#Data Infrastructure
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Mastering Power BI Data Migration with Dataflows
Data migration is a vital step for organizations looking to modernize their data infrastructure, and Power BI dataflows provide an efficient way to handle this transition. With features like centralized data preparation, reusability, and seamless integration with Azure Data Lake Storage, dataflows streamline the ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) process for businesses.
Why Choose Power BI Dataflows for Data Migration?
🔹 Reusability – Apply transformations across multiple Power BI reports, ensuring consistency. 🔹 Simplified ETL Process – Use Power Query Editor to transform and clean data effortlessly. 🔹 Azure Data Lake Integration – Secure and scalable storage for large datasets. 🔹 Improved Data Consistency – Centralized data management eliminates inconsistencies across reports.
Step-by-Step Guide to Dataflow Migration
📌 Migrating Queries from Power BI Desktop: ✅ Copy M code from Power Query Editor and paste it into a new dataflow in the Power BI service. ✅ Save and refresh the dataflow to activate the new data pipeline.
📌 Upgrading from Dataflow Gen1 to Gen2: ✅ Assess existing dataflows and review Microsoft’s migration guidelines. ✅ Update connections and ensure reports are linked to Dataflow Gen2 for better performance and scalability.
0 notes
Text
Anand Jayapalan on Why Software-Defined Storage is the Key to Future-Proofing Your Data Infrastructure
Anand Jayapalan: Exploring Software-Defined Storage as the Future of Scalable and Flexible Data Solutions
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, the need for scalable and flexible data solutions has reached an all-time high. As businesses generate vast amounts of data, traditional storage methods are increasingly being pushed beyond their limits. This is where Software-Defined Storage (SDS) emerges as a game-changer. For data storage solutions experts like Anand Jayapalan, SDS represents a transformative approach that decouples storage hardware from the software that manages it. This separation offers unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and efficiency—crucial for meeting the demands of modern, data-driven enterprises.

In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, the demand for scalable and flexible data solutions has never been higher. As businesses continue to generate massive amounts of data, traditional storage methods are increasingly being stretched to their limits. This is where Software-Defined Storage (SDS) steps in as a game-changer. By decoupling storage hardware from the software that manages it, SDS offers unprecedented levels of scalability, flexibility, and efficiency that are essential for modern data-driven enterprises.
As organizations grow and their data needs expand, the ability to scale storage solutions without significant hardware investments becomes critical. SDS allows companies to do just that by leveraging commodity hardware and abstracting the storage management layer. This abstraction enables businesses to scale their storage capacity seamlessly, whether they are handling on-premises data, cloud storage, or a hybrid environment. With SDS, the days of being locked into expensive, proprietary storage solutions are numbered.
Moreover, the flexibility offered by SDS is unmatched. It provides the agility needed to adapt to changing data requirements and workloads without the need for disruptive hardware upgrades. Whether you're dealing with structured or unstructured data, SDS can dynamically allocate resources to meet the specific demands of your applications. This level of customization ensures that businesses can optimize their storage infrastructure to maximize performance while minimizing costs.
The Advantages of Implementing Software-Defined Storage in Your Organization
One of the most significant benefits of SDS is its ability to simplify storage management. Traditional storage solutions often require specialized knowledge and manual intervention to manage, scale, and troubleshoot. In contrast, SDS automates many of these processes, reducing the need for specialized skills and allowing IT teams to focus on more strategic initiatives. This automation not only improves efficiency but also reduces the risk of human error, which can lead to data loss or downtime.
Another critical advantage of SDS is its ability to enhance data availability and resilience. By distributing data across multiple nodes and providing built-in redundancy, SDS ensures that your data is always accessible, even in the event of hardware failures. This level of reliability is essential for businesses that rely on uninterrupted access to their data for daily operations.
Finally, SDS delivers substantial cost savings compared to traditional storage solutions. By utilizing off-the-shelf hardware and minimizing reliance on costly, proprietary systems, businesses can achieve equivalent levels of performance and reliability at a fraction of the cost. For IT professionals like Anand Jayapalan, SDS's ability to scale storage resources as needed is particularly advantageous, ensuring that companies pay only for the storage they use, rather than over-provisioning to anticipate future growth.
0 notes
Text
Cloud vs On-Prem Data Warehouse: Making the Right Choice for Your Business
In today's data-driven world, businesses face a critical decision when it comes to choosing the right data warehouse solution. The debate between cloud and on-premise data warehouses has been ongoing, with each option offering distinct advantages and challenges. This article will delve into the practical differences between cloud and on-premise data warehouses, offering real-world examples and data-driven insights to help you make an informed decision.

What is a Cloud Data Warehouse?
A cloud data warehouse is a scalable and flexible data storage solution hosted on cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure. Unlike traditional on-premise data warehouses, cloud data warehouses eliminate the need for physical infrastructure, offering businesses the ability to store and manage data with ease and efficiency.
On-Premise Data Warehouse: A Legacy Approach
An on-premise data warehouse is a traditional data storage solution where the data is hosted on local servers within a company's own data center. This model offers complete control over the data and the infrastructure but comes with significant upfront costs and ongoing maintenance requirements.
Key Differences Between Cloud and On-Premise Data Warehouses
1. Cost Efficiency
Cloud Data Warehouse:
Pros: The pay-as-you-go model allows businesses to scale resources up or down based on demand, reducing unnecessary costs. There is no need for significant capital investment in hardware or software.
Cons: Long-term costs can add up if not managed properly, especially with increasing data volumes and computational needs.
On-Premise Data Warehouse:
Pros: Once the initial investment is made, ongoing costs can be more predictable. No recurring subscription fees.
Cons: High upfront costs for hardware, software, and skilled IT personnel. Ongoing maintenance, power, and cooling expenses add to the total cost of ownership (TCO).
2. Scalability
Cloud Data Warehouse:
Pros: Cloud solutions offer almost infinite scalability. Businesses can adjust their storage and processing power according to their needs without physical limitations.
Cons: Rapid scaling can lead to unexpectedly high costs if usage is not carefully monitored.
On-Premise Data Warehouse:
Pros: Customizable to specific business needs. Scaling is possible but requires additional hardware and can be time-consuming.
Cons: Scaling is limited by the physical infrastructure, often requiring significant time and financial investment.
3. Performance
Cloud Data Warehouse:
Pros: Advanced cloud architectures are optimized for performance, offering faster query processing and better data handling capabilities.
