#amazon s3 tutorial
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
0 notes
Text
Amazon Simple Storage Service Tutorial | AWS S3 Bucket Explained with Example for Cloud Developer
Full Video Link https://youtube.com/shorts/7xbakEXjvHQ Hi, a new #video on #aws #simplestorageservice #s3bucket #cloudstorage is published on #codeonedigest #youtube channel. @java #java #awscloud @awscloud #aws @AWSCloudIndia #Cloud #
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is an object storage service that offers industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance. Customers of all sizes and industries can use Amazon S3 to store and protect any amount of data. Amazon S3 provides management features so that you can optimize, organize, and configure access to your data to meet your specific business,…

View On WordPress
#amazon s3#amazon s3 bucket#amazon s3 tutorial#amazon web services#aws#aws cloud#aws s3#aws s3 bucket#aws s3 bucket tutorial#aws s3 interview questions and answers#aws s3 object lock#aws s3 object lock governance mode#aws s3 object storage#aws s3 tutorial#aws storage services#cloud computing#s3 bucket#s3 bucket creation#s3 bucket in aws#s3 bucket policy#s3 bucket public access#s3 bucket tutorial#simple storage service (s3)
0 notes
Video
youtube
Complete Hands-On Guide: Upload, Download, and Delete Files in Amazon S3 Using EC2 IAM Roles
Are you looking for a secure and efficient way to manage files in Amazon S3 using an EC2 instance? This step-by-step tutorial will teach you how to upload, download, and delete files in Amazon S3 using IAM roles for secure access. Say goodbye to hardcoding AWS credentials and embrace best practices for security and scalability.
What You'll Learn in This Video:
1. Understanding IAM Roles for EC2: - What are IAM roles? - Why should you use IAM roles instead of hardcoding access keys? - How to create and attach an IAM role with S3 permissions to your EC2 instance.
2. Configuring the EC2 Instance for S3 Access: - Launching an EC2 instance and attaching the IAM role. - Setting up the AWS CLI on your EC2 instance.
3. Uploading Files to S3: - Step-by-step commands to upload files to an S3 bucket. - Use cases for uploading files, such as backups or log storage.
4. Downloading Files from S3: - Retrieving objects stored in your S3 bucket using AWS CLI. - How to test and verify successful downloads.
5. Deleting Files in S3: - Securely deleting files from an S3 bucket. - Use cases like removing outdated logs or freeing up storage.
6. Best Practices for S3 Operations: - Using least privilege policies in IAM roles. - Encrypting files in transit and at rest. - Monitoring and logging using AWS CloudTrail and S3 access logs.
Why IAM Roles Are Essential for S3 Operations: - Secure Access: IAM roles provide temporary credentials, eliminating the risk of hardcoding secrets in your scripts. - Automation-Friendly: Simplify file operations for DevOps workflows and automation scripts. - Centralized Management: Control and modify permissions from a single IAM role without touching your instance.
Real-World Applications of This Tutorial: - Automating log uploads from EC2 to S3 for centralized storage. - Downloading data files or software packages hosted in S3 for application use. - Removing outdated or unnecessary files to optimize your S3 bucket storage.
AWS Services and Tools Covered in This Tutorial: - Amazon S3: Scalable object storage for uploading, downloading, and deleting files. - Amazon EC2: Virtual servers in the cloud for running scripts and applications. - AWS IAM Roles: Secure and temporary permissions for accessing S3. - AWS CLI: Command-line tool for managing AWS services.
Hands-On Process: 1. Step 1: Create an S3 Bucket - Navigate to the S3 console and create a new bucket with a unique name. - Configure bucket permissions for private or public access as needed.
2. Step 2: Configure IAM Role - Create an IAM role with an S3 access policy. - Attach the role to your EC2 instance to avoid hardcoding credentials.
3. Step 3: Launch and Connect to an EC2 Instance - Launch an EC2 instance with the IAM role attached. - Connect to the instance using SSH.
4. Step 4: Install AWS CLI and Configure - Install AWS CLI on the EC2 instance if not pre-installed. - Verify access by running `aws s3 ls` to list available buckets.
5. Step 5: Perform File Operations - Upload files: Use `aws s3 cp` to upload a file from EC2 to S3. - Download files: Use `aws s3 cp` to download files from S3 to EC2. - Delete files: Use `aws s3 rm` to delete a file from the S3 bucket.
6. Step 6: Cleanup - Delete test files and terminate resources to avoid unnecessary charges.
Why Watch This Video? This tutorial is designed for AWS beginners and cloud engineers who want to master secure file management in the AWS cloud. Whether you're automating tasks, integrating EC2 and S3, or simply learning the basics, this guide has everything you need to get started.
Don’t forget to like, share, and subscribe to the channel for more AWS hands-on guides, cloud engineering tips, and DevOps tutorials.
#youtube#aws iamiam role awsawsaws permissionaws iam rolesaws cloudaws s3identity & access managementaws iam policyDownloadand Delete Files in Amazon#IAMrole#AWS#cloudolus#S3#EC2
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Journey to AWS Proficiency: Unveiling Core Services and Certification Paths
Amazon Web Services, often referred to as AWS, stands at the forefront of cloud technology and has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals leverage the power of the cloud. This blog serves as your comprehensive guide to understanding AWS, exploring its core services, and learning how to master this dynamic platform. From the fundamentals of cloud computing to the hands-on experience of AWS services, we'll cover it all. Additionally, we'll discuss the role of education and training, specifically highlighting the value of ACTE Technologies in nurturing your AWS skills, concluding with a mention of their AWS courses.

The Journey to AWS Proficiency:
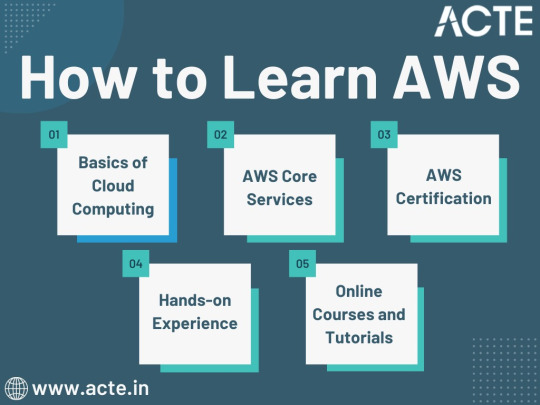
1. Basics of Cloud Computing:
Getting Started: Before diving into AWS, it's crucial to understand the fundamentals of cloud computing. Begin by exploring the three primary service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Gain a clear understanding of what cloud computing is and how it's transforming the IT landscape.
