#Suisse Works
Text

TOLIX
#TOLIX#design#studio#objects#manufacture#assises#chaises#fauteuils#tabourets#rangements#tables#shop#typography#type#typeface#font#Suisse Works#2024#Week 06#website#web design#inspire#inspiration#happywebdesign
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
I’M STARTING THE PROCESS OF GETTING MY SWISS PASSPORT BABYYY🥰🥰🥰
#slay#passport lottery#suisse#my french needs to improve asap#oui oui#mec#bien sur#i love a challenge#i hope i don’t get interviewed by cops#i’m gonna have to pretend i’m not a socialist#ooh character work#exciting#i’ll dress up#i’ll wear my red mini skirt#just kidding#i will look professional#my french will be so good#angèle#stromae#vendredi sur mer#écoute chérie#let’s gooooo#traveling will be even easier#i won’t have to be terrified of losing my health insurance#i’ll get to see my family more#i’ll hopefully take better care of my parents#yayayay#third culture kid#wow it’s seven AM and the energy is way too high#i need to stop drinking caffeine
0 notes
Text

0 notes
Text
Supertrend Indicator: How to Use to Trade Binary Options
Supertrend Indicator: How to Use to Trade Binary Options
If you are looking for an easy-to-use trend-following indicator with some added features, look no further than SuperTrend. This indicator is plotted on prices and its placement indicates the current trend.
But picking trends isn’t the only use the Supertrend indicator has, you can also use it as either a support or resistance level.
In this post, I will not only teach you how the Supertrend…
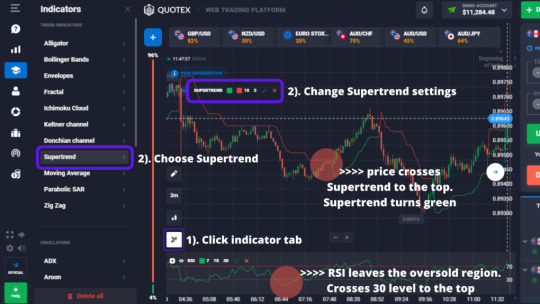
View On WordPress
#2 supertrend strategy#3 supertrend combination supertrends 2022 credit suisse#3 supertrend indicator strategy#3 supertrend scanner#3 supertrend strategy afl#3 supertrend strategy tradingview#3x supertrend indicator#4h supertrend#best combination with supertrend indicator#best settings for supertrend indicator#best supertrend indicator#best supertrend settings for nifty#best time frame for supertrend indicator#best way to use supertrend indicator#does supertrend indicator repaint#does supertrend indicator work#does supertrend work#forex supertrend indicator#formula for supertrend indicator#free charts with supertrend indicator#github supertrend python#gold supertrend#how accurate is supertrend#how accurate is supertrend indicator#how does supertrend indicator work#how does supertrend work#how is supertrend calculated#how is supertrend indicator calculated#how is the supertrend indicator calculated#how many super troopers are there
1 note
·
View note
Text
Credit Suisse CEO: Return to office is 'unrealistic'
Credit Suisse CEO: Return to office is ‘unrealistic’
Credit Suisse CEO: Return to office is ‘unrealistic’ | Fortune
You need to enable JavaScript to view this site.
Source link
View On WordPress
#credit suisse#credit suisse ceo thomas gottstein#credit suisse remote work#credit suisse return to office#credit suisse thomas gottstein#credit suisse work from home#thomas gottstein#wall street remote work#wall street return to office#wall street work from home
0 notes
Text
Credit Suisse CEO: Return to office is 'unrealistic'
Credit Suisse CEO: Return to office is ‘unrealistic’
Credit Suisse CEO: Return to office is ‘unrealistic’ | Fortune
You need to enable JavaScript to view this site.
Source link

View On WordPress
#credit suisse#credit suisse ceo thomas gottstein#credit suisse remote work#credit suisse return to office#credit suisse thomas gottstein#credit suisse work from home#thomas gottstein#wall street remote work#wall street return to office#wall street work from home
0 notes
Photo

Claude Monet
Claude Monet (1840-1926) was a French impressionist painter who transformed modern art with his emphasis on light brushstrokes, bright colours, and uncluttered nature. Famed for his landscapes and series of paintings that captured the same view in different momentary atmospheric conditions, Monet is heralded as one of the greatest and most influential artists of all time.
Early Life
Oscar-Claude Monet was born in Paris on 14 November 1840. The job of Monet's father, Claude-Adolphe, is not known except that it was a humble one and that the family often struggled financially. In 1845, the Monets moved to Le Havre on the northern coast of France where Claude-Adolphe worked in his brother-in-law's thriving wholesale grocery business. Oscar-Claude's favourite subject at school was art, and, fascinated by the boats in the busy harbour, he often sketched them. From 15, he made money by selling caricatures, some of which were displayed in a local shop window each Sunday, which became a minor local attraction. Monet's aunt, Marie-Jeanne Lecadre, was an amateur painter and she encouraged Oscar-Claude, introducing him to the artist Amand Gautier (1825-1894).
Another artistic influence was the landscape painter Eugène Boudin (1824-1898) and the pair went painting together en plein air (outdoors), as opposed to the traditional method of painting in the studio. Still only 17, Monet produced his first outdoor painting, View from Rouelles, in 1858. Monet later described the experience:
Boudin put up his easel and set to work…for me it was like the rending of a veil; I understood; I grasped what painting could be…my destiny as a painter opened up before me. If I have indeed become a painter; I owe it to Eugène Boudin…Gradually my eyes were opened and I understood nature.
(Hodge, 15)
In April 1859, Monet gathered together his savings from his caricatures sales and went to study art in Paris. He enrolled in the unconventional Académie Suisse and started to make friends with artists like Camille Pissarro (1830-1903) and Paul Cézanne (1839-1906). More caricatures helped eke out his savings.
