest advice.
🧁I believe that it's not only 5th house that represents memories, but every house represents some memory you have from your early childhood. Every house is something special. The sign that you have in this house is the sign that reminds you most of this event of your life. So for ex.: aries in 3rd house -maybe this person were your best friend and remind you the most of your high school experience. Taurus in 4th house- this person maybe remind you the most of your home or your childhood, family life. Maybe you grew up with this person. Leo in 8th house-this person probably reminds you most of a dark/deep period of your life. Maybe you could spend the most intense times with this person and share the most secrets.
🎸For personal readings u can sign up here: https://snipfeed.co/bekylibra 🎸
-Rebekah💿🧚🏼♀️☁️
654 notes
·
View notes
Text
Delphi: museum.
Warning: long post, many images.
A while ago, I went to Greece with my dad and while there, we stopped at Delphi. It was an amazing experience. I've been wanting to share the images and I'm now getting to it! This will be split into two parts, the first (this post) about the museum and the second about the site.
This post will include the images of the statues and the explanation boards next to them in text form, as with the images of them it is more than 30 images. Message or comment if you'd like a picture of the explanation boards! It won't include everything in the museum, just what I thought was interesting. I'll try to seperate things into "chapters" to make them more easily digestible. I will add image ID in the ALT to almost every pic. If there is no ALT attached, it means I'm not entirely sure which part is being depicted, but the text below explaining the scene should contain it, I just can't attach it.
East Side: beginnings of Trojan War.



An assembly of the gods is represented on the east side of the frieze. Gods protecting the Trojans are seated to the left: Ares, Aphrodite, Artemis, Apollo and Zeus in a luxurious throne. The (now lost) figure of Thetis, mother of Achilles, would be touching Zeus's knees, pleading for her son's safety. Goddesses-protecting the Achaeans (Athena, Hera and Demeter) are seated to the right. A little further starts the vivid narration of the Trojan War. Round the body of a dead warrior Trojan heroes (to the left) fight against Achaeans (to the right). Closing the scene, the elderly figure of Nestor urges the Achaeans to win the battle.
North Side: Gigantomachy.





Subject-matter of the north side is the Gigantomachy, the battle of the Olympian gods against the Giants, children of Gaia. The myth of the conflict, which was victorious for the gods, is a favourite theme in ancient Greek art, symbolizing the triumph of order and civilization over savagery and anarchy. The gods fight hard to subdue the giants, who attack from the right with spears, swords and stones. Some of them from the left, Hephaistos - dressed in a short chiton, typical of craftsmen - stands in front of his bellows preparing fire-balls. Nearby are Demeter and Kore, then Dionysus in a panther's skin and Cybele on a chariot drawn by lions. The pair of gods whose helmet-crest is shaped like a kantharos (vase) and he is named after this. The inscription on the shield of the fourth giant refers to the sculptor of the relief but, unfortunately, his name is not preserved. Following would be Zeus on his chariot, then Hera, Athena, Ares armed with helmet and shield, and Hermes wearing the conical pilos, characteristic of Arcadian shepherds. The last figure is fragmentary - probably Poseidon accompanied by his wife, Amphitrite.
West Side: Judgment of Paris (probably).


The few figures preserved from the west side of the frieze lead to the assumption that here the subject was the judgment of Paris at the beauty contest among Athena, Aphrodite and Hera. He voted for Aphrodite and, in return, earned the most beautiful woman in the world, Helene, the wife of king Menelaos. It was her abduction that triggered the Trojan War. First of the contestants is goddess Athena, who appears as if she is mounting her winged chariot. Hermes frames the scene to the left. Aphrodite is graciously stepping of her own chariot, touching her necklace with a coquettish gesture. The missing part of the frieze would feature Hera, ready for departure after her unsuccessful participation. Last would be the judge Paris.
Sphinx.

In about 560 BC, preceding the construction of the luxurious Siphnian treasury, another rich island of the Cyclades, Naxos, sends a grandiose offering to Apollo of Delphi: the statue of the mythical Sphinx, whose the colossal size, imposing outlook and location in the sanctuary (near the rock of Sibylla and in the foreground of the polygonal retaining wall of the temple) commemorates the political and artistic supremacy of Naxos in the archaic era. The daemonic creature with the female face and the enigmatic smile, the body of a lion and wings of a bird, was supposed to be warding off the evil. It was seated on the capital of the very tall Ionic column, regarded as the oldest element in the Ionic order at Delphi. In total, the Naxian dedication reached 12.50m in height. Carved in a huge block of Naxian marble, the Sphinx combines the solid and firm structure with a tendency for decoration in rendering the hair, breast and wings, which reduces the impression of massive volume. As we learn from an inscription of the 4th c. BC incised on the column base, the priests of Apollo honoured the people of Naxos with the privilege of promanteia, that is, priority in receiving an oracle.
Intermission: random pic and text from a banner.

The dispute between Heracles and Apollo for the Delphic tripod was a very popular illustrated theme in ancient times, a fact that underlines the gravity of the Delphic oracle and its prophecies. In fact, Apollo is recognized as the most important oracular god, who responded to the inner need of humans to know their future and make the right decisions. At Delphi, consultations took place once a month in the temple's adyton, where the god's will was expressed through the inarticulate cries of Pythia, which the priests then interpreted and most probably put into verse. Six hundred and fifteen prophecies have been saved in literary sources and on a very limited number of inscriptions. They were in answer to various questions of a military, religious, state-related or personal nature, such as forming a family, winning at the games etc. The interpretation of these prophecies (oracles) was always ambiguous, which meant that they could be interpreted by the person asking the question; this is why Apollo was also known as Loxias, which meant oblique or ambiguous.
West Pediment of the Temple of Apollo: archaic and classical.

The west pediment of the archaic temple of Apollo, depicting the Gigantomachy (battle between the Olympian gods and giants). From the left part of the composition the figures have been preserved of a giant on his knees (Enceladus?), Athena wearing a breastplate and charging, the lower part of a male figure (perhaps Dionysus) and fragments of two horses from Zeus' chariot which occupied the centre of the pediment. Traces of rich colour decoration are preserved on the stuccoed poros figures (510-500 BC). This is the pediment admired by the women of the chorus in Euripides' lon:
But also here in this temple of divine Loxias [Apollo], son of Leto ... observe the battle of the Giants painted on the stone walls. ... See there, where the goddess Athena strikes Enceladus and brandishes her openwork gorgon shield. (Eur. Ion 190 et seq.)

The west pediment of the classical Temple of Apollo, depicting Dionysus among the Thyiads (women in the god's entourage who, according to poetic tradition, held dances on Mt. Parnassus). In the centre stands Dionysus, in the rare iconographic type of the cithara (type of lyre) player. He is wearing a tunic (chiton) girt below the chest, a mantle (himation) draped over his shoulders and the characteristic mitra (headband) of the initiated. The cithara he holds in his left hand places him on equal terms with the god of music, Apollo, and reconciles the different realms of the two deities who are both depicted on the same temple. Work of the Athenian sculptors Praxias and Androsthenes, circa 330 BC.
East Pediment of the Temple of Apollo: archaic and classical.