Key Concepts: Delve into the key concepts and advantages of cloud computing, such as scalability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and disaster recovery. Simultaneously, explore the potential challenges and drawbacks to get a comprehensive view of cloud technology.
2. AWS Core Services:
Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2): Start your AWS journey with Amazon EC2, which provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud. Learn how to create virtual servers, known as instances, and configure them to your specifications. Gain an understanding of the different instance types and how to deploy applications on EC2.
Simple Storage Service (S3): Explore Amazon S3, a secure and scalable storage service. Discover how to create buckets to store data and objects, configure permissions, and access data using a web interface or APIs.
Relational Database Service (RDS): Understand the importance of databases in cloud applications. Amazon RDS simplifies database management and maintenance. Learn how to set up, manage, and optimize RDS instances for your applications. Dive into database engines like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and more.
3. AWS Certification:
Certification Paths: AWS offers a range of certifications for cloud professionals, from foundational to professional levels. Consider enrolling in certification courses to validate your knowledge and expertise in AWS. AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner, AWS Certified Solutions Architect, and AWS Certified DevOps Engineer are some of the popular certifications to pursue.
Preparation: To prepare for AWS certifications, explore recommended study materials, practice exams, and official AWS training. ACTE Technologies, a reputable training institution, offers AWS certification training programs that can boost your confidence and readiness for the exams.
4. Hands-on Experience:
AWS Free Tier: Register for an AWS account and take advantage of the AWS Free Tier, which offers limited free access to various AWS services for 12 months. Practice creating instances, setting up S3 buckets, and exploring other services within the free tier. This hands-on experience is invaluable in gaining practical skills.
5. Online Courses and Tutorials:
Learning Platforms: Explore online learning platforms like Coursera, edX, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning. These platforms offer a wide range of AWS courses taught by industry experts. They cover various AWS services, architecture, security, and best practices.
Official AWS Resources: AWS provides extensive online documentation, whitepapers, and tutorials. Their website is a goldmine of information for those looking to learn more about specific AWS services and how to use them effectively.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) represents an exciting frontier in the realm of cloud computing. As businesses and individuals increasingly rely on the cloud for innovation and scalability, AWS stands as a pivotal platform. The journey to AWS proficiency involves grasping fundamental cloud concepts, exploring core services, obtaining certifications, and acquiring practical experience. To expedite this process, online courses, tutorials, and structured training from renowned institutions like ACTE Technologies can be invaluable. ACTE Technologies' comprehensive AWS training programs provide hands-on experience, making your quest to master AWS more efficient and positioning you for a successful career in cloud technology.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
AWS Mastery Unveiled: Your Step-by-Step Journey into Cloud Proficiency
In today's rapidly evolving tech landscape, mastering cloud computing is a strategic move for individuals and businesses alike. Amazon Web Services (AWS), as a leading cloud services provider, offers a myriad of tools and services to facilitate scalable and efficient computing. With AWS Training in Hyderabad, professionals can gain the skills and knowledge needed to harness the capabilities of AWS for diverse applications and industries. Whether you're a seasoned IT professional or a beginner eager to dive into the cloud, here's a step-by-step guide to learning and mastering Amazon AWS.

1. Start with AWS Documentation:
The foundation of your AWS journey begins with the official AWS documentation. This vast resource provides detailed information, tutorials, and guides for each AWS service. Take the time to familiarize yourself with the terminologies and fundamental concepts. Understanding the basics lays a solid groundwork for more advanced learning.
2. Enroll in AWS Training and Certification:
AWS provides a dedicated training and certification program to empower individuals with the skills required in today's cloud-centric environment. Explore the AWS Training and Certification portal, which offers a range of courses, both free and paid. Commence your AWS certification journey with the AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner, progressively advancing to specialized certifications aligned with your career goals.
3. Hands-On Practice with AWS Free Tier:
Theory is valuable, but hands-on experience is paramount. AWS Free Tier allows you to experiment with various services without incurring charges. Seize this opportunity to get practical, testing different services and scenarios. This interactive approach reinforces theoretical knowledge and builds your confidence in navigating the AWS console.
4. Explore Online Courses and Tutorials:
Several online platforms offer structured AWS courses. Websites like Coursera, Udemy, and A Cloud Guru provide video lectures, hands-on labs, and real-world projects. These courses cover a spectrum of topics, from foundational AWS concepts to specialized domains like AWS security and machine learning. To master the intricacies of AWS and unlock its full potential, individuals can benefit from enrolling in the Top AWS Training Institute. This training ensures that professionals gain the expertise needed to navigate the complexities of AWS, empowering them to contribute effectively to their organizations' digital transformation and success.
5. Build Projects and Apply Knowledge:
The true test of your AWS proficiency lies in applying your knowledge to real-world projects. Start small, perhaps by deploying a static website on Amazon S3. As you gain confidence, move on to more complex projects, such as configuring a virtual server on Amazon EC2 or creating a serverless application using AWS Lambda. Practical application solidifies your understanding and hones your problem-solving skills.
6. Join AWS Communities and Forums:
Learning is a collaborative effort. Joining AWS communities and forums allows you to connect with like-minded individuals, seek advice, and share your experiences. Platforms like the AWS Developer Forums provide a space for discussing challenges and learning from others' insights. Networking within the AWS community can open doors to valuable opportunities and collaborations.
7. Read AWS Whitepapers and Case Studies:
AWS regularly publishes whitepapers covering best practices, architecture recommendations, and real-world case studies. Delve into these resources to gain deeper insights into how AWS services are applied in diverse scenarios. Whitepapers provide a wealth of knowledge on topics such as security, scalability, and cost optimization.
8. Experiment with AWS CLI and SDKs:
Command Line Interface (CLI) proficiency is a valuable skill for any AWS practitioner. Familiarize yourself with the AWS CLI, as well as Software Development Kits (SDKs) for your preferred programming languages. Automating tasks through the CLI and integrating AWS services into your applications enhances efficiency and allows for more sophisticated configurations.