Cons: Performance can be affected by network latency and bandwidth limitations.
On-Premise Data Warehouse:
Pros: Performance is highly controlled, with low latency since data is processed on-site.
Cons: Performance improvements require hardware upgrades, which can be costly and time-consuming.
4. Security and Compliance
Cloud Data Warehouse:
Pros: Leading cloud providers offer robust security features, including encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2.
Cons: Data security in the cloud is a shared responsibility. Organizations must ensure that they implement proper security measures on their end.
On-Premise Data Warehouse:
Pros: Complete control over security policies and compliance with regulatory requirements. Data remains within the company's own environment.
Cons: Higher responsibility for maintaining security, requiring dedicated IT staff and resources.
Live Examples: Cloud vs On-Premise in Action
Cloud Data Warehouse: Netflix
Netflix is a prime example of a company leveraging cloud data warehouses to manage its massive data volumes. By using AWS Redshift, Netflix can analyze petabytes of data in real-time, optimizing its recommendation algorithms and improving user experience. The scalability and performance of cloud data warehouses allow Netflix to handle peak loads, such as during new content releases, without compromising speed or reliability.
On-Premise Data Warehouse: Bank of America
Bank of America relies on an on-premise data warehouse to maintain full control over its sensitive financial data. By keeping data in-house, the bank ensures that all security and compliance requirements are met without relying on external cloud providers. While the costs and complexity of managing an on-premise solution are higher, the bank prioritizes control and security over the flexibility offered by cloud solutions.
Data-Driven Insights: Market Trends and Future Outlook
Market Growth: According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global cloud data warehouse market is expected to grow from $4.7 billion in 2021 to $12.9 billion by 2026, at a CAGR of 23.8%. This growth is driven by the increasing adoption of cloud technologies, the need for real-time analytics, and the flexibility offered by cloud solutions.
Hybrid Approaches: Many organizations are adopting hybrid models, combining both cloud and on-premise data warehouses to balance the benefits of both. For instance, sensitive data may be stored on-premise, while less critical data is managed in the cloud.
AI and Machine Learning Integration: Cloud data warehouses are increasingly integrating AI and machine learning tools to enhance data processing capabilities. This trend is expected to accelerate, with cloud providers offering more advanced analytics and automation features.
Making the Right Choice: Key Considerations
Business Needs: Assess your organization’s specific needs, including data volume, security requirements, budget, and long-term goals.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider both the short-term and long-term costs associated with each solution, including maintenance, upgrades, and scalability.
Security and Compliance: Ensure that your chosen solution meets all regulatory requirements and provides the necessary security features to protect your data.
Scalability and Performance: Evaluate the scalability and performance needs of your organization, and choose a solution that can grow with your business.
Conclusion
Choosing between a cloud and an on-premise data warehouse is a decision that requires careful consideration of various factors, including cost, scalability, performance, and security. While cloud data warehouses offer flexibility, scalability, and advanced analytics, on-premise solutions provide greater control and security. By understanding your organization’s unique needs and long-term goals, you can make an informed decision that will support your data management strategy for years to come.
#Cloud Data Warehouse#On Premise Data Warehouse#Data Storage#Data Management#Cloud Computing#Enterprise Data#Hybrid Cloud#Data Analytics#Data Security#Digital Transformation#Data Infrastructure#Business Intelligence
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Unleashing The Power Of Data

Riding the Data Tsunami: How Hyperscale Unleashes Business Potential
The data analytics world is experiencing a seismic shift, evolving from the simplicity of spreadsheets to the depth of AI-driven insights. This journey has fundamentally transformed how businesses leverage data to drive decision-making, enhance customer experiences, and streamline operations. At the forefront of this revolution are hyperscale data analytics, empowering organizations to navigate and decipher vast seas of data like never before, unlocking boundless potential in the digital age.
Data Analytics Overtime: Evolution and Impact
The evolution of modern data analytics is a tale of innovation and growth. Initially reliant on manual spreadsheets, businesses faced the challenges of inefficiency and error-prone processes. However, advancements in technology have ushered in a new era. Relational databases streamlined data storage and retrieval, while business intelligence (BI) tools enabled sophisticated visualization and reporting.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) propelled analytics into new realms, offering predictive insights and automating complex tasks. This evolution underscores the importance of hyperscale solutions in managing the vast data landscapes of contemporary businesses.
Understanding Hyperscale Data Analytics
Hyperscale analytics is intertwined with data centers designed to manage and process enormous quantities of data. These centers serve as the foundation for handling, storing, and analyzing data at an unprecedented scale, supporting the needs of big data and analytics applications. The essence of hyperscale analytics lies in its ability to accommodate exponential data growth, ensuring infrastructure can scale seamlessly.
This capability is critical for organizations reliant on real-time analysis to inform decision-making, optimize operations, and innovate. Hyperscale computing optimizes efficiency, enabling quick adaptation without physical upgrades, thus enhancing performance for big data projects. Despite potential drawbacks such as unpredictable costs, businesses view hyperscale solutions as strategic investments for operational efficiency and innovation support.
Why Hyperscale is Necessary?
In various sectors, the surge in data volume demands hyperscale solutions for efficient management and analysis. Traditional systems struggle with scalability, speed, and resource efficiency under the weight of big data. Hyperscale architecture, however, dynamically scales with data, supporting rapid expansion without conventional limitations. This necessity arises from the imperative to swiftly harness insights from large datasets, ensuring organizations remain competitive and agile.
Organizations encounter challenges when managing large datasets, including data storage and integration issues, ensuring data quality and security, and handling the complexity of analysis. The sheer volume of data overwhelms traditional tools, hindering meaningful insights extraction. Additionally, real-time analysis demands advanced computational power and sophisticated tools. Ensuring data privacy and compliance further complicates matters. These challenges emphasize the need for robust, scalable solutions to leverage big data efficiently for informed decision-making.
Limitations of traditional data management solutions in handling big data
Traditional data management solutions face limitations with big data due to scalability issues, difficulty processing and analyzing data in real-time, and inefficiency in handling the variety and velocity of big data. They need help integrating diverse data types and sources seamlessly and need help with performance and reliability as data volume grows. These systems may also not provide the analytical tools and computational power required to extract valuable insights from large datasets, leading to challenges in decision-making and operational efficiency.