The east pediment of the archaic temple of Apollo, a work of Parian marble. The centre of the pediment was occupied by Apollo's four-horse chariot framed by kouroi (young men) and korai (young women). In both corners are animal groups depicting a lion mauling a gentle beast. The interpretation of the subject is based on verses from Aeschylus' Eumenides, in which the Pythia stands before the temple of Apollo and narrates the god's arrival at Delphi from Athens. Apollo is seen off by the Athenians and greeted with great honours by the people of Delphi and their king, Delphos (510-500 BC).
And thence he (Apollo) came unto this land of Parnassus and at his side, with awe revering him, were the children of Hephaestus, preparing the way and taming the land that once was wilderness. And he was received with honour by all the people and Delphos, their chieftain-king. (Aesch. Eumenides 12-16)


The east pediment of the classical Temple of Apollo, depicting Apollo, Leto and Artemis among the Muses. The god is seated on a tripod in the centre, wearing a mantle (himation) that leaves his chest bare. He is holding a branch of laurel and a wide shallow cup (phiale), symbols of his oracle. The Muses, some standing and others seated in a rocky place, provide the link between the deity and the world of arts and letters. Wark of the Athenian sculptors Praxias and Androsthenes, circa 330 BC.
Intermission: more banners.
In ancient Greek mythology, Apollo is presented as the patron of musical creation, poetry and the arts, a representative of moderation and harmony. According to Hesiod, singers and guitarists originated from Apollo himself, just like kings did from Zeus. Apollo accompanied the song and dance of the Muses with his lyre, which is why he was called Mousagetes (Leader of the Muses). It is also why Apollo is often depicted as a Kitharoidos holding his lyre with seven strings, both in the art of ancient Greece and western Europe. Delphi was inextricably tied to music. According to the tradition, when Apollo returned from the north in spring, he was serenaded by the song of the cicadas, nightingales and swallows, and nature was appeased. Very important musical contests also took place at the sanctuary; evidence of those games consist the inscribed verses of two hymns to Apollo from the Athenian Treasury, considered to be the oldest surviving "musical compositions" of classical antiquity, dating back to the 2nd century BC.
Nike.

In antiquity, the winged goddess Nike was considered to be the one who expressed the will of the gods: she announced, rewarded and glorified the victors. We often encounter the figure of Nike in the plastic arts, pottery, coroplasty and goldsmithing. The Nikes found at the sanctuary of Delphi come from public buildings, where they were used as symbols of victory in literal or metaphorical battlefields. The topic of the founding myth behind the Delphi oracle was the slaying of the dragon, namely the victory of Apollo against Python, son of the first goddess of the sanctuary, Gaea. In memory of this victory, panhellenic festivals were held in Apollo's honour, the infamous Pythian Games. Every four years, crowds arrived in Delphi from every corner of the ancient world, since the games constituted an excellent opportunity to interact socially, to practice diplomacy and to exhibit political power. Their focal point were the music and athletic games, which conferred unprecedented fame and glory upon the winners and their cities.
The Tholos.
The most impressive monument in the sanctuary of Athena Pronaia, the tholos, stands out for its unusual circular shape and partial reconstruction, in tvis celebrated treatise De architectura ('On architecture"), Vitruvius attributes the design of the building to Theodoros of Phocaea or Phocis. All orders of classical dungn are successfully represented in the structure. The 20 columns of the outer doric peristyle are crowned by a frieze with metopes in relief. The circular sekos, the central part of the edifice with built walls, is also crowned by a doric frieze with triglyphs and metopes in relief, but smaller in size. A bench which ran along the inner circumference of the sekos supported 10 engaged half-columns in the corinthian order. The material used for the building was white marble from the quarries of Mt. Penteli and the island of Paros (particularly for the metopes in relief), an well as dark limestone from Eleusis for highlighting certain structural details. Marble was also used for the roof, the form of which has long been a subject of debate, especially after two series of simas (eaves troughs) were attributed to it, and it is theoretically restored as conical or octagonal, its ends were decorated with acrofena-statues of female figures in vivid, almost dancing movement. The tholos, one of the most beautiful buildings of antiquity, was erected circa 380 BC. Its actual function remains unknown and many hypotheses have been put forward. It has been associated with chthonic cult and variously interpreted as a heroon, temple, armoury, etc. It is worth noting that Pausanias does not refer to the tholos as a temple and in fact makes no mention whatsoever to the building in his Description of Greece. The subjects of the large exterior metopes of the tholos were the Amazonomachy and Centauromachy, rendered with impressive realism and plasticity. With the contortion of the bodies, the sculptor manages to impart a sense of momentary motion, while the style and clothing of the warriors bring to mind the relief sculptures that adormed the temple of Apollo at Bassai near the ancient city of Phigalia and the temple of Asklepios at Epidauros. The smaller interior metopes of the thelos possibly depicted a congregation of the gods, to which the static or motionless figures have been attributed, and a battle scene, to which the more active figures belong. The sculptors of the metopes displayed incomparable skill in working the marble and rendering details. The high relief, freedom of movement and intensity of action bring the scenes to life, while at the same time introducing a pioneering artistic movement to the iconographic tradition of the 4th century BC, which competes with sculpture in the round.
Antinoos.