9. Attend AWS Events and Webinars:
Stay abreast of the latest AWS trends, updates, and best practices by attending AWS events, webinars, and conferences. These platforms often feature expert speakers, product announcements, and in-depth discussions on specific AWS topics. Engaging with industry leaders and experts provides valuable insights into the current state and future direction of AWS.
10. Stay Updated and Adapt:
The cloud computing landscape is dynamic, with AWS continually introducing new services and updates. Subscribe to AWS newsletters, follow AWS blogs, and listen to AWS-focused podcasts to stay informed about the latest developments. Continuous learning is key to adapting to the evolving cloud technology landscape.

In conclusion, mastering Amazon AWS is a journey that combines theoretical understanding, hands-on experience, and active participation in the AWS community. By following these ten steps, you can develop a comprehensive skill set that empowers you to leverage AWS effectively, whether you're building applications, optimizing processes, or advancing your career in the cloud.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Storing images in mySql DB - explanation + Uploadthing example/tutorial
(Scroll down for an uploadthing with custom components tutorial)
My latest project is a photo editing web application (Next.js) so I needed to figure out how to best store images to my database. MySql databases cannot store files directly, though they can store them as blobs (binary large objects). Another way is to store images on a filesystem (e.g. Amazon S3) separate from your database, and then just store the URL path in your db.
Why didn't I choose to store images with blobs?
Well, I've seen a lot of discussions on the internet whether it is better to store images as blobs in your database, or to have them on a filesystem. In short, storing images as blobs is a good choice if you are storing small images and a smaller amount of images. It is safer than storing them in a separate filesystem since databases can be backed up more easily and since everything is in the same database, the integrity of the data is secured by the database itself (for example if you delete an image from a filesystem, your database will not know since it only holds a path of the image). But I ultimately chose uploading images on a filesystem because I wanted to store high quality images without worrying about performance or database constraints. MySql has a variety of constraints for data sizes which I would have to override and operations with blobs are harder/more costly for the database.
Was it hard to set up?
Apparently, hosting images on a separate filesystem is kinda complicated? Like with S3? Or so I've heard, never tried to do it myself XD BECAUSE RECENTLY ANOTHER EASIER SOLUTION FOR IT WAS PUBLISHED LOL. It's called uploadthing!!!
What is uploadthing and how to use it?
Uploadthing has it's own server API on which you (client) post your file. The file is then sent to S3 to get stored, and after it is stored S3 returns file's URL, which then goes trough uploadthing servers back to the client. After that you can store that URL to your own database.

Here is the graph I vividly remember taking from uploadthing github about a month ago, but can't find on there now XD It's just a graphic version of my basic explanation above.
The setup is very easy, you can just follow the docs which are very straightforward and easy to follow, except for one detail. They show you how to set up uploadthing with uploadthing's own frontend components like <UploadButton>. Since I already made my own custom components, I needed to add a few more lines of code to implement it.
Uploadthing for custom components tutorial
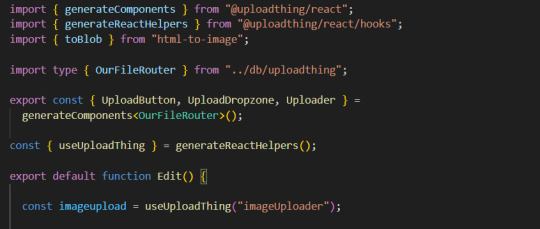
1. Imports
You will need to add an additional import generateReactHelpers (so you can use uploadthing functions without uploadthing components) and call it as shown below
2. For this example I wanted to save an edited image after clicking on the save button.
In this case, before calling the uploadthing API, I had to create a file and a blob (not to be confused with mySql blob) because it is actually an edited picture taken from canvas, not just an uploaded picture, therefore it's missing some info an uploaded image would usually have (name, format etc.). If you are storing an uploaded/already existing picture, this step is unnecessary. After uploading the file to uploadthing's API, I get it's returned URL and send it to my database.

You can find the entire project here. It also has an example of uploading multiple files in pages/create.tsx
I'm still learning about backend so any advice would be appreciated. Writing about this actually reminded me of how much I'm interested in learning about backend optimization c: Also I hope the post is not too hard to follow, it was really hard to condense all of this information into one post ;_;
#codeblr#studyblr#webdevelopment#backend#nextjs#mysql#database#nodejs#programming#progblr#uploadthing
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Creating a Scalable Amazon EMR Cluster on AWS in Minutes

Minutes to Scalable EMR Cluster on AWS
AWS EMR cluster
Spark helps you easily build up an Amazon EMR cluster to process and analyse data. This page covers Plan and Configure, Manage, and Clean Up.
This detailed guide to cluster setup:
Amazon EMR Cluster Configuration
Spark is used to launch an example cluster and run a PySpark script in the course. You must complete the “Before you set up Amazon EMR” exercises before starting.
While functioning live, the sample cluster will incur small per-second charges under Amazon EMR pricing, which varies per location. To avoid further expenses, complete the tutorial’s final cleaning steps.
The setup procedure has numerous steps:
Amazon EMR Cluster and Data Resources Configuration
This initial stage prepares your application and input data, creates your data storage location, and starts the cluster.
Setting Up Amazon EMR Storage:
Amazon EMR supports several file systems, but this article uses EMRFS to store data in an S3 bucket. EMRFS reads and writes to Amazon S3 in Hadoop.
This lesson requires a specific S3 bucket. Follow the Amazon Simple Storage Service Console User Guide to create a bucket.
You must create the bucket in the same AWS region as your Amazon EMR cluster launch. Consider US West (Oregon) us-west-2.
Amazon EMR bucket and folder names are limited. Lowercase letters, numerals, periods (.), and hyphens (-) can be used, but bucket names cannot end in numbers and must be unique across AWS accounts.
The bucket output folder must be empty.
Small Amazon S3 files may incur modest costs, but if you’re within the AWS Free Tier consumption limitations, they may be free.
Create an Amazon EMR app using input data:
Standard preparation involves uploading an application and its input data to Amazon S3. Submit work with S3 locations.
The PySpark script examines 2006–2020 King County, Washington food business inspection data to identify the top ten restaurants with the most “Red” infractions. Sample rows of the dataset are presented.
Create a new file called health_violations.py and copy the source code to prepare the PySpark script. Next, add this file to your new S3 bucket. Uploading instructions are in Amazon Simple Storage Service’s Getting Started Guide.
