#Healthcare
Text
404 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Since it was first identified in 1983, HIV has infected more than 85 million people and caused some 40 million deaths worldwide.
While medication known as pre-exposure prophylaxis, or PrEP, can significantly reduce the risk of getting HIV, it has to be taken every day to be effective. A vaccine to provide lasting protection has eluded researchers for decades. Now, there may finally be a viable strategy for making one.
An experimental vaccine developed at Duke University triggered an elusive type of broadly neutralizing antibody in a small group of people enrolled in a 2019 clinical trial. The findings were published today [May 17, 2024] in the scientific journal Cell.
“This is one of the most pivotal studies in the HIV vaccine field to date,” says Glenda Gray, an HIV expert and the president and CEO of the South African Medical Research Council, who was not involved in the study.
A few years ago, a team from Scripps Research and the International AIDS Vaccine Initiative (IAVI) showed that it was possible to stimulate the precursor cells needed to make these rare antibodies in people. The Duke study goes a step further to generate these antibodies, albeit at low levels.
“This is a scientific feat and gives the field great hope that one can construct an HIV vaccine regimen that directs the immune response along a path that is required for protection,” Gray says.
-via WIRED, May 17, 2024. Article continues below.
Vaccines work by training the immune system to recognize a virus or other pathogen. They introduce something that looks like the virus—a piece of it, for example, or a weakened version of it—and by doing so, spur the body’s B cells into producing protective antibodies against it. Those antibodies stick around so that when a person later encounters the real virus, the immune system remembers and is poised to attack.
While researchers were able to produce Covid-19 vaccines in a matter of months, creating a vaccine against HIV has proven much more challenging. The problem is the unique nature of the virus. HIV mutates rapidly, meaning it can quickly outmaneuver immune defenses. It also integrates into the human genome within a few days of exposure, hiding out from the immune system.
“Parts of the virus look like our own cells, and we don’t like to make antibodies against our own selves,” says Barton Haynes, director of the Duke Human Vaccine Institute and one of the authors on the paper.
The particular antibodies that researchers are interested in are known as broadly neutralizing antibodies, which can recognize and block different versions of the virus. Because of HIV’s shape-shifting nature, there are two main types of HIV and each has several strains. An effective vaccine will need to target many of them.
Some HIV-infected individuals generate broadly neutralizing antibodies, although it often takes years of living with HIV to do so, Haynes says. Even then, people don’t make enough of them to fight off the virus. These special antibodies are made by unusual B cells that are loaded with mutations they’ve acquired over time in reaction to the virus changing inside the body. “These are weird antibodies,” Haynes says. “The body doesn’t make them easily.”
Haynes and his colleagues aimed to speed up that process in healthy, HIV-negative people. Their vaccine uses synthetic molecules that mimic a part of HIV’s outer coat, or envelope, called the membrane proximal external region. This area remains stable even as the virus mutates. Antibodies against this region can block many circulating strains of HIV.
The trial enrolled 20 healthy participants who were HIV-negative. Of those, 15 people received two of four planned doses of the investigational vaccine, and five received three doses. The trial was halted when one participant experienced an allergic reaction that was not life-threatening. The team found that the reaction was likely due to an additive in the vaccine, which they plan to remove in future testing.
Still, they found that two doses of the vaccine were enough to induce low levels of broadly neutralizing antibodies within a few weeks. Notably, B cells seemed to remain in a state of development to allow them to continue acquiring mutations, so they could evolve along with the virus. Researchers tested the antibodies on HIV samples in the lab and found that they were able to neutralize between 15 and 35 percent of them.
Jeffrey Laurence, a scientific consultant at the Foundation for AIDS Research (amfAR) and a professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medical College, says the findings represent a step forward, but that challenges remain. “It outlines a path for vaccine development, but there’s a lot of work that needs to be done,” he says.
For one, he says, a vaccine would need to generate antibody levels that are significantly higher and able to neutralize with greater efficacy. He also says a one-dose vaccine would be ideal. “If you’re ever going to have a vaccine that’s helpful to the world, you’re going to need one dose,” he says.
Targeting more regions of the virus envelope could produce a more robust response. Haynes says the next step is designing a vaccine with at least three components, all aimed at distinct regions of the virus. The goal is to guide the B cells to become much stronger neutralizers, Haynes says. “We’re going to move forward and build on what we have learned.”