Cult statue of Antinoos, a youth of extraordinary beauty from Bithynia, beloved companion of the Emperor Hadrian. Antinoos had barely reached adulthood when he drowned in the Nile. He was thereafter heroised and worshipped as a demigod in many parts of the Eastern Empire by order of the emperor. One of the most beautiful statues of the youth was erected in the sanctuary at Delphi. It was found very well preserved during excavations, still shining thanks to the special oil used in antiquity to polish the 'skin' of marble cult statues. Holes are still visible in the profuse hair, which were used to attach a bronze wreath of laurel leaves on the head. The work is representative of classicism at the time of the philhellene Emperor Hadrian (117-138 AD). With its heroic-divine nudity, the statue follows the stylistic traditions of the great 5th and 4th century BC artists, but lacks the inner vitality of the archetypes.
#hellenic polytheism#helpol#informational#oracle of delphi#delphi#greece#ancient greece#greek mythology#zeus#ares#twelve olympians#aphrodite#greek gods#greek goddess#hermes#athena#greek myths#hera#apollo#dionysus#artemis#demeter#trojan war#paris of troy#judgment of paris#poseidon#amphibia#amphitrite#cybele#kore
35 notes
·
View notes
Note
hiiiiii like i've wanted to send u a request for like a while and i'm so happy i finally got u
i sadly forgot my og idea buuuuuut luckily i got a new one cus i'm bestie besties with a lurker who is like a friend with a writer cus they know each other irl and cus she gave me a lil spoilie
i wanna use like what i was told for dis request
like ik the thing is about a champion/warrior and their god and like it's a certain king being absolutely PATHETIC for like the first one (like ik my opinion cus i luv pathetic men and like i wanna know ur ideas about this)
like i love the idea of cod boys being a god or champion cus like y'know the smut that can be made
so could i request my second fav boy soap or even ghost being a SIMP like full on worshipping their god after hunting for their pretty
LUV u darlin and like KEEP ON writing because i am GOBBLIN up everything u and my other favs make but make sure u also rest
Cw: God/Champion stuff??, inaccurate Greek mythology, worshipping, offering/gifts/sacrifice, oracle, tell me if I missed any. Note: this reminds me of… the name’s on the tip of my tongue, but I can’t remember exactly who wrote about this before. Could you also send me the @ of your writer friend? I’d like to credit them if possible. And thank you! Just make sure to take breaks in between of reading, yeah? You have to rest your eyes every hour or so.
Johnny couldn’t believe his eyes when he stumbled into this small sanctuary outside the sacred precinct, outside any protective walls and guarded cities. Nestled into the side side of a mountain, the marble stones carved intricately in pretty vines and gentle flowers only to be placed in an isolated place. Away from any travellers and warriors, and hidden away from prying eyes of thieves and charlatans. This little, marble shrine made of white marble, painted murals and gold ordained altar - one of the prettiest he’s seen - was left near forgotten, overgrown with fauna and collecting dust.
And despite that, the statue that stood behind the altar, tall and imposing, curves soft and tunic flattering, the Goddess loomed over him with a shadow of warmth and compassion, much unlike the statues of the ruling Gods and Goddesses he was used to —it was ethereal. Your image was one of love and care, a stark dichotomy to the arrogance and self-importance of Zeus and his siblings. You were welcoming towards him when they spurned him for his foreign appearance: a child of slaves that had bought their freedom, a potent sign of determination and strength.
“Perhaps that Oracle wasn’t crazy,” he gawked at the falling leafage, ribbons of round leaves hiding the entrance, parting like a curtain to the main stage of a theatre.
He had tried his luck with the Oracle of Delphi, in a drunken daze that failed to strip him from his embarrassing misadventures around Delphi’s bars and temple. Johnny had wanted to see what all the fuss was about, the mile long travel many made to see her and her prophesies. He wanted to know if she was a true oracle or a scam, a charlatan like many others, but lo and behold, she was blessed with the sight.
He still remembered her words, her words spoken from the Gods’ whims, giving him the blessing of finding a Goddess he would willingly kneel to, one that would show him the same love and devotion he gave. She foretold that he would meet a Goddess of Health and Hunting that he wanted to worship, a give and take cycle —of life and death. And here he stood, before the statue of a benevolent Goddess he knew he already loved.
You were a minor Goddess, able to gift your champions with totems and blessings, but not a miracle. Your sacred temple was warm, the air filled with the scent of fresh spring and dewy mornings, candles miraculously lit, wrapping the room in a golden embrace that felt akin to a mother’s kiss. Johnny’s eyes wandered around the room, taking it in while he walked to the altar, he stared at the dusty and empty marble, a sad sight for a Goddess so warm.
He searched around his belt, looking around his clothes and padded leather for an offering to wake you up. Something simply - anything - would work, if only to rouse you from your slumber, be it a year or a century long sleep, he would wake you and dub himself your champion. He picked a pelt, an apt offering for a Goddess of Health and Hunting. It was freshly skinned and cured, brushed with care and killed with sympathy. He wasn’t a ruthless killer or an avaricious hunter, he took what he needed and left what he didn’t.
Nodding at the brown pelt, he wiped away the dust that had collected and placed it on the marble, taking care to place it flat and straightened the fur. He took a step back to admire the sight, eyes filled with wonder at the sudden glow, bathing him in a calming light. He felt better, his once aching arms gone, his bruises gone and his strength returned. Waking you had brought a blessing, you had healed him of his aches and pains, restoring him to his peak.
“Welcome,” he heard you whisper, your voice sounding like a bird’s song, pretty and awestricking, “Will you become my champion, dear warrior?���
How could he say no at your sweet plea? You were the warmest being he has ever met, your very essence an embrace full of passion.
“If yer wish me so, Goddess.”
“Thank you,” you chuckled and he’d never felt so lovesick before, his heart so full, yet light.
Taglist: @sae1kie @yeoldedumbslut @bvxygriimes @distracteddragoness @konigsblog @im-making-an-effort @daisychainsinknots @h0n3y-l3m0n05 @danielle143 @tuttifuckinfruttifriday @notspiders @brokenpieces-72 @petwifed @randominstake @haven-1307 @shironasumi @sparky--bunny @bloobewy @cod-z @sweetnanah @aldis-nuts @evolutionarry @kaoyamamegami @cassiecasluciluce
#x reader#cod mw2#cod mw2 x reader#soap mw2#soap mactavish#soap#soap cod#john soap mactavish#soap x reader#soap x you#Champion!soap#Goddess!reader#greek mythology#champion au
106 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Ancient Greek Sculpture
The sculpture of ancient Greece from 800 to 300 BCE took inspiration from Egyptian and Near Eastern monumental art, and evolved into a uniquely Greek vision of the art form. Greek artists captured the human form in a way never before seen where sculptors were particularly concerned with proportion, poise, and the idealised perfection of the human body.
Greek sculptural figures in stone and bronze have become some of the most recognisable pieces of art ever produced by any civilization and the Greek artistic vision of the human form was much copied in antiquity and has been ever since.
Influences & Evolution of Greek Art
From the 8th century BCE, Archaic Greece saw a rise in the production of small solid figures in clay, ivory, and bronze. No doubt, wood too was a commonly used medium but its susceptibility to erosion has meant few examples have survived. Bronze figures, human heads and, in particular, griffins were used as attachments to bronze vessels such as cauldrons. In style, the human figures resemble those in contemporary Geometric pottery designs, having elongated limbs and a triangular torso. Animal figures were also produced in large numbers, especially the horse, and many have been found across Greece at sanctuary sites such as Olympia and Delphi, indicating their common function as votive offerings.
The oldest Greek stone sculptures (of limestone) date from the mid-7th century BCE and were found at Thera. In this period, bronze free-standing figures with their own base became more common, and more ambitious subjects were attempted such as warriors, charioteers, and musicians. Marble sculpture appears from the early 6th century BCE and the first monumental, life-size statues began to be produced. These had a commemorative function, either offered at sanctuaries in symbolic service to the gods or used as grave markers.
The earliest large stone figures (kouroi - nude male youths and kore - clothed female figures) were rigid as in Egyptian monumental statues with the arms held straight at the sides, the feet are almost together and the eyes stare blankly ahead without any particular facial expression. These rather static figures slowly evolved though and with ever greater details added to hair and muscles, the figures began to come to life.
Slowly, arms become slightly bent giving them muscular tension and one leg (usually the right) is placed slightly more forward, giving a sense of dynamic movement to the statue. Excellent examples of this style of figure are the kouroi of Argos, dedicated at Delphi (c. 580 BCE). Around 480 BCE, the last kouroi become ever more life-like, the weight is carried on the left leg, the right hip is lower, the buttocks and shoulders more relaxed, the head is not quite so rigid, and there is a hint of a smile. Female kore followed a similar evolution, particularly in the sculpting of their clothes which were rendered in an ever-more realistic and complex way. A more natural proportion of the figure was also established where the head became 1:7 with the body, irrespective of the actual size of the statue. By 500 BCE Greek sculptors were finally breaking away from the rigid rules of Archaic conceptual art and beginning to reproduce what they actually observed in real life.
In the Classical period, Greek sculptors would break off the shackles of convention and achieve what no-one else had ever before attempted. They created life-size and life-like sculpture which glorified the human and especially nude male form. Even more was achieved than this though. Marble turned out to be a wonderful medium for rendering what all sculptors strive for: that is to make the piece seem carved from the inside rather than chiselled from the outside. Figures become sensuous and appear frozen in action; it seems that only a second ago they were actually alive. Faces are given more expression and whole figures strike a particular mood. Clothes too become more subtle in their rendering and cling to the contours of the body in what has been described as 'wind-blown' or the 'wet-look'. Quite simply, the sculptures no longer seemed to be sculptures but were figures instilled with life and verve.
Continue reading...
67 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The ancient view saw little discord between Apollo and Dionysus in shared cuIts in Thebes, Sicilian Naxos, and in the mysteries of Attic Phlya in which Apollo had the title Dionysodotes, Giver of Dionysus, or Saviour, according to the Platonic commentator Olympiodorus.
Both gods appeared side by side in Attic vase painting from the 6th century B.C. In Delphi the dithyramb usually marked the beginning of winter, but on occasion Dionysus could also be praised with the Apolline paean. The 4th century temple divided the honours equally between the two : the east pediment showed Apollo with the Muses and the west Dionysus together with the Thyiades, while a contemporary red- figure vase has both gods cordially shaking hands across the omphalos in the sanctuary."
– Bernard C. Dietrich, "Divine Madness and Conflict at Delphi"
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
PART 1 | HEAVEN ━━ Marcus Acacius