In June 1861, Monet's studies were rudely interrupted by conscription into the French army. Joining the African Light Cavalry, he was shipped off to Algeria. The bright colours of North Africa left a lasting impression on the young artist, who continued to sketch when he could. Then, after contracting typhoid in 1862, Monet was invalided back home. Six months later, Aunt Marie-Jeanne bought her nephew out of the army. Now 22, he dropped the Oscar from his name and began to paint again. It was at Le Havre that Monet met the Dutch artist Johan Barthold Jongkind (1819-1891), whose work he already admired for its broad and bold brushstrokes and which captured effects of the weather on seascapes. As Monet noted, Jongkind "became from this moment, my true master; and it is to him that I owe the final development of my painter's eye" (Hodge, 19).
Continue reading...
46 notes
·
View notes
Text
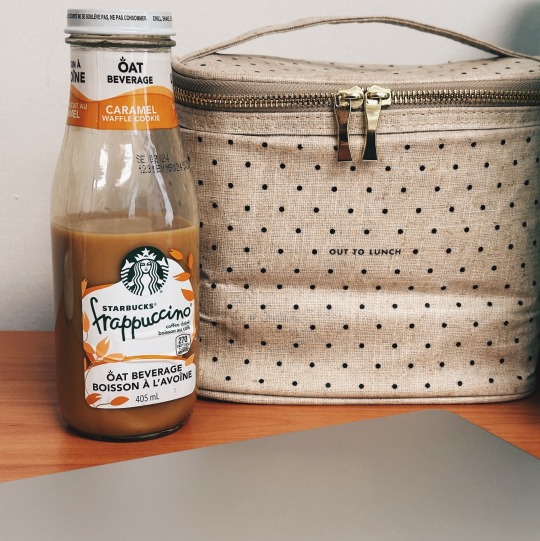


100 Days of Productivity [Day: 83] || 100 Jours de Productivité [Jour: 83]
this was my first year doing documentation for a company audit. I've never done this kind of stuff before but I'm exhausted. you don't really realize how hard back-tracking is when it's from before you started working there. that being said, everything went well, we've been cleared, & no one is getting fired or taken to court for fraud lol.
my sweet mum also sent me a care package & in it sent me some of my favourite bottled/canned coffee drinks. this made my cry so hard for some reason. though I love it here, I still struggle with missing home.
academic work:
-finish unit 1.2 - 1.4 of independent course
-listen to podcasts in slow french
-re-write course notes [focus on accents]
-start comparison notes between different French varieties [ie. Cajun, Belgian, Canadian, Swiss etc.]
freelance work:
-make ivory paper
-start putting together round-back book for binding
-take books out of press & cut signatures for new ones
office work:
-enter payroll
-start data sheet for last month's write-offs
-edit spreadsheets
-answer all emails
currently listening // Two Lives by MARION
C'était ma première année de documentation pour un audit d'entreprise. Je n'avais jamais fait ce genre de choses auparavant, mais je suis épuisée. on ne se rend pas vraiment compte à quel point il est difficile de rassembler des informations lorsqu'elles datent de plusieurs années avant que l'on ne commence à travailler dans une entreprise. cela dit, tout s'est bien passé, nous avons été blanchis, et personne n'a été licencié ou poursuivi en justice pour fraude lol.
ma douce maman m'a également envoyé un colis et, dans celui-ci, quelques-unes de mes boissons au café préférées en bouteille ou en boîte. cela m'a fait pleurer très fort pour une raison ou une autre. bien que j'aime être ici, j'ai toujours du mal à m'ennuyer de chez moi.
travail académique :
-Finir l'unité 1.2 - 1.4 du cours indépendant.
-écouter des podcasts en français lent
-réécrire les notes de cours [accent sur les accents] -commencer les notes de comparaison entre les différents français
-commencer les notes de comparaison entre les différentes variétés de français (cajun, belge, canadien, suisse, etc.).
travail en freelance :
-faire du papier ivoire
-commencer à assembler un livre à dos rond pour la reliure
-retirer les livres de la presse et découper les signatures pour de nouveaux livres
travail de bureau :
-saisir les salaires
-commencer la feuille de données pour les amortissements du mois dernier
- éditer les feuilles de calcul
-répondre à tous les courriels
chanson // Two Lives par MARION
#100 days of productivity#day 83#100dop#100 jours de productivité#jour 83#100jdp#studyblr#study blog#studyspo#study motivation#study aesthetic#bookish#gradblr#langblr#language learning
28 notes
·
View notes
Text


A hundred years ago the question of housing was as pressing as it is today: in view of the unbroken influx of people into the metropolitan areas housing construction is an issue cities, planners and architects intensely struggle with, especially because land costs and thus rents are constantly increasing as well. But the development of housing also is a story of innovation, imagination and progress: not so much in terms of extravaganza but in terms of models that others can build upon. This genealogy, at least in terms of Europe, has been comprehensively processed by Orsina Simona Pierini, Carmen Espegel, Dick van Gameren and Mark Swenarton in their weighty „Housing Atlas: Europe - 20th Century“, published late last year by Lund Humohries. In chronological order the atlas covers 87 projects ranging from Parker and Unwin’s Hampstead Garden Suburb in London to Herzog & De Meuron’s Rue des Suisses in Paris with each project being documented in a uniform set of plans and comprehensive illustrations. The dossiers are further contextualized by four essays penned by each of the contributing authors that address a wide range of topics related to housing in 20th century Europe, e.g. the relationship between the public and the private, the increasingly un-contextual designs of the postwar decades or the translation of past insights into new projects. To these more detailed essays Mark Swenarton provides a bracket by recounting the history of housing and by establishing a sequence of developments that facilitate the understanding of the projects featured.
With the present atlas the authors have written nothing less than a reference work on 20th century European housing: by establishing a canon of exemplary projects and supplementing them with excellent plan material the book qualifies for any professional’s library as a go-to source for inspirational housing designs. Highly recommended!