Download and unzip the food_establishment_data.zip file, save the CSV file to your computer as food_establishment_data.csv, then upload it to the same S3 bucket to create the example input data. Again, see the Amazon Simple Storage Service Getting Started Guide for uploading instructions.
“Prepare input data for processing with Amazon EMR” explains EMR data configuration.
Create an Amazon EMR Cluster:
Apache Spark and the latest Amazon EMR release allow you to launch the example cluster after setting up storage and your application. This may be done with the AWS Management Console or CLI.
Console Launch:
Launch Amazon EMR after login into AWS Management Console.
Start with “EMR on EC2” > “Clusters” > “Create cluster”. Note the default options for “Release,” “Instance type,” “Number of instances,” and “Permissions”.
Enter a unique “Cluster name” without <, >, $, |, or `. Install Spark from “Applications” by selecting “Spark”. Note: Applications must be chosen before launching the cluster. Check “Cluster logs” to publish cluster-specific logs to Amazon S3. The default destination is s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/logs. Replace with S3 bucket. A new ‘logs’ subfolder is created for log files.
Select your two EC2 keys under “Security configuration and permissions”. For the instance profile, choose “EMR_DefaultRole” for Service and “EMR_EC2_DefaultRole” for IAM.
Choose “Create cluster”.
The cluster information page appears. As the EMR fills the cluster, its “Status” changes from “Starting” to “Running” to “Waiting”. Console view may require refreshing. Status switches to “Waiting” when cluster is ready to work.
AWS CLI’s aws emr create-default-roles command generates IAM default roles.
Create a Spark cluster with aws emr create-cluster. Name your EC2 key pair –name, set –instance-type, –instance-count, and –use-default-roles. The sample command’s Linux line continuation characters () may need Windows modifications.
Output will include ClusterId and ClusterArn. Remember your ClusterId for later.
Check your cluster status using aws emr describe-cluster –cluster-id myClusterId>.
The result shows the Status object with State. As EMR deployed the cluster, the State changed from STARTING to RUNNING to WAITING. When ready, operational, and up, the cluster becomes WAITING.
Open SSH Connections
Before connecting to your operating cluster via SSH, update your cluster security groups to enable incoming connections. Amazon EC2 security groups are virtual firewalls. At cluster startup, EMR created default security groups: ElasticMapReduce-slave for core and task nodes and ElasticMapReduce-master for main.
Console-based SSH authorisation:
Authorisation is needed to manage cluster VPC security groups.
Launch Amazon EMR after login into AWS Management Console.
Select the updateable cluster under “Clusters”. The “Properties” tab must be selected.
Choose “Networking” and “EC2 security groups (firewall)” from the “Properties” tab. Select the security group link under “Primary node”.
EC2 console is open. Select “Edit inbound rules” after choosing “Inbound rules”.
Find and delete any public access inbound rule (Type: SSH, Port: 22, Source: Custom 0.0.0.0/0). Warning: The ElasticMapReduce-master group’s pre-configured rule that allowed public access and limited traffic to reputable sources should be removed.
Scroll down and click “Add Rule”.
Choose “SSH” for “Type” to set Port Range to 22 and Protocol to TCP.
Enter “My IP” for “Source” or a range of “Custom” trustworthy client IP addresses. Remember that dynamic IPs may need updating. Select “Save.”
When you return to the EMR console, choose “Core and task nodes” and repeat these steps to provide SSH access to those nodes.
Connecting with AWS CLI:
SSH connections may be made using the AWS CLI on any operating system.
Use the command: AWS emr ssh –cluster-id –key-pair-file <~/mykeypair.key>. Replace with your ClusterId and the full path to your key pair file.
After connecting, visit /mnt/var/log/spark to examine master node Spark logs.
The next critical stage following cluster setup and access configuration is phased work submission.
#AmazonEMRcluster#EMRcluster#DataResources#SSHConnections#AmazonEC2#AWSCLI#technology#technews#technologynews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
Getting Started with AWS: A Beginner’s Guide to Cloud Computing

In today’s digital-first world, cloud computing has transformed the way businesses and individuals operate. Amazon Web Services (AWS), a world leader in cloud solutions, is leading this change. For those just stepping into the world of technology or looking to boost their career, learning AWS is a great place to start. It’s a gateway to understanding cloud infrastructure, developing in-demand skills, and launching exciting projects.
What is AWS?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a cloud computing platform that offers over 200 fully featured services. These services cover computing, storage, databases, networking, analytics, artificial intelligence, security, and more. What sets AWS apart is its scalability and flexibility—users can easily increase or decrease resources as per their needs.
Why Should Beginners Learn AWS?
Learning AWS opens up numerous possibilities, both professionally and personally. Here's why it's worth your time:
High Demand Skills: AWS expertise is in high demand across industries, including finance, healthcare, retail, and IT.
Beginner-Friendly Learning Path: With the AWS Free Tier and tons of tutorials available, it's easier than ever to start learning.
Boosts Employability: Even basic AWS knowledge can make your resume stand out.
Supports Online Learning: Ideal for those seeking flexible and remote education opportunities.
Career Jumpstart: From freelancing to landing a job in cloud support or DevOps, AWS knowledge helps beginners start strong.
Essential AWS Services for Beginners
When getting started with AWS, focus on a few core services that provide a solid foundation:
Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud): This service allows you to create and manage virtual servers, a fundamental part of many cloud applications.
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service): A highly scalable storage service used for backup, archiving, and big data analytics.
AWS Lambda: Lets you run code without managing servers, great for beginners learning about serverless architecture.
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service): Makes database management easier by automating tasks like backups and scaling.
AWS IAM (Identity and Access Management): Essential for managing permissions and ensuring secure access to AWS resources.
How to Start Learning AWS
The beauty of AWS is that you can start learning today—no advanced degree or professional background required.
Sign Up for AWS Free Tier: It offers access to a range of services for free for 12 months. This is perfect for hands-on practice.
Enroll in Online Courses: Platforms like EasyShiksha.com offer structured courses that simplify AWS concepts for beginners.
Follow Tutorials and Guides: AWS itself offers learning paths, and so do many third-party educators.
Join Study Groups or Communities: Connect with others to ask questions, share resources, and stay motivated.
Participate in a Free Internship: Apply your skills in real-world projects by joining a free internship that focuses on AWS or cloud environments.