summary: acacius' mother forged a blood pact with the goddess of love, vowing to safeguard and elevate her son, while dedicating her life as a delphi in return. through all general acacius' triumphs, you as the daughter of venus deftly orchestrated his victory as promised but then gradually nurturing a forbidden attachment.
author's note: don't get me started how i almost died with the trailer and the photos of papi pedroooooo so i had to do this (also i can use my greek mythology knowledge for some good use) so yup reader is an immortal goddess and possibly daughter of venus, idfc anymore because i'm making my own lore! they're going to be arwen and aragorn-esque ending coz i eat those kind of tropes lmfao
warnings: eventual smut to later chapters. mentions of misogyny, violence and also implications of sexual abuse.
word count: 4.4k
In the heart of a desolate village, a young woman stood at the fringes of society, shunned and abandoned for bearing the child of a powerful general. Clutching her infant son tightly to her chest, she wandered aimlessly, her heart heavy with despair and fear. The whispers of the villagers echoed in her mind, a cacophony of judgment and scorn. Tears streamed down her face as she made her way to the grand temple of Venus, the goddess of love, her last beacon of hope.
The temple, with its towering marble columns and intricate carvings, loomed before her like a sanctuary in the midst of her turmoil. The air grew thick with an impending storm as she fell to her knees at the entrance, her cries piercing the silence of the sacred place. "Great Venus, goddess of love and mercy," she sobbed, her voice trembling, "I beg of you, protect my son and guide us, for we have nowhere else to go. I fear for his life, for he is innocent."
As her desperate pleas echoed within the hallowed halls, the wind suddenly picked up, swirling around her with a fierce intensity. The sky darkened, and the deafening roar of thunder cracked through the air. In the midst of this tempest, a radiant light descended upon the temple. From the ethereal glow emerged a figure of unparalleled beauty, clothed in pure white robes that flowed like water.
Venus, the goddess of love, knelt before the fallen woman. Her presence was divine, her skin like alabaster, flawless and luminous. Her eyes, a captivating shade of deep blue, held the wisdom of the ages and the compassion of a thousand hearts. Golden hair cascaded down her back in waves, shimmering as if woven from sunlight. A gentle smile graced her lips, exuding warmth and serenity.
"Rise, my child," Venus spoke, her voice a melodious symphony that filled the air with hope. "Do not despair, for I have heard your cries and felt your anguish. I can offer you and your son protection, but it comes with a price. You must dedicate your life to me, serve as my devotee, and in return, I shall ensure your son’s safety and guide you both to a brighter future."
The young woman, overwhelmed by the goddess's presence and her words, gazed into the loving eyes of Venus. With unwavering determination and gratitude, she nodded. "I will do as you ask, great goddess. My life is yours to command, if it means my son will be safe."
Venus gently lifted the woman to her feet, her touch tender and reassuring. "Then it shall be so. From this moment forth, you are under my protection. Fear not, for love shall guide your path, and together, we shall overcome all obstacles."
With that, the storm subsided, leaving behind a serene sky. The young woman, now filled with renewed hope and purpose, cradled her son as they both embraced the divine path laid before them by the goddess of love.
Years had gone by, the once forsaken young woman found solace and purpose as a devoted Delphi. She served with unwavering faith, her every breath a testament to the sacred bond she had formed with the goddess of love. Her son, Acacius, grew under the protective aegis of the temple, receiving the finest education and training from the wise sorceresses who resided there. His days were filled with rigorous training and study, molding him into a formidable warrior.
One golden afternoon, the courtyard of the temple buzzed with activity. Acacius, now a young man of remarkable prowess, moved with grace and strength as he sparred with his fellow trainees. His body, chiseled and powerful, gleamed with sweat under the sun. Every muscle in his arms and chest rippled with the precision and control honed through years of discipline. His jawline was sharp, his dark hair tousled, and his piercing eyes focused, exuding an aura of confidence and determination.
From a distance, Venus, resplendent in her divine beauty, emerged from the temple accompanied by you, her daughter. Venus’ robes flowed like liquid moonlight, and her presence illuminated the courtyard. While you, whose divine essence shimmered with an ethereal glow, stood by your mother’s side, your eyes subtly observing Acacius as he trained vigorously.
"Look at him, my daughter," Venus spoke, her voice a soothing melody. "Acacius’ mother devoted her life to serving as a Delphi, and it is now your duty to watch over him. He has grown into a man of great potential."
You were hesitant and prideful, replied, "Mother, surely I am capable of far more important tasks than merely watching over a mortal."
Venus laughed, "Ah, my dear, I see great things in Acacius. I made an unbreakable oath to his mother to protect him and guide him to victory. This task is of utmost importance, and you, my daughter, are perfectly suited for it."
Reluctantly, you agreed, though you felt the weight of the responsibility. As Venus gracefully returned to the temple, your gaze lingered on Acacius. You had watched him grow from a vulnerable child into the powerful warrior he had become. His masculine form, sculpted by relentless training, was a testament to his dedication and strength. His broad shoulders, strong arms, and defined torso were a sight to behold, each movement exuding a raw, magnetic energy.
As the daughter of Venus, you had spent millennia observing the ways of mortals. From the heights of the celestial realm to the depths of human existence, you had witnessed the endless cycles of birth, love, ambition, and vanity that defined their ephemeral lives. Mortal men, in particular, seemed ensnared by their own reflections, driven by a relentless pursuit of power, beauty, and validation. Their obsessions with vanity, you mused, were like chains binding them to an endless quest for an ever-elusive perfection.
In the sanctity of your divine solitude, you pondered these thoughts, your mind weaving through the countless interactions you had with mortals over the ages. Vanity, you concluded, was a double-edged sword. It spurred men to greatness but also led them to their downfall. How often have you seen warriors, poets, and kings, their hearts consumed by the desire for eternal youth, adoration, and glory? They built monuments to themselves, adorned their bodies in opulent garb, and sought the fleeting approval of their peers, all the while neglecting the deeper virtues of humility, wisdom, and compassion.
Living among mortals, you had grown accustomed to their ways, understanding the fragile nature of their existence. Yet, with each passing century, you have grown more disillusioned by their unchanging flaws. Despite the wisdom imparted by time and the guidance of the gods, mortals remained predictably obsessed with their own image.
When your mother, Venus, entrusted you with the responsibility of watching over Acacius, you could not help but feel a familiar pang of skepticism. Was he not just another man, destined to be ensnared by the same vanities as those before him? Despite his formidable strength and the disciplined mind he had cultivated, you feared that beneath his heroic exterior lay the same vulnerabilities that had claimed countless others.
As you observed Acacius from the shadows, your thoughts grew heavier. You remembered how, as a boy, he had shown signs of the same traits that plagued mortal men: the pride in his burgeoning strength, the flicker of arrogance in his victories, and the longing in his eyes for recognition and admiration. He seemed no different from the countless men who had walked the earth, striving for greatness yet ultimately ensnared by their own hubris.
Your divine heart, though swayed by eons of witnessing human folly, felt a curious twinge as she watched him. There was something about Acacius, a glimmer of potential, that both made you intrigued and worried. Could he break the cycle? Or would he, too, succumb to the inevitable downfall of vanity?
As you silently vowed to fulfill her mother’s promise, you found yourself grappling with an unexpected sense of protectiveness. Despite your reservations, there was an undeniable bond formed by watching him grow, a reluctant admiration for his resilience and strength. You feared for him, not because you doubted his abilities, but because she understood the weight of his mortality.