26 notes
·
View notes
Text





We can't see any Plymouth lettering. So it will probably be, since a Swiss car, a Valiant Signet assembled there by Automontage Schinznach AG in painstaking manual work with Swiss windows, carpets, seats, radiators etc. Powered by the 2.8 liter Slant Six engine, the car was sold somewhat pompously as a Chrysler, as the Plymouth brand was unknown there at first.
„MONTAGE SUISSE – Mehrwert durch Schweizer Montage“ („Added value through Swiss assembly") was their advertising slogan. And indeed, the rust prevention was significantly better than in the American models. Likewise, more reliable electrics were provided.
#plymouth#plymouth valiant#valiant signet#chysler valiant signet#Chrysler Valiant Montage Suisse#streetfightingcars#alfaromeole#autolandish#photographers on tumblr#vintage cars
68 notes
·
View notes
Text

MOUTHWASH Studio
#MOUTHWASH#design#studio#Los Angeles#portfolio#white#typography#type#typeface#font#Suisse Works#Suisse Intl#2024#Week 06#website#web design#inspire#inspiration#happywebdesign
2 notes
·
View notes
Text









La Galerie des Cotelles Set
A retexture by La Comtesse Zouboff — Original Mesh by @thejim07
At the very moment when Louis XIV wrote the first version of 《Manière de montre les jardins de Versailles》, he expressed his desire to recreate his words as images.
In 1688, he comissioned an outstanding set of 24 paintings describing the different groves in gardens with mythological allegories to be placed in the galerie at the Trianon de Marbre.
The ornamentation of the gallery linking Trianon to Trianon-sous-bois was entrusted to three painters between 1688 and 1689: Jean Cotelle painted twenty-one of the twenty-four canvases hung in this room, Etienne Allegrain two others, and Jean-Baptiste Martin.
This gallery, decorated around 1690, bears the name of the author of most of the paintings which appear there and which represent views of the groves of Versailles and Trianon, embellished with mythological figures.
This set remained in place until the First Empire. Napoleon I considered replacing them with paintings to his glory. The works will return to their original location in 1913 after being restored to 《La Colection Royale》 by Louis Philippe and can be seen there to this day.
-------------------------------------------------------
This set contains 24 paintings with the original frame swatches, fully recolourable. They are:
View of the Amphitheater of the Grove of the Théâtre d'Eau with the Toilette of Psyche.
View of the Bassin du Dragon and the Gutter of the Neptune Fountain with Apollo Slaying the Serpent Python.
View of the Colonnade Grove with Apollo Served by the Nymphs.
View of the Entrance of the Labyrinth Grove with Nymphs and Cupid Catching Birds in their Nets.
View of the Fountain of the Fifty-Two Jets, or Plat-Fond at the Trianon with Mars and Venus.
View of the Grove of l'Encelade with Jupiter Slaying Enceladus the Giant with the Feast of Lycaon.
View of the Grove of L'Étoile or la Montagne d'Eau with Diana Saving Arethusa from Alpheus.
View of the Grove of the Arc de Triomphe Towards the Fountain of La France Triomphante with Nymphs Chaining Captives.
View of the Grove of the Arc de Triomphe with Venus and Adonis on a Chariot Driven by Cupid.
View of the Grove of the Baths of Apollo or des Dômes with Diana and her Nymphs.
View of the Grove of the Labyrinth Showing the Fountain of the Fight of the Animals and the Two Fountains of the Fox and the Crane with Diana and the Nymphs.
View of the Grove of the Salle de Bal with Armide Crowning Renaud.
View of the Grove of the Théâtre d'Eau with the Toilette of Psyche.
View of the Marais or Chêne-Vert Grove with Nymphs Playing Various Games.
View of the Neptune Fountain, the Bassin du Dragon and the Allée d'Eau with the Judgement of Paris.
View of the Orangerie and the Palace from the Pièce d'Eau des Suisses with the Abduction of Helen of Troy.
View of the Orangerie of Versailles and the Pièce d'Eau des Suisses with Vertumnus and Pomona.
View of the Parterre d'Eau with the Apotheosis of Venus.
View of the Parterres of the Trianon de Marbre with Zephyrus and Sleeping Flora
View of the Trois-Fontaines Grove with Garden Loves.
View of the Trois-Fontaines Grove with Venus and the Nymphs.
View of the Feast or Council Room Grove in the Palace of Versailles.
View of the Grove of the Miroir d'Eau Fountain and the Île-Royale in the Palace of Versailles.
Perspective view of the Grove of the Galerie des Antiques.
Found under decor > paintings for 1.850§
(you can just search for "Cotelle" using the catalog search mod to find the entire ser much easier!)
Retextured from:"The virgin of the Rosary" found here
Disclaimer!
All of the paintings shown here aren't as blurry as in the screenshots and its colors are more vibrant in-game!
Cc shown here:
Walls, door and bench by @thejim07
Floor by @martassimsbookcc
Windows by @missyzim
Chandelier and garland by @hydrangeachainsaw
Pediment by Mutske (TSR)
Consoles by ShinoKCR (TSR)

Drive
(Sims3Pack | Package)
(Useful tags below)
@joojconverts @ts3history @ts3historicalccfinds @deniisu-sims @katsujiiccfinds @gifappels-stuff
-------------------------------------------------------
#the sims 3#ts3#s3cc#sims 3#sims 3 cc#sims 3 download#sims 3 decor#sims 3 paintings#baroque#trianon#louis xiv#palace of versailles#wall decor
76 notes
·
View notes
Text
Warning signs of the instability of the global financial system abounded in the months leading up to the 2008 Lehman Brothers crash. Among these early signs were the astounding revelations about UBS, the world’s largest private bank, by Stephanie Gibaud, who was employee at the bank’s French division. Gibaud refused instructions given to her and other employees to delete all their company files. In doing so, she helped reveal a vast web of corruption and fraud linking UBS to a shadowy tax evasion scheme. More than 15 years later, Gibaud has endured harassment, professional ostracization, lawsuits, and threats. She joins The Chris Hedges Report to speak on her ordeal and the extent of corruption in the international banking system.