Industry Applications of Hyperscale Data Analytics
Various sectors leverage hyperscale analytics for enhanced decision-making and operational efficiency. AdTech utilizes big data for targeted advertising, while financial services employ it for risk analysis. Telecommunications optimize networks, and geospatial industries monitor trends and disasters in real time. These applications illustrate how hyperscale analytics supports sectors in handling large-scale data challenges efficiently.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing hyperscale solutions can present challenges such as significant initial costs and operational complexity. However, careful planning and investment can ensure successful implementation and maximization of benefits. Businesses must evaluate scalability needs, assess technical readiness, and invest in personnel or training. Long-term cost-benefit analysis is crucial to align investments with strategic goals.
Concluding Thoughts
In a data-driven world, hyperscale data analytics solutions are indispensable for navigating vast data landscapes. These solutions empower organizations to efficiently manage and analyze large datasets, driving innovation and sustained growth. As we embrace the possibilities, let's remember the transformative role of hyperscale analytics in turning data into strategic assets. We encourage organizations to explore the potential with Coditude, a product engineering company paving the way for innovation and competitive advantage.
#data analytics#hyperscale revolution#big data#hyper scale solutions#coditude#digital age#data management#data infrastructure#scalability
0 notes
Text
Home - Mobius Risk Group

Successfully navigate and excel in global commodity markets through Mobius Risk Group’s award-winning technology and unmatched market experience.
1 note
·
View note
Text
What is the difference between Data Scientist and Data Engineers ?
In today’s data-driven world, organizations harness the power of data to gain valuable insights, make informed decisions, and drive innovation. Two key players in this data-centric landscape are data scientists and data engineers. Although their roles are closely related, each possesses unique skills and responsibilities that contribute to the successful extraction and utilization of data. In…
View On WordPress
#Big Data#Business Intelligence#Data Analytics#Data Architecture#Data Compliance#Data Engineering#Data Infrastructure#Data Insights#Data Integration#Data Mining#Data Pipelines#Data Science#data security#Data Visualization#Data Warehousing#Data-driven Decision Making#Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)#Machine Learning#Predictive Analytics
1 note
·
View note
Photo

Nvidia has announced the availability of DGX Cloud on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. DGX Cloud is a fast, easy and secure way to deploy deep learning and AI applications. It is the first fully integrated, end-to-end AI platform that provides everything you need to train and deploy your applications.
#AI#Automation#Data Infrastructure#Enterprise Analytics#ML and Deep Learning#AutoML#Big Data and Analytics#Business Intelligence#Business Process Automation#category-/Business & Industrial#category-/Computers & Electronics#category-/Computers & Electronics/Computer Hardware#category-/Computers & Electronics/Consumer Electronics#category-/Computers & Electronics/Enterprise Technology#category-/Computers & Electronics/Software#category-/News#category-/Science/Computer Science#category-/Science/Engineering & Technology#Conversational AI#Data Labelling#Data Management#Data Networks#Data Science#Data Storage and Cloud#Development Automation#DGX Cloud#Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity#enterprise LLMs#Generative AI
0 notes
Text
In some of the work you’ve done on data centers, you talk about how AI is presented as a climate solution, even as it requires resource-intensive data centers and computing to power it. What do you think is the risk of presenting resource-intensive AI as a solution to climate change? This is something that’s already happening, which is basically the imposition of ecological visions of a few, especially in the Global North with private interests, onto the rest of the world. We can see this operating not only when it comes to data centers, but also lithium extraction. Lithium is used for rechargeable batteries, which is a key component of so-called transition technologies, such as electric vehicles. If we want to design a transition towards new forms of energy or less carbon-intensive energies, we need to cooperate with these communities and a very important actor are the ones that are participating in the AI value chain. Companies have a big interest in hiding this value chain, in making sure that these communities don’t have a voice in the media, in regulatory discussions, and so on, because this is crucial for their business model and for the technical capacities that they need. There is a big interest in silencing them. This is why they don’t provide information about what they do. It’s also very important that as we discuss AI governance or regulation, we ask how we can incorporate these communities. If you look at what’s happening in Europe, there is upcoming regulation that is going to request that companies provide some transparency when it comes to energy use. But what about something more radical? What about incorporating these communities in the very governance of data centers? Or if we really want more just technologies for environmental transition, why not have a collective discussion, incorporating actors from different contexts and regions of the world to discuss what will be the most efficient — if you want to use that word — way of allocating data centers. In the case of indigenous communities in the Atacama Desert, water is sacred. They have a special relationship with water. One of the few words that they still have is uma, which stands for water. So how do we make sure that these companies respect the way these communities relate to the environment? It’s impossible to think of any kind of transition without considering and respecting the ecological visions of these groups. I don’t really believe in any technologically intensive form of transition that’s made by technocrats in the Global North and that ignores the effects that these infrastructures are having in the rest of the world and the visions of these communities.
65 notes
·
View notes
Text
🥰🥰🥰🥰🥰
#cuddled sweetly from a girl who complains about bad data sharing practices the whole time…#box opener#🌸 is the sweetest and cutest and coziest and got so excited that i looked cozy in pajamas and hand knit socks#soft hair. pettable. loves podcasts about sustainable energy infrastructure development#girlfriend tag
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Linkty Dumpty

I was supposed to be on vacation, and while I didn’t do any blogging for a month, that didn’t mean that I stopped looking at my distraction rectangle and making a list of things I wanted to write about. Consequentially, the link backlog is massive, so it’s time to declare bankruptcy with another linkdump:
https://pluralistic.net/tag/linkdump/
[Image ID: John Holbo’s ‘trolley problem’ art, a repeating pattern of trolleys, tracks, people on tracks, and people standing at track switches]++
Let’s kick things off with a little graphic whimsy. You’ve doubtless seen the endless Trolley Problem memes, working from the same crude line drawings? Well, philosopher John Holbo got tired of that artwork, and he whomped up a fantastic alternative, which you can get as a poster, duvet, sticker, tee, etc:
https://www.redbubble.com/shop/ap/145078097
The trolley problem has been with us since 1967, but it’s enjoying a renaissance thanks to the insistence of “AI” weirdos that it is very relevant to our AI debate. A few years back, you could impress uninformed people by dropping the Trolley Problem into a discussion:
https://memex.craphound.com/2016/10/25/mercedes-weird-trolley-problem-announcement-continues-dumb-debate-about-self-driving-cars/
Amazingly, the “AI” debate has only gotten more tedious since the middle of the past decade. But every now and again, someone gets a stochastic parrot to do something genuinely delightful, like the Jolly Roger Telephone Company, who sell chatbots that will pretend to be tantalyzingly confused marks in order to tie up telemarketers and waste their time:
https://jollyrogertelephone.com/
Jolly Roger sells different personas: “Whitebeard” is a confused senior who keeps asking the caller’s name, drops nonsequiturs into the conversation, and can’t remember how many credit-cards he has. “Salty Sally” is a single mom with a houseful of screaming, demanding children who keep distracting her every time the con artist is on the verge of getting her to give up compromising data. “Whiskey Jack” is drunk:
https://www.wsj.com/articles/people-hire-phone-bots-to-torture-telemarketers-2dbb8457
The bots take a couple minutes to get the sense of the conversation going. During that initial lag, they have a bunch of stock responses like “there’s a bee on my arm, but keep going,” or grunts like “huh,” and “uh-huh.” The bots can keep telemarketers and scammers on the line for quite a long time. Scambaiting is an old and honorable vocation, and it’s good that it has received a massive productivity gain from automation. This is the AI Dividend I dream of.
