#Data Filtering
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Nexus: The Dawn of IoT Consciousness – The Revolution Illuminating Big Data Chaos
#Advantech IoT#Aware World#Big Data#Big Data Chaos#Bosch IoT#Cisco IoT#Connected World#Contextual Awareness#Contextual Understanding#Continuous Improvement#Data Filtering#Distributed Intelligence#Edge AI#edge computing#Edge Data#Edge Intelligence#Edge Processing#HPE Edge#Intelligent Systems#Internet of Things#IoT#IoT Awareness#IoT Consciousness#IoT Ecosystem#IoT Hardware#IoT Networking#IoT Platform#Lean Efficiency#Nexus#Operational Optimization
0 notes
Text
How to Use Telemetry Pipelines to Maintain Application Performance.
Sanjay Kumar Mohindroo Sanjay Kumar Mohindroo. skm.stayingalive.in Optimize application performance with telemetry pipelines—enhance observability, reduce costs, and ensure security with efficient data processing. 🚀 Discover how telemetry pipelines optimize application performance by streamlining observability, enhancing security, and reducing costs. Learn key strategies and best…
#AI-powered Observability#Anonymization#Application Performance#Cloud Computing#Cost Optimization#Cybersecurity#Data Aggregation#Data Filtering#Data Normalization#Data Processing#Data Retention Policies#Debugging Techniques#DevOps#digital transformation#Edge Telemetry Processing#Encryption#GDPR#HIPAA#Incident Management#IT Governance#Latency Optimization#Logging#Machine Learning in Observability#Metrics#Monitoring#News#Observability#Real-Time Alerts#Regulatory Compliance#Sanjay Kumar Mohindroo
0 notes
Text
So, um.
I may be starting to get a weeeee bit annoyed with people on the r/Hermitcraft subreddit.
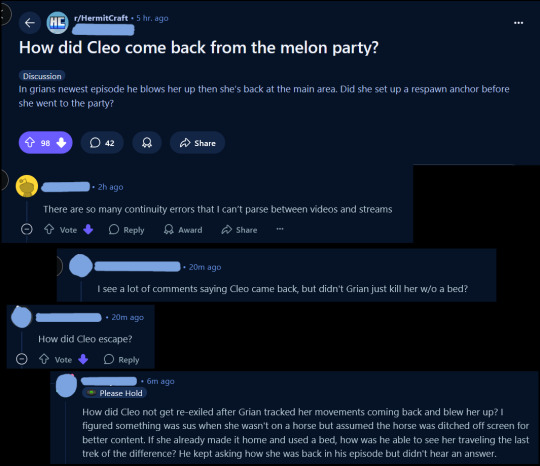
Like, when I made the meme that is still getting an insane amount of notes (holy crap thank you so much I am super flattered), it was understandable that people didn't know what it was in reference to. I went, "ah, probably should have linked Cleo's vid!" and lived and learned, you know?
But Cleo's video has been out for a week. It's only twenty minutes long, and the moment when they and Grian meet up is five minutes into the video.
And like. Grian seems to really want people to see his friends' videos? Like when Gem's snail arrived, he deliberately left that plot thread dangling to be answered in Gem's video. The guy has made an eight hour video showing off the other Hermits' bases. I also highly suspect that one reason Grian is one of the last people to upload collab videos he's in is because his higher subscriber count means his video will automatically racket up to the top of the recommended page, and he wants his friends' videos to get a head start on him.
So the fact that there's this significant amount of Grian fans who won't even watch five minutes of someone else's video to get an answer that Grian left hanging is ... it's just super disappointing, ngl.
And just. Don't even get me started on that "continuity error" comment. I actually had a pretty long response to that on reddit. TL;DR: it's not a continuity error because there's perfect continuity as long as you watch Cleo's video.
Grian does not have to fill in the gaps, that's not his responsibility, nor should it be. The point of a series like Hermitcraft is that you get multiple perspectives. If you're upset that one perspective doesn't show everything, then you shouldn't be watching SMPs.
#hermitcraft#hermitcraft fandom#data rants#hermitcraft fandom discourse#hermitcraft fandom salt#uh what other tags should I put so people can filter this#hermitcraft fandom critical#hermitcraft fandom negative#hermitcraft spoilers
2K notes
·
View notes
Text


snow miku 2024 🧡🥄❄
art print on my etsy for the holidays!