With a sigh, you resigned yourself to the task. "Acacius may be like other men," you thought, "but perhaps there lies within him a spark of something more." You would watch over him, guide him, and protect him from the shadows, ever vigilant and ever hopeful that he might transcend the very vanities that ensnared his kind. As the daughter of Venus, you knew that love and duty were bound by unbreakable threads, and you would honor them both, even if it meant confronting your own doubts and fears.
As you observed him and embedded in your own thoughts, Acacius suddenly paused and turned his head, his sharp eyes meeting yours across the courtyard. Startled, you quickly retreated into the shadows, your divine essence blending with the darkened corners of the temple.
Hidden from view, your heart pounded. You realized the gravity of your new role, feeling a mixture of trepidation and an unspoken bond with the man she would protect and guide. As Acacius resumed his training, unaware of the divine eyes watching over him, you knew this won’t be an easy responsibility.
As the daughter of Venus, you have watched over Acacius from the shadows, your divine presence hidden but your influence ever-present. From the moment he drew his sword, you felt the weight of your mother's promise pressing upon your shoulders, a vow to guide and protect him, to steer him towards greatness. Acacius was more than a mortal; he was the culmination of a divine pact, and your duty to him was as sacred as the bond forged between his mother and Venus.
In his youth, you whispered wisdom into the ears of his mentors, guiding their hands as they trained him in the arts of war and leadership. You ensured that the best teachers found their way to him, that he learned not only the strategies of battle but also the virtues of honor, compassion, and justice. Through subtle interventions, you shaped his character, molding him into a man worthy of the destiny laid before him.
As he grew, so did the challenges he faced. You were there in the thick of his battles, unseen but ever vigilant. During his early skirmishes, you would nudge his instincts, sharpening his reflexes and lending him the strength he needed to overcome his foes. When he faltered, you were the whisper of encouragement that steeled his resolve, the invisible hand that steadied his sword.
In the grand halls of strategy and politics, you guided his thoughts, helping him navigate the treacherous waters of Roman ambition. You planted seeds of wisdom in his mind, urging him to form alliances that would strengthen his position, to make decisions that would earn him the respect of his peers and the loyalty of his men. You were the unseen force that smoothed the path before him, ensuring that every step he took led him closer to his destiny.
When he was appointed as a general under Maximus Decimus Meridius, you knew that your efforts were bearing fruit. Acacius had become a formidable leader, his name spoken with reverence and fear across the empire. Yet, his journey was far from over. Under the rule of Emperor Geta and his co-Augusti, Caracalla, Acacius faced new trials. The invasion of Caledonia was a test of his mettle, a crucible that would forge his legacy.
As the Romans prepared for their campaign, you took on the guise of a tradesman’s daughter in Caledonia, positioning yourself to be near him, to watch over him more closely. The battles were fierce, and the land was unforgiving. You ensured that crucial information reached him at the right moments, that his strategies were sound and his decisions unerring. You softened the hearts of those who might have betrayed him, turned the tides of fortune in his favor.
Through the years, you have been his silent guardian, his invisible ally. You have seen him rise from a young warrior to a revered general, each victory a testament to the bond you honored. Even now, as you stand among the captured townspeople, disguised and hidden, your purpose remains unchanged. You are here to protect him, to guide him, and to ensure that he fulfills the destiny that was promised.
In the moments when doubt clouded his heart, you were the light that pierced the darkness. When he faced insurmountable odds, you were the strength that carried him through. You have watched over him with a mixture of pride and affection, your heart swelling with each triumph and breaking with each loss. Acacius is more than just a mortal; he is a living embodiment of the divine promise you are bound to uphold.
Amidst the chaos of the Roman invasion of Caledonia, the air was thick with smoke and the cries of the conquered. The formidable General Acacius, now a seasoned leader under Emperor Geta and his co-Augusti, Caracalla, surveyed the battlefield with a steely gaze. His once youthful visage was now marked by the scars of countless battles, his presence commanding and unwavering.
In the midst of the turmoil, you risked disguising as a daughter of a tradesman, moved with quiet resolve. Clad in the coarse, earth-toned garb of a peasant, she blended seamlessly with the captured townspeople. Yet, even in your humble attire, your divine essence could not be wholly concealed. Your skin, a flawless alabaster, stood out against the grime and soot of the war-torn village. Your eyes, a striking shade of hazel, gleamed with an unearthly light, and your movements, though tempered to appear modest, held an innate grace that betrayed your true nature.
The Roman soldiers, drunk on victory, rounded up the women of Caledonia, separating them from their families with ruthless efficiency. Among the throng, the disguised goddess maintained a facade of fear and helplessness, your heart pounding as she witnessed the suffering of the innocent. The brutality of the soldiers, their coarse laughter, and lecherous gazes made you shudder inwardly, but you knew you must maintain your cover.
General Acacius, his mind burdened with the responsibilities of command, scanned the scene with a practiced eye. His soldiers were securing the captives, ensuring the spoils of war were collected. His gaze fell upon the group of captured women, and for a moment, he saw them as mere pawns in the grand scheme of conquest. But then, his eyes landed on you.
Despite your plain clothing, something about you stood out. Your skin, untouched by the harshness of the elements, was too smooth, too luminous for a common peasant. Your hair, though partially hidden beneath a simple headscarf, shone with a subtle, otherworldly luster. You moved with a quiet dignity, your posture erect even in the face of despair. Acacius's sharp eyes missed nothing, maybe a nobility pretending to be a peasant so they can escape from the invasion. He finds it as a clever tactic.
As one of his soldiers, emboldened by the chaos, approached her with lecherous intent, Acacius felt a surge of anger. The soldier, a brutish figure, reached out to grasp your arm, his intentions clear. Before he could lay a hand on you, Acacius's voice rang out, authoritative and cold.
"Stand down," he commanded, his tone brooking no argument. The soldier froze, his hand hovering in the air. "Do not touch her."
The soldier, taken aback, stammered a protest, "But, General, she's just a—"
"Bring her to me," Acacius cut him off, his gaze fixed on the disguised goddess. "Now."
The soldier, reluctant but obedient, withdrew his hand and roughly pushed you forward. You stumbled slightly but quickly regained your balance, your eyes meeting Acacius with a mixture of apprehension and curiosity. As you were brought before him, he could see the subtle details that marked you as different: the refinement in your features, the intelligence in your eyes, the air of quiet strength exuded within you.
"Who are you?" Acacius asked, his voice softer but still commanding. "You do not belong here, do you?"
You hesitated, you mind racing to craft a plausible response. "I am the daughter of a tradesman," you said, your voice steady despite the fear you felt. "Captured like the others. Please, I mean no harm."
Acacius studied you for a long moment, his instincts telling him there was more to your story. "Take her to my tent," Acacius declared, his voice carrying an edge of finality. "She will be my personal cupbearer."
The soldiers, recognizing the unwavering tone of their general, nodded in agreement. They stepped back, leaving you untouched. Acacius's gaze softened slightly as he looked at you, a mixture of curiosity and protectiveness in his eyes.
"Find her something clean to wear," he instructed, his tone gentle yet firm.
Two soldiers led you through the encampment, their grip on your arms firm but not harsh. They guided you to the lavish tent of General Acacius, a striking contrast to the roughness of the battlefield outside. The tent was grand, its exterior adorned with rich fabrics and ornate decorations. Inside, it was a sanctuary of luxury and comfort amidst the chaos of war.
The interior of the tent was spacious, with plush carpets covering the ground and opulent cushions scattered around. Rich tapestries adorned the walls, depicting scenes of Roman victories and mythological grandeur. A large, intricately carved wooden table stood at the center, laden with an array of sumptuous food and fine wine. The scent of incense filled the air, mingling with the aroma of roasted meats and freshly baked bread.