The less-fun AI debate is the one over artists’ rights and tech. I am foresquare for the artists here, but I think that the preferred solutions (like creating a new copyright over the right to train a model with your work) will not lead to the hoped-for outcome. As with other copyright expansions — 40 years’ worth of them now — this right will be immediately transferred to the highly concentrated media sector, who will simply amend their standard, non-negotiable contracting terms to require that “training rights” be irrevocably assigned to them as a condition of working.
The real solution isn’t to treat artists as atomic individuals — LLCs with an MFA — who bargain, business-to-business, with corporations. Rather, the solutions are in collective power, like unions. You’ve probably heard about the SAG-AFTRA actors’ strike, in which creative workers are bargaining as a group to demand fair treatment in an age of generative models. SAG-AFTRA president Fran Drescher’s speech announcing the strike made me want to stand up and salute:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J4SAPOX7R5M
The actors’ strike is historic: it marks the first time actors have struck since 2000, and it’s the first time actors and writers have co-struck since 1960. Of course, writers in the Writers Guild of America (West and East) have been picketing since since April, and one of their best spokespeople has been Adam Conover, a WGA board member who serves on the negotiating committee. Conover is best known for his stellar Adam Ruins Everything comedy-explainer TV show, which pioneered a technique for breaking down complex forms of corporate fuckery and making you laugh while he does it. Small wonder that he’s been so effective at conveying the strike issues while he pickets.
Writing for Jacobin, Alex N Press profiles Conover and interviews him about the strike, under the excellent headline, “Adam Pickets Everything.” Conover is characteristically funny, smart, and incisive — do read:
https://jacobin.com/2023/07/adam-conover-wga-strike
Of course, not everyone in Hollywood is striking. In late June, the DGA accepted a studio deal with an anemic 41% vote turnout:
https://www.theverge.com/2023/6/26/23773926/dga-amptp-new-deal-strike
They probably shouldn’t have. In this interview with The American Prospect’s Peter Hong, the brilliant documentary director Amy Ziering breaks down how Netflix and the other streamers have rugged documentarians in a classic enshittification ploy that lured in filmmakers, extracted everything they had, and then discarded the husks:
https://prospect.org/culture/2023-06-21-drowned-in-the-stream/
Now, the streaming cartel stands poised to all but kill off documentary filmmaking. Pressured by Wall Street to drive high returns, they’ve become ultraconservative in their editorial decisions, making programs and films that are as similar as possible to existing successes, that are unchallenging, and that are cheap. We’ve gone directly from a golden age of docs to a dark age.
In a time of monopolies, it’s tempting to form countermonopolies to keep them in check. Yesterday, I wrote about why the FTC and Lina Khan were right to try to block the Microsoft/Activision merger, and I heard from a lot of people saying this merger was the only way to check Sony’s reign of terror over video games:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/14/making-good-trouble/#the-peoples-champion
But replacing one monopolist with another isn’t good for anyone (except the monopolists’ shareholders). If we want audiences and workers — and society — to benefit, we have to de-monopolize the sector. Last month, I published a series with EFF about how we should save the news from Big Tech:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2023/04/saving-news-big-tech
After that came out, the EU Observer asked me to write up version of it with direct reference to the EU, where there are a lot of (in my opinion, ill-conceived but well-intentioned) efforts to pry Big Tech’s boot off the news media’s face. I’m really happy with how it came out, and the header graphic is awesome:
https://euobserver.com/opinion/157187
De-monopolizing tech has become my life’s work, both because tech is foundational (tech is how we organize to fight over labor, gender and race equality, and climate justice), and because tech has all of these technical aspects, which open up new avenues for shrinking Big Tech, without waiting decades for traditional antitrust breakups to run their course (we need these too, though!).
I’ve written a book laying out a shovel-ready plan to give tech back to its users through interoperability, explaining how to make new regulations (and reform old ones), what they should say, how to enforce them, and how to detect and stop cheating. It’s called “The Internet Con: How To Seize the Means of Computation” and it’s coming from Verso Books this September:
https://www.versobooks.com/products/3035-the-internet-con

[Image ID: The cover of the Verso Books hardcover of ‘The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of Computation]
I just got my first copy in the mail yesterday, and it’s a gorgeous little package. The timing was great, because I spent the whole week in the studio at Skyboat Media recording the audiobook — the first audiobook of mine that I’ve narrated. It was a fantastic experience, and I’ll be launching a Kickstarter to presell the DRM-free audio and ebooks as well as hardcovers, in a couple weeks.
Though I like doing these crowdfunders, I do them because I have to. Amazon’s Audible division, the monopolist that controls >90% of the audiobook market, refuses to carry my work because it is DRM-free. When you buy a DRM-free audiobook, that means that you can play it on anyone’s app, not just Amazon’s. Every audiobook you’ve ever bought from Audible will disappear the moment you decide to break up with Amazon, which means that Amazon can absolutely screw authors and audiobook publishers because they’ve taken our customers hostage.
