#aws lambda function example
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
AWS Lambda Compute Service Tutorial for Amazon Cloud Developers
Full Video Link - https://youtube.com/shorts/QmQOWR_aiNI Hi, a new #video #tutorial on #aws #lambda #awslambda is published on #codeonedigest #youtube channel. @java @awscloud @AWSCloudIndia @YouTube #youtube @codeonedigest #codeonedigest #aws #amaz
AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that runs your code in response to events and automatically manages the underlying compute resources for you. These events may include changes in state such as a user placing an item in a shopping cart on an ecommerce website. AWS Lambda automatically runs code in response to multiple events, such as HTTP requests via Amazon API Gateway, modifications…

View On WordPress
#amazon lambda java example#aws#aws cloud#aws lambda#aws lambda api gateway#aws lambda api gateway trigger#aws lambda basic#aws lambda code#aws lambda configuration#aws lambda developer#aws lambda event trigger#aws lambda eventbridge#aws lambda example#aws lambda function#aws lambda function example#aws lambda function s3 trigger#aws lambda java#aws lambda server#aws lambda service#aws lambda tutorial#aws training#aws tutorial#lambda service
0 notes
Note
Asbel, Richard, and Lambda is along for the ride, and #50
#50: “why does anyone have to be naked?” wc: 1 631 read on ao3 here
The whole thing is starting to get sort of…strange.
Probably thanks to Asbel’s influence, Lambda’s disdain for humans has in some areas melted into a genuine, at times even rather endearing curiosity about them. It’s a bit cute, even, when the timing isn’t completely awful. Sometimes, Asbel even lets the others hold his hand and explain something that, to the rest of them, is incredibly simple—why Cheria enjoys the sound of the piano, how Lady Kerri has been teaching Sophie to tend to the flowerbeds, the compulsion Hubert has to collect figures and models that serve no real purpose beyond looking nice on a secret shelf in his bedroom—so that Lambda can interrogate them properly. This is all well and good, but when it comes to Richard, Lambda’s questions are a little bit different.
He takes some comfort in the knowledge that Asbel is as flustered by Lambda’s interjections as he is—or maybe even a little more, if only because so much of it seems to be coming directly from his own head. It’s not as if Lambda is a stranger to Richard’s feelings for Asbel, either; but they had both been rather more focussed on other things at the time, and any notions of a romantic reunion had been buried deep down long before Asbel found him in the catacombs again.
Their relationship already feels complicated enough without adding Lambda’s probing questions to the equation, but even if he has ever considered the same, Richard knows Asbel would not have entertained the thought for any longer than the time taken to disregard it completely. The last thing Asbel wants to do is exclude Lambda, even—or perhaps especially?—when it comes to matters of intimacy. Richard can understand, a bit; these are, after all, some of the biggest joys of being human. The brush of hands, of lips, skin on skin—he certainly cannot blame Lambda for wanting to understand it.
Unfortunately, it also meant that their first kiss was cut short by Lambda’s voice ringing through Richard’s head, demanding to know, “What exactly is the benefit to this action?”
So the kiss had stopped, while Richard tried to come up with a justification for kissing that satisfied Lambda, who stubbornly would not accept anything amongst “It feels nice” or “It allows you to let your guard down around someone you love” or “It stimulates physical arousal, which is a necessary biological function.”
Finally, Asbel suggested, “It brings you closer to the other person,” which for reasons far beyond Richard was enough to satiate their friend’s curiosity. Even though Richard is still fairly certain it was no better an explanation than any he had given.
That’s pretty much par for the course, though. Lambda is often calling Asbel a weak, soft-hearted fool, amongst other similarly barbed epithets, but Richard isn’t so blind to the adoration with which Lambda considers his host. Sometimes, even, he wonders if he is in part responsible for it: as if he has loved Asbel so deeply, for so long, that when Lambda left his mindscape for good he carried a fraction of the emotion away with him.
That was, in any case, one of the more mild iterations of this scene, which has played out more times than Richard could even hope to keep track of between both his hands and his feet. Some of the queries are very innocent: “ What exactly qualifies something as ‘cute’? ” or “Why is it that Asbel belives he must wipe the whipped cream from your lip, Richard? Are you incapable of such a simple action? ” Others, however…a little less so, though when they’ve been about Asbel, Richard can’t deny they’ve had their own enjoyability.
There was that time, for example, when Asbel reached out for his hand and said, very lightly, apparently having no idea as to the nature of the question, “Lambda would like to ask you something, Richard.” And then that all-too familiar voice was in his head: “What exactly is the purpose of Asbel’s preoccupation with touching your hair? Would pulling on it not harm you? It seems unlike him to wish you pain.”
Asbel heard it, too. And pulled his hand away as if he had been burned, although Richard was mostly amused by it all. He had taken some time to think of an answer before winking at Asbel and answering, “I don’t believe his intentions are to harm me, Lambda. As it turns out, pain and pleasure run on a parallel spectrum for us humans. I believe, in a roundabout way, what Asbel really wants is to make me feel good.”
He thought Asbel might melt into the floor, then. It was painstakingly cute.
There had also been that time when they had been kissing on Asbel’s bed and Lambda had spoken up to wonder, “Why does Asbel keep thinking he wants you on top of him? Would he not suffocate?”
They haven’t expressly given Lambda “the Talk,” if only because his questions about intimacy come at such inopportune times. In this case, for example, Asbel had pulled away from Richard and thrown his face against the pillow instead in a show of adorable despair. This may be another reason why Asbel has yet to broach the subject with him: he himself is still too embarrassed by the very idea of sex that any time he has grown hard under Richard’s ministrations, he has put a stop to them and excused himself to deal with the problem on his own.
Richard doesn’t mind waiting, of course. And now, months since that first awkward kiss later, they are finally here, which Richard’s hands under the hems of Asbel’s shirt. He doesn’t speak his question, though he pauses long enough for Asbel to break their kiss and answer, which he does with a minute, breathless nod of the head.
His shirt is pulled up over his head and delicately thrown to the floor with their jackets, shoes, and Richard’s gloves. Reverently, Richard runs his hands over Asbel’s bare torso, eliciting a shiver.
“I won’t put you through the pains of undoing my clothing,” Richard murmurs at last, pulling back in order to deal with it himself. Asbel watches his deft fingers with a sort of burning desire, which only makes Richard ache all the more to continue touching him. But when finally the garment has been graciously discarded and his hands snake up around Asbel’s neck again to draw him closer, Lambda speaks up, breaking them out of their lustful stupors in record time:
“I was beginning to understand all this kissing nonsense, but this brings another question to mind…”
Asbel stifles a snort while Richard stares down at him, aghast. “Lambda, your timing never fails to impress.”
Ignoring him, Lambda asks, “ Why does anyone have to be naked?”
Now, it is Richard trying hard not to laugh. Asbel ducks his head, shame colouring his face all over again.
“Well,” Richard says, “it is rather hard to have intercourse with one’s clothes on. Not impossible,” he adds. “But I don’t particularly fancy dealing with any stains on my clothing, myself.”
“Stains?”
“Asbel,” Richard says, chiding, “don’t tell me you have still yet to explain to our friend about the birds and the bees?”
“Not…exactly,” Asbel mumbles to his bedsheets.
“Well, that won’t do.”
“What, pray tell, are these birds and bees? It seems unwise to approach monsters unclothed.”
“It’s a metaphor,” Richard explains. “Although, I must admit, I am uncertain where the idiom comes from myself. In essence, though, it is a euphemistic way people talk about sexual intercourse. And before you wonder what benefit sex has beyond procreation, which of course Asbel and myself would have a hard time with given our incompatible anatomy, I will suggest that the purpose is it feels good. Wouldn’t you agree, Asbel?”
Asbel glances up at him, cheeks burning all the way up to his ears. “I…I guess. Sure.”
“Lambda’s never going to believe in your conviction if you say it like that.”
Asbel winces. “Um, right. Yeah, of course. It feels great. Probably.”
“Is that supposed to be more convincing?”
“I don’t know!”
“Perhaps,” Richard interjects smoothly, “Lambda could better learn through a demonstration?”
As the intention registers, Asbel’s eyes widen. He opens his mouth and then slams it shut again and shakes his head. “I— You want him to take control of my body?”
“Heavens, no. Then you wouldn’t learn anything, either.” Gently, Richard sweeps his hand back to Asbel’s front and cups his chin. He leans close again, so that he can feel his own breaths against Asbel’s parted lips. “He can watch, though, can’t he?”
At once, a different emotion overtakes Asbel’s gaze. He slackens in Richard’s hold. “Well…if he wants to. What do you think, Lambda? You can stop us any time, if you feel uncomfortable.”
“Why would I feel uncomfortable?”
“Because Asbel will be making all sorts of indecent noises,” Richard supplies cheerfully. “Though something tells me you’ve heard those before, too.”
“Richard!” Asbel hisses, but Lambda tellingly doesn’t deny it.
“Then I fail to see how this will be a new experience in understanding you humans.”
“Well, I suppose you’ll see from his perspective why I needed to be naked as well.” Richard closes the gap between himself and Asbel with the swift, chaste kiss against his lips. When he pulls back, he adds, “Please save your questions for after, though. We may be a touch too occupied to answer coherently.”
Silence, for a beat. And then Lambda says, a bit sullenly, “Fine. I accept. Show me this intercourse, if you please.”
Richard grins, and pushes Asbel down until his back hits the bed. “Gladly,” he says, before descending ravenously upon them both.
#tales of#graces#*fic#mine#*reqs#richass#i don't even know what the ship name for either of them with lambda is let alone both of them lol#this fic is just teaching the voyeuristic alien in your boyfriend's head the meaning of love through intimacy anyway#richard is a bit of a freak but well-intentioned of course#answered#mchalenwrites
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
How can you optimize the performance of machine learning models in the cloud?
Optimizing machine learning models in the cloud involves several strategies to enhance performance and efficiency. Here’s a detailed approach:

Choose the Right Cloud Services:
Managed ML Services:
Use managed services like AWS SageMaker, Google AI Platform, or Azure Machine Learning, which offer built-in tools for training, tuning, and deploying models.
Auto-scaling:
Enable auto-scaling features to adjust resources based on demand, which helps manage costs and performance.
Optimize Data Handling:
Data Storage:
Use scalable cloud storage solutions like Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, or Azure Blob Storage for storing large datasets efficiently.
Data Pipeline:
Implement efficient data pipelines with tools like Apache Kafka or AWS Glue to manage and process large volumes of data.
Select Appropriate Computational Resources:
Instance Types:
Choose the right instance types based on your model’s requirements. For example, use GPU or TPU instances for deep learning tasks to accelerate training.
Spot Instances:
Utilize spot instances or preemptible VMs to reduce costs for non-time-sensitive tasks.
Optimize Model Training:
Hyperparameter Tuning:
Use cloud-based hyperparameter tuning services to automate the search for optimal model parameters. Services like Google Cloud AI Platform’s HyperTune or AWS SageMaker’s Automatic Model Tuning can help.
Distributed Training:
Distribute model training across multiple instances or nodes to speed up the process. Frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch support distributed training and can take advantage of cloud resources.
Monitoring and Logging:
Monitoring Tools:
Implement monitoring tools to track performance metrics and resource usage. AWS CloudWatch, Google Cloud Monitoring, and Azure Monitor offer real-time insights.
Logging:
Maintain detailed logs for debugging and performance analysis, using tools like AWS CloudTrail or Google Cloud Logging.
Model Deployment:
Serverless Deployment:
Use serverless options to simplify scaling and reduce infrastructure management. Services like AWS Lambda or Google Cloud Functions can handle inference tasks without managing servers.
Model Optimization:
Optimize models by compressing them or using model distillation techniques to reduce inference time and improve latency.
Cost Management:
Cost Analysis:
Regularly analyze and optimize cloud costs to avoid overspending. Tools like AWS Cost Explorer, Google Cloud’s Cost Management, and Azure Cost Management can help monitor and manage expenses.
By carefully selecting cloud services, optimizing data handling and training processes, and monitoring performance, you can efficiently manage and improve machine learning models in the cloud.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mastering AWS DevOps in 2025: Best Practices, Tools, and Real-World Use Cases
In 2025, the cloud ecosystem continues to grow very rapidly. Organizations of every size are embracing AWS DevOps to automate software delivery, improve security, and scale business efficiently. Mastering AWS DevOps means knowing the optimal combination of tools, best practices, and real-world use cases that deliver success in production.
This guide will assist you in discovering the most important elements of AWS DevOps, the best practices of 2025, and real-world examples of how top companies are leveraging AWS DevOps to compete.
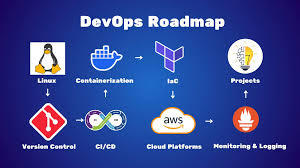
What is AWS DevOps
AWS DevOps is the union of cultural principles, practices, and tools on Amazon Web Services that enhances an organization's capacity to deliver applications and services at a higher speed. It facilitates continuous integration, continuous delivery, infrastructure as code, monitoring, and cooperation among development and operations teams.
Why AWS DevOps is Important in 2025
As organizations require quicker innovation and zero downtime, DevOps on AWS offers the flexibility and reliability to compete. Trends such as AI integration, serverless architecture, and automated compliance are changing how teams adopt DevOps in 2025.
Advantages of adopting AWS DevOps:
1 Faster deployment cycles
2 Enhanced system reliability
3 Flexible and scalable cloud infrastructure
4 Automation from code to production
5 Integrated security and compliance
Best AWS DevOps Tools to Learn in 2025
These are the most critical tools fueling current AWS DevOps pipelines:
AWS CodePipeline
Your release process can be automated with our fully managed CI/CD service.
AWS CodeBuild
Scalable build service for creating ready-to-deploy packages, testing, and building source code.
AWS CodeDeploy
Automates code deployments to EC2, Lambda, ECS, or on-prem servers with zero-downtime approaches.
AWS CloudFormation and CDK
For infrastructure as code (IaC) management, allowing repeatable and versioned cloud environments.
Amazon CloudWatch
Facilitates logging, metrics, and alerting to track application and infrastructure performance.
AWS Lambda
Serverless compute that runs code in response to triggers, well-suited for event-driven DevOps automation.
AWS DevOps Best Practices in 2025
1. Adopt Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Utilize AWS CloudFormation or Terraform to declare infrastructure. This makes it repeatable, easier to collaborate on, and version-able.
2. Use Full CI/CD Pipelines
Implement tools such as CodePipeline, GitHub Actions, or Jenkins on AWS to automate deployment, testing, and building.
3. Shift Left on Security
Bake security in early with Amazon Inspector, CodeGuru, and Secrets Manager. As part of CI/CD, automate vulnerability scans.
4. Monitor Everything
Utilize CloudWatch, X-Ray, and CloudTrail to achieve complete observability into your system. Implement alerts to detect and respond to problems promptly.
5. Use Containers and Serverless for Scalability
Utilize Amazon ECS, EKS, or Lambda for autoscaling. These services lower infrastructure management overhead and enhance efficiency.
Real-World AWS DevOps Use Cases
Use Case 1: Scalable CI/CD for a Fintech Startup
AWS CodePipeline and CodeDeploy were used by a financial firm to automate deployments in both production and staging environments. By containerizing using ECS and taking advantage of CloudWatch monitoring, they lowered deployment mistakes by 80 percent and attained near-zero downtime.
Use Case 2: Legacy Modernization for an Enterprise
A legacy enterprise moved its on-premise applications to AWS with CloudFormation and EC2 Auto Scaling. Through the adoption of full-stack DevOps pipelines and the transformation to microservices with EKS, they enhanced time-to-market by 60 percent.
Use Case 3: Serverless DevOps for a SaaS Product
A SaaS organization utilized AWS Lambda and API Gateway for their backend functions. They implemented quick feature releases and automatically scaled during high usage without having to provision infrastructure using CodeBuild and CloudWatch.
Top Trends in AWS DevOps in 2025
AI-driven DevOps: Integration with CodeWhisperer, CodeGuru, and machine learning algorithms for intelligence-driven automation
Compliance-as-Code: Governance policies automated using services such as AWS Config and Service Control Policies
Multi-account strategies: Employing AWS Organizations for scalable, secure account management
Zero Trust Architecture: Implementing strict identity-based access with IAM, SSO, and MFA
Hybrid Cloud DevOps: Connecting on-premises systems to AWS for effortless deployments
Conclusion
In 2025, becoming a master of AWS DevOps means syncing your development workflows with cloud-native architecture, innovative tools, and current best practices. With AWS, teams are able to create secure, scalable, and automated systems that release value at an unprecedented rate.
Begin with automating your pipelines, securing your deployments, and scaling with confidence. DevOps is the way of the future, and AWS is leading the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What distinguishes AWS DevOps from DevOps? While AWS DevOps uses AWS services and tools to execute DevOps, DevOps itself is a practice.
Can small teams benefit from AWS DevOps
Yes. AWS provides fully managed services that enable small teams to scale and automate without having to handle complicated infrastructure.
Which programming languages does AWS DevOps support
AWS supports the big ones - Python, Node.js, Java, Go, .NET, Ruby, and many more.
Is AWS DevOps for enterprise-scale applications
Yes. Large enterprises run large-scale, multi-region applications with millions of users using AWS DevOps.
1 note
·
View note
Text
In today's competitive job market, a well-crafted resume is crucial for any programmer looking to secure a new position. While technical skills are a given, there are other essential skills that can make your resume stand out from the rest. Here are some key skills to consider highlighting on your programmer resume. 1. Programming Languages One of the first things employers look for in a programmer’s resume is proficiency in programming languages. Highlight your expertise in widely-used languages such as Python, Java, JavaScript, C++, and SQL. If you have experience with specialized languages relevant to the job you're applying for, such as Swift for iOS development or Kotlin for Android development, be sure to include those as well. Employers appreciate candidates who have a strong foundation in multiple programming languages. 2. Frameworks and Libraries Employers value programmers who are familiar with popular frameworks and libraries, as these tools can significantly speed up the development process. Include skills in frameworks such as React, Angular, Django, Flask, and Spring. Mentioning experience with libraries like TensorFlow for machine learning or Pandas for data analysis can also be beneficial. Demonstrating your ability to work with these tools shows that you are capable of producing efficient and scalable code. 3. Version Control Systems Proficiency in version control systems is a must-have for any programmer. Git is the most widely used version control system, so be sure to highlight your experience with it. Mention your familiarity with platforms such as GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket. Employers look for candidates who can manage code changes effectively and collaborate with other developers seamlessly. 4. Development Methodologies Understanding and experience with development methodologies like Agile and Scrum can set you apart from other candidates. Employers value programmers who can thrive in a team-oriented, iterative development environment. Highlight your experience participating in sprint planning, stand-up meetings, and retrospective sessions. This demonstrates your ability to contribute to a productive and collaborative workflow. 5. Problem-Solving and Analytical Skills Programming is fundamentally about solving problems. Your ability to think critically and approach challenges methodically is a crucial skill. Provide examples of how you’ve used your problem-solving skills in past projects, such as debugging complex issues, optimizing code performance, or implementing innovative solutions. This showcases your analytical mindset and your capability to tackle obstacles effectively. 6. Database Management Knowledge of database management systems is another essential skill for programmers. Highlight your experience with SQL databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle, as well as NoSQL databases such as MongoDB and Cassandra. Employers seek candidates who can design, implement, and maintain robust database solutions. 7. Cloud Computing With the growing reliance on cloud technologies, experience with cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud is highly valuable. Mention your skills in deploying applications, managing cloud infrastructure, and using cloud services such as AWS Lambda or Azure Functions. This demonstrates your ability to work with modern infrastructure and scale applications efficiently. 8. Soft Skills While technical skills are crucial, soft skills are equally important. Effective communication, teamwork, and time management skills are essential for any programmer. Highlight your ability to articulate complex technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders, collaborate with team members, and manage project deadlines. Employers look for well-rounded candidates who can contribute positively to the work environment. 9. Continuous Learning and Adaptability The tech industry is constantly evolving, and employers value programmers who are committed to continuous learning.
Mention any certifications, courses, or workshops you’ve completed to stay updated with the latest trends and technologies. Demonstrating your willingness to adapt and grow in your career shows that you are proactive and dedicated to maintaining your expertise. 10. Project Management Tools Familiarity with project management tools such as JIRA, Trello, or Asana can be a plus. These tools help in tracking project progress, managing tasks, and ensuring timely delivery of projects. Highlighting your experience with these tools shows that you are organized and can efficiently manage project workflows. Conclusion Creating a standout resume involves more than just listing technical skills. By showcasing a combination of technical prowess, soft skills, and a commitment to continuous learning, you can present yourself as a well-rounded candidate. Tailoring your resume to highlight these key skills will not only help you get noticed by potential employers but also increase your chances of landing your desired programming job.
0 notes
Text
Introduction: The Evolution of Web Scraping
Traditional Web Scraping involves deploying scrapers on dedicated servers or local machines, using tools like Python, BeautifulSoup, and Selenium. While effective for small-scale tasks, these methods require constant monitoring, manual scaling, and significant infrastructure management. Developers often need to handle cron jobs, storage, IP rotation, and failover mechanisms themselves. Any sudden spike in demand could result in performance bottlenecks or downtime. As businesses grow, these challenges make traditional scraping harder to maintain. This is where new-age, cloud-based approaches like Serverless Web Scraping emerge as efficient alternatives, helping automate, scale, and streamline data extraction.

Challenges of Manual Scraper Deployment (Scaling, Infrastructure, Cost)
Manual scraper deployment comes with numerous operational challenges. Scaling scrapers to handle large datasets or traffic spikes requires robust infrastructure and resource allocation. Managing servers involves ongoing costs, including hosting, maintenance, load balancing, and monitoring. Additionally, handling failures, retries, and scheduling manually can lead to downtime or missed data. These issues slow down development and increase overhead. In contrast, Serverless Web Scraping removes the need for dedicated servers by running scraping tasks on platforms like AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions, offering auto-scaling and cost-efficiency on a pay-per-use model.
Introduction to Serverless Web Scraping as a Game-Changer

What is Serverless Web Scraping?
Serverless Web Scraping refers to the process of extracting data from websites using cloud-based, event-driven architecture, without the need to manage underlying servers. In cloud computing, "serverless" means the cloud provider automatically handles infrastructure scaling, provisioning, and resource allocation. This enables developers to focus purely on writing the logic of Data Collection, while the platform takes care of execution.
Popular Cloud Providers like AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions offer robust platforms for deploying these scraping tasks. Developers write small, stateless functions that are triggered by events such as HTTP requests, file uploads, or scheduled intervals—referred to as Scheduled Scraping and Event-Based Triggers. These functions are executed in isolated containers, providing secure, cost-effective, and on-demand scraping capabilities.
The core advantage is Lightweight Data Extraction. Instead of running a full scraper continuously on a server, serverless functions only execute when needed—making them highly efficient. Use cases include:
Scheduled Scraping (e.g., extracting prices every 6 hours)
Real-time scraping triggered by user queries
API-less extraction where data is not available via public APIs
These functionalities allow businesses to collect data at scale without investing in infrastructure or DevOps.
Key Benefits of Serverless Web Scraping
Scalability on Demand
One of the strongest advantages of Serverless Web Scraping is its ability to scale automatically. When using Cloud Providers like AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, or Google Cloud Functions, your scraping tasks can scale from a few requests to thousands instantly—without any manual intervention. For example, an e-commerce brand tracking product listings during flash sales can instantly scale their Data Collection tasks to accommodate massive price updates across multiple platforms in real time.
Cost-Effectiveness (Pay-as-You-Go Model)
Traditional Web Scraping involves paying for full-time servers, regardless of usage. With serverless solutions, you only pay for the time your code is running. This pay-as-you-go model significantly reduces costs, especially for intermittent scraping tasks. For instance, a marketing agency running weekly Scheduled Scraping to track keyword rankings or competitor ads will only be billed for those brief executions—making Serverless Web Scraping extremely budget-friendly.
Zero Server Maintenance
Server management can be tedious and resource-intensive, especially when deploying at scale. Serverless frameworks eliminate the need for provisioning, patching, or maintaining infrastructure. A developer scraping real estate listings no longer needs to manage server health or uptime. Instead, they focus solely on writing scraping logic, while Cloud Providers handle the backend processes, ensuring smooth, uninterrupted Lightweight Data Extraction.
Improved Reliability and Automation
Using Event-Based Triggers (like new data uploads, emails, or HTTP calls), serverless scraping functions can be scheduled or executed automatically based on specific events. This guarantees better uptime and reduces the likelihood of missing important updates. For example, Azure Functions can be triggered every time a CSV file is uploaded to the cloud, automating the Data Collection pipeline.
Environmentally Efficient
Traditional servers consume energy 24/7, regardless of activity. Serverless environments run functions only when needed, minimizing energy usage and environmental impact. This makes Serverless Web Scraping an eco-friendly option. Businesses concerned with sustainability can reduce their carbon footprint while efficiently extracting vital business intelligence.

Ideal Use Cases for Serverless Web Scraping
1. Market and Price Monitoring
Serverless Web Scraping enables retailers and analysts to monitor competitor prices in real-time using Scheduled Scraping or Event-Based Triggers.
Example:
A fashion retailer uses AWS Lambda to scrape competitor pricing data every 4 hours. This allows dynamic pricing updates without maintaining any servers, leading to a 30% improvement in pricing competitiveness and a 12% uplift in revenue.
2. E-commerce Product Data Collection
Collect structured product information (SKUs, availability, images, etc.) from multiple e-commerce platforms using Lightweight Data Extraction methods via serverless setups.
Example:
An online electronics aggregator uses Google Cloud Functions to scrape product specs and availability across 50+ vendors daily. By automating Data Collection, they reduce manual data entry costs by 80%.
3. Real-Time News and Sentiment Tracking
Use Web Scraping to monitor breaking news or updates relevant to your industry and feed it into dashboards or sentiment engines.
Example:
A fintech firm uses Azure Functions to scrape financial news from Bloomberg and CNBC every 5 minutes. The data is piped into a sentiment analysis engine, helping traders act faster based on market sentiment—cutting reaction time by 40%.
4. Social Media Trend Analysis
Track hashtags, mentions, and viral content in real time across platforms like Twitter, Instagram, or Reddit using Serverless Web Scraping.
Example:
A digital marketing agency leverages AWS Lambda to scrape trending hashtags and influencer posts during product launches. This real-time Data Collection enables live campaign adjustments, improving engagement by 25%.
5. Mobile App Backend Scraping Using Mobile App Scraping Services
Extract backend content and APIs from mobile apps using Mobile App Scraping Services hosted via Cloud Providers.
Example:
A food delivery startup uses Google Cloud Functions to scrape menu availability and pricing data from a competitor’s app every 15 minutes. This helps optimize their own platform in real-time, improving response speed and user satisfaction.
Technical Workflow of a Serverless Scraper
In this section, we’ll outline how a Lambda-based scraper works and how to integrate it with Web Scraping API Services and cloud triggers.
1. Step-by-Step on How a Typical Lambda-Based Scraper Functions
A Lambda-based scraper runs serverless functions that handle the data extraction process. Here’s a step-by-step workflow for a typical AWS Lambda-based scraper:
Step 1: Function Trigger
Lambda functions can be triggered by various events. Common triggers include API calls, file uploads, or scheduled intervals.
For example, a scraper function can be triggered by a cron job or a Scheduled Scraping event.
Example Lambda Trigger Code:
Lambda functionis triggered based on a schedule (using EventBridge or CloudWatch).
requests.getfetches the web page.
BeautifulSoupprocesses the HTML to extract relevant data.
Step 2: Data Collection
After triggering the Lambda function, the scraper fetches data from the targeted website. Data extraction logic is handled in the function using tools like BeautifulSoup or Selenium.
Step 3: Data Storage/Transmission
After collecting data, the scraper stores or transmits the results:
Save data to AWS S3 for storage.
Push data to an API for further processing.
Store results in a database like Amazon DynamoDB.
2. Integration with Web Scraping API Services
Lambda can be used to call external Web Scraping API Services to handle more complex scraping tasks, such as bypassing captchas, managing proxies, and rotating IPs.
For instance, if you're using a service like ScrapingBee or ScraperAPI, the Lambda function can make an API call to fetch data.
Example: Integrating Web Scraping API Services
In this case, ScrapingBee handles the web scraping complexities, and Lambda simply calls their API.
3. Using Cloud Triggers and Events
Lambda functions can be triggered in multiple ways based on events. Here are some examples of triggers used in Serverless Web Scraping:
Scheduled Scraping (Cron Jobs Cron Jobs):
You can use AWS EventBridge or CloudWatch Events to schedule your Lambda function to run at specific intervals (e.g., every hour, daily, or weekly).
Example: CloudWatch Event Rule (cron job) for Scheduled Scraping:
This will trigger the Lambda function to scrape a webpage every hour.
File Upload Trigger (Event-Based):
Lambda can be triggered by file uploads in S3. For example, after scraping, if the data is saved as a file, the file upload in S3 can trigger another Lambda function for processing.
Example: Trigger Lambda on S3 File Upload:
By leveraging Serverless Web Scraping using AWS Lambda, you can easily scale your web scraping tasks with Event-Based Triggers such as Scheduled Scraping, API calls, or file uploads. This approach ensures that you avoid the complexity of infrastructure management while still benefiting from scalable, automated data collection. Learn More
#LightweightDataExtraction#AutomatedDataExtraction#StreamlineDataExtraction#ServerlessWebScraping#DataMining
0 notes
Text

Edge Computing for Web Developers: How to Speed Up Your Apps
In today’s digital race, milliseconds matter.
Whether you’re building a real-time dashboard, an e-commerce platform, or a SaaS product, users expect one thing — speed. But traditional cloud setups, while powerful, aren’t always fast enough when data has to travel halfway across the globe.
Enter: Edge Computing — a game-changing strategy that moves computing closer to users and supercharges web performance.
What Is Edge Computing (And Why Should You Care)?
Imagine you’re ordering pizza. Would you rather get it from a kitchen next door or one 500 miles away?
That’s the difference between centralized cloud and edge computing.
Edge computing is about processing data as close to the user as possible — often on local servers or network nodes instead of a distant data center. For web developers, this means fewer delays, faster responses, and smoother user experiences.
And in an age where a one-second delay can drop conversions by 7%, that’s a big deal.
How Does It Actually Work?
Here’s the simple version:
You deploy some parts of your app (like APIs, static files, and authentication logic) to a central server and across multiple edge locations worldwide.
When a user in New York accesses your app, it loads from a nearby edge server, not from a main server in Singapore.
Result? Lower latency, less server load, and faster load times.
What Can Web Developers Use Edge Computing For?
Edge computing isn’t just for heavy tech infrastructure — it’s now developer-friendly and API-driven. Here’s how you can use it:
1. Deliver Static Assets Faster
CDNs (Content Delivery Networks) like Cloudflare, Vercel, or Netlify already do this — they serve your HTML, CSS, JS, and images from edge locations.
Bonus Tip: Combine with image optimization at the edge to slash load times.
2. Run Serverless Functions at the Edge
Think dynamic actions like form submissions, authentication, or geolocation-based content. Platforms like Cloudflare Workers, Vercel Edge Functions, and AWS Lambda@Edge let you run logic closer to your users.
Example: Show region-specific content without needing the user to wait for a central server to decide.
3. Improve API Response Times
You can cache API responses or compute lightweight operations at the edge to reduce back-and-forth trips to the origin server.
Imagine: A travel app loading nearby attractions instantly by computing distance at the edge, not centrally.
4. Secure Your App Better
Edge networks can block threats before they ever reach your main server, including bots, DDoS attacks, and suspicious traffic.
It’s like having a security guard posted on every street corner, not just your front door.
But… Does Every App Need Edge Computing?
Not necessarily. If your app is local, low-traffic, or non-latency-sensitive, traditional cloud might be enough.
But if you’re scaling globally, working with real-time data, or want lightning-fast load speeds, edge computing is your secret weapon.
Real-World Impact: Numbers Don’t Lie
Vercel reported a 50% performance boost for apps deployed with edge functions.
Retailers using edge caching see a 20–30% decrease in bounce rates.
Streaming platforms improved video start times by up to 60% with edge delivery.
These aren’t just nice-to-haves — they’re competitive advantages.
Getting Started: Tools You Should Know
Here are a few platforms and tools that make edge computing accessible for developers:
Cloudflare Workers — Write JavaScript functions that run at the edge.
Vercel — Perfect for Next.js and frontend teams, with edge function support.
Netlify Edge Functions — Simplified edge logic built into your CI/CD.
AWS Lambda@Edge — Enterprise-grade, with tight AWS integration.
Pro tip: If you’re already using frameworks like Next.js, Nuxt, or SvelteKit, edge-ready deployments are often just one setting away.
Final Thoughts: Why This Matters to You
For developers: Edge computing lets you build faster, more responsive apps without reinventing your stack.
For business owners: It means happier users, lower customer loss, and more conversions.
In a world where speed = success, edge computing isn’t the future — it’s the edge you need today.
0 notes
Text
Cloud Cost Optimization: Proven Tactics to Cut Spend Without Sacrificing Performance
As cloud adoption becomes ubiquitous in 2025, companies are reaping the benefits of scalability, flexibility, and agility. But with great power comes… surprisingly high bills. Many businesses discover too late that cloud spending can spiral out of control without a clear cost optimization strategy.
Cloud cost optimization isn’t just about cutting expenses—it's about maximizing value. It's the practice of eliminating waste, improving efficiency, and ensuring every dollar spent on cloud services contributes directly to business goals.
Here’s how startups, enterprises, and DevOps teams can reduce cloud costs without compromising on performance or reliability.
💸 Why Cloud Costs Get Out of Hand
Before diving into solutions, it’s essential to understand why cloud costs often balloon:
Overprovisioned resources (e.g., oversized VMs or underused storage)
Idle or zombie workloads running without active usage
Lack of visibility across multi-cloud environments
On-demand pricing instead of reserved or spot instances
Inefficient code or architecture that uses more compute than necessary
These issues can silently eat up budgets, especially at scale.
✅ Tactics to Optimize Cloud Spend (Without Sacrificing Performance)
1. Right-Size Your Resources
Avoid overprovisioning by analyzing usage patterns and matching instance types to actual workloads.
Use tools like AWS Trusted Advisor, Azure Advisor, or GCP Recommender
Set autoscaling policies to match demand dynamically
Schedule non-production environments to shut down after hours
2. Adopt Reserved and Spot Instances
Commit to reserved instances for predictable workloads to enjoy significant discounts (up to 75% in some cases). Use spot or preemptible instances for non-critical, fault-tolerant workloads like batch processing.
3. Monitor and Analyze Continuously
Implement real-time monitoring to track usage and cost trends.
Use native cost tools (e.g., AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management)
Set up budgets and alerts
Tag resources for better accountability and analysis
4. Eliminate Idle and Orphaned Resources
Review:
Unattached volumes (e.g., EBS, disks)
Idle load balancers and databases
Unused snapshots and backups
Unassociated IPs and DNS records
Automate cleanup scripts or integrate with tools like Cloud Custodian.
5. Optimize Storage Classes and Data Transfers
Move infrequently accessed data to cheaper storage tiers (e.g., AWS Glacier, Azure Archive). Minimize cross-region and egress traffic to reduce network transfer costs.
6. Leverage Serverless and Containerization
Shift from traditional VMs to serverless (like AWS Lambda or Azure Functions) for burst workloads or low-traffic APIs. For more control, use container orchestration with Kubernetes or ECS to improve density and resource sharing.
7. Implement FinOps Culture
Cost optimization is not a one-time task—it’s a cross-functional responsibility. Introduce FinOps practices by:
Involving finance, engineering, and product teams in cloud budgeting
Creating shared accountability for resource usage
Automating reporting and optimization recommendations
📊 Tools for Effective Cloud Cost Optimization
Tool Purpose AWS Cost Explorer / Azure Cost Management Budgeting and forecasting CloudHealth / Spot.io / Apptio Cloudability Advanced cost optimization Kubecost Kubernetes resource cost tracking Cloud Custodian / Terraform / Pulumi Automated governance and clean-up Datadog / New Relic Real-time performance and cost correlation
🧠 Cost Optimization = Performance Optimization
Cloud cost and performance are often viewed as a trade-off, but they’re closely linked. Optimizing architecture, automating scale, and refactoring inefficient code often reduce both cost and latency.
For example:
Moving to event-driven architecture can reduce unnecessary compute
Compressing data reduces storage and transfer fees
Choosing faster regions or CDNs improves performance and lowers user latency
🏁 Final Thoughts
In 2025, cloud success isn’t defined by how much you spend—it’s defined by how smartly you spend. Cloud cost optimization empowers organizations to grow without waste, innovate without fear, and align infrastructure investments with strategic outcomes.
At Salzen Cloud, we help companies implement end-to-end cloud optimization strategies that enhance efficiency, ensure transparency, and support business agility—without ever compromising on performance.
0 notes
Text
AWS Introduces AWS MCP Servers for Serverless, ECS, & EKS

MCP AWS server
The AWS Labs GitHub repository now has Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers for AWS Serverless, Amazon ECS, and Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service. Real-time contextual responses from open-source solutions trump AI development assistants' pre-trained knowledge. MCP servers provide current context and service-specific information to help you avoid deployment issues and improve service interactions, while AI assistant Large Language Models (LLM) use public documentation.
These open source solutions can help you design and deploy apps faster by using Amazon Web Services (AWS) features and configurations. These MCP servers enable AI code assistants with deep understanding of Amazon ECS, Amazon EKS, and AWS Serverless capabilities, speeding up the code-to-production process in your IDE or debugging production issues. They integrate with popular AI-enabled IDEs like Amazon Q Developer on the command line to allow you design and deploy apps using natural language commands.
Specialist MCP servers' functions:
With Amazon ECS MCP Server, applications can be deployed and containerised quickly. It helps configure AWS networking, load balancers, auto-scaling, task definitions, monitoring, and services. Real-time troubleshooting can fix deployment difficulties, manage cluster operations, and apply auto-scaling using natural language.
Amazon EKS MCP Server gives AI helpers contextual, up-to-date information for Kubernetes EKS environments. By providing the latest EKS features, knowledge base, and cluster state data, it enables AI code assistants more exact, customised aid throughout the application lifecycle.
The AWS Serverless MCP Server enhances serverless development. AI coding helpers learn AWS services, serverless patterns, and best practices. Integrating with the AWS Serverless Application Model Command Line Interface (AWS SAM CLI) to manage events and deploy infrastructure using tried-and-true architectural patterns streamlines function lifecycles, service integrations, and operational requirements. It also advises on event structures, AWS Lambda best practices, and code.
Users are directed to the AWS Labs GitHub repository for installation instructions, example settings, and other specialist servers, such as Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases Retrieval and AWS Lambda function transformation servers.
AWS MCP server operation
Giving Context: The MCP servers give AI assistants current context and knowledge about specific AWS capabilities, configurations, and even your surroundings (such as the EKS cluster state), eliminating the need for broad or outdated knowledge. For more accurate service interactions and fewer deployment errors, this is crucial.
They enable AI code assistance deep service understanding of AWS Serverless, ECS, and EKS. This allows the AI to make more accurate and tailored recommendations from code development to production issues.
The servers allow developers to construct and deploy apps using natural language commands using AI-enabled IDEs and tools like Amazon Q Developer on the command line. The AI assistant can use the relevant MCP server to get context or do tasks after processing the natural language query.
Aiding Troubleshooting and Service Actions: Servers provide tools and functionality for their AWS services. As an example:
Amazon ECS MCP Server helps configure load balancers and auto-scaling. Real-time debugging tools like fetch_task_logs can help the AI assistant spot issues in natural language queries.
The Amazon EKS MCP Server provides cluster status data and utilities like search_eks_troubleshoot_guide to fix EKS issues and generate_app_manifests to build Kubernetes clusters.
In addition to contextualising serverless patterns, best practices, infrastructure as code decisions, and event schemas, the AWS Serverless MCP Server communicates with the AWS SAM CLI. An example shows how it can help the AI helper discover best practices and architectural demands.
An AI assistant like Amazon Q can communicate with the right AWS MCP server for ECS, EKS, or Serverless development or deployment questions. This server can activate service-specific tools or provide specialised, current, or real-time information to help the AI assistant reply more effectively and accurately. This connection accelerates coding-to-production.
#AWSMCPserver#AmazonElasticContainerService#ModelContextProtocol#integrateddevelopmentenvironment#commandline#AmazonECS#technology#technews#technologynews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
From Idea to Production: Integrating the Token Metrics API in Your App

Building a crypto app—whether for portfolio tracking, market research, or social trading—demands reliable intelligence. With the Token Metrics API, you get a production-ready data layer that seamlessly scales from prototype to enterprise.
Core API Features
AI Reports & Conversational Agent: Generate on-demand, natural-language summaries of token performance. Build chatbots that answer “What’s the Investor Grade on SUI?” with live data.
Performance Analytics: Fetch historical ROI, volatility trajectories, and predictive rankings to power charts, tables, or heatmaps.
RESTful Architecture: Modular endpoints let you query only what you need—minimizing latency and overhead.
SDK Support: Python and Node.js wrappers accelerate integration into backend services or serverless functions.
Step-by-Step Integration
API Key Management: Store your key securely (e.g., environment variable).
SDK Initialization:
from tokenmetrics import TokenMetricsClient
client = TokenMetricsClient(api_key="YOUR_KEY")
Fetch Data (example: top 10 bullish tokens):
const { getTradingSignals } = require("tokenmetrics-sdk");
const signals = await getTradingSignals({ timeframe: "1h", filter: "bullish" });
Render in UI: Visualize grades as colored badges, embed sentiment word clouds, or display ROI charts.
Automated Updates: Use scheduled functions (e.g., AWS Lambda) to refresh data every hour via the API.
Use Case: Mobile Portfolio App
A mobile fintech startup built a React Native app that integrates Token Metrics’ Trader Grades and Market Sentiment endpoints. Users see a consolidated watchlist where each token’s grade is updated in real time. Push notifications alert them if a token moves from neutral to strong-buy. All of this runs on a backend microservice that queries the API every 15 minutes, processes data, and feeds it to the app via GraphQL.
Why SDKs Matter
By leveraging the official SDKs, developers skip the boilerplate of HTTP requests, JSON parsing, and error handling. Instead, they work with intuitive methods and objects. This reduces time-to-market and lowers the risk of integration bugs.
Pricing & Free Tier
Get started with $0 by using the free tier. When you outgrow it, upgrade to the $99 plan—or pay with $TMAI for discounts up to 35%. No hidden costs, just predictable pricing that grows with your usage.
0 notes
Text
How Coding Brushup Prepares You for Real-World Coding Challenges
In today’s competitive tech industry, mastering theoretical concepts is no longer enough. Employers now expect developers to possess hands-on experience, problem-solving skills, and the ability to build real-world applications from scratch. This is where Coding Brushup stands out. Through its extensive course offerings, including Coding Brushup Programming Courses, Coding Brushup Full Stack Developer Training, and specialized paths like Coding Brushup Java Courses and Coding Brushup Data Science Courses, it equips learners with industry-relevant skills to tackle modern development challenges.

Real-World Learning with Coding Brushup Courses
The core philosophy behind Coding Brushup Courses is practical learning. While traditional education often emphasizes theory, Coding Brushup bridges the gap between academia and the tech industry by providing learners with project-based training, real coding scenarios, and interview-level problem-solving exercises.
Whether you're taking Coding Brushup Web Development Courses or exploring Coding Brushup Cloud Computing Courses, the focus remains consistent: prepare you not only to write code but to solve problems like a professional developer.
1. Hands-On Training for In-Demand Skills
From day one, Coding Brushup Programming Courses encourage students to build real applications. By working on mini-projects and capstone challenges, learners don’t just understand syntax—they learn how to apply logic, structure programs, and debug like a pro. Courses are updated regularly to align with the current job market, ensuring learners are not left behind with outdated knowledge.
For example, in Coding Brushup Python Courses, students go beyond loops and functions to implement automation scripts, data manipulation tasks, and backend APIs. The Coding Brushup React Courses offer an immersive experience in front-end development, where students build responsive, scalable web apps using modern JavaScript frameworks.
2. Comprehensive Full Stack Training
A standout feature is the Coding Brushup Full Stack Developer Training. This program integrates front-end, back-end, and database development to give learners a 360-degree view of software engineering. Learners build applications using technologies like React, Node.js, Spring Boot, MongoDB, and more—exactly what today’s employers seek in a developer.
Students start with foundational skills in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, gradually advancing to more complex tasks like setting up APIs with Spring Boot (covered in Coding Brushup Spring Boot Courses) and deploying projects on cloud platforms (highlighted in Coding Brushup Cloud Computing Courses).
3. Project-Based Learning that Mimics the Workplace
Real-world coding challenges don’t come with detailed instructions. Coding Brushup Courses teach students how to handle ambiguity, understand client requirements, and implement scalable solutions—skills that are essential for software engineering roles.
Every track, from Coding Brushup Java Courses to Coding Brushup Data Science Courses, integrates hands-on projects. These projects simulate actual workplace problems, such as building RESTful APIs, designing user dashboards, integrating third-party APIs, and deploying solutions to the cloud.
4. Industry-Relevant Curriculum and Tools
To ensure that students are ready for their first or next job, Coding Brushup incorporates tools and technologies widely used in the tech industry. You’ll work with Git, GitHub, Docker, AWS, and real development environments. For instance, Coding Brushup Web Development Courses integrate version control systems, testing frameworks, and CI/CD practices to simulate professional workflows.
In Coding Brushup Cloud Computing Courses, learners gain experience with services like AWS EC2, S3, and Lambda, empowering them to build and deploy applications at scale. Meanwhile, Coding Brushup Java Courses focus on scalable enterprise application development with Spring Boot and Hibernate.
5. Supportive Learning Ecosystem
Beyond technical content, Coding Brushup Courses offer mentorship, community support, and career guidance. This human-centric approach ensures learners don’t feel lost, especially when tackling complex topics like data structures, algorithms, and system design.
In the Coding Brushup Python Courses, for example, regular code reviews and expert feedback help students continuously improve their code quality. The Coding Brushup React Courses come with discussion forums and weekly live sessions to clarify concepts and share solutions.
6. Interview Preparation and Job Readiness
Cracking tech interviews is another real-world challenge that many developers face. With its structured approach to interview preparation, Coding Brushup gives you an edge. Dedicated modules on DSA (Data Structures & Algorithms), mock interviews, and resume-building are part of many course tracks.
For instance, the Coding Brushup Full Stack Developer Training includes coding challenges that mirror actual technical interviews. Learners tackle problems in Java, Python, and JavaScript—reinforcing their understanding across different stacks.
7. Specialized Tracks to Suit Every Learner
One of the biggest advantages of Coding Brushup is the variety of specialized programs it offers. These tracks allow learners to focus on specific domains:
● Coding Brushup Java Courses for strong backend foundations.
● Coding Brushup Python Courses for data scripting, web backends, and ML basics.
● Coding Brushup React Courses for frontend developers.
● Coding Brushup Spring Boot Courses for enterprise backend systems.
● Coding Brushup Web Development Courses for full website creation and design.
● Coding Brushup Cloud Computing Courses for deployment and DevOps practices.
● Coding Brushup Data Science Courses for data analytics and predictive modeling.
Each of these tracks offers hands-on projects, industry-standard tools, and skill-based learning, making you a job-ready developer.
Conclusion: Learn to Code Like You Work in Tech
If you're serious about transitioning into tech or leveling up your current skills, Coding Brushup is the right platform. With courses built around real-world projects, expert instruction, and industry alignment, it prepares you for the challenges that modern developers face.
From Coding Brushup Programming Courses to advanced topics in Coding Brushup Data Science Courses and Cloud Computing, the platform delivers a holistic learning experience. Whether you want to specialize through Coding Brushup Java Courses, React Courses, or the all-encompassing Full Stack Developer Training, you’ll be learning with purpose and preparing to code like a professional.
Start your journey today with Coding Brushup Courses and become the developer the industry is looking for.
#coding brushup#programming#coding brushup for python#Coding brushup Java Course#coding brushup programming course
0 notes
Text
How Modern Data Engineering Powers Scalable, Real-Time Decision-Making
In today's world, driven by technology, businesses have evolved further and do not want to analyze data from the past. Everything from e-commerce websites providing real-time suggestions to banks verifying transactions in under a second, everything is now done in a matter of seconds. Why has this change taken place? The modern age of data engineering involves software development, data architecture, and cloud infrastructure on a scalable level. It empowers organizations to convert massive, fast-moving data streams into real-time insights.
From Batch to Real-Time: A Shift in Data Mindset
Traditional data systems relied on batch processing, in which data was collected and analyzed after certain periods of time. This led to lagging behind in a fast-paced world, as insights would be outdated and accuracy would be questionable. Ultra-fast streaming technologies such as Apache Kafka, Apache Flink, and Spark Streaming now enable engineers to create pipelines that help ingest, clean, and deliver insights in an instant. This modern-day engineering technique shifts the paradigm of outdated processes and is crucial for fast-paced companies in logistics, e-commerce, relevancy, and fintech.
Building Resilient, Scalable Data Pipelines
Modern data engineering focuses on the construction of thoroughly monitored, fault-tolerant data pipelines. These pipelines are capable of scaling effortlessly to higher volumes of data and are built to accommodate schema changes, data anomalies, and unexpected traffic spikes. Cloud-native tools like AWS Glue and Google Cloud Dataflow with Snowflake Data Sharing enable data sharing and integration scaling without limits across platforms. These tools make it possible to create unified data flows that power dashboards, alerts, and machine learning models instantaneously.
Role of Data Engineering in Real-Time Analytics
Here is where these Data Engineering Services make a difference. At this point, companies providing these services possess considerable technical expertise and can assist an organization in designing modern data architectures in modern frameworks aligned with their business objectives. From establishing real-time ETL pipelines to infrastructure handling, these services guarantee that your data stack is efficient and flexible in terms of cost. Companies can now direct their attention to new ideas and creativity rather than the endless cycle of data management patterns.
Data Quality, Observability, and Trust
Real-time decision-making depends on the quality of the data that powers it. Modern data engineering integrates practices like data observability, automated anomaly detection, and lineage tracking. These ensure that data within the systems is clean and consistent and can be traced. With tools like Great Expectations, Monte Carlo, and dbt, engineers can set up proactive alerts and validations to mitigate issues that could affect economic outcomes. This trust in data quality enables timely, precise, and reliable decisions.
The Power of Cloud-Native Architecture
Modern data engineering encompasses AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. They provide serverless processing, autoscaling, real-time analytics tools, and other services that reduce infrastructure expenditure. Cloud-native services allow companies to perform data processing, as well as querying, on exceptionally large datasets instantly. For example, with Lambda functions, data can be transformed. With BigQuery, it can be analyzed in real-time. This allows rapid innovation, swift implementation, and significant long-term cost savings.
Strategic Impact: Driving Business Growth
Real-time data systems are providing organizations with tangible benefits such as customer engagement, operational efficiency, risk mitigation, and faster innovation cycles. To achieve these objectives, many enterprises now opt for data strategy consulting, which aligns their data initiatives to the broader business objectives. These consulting firms enable organizations to define the right KPIs, select appropriate tools, and develop a long-term roadmap to achieve desired levels of data maturity. By this, organizations can now make smarter, faster, and more confident decisions.
Conclusion
Investing in modern data engineering is more than an upgrade of technology — it's a shift towards a strategic approach of enabling agility in business processes. With the adoption of scalable architectures, stream processing, and expert services, the true value of organizational data can be attained. This ensures that whether it is customer behavior tracking, operational optimization, or trend prediction, data engineering places you a step ahead of changes before they happen, instead of just reacting to changes.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Integrating ROSA Applications with AWS Services (CS221)
As cloud-native architectures become the backbone of modern application deployments, combining the power of Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA) with native AWS services unlocks immense value for developers and DevOps teams alike. In this blog post, we explore how to integrate ROSA-hosted applications with AWS services to build scalable, secure, and cloud-optimized solutions — a key skill set emphasized in the CS221 course.
🚀 What is ROSA?
Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA) is a managed OpenShift platform that runs natively on AWS. It allows organizations to deploy Kubernetes-based applications while leveraging the scalability and global reach of AWS, without managing the underlying infrastructure.
With ROSA, you get:
Fully managed OpenShift clusters
Integrated with AWS IAM and billing
Access to AWS services like RDS, S3, DynamoDB, Lambda, etc.
Native CI/CD, container orchestration, and operator support
🧩 Why Integrate ROSA with AWS Services?
ROSA applications often need to interact with services like:
Amazon S3 for object storage
Amazon RDS or DynamoDB for database integration
Amazon SNS/SQS for messaging and queuing
AWS Secrets Manager or SSM Parameter Store for secrets management
Amazon CloudWatch for monitoring and logging
Integration enhances your application’s:
Scalability — Offload data, caching, messaging to AWS-native services
Security — Use IAM roles and policies for fine-grained access control
Resilience — Rely on AWS SLAs for critical components
Observability — Monitor and trace hybrid workloads via CloudWatch and X-Ray
🔐 IAM and Permissions: Secure Integration First
A crucial part of ROSA-AWