#serverless computing aws
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Serverless computing has been gaining popularity as a powerful and efficient solution for building and deploying applications.
#serverless computing#serverless architecture#aws serverless architecture#serverless computing aws#serverless cloud computing
0 notes
Text
#Serverless architecture beyond AWS Lambda#Event-driven systems and edge computing#Backend-as-a-Service (BaaS) in modern applications#Spotify
0 notes
Text
Serverless Computing: Streamlining Web Application Deployment
0 notes
Text
Building Your Serverless Sandbox: A Detailed Guide to Multi-Environment Deployments (or How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Love the Cloud)
Introduction Welcome, intrepid serverless adventurers! In the wild world of cloud computing, creating a robust, multi-environment deployment pipeline is crucial for maintaining code quality and ensuring smooth transitions from development to production.Here is part 1 and part 2 of this series. Feel free to read them before continuing on. This guide will walk you through the process of setting…
#automation#aws#AWS S3#CI/CD#Cloud Architecture#cloud computing#cloud security#continuous deployment#DevOps#GitLab#GitLab CI#IAM#Infrastructure as Code#multi-environment deployment#OIDC#pipeline optimization#sandbox#serverless#software development#Terraform
0 notes
Text
Headless - Serverless Computing In AWS
#Unlocking Efficiency: Harnessing Headless — Serverless Computing in AWS#Harnessing Headless — Serverless Computing in AWS#Headless — Serverless Computing in AWS#Serverless Computing in AWS#Headless Computing in AWS#Headless in AWS#Serverless in AWS#Amazon Web Services Company In India#Amazon Web Services Company India#Amazon Web Services Company#Amazon Web Services#AWS Services Company In India#AWS Services Company India#AWS Services Company#AWS Services#Lucid Outsourcing Solutions#Lucid Outsourcing#Lucid Solutions
0 notes
Text
Unraveling the 5 Layers of Software Development

In the realm of software development services, every application is built upon a foundation of interconnected layers, each serving a specific purpose in delivering functionality to end-users. Understanding these layers and the technologies that power them is crucial for developers aiming to create robust and efficient software solutions. In this blog, we'll explore the five key layers of software architecture: User Interface (UI), Application Programming Interface (API), Database (DB), Business Logic, and Hosting, along with examples of technologies commonly used in each layer.

User Interface (UI): The UI layer is what users interact with directly. It encompasses everything from the visual design to the user experience (UX). Technologies used in this layer focus on creating intuitive, responsive, and aesthetically pleasing interfaces. Some popular UI Design technologies include:
HTML/CSS/JavaScript: These front-end technologies form the backbone of web-based UIs. HTML defines the structure, CSS styles the elements, and JavaScript adds interactivity.
React.js/Vue.js/Angular: These JavaScript frameworks are used to build dynamic and interactive user interfaces for web applications.
Swift/Kotlin: For mobile application development, languages like Swift (for iOS) and Kotlin (for Android) are used to develop native user interfaces.

Application Programming Interface (API): The API layer acts as an intermediary between the UI and the business logic, enabling communication and data exchange. APIs define the endpoints and protocols through which different software components interact. Common technologies used in API development services include:
RESTful APIs: Representational State Transfer (REST) is a popular architectural style for designing networked applications. RESTful APIs use HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE to perform operations on resources.
GraphQL: An alternative to REST, GraphQL provides a more flexible and efficient approach to querying and manipulating data. It allows clients to request only the data they need, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching.
Express.js/Django/Rails: Frameworks like Express.js (for Node.js), Django (for Python), and Rails (for Ruby) are commonly used to build web APIs quickly and efficiently.
Database (DB): The database layer is responsible for storing, retrieving, and managing data. It provides a persistent storage solution for an application's information. Various types of databases exist, including relational databases, NoSQL databases, and in-memory databases. Some popular database technologies include:
MySQL/PostgreSQL: Relational database management systems (RDBMS) like MySQL and PostgreSQL are widely used for structured data storage and management.
MongoDB: A popular NoSQL database, MongoDB is designed for storing unstructured or semi-structured data in JSON-like documents.
Redis: An in-memory data structure store, Redis is often used as a caching layer or for real-time data processing.

Business Logic: The business logic layer contains the application's core functionality and rules. It processes requests from the UI, interacts with the database, and performs the necessary operations to fulfill user actions. While business logic can be implemented in various programming languages, some technologies commonly used for this layer include:
Java/C#: Object-oriented languages like Java and C# are often chosen for building robust and scalable business logic components.
Node.js/Python: JavaScript (with Node.js) and Python are also popular choices, especially for applications requiring agility and rapid development.
Spring/.NET Core: Frameworks like Spring (for Java) and .NET Core (for C#) provide tools and libraries for building enterprise-grade business logic components.
Hosting: The hosting layer encompasses the infrastructure and environment where the application runs. It includes servers, cloud platforms, containers, and other deployment options. Popular hosting technologies and platforms include:
Amazon Web Services (AWS)/Microsoft Azure/Google Cloud Platform (GCP): These cloud service providers offer a range of hosting solutions, including virtual machines, containers, and serverless computing.
Docker/Kubernetes: Containerization technologies like Docker and orchestration platforms like Kubernetes provide efficient ways to package, deploy, and manage applications across different environments.
Heroku/Netlify/Vercel: These platforms offer simplified hosting solutions specifically tailored for web applications, providing features like continuous deployment, scalability, and managed infrastructure.
In conclusion, navigating the various layers of software architecture requires a comprehensive understanding of each layer's purpose and the technologies that power them. By leveraging the right technologies for UI, API, DB, logic, and hosting, developers can build robust, scalable, and maintainable software solutions that meet the needs of modern users and businesses.
#webdesign#mobileappdevelopment#appdevelopment#web developers#webdevelopment#youtube#apiintegration#thememakker#webdevelopmentcompany#hosting#database#serverless computing#api#uiuxdesign#ui#ux#aws#ror#docker#java#kubernetes#hire developers#webservices
0 notes
Text
Serverless computing is not a new concept, but when you combine it with AWS Lambda and API Gateway, it becomes a game-changer. This powerful trio empowers developers to create and deploy applications without the hassle of server management.
Explore the world of serverless, where innovation, scalability, and simplified management take center stage. Also, you can experience the future of software development with serverless and unlock the full potential of your project.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Serverless Showdown: AWS Lambda vs. Azure Functions 🚀💻 Which cloud computing giant takes the crown?
1 note
·
View note
Video
youtube
(via AWS Fargate Serverless Compute Service Tutorial for Amazon Cloud Developers) Full Video Link - https://www.youtube.com/shorts/e1kMx8MOQ8kCheck out the latest technology video on CodeOneDigest's YouTube channel! A new video tutorial on AWS Fargate serverless compute service has just been published. Learn all about AWS Fargate by watching this video. #video #tutorial #aws #fargate #awsfargate #codeonedigest #youtube@java @awscloud @AWSCloudIndia @YouTube #youtube @codeonedigest #codeonedigest #aws #amazonwebservices #aws #awscloud #aws #awstutorial #awscloud #aws #amazonwebservices #cloudcomputing #awscloud #awstutorial #awstraining #awsfargate #awsfargatetutorial #awsfargatedemo #awsecsfargatetutorial #awsecsfargate #awsecsfargatedeployment #awsfargateserverless #awsserverlessfargate #awsfargateservice #serverlessfargate #serverlesscomputing #fargateaws #fargateawstutorial #amazonfargate #amazonfargatetutorial #fargateservice #fargatedockercompose #awscloudcomputing #awsfargateexplained
1 note
·
View note
Text
Understanding Serverless Computing in AWS: A Modern Approach to Scalable Cloud Architecture
In today’s fast-paced digital world, businesses are under constant pressure to deliver reliable, scalable, and cost-effective applications. Traditional server-based models often fall short in terms of agility and efficiency. Enter serverless computing, a revolutionary approach that lets developers build and run applications without worrying about managing infrastructure. At the forefront of this innovation is Amazon Web Services (AWS), which offers a robust serverless ecosystem designed to accelerate development and minimize operational complexity.
What is Serverless Computing in AWS?
Serverless computing in AWS training allows you to execute code without provisioning or managing servers. Instead of handling the heavy lifting—like capacity planning, scaling, patching, and server management—AWS takes care of it all. Developers simply upload their code as individual functions, and AWS automatically handles the rest.
This model is primarily powered by AWS Lambda, the core compute service that enables the execution of event-driven functions. These functions can be triggered by events from a wide range of AWS services, including S3, DynamoDB, API Gateway, and CloudWatch.
Why Serverless is Gaining Popularity
Focus on Code, Not Infrastructure
One of the most appealing aspects of serverless computing is its simplicity. Developers can focus solely on writing the application logic without spending time on backend server management. This results in faster development cycles and reduced time to market.
Built for Events and Automation
Serverless applications in AWS are event-driven. This means they respond automatically to specific triggers—such as file uploads, database changes, API calls, or scheduled tasks. This architecture promotes a highly automated and responsive system design..
Key Benefits of AWS Serverless Computing
Seamless Auto-Scaling
With AWS Lambda, your functions scale automatically based on demand. Whether you have ten users or ten thousand, Lambda ensures that the right number of function instances are running to handle the load. There’s no need for manual intervention or configuration adjustments.
Pay Only for What You Use
Serverless computing follows a pay-per-use billing model. You're only charged for the number of requests your function receives and the time it takes to run. This makes it a highly cost-efficient option, especially for startups and businesses with fluctuating workloads.
Stateless Function Execution
Each serverless function is stateless, which means every invocation is independent. There's no shared state between executions, ensuring higher reliability and making horizontal scaling effortless. For persistent data storage, you can integrate with AWS services like DynamoDB or S3.
Broad Language Support
AWS Lambda supports a variety of programming languages including Python, Node.js, Java, Ruby, C#, and PowerShell. Additionally, AWS allows developers to bring in custom runtimes for even more flexibility in building their functions.
Seamless Integration Across AWS Ecosystem
One of the biggest advantages of going serverless with AWS is the seamless integration across its vast array of services. Whether it’s storing data in Amazon S3, managing authentication with Amazon Cognito, or coordinating workflows with Step Functions, AWS provides all the building blocks needed for modern application development.
Ideal Use Cases for Serverless Architectures
Serverless computing is not just a theoretical concept—it’s being actively used in a wide range of applications:
Web and mobile backends: Handle API calls, user authentication, and data processing without managing servers.
Data processing pipelines: Automate workflows such as log analysis, image processing, and data transformation.
Real-time notifications: Send instant alerts or push notifications based on event triggers.
Scheduled tasks: Run periodic functions for cleanups, data sync, or maintenance.
Challenges to Keep in Mind
While serverless offers numerous advantages, it’s important to be aware of some limitations:
Cold starts: Functions may experience slight delays when invoked after a period of inactivity.
Execution limits: AWS Lambda has limits on execution duration, memory, and package size.
Monitoring complexity: Debugging and monitoring distributed functions may require additional tools like AWS CloudWatch or third-party observability platforms.
The Future of Serverless in Cloud Computing
Serverless computing is evolving rapidly and is now considered a mainstream approach for cloud-native applications. With continued enhancements in tooling, performance, and integration capabilities, serverless is poised to become the backbone of scalable, resilient, and agile application development in the coming years.
Conclusion: Why You Should Consider Serverless with AWS
If you're aiming to build applications that are agile, scalable, and cost-efficient, AWS serverless architecture is a powerful option to explore. By eliminating the overhead of server management, you can redirect your efforts toward innovation and delivering value to your users.
Ready to get started? Whether you're launching a startup or modernizing legacy systems, adopting serverless computing with AWS can simplify your cloud journey and enhance your productivity. Dive in today and experience the future of application development—without the servers.
0 notes
Text
How Python Powers Scalable and Cost-Effective Cloud Solutions

Explore the role of Python in developing scalable and cost-effective cloud solutions. This guide covers Python's advantages in cloud computing, addresses potential challenges, and highlights real-world applications, providing insights into leveraging Python for efficient cloud development.
Introduction
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are increasingly leveraging cloud computing to enhance scalability, optimize costs, and drive innovation. Among the myriad of programming languages available, Python has emerged as a preferred choice for developing robust cloud solutions. Its simplicity, versatility, and extensive library support make it an ideal candidate for cloud-based applications.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into how Python empowers scalable and cost-effective cloud solutions, explore its advantages, address potential challenges, and highlight real-world applications.
Why Python is the Preferred Choice for Cloud Computing?
Python's popularity in cloud computing is driven by several factors, making it the preferred language for developing and managing cloud solutions. Here are some key reasons why Python stands out:
Simplicity and Readability: Python's clean and straightforward syntax allows developers to write and maintain code efficiently, reducing development time and costs.
Extensive Library Support: Python offers a rich set of libraries and frameworks like Django, Flask, and FastAPI for building cloud applications.
Seamless Integration with Cloud Services: Python is well-supported across major cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
Automation and DevOps Friendly: Python supports infrastructure automation with tools like Ansible, Terraform, and Boto3.
Strong Community and Enterprise Adoption: Python has a massive global community that continuously improves and innovates cloud-related solutions.
How Python Enables Scalable Cloud Solutions?
Scalability is a critical factor in cloud computing, and Python provides multiple ways to achieve it:
1. Automation of Cloud Infrastructure
Python's compatibility with cloud service provider SDKs, such as AWS Boto3, Azure SDK for Python, and Google Cloud Client Library, enables developers to automate the provisioning and management of cloud resources efficiently.
2. Containerization and Orchestration
Python integrates seamlessly with Docker and Kubernetes, enabling businesses to deploy scalable containerized applications efficiently.
3. Cloud-Native Development
Frameworks like Flask, Django, and FastAPI support microservices architecture, allowing businesses to develop lightweight, scalable cloud applications.