-via WIRED, May 17, 2024
#hiv#aids#aids crisis#virology#immunology#viruses#vaccines#infectious diseases#vaccination#immune system#public health#medicine#healthcare#hiv aids#hiv prevention#good news#hope#medical news
614 notes
·
View notes
Text
#investment#足立梨花#dogs of tumblr#高中生#sidon#rachel weisz#healthcare#bd/sm brat#nails#rilakkuma#[yellowjackets]#Sasuke Uchiha#regulus black x reader#lancap#animal rights
130 notes
·
View notes
Text
#dogs of tumblr#高中生#sidon#rachel weisz#healthcare#bd/sm brat#nails#rilakkuma#[yellowjackets]#Sasuke Uchiha#lancap
129 notes
·
View notes
Text
#maddie ziegler#jensen ackles#emmys#soledad#investment#足立梨花#dogs of tumblr#高中生#sidon#rachel weisz#healthcare#bd/sm brat
126 notes
·
View notes
Text
"In a significant medical milestone, Chinese scientists have successfully cured a patient's diabetes using a groundbreaking cell therapy. This pioneering treatment was developed by a team from Shanghai Changzheng Hospital, the Centre for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science under the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Renji Hospital, and was detailed in the journal Cell Discovery on April 30."
"The new therapy involves programming the patient's peripheral blood mononuclear cells, transforming them into "seed cells" to recreate pancreatic islet tissue in an artificial environment. This approach leverages the body's regenerative capabilities, an emerging field known as regenerative medicine."
"Our technology has matured and it has pushed boundaries in the field of regenerative medicine for the treatment of diabetes," Yin stated."
This is GROUNDBREAKING and incredible recent news. I've been seeing some US news sources cry 'but what about capitalism,' and it's disgusting. The US among any country without universal and accessible healthcare see cures and prevention as threats. There's WAY more business in sick people and keeping people sick, right US Government? Deplorable.
#china#science#breaking news#global news#world news#diabetes#diabetes research#research#medical study#public health#united states#fuck capitalism#abolish capitalism#anti capitalism#medicine#healthcare#news
50 notes
·
View notes
Text



#halsey#the end#song lyrics#lyrics#love#hold me#recovery#recover#mental health#mental illness#chronic illness#invisible illness#illness#therapy#health#healthcare#mental#therap#quotes#ashley frangipane#halsey lyrics
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
how i feel at work getting misgendered by my patients (theyre not being transphobic im just pretty)
#trans#transmasc#phlebotomist#phlebotomy#healthcare#healthcare field#healthcare worker#genderfluid#butch lesbian#butch tboy
24 notes
·
View notes
Text

Doctor Beverly Crusher
@SpaceDocMom
Fatphobia has never cured anything. emojis: black heart, blue heart, masked, spoon
5:05 PM · Jun 5, 2024
x.com/SpaceDocMom/status/1798385669892710865
#star trek#doctor crusher#star trek the next generation#star trek memes#star trek tng#kindness#support#care#compassion#health care#healthcare#fatphobia#medical fatphobia#medical gaslighting#spoons#spoonies
23 notes
·
View notes
Text

Gee, I thought these people were the ones who were like “If you don’t like it, you can just move to a blue state.”
And now they’re mad the guy is doing just that?
You can’t oppress and discriminate against someone then be mad when they take their highly useful skill elsewhere.
#lgbtq#news#louisiana#democrats#republicans#politics#healthcare#Nbc#nbc news#transgender#medicine#ron desantis
88K notes
·
View notes
Text
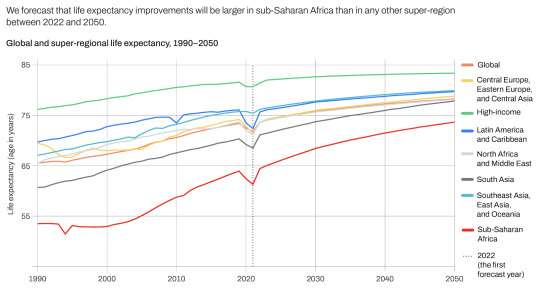
"Global life expectancy is forecasted to increase from 73.6 years of age in 2022 to 78.1 years of age in 2050 (a 4.5-year increase).
Life expectancy increases are projected to be greater in countries with lower life expectancies, reducing global disparities.
There will be a continued shift in disease burden from communicable, maternal, neonatal, and nutritional diseases to non-communicable diseases (NCDs).
The latest findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study (GBD) 2021, published today in The Lancet [May 17, 2024], forecast that global life expectancy will increase by 4.9 years in males and 4.2 years in females between 2022 and 2050.
Increases are expected to be largest in countries where life expectancy is lower, contributing to a convergence of increased life expectancy across geographies. The trend is largely driven by public health measures that have prevented and improved survival rates from cardiovascular diseases, COVID-19, and a range of communicable, maternal, neonatal, and nutritional diseases (CMNNs)...
Global life expectancy is forecasted to increase from 73.6 years of age in 2022 to 78.1 years of age in 2050 (a 4.5-year increase). Global healthy life expectancy (HALE) – the average number of years a person can expect to live in good health – will increase from 64.8 years in 2022 to 67.4 years in 2050 (a 2.6-year increase).