If you are unwise enough to pursue an MBA, you will learn a term of art for this kind of market structure: it’s a “moat,” that is, an element of the market that makes it hard for new firms to enter the market and compete with you. Warren Buffett pioneered the use of this term, and now it’s all but mandatory for anyone launching a business or new product to explain where their moat will come from.
As Dan Davies writes, these “moats” aren’t really moats in the Buffett sense. With Coke and Disney, he says, a “moat” was “the fact that nobody else could make such a great product that everyone wanted.” In other words, “making a good product,” is a great moat:
https://backofmind.substack.com/p/stuck-in-the-moat
But making a good product is a lot of work and not everyone is capable of it. Instead, “moat” now just means some form of lock in. Davies counsels us to replace “moat” with:
our subscription system and proprietary interface mean that our return on capital is protected by a strong Berlin Wall, preventing our customers from getting out to a freer society and forcing them to consume our inferior products for lack of alternative.
I really like this. It pairs well with my 2020 observation that the fight over whether “IP” is a meaningful term can be settled by recognizing that IP has a precise meaning in business: “Any policy that lets me reach beyond the walls of my firm to control the conduct of my competitors, critics and customers”:
https://locusmag.com/2020/09/cory-doctorow-ip/
To see how that works in the real world, check out “The Anti-Ownership Ebook Economy,” a magisterial piece of scholarship from Sarah Lamdan, Jason M. Schultz, Michael Weinberg and Claire Woodcock:
https://www.nyuengelberg.org/outputs/the-anti-ownership-ebook-economy/
Something happened when we shifted to digital formats that created a loss of rights for readers. Pulling back the curtain on the evolution of ebooks offers some clarity to how the shift to digital left ownership behind in the analog world.
The research methodology combines both anonymous and named sources in publishing, bookselling and librarianship, as well as expert legal and economic analysis. This is an eminently readable, extremely smart, and really useful contribution to the scholarship on how “IP” (in the modern sense) has transformed books from something you own to something that you can never own.
The truth is, capitalists hate capitalism. Inevitably, the kind of person who presides over a giant corporation and wields power over millions of lives — workers, suppliers and customers — believes themselves to be uniquely and supremely qualified to be a wise dictator. For this kind of person, competition is “wasteful” and distracts them from the important business of making everyone’s life better by handing down unilateral — but wise and clever — edits. Think of Peter Thiel’s maxim, “competition is for losers.”
That’s why giant companies love to merge with each other, and buy out nascent competitors. By rolling up the power to decide how you and I and everyone else live our lives, these executives ensure that they can help us little people live the best lives possible. The traditional role of antitrust enforcement is to prevent this from happening, countering the delusions of would-be life-tenured autocrats of trade with public accountability and enforcement:
https://marker.medium.com/we-should-not-endure-a-king-dfef34628153
Of course, for 40 years, we’ve had neoliberal, Reaganomics-poisoned antitrust, where monopolies are celebrated as “efficient” and their leaders exalted as geniuses whose commercial empires are evidence of merit, not savagery. That era is, thankfully, coming to an end, and not a moment too soon.
Leading the fight is the aforementioned FTC chair Lina Khan, who is taking huge swings at even bigger mergers. But the EU is no slouch in this department: they’re challenging the Adobe/Figma merger, a $20b transaction that is obviously and solely designed to recapture customers who left Adobe because they didn’t want to struggle under its yoke any longer:
https://gizmodo.com/adobe-figma-acquisition-likely-to-face-eu-investigation-1850555562
For autocrats of trade, this is an intolerable act of disloyalty. We owe them our fealty and subservience, because they are self-evidently better at understanding what we need than we could ever be. This unwarranted self-confidence from the ordinary mediocrities who end up running giant tech companies gets them into a whole lot of hot water.
One keen observer of the mind-palaces that tech leaders trap themselves in is Anil Dash, who describes the conspiratorial, far-right turn of the most powerful men (almost all men!) in Silicon Valley in a piece called “‘VC Qanon’ and the radicalization of the tech tycoons”:
https://www.anildash.com/2023/07/07/vc-qanon/
Dash builds on an editorial he published in Feb, “The tech tycoon martyrdom charade,” which explores the sense of victimhood the most powerful, wealthiest people in the Valley project:
https://www.anildash.com/2023/02/27/tycoon-martyrdom-charade/
These dudes are prisoners of their Great Man myth, and leads them badly astray. And while all of us are prone to lapses in judgment and discernment, Dash makes the case that tech leaders are especially prone to it:
Nobody becomes a billionaire by accident. You have to have wanted that level of power, control and wealth more than you wanted anything else in your life. They all sacrifice family, relationships, stability, community, connection, and belonging in service of keeping score on a scale that actually yields no additional real-world benefits on the path from that first $100 million to the tens of billions.
This makes billionaires “a cohort that is, counterintutively, very easily manipulated.” What’s more, they’re all master manipulators, and they all hang out with each other, which means that when a conspiratorial belief takes root in one billionaire’s brain, it spreads to the rest of them like wildfire.
Then, billionaires “push each other further and further into extreme ideas because their entire careers have been predicated on the idea that they’re genius outliers who can see things others can’t, and that their wealth is a reward for that imagined merit.”
They live in privileged bubbles, which insulates them from disconfirming evidence — ironic, given how many of these bros think they are wise senators in the agora.
There are examples of billionaires’ folly all around us today, of course. Take privacy: the idea that we can — we should — we must — spy on everyone, all the time, in every way, to eke out tiny gains in ad performance is objectively batshit. And yet, wealthy people decreed this should be so, and it was, and made them far richer.
Leaked data from Microsoft’s Xandr ad-targeting database reveals how the commercial surveillance delusion led us to a bizarre and terrible place, as reported on by The Markup:
https://themarkup.org/privacy/2023/06/08/from-heavy-purchasers-of-pregnancy-tests-to-the-depression-prone-we-found-650000-ways-advertisers-label-you
The Markup’s report lets you plumb 650,000 targeting categories, searching by keyword or loading random sets, 20 at a time. Do you want to target gambling addicts, people taking depression meds or Jews? Xandr’s got you covered. What could possibly go wrong?
The Xandr files come from German security researcher Wolfie Christl from Cracked Labs. Christi is a European, and he’s working with the German digital rights group Netzpolitik to get the EU to scrutinize all the ways that Xandr is flouting EU privacy laws.