4. Serverless Computing
Python's support for serverless platforms, including AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions, allows developers to build applications that automatically scale in response to demand, optimizing resource utilization and cost.
5. AI and Big Data Scalability
Python’s dominance in AI and data science makes it an ideal choice for cloud-based AI/ML services like AWS SageMaker, Google AI, and Azure Machine Learning.
Looking for expert Python developers to build scalable cloud solutions? Hire Python Developers now!
Advantages of Using Python for Cloud Computing
Cost Efficiency: Python’s compatibility with serverless computing and auto-scaling strategies minimizes cloud costs.
Faster Development: Python’s simplicity accelerates cloud application development, reducing time-to-market.
Cross-Platform Compatibility: Python runs seamlessly across different cloud platforms.
Security and Reliability: Python-based security tools help in encryption, authentication, and cloud monitoring.
Strong Community Support: Python developers worldwide contribute to continuous improvements, making it future-proof.
Challenges and Considerations
While Python offers many benefits, there are some challenges to consider:
Performance Limitations: Python is an interpreted language, which may not be as fast as compiled languages like Java or C++.
Memory Consumption: Python applications might require optimization to handle large-scale cloud workloads efficiently.
Learning Curve for Beginners: Though Python is simple, mastering cloud-specific frameworks requires time and expertise.
Python Libraries and Tools for Cloud Computing
Python’s ecosystem includes powerful libraries and tools tailored for cloud computing, such as:
Boto3: AWS SDK for Python, used for cloud automation.
Google Cloud Client Library: Helps interact with Google Cloud services.
Azure SDK for Python: Enables seamless integration with Microsoft Azure.
Apache Libcloud: Provides a unified interface for multiple cloud providers.
PyCaret: Simplifies machine learning deployment in cloud environments.
Real-World Applications of Python in Cloud Computing
1. Netflix - Scalable Streaming with Python
Netflix extensively uses Python for automation, data analysis, and managing cloud infrastructure, enabling seamless content delivery to millions of users.
2. Spotify - Cloud-Based Music Streaming
Spotify leverages Python for big data processing, recommendation algorithms, and cloud automation, ensuring high availability and scalability.
3. Reddit - Handling Massive Traffic
Reddit uses Python and AWS cloud solutions to manage heavy traffic while optimizing server costs efficiently.
Future of Python in Cloud Computing
The future of Python in cloud computing looks promising with emerging trends such as:
AI-Driven Cloud Automation: Python-powered AI and machine learning will drive intelligent cloud automation.
Edge Computing: Python will play a crucial role in processing data at the edge for IoT and real-time applications.
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies: Python’s flexibility will enable seamless integration across multiple cloud platforms.
Increased Adoption of Serverless Computing: More enterprises will adopt Python for cost-effective serverless applications.
Conclusion
Python's simplicity, versatility, and robust ecosystem make it a powerful tool for developing scalable and cost-effective cloud solutions. By leveraging Python's capabilities, businesses can enhance their cloud applications' performance, flexibility, and efficiency.
Ready to harness the power of Python for your cloud solutions? Explore our Python Development Services to discover how we can assist you in building scalable and efficient cloud applications.
FAQs
1. Why is Python used in cloud computing?
Python is widely used in cloud computing due to its simplicity, extensive libraries, and seamless integration with cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure.
2. Is Python good for serverless computing?
Yes! Python works efficiently in serverless environments like AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions, making it an ideal choice for cost-effective, auto-scaling applications.
3. Which companies use Python for cloud solutions?
Major companies like Netflix, Spotify, Dropbox, and Reddit use Python for cloud automation, AI, and scalable infrastructure management.
4. How does Python help with cloud security?
Python offers robust security libraries like PyCryptodome and OpenSSL, enabling encryption, authentication, and cloud monitoring for secure cloud applications.
5. Can Python handle big data in the cloud?
Yes! Python supports big data processing with tools like Apache Spark, Pandas, and NumPy, making it suitable for data-driven cloud applications.
#Python development company#Python in Cloud Computing#Hire Python Developers#Python for Multi-Cloud Environments
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How-To IT
Topic: Core areas of IT
1. Hardware
• Computers (Desktops, Laptops, Workstations)
• Servers and Data Centers
• Networking Devices (Routers, Switches, Modems)
• Storage Devices (HDDs, SSDs, NAS)
• Peripheral Devices (Printers, Scanners, Monitors)
2. Software
• Operating Systems (Windows, Linux, macOS)
• Application Software (Office Suites, ERP, CRM)
• Development Software (IDEs, Code Libraries, APIs)
• Middleware (Integration Tools)
• Security Software (Antivirus, Firewalls, SIEM)
3. Networking and Telecommunications
• LAN/WAN Infrastructure
• Wireless Networking (Wi-Fi, 5G)
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks)
• Communication Systems (VoIP, Email Servers)
• Internet Services
4. Data Management
• Databases (SQL, NoSQL)
• Data Warehousing
• Big Data Technologies (Hadoop, Spark)
• Backup and Recovery Systems
• Data Integration Tools
5. Cybersecurity
• Network Security
• Endpoint Protection
• Identity and Access Management (IAM)
• Threat Detection and Incident Response
• Encryption and Data Privacy
6. Software Development
• Front-End Development (UI/UX Design)
• Back-End Development
• DevOps and CI/CD Pipelines
• Mobile App Development
• Cloud-Native Development
7. Cloud Computing
• Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
• Platform as a Service (PaaS)
• Software as a Service (SaaS)
• Serverless Computing
• Cloud Storage and Management
8. IT Support and Services
• Help Desk Support
• IT Service Management (ITSM)
• System Administration
• Hardware and Software Troubleshooting
• End-User Training
9. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
• AI Algorithms and Frameworks
• Natural Language Processing (NLP)
• Computer Vision
• Robotics
• Predictive Analytics
10. Business Intelligence and Analytics
• Reporting Tools (Tableau, Power BI)
• Data Visualization
• Business Analytics Platforms
• Predictive Modeling
11. Internet of Things (IoT)
• IoT Devices and Sensors
• IoT Platforms
• Edge Computing
• Smart Systems (Homes, Cities, Vehicles)
12. Enterprise Systems
• Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
• Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
• Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS)
• Supply Chain Management Systems
13. IT Governance and Compliance
• ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
• COBIT (Control Objectives for Information Technologies)
• ISO/IEC Standards
• Regulatory Compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, SOX)
14. Emerging Technologies
• Blockchain
• Quantum Computing
• Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
• 3D Printing
• Digital Twins
15. IT Project Management
• Agile, Scrum, and Kanban
• Waterfall Methodology
• Resource Allocation
• Risk Management
16. IT Infrastructure
• Data Centers
• Virtualization (VMware, Hyper-V)
• Disaster Recovery Planning
• Load Balancing
17. IT Education and Certifications
• Vendor Certifications (Microsoft, Cisco, AWS)
• Training and Development Programs
• Online Learning Platforms
18. IT Operations and Monitoring
• Performance Monitoring (APM, Network Monitoring)
• IT Asset Management
• Event and Incident Management
19. Software Testing
• Manual Testing: Human testers evaluate software by executing test cases without using automation tools.
• Automated Testing: Use of testing tools (e.g., Selenium, JUnit) to run automated scripts and check software behavior.
• Functional Testing: Validating that the software performs its intended functions.
• Non-Functional Testing: Assessing non-functional aspects such as performance, usability, and security.
• Unit Testing: Testing individual components or units of code for correctness.
• Integration Testing: Ensuring that different modules or systems work together as expected.
• System Testing: Verifying the complete software system’s behavior against requirements.
• Acceptance Testing: Conducting tests to confirm that the software meets business requirements (including UAT - User Acceptance Testing).
• Regression Testing: Ensuring that new changes or features do not negatively affect existing functionalities.
• Performance Testing: Testing software performance under various conditions (load, stress, scalability).
• Security Testing: Identifying vulnerabilities and assessing the software’s ability to protect data.
• Compatibility Testing: Ensuring the software works on different operating systems, browsers, or devices.
• Continuous Testing: Integrating testing into the development lifecycle to provide quick feedback and minimize bugs.
• Test Automation Frameworks: Tools and structures used to automate testing processes (e.g., TestNG, Appium).
19. VoIP (Voice over IP)
VoIP Protocols & Standards
• SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)
• H.323
• RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol)
• MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol)
VoIP Hardware
• IP Phones (Desk Phones, Mobile Clients)
• VoIP Gateways
• Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs)
• VoIP Servers
• Network Switches/ Routers for VoIP
VoIP Software
• Softphones (e.g., Zoiper, X-Lite)
• PBX (Private Branch Exchange) Systems
• VoIP Management Software
• Call Center Solutions (e.g., Asterisk, 3CX)
VoIP Network Infrastructure
• Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) for VoIP
• VoIP Traffic Shaping & Bandwidth Management
• Firewall and Security Configurations for VoIP
• Network Monitoring & Optimization Tools
VoIP Security
• Encryption (SRTP, TLS)
• Authentication and Authorization
• Firewall & Intrusion Detection Systems
• VoIP Fraud DetectionVoIP Providers
• Hosted VoIP Services (e.g., RingCentral, Vonage)
• SIP Trunking Providers
• PBX Hosting & Managed Services
VoIP Quality and Testing
• Call Quality Monitoring
• Latency, Jitter, and Packet Loss Testing
• VoIP Performance Metrics and Reporting Tools
• User Acceptance Testing (UAT) for VoIP Systems
Integration with Other Systems
• CRM Integration (e.g., Salesforce with VoIP)
• Unified Communications (UC) Solutions
• Contact Center Integration
• Email, Chat, and Video Communication Integration
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
#Serverless Application#Serverless Services#serverless technology#serverless architecture#serverless Computing#cloud service platform#AWS Services
0 notes
Text
The Future of Web Development: Trends, Techniques, and Tools
Web development is a dynamic field that is continually evolving to meet the demands of an increasingly digital world. With businesses relying more on online presence and user experience becoming a priority, web developers must stay abreast of the latest trends, technologies, and best practices. In this blog, we’ll delve into the current landscape of web development, explore emerging trends and tools, and discuss best practices to ensure successful web projects.