Benefits of AWS for Beginners
Learning AWS offers more than just technical know-how—it shapes your thinking and equips you with modern problem-solving skills.
Build and deploy real applications in a virtual environment
Understand modern DevOps workflows and automation
Learn about system design and cloud architecture
Access global resources and tools used by Fortune 500 companies
Unlock potential career paths in cloud support, DevOps, data engineering, and more
Participate in free internship programs to gain hands-on industry experience
Real-World Applications of AWS
AWS is not just for IT professionals—it’s everywhere. From startups building their first apps to enterprises running global operations, AWS powers it all.
Education: Schools and universities use AWS to deliver online courses, manage student data, and conduct virtual labs.
Healthcare: Secure patient records, data analytics, and telehealth platforms often run on AWS infrastructure.
E-commerce: Online stores host their websites, manage transactions, and scale customer support using AWS services.
Media & Entertainment: Video streaming platforms rely on AWS for content storage, delivery, and user engagement.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is the future, and AWS is a key to unlocking it. Whether you're a beginner exploring new tech skills, a student looking to enhance your resume, or someone seeking a career change, AWS offers a practical and accessible path forward. With tools, tutorials, and even free internship programs, AWS gives you the foundation to learn, grow, and succeed.
To get started with AWS learning and hands-on training, visit easyshiksha.com. EasyShiksha.com offers beginner-friendly online courses and career-boosting opportunities to help you take your first confident steps into the cloud.
0 notes
Text
AWS Certified Solutions Architect (SAA-C03): The Roadmap to Success
Introduction
The AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate (SAA-C03) certification is a valuable credential for IT professionals looking to validate their cloud computing expertise. This certification focuses on designing cost-effective, scalable, and secure solutions on the AWS platform. It is widely recognized in the industry and is ideal for those aiming to advance their careers in cloud architecture.

Who Should Take the SAA-C03 Exam?
This certification is designed for individuals who have experience working with AWS and want to enhance their cloud solution architecture skills. It is best suited for solutions architects, developers, DevOps engineers, IT consultants, and professionals who design and implement distributed systems on AWS.
Prerequisites for the Exam
Although there are no official prerequisites, AWS recommends at least one year of hands-on experience designing cloud solutions. Familiarity with AWS core services, networking, security, and best practices is beneficial. Candidates should also have a basic understanding of high-availability architectures and cost optimization strategies.
Exam Structure and Format
The SAA-C03 exam consists of multiple-choice and multiple-response questions. Candidates have 130 minutes to complete the exam, which costs $150. The exam can be taken online or at Pearson VUE testing centers. AWS does not disclose the exact passing score, but candidates should aim for at least 70%–75%.
Exam Domains and Topics
The exam is divided into four key domains:
1. Design Secure Architectures (30%)
This domain focuses on implementing AWS security best practices. Candidates should understand identity and access management (IAM), data encryption, and compliance frameworks.
2. Design Resilient Architectures (26%)
Candidates must demonstrate knowledge of high-availability and fault-tolerant systems. This includes using Auto Scaling, Load Balancers, and AWS services to ensure system reliability.
3. Design High-Performing Architectures (24%)
This section covers performance optimization, database selection, and choosing the right storage and networking solutions. It also includes caching strategies and content delivery networks (CDNs).
4. Design Cost-Optimized Architectures (20%)
This domain tests candidates on AWS cost management tools, pricing models, and methods for optimizing resource utilization to reduce costs.
Key AWS Services to Focus On
Understanding core AWS services is essential for passing the exam. Some important services include:
Compute: Amazon EC2, AWS Lambda, and Elastic Load Balancing.
Storage: Amazon S3, Amazon EBS, and Amazon Glacier.
Databases: Amazon RDS, Amazon DynamoDB, and Amazon Aurora.
Networking: VPC, Route 53, AWS CloudFront, and AWS Direct Connect.
Security: IAM, AWS KMS, AWS Shield, and AWS WAF.
Monitoring: Amazon CloudWatch, AWS Trusted Advisor, and AWS Cost Explorer.
Study Tips for the SAA-C03 Exam
1. Take AWS Official Training
AWS offers a variety of free and paid training courses to help candidates prepare. The AWS Skill Builder platform provides structured learning paths for certification preparation.
2. Gain Hands-On Experience
Practical knowledge is essential for understanding AWS services. Set up a free-tier AWS account and practice deploying and managing cloud resources.
3. Use Practice Exams
Taking mock tests helps candidates identify weak areas. Platforms like Udemy, Whizlabs, and Tutorials Dojo offer high-quality practice exams.
4. Join Study Groups and Online Communities
Engaging with AWS communities on LinkedIn, Reddit, and Discord can provide valuable insights and study resources.
5. Read AWS Whitepapers and Documentation
AWS provides whitepapers on best practices, security, and cost optimization. Reviewing these documents can improve understanding of key exam topics.
Career Benefits of the AWS SAA-C03 Certification
1. Higher Salary Potential
AWS-certified professionals earn competitive salaries, with average earnings exceeding $130,000 per year.
2. Industry Recognition
The certification is globally recognized and demonstrates expertise in cloud computing, making professionals more attractive to employers.
3. Expanded Job Opportunities
Holding this certification can open doors to roles such as AWS Solutions Architect, Cloud Engineer, and DevOps Engineer.
4. Enhanced Cloud Knowledge
The certification process helps candidates develop a deeper understanding of cloud architecture and AWS services.Learn More: AWS Certified Solutions Architect (SAA-C03)
0 notes
Text
Deploying a Vue.js Application to the Cloud with AWS S3
Deploying a Vue.js Application to the Cloud with AWS S3 Introduction In this tutorial, we will walk you through the process of deploying a Vue.js application to the cloud using Amazon Web Services (AWS) Simple Storage Service (S3). This will provide you with a scalable, secure, and cost-effective solution for hosting your Vue.js application. What you will learn How to create a Vue.js…
0 notes
Text
To get 100% on your first attempt at the Amazon CLF-C02 (AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner) exam, follow these steps:
1. Understand the Exam Structure
Domains Covered:
Cloud Concepts (24%)
Security and Compliance (30%)
Cloud Technology and Services (34%)
Billing, Pricing, and Support (12%)
Number of Questions: ~65 (Multiple-choice & Multiple-response)
Time Limit: 90 minutes
Passing Score: ~700/1000
2. Study the Right Resources
AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials Course (Free on AWS Training)
AWS Whitepapers:
AWS Well-Architected Framework
AWS Pricing Overview
AWS Security Best Practices
AWS FAQs (for services like EC2, S3, IAM, RDS, etc.)