Billionaires’ big ideas lead us astray in more tangible ways, of course. Writing in The Conversation, John Quiggin asks us to take a hard look at the much ballyhooed (and expensively ballyhooed) “nuclear renaissance”:
https://theconversation.com/dutton-wants-australia-to-join-the-nuclear-renaissance-but-this-dream-has-failed-before-209584
Despite the rhetoric, nukes aren’t cheap, and they aren’t coming back. Georgia’s new nuclear power is behind schedule and over budget, but it’s still better off than South Carolina’s nukes, which were so over budget that they were abandoned in 2017. France’s nuke is a decade behind schedule. Finland’s opened this year — 14 years late. The UK’s Hinkley Point C reactor is massively behind schedule and over budget (and when it’s done, it will be owned by the French government!).
China’s nuclear success story also doesn’t hold up to scrutiny — they’ve brought 50GW of nukes online, sure, but they’re building 95–120GW of solar every year.
Solar is the clear winner here, along with other renewables, which are plummeting in cost (while nukes soar) and are accelerating in deployments (while nukes are plagued with ever-worsening delays).
This is the second nuclear renaissance — the last one, 20 years ago, was a bust, and that was before renewables got cheap, reliable and easy to manufacture and deploy. You’ll hear fairy-tales about how the early 2000s bust was caused by political headwinds, but that’s simply untrue: there were almost no anti-nuke marches then, and governments were scrambling to figure out low-carbon alternatives to fossil fuels (this was before the latest round of fossil fuel sabotage).
The current renaissance is also doomed. Yes, new reactors are smaller and safer and won’t have the problems intrinsic to all megaprojects, but designs like VOYGR have virtually no signed deals. Even if they do get built, their capacity will be dwarfed by renewables — a Gen III nuke will generate 710MW of power. Globally, we add that much solar every single day.
And solar power is cheap. Even after US subsidies, a Gen III reactor would charge A$132/MWh — current prices are as low as A$64-$114/MWh.
Nukes are getting a charm offensive because wealthy people are investing in hype as a way of reaping profits — not as a way of generating safe, cheap, reliable energy.
Here in the latest stage of capitalism, value and profit are fully decoupled. Monopolists are shifting more and more value from suppliers and customers to their shareholders every day. And when the customer is the government, the depravity knows no bounds. In Responsible Statecraft, Connor Echols describes how military contractors like Boeing are able to bill the Pentagon $52,000 for a trash can:
https://responsiblestatecraft.org/2023/06/20/the-pentagons-52000-trash-can/
Military Beltway Bandits are nothing new, of course, but they’ve gotten far more virulent since the Obama era, when Obama’s DoD demanded that the primary contractors merge to a bare handful of giant firms, in the name of “efficiency.” As David Dayen writes in his must-read 2020 book Monopolized, this opened the door to a new kind of predator:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/01/29/fractal-bullshit/#dayenu
The Obama defense rollups were quickly followed by another wave of rollups, these ones driven by Private Equity firms who cataloged which subcontractors were “sole suppliers” of components used by the big guys. These companies were all acquired by PE funds, who then lowered the price of their products, selling them below cost.
This maximized the use of those parts in weapons and aircraft sold by primary contractors like Boeing, which created a durable, long-lasting demand for fresh parts for DoD maintenance of its materiel. PE-owned suppliers hits Uncle Sucker with multi-thousand-percent markups for these parts, which have now wormed their way into every corner of the US arsenal.
Yes, this is infuriating as hell, but it’s also so grotesquely wrong that it’s impossible to defend, as we see in this hilarious clip of Rep Katie Porter grilling witnesses on US military waste:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TJhf6l1nB9A
Porter pulls out the best version yet of her infamous white-board and makes her witnesses play defense ripoff Jepoardy!, providing answers to a series of indefensible practices.
It’s sure nice when our government does something for us, isn’t it? We absolutely can have nice things, and we’re about to get them. The Infrastructure Bill contains $42B in subsidies for fiber rollouts across the country, which will be given to states to spend. Ars Technica’s Jon Brodkin breaks down the state-by-state spending:
https://arstechnica.com/tech-policy/2023/06/us-allocates-42b-in-broadband-funding-find-out-how-much-your-state-will-get/
Texas will get $3.31B, California will get $1.86B, and 17 other states will get $1B or more. As the White House announcement put it, “High-speed Internet is no longer a luxury.”
To understand how radical this is, you need to know that for decades, the cable and telco sector has grabbed billions in subsidies for rural and underserved communities, and then either stole the money outright, or wasted it building copper networks that run at a fraction of a percent of fiber speeds.
This is how America — the birthplace of the internet — ended up with some of the world’s slowest, most expensive broadband, even after handing out tens of billions of dollars in subsidies. Those subsidies were gobbled up by greedy, awful phone companies — these ones must be spent wisely, on long-lasting, long-overdue fiber infrastructure.
That’s a good note to end on, but I’ve got an even better one: birds in the Netherlands are tearing apart anti-bird strips and using them to build their nests. Wonderful creatures 1, hostile architecture, 0. Nature is healing:
https://www.theguardian.com/science/2023/jul/11/crows-and-magpies-show-their-metal-by-using-anti-bird-spikes-to-build-nests

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this thread to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/15/in-the-dumps/#what-vacation

Next Tues, Jul 18, I'm hosting the first Clarion Summer Write-In Series, an hour-long, free drop-in group writing and discussion session. It's in support of the Clarion SF/F writing workshop's fundraiser to offer tuition support to students:
https://mailchi.mp/theclarionfoundation/clarion-write-ins

[Image iD: A dump-truck, dumping out a load of gravel. A caricature of Humpty Dumpty clings to its lip, restrained by a group of straining, Lilliputian men.]