Chris Hedges: Stephanie Gibaud in June, 2008, was ordered by one of her managers at the UBS Bank in Paris, to destroy all her computer files that related to customers with offshore accounts in Switzerland. The order came in the wake of the 2007 American banker, Bradley Birkenfeld’s disclosure of client information to the US Department of Justice, which suggested that UBS was facilitating massive tax evasion schemes for its American clients, which ultimately led to a penalty of $780 million. Swiss banks have long been havens for those seeking to avoid taxes. In 2014, for example, Credit Suisse, which would also plead guilty to sheltering money for its clients so they could avoid paying taxes, had to pay $2.6 billion in penalties.
Gibaud, however, was the only bank employee at UBS who refused to delete her files. She protested to UBS management and French regulators. Her documents would eventually help to identify 38,000 offshore bank accounts amounting to $12 billion. UBS responded by trying to fire her as part of a mass redundancy of 100 employees during the 2008 financial crisis. The French Ministry of Work intervened, but her life at UBS became excruciating. She suffered harassment and discrimination along with social and professional isolation. She endured constant anxiety and depression. UBS fired her finally in 2012. She was sued for defamation by the bank after writing her book, The Woman Who Knew Too Much, part of a series of lawsuits that plague her to this day.
She requested compensation totaling 3.5 million euros and the judge gave her 4,500 euros, which barely covered her legal fees. UBS was eventually forced to pay a record fine in 2019 of $4.9 billion, but Gibaud found herself financially ruined and blacklisted from the financial sector where she had spent her career. The French legal system does not compensate whistleblowers, unlike the US. The Commodities Future Trading Commission, for example, recently awarded an anonymous whistleblower around $200 million for providing information about Deutsche Bank’s manipulation of the LIBOR benchmark. Birkenfeld, who exposed UBS’s offshore accounts for American clients, was handed a check from the US Treasury for $104 million, minus taxes. Gibaud is currently battling in the French courts to become the first legally recognized whistleblower, which could pave the way for greater protection and compensation.
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
Stage 7 of La Vuelta Feminina was almost tailor-made for Marianne Vos (Visma Lease-a-Bike), an uphill drag after a long day in the cross-winds. What can we say about the greatest of all time, she knows how to get there safely and has the snap to finish. And her team controlled the breakaways, including a decently strong one spurred by Olympic champ Anna Kiesenhofer (Roland).

Vos was in good position heading into the final left-hander, right behind Elisa Longo Borghini (Lidl-Trek). The group was headed by Kristen Faulkner (EF Education-Cannondale), who had a nice lead-out from teammate Alison Jackson and then hammered the climb. Faulkner would take second on the stage, despite doing a lot of work on the front. Her climbing ability reminds us that she took second in the Tour de Suisse in 2022. It's nice to see such a new team like EF so active in this Vuelta.
Demi Vollering (SD Worx-Protime) started out of position (what is going on with that team?) but closed to fourth on the stage, right behind ELB, so the GC is unchanged going into the final mountaintop stage.
#wwt#womensworldtour#bikegirls#girlsonbikes#lidl-trek#sdworx#marianne vos#demi vollering#elisa longo borghini#Kristen Faulkner#EF Education Cannondale#Alison Jackson#Anna Kiesenhofer#Roland
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
[A]bout two third of the Swiss population visited the “Village noir” in Geneva. How is it possible that [...] the exhibition of 200 African people that two million people visited has fallen into oblivion? [...] Today, Geneva is considered one of the capitals of [so-called] [”]human rights[”]. Back in 1896, during the Swiss Second National Exhibition, it hosted a human zoo. There are very few visible references to it, except for one street called after its corresponding “white” exhibition, the “Village Suisse”. However, several researchers’ archival work helped unearth the history of the first Swiss “Village noir”. Inhabited by more than 200 individuals from Senegal, the village was situated a few streets from the city’s central square, the Plaine de Plainpalais. For six months, paying visitors observed these “actors” living their lives. Their religious ceremonies were advertised as public events. Tourists could take pictures with the African troupe and walk around their dwellings. [...]
Far from being a Swiss peculiarity, human zoos were spread around the West. Human exhibitions were a form of entertainment [...] [popularized] in the early 19th century in Great Britain. [...] [O]ne of the most famous shows was Sara Baartman, the “Hottenton Venus”. [...] [S]he was brought to Europe from South Africa to participate in an exhibition. Such “freak shows” spread around Europe and North America [...]. [I]n the late 19th century [...] shows became part of national and colonial exhibitions. The first ethnic exhibition of Nubians occurred in 1877 in Paris [...]. For the ticket-buying public, the experience was comparable to a visit to a regular zoo; it was about observing “exotic animals”.
As it often happens with animals, organisers re-created the subjects’ “natural habitat” [...]. The setting was constructed to perform authenticity. On the one hand, the civilisational discourse justifying colonial expansion and domination exaggerated the living representation and exhibition of the “savage” in need of enlightenment. On the other hand, the alleged brutality of the “native” was displayed through the mise-en-scène of their “primitive life”. These exhibitions did not present savagery; they invented a specific kind, which prepared the ground and fuelled further expansions and the ruling of “barbarian” and “uncivilised” societies. [...] All activities were meant to nourish Westerners’ enthusiasm for the exotic [...].
The turn of the century was among the highest points of scientific racism.
This was when the pseudo-scientific attempts to create a superior race thrived within Western anthropology and biology academic departments. For eugenicists, human zoos provided ‘samples’ for racist theories. During the Geneva National Exposition of 1896, Emile Yung gave a conference where he presented 15 people from the “Village noir”. He compared their skin colour and skull size to those of a Genevan. This process aimed to demonstrate how the size of the skull affected the level of civilisation and mental capacities. These ideas were spread among schoolteachers and helped crystallise and expand racist stereotypes. [...] Visitors were presented with an invented representation of Africa [...].
Moreover, as Patricia Purtschert of the University of Bern suggests, evolutionism and racist human-development theories at the core of the exhibitions had clear educational goals.