AWS Skill Builder (practice tests & labs)
3. Take Practice Exams
Use AWS Official Practice Tests and Udemy / Whizlabs / Tutorials Dojo practice questions.
Analyze mistakes and review weak topics.
4. Hands-On Experience
Create a Free AWS Account and practice:
Launching an EC2 instance
Creating an S3 bucket
Configuring IAM users, groups, and policies
Exploring AWS Billing Dashboard
5. Exam Strategy
Read questions carefully (watch for tricky wording).
Eliminate incorrect choices before selecting your answer.
Manage your time well (1.5 minutes per question).
Mark for review if unsure and revisit before submitting.
Clearcatnet is a great resource for preparing for the AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner (CLF-C02) exam. They provide:
High-quality practice questions that closely match the real exam Detailed explanations for each answer Updated content aligned with AWS exam objectives Exam simulations to help you get comfortable with the format
Using ClearCat along with AWS official resources, whitepapers, and hands-on practice will boost your chances of scoring 100% on your first attempt
1 note
·
View note
Text
AWS Lambda Compute Service Tutorial for Amazon Cloud Developers
Full Video Link - https://youtube.com/shorts/QmQOWR_aiNI Hi, a new #video #tutorial on #aws #lambda #awslambda is published on #codeonedigest #youtube channel. @java @awscloud @AWSCloudIndia @YouTube #youtube @codeonedigest #codeonedigest #aws #amaz
AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that runs your code in response to events and automatically manages the underlying compute resources for you. These events may include changes in state such as a user placing an item in a shopping cart on an ecommerce website. AWS Lambda automatically runs code in response to multiple events, such as HTTP requests via Amazon API Gateway, modifications…

View On WordPress
#amazon lambda java example#aws#aws cloud#aws lambda#aws lambda api gateway#aws lambda api gateway trigger#aws lambda basic#aws lambda code#aws lambda configuration#aws lambda developer#aws lambda event trigger#aws lambda eventbridge#aws lambda example#aws lambda function#aws lambda function example#aws lambda function s3 trigger#aws lambda java#aws lambda server#aws lambda service#aws lambda tutorial#aws training#aws tutorial#lambda service
0 notes
Text
aws cloud,
aws cloud,
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is one of the leading cloud computing platforms, offering a wide range of services that enable businesses, developers, and organizations to build and scale applications efficiently. AWS provides cloud solutions that are flexible, scalable, and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for enterprises and startups alike.
Key Features of AWS Cloud
AWS offers an extensive range of features that cater to various computing needs. Some of the most notable features include:
Scalability and Flexibility – AWS allows businesses to scale their resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance without unnecessary costs.
Security and Compliance – With robust security measures, AWS ensures data protection through encryption, identity management, and compliance with industry standards.
Cost-Effectiveness – AWS follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model, reducing upfront capital expenses and providing cost transparency.
Global Infrastructure – AWS operates data centers worldwide, offering low-latency performance and high availability.
Wide Range of Services – AWS provides a variety of services, including computing, storage, databases, machine learning, and analytics.
Popular AWS Services
AWS offers numerous services across various categories. Some of the most widely used services include:
1. Compute Services
Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) – Virtual servers for running applications.
AWS Lambda – Serverless computing that runs code in response to events.
2. Storage Services
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) – Object storage for data backup and archiving.
Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store) – Persistent block storage for EC2 instances.
3. Database Services
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) – Managed relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server.
Amazon DynamoDB – A fully managed NoSQL database for fast and flexible data access.
4. Networking & Content Delivery
Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) – Secure cloud networking.
Amazon CloudFront – Content delivery network for faster content distribution.
5. Machine Learning & AI
Amazon SageMaker – A fully managed service for building and deploying machine learning models.
AWS AI Services – Includes tools like Amazon Rekognition (image analysis) and Amazon Polly (text-to-speech).
Benefits of Using AWS Cloud
Organizations and developers prefer AWS for multiple reasons:
High Availability – AWS ensures minimal downtime with multiple data centers and redundant infrastructure.
Enhanced Security – AWS follows best security practices, including data encryption, DDoS protection, and identity management.
Speed and Agility – With AWS, businesses can deploy applications rapidly and scale effortlessly.
Cost Savings – The pay-as-you-go model reduces IT infrastructure costs and optimizes resource allocation.
Getting Started with AWS
If you are new to AWS, follow these steps to get started:
Create an AWS Account – Sign up on the AWS website.
Choose a Service – Identify the AWS services that suit your needs.
Learn AWS Basics – Use AWS tutorials, documentation, and training courses.
Deploy Applications – Start small with free-tier resources and gradually scale.
Conclusion
AWS Cloud is a powerful and reliable platform that empowers businesses with cutting-edge technology. Whether you need computing power, storage, networking, or machine learning, AWS provides a vast ecosystem of services to meet diverse requirements. With its scalability, security, and cost efficiency, AWS continues to be a top choice for cloud computing solutions.
0 notes
Text
Elevate Your Career With AWS: A In-depth Guide to Becoming an AWS Expert
In the fast-paced and ever-evolving realm of modern technology, proficiency in Amazon Web Services (AWS) has emerged as an invaluable asset, a passport to the boundless opportunities of the digital age. AWS, the colossal titan of cloud computing, offers an extensive array of services that have revolutionized the way businesses operate, innovate, and scale in today's interconnected world. However, mastering AWS is not a mere task; it is a journey that calls for a structured approach, hands-on experience, and access to a treasure trove of reputable learning resources.

Welcome to the world of AWS mastery, where innovation knows no bounds, where your skills become the catalyst for transformative change. Your journey begins now, as we set sail into the horizon of AWS excellence, ready to explore the limitless possibilities that await in the cloud.
Step 1: Setting Sail - Sign Up for AWS
Your AWS voyage begins with a simple yet crucial step - signing up for an AWS account. Fortunately, AWS offers the Free Tier, a generous offering that grants limited free access to many AWS services for the first 12 months. This enables you to explore AWS, experiment with its services, and learn without incurring costs.