As you stood in the middle of the tent, feeling the weight of her disguise, General Acacius entered. His armor gleamed in the soft light of the tent, and his eyes locked onto yours with an intensity that made your heart race. He moved with the confidence of a seasoned warrior, yet there was a gentleness in his approach.
"Sit with me," he said, gesturing to the cushions by the table.
You hesitated but complied, lowering yourself onto the soft cushions. Acacius sat across from you, his gaze never leaving yours like a lion observing his prey. He offered you a plate of food, the array of delicacies a testament to the wealth and power he commanded.
"Please, eat," he urged, but you shook your head, declining politely.
"I’m not hungry, my Lord," you explained, your voice steady.
Acacius leaned back, studying you intently. "What kind of business does your father have?"
You took a breath, weaving the story you had prepared. "My father is a tradesman, specializing in silk. We travel far and wide, even to the distant lands of China, to procure the finest silk. He sells it to the emperor and to those of noble birth."
Acacius nodded, intrigued. "A tradesman of silk, you say? But then, you do not seem like a mere peasant."
You lowered your eyes, the weight of your divine secret heavy upon you. "We have faced many hardships, but my father has always ensured that we present ourselves with dignity."
Acacius leaned forward, his gaze unwavering. "Tell me," he said, his voice low and measured, "does your family live in Caledonia?"
Your heart is pounding. "Yes," you replied, your voice steady. "We come from an impoverished background. My father sought to make a better life for us through his trade."
Acacius studied you closely, his eyes dark and intense. As he reached for a cluster of grapes, he popped one into his mouth, chewing thoughtfully. The act, so casual and yet so intimate, made your pulse quicken. His scrutiny was unrelenting, and you felt as though he could see through the layers of your disguise.
"You should know," he began, his tone carrying a note of warning, "that the nobility of Caledonia will be captured. There is no escape for them."
You remained silent, her expression carefully neutral. You knew he was testing you, probing for any signs of deceit. His words, though intended to intimidate, also carried a hint of concern.
"My soldiers are ruthless," he continued, his voice growing colder. "They would take advantage of you if given the chance."
You nodded silently, acknowledging the gravity of his warning. Your heart ached at the thought of the suffering around you, but you knew she had to maintain your composure.
As Acacius spoke, the flap of the tent was pushed aside, and a soldier entered, carrying a bundle of fresh clothes. They were simple but clean, likely taken from a Caledonian household. The soldier handed the bundle to Acacius, who thanked him with a curt nod.
"Here," Acacius said, extending the clothes to you. "Put these on."
You rose from your seat and took the bundle obediently, your fingers brushing against his for the briefest moment. The contact sent a shiver through you, a reminder of the thin line she walked between mortal and divinity.
"You may change behind the screen," he said, gesturing to a beautifully carved wooden partition that provided a modicum of privacy within the tent.
You nodded and moved behind the screen, the fabric rustling softly as you slipped out of your peasant clothes. The new garments were a marked improvement, though still modest. As you dressed, you could feel Acacius's presence just beyond the screen, his protective aura enveloping you like a shield.
When you emerged, you found him watching you intently, his eyes reflecting a mixture of curiosity and something deeper, something you could not quite name. The new clothes fit you well, accentuating your grace and poise even in their simplicity.
"Better," he murmured, his voice softening. "You look more like the person you claim to be."
You offered a faint smile, lowering her gaze. "Thank you."
Days passed, and you, now working as a cupbearer in General Acacius's camp, endeavored to maintain your humble facade. Despite your best efforts to appear as an ordinary servant, your innate grace and poise occasionally betrayed your true nature. Acacius, ever observant, began to notice the subtle refinement in your movements, the way you carried yourself with a dignity that spoke of nobility.
Your body language, though deliberately subdued, hinted at a life of privilege and education. You moved with an elegance that seemed out of place in the rough-and-tumble environment of a military camp. The way you poured water into cups, the delicate curve of your fingers as you handled the pitchers, all bespoke a background far removed from the impoverished tale you had spun.
One afternoon, a group of generals gathered in Acacius's lavish tent for a luncheon. As you silently poured water into their cups, you could feel the weight of their gazes upon you. The generals, their voices booming with laughter and boasts, paid little heed to the solemnity of their surroundings. One of them, a burly man with a coarse beard, eyed you with a lecherous grin.
"Acacius," he called out, his voice thick with drink, "is your cupbearer good in bed?"
The tent erupted in raucous laughter, the crude jest echoing off the walls. Acacius, seated at the head of the table, narrowed his eyes. His gaze hardened, and he fixed the offending general with a stern look.
"Such things are not to be discussed," he said, his tone carrying a quiet authority that silenced the laughter.
The general, still chuckling, raised his hands in mock surrender. "Ah, Acacius, always so reserved. You'd do well to indulge a bit more."
The disguised goddess watched the exchange with keen interest, your heart pounding. You knew Acacius's character well, having observed him for years. You despised these gatherings, these displays of vanity and ego. He found no pleasure in the idle boasts of his peers, preferring the company of his own thoughts and strategies.
As you continued your duties, pouring water and refilling cups, you could sense Acacius's discomfort. He was a man of action, a warrior with a clear sense of purpose. These luncheons, with their empty chatter and frivolous banter, were a stark contrast to the disciplined life he led. You admired his restraint, his ability to maintain his composure in the face of such provocation.
The generals continued their revelry, their conversations shifting from one boast to another. They spoke of past victories, of conquests and spoils, their voices a cacophony of pride and self-importance. Acacius, though present in body, seemed distant, his mind likely focused on the next battle, the next challenge.
As you moved around the table, you caught his eye for a brief moment. In that instant, you saw a flicker of something deeper, a connection that transcended. You knew that he valued substance over show, strategy over vanity. His reluctance to engage in their crude jests and hollow boasts only endeared him to you more.
The luncheon dragged on, the generals growing more boisterous with each passing moment. Acacius, ever the disciplined leader, maintained his stoic demeanor, responding to their jibes with measured patience. You could see the tension in his posture, the tightness in his jaw, and felt a pang of empathy.
As the daughter of Venus, you had always found mortal men to be easily swayed by vanity and ambition. They are like clay, molded by the hands of society and their peers, their true selves often buried beneath layers of ego and pride. But Acacius is different. Despite the pressures and temptations that come with his rank, he remains steadfast and true to his values. You're secretly proud of him, of the strength he shows in resisting the crudeness and arrogance that so often define his comrades.
That evening, after the generals had left and the camp had settled into a quiet lull, you found Acacius outside his tent, gazing up at the night sky. The stars twinkled above, their light casting a gentle glow on his strong, chiseled features. There was a tranquility in the air, a moment of peace amidst the chaos of war.
You approached him silently, your heart swelling with admiration for the man he had become. "Thank you for everything, My Lord," you said softly, breaking the silence.
He turned to look at you, his eyes reflecting the starlight. "You don’t need to thank me," he replied, his voice steady.
You nodded, understanding the brusqueness of his words. "Even so, I am forever grateful."
As you turned to return to the tent, you could feel his gaze lingering on you. There was a mystery in his eyes, a curiosity that you knew he could not easily dispel. You wondered what he saw when he looked at you—this woman who appeared from nowhere, cloaked in the guise of a humble servant yet betraying hints of refinement and grace.