Thus, scientific racism developed within academia went hand in hand with popular racism: human zoos were places where these two faces of the same coin met. [...]
Indeed, Swiss scientists were active in shaping colonial mentalities. [...] Unlike other countries, Switzerland did not stop its human exhibitions during the interwar period. Until the 1960s, the national circus Knie presented the “Völkerschauen”. It included the display of [”]Eskimos[”], Catholic Indians, “mysterious Egyptians” or people with albinism. [...]
---
All text above by: Letizia Gaja Pinoja. “Dehumanisation, animalisation: Inside the terrible world of Swiss human zoos.” The Conversation. 23 June 2023. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me.]
39 notes
·
View notes
Text

Footnotes 1 - 100
[1] Origin of Species, chap. iii.
[2] Nineteenth Century, Feb. 1888, p. 165.
[3] Leaving aside the pre-Darwinian writers, like Toussenel, Fée, and many others, several works containing many striking instances of mutual aid — chiefly, however, illustrating animal intelligence were issued previously to that date. I may mention those of Houzeau, Les facultés etales des animaux, 2 vols., Brussels, 1872; L. Büchner’s Aus dem Geistesleben der Thiere, 2nd ed. in 1877; and Maximilian Perty’s Ueber das Seelenleben der Thiere, Leipzig, 1876. Espinas published his most remarkable work, Les Sociétés animales, in 1877, and in that work he pointed out the importance of animal societies, and their bearing upon the preservation of species, and entered upon a most valuable discussion of the origin of societies. In fact, Espinas’s book contains all that has been written since upon mutual aid, and many good things besides. If I nevertheless make a special mention of Kessler’s address, it is because he raised mutual aid to the height of a law much more important in evolution than the law of mutual struggle. The same ideas were developed next year (in April 1881) by J. Lanessan in a lecture published in 1882 under this title: La lutte pour l’existence et l’association pour la lutte. G. Romanes’s capital work, Animal Intelligence, was issued in 1882, and followed next year by the Mental Evolution in Animals. About the same time (1883), Büchner published another work, Liebe und Liebes-Leben in der Thierwelt, a second edition of which was issued in 1885. The idea, as seen, was in the air.
[4] Memoirs (Trudy) of the St. Petersburg Society of Naturalists, vol. xi. 1880.
[5] See Appendix I.
[6] George J. Romanes’s Animal Intelligence, 1st ed. p. 233.
[7] Pierre Huber’s Les fourmis indigëes, Génève, 1861; Forel’s Recherches sur les fourmis de la Suisse, Zurich, 1874, and J.T. Moggridge’s Harvesting Ants and Trapdoor Spiders, London, 1873 and 1874, ought to be in the hands of every boy and girl. See also: Blanchard’s Métamorphoses des Insectes, Paris, 1868; J.H. Fabre’s Souvenirs entomologiques, Paris, 1886; Ebrard’s Etudes des mœurs des fourmis, Génève, 1864; Sir John Lubbock’s Ants, Bees, and Wasps, and so on.
[8] Forel’s Recherches, pp. 244, 275, 278. Huber’s description of the process is admirable. It also contains a hint as to the possible origin of the instinct (popular edition, pp. 158, 160). See Appendix II.
[9] The agriculture of the ants is so wonderful that for a long time it has been doubted. The fact is now so well proved by Mr. Moggridge, Dr. Lincecum, Mr. MacCook, Col. Sykes, and Dr. Jerdon, that no doubt is possible. See an excellent summary of evidence in Mr. Romanes’s work. See also Die Pilzgaerten einiger Süd-Amerikanischen Ameisen, by Alf. Moeller, in Schimper’s Botan. Mitth. aus den Tropen, vi. 1893.
[10] This second principle was not recognized at once. Former observers often spoke of kings, queens, managers, and so on; but since Huber and Forel have published their minute observations, no doubt is possible as to the free scope left for every individual’s initiative in whatever the ants do, including their wars.
[11] H.W. Bates, The Naturalist on the River Amazons, ii. 59 seq.
[12] N. Syevertsoff, Periodical Phenomena in the Life of Mammalia, Birds, and Reptiles of Voronèje, Moscow, 1855 (in Russian).
[13] A. Brehm, Life of Animals, iii. 477; all quotations after the French edition.
[14] Bates, p. 151.
[15] Catalogue raisonné des oiseaux de la faune pontique, in Démidoff’s Voyage; abstracts in Brehm, iii. 360. During their migrations birds of prey often associate. One flock, which H. Seebohm saw crossing the Pyrenees, represented a curious assemblage of “eight kites, one crane, and a peregrine falcon” (The Birds of Siberia, 1901, p. 417).
[16] Birds in the Northern Shires, p. 207.
[17] Max. Perty, Ueber das Seelenleben der Thiere (Leipzig, 1876), pp. 87, 103.
[18] G. H. Gurney, The House-Sparrow (London, 1885), p. 5.
[19] Dr. Elliot Couës, Birds of the Kerguelen Island, in Smithsonian Miscellaneous Collections, vol. xiii. No. 2, p. 11.
[20] Brehm, iv. 567.
[21] As to the house-sparrows, a New Zealand observer, Mr. T.W. Kirk, described as follows the attack of these “impudent” birds upon an “unfortunate” hawk. — “He heard one day a most unusual noise, as though all the small birds of the country had joined in one grand quarrel. Looking up, he saw a large hawk (C. gouldi — a carrion feeder) being buffeted by a flock of sparrows. They kept dashing at him in scores, and from all points at once. The unfortunate hawk was quite powerless. At last, approaching some scrub, the hawk dashed into it and remained there, while the sparrows congregated in groups round the bush, keeping up a constant chattering and noise” (Paper read before the New Zealand Institute; Nature, Oct. 10, 1891).
[22] Brehm, iv. 671 seq.
[23] R. Lendenfeld, in Der zoologische Garten, 1889.