#pluralistic#infrastructure#broadband#linkdumps#fran drescher#labor#strikes#libraries#big tech#sag aftra#writer's strike#commercial surveillance#actor's strike#data brokers#ebooks#moats and walls#drm#licensing#glam#publishing#military privacy#copyfight#platform economics#nukes#adam conover#pentagon#birds#mergers#delightful creatures#hostile architecture
113 notes
·
View notes
Text
[T]he Dutch Republic, like its successor the Kingdom of the Netherlands, [...] throughout the early modern period had an advanced maritime [trading, exports] and (financial) service [banking, insurance] sector. Moreover, Dutch involvement in Atlantic slavery stretched over two and a half centuries. [...] Carefully estimating the scope of all the activities involved in moving, processing and retailing the goods derived from the forced labour performed by the enslaved in the Atlantic world [...] [shows] more clearly in what ways the gains from slavery percolated through the Dutch economy. [...] [This web] connected them [...] to the enslaved in Suriname and other Dutch colonies, as well as in non-Dutch colonies such as Saint Domingue [Haiti], which was one of the main suppliers of slave-produced goods to the Dutch economy until the enslaved revolted in 1791 and brought an end to the trade. [...] A significant part of the eighteenth-century Dutch elite was actively engaged in financing, insuring, organising and enabling the slave system, and drew much wealth from it. [...] [A] staggering 19% (expressed in value) of the Dutch Republic's trade in 1770 consisted of Atlantic slave-produced goods such as sugar, coffee, or indigo [...].
---
One point that deserves considerable emphasis is that [this slave-based Dutch wealth] [...] did not just depend on the increasing output of the Dutch Atlantic slave colonies. By 1770, the Dutch imported over fl.8 million worth of sugar and coffee from French ports. [...] [T]hese [...] routes successfully linked the Dutch trade sector to the massive expansion of slavery in Saint Domingue [the French colony of Haiti], which continued until the early 1790s when the revolution of the enslaved on the French part of that island ended slavery.
Before that time, Dutch sugar mills processed tens of millions of pounds of sugar from the French Caribbean, which were then exported over the Rhine and through the Sound to the German and Eastern European ‘slavery hinterlands’.
---
Coffee and indigo flowed through the Dutch Republic via the same trans-imperial routes, while the Dutch also imported tobacco produced by slaves in the British colonies, [and] gold and tobacco produced [by slaves] in Brazil [...]. The value of all the different components of slave-based trade combined amounted to a sum of fl.57.3 million, more than 23% of all the Dutch trade in 1770. [...] However, trade statistics alone cannot answer the question about the weight of this sector within the economy. [...] 1770 was a peak year for the issuing of new plantation loans [...] [T]he main processing industry that was fully based on slave-produced goods was the Holland-based sugar industry [...]. It has been estimated that in 1770 Amsterdam alone housed 110 refineries, out of a total of 150 refineries in the province of Holland. These processed approximately 50 million pounds of raw sugar per year, employing over 4,000 workers. [...] [I]n the four decades from 1738 to 1779, the slave-based contribution to GDP alone grew by fl.20.5 million, thus contributing almost 40% of all growth generated in the economy of Holland in this period. [...]
---
These [slave-based Dutch commodity] chains ran from [the plantation itself, through maritime trade, through commodity processing sites like sugar refineries, through export of these goods] [...] and from there to European metropoles and hinterlands that in the eighteenth century became mass consumers of slave-produced goods such as sugar and coffee. These chains tied the Dutch economy to slave-based production in Suriname and other Dutch colonies, but also to the plantation complexes of other European powers, most crucially the French in Saint Domingue [Haiti], as the Dutch became major importers and processers of French coffee and sugar that they then redistributed to Northern and Central Europe. [...]
The explosive growth of production on slave plantations in the Dutch Guianas, combined with the international boom in coffee and sugar consumption, ensured that consistently high proportions (19% in 1770) of commodities entering and exiting Dutch harbors were produced on Atlantic slave plantations. [...] The Dutch economy profited from this Atlantic boom both as direct supplier of slave-produced goods [from slave plantations in the Dutch Guianas, from Dutch processing of sugar from slave plantations in French Haiti] and as intermediary [physically exporting sugar and coffee] between the Atlantic slave complexes of other European powers and the Northern and Central European hinterland.
---
Text above by: Pepijn Brandon and Ulbe Bosma. "Slavery and the Dutch economy, 1750-1800". Slavery & Abolition Volume 42, Issue 1. 2021. [Text within brackets added by me for clarity. Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Presented here for commentary, teaching, criticism purposes.]
#abolition#these authors lead by pointing out there is general lack of discussion on which metrics or data to use to demonstrate#extent of slaverys contribution to dutch metropolitan wealth when compared to extensive research#on how british slavery profits established infrastructure textiles banking and industrialisation at home domestically in england#so that rather than only considering direct blatant dutch slavery in guiana caribbean etc must also look at metropolitan business in europe#in this same issue another similar article looks at specifically dutch exporting of slave based coffee#and the previously unheralded importance of the dutch export businesses to establishing coffee mass consumption in europe#via shipment to germany#which ties the expansion of french haiti slavery to dutch businesses acting as intermediary by popularizing coffee in europe#which invokes the concept mentioned here as slavery hinterlands#and this just atlantic lets not forget dutch wealth from east india company and cinnamon and srilanka etc#and then in following decades the immense dutch wealth and power in java#tidalectics#caribbean#archipelagic thinking#carceral geography#ecologies#intimacies of four continents#indigenous#sacrifice zones#slavery hinterlands#european coffee#indigenous pedagogies#black methodologies
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unbelievable talking to someone with a car who can drive who is at once condesendly incredulous at the idea you would walk to the shops and also disagreeing that the civil infrastructure isnt hostile TO walking based on the fact they walked to a restaurant exactly once. As if the fact that they are in the possession of the ability to walk that distance but as a rule. Drives the LESS THAN FIVE MINUTES. To the location. Instead. Every other time. Is not itself. All the evidence needed.
#some shit#just what. willful ignorance or a complete lack of ability to take other peoples reported experiences seriously#<- snort. well. i have some data that swings that pendulum#grinds my face into the counter. unbelievable. unbelievable#i live somewear so beautiful but fucked if they dont wanna parcel it in car only accessible chunks.#dead eyed stare to the audience. if u take my posting in bad faith and do not do any of ur own looking into to what#accessible and uncar centric infrastructure can do for disabled ppl or what other what aboutism you can think of#i will kill you. dead.#if you want to ask me in good faith cause u like the topic and are tired of the way things are. ☺️thats okay.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Industry First: UCIe Optical Chiplet Unveiled by Ayar Labs
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/industry-first-ucie-optical-chiplet-unveiled-by-ayar-labs/
Industry First: UCIe Optical Chiplet Unveiled by Ayar Labs


Ayar Labs has unveiled the industry’s first Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe) optical interconnect chiplet, designed specifically to maximize AI infrastructure performance and efficiency while reducing latency and power consumption for large-scale AI workloads.