Step 2: Unveiling the Map - Official AWS Documentation
Before you embark on your AWS adventure, it's essential to understand the lay of the land. AWS provides extensive documentation for all its services. This documentation is a treasure of knowledge, offering insights into each service, its use cases, and comprehensive guides on how to configure and utilize them. It's a valuable resource that is regularly updated to keep you informed about the latest developments.
Step 3: Guided Tours - Online Courses and Tutorials
While solo exploration is commendable, guided tours can significantly enhance your learning experience. Enroll in online courses and tutorials offered by reputable platforms such as Coursera, Udemy, ACTE, or AWS Training and Certification. These courses often include video lectures, hands-on labs, and quizzes to reinforce your understanding. Consider specialized AWS training programs like those offered by ACTE Technologies, where expert-led courses can take your AWS skills to the next level.
Step 4: Raising the Flag - AWS Certification
Achieving AWS certification is akin to hoisting your flag of expertise in the AWS realm. AWS offers a range of certifications that validate your proficiency in specific AWS areas, including Solutions Architect, Developer, SysOps Administrator, and more. Preparing for these certifications provides in-depth knowledge, and there are study guides and practice exams available to aid your preparation.
Step 5: Hands-on Deck - Practical Experience
In the world of AWS, knowledge is best acquired through hands-on experience. Create AWS accounts designated for practice purposes, set up virtual machines (EC2 instances), configure storage (S3), and experiment with various AWS services. Building real projects is an effective way to solidify your understanding and showcase your skills.
Step 6: Navigating the AWS Console and CLI
As you progress, it's essential to be fluent in navigating AWS. Familiarize yourself with the AWS Management Console, a web-based interface for managing AWS resources. Additionally, learn to wield the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI), a powerful tool for scripting and automating tasks, giving you the agility to manage AWS resources efficiently.
Step 7: Joining the Crew - Community Engagement
Learning is often more enriching when you're part of a community. Join AWS-related forums and communities, such as the AWS subreddit and AWS Developer Forums. Engaging with others who are on their own AWS learning journeys can help you get answers to your questions, share experiences, and gain valuable insights.
Step 8: Gathering Wisdom - Blogs and YouTube Channels
Stay updated with the latest trends and insights in the AWS ecosystem by following AWS blogs and YouTube channels. These platforms provide tutorials, case studies, and deep dives into AWS services. Don't miss out on AWS re:Invent sessions, available on YouTube, which offer in-depth explorations of AWS services and solutions.
Step 9: Real-World Adventures - Projects
Application of your AWS knowledge to practical projects is where your skills truly shine. Whether it's setting up a website, creating a scalable application, or orchestrating a complex migration to AWS, hands-on experience is invaluable. Real-world projects not only demonstrate your capabilities but also prepare you for the challenges you might encounter in a professional setting.
Step 10: Staying on Course - Continuous Learning
The AWS landscape is ever-evolving, with new services and features being introduced regularly. Stay informed by following AWS news, subscribing to newsletters, and attending AWS events and webinars. Continuous learning is the compass that keeps you on course in the dynamic world of AWS.
Step 11: Guiding Lights - Mentorship
If possible, seek out a mentor with AWS experience. Mentorship provides valuable guidance and insights as you learn. Learning from someone who has navigated the AWS waters can accelerate your progress and help you avoid common pitfalls.

Mastering AWS is not a destination; it's a continuous journey. As you gain proficiency, you can delve into advanced topics and specialize in areas that align with your career goals. The key to mastering AWS lies in a combination of self-study, hands-on practice, and access to reliable learning resources.
In conclusion, ACTE Technologies emerges as a trusted provider of IT training and certification programs, including specialized AWS training. Their expert-led courses and comprehensive curriculum make them an excellent choice for those looking to enhance their AWS skills. Whether you aim to propel your career or embark on a thrilling journey into the world of cloud computing, ACTE Technologies can be your steadfast partner on the path to AWS expertise.
AWS isn't just a skill; it's a transformative force in the world of technology. It's the catalyst for innovation, scalability, and boundless possibilities. So, set sail on your AWS journey, armed with knowledge, practice, and the determination to conquer the cloud. The world of AWS awaits your exploration.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Role of the AWS Software Development Kit (SDK) in Modern Application Development
The Amazon Web Services (AWS) Software Development Kit (SDK) serves as a fundamental tool for developers aiming to create robust, scalable, and secure applications using AWS services. By streamlining the complexities of interacting with AWS's extensive ecosystem, the SDK enables developers to prioritize innovation over infrastructure challenges.
Understanding AWS SDK
The AWS SDK provides a comprehensive suite of software tools, libraries, and documentation designed to facilitate programmatic interaction with AWS services. By abstracting the intricacies of direct HTTP requests, it offers a more intuitive and efficient interface for tasks such as instance creation, storage management, and database querying.
The AWS SDK is compatible with multiple programming languages, including Python (Boto3), Java, JavaScript (Node.js and browser), .NET, Ruby, Go, PHP, and C++. This broad compatibility ensures that developers across diverse technical environments can seamlessly integrate AWS features into their applications.
Key Features of AWS SDK
Seamless Integration: The AWS SDK offers pre-built libraries and APIs designed to integrate effortlessly with AWS services. Whether provisioning EC2 instances, managing S3 storage, or querying DynamoDB, the SDK simplifies these processes with clear, efficient code.
Multi-Language Support: Supporting a range of programming languages, the SDK enables developers to work within their preferred coding environments. This flexibility facilitates AWS adoption across diverse teams and projects.
Robust Security Features: Security is a fundamental aspect of the AWS SDK, with features such as automatic API request signing, IAM integration, and encryption options ensuring secure interactions with AWS services.
High-Level Abstractions: To reduce repetitive coding, the SDK provides high-level abstractions for various AWS services. For instance, using Boto3, developers can interact with S3 objects directly without dealing with low-level request structures.
Support for Asynchronous Operations: The SDK enables asynchronous programming, allowing non-blocking operations that enhance the performance and responsiveness of high-demand applications.
Benefits of Using AWS SDK
Streamlined Development: By offering pre-built libraries and abstractions, the AWS SDK significantly reduces development overhead. Developers can integrate AWS services efficiently without navigating complex API documentation.
Improved Reliability: Built-in features such as error handling, request retries, and API request signing ensure reliable and robust interactions with AWS services.
Cost Optimization: The SDK abstracts infrastructure management tasks, allowing developers to focus on optimizing applications for performance and cost efficiency.
Comprehensive Documentation and Support: AWS provides detailed documentation, tutorials, and code examples, catering to developers of all experience levels. Additionally, an active developer community offers extensive resources and guidance for troubleshooting and best practices.
Common Use Cases
Cloud-Native Development: Streamline the creation of serverless applications with AWS Lambda and API Gateway using the SDK.
Data-Driven Applications: Build data pipelines and analytics platforms by integrating services like Amazon S3, RDS, or Redshift.
DevOps Automation: Automate infrastructure management tasks such as resource provisioning and deployment updates with the SDK.
Machine Learning Integration: Incorporate machine learning capabilities into applications by leveraging AWS services such as SageMaker and Rekognition.
Conclusion
The AWS Software Development Kit is an indispensable tool for developers aiming to fully leverage the capabilities of AWS services. With its versatility, user-friendly interface, and comprehensive features, it serves as a critical resource for building scalable and efficient applications. Whether you are a startup creating your first cloud-native solution or an enterprise seeking to optimize existing infrastructure, the AWS SDK can significantly streamline the development process and enhance application functionality.
Explore the AWS SDK today to unlock new possibilities in cloud-native development.
0 notes
Text
Build A Smarter Security Chatbot With Amazon Bedrock Agents

Use an Amazon Security Lake and Amazon Bedrock chatbot for incident investigation. This post shows how to set up a security chatbot that uses an Amazon Bedrock agent to combine pre-existing playbooks into a serverless backend and GUI to investigate or respond to security incidents. The chatbot presents uniquely created Amazon Bedrock agents to solve security vulnerabilities with natural language input. The solution uses a single graphical user interface (GUI) to directly communicate with the Amazon Bedrock agent to build and run SQL queries or advise internal incident response playbooks for security problems.
User queries are sent via React UI.
Note: This approach does not integrate authentication into React UI. Include authentication capabilities that meet your company's security standards. AWS Amplify UI and Amazon Cognito can add authentication.
Amazon API Gateway REST APIs employ Invoke Agent AWS Lambda to handle user queries.
User queries trigger Lambda function calls to Amazon Bedrock agent.
Amazon Bedrock (using Claude 3 Sonnet from Anthropic) selects between querying Security Lake using Amazon Athena or gathering playbook data after processing the inquiry.
Ask about the playbook knowledge base:
The Amazon Bedrock agent queries the playbooks knowledge base and delivers relevant results.
For Security Lake data enquiries:
The Amazon Bedrock agent takes Security Lake table schemas from the schema knowledge base to produce SQL queries.
When the Amazon Bedrock agent calls the SQL query action from the action group, the SQL query is sent.
Action groups call the Execute SQL on Athena Lambda function to conduct queries on Athena and transmit results to the Amazon Bedrock agent.
After extracting action group or knowledge base findings:
The Amazon Bedrock agent uses the collected data to create and return the final answer to the Invoke Agent Lambda function.
The Lambda function uses an API Gateway WebSocket API to return the response to the client.
API Gateway responds to React UI via WebSocket.
The chat interface displays the agent's reaction.
Requirements
Prior to executing the example solution, complete the following requirements:
Select an administrator account to manage Security Lake configuration for each member account in AWS Organisations. Configure Security Lake with necessary logs: Amazon Route53, Security Hub, CloudTrail, and VPC Flow Logs.
Connect subscriber AWS account to source Security Lake AWS account for subscriber queries.
Approve the subscriber's AWS account resource sharing request in AWS RAM.
Create a database link in AWS Lake Formation in the subscriber AWS account and grant access to the Security Lake Athena tables.
Provide access to Anthropic's Claude v3 model for Amazon Bedrock in the AWS subscriber account where you'll build the solution. Using a model before activating it in your AWS account will result in an error.
When requirements are satisfied, the sample solution design provides these resources:
Amazon S3 powers Amazon CloudFront.
Chatbot UI static website hosted on Amazon S3.
Lambda functions can be invoked using API gateways.
An Amazon Bedrock agent is invoked via a Lambda function.
A knowledge base-equipped Amazon Bedrock agent.
Amazon Bedrock agents' Athena SQL query action group.
Amazon Bedrock has example Athena table schemas for Security Lake. Sample table schemas improve SQL query generation for table fields in Security Lake, even if the Amazon Bedrock agent retrieves data from the Athena database.
A knowledge base on Amazon Bedrock to examine pre-existing incident response playbooks. The Amazon Bedrock agent might propose investigation or reaction based on playbooks allowed by your company.
Cost
Before installing the sample solution and reading this tutorial, understand the AWS service costs. The cost of Amazon Bedrock and Athena to query Security Lake depends on the amount of data.
Security Lake cost depends on AWS log and event data consumption. Security Lake charges separately for other AWS services. Amazon S3, AWS Glue, EventBridge, Lambda, SQS, and SNS include price details.
Amazon Bedrock on-demand pricing depends on input and output tokens and the large language model (LLM). A model learns to understand user input and instructions using tokens, which are a few characters. Amazon Bedrock pricing has additional details.
The SQL queries Amazon Bedrock creates are launched by Athena. Athena's cost depends on how much Security Lake data is scanned for that query. See Athena pricing for details.
Clear up
Clean up if you launched the security chatbot example solution using the Launch Stack button in the console with the CloudFormation template security_genai_chatbot_cfn:
Choose the Security GenAI Chatbot stack in CloudFormation for the account and region where the solution was installed.
Choose “Delete the stack”.
If you deployed the solution using AWS CDK, run cdk destruct –all.
Conclusion
The sample solution illustrates how task-oriented Amazon Bedrock agents and natural language input may increase security and speed up inquiry and analysis. A prototype solution using an Amazon Bedrock agent-driven user interface. This approach may be expanded to incorporate additional task-oriented agents with models, knowledge bases, and instructions. Increased use of AI-powered agents can help your AWS security team perform better across several domains.
The chatbot's backend views data normalised into the Open Cybersecurity Schema Framework (OCSF) by Security Lake.
#securitychatbot#AmazonBedrockagents#graphicaluserinterface#Bedrockagent#chatbot#chatbotsecurity#Technology#TechNews#technologynews#news#govindhtech
0 notes