CONTINUE READING: PART 2 | PART 3 ━━ AVAILABLE ON AO3

☆ MASTERLIST | NAVIGATION | SOCIALS | SIGN OFF BANNER MADE BY. @ALDERAANDORS ☆

#marcus acacius#gladiator 2#pedro pascal#marcus acacius x reader#marcus acacius x you#marcus acacius x y/n#marcus acacius x female reader#smut#pedro pascal x reader#pedro pascal x y/n#pedro pascal x you#pedro pascal characters#ancient rome#gladiator#general acacius#general marcus acacius#general acacius x reader#general acacius x you#general acacius x y/n#female reader#pedro pascal smut#marcus acacius smut#marcus acacius fic#marcus acacius fanfiction
128 notes
·
View notes
Text
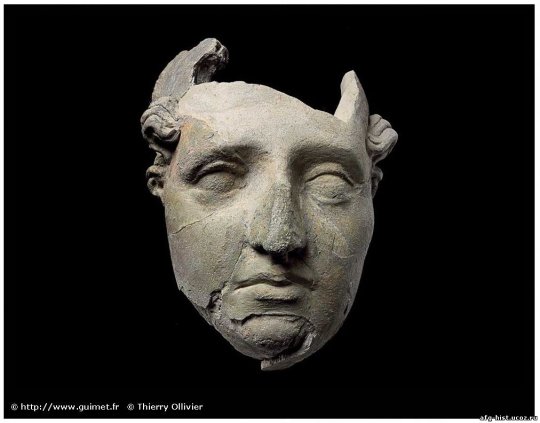
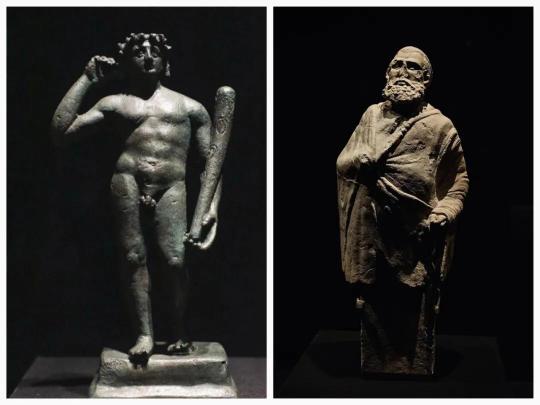





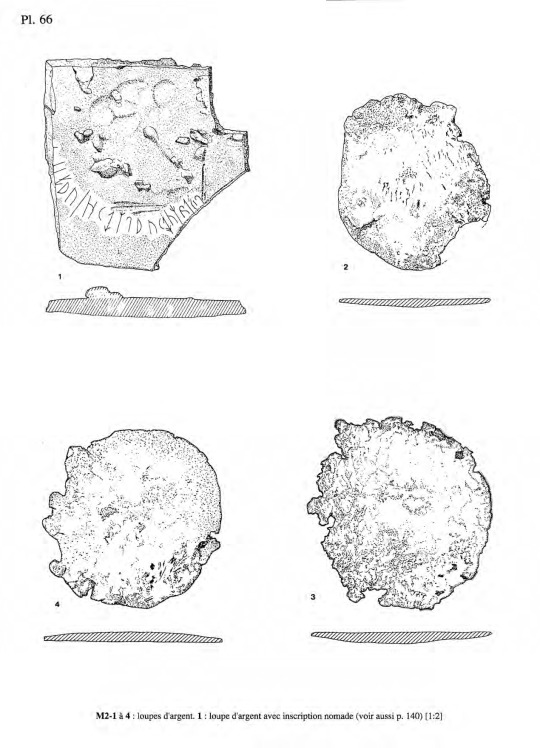





















Ai Khanoum 3rd C. BCE - 2nd C. CE. More images on my blog, link at bottom.
"These wise sayings of men of old, The words of famous men, are consecrated At holy Delphi, where Klearchos copied them from carefully To set them up, shining from afar, in the sanctuary of Kineas.
As a child, be well behaved; As a young man, self-controlled; In middle age, be just; As an elder, be of good counsel; And when you come to the end, be without grief.
—trans. of Ai Khanoum stele by Shane Wallace and Rachel Mairs.
Ai-Khanoum (/aɪ ˈhɑːnjuːm/, meaning Lady Moon; Uzbek Latin: Oyxonim) is the archaeological site of a Hellenistic city in Takhar Province, Afghanistan. The city, whose original name is unknown, was likely founded by an early ruler of the Seleucid Empire and served as a military and economic centre for the rulers of the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom until its destruction c. 145 BC. Rediscovered in 1961, the ruins of the city were excavated by a French team of archaeologists until the outbreak of conflict in Afghanistan in the late 1970s.
The city was probably founded between 300 and 285 BC by an official acting on the orders of Seleucus I Nicator or his son Antiochus I Soter, the first two rulers of the Seleucid dynasty. There is a possibility that the site was known to the earlier Achaemenid Empire, who established a small fort nearby. Ai-Khanoum was originally thought to have been a foundation of Alexander the Great, perhaps as Alexandria Oxiana, but this theory is now considered unlikely. Located at the confluence of the Amu Darya (a.k.a. Oxus) and Kokcha rivers, surrounded by well-irrigated farmland, the city itself was divided between a lower town and a 60-metre-high (200 ft) acropolis. Although not situated on a major trade route, Ai-Khanoum controlled access to both mining in the Hindu Kush and strategically important choke points. Extensive fortifications, which were continually maintained and improved, surrounded the city.
Many of the present ruins date from the time of Eucratides I, who substantially redeveloped the city and who may have renamed it Eucratideia, after himself. Soon after his death c. 145 BC, the Greco-Bactrian kingdom collapsed—Ai-Khanoum was captured by Saka invaders and was generally abandoned, although parts of the city were sporadically occupied until the 2nd century AD. Hellenistic culture in the region would persist longer only in the Indo-Greek kingdoms.
It is likely that Ai-Khanoum was already under attack by nomadic tribes when Eucratides was assassinated in around 144 BC. This invasion was probably carried out by Saka tribes driven south by the Yuezhi peoples, who in turn formed a second wave of invaders, in around 130 BC. The treasury complex shows signs of having been plundered in two assaults, fifteen years apart.
Although the first assault led to the end of Hellenistic rule in the city, Ai-Khanoum continued to be inhabited; it remains unknown whether this reoccupation was effected by Greco-Bactrian survivors or nomadic invaders. During this time, public buildings such as the palace and sanctuary were repurposed as residential dwellings and the city maintained some semblance of normality: some sort of authority, possibly cultish in origin, encouraged the inhabitants to reuse the raw building materials now freely available in the city for their own ends, whether for construction or trade. A silver ingot engraved with runic letters and buried in a treasury room provides support for the theory that the Saka occupied the city, with tombs containing typical nomadic grave goods also being dug into the acropolis and the gymnasium. The reoccupation of the city was soon terminated by a huge fire. It is unknown when the final occupants of Ai-Khanoum abandoned the city. The final signs of any habitation date from the 2nd century AD; by this time, more than 2.5 metres (8.2 ft) of earth had accumulated in the palace.
While on a hunting trip in 1961, the King of Afghanistan, Mohammed Zahir Shah, rediscovered the city. An archaeological delegation, led by Paul Bernard, unearthed the remains of a huge palace in the lower town, along with a large gymnasium, a theatre capable of holding 6,000 spectators, an arsenal, and two sanctuaries. Several inscriptions were found, along with coins, artefacts, and ceramics. The onset of the Soviet-Afghan War in the late 1970s halted scholarly progress and during the following conflicts in Afghanistan, the site was extensively looted."
-taken from Wikipedia
...
"The silver ingot engraved with runic characters found during the excavations of the Treasury could suggest they were Sakā/Sai. This inscription comprises 21 characters of a script and a language that are unknown and both attributed to nomadic people of Sakā origin, by comparison with a dozen similar inscriptions coming from an area extending from Ghazni in Afghanistan to Almaty in Kazakhstan, and dated between the 5th century BC and the 8th century AD."
-taken from Ai Khanoum after 145 BC: The Post-Palatial Occupation by Laurianne Martinez-Sève, University of Lille, 2018
#ancient history#antiquities#art#paganism#statue#museums#sculpture#history#greek art#greek gods#ancient greek#greek myth#scythian#pagan#ancient art#afghanistan
219 notes
·
View notes
Text