This breakthrough will help address the increasing demands of advanced computing architectures, especially as AI systems continue to scale. By incorporating a UCIe electrical interface, the new chiplet is designed to eliminate data bottlenecks while enabling seamless integration with chips from different vendors, fostering a more accessible and cost-effective ecosystem for adopting advanced optical technologies.
The chiplet, named TeraPHY™, achieves 8 Tbps bandwidth and is powered by Ayar Labs’ 16-wavelength SuperNova™ light source. This optical interconnect technology aims to overcome the limitations of traditional copper interconnects, particularly for data-intensive AI applications.
“Optical interconnects are needed to solve power density challenges in scale-up AI fabrics,” said Mark Wade, CEO of Ayar Labs.
The integration with the UCIe standard is particularly significant as it allows chiplets from different manufacturers to work together seamlessly. This interoperability is critical for the future of chip design, which is increasingly moving toward multi-vendor, modular approaches.
The UCIe Standard: Creating an Open Chiplet Ecosystem
The UCIe Consortium, which developed the standard, aims to build “an open ecosystem of chiplets for on-package innovations.” Their Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express specification addresses industry demands for more customizable, package-level integration by combining high-performance die-to-die interconnect technology with multi-vendor interoperability.
“The advancement of the UCIe standard marks significant progress toward creating more integrated and efficient AI infrastructure thanks to an ecosystem of interoperable chiplets,” said Dr. Debendra Das Sharma, Chair of the UCIe Consortium.
The standard establishes a universal interconnect at the package level, enabling chip designers to mix and match components from different vendors to create more specialized and efficient systems. The UCIe Consortium recently announced its UCIe 2.0 Specification release, indicating the standard’s continued development and refinement.
Industry Support and Implications
The announcement has garnered strong endorsements from major players in the semiconductor and AI industries, all members of the UCIe Consortium.
Mark Papermaster from AMD emphasized the importance of open standards: “The robust, open and vendor neutral chiplet ecosystem provided by UCIe is critical to meeting the challenge of scaling networking solutions to deliver on the full potential of AI. We’re excited that Ayar Labs is one of the first deployments that leverages the UCIe platform to its full extent.”
This sentiment was echoed by Kevin Soukup from GlobalFoundries, who noted, “As the industry transitions to a chiplet-based approach to system partitioning, the UCIe interface for chiplet-to-chiplet communication is rapidly becoming a de facto standard. We are excited to see Ayar Labs demonstrating the UCIe standard over an optical interface, a pivotal technology for scale-up networks.”
Technical Advantages and Future Applications
The convergence of UCIe and optical interconnects represents a paradigm shift in computing architecture. By combining silicon photonics in a chiplet form factor with the UCIe standard, the technology allows GPUs and other accelerators to “communicate across a wide range of distances, from millimeters to kilometers, while effectively functioning as a single, giant GPU.”
The technology also facilitates Co-Packaged Optics (CPO), with multinational manufacturing company Jabil already showcasing a model featuring Ayar Labs’ light sources capable of “up to a petabit per second of bi-directional bandwidth.” This approach promises greater compute density per rack, enhanced cooling efficiency, and support for hot-swap capability.
“Co-packaged optical (CPO) chiplets are set to transform the way we address data bottlenecks in large-scale AI computing,” said Lucas Tsai from Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC). “The availability of UCIe optical chiplets will foster a strong ecosystem, ultimately driving both broader adoption and continued innovation across the industry.”
Transforming the Future of Computing
As AI workloads continue to grow in complexity and scale, the semiconductor industry is increasingly looking toward chiplet-based architectures as a more flexible and collaborative approach to chip design. Ayar Labs’ introduction of the first UCIe optical chiplet addresses the bandwidth and power consumption challenges that have become bottlenecks for high-performance computing and AI workloads.
The combination of the open UCIe standard with advanced optical interconnect technology promises to revolutionize system-level integration and drive the future of scalable, efficient computing infrastructure, particularly for the demanding requirements of next-generation AI systems.
The strong industry support for this development indicates the potential for a rapidly expanding ecosystem of UCIe-compatible technologies, which could accelerate innovation across the semiconductor industry while making advanced optical interconnect solutions more widely available and cost-effective.
#accelerators#adoption#ai#AI chips#AI Infrastructure#AI systems#amd#Announcements#applications#approach#architecture#bi#CEO#challenge#chip#Chip Design#chips#collaborative#communication#complexity#computing#cooling#data#Design#designers#development#driving#efficiency#express#factor
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
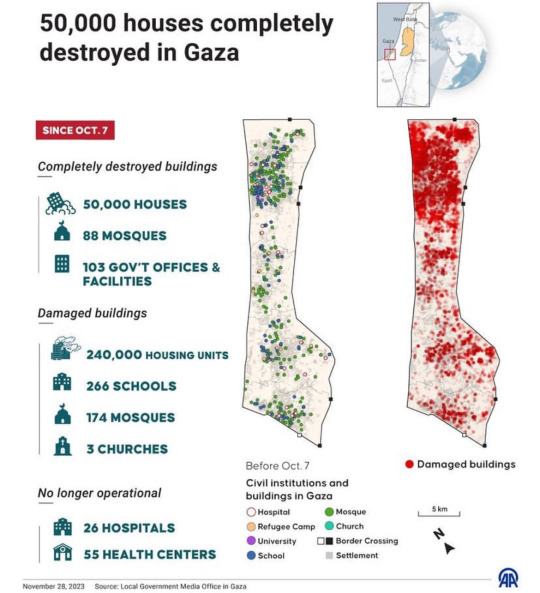
#free gaza#free palestine#gaza#palestine#from the river to the sea palestine will be free#israel#pray for palestine#ceasefire#america#usa#gaza strip#infrastructure#genocide#ethnic cleansing#climate change#mass destruction#data#graphs#visual learner#hospitals#mosque#homes#houses#school#schools#churches
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
sunshine, lollipops and rainbows
#gotta love automatic updates#it looks like its still working hut worse comes to worst i recert to an older version of the os#stupid stupid dumb dumb i swear to god i turned off automatic updates#i carry around two phones cause of this bs#one works with the newer apps i need to use and has my data pln and this phone has my legacy shit on it#just so happens my legacy shit is KIND OF IMPORTANT#thinking about all the infrastructure thats running on 20 year old laptops that has post it notes that say SERVER DO NOT CLOSE
10 notes
·
View notes