[24] Syevettsoff’s Periodical Phenomena, p. 251.
[25] Seyfferlitz, quoted by Brehm, iv. 760.
[26] The Arctic Voyages of A.E. Nordenskjöld, London, 1879, p. 135. See also the powerful description of the St. Kilda islands by Mr. Dixon (quoted by Seebohm), and nearly all books of Arctic travel.
[27] See Appendix III.
[28] Elliot Couës, in Bulletin U.S. Geol. Survey of Territories, iv. No. 7, pp. 556, 579, etc. Among the gulls (Larus argentatus), Polyakoff saw on a marsh in Northern Russia, that the nesting grounds of a very great number of these birds were always patrolled by one male, which warned the colony of the approach of danger. All birds rose in such case and attacked the enemy with great vigour. The females, which had five or six nests together On each knoll of the marsh, kept a certain order in leaving their nests in search of food. The fledglings, which otherwise are extremely unprotected and easily become the prey of the rapacious birds, were never left alone (“Family Habits among the Aquatic Birds,” in Proceedings of the Zool. Section of St. Petersburg Soc. of Nat., Dec. 17, 1874).
[29] Brehm Father, quoted by A. Brehm, iv. 34 seq. See also White’s Natural History of Selborne, Letter XI.
[30] Dr. Couës, Birds of Dakota and Montana, in Bulletin U.S. Survey of Territories, iv. No. 7.
[31] It has often been intimated that larger birds may occasionally transport some of the smaller birds when they cross together the Mediterranean, but the fact still remains doubtful. On the other side, it is certain that some smaller birds join the bigger ones for migration. The fact has been noticed several times, and it was recently confirmed by L. Buxbaum at Raunheim. He saw several parties of cranes which had larks flying in the midst and on both sides of their migratory columns (Der zoologische Garten, 1886, p. 133).
[32] H. Seebohm and Ch. Dixon both mention this habit.
[33] The fact is well known to every field-naturalist, and with reference to England several examples may be found in Charles Dixon’s Among the Birds in Northern Shires. The chaffinches arrive during winter in vast flocks; and about the same time, i.e. in November, come flocks of bramblings; redwings also frequent the same places “in similar large companies,” and so on (pp. 165, 166).
[34] S.W. Baker, Wild Beasts, etc., vol. i. p. 316.
[35] Tschudi, Thierleben der Alpenwelt, p. 404.
[36] Houzeau’s Études, ii. 463.
[37] For their hunting associations see Sir E. Tennant’s Natural History of Ceylon, quoted in Romanes’s Animal Intelligence, p. 432.
[38] See Emil Hüter’s letter in L. Büchner’s Liebe.
[39] See Appendix IV.
[40] With regard to the viscacha it is very interesting to note that these highly-sociable little animals not only live peaceably together in each village, but that whole villages visit each other at nights. Sociability is thus extended to the whole species — not only to a given society, or to a nation, as we saw it with the ants. When the farmer destroys a viscacha-burrow, and buries the inhabitants under a heap of earth, other viscachas — we are told by Hudson — “come from a distance to dig out those that are buried alive” (l.c., p. 311). This is a widely-known fact in La Plata, verified by the author.
[41] Handbuch für Jäger und Jagdberechtigte, quoted by Brehm, ii. 223.
[42] Buffon’s Histoire Naturelle.
[43] In connection with the horses it is worthy of notice that the quagga zebra, which never comes together with the dauw zebra, nevertheless lives on excellent terms, not only with ostriches, which are very good sentries, but also with gazelles, several species of antelopes, and gnus. We thus have a case of mutual dislike between the quagga and the dauw which cannot be explained by competition for food. The fact that the quagga lives together with ruminants feeding on the same grass as itself excludes that hypothesis, and we must look for some incompatibility of character, as in the case of the hare and the rabbit. Cf., among others, Clive Phillips-Wolley’s Big Game Shooting (Badminton Library), which contains excellent illustrations of various species living together in East Africa.
[44] Our Tungus hunter, who was going to marry, and therefore was prompted by the desire of getting as many furs as he possibly could, was beating the hill-sides all day long on horseback in search of deer. His efforts were not rewarded by even so much as one fallow deer killed every day; and he was an excellent hunter.
[45] According to Samuel W. Baker, elephants combine in larger groups than the “compound family.” “I have frequently observed,” he wrote, “in the portion of Ceylon known as the Park Country, the tracks of elephants in great numbers which have evidently been considerable herds that have joined together in a general retreat from a ground which they considered insecure” (Wild Beasts and their Ways, vol. i. p. 102).
[46] Pigs, attacked by wolves, do the same (Hudson, l.c.).
[47] Romanes’s Animal Intelligence, p. 472.
[48] Brehm, i. 82; Darwin’s Descent of Man, ch. iii. The Kozloff expedition of 1899–1901 have also had to sustain in Northern Thibet a similar fight.
[49] The more strange was it to read in the previously-mentioned article by Huxley the following paraphrase of a well-known sentence of Rousseau: “The first men who substituted mutual peace for that of mutual war — whatever the motive which impelled them to take that step — created society” (Nineteenth Century, Feb. 1888, p. 165). Society has not been created by man; it is anterior to man.
[50] Such monographs as the chapter on “Music and Dancing in Nature” which we have in Hudson’s Naturalist on the La Plata, and Carl Gross’ Play of Animals, have already thrown a considerable light upon an instinct which is absolutely universal in Nature.
[51] Not only numerous species of birds possess the habit of assembling together — in many cases always at the same spot — to indulge in antics and dancing performances, but W.H. Hudson’s experience is that nearly all mammals and birds (“probably there are really no exceptions”) indulge frequently in more or less regular or set performances with or without sound, or composed of sound exclusively (p. 264).
[52] For the choruses of monkeys, see Brehm.
[53] Haygarth, Bush Life in Australia, p. 58.