[Note: I cut out significant chunks of this article because they're being really shitty about "disability-adjusted life years," where they explicitly say that years lived as a disabled person don't count/don't count as much. Fuck that! Our lives are worth living!!!! Sincerely, your local disabled blogger.]
“In addition to an increase in life expectancy overall, we have found that the disparity in life expectancy across geographies will lessen,” said Dr. Chris Murray, Chair of Health Metrics Sciences at the University of Washington and Director of the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME). “This is an indicator that while health inequalities between the highest- and lowest-income regions will remain, the gaps are shrinking, with the biggest increases anticipated in sub-Saharan Africa.” ...
The Global Burden of Disease Study (GBD) is the largest and most comprehensive effort to quantify health loss across places and over time. It draws on the work of nearly 12,000 collaborators across more than 160 countries and territories. GBD 2021 – the newly published most recent round of GBD results – includes more than 607 billion estimates of 371 diseases and injuries and 88 risk factors in 204 countries and territories. The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation coordinates the study."
-via Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, May 17, 2024
--
Note: Obviously we need to make these gaps/disparities close completely!!! And it's also really good to see that we're on the right track.
I genuinely believe that the medical revolution that has just started this decade, along with the huge increase and revolution in communication technology, will make improvements in health and life expectancy come even faster than forecasted. Especially in low-income and low-life-expectancy countries
59 notes
·
View notes
Text

11K notes
·
View notes
Text
Horrible fact of the day: Chevron just released a new boat fuel that WILL give you cancer.
Not "might", not "could", WILL. It has a cancer ratio of 1.3:1, as in, in a group of 10 people, 10 would contract CANCER.
(Edit: apparently some articles are now saying 1.4:1, and some are saying a little under that. Either way, the consensus seems to be anywhere between a 95-100+% of contracting cancer, with some expectations of this fuel not even needing a full lifetime of exposure for you to get Cancer.)
The EPA's safety limit is 1:1,000,000 as in 1 in a million people get cancer.
The EPA approved it anyways. I am not joking. The EPA approved a boat fuel that has a near 100% chance of giving someone cancer. It has such a good chance of giving someone cancer that if you DIDN'T get cancer YOU WOULD BE AN OUTLIER.
Fuck the oil industries.
Edit: If you find this (rightfully) horrifying, have you considered industrial sabotage? /hj
This isn't something we can vote away. This isn't something the rich are gonna apologize and make a 10 minute apology video for this. They don't care if you starve or wither in hospitals or get blown up in their wars.
If you don't know where to get started:
If you already know what to do, then it's time to do it. Participate in mutual aid, raise awareness in real life as well as online, participate in or train in self defense and emergency medical training classes.
#anarchy#chevron#fuel#oil#news#health#healthcare#cancer#research#anarchism#leftism#anarchist#leftist#communist#socialism#socialist#eco#green#earth
34K notes
·
View notes
Text
The study itself is titled, “Long-Term Regret and Satisfaction With Decision Following Gender-Affirming Mastectomy,” and sought to study the rate of regret and satisfaction after 2 years or more following gender affirming top surgery. The study’s results were stunning - in 139 surgery patients, the median regret score was 0/100 and the median satisfaction score was 5/5 with similar means as well. In other words… regret was virtually nonexistent in the study among post-op transgender people.
In fact, the regret was so low that many statistical techniques would not even work due to the uniformity of the numbers:
In this cross-sectional survey study of participants who underwent gender-affirming mastectomy 2.0 to 23.6 years ago, respondents had a high level of satisfaction with their decision and low rates of decisional regret. The median Satisfaction With Decision score was 5 on a 5-point scale, and the median decisional regret score was 0 on a 100-point scale. This extremely low level of regret and dissatisfaction and lack of variance in scores impeded the ability to determine meaningful associations among these results, clinical outcomes, and demographic information.
The numbers are in line with many other studies on satisfaction among transgender people. Detransition rates, for instance, have been pegged at somewhere between 1-3%, with transgender youth seeing very low detransition rates. Surgery regret is in line with at least 27 other studies that show a pooled regret rate of around 1% - compare this to regret rates from things like knee surgery, which can be as high as 30%. Gender affirming care appears to be extremely well tolerated with very low instances of regret when compared to other medically necessary care.
[...]
The intense conservative backlash, to the point of disputing reputable scientific journals, likely stems from the fact that reduced regret rates weaken a central narrative these figures have championed in legal and legislative spaces. Over the past three years, anti-trans entities have showcased political detransitioners, reminiscent of the ex-gay campaigns from the 1990s and 2000s, to argue that regrets over gender transition and detransition are widespread. Some have even asserted detransition rates of up to 80%, a claim that has been broadly debunked. Yet, research consistently struggles to find substantial evidence supporting this narrative. The rarity of detransition and regret is underscored by Florida's inability to enlist a single resident to bear witness against a lawsuit challenging the state's ban on gender-affirming care.
19K notes
·
View notes