Understanding Web Development
Web development involves the creation and maintenance of websites and web applications. It encompasses a variety of tasks, including front-end development (what users see and interact with) and back-end development (the server-side that powers the application). A successful web project requires a blend of design, programming, and usability skills, with a focus on delivering a seamless user experience.
Key Trends in Web Development
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): PWAs are web applications that provide a native app-like experience within the browser. They offer benefits like offline access, push notifications, and fast loading times. By leveraging modern web capabilities, PWAs enhance user engagement and can lead to higher conversion rates.
Single Page Applications (SPAs): SPAs load a single HTML page and dynamically update content as users interact with the app. This approach reduces page load times and provides a smoother experience. Frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js have made developing SPAs easier, allowing developers to create responsive and efficient applications.
Responsive Web Design: With the increasing use of mobile devices, responsive design has become essential. Websites must adapt to various screen sizes and orientations to ensure a consistent user experience. CSS frameworks like Bootstrap and Foundation help developers create fluid, responsive layouts quickly.
Voice Search Optimization: As voice-activated devices like Amazon Alexa and Google Home gain popularity, optimizing websites for voice search is crucial. This involves focusing on natural language processing and long-tail keywords, as users tend to speak in full sentences rather than typing short phrases.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI is transforming web development by enabling personalized user experiences and smarter applications. Chatbots, for instance, can provide instant customer support, while AI-driven analytics tools help developers understand user behavior and optimize websites accordingly.
Emerging Technologies in Web Development
JAMstack Architecture: JAMstack (JavaScript, APIs, Markup) is a modern web development architecture that decouples the front end from the back end. This approach enhances performance, security, and scalability by serving static content and fetching dynamic content through APIs.
WebAssembly (Wasm): WebAssembly allows developers to run high-performance code on the web. It opens the door for languages like C, C++, and Rust to be used for web applications, enabling complex computations and graphics rendering that were previously difficult to achieve in a browser.
Serverless Computing: Serverless architecture allows developers to build and run applications without managing server infrastructure. Platforms like AWS Lambda and Azure Functions enable developers to focus on writing code while the cloud provider handles scaling and maintenance, resulting in more efficient workflows.
Static Site Generators (SSGs): SSGs like Gatsby and Next.js allow developers to build fast and secure static websites. By pre-rendering pages at build time, SSGs improve performance and enhance SEO, making them ideal for blogs, portfolios, and documentation sites.
API-First Development: This approach prioritizes building APIs before developing the front end. API-first development ensures that various components of an application can communicate effectively and allows for easier integration with third-party services.
Best Practices for Successful Web Development
Focus on User Experience (UX): Prioritizing user experience is essential for any web project. Conduct user research to understand your audience's needs, create wireframes, and test prototypes to ensure your design is intuitive and engaging.
Emphasize Accessibility: Making your website accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, is a fundamental aspect of web development. Adhere to the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) by using semantic HTML, providing alt text for images, and ensuring keyboard navigation is possible.
Optimize Performance: Website performance significantly impacts user satisfaction and SEO. Optimize images, minify CSS and JavaScript, and leverage browser caching to ensure fast loading times. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights can help identify areas for improvement.
Implement Security Best Practices: Security is paramount in web development. Use HTTPS to encrypt data, implement secure authentication methods, and validate user input to protect against vulnerabilities. Regularly update dependencies to guard against known exploits.
Stay Current with Technology: The web development landscape is constantly changing. Stay informed about the latest trends, tools, and technologies by participating in online courses, attending webinars, and engaging with the developer community. Continuous learning is crucial to maintaining relevance in this field.
Essential Tools for Web Development
Version Control Systems: Git is an essential tool for managing code changes and collaboration among developers. Platforms like GitHub and GitLab facilitate version control and provide features for issue tracking and code reviews.
Development Frameworks: Frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js streamline the development process by providing pre-built components and structures. For back-end development, frameworks like Express.js and Django can speed up the creation of server-side applications.
Content Management Systems (CMS): CMS platforms like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal enable developers to create and manage websites easily. They offer flexibility and scalability, making it simple to update content without requiring extensive coding knowledge.
Design Tools: Tools like Figma, Sketch, and Adobe XD help designers create user interfaces and prototypes. These tools facilitate collaboration between designers and developers, ensuring that the final product aligns with the initial vision.
Analytics and Monitoring Tools: Google Analytics, Hotjar, and other analytics tools provide insights into user behavior, allowing developers to assess the effectiveness of their websites. Monitoring tools can alert developers to issues such as downtime or performance degradation.
Conclusion
Web development is a rapidly evolving field that requires a blend of creativity, technical skills, and a user-centric approach. By understanding the latest trends and technologies, adhering to best practices, and leveraging essential tools, developers can create engaging and effective web experiences. As we look to the future, those who embrace innovation and prioritize user experience will be best positioned for success in the competitive world of web development. Whether you are a seasoned developer or just starting, staying informed and adaptable is key to thriving in this dynamic landscape.
more about details :- https://fabvancesolutions.com/
#fabvancesolutions#digitalagency#digitalmarketingservices#graphic design#startup#ecommerce#branding#marketing#digitalstrategy#googleimagesmarketing
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How can you optimize the performance of machine learning models in the cloud?
Optimizing machine learning models in the cloud involves several strategies to enhance performance and efficiency. Here’s a detailed approach:

Choose the Right Cloud Services:
Managed ML Services:
Use managed services like AWS SageMaker, Google AI Platform, or Azure Machine Learning, which offer built-in tools for training, tuning, and deploying models.
Auto-scaling:
Enable auto-scaling features to adjust resources based on demand, which helps manage costs and performance.
Optimize Data Handling:
Data Storage:
Use scalable cloud storage solutions like Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, or Azure Blob Storage for storing large datasets efficiently.
Data Pipeline:
Implement efficient data pipelines with tools like Apache Kafka or AWS Glue to manage and process large volumes of data.
Select Appropriate Computational Resources:
Instance Types:
Choose the right instance types based on your model’s requirements. For example, use GPU or TPU instances for deep learning tasks to accelerate training.
Spot Instances:
Utilize spot instances or preemptible VMs to reduce costs for non-time-sensitive tasks.
Optimize Model Training:
Hyperparameter Tuning:
Use cloud-based hyperparameter tuning services to automate the search for optimal model parameters. Services like Google Cloud AI Platform’s HyperTune or AWS SageMaker’s Automatic Model Tuning can help.
Distributed Training:
Distribute model training across multiple instances or nodes to speed up the process. Frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch support distributed training and can take advantage of cloud resources.
Monitoring and Logging:
Monitoring Tools:
Implement monitoring tools to track performance metrics and resource usage. AWS CloudWatch, Google Cloud Monitoring, and Azure Monitor offer real-time insights.
Logging:
Maintain detailed logs for debugging and performance analysis, using tools like AWS CloudTrail or Google Cloud Logging.
Model Deployment:
Serverless Deployment:
Use serverless options to simplify scaling and reduce infrastructure management. Services like AWS Lambda or Google Cloud Functions can handle inference tasks without managing servers.
Model Optimization:
Optimize models by compressing them or using model distillation techniques to reduce inference time and improve latency.
Cost Management:
Cost Analysis:
Regularly analyze and optimize cloud costs to avoid overspending. Tools like AWS Cost Explorer, Google Cloud’s Cost Management, and Azure Cost Management can help monitor and manage expenses.
By carefully selecting cloud services, optimizing data handling and training processes, and monitoring performance, you can efficiently manage and improve machine learning models in the cloud.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring the Power of Amazon Web Services: Top AWS Services You Need to Know
In the ever-evolving realm of cloud computing, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has established itself as an undeniable force to be reckoned with. AWS's vast and diverse array of services has positioned it as a dominant player, catering to the evolving needs of businesses, startups, and individuals worldwide. Its popularity transcends boundaries, making it the preferred choice for a myriad of use cases, from startups launching their first web applications to established enterprises managing complex networks of services. This blog embarks on an exploratory journey into the boundless world of AWS, delving deep into some of its most sought-after and pivotal services.

As the digital landscape continues to expand, understanding these AWS services and their significance is pivotal, whether you're a seasoned cloud expert or someone taking the first steps in your cloud computing journey. Join us as we delve into the intricate web of AWS's top services and discover how they can shape the future of your cloud computing endeavors. From cloud novices to seasoned professionals, the AWS ecosystem holds the keys to innovation and transformation.
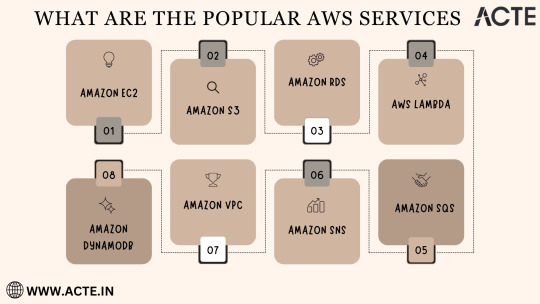
Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud): The Foundation of Scalability At the core of AWS's capabilities is Amazon EC2, the Elastic Compute Cloud. EC2 provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud, allowing you to run virtual servers, commonly referred to as instances. These instances serve as the foundation for a multitude of AWS solutions, offering the scalability and flexibility required to meet diverse application and workload demands. Whether you're a startup launching your first web application or an enterprise managing a complex network of services, EC2 ensures that you have the computational resources you need, precisely when you need them.
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service): Secure, Scalable, and Cost-Effective Data Storage When it comes to storing and retrieving data, Amazon S3, the Simple Storage Service, stands as an indispensable tool in the AWS arsenal. S3 offers a scalable and highly durable object storage service that is designed for data security and cost-effectiveness. This service is the choice of businesses and individuals for storing a wide range of data, including media files, backups, and data archives. Its flexibility and reliability make it a prime choice for safeguarding your digital assets and ensuring they are readily accessible.
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service): Streamlined Database Management Database management can be a complex task, but AWS simplifies it with Amazon RDS, the Relational Database Service. RDS automates many common database management tasks, including patching, backups, and scaling. It supports multiple database engines, including popular options like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server. This service allows you to focus on your application while AWS handles the underlying database infrastructure. Whether you're building a content management system, an e-commerce platform, or a mobile app, RDS streamlines your database operations.
AWS Lambda: The Era of Serverless Computing Serverless computing has transformed the way applications are built and deployed, and AWS Lambda is at the forefront of this revolution. Lambda is a serverless compute service that enables you to run code without the need for server provisioning or management. It's the perfect solution for building serverless applications, microservices, and automating tasks. The unique pricing model ensures that you pay only for the compute time your code actually uses. This service empowers developers to focus on coding, knowing that AWS will handle the operational complexities behind the scenes.
Amazon DynamoDB: Low Latency, High Scalability NoSQL Database Amazon DynamoDB is a managed NoSQL database service that stands out for its low latency and exceptional scalability. It's a popular choice for applications with variable workloads, such as gaming platforms, IoT solutions, and real-time data processing systems. DynamoDB automatically scales to meet the demands of your applications, ensuring consistent, single-digit millisecond latency at any scale. Whether you're managing user profiles, session data, or real-time analytics, DynamoDB is designed to meet your performance needs.
Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud): Tailored Networking for Security and Control Security and control over your cloud resources are paramount, and Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) empowers you to create isolated networks within the AWS cloud. This isolation enhances security and control, allowing you to define your network topology, configure routing, and manage access. VPC is the go-to solution for businesses and individuals who require a network environment that mirrors the security and control of traditional on-premises data centers.
Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service): Seamless Communication Across Channels Effective communication is a cornerstone of modern applications, and Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service) is designed to facilitate seamless communication across various channels. This fully managed messaging service enables you to send notifications to a distributed set of recipients, whether through email, SMS, or mobile devices. SNS is an essential component of applications that require real-time updates and notifications to keep users informed and engaged.
Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service): Decoupling for Scalable Applications Decoupling components of a cloud application is crucial for scalability, and Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service) is a fully managed message queuing service designed for this purpose. It ensures reliable and scalable communication between different parts of your application, helping you create systems that can handle varying workloads efficiently. SQS is a valuable tool for building robust, distributed applications that can adapt to changes in demand.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cloud computing, Amazon Web Services (AWS) stands as a colossus, offering a diverse array of services that address the ever-evolving needs of businesses, startups, and individuals alike. AWS's popularity transcends industry boundaries, making it the go-to choice for a wide range of use cases, from startups launching their inaugural web applications to established enterprises managing intricate networks of services.
To unlock the full potential of these AWS services, gaining comprehensive knowledge and hands-on experience is key. ACTE Technologies, a renowned training provider, offers specialized AWS training programs designed to provide practical skills and in-depth understanding. These programs equip you with the tools needed to navigate and excel in the dynamic world of cloud computing.
With AWS services at your disposal, the possibilities are endless, and innovation knows no bounds. Join the ever-growing community of cloud professionals and enthusiasts, and empower yourself to shape the future of the digital landscape. ACTE Technologies is your trusted guide on this journey, providing the knowledge and support needed to thrive in the world of AWS and cloud computing.
8 notes
·
View notes