[54] To quote but a few instances, a wounded badger was carried away by another badger suddenly appearing on the scene; rats have been seen feeding a blind couple (Seelenleben der Thiere, p. 64 seq.). Brehm himself saw two crows feeding in a hollow tree a third crow which was wounded; its wound was several weeks old (Hausfreund, 1874, 715; Büchner’s Liebe, 203). Mr. Blyth saw Indian crows feeding two or three blind comrades; and so on.
[55] Man and Beast, p. 344.
[56] L.H. Morgan, The American Beaver, 1868, p. 272; Descent of Man, ch. iv.
[57] One species of swallow is said to have caused the decrease of another swallow species in North America; the recent increase of the missel-thrush in Scotland has caused the decrease of the song.thrush; the brown rat has taken the place of the black rat in Europe; in Russia the small cockroach has everywhere driven before it its greater congener; and in Australia the imported hive-bee is rapidly exterminating the small stingless bee. Two other cases, but relative to domesticated animals, are mentioned in the preceding paragraph. While recalling these same facts, A.R. Wallace remarks in a footnote relative to the Scottish thrushes: “Prof. A. Newton, however, informs me that these species do not interfere in the way here stated” (Darwinism, p. 34). As to the brown rat, it is known that, owing to its amphibian habits, it usually stays in the lower parts of human dwellings (low cellars, sewers, etc.), as also on the banks of canals and rivers; it also undertakes distant migrations in numberless bands. The black rat, on the contrary, prefers staying in our dwellings themselves, under the floor, as well as in our stables and barns. It thus is much more exposed to be exterminated by man; and we cannot maintain, with any approach to certainty, that the black rat is being either exterminated or starved out by the brown rat and not by man.
[58] “But it may be urged that when several closely-allied species inhabit the same territory, we surely ought to find at the present time many transitional forms.... By my theory these allied species are descended from a common parent; and during the process of modification, each has become adapted to the conditions of life of its own region, and has supplanted and exterminated its original parent-form and all the transitional varieties between its past and present states” (Origin of Species, 6th ed. p. 134); also p. 137, 296 (all paragraph “On Extinction”).
[59] According to Madame Marie Pavloff, who has made a special study of this subject, they migrated from Asia to Africa, stayed there some time, and returned next to Asia. Whether this double migration be confirmed or not, the fact of a former extension of the ancestor of our horse over Asia, Africa, and America is settled beyond doubt.
[60] The Naturalist on the River Amazons, ii. 85, 95.
[61] Dr. B. Altum, Waldbeschädigungen durch Thiere und Gegenmittel (Berlin, 1889), pp. 207 seq.
[62] Dr. B. Altum, ut supra, pp. 13 and 187.
[63] A. Becker in the Bulletin de la Société des Naturalistes de Moscou, 1889, p. 625.
[64] See Appendix V.
[65] Russkaya Mysl, Sept. 1888: “The Theory of Beneficency of Struggle for Life, being a Preface to various Treatises on Botanics, Zoology, and Human Life,” by an Old Transformist.
[66] “One of the most frequent modes in which Natural Selection acts is, by adapting some individuals of a species to a somewhat different mode of life, whereby they are able to seize unappropriated places in Nature” (Origin of Species, p. 145) — in other words, to avoid competition.
[67] See Appendix VI.
[68] Nineteenth Century, February 1888, p. 165
[69] The Descent of Man, end of ch. ii. pp. 63 and 64 of the 2nd edition.
[70] Anthropologists who fully endorse the above views as regards man nevertheless intimate, sometimes, that the apes live in polygamous families, under the leadership of “a strong and jealous male.” I do not know how far that assertion is based upon conclusive observation. But the passage from Brehm’s Life of Animals, which is sometimes referred to, can hardly be taken as very conclusive. It occurs in his general description of monkeys; but his more detailed descriptions of separate species either contradict it or do not confirm it. Even as regards the cercopithèques, Brehm is affirmative in saying that they “nearly always live in bands, and very seldom in families” (French edition, p. 59). As to other species, the very numbers of their bands, always containing many males, render the “polygamous family” more than doubtful further observation is evidently wanted.
[71] Lubbock, Prehistoric Times, fifth edition, 1890.
[72] That extension of the ice-cap is admitted by most of the geologists who have specially studied the glacial age. The Russian Geological Survey already has taken this view as regards Russia, and most German specialists maintain it as regards Germany. The glaciation of most of the central plateau of France will not fail to be recognized by the French geologists, when they pay more attention to the glacial deposits altogether.
[73] Prehistoric Times, pp. 232 and 242.
[74] Bachofen, Das Mutterrecht, Stuttgart, 1861; Lewis H. Morgan, Ancient Society, or Researches in the Lines of Human Progress from Savagery through Barbarism to Civilization, New York, 1877; J.F. MacLennan, Studies in Ancient History, 1st series, new edition, 1886; 2nd series, 1896; L. Fison and A.W. Howitt, Kamilaroi and Kurnai, Melbourne. These four writers — as has been very truly remarked by Giraud Teulon, — starting from different facts and different general ideas, and following different methods, have come to the same conclusion. To Bachofen we owe the notion of the maternal family and the maternal succession; to Morgan — the system of kinship, Malayan and Turanian, and a highly gifted sketch of the main phases of human evolution; to MacLennan — the law of exogeny; and to Fison and Howitt — the cuadro, or scheme, of the conjugal societies in Australia. All four end in establishing the same fact of the tribal origin of the family. When Bachofen first drew attention to the maternal family, in his epoc.making work, and Morgan described the clan-organization, — both concurring to the almost general extension of these forms and maintaining that the marriage laws lie at the very basis of the consecutive steps of human evolution, they were accused of exaggeration. However, the most careful researches prosecuted since, by a phalanx of students of ancient law, have proved that all races of mankind bear traces of having passed through similar stages of development of marriage laws, such as we now see in force among certain savages. See the works of Post, Dargun, Kovalevsky, Lubbock, and their numerous followers: Lippert, Mucke, etc.
[75] See Appendix VII.