#vocaloid#hatsune miku#snow miku#snow miku 2024#miku#anime#art#illustration#vocaloid fanart#highlight reel#yukine#art prints#this took so long you would not believe it ive been chipping away at it for over a week but my brothers bf flew in so i had my hands full#on top of how long it took to make at all#faaaalls over. at least it's done. i am done with it its finished YIPPIEEE#i needed to make something big and impressive to feel something#and also this is the cutest miku in the World ok. peak miku. does not get cuter than this one#im upset that i had to Crunch It. the textures were so beautiful. kraft paper and noise and a slight chromatic abberation for nostalgia#... and then i had to jpg deepfry it and put that obnoxious anti-data training filter over it. god.#kill people who use and train AI it is always morally correct
248 notes
·
View notes
Text













#house md#gregory house#james wilson#hilson#long post#longpost#screencap#s05e17 “The Social Contract”#amazing interaction#wilson thinks that when he doesnt filter himself its a “reality” things he saying#very close to the position of “im not an asshole im just being real”#which makes sense only if you dont have much experience#and it seems wilson only does it with house#a georg of any data pool#and yeah babe this is still social contract you not escaping it by just labeling it differently#hes even arriving at that point at the end there#and house was already “there” earlier in the episode hes just doing it back to wilson now#im unwell and house would not cure me
626 notes
·
View notes
Text
look computational psychiatry is a concept with a certain amount of cursed energy trailing behind it, but I'm really getting my ass chapped about a fundamental flaw in large scale data analysis that I've been complaining about for years. Here's what's bugging me:
When you're trying to understand a system as complex as behavioral tendencies, you cannot substitute large amounts of "low quality" data (data correlating more weakly with a trait of interest, say, or data that only measures one of several potential interacting factors that combine to create outcomes) for "high quality" data that inquiries more deeply about the system.
The reason for that is this: when we're trying to analyze data as scientists, we leave things we're not directly interrogating as randomized as possible on the assumption that either there is no main effect of those things on our data, or that balancing and randomizing those things will drown out whatever those effects are.
But the problem is this: sometimes there are not only strong effects in the data you haven't considered, but also they correlate: either with one of the main effects you do know about, or simply with one another.
This means that there is structure in your data. And you can't see it, which means that you can't account for it. Which means whatever your findings are, they won't generalize the moment you switch to a new population structured differently. Worse, you are incredibly vulnerable to sampling bias because the moment your sample fails to reflect the structure of the population you're up shit creek without a paddle. Twin studies are notoriously prone to this because white and middle to upper class twins are vastly more likely to be identified and recruited for them, because those are the people who respond to study queries and are easy to get hold of. GWAS data, also extremely prone to this issue. Anything you train machine learning datasets like ChatGPT on, where you're compiling unbelievably big datasets to try to "train out" the noise.
These approaches presuppose that sampling depth is enough to "drown out" any other conflicting main effects or interactions. What it actually typically does is obscure the impact of meaningful causative agents (hidden behind conflicting correlation factors you can't control for) and overstate the value of whatever significant main effects do manage to survive and fall out, even if they explain a pitiably small proportion of the variation in the population.
It's a natural response to the wondrous power afforded by modern advances in computing, but it's not a great way to understand a complex natural world.
#sciblr#big data#complaints#this is a small meeting with a lot of clinical focus which is making me even more irritated natch#see also similar complaints when samples are systematically filtered
125 notes
·
View notes
Text
MIT scientists pin down the origins of a fast radio burst
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/mit-scientists-pin-down-the-origins-of-a-fast-radio-burst/
MIT scientists pin down the origins of a fast radio burst


Fast radio bursts are brief and brilliant explosions of radio waves emitted by extremely compact objects such as neutron stars and possibly black holes. These fleeting fireworks last for just a thousandth of a second and can carry an enormous amount of energy — enough to briefly outshine entire galaxies.
Since the first fast radio burst (FRB) was discovered in 2007, astronomers have detected thousands of FRBs, whose locations range from within our own galaxy to as far as 8 billion light-years away. Exactly how these cosmic radio flares are launched is a highly contested unknown.
Now, astronomers at MIT have pinned down the origins of at least one fast radio burst using a novel technique that could do the same for other FRBs. In their new study, appearing today in the journal Nature, the team focused on FRB 20221022A — a previously discovered fast radio burst that was detected from a galaxy about 200 million light-years away.
The team zeroed in further to determine the precise location of the radio signal by analyzing its “scintillation,” similar to how stars twinkle in the night sky. The scientists studied changes in the FRB’s brightness and determined that the burst must have originated from the immediate vicinity of its source, rather than much further out, as some models have predicted.
The team estimates that FRB 20221022A exploded from a region that is extremely close to a rotating neutron star, 10,000 kilometers away at most. That’s less than the distance between New York and Singapore. At such close range, the burst likely emerged from the neutron star’s magnetosphere — a highly magnetic region immediately surrounding the ultracompact star.
The team’s findings provide the first conclusive evidence that a fast radio burst can originate from the magnetosphere, the highly magnetic environment immediately surrounding an extremely compact object.
“In these environments of neutron stars, the magnetic fields are really at the limits of what the universe can produce,” says lead author Kenzie Nimmo, a postdoc in MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research. “There’s been a lot of debate about whether this bright radio emission could even escape from that extreme plasma.”
“Around these highly magnetic neutron stars, also known as magnetars, atoms can’t exist — they would just get torn apart by the magnetic fields,” says Kiyoshi Masui, associate professor of physics at MIT. “The exciting thing here is, we find that the energy stored in those magnetic fields, close to the source, is twisting and reconfiguring such that it can be released as radio waves that we can see halfway across the universe.”
The study’s MIT co-authors include Adam Lanman, Shion Andrew, Daniele Michilli, and Kaitlyn Shin, along with collaborators from multiple institutions.
Burst size
Detections of fast radio bursts have ramped up in recent years, due to the Canadian Hydrogen Intensity Mapping Experiment (CHIME). The radio telescope array comprises four large, stationary receivers, each shaped like a half-pipe, that are tuned to detect radio emissions within a range that is highly sensitive to fast radio bursts.
Since 2020, CHIME has detected thousands of FRBs from all over the universe. While scientists generally agree that the bursts arise from extremely compact objects, the exact physics driving the FRBs is unclear. Some models predict that fast radio bursts should come from the turbulent magnetosphere immediately surrounding a compact object, while others predict that the bursts should originate much further out, as part of a shockwave that propagates away from the central object.
To distinguish between the two scenarios, and determine where fast radio bursts arise, the team considered scintillation — the effect that occurs when light from a small bright source such as a star, filters through some medium, such as a galaxy’s gas. As the starlight filters through the gas, it bends in ways that make it appear, to a distant observer, as if the star is twinkling. The smaller or the farther away an object is, the more it twinkles. The light from larger or closer objects, such as planets in our own solar system, experience less bending, and therefore do not appear to twinkle.
The team reasoned that if they could estimate the degree to which an FRB scintillates, they might determine the relative size of the region from where the FRB originated. The smaller the region, the closer in the burst would be to its source, and the more likely it is to have come from a magnetically turbulent environment. The larger the region, the farther the burst would be, giving support to the idea that FRBs stem from far-out shockwaves.
Twinkle pattern
To test their idea, the researchers looked to FRB 20221022A, a fast radio burst that was detected by CHIME in 2022. The signal lasts about two milliseconds, and is a relatively run-of-the-mill FRB, in terms of its brightness. However, the team’s collaborators at McGill University found that FRB 20221022A exhibited one standout property: The light from the burst was highly polarized, with the angle of polarization tracing a smooth S-shaped curve. This pattern is interpreted as evidence that the FRB emission site is rotating — a characteristic previously observed in pulsars, which are highly magnetized, rotating neutron stars.
To see a similar polarization in fast radio bursts was a first, suggesting that the signal may have arisen from the close-in vicinity of a neutron star. The McGill team’s results are reported in a companion paper today in Nature.
The MIT team realized that if FRB 20221022A originated from close to a neutron star, they should be able to prove this, using scintillation.
In their new study, Nimmo and her colleagues analyzed data from CHIME and observed steep variations in brightness that signaled scintillation — in other words, the FRB was twinkling. They confirmed that there is gas somewhere between the telescope and FRB that is bending and filtering the radio waves. The team then determined where this gas could be located, confirming that gas within the FRB’s host galaxy was responsible for some of the scintillation observed. This gas acted as a natural lens, allowing the researchers to zoom in on the FRB site and determine that the burst originated from an extremely small region, estimated to be about 10,000 kilometers wide.
“This means that the FRB is probably within hundreds of thousands of kilometers from the source,” Nimmo says. “That’s very close. For comparison, we would expect the signal would be more than tens of millions of kilometers away if it originated from a shockwave, and we would see no scintillation at all.”
“Zooming in to a 10,000-kilometer region, from a distance of 200 million light years, is like being able to measure the width of a DNA helix, which is about 2 nanometers wide, on the surface of the moon,” Masui says. “There’s an amazing range of scales involved.”
The team’s results, combined with the findings from the McGill team, rule out the possibility that FRB 20221022A emerged from the outskirts of a compact object. Instead, the studies prove for the first time that fast radio bursts can originate from very close to a neutron star, in highly chaotic magnetic environments.
“These bursts are always happening, and CHIME detects several a day,” Masui says. “There may be a lot of diversity in how and where they occur, and this scintillation technique will be really useful in helping to disentangle the various physics that drive these bursts.”
This research was supported by various institutions including the Canada Foundation for Innovation, the Dunlap Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Toronto, the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research, the Trottier Space Institute at McGill University, and the University of British Columbia.
#000#2022#amazing#Astronomy#Astronomy and astrophysics#Astrophysics#atoms#author#billion#Black holes#Canada#comparison#data#diversity#DNA#driving#Emissions#energy#Environment#explosions#fast radio bursts#Filters#Foundation#galaxies#Galaxy#gas#Giving#how#hydrogen#Innovation
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
me clicking “not interested” on a post about a canon x canon ship involving my f/o knowing full well it doesn’t do anything

#tumblr is SLIGHTLY better for this bc of the filter but. sometimes people don’t tag their posts correctly which doesn’t help#sigh#self ship#self ship community#self shipping#selfship#f/o community#selfshipping#f/o#self insert#romantic f/o#fictional other#selfshipper#selfship problems#selfship meme#selfshipping meme#selfshipping community#but fr#i thought the algorithms were supposed to be smart smh#if you’re gonna take my data AT LEAST you should know what i don’t want to see!!#but nooooo it automatically goes- oh! you like this character!! well here’s art of them being in love with this other character!!#ugh
91 notes
·
View notes
Text
Realized this week that I use youtube like I use tumblr and that is specifically creating my own experience and specifying exactly what videos I want to see versus having an algorithm tell me (outside of the little pane of recommended or similar videos next to a video you're currently watching) and that realization has made me very happy.
#i've had both my search and watch history turned off for years#and it was never a problem#then youtube decided “hey if you're not giving us your data then we're not showing you any videos of any kind on the home page”#so I got limited down to who was already subscribed to and whatever came up in the recs pane next to a vid#but I think in a way (with the addition of an ad blocker and a youtube search algorithm bs filter)#I've ended up really only seeing what I want to see and not a bunch of random stuff?#idk#the connection is there but words are not wording#sunny's shenanigans
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hi, are there any blogs here that thirst-post about Data and/or any of the Soong androids here that also DON’T ship datalore? Please I need more android content! 💛
#Star Trek#Star Trek TNG#data soong#lore soong#data star trek#lore star trek#not trying to get ppl mad w/ the datalore thing#it’s just really not my thing but I can’t filter the tag#since it’s the name of an episode
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
why is a post about high eating disorder rates in trans men tagged as transandrophobia. do you think trans women are immune from diet culture and systematic fatphobia. why.
#the post itself is fine. it's all reposted content from tiktok on data that compares trans men to cis women#but my filters picked up on op's tags and :/ how stupid do you have to be#if the data in question included trans women I promise you it would be clear that this is not a problem specific to trans men
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tried to sleep in. Had a convincing dream that coworker died in a road accident. Woke up in dream. Checked news in dream. Real. Woke up in real life. Checked news in real life. Not real.
#clairvoyance disproved. [wakes up in sweat] do I still have to send him the filter data sheet of money#*on Monday. Christ alive#kelsey rambles
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
There's a positivity blog that I follow that does this, so I think I want to start doing this too as a way to assure myself that I'm doing fine
Accomplishments of the day:
Folded half of the laundry that I fell behind on
Put things on hangers and back into the closet where they belong
Showered
Keeping up with my meals and snacks (so far)
Keeping up with hydration
Got my grocery shopping done and put away
Took out the recycling
Brushed my hair and teeth
Took my meds on time
Taking a moment to step back and let myself decompress (would say took, but this is something I'm in the middle of doing rn triggers go brrr rhjajs /lh)
#data log: personal#data log: accomplishments of the day#<- that'll be the tag for that if anyone wants to filter it#anyway apologies in advance to legit everyone my phone is currently muted except for calls#so if I'm slow to reply anywhere that's why /lh
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pro tip: when posting your art add a overlay layer on top of the finished piece and add a picture of the most disturbed, ugly, and non-sense ai pic you can find so you can force the machine to inbreed
#gotta do it w my next pieces#you can also use AI disturbance filters or noise filters#also use it on photos of loved ones you fear migth get used for data if you post#anti ai#ai is not art#boycott ai
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pattern sorting website should be up after work tonight! Everything seems to be working okay, just gotta clean up the dataset a little more and get everything public
#chit chat#there's a lot of misplaced knitting patterns in the data set#so I'm trying to filter those out beforehand
15 notes
·
View notes