Theseus #11: Murdered in Exile
Regretting the loss of his friend Pirithous, Theseus makes his way back to Athens to find the city in rebellion. Helens brothers, Castor and Pollux, have rescued their sister and Athens is on the brink of war with the Spartans. A new Athenian king, Menestheus, has turned the citizens against Theseus, forcing him to send his children away and flee to the island of Scyros under the protection of King Lycomedes. But King lycomedes betrays Theseus, leading him up to a view point on a high cliff, and pushing him off to his death. Thus, Theseus life ends in murder and exile.
A few hundred years later, the Greeks fight the Persians in the battle of Marathon (490 B.C.) During this battle many warriors claim to see the ghost of Theseus leading a charge into battle. General Cimon receives a prophecy from the Oracle at Delphi, instructing him to retrieve Theseus body from Scyros. Cimon overtakes the island, and seeing an eagle digging, locates the giant bones of Theseus. Cimon relocates them back to Athens and seals them within a grand Tomb. In addition, in his honor, the temple known as the Theseion is built, as well as the creation of the festival Theseia.
The Theseion temple was established as hero-cult sanctuary for the poor and oppressed. The remains of a Doric temple North West of the Agora was thought to be the Theseion, but many modern scholars believe this to be the Temple of Hephaestus.
The actual tomb of Theseus was rumored to be near the Lyceum, and the design of the tomb is rumored to look like the Tomb of Mausolus in Halicarnassus There is much debate as to whether Theseus was a real, historical king, as his grave or body has never been found.
The Theseia Festival consisted of athletic competitions for Athenian males to compete and show their military skills as well as processions and sacrifices.
Like this art? It will be in my illustrated book with over 130 other full page illustrations coming in Aug/Sept to kickstarter. to get unseen free hi-hes art subscribe to my email newsletter
Follow my backerkit kickstarter notification page.
Thank you for supporting independent artists! 🤘❤️🏛😁
#greekmythology#greekgods#pjo#mythology#classics#classicscommunity#myths#ancientgreece#Theseus#AthenianMythology#Theseion#art
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
Athena and Childbirth [Excerpt]
Book: Athena by Susan Deacy (Highy recommend)

"One of the most distinctive aspects of Athena in Athens is her association with Erichthonios, whose extraordinary conception and birth is due largely to her, and whom she strives to protect by placing him in a chest and eventually rearing him in her temple."
"In some versions of the myth of Apollo’s birth, Athena is said to have loosened the girdle of Leto to enable her to give birth. One account (Pausanias 1.31.1) locates this act at a place called Zoster (‘Girdle’) on the coast of Attica. Leto then went on to Delos, the site of the birth of Apollo and Artemis."
"At Delphi, too, Athena may have been envisaged in this role. […] As Athena Pronaia (‘before the temple’), she functioned as guardian of the temple of Apollo. That she seems to have had the role of guardian of the god himself may be indicated by the presence in the sanctuary of an altar of Athena Zosteria (‘of the girdle’) which may recall the assistance that Athena gave Apollo’s mother Leto in childbirth."
"It may look curious that the virgin Athena should have been linked with childbirth. The notion of a virgin goddess with power over childbirth, however, is attested widely in Greece and beyond, in the Greek Artemis, for example."
"What lies behind Athena’s interventions that enable the production of children is not so much a safeguarding of childbirth per se, but an ability to allow individuals to be born in unusual circumstances, from her own ‘son’ Erichthonios to Apollo and Artemis, whose birth had been prevented by Hera until Athena’s intervention that enabled the children to be born. With this in mind, let us turn briefly to a story told by Pausanias (5.3.2) about a sanctuary of Athena in Elis:
The women of Elis, it is said, prayed to Athena to make them conceive as soon as they next slept with their husbands because the country was deprived of its youth. Their prayer was answered, and they established a sanctuary of Athena Meter (‘mother’) and because both wives and husbands experienced extreme delight in their union, they called the place Bady (‘sweet’)."
"Again, it is due to Athena that children come to be born when circumstances had been preventing this. The Orphic literature, too, draws on these abilities of Athena, here in relation to Dionysos. The young god had been lured away from his protectors, the Kouretes, by the Titans, who killed him, dismembered his body and ate him (West 1983: 74.) But Athena managed to get hold of his still-beating heart, which she placed in a chest, out of which the god was reborn. Dionysos, the ‘Twice-born’ god here has a third birth under Athena’s patronage out of his still-beating heart.
Athena was herself born in strange circumstances: contained in the body of Zeus until the blow from Hephaistos’ axe allowed her to leap forth. She is involved, too, in the production of children in comparably strange circumstances. Pegasos and Chrysaor emerge from the severed neck of Medusa in a way that comes closest in myth to her own emergence. Chrysaor especially evokes Athena in the manner of his birth in that he is born as a warrior. His name, ‘Golden Sword’, is also fitting for a figure who emerges in armour, paralleling perhaps the dazzling display of Athena’s birth.
When Athena functions as a goddess involved in childbirth, what she brings to bear is her capacity as a situation inverter. This provides us with yet another instance of her role as the power able to bring about what was seemingly impossible, here the production of children in unusual circumstances."

#Nell Reads Books#Susan Deacy#athena goddess#athena deity#athena devotion#paganism#helpol#hellenic polytheism#paganblr#athena
45 notes
·
View notes