[76] For the Semites and the Aryans, see especially Prof. Maxim Kovalevsky’s Primitive Law (in Russian), Moscow, 1886 and 1887. Also his Lectures delivered at Stockholm (Tableau des origines et de l’évolution de la famille et de la propriété, Stockholm, 1890), which represents an admirable review of the whole question. Cf. also A. Post, Die Geschlechtsgenossenschaft der Urzeit, Oldenburg 1875.
[77] It would be impossible to enter here into a discussion of the origin of the marriage restrictions. Let me only remark that a division into groups, similar to Morgan’s Hawaian, exists among birds; the young broods live together separately from their parents. A like division might probably be traced among some mammals as well. As to the prohibition of relations between brothers and sisters, it is more likely to have arisen, not from speculations about the bad effects of consanguinity, which speculations really do not seem probable, but to avoid the too-easy precocity of like marriages. Under close cohabitation it must have become of imperious necessity. I must also remark that in discussing the origin of new customs altogether, we must keep in mind that the savages, like us, have their “thinkers” and savants — wizards, doctors, prophets, etc. — whose knowledge and ideas are in advance upon those of the masses. United as they are in their secret unions (another almost universal feature) they are certainly capable of exercising a powerful influence, and of enforcing customs the utility of which may not yet be recognized by the majority of the tribe.
[78] Col. Collins, in Philips’ Researches in South Africa, London, 1828. Quoted by Waitz, ii. 334.
[79] Lichtenstein’s Reisen im südlichen Afrika, ii. Pp. 92, 97. Berlin, 1811.
[80] Waitz, Anthropologie der Naturvolker, ii. pp. 335 seq. See also Fritsch’s Die Eingeboren Afrika’s, Breslau, 1872, pp. 386 seq.; and Drei Jahre in Süd Afrika. Also W. Bleck, A Brief Account of Bushmen Folklore, Capetown, 1875.
[81] Elisée Reclus, Géographie Universelle, xiii. 475.
[82] P. Kolben, The Present State of the Cape of Good Hope, translated from the German by Mr. Medley, London, 1731, vol. i. pp. 59, 71, 333, 336, etc.
[83] Quoted in Waitz’s Anthropologie, ii. 335 seq.
[84] The natives living in the north of Sidney, and speaking the Kamilaroi language, are best known under this aspect, through the capital work of Lorimer Fison and A.W. Howitt, Kamilaroi and Kurnaii, Melbourne, 1880. See also A.W. Howitt’s “Further Note on the Australian Class Systems,” in Journal of the Anthropological Institute, 1889, vol. xviii. p. 31, showing the wide extension of the same organization in Australia.
[85] The Folklore, Manners, etc., of Australian Aborigines, Adelaide, 1879, p. 11.
[86] Gray’s Journals of Two Expeditions of Discovery in North-West and Western Australia, London, 1841, vol. ii. pp. 237, 298.
[87] Bulletin de la Société d’Anthropologie, 1888, vol. xi. p. 652. I abridge the answers.
[88] Bulletin de la Société d’Anthropologie, 1888, vol. xi. p. 386.
[89] The same is the practice with the Papuas of Kaimani Bay, who have a high reputation of honesty. “It never happens that the Papua be untrue to his promise,” Finsch says in Neuguinea und seine Bewohner, Bremen, 1865, p. 829.
[90] Izvestia of the Russian Geographical Society, 1880, pp. 161 seq. Few books of travel give a better insight into the petty details of the daily life of savages than these scraps from Maklay’s notebooks.
[91] L.F. Martial, in Mission Scientifique au Cap Horn, Paris, 1883, vol. i. pp. 183–201.
[92] Captain Holm’s Expedition to East Greenland.
[93] In Australia whole clans have been seen exchanging all their wives, in order to conjure a calamity (Post, Studien zur Entwicklungsgeschichte des Familienrechts, 1890, p. 342). More brotherhood is their specific against calamities.
[94] Dr. H. Rink, The Eskimo Tribes, p. 26 (Meddelelser om Grönland, vol. xi. 1887).
[95] Dr. Rink, loc. cit. p. 24. Europeans, grown in the respect of Roman law, are seldom capable of understanding that force of tribal authority. “In fact,” Dr. Rink writes, “it is not the exception, but the rule, that white men who have stayed for ten or twenty years among the Eskimo, return without any real addition to their knowledge of the traditional ideas upon which their social state is based. The white man, whether a missionary or a trader, is firm in his dogmatic opinion that the most vulgar European is better than the most distinguished native.” — The Eskimo Tribes, p. 31.
[96] Dall, Alaska and its Resources, Cambridge, U.S., 1870.
[97] Dall saw it in Alaska, Jacobsen at Ignitok in the vicinity of the Bering Strait. Gilbert Sproat mentions it among the Vancouver indians; and Dr. Rink, who describes the periodical exhibitions just mentioned, adds: “The principal use of the accumulation of personal wealth is for periodically distributing it.” He also mentions (loc. cit. p. 31) “the destruction of property for the same purpose,’ (of maintaining equality).
[98] See Appendix VIII.
[99] Veniaminoff, Memoirs relative to the District of Unalashka (Russian), 3 vols. St. Petersburg, 1840. Extracts, in English, from the above are given in Dall’s Alaska. A like description of the Australians’ morality is given in Nature, xlii. p. 639.
[100] It is most remarkable that several writers (Middendorff, Schrenk, O. Finsch) described the Ostyaks and Samoyedes in almost the same words. Even when drunken, their quarrels are insignificant. “For a hundred years one single murder has been committed in the tundra;” “their children never fight;” “anything may be left for years in the tundra, even food and gin, and nobody will touch it;” and so on. Gilbert Sproat “never witnessed a fight between two sober natives” of the Aht Indians of Vancouver Island. “Quarreling is also rare among their children.” (Rink, loc. cit.) And so on.
#organization#revolution#mutual aid#anarchism#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#anarchy#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#climate change#anarchy works#environmentalism#environment#solarpunk#anti colonialism#a factor of evolution#petr kropotkin
16 notes
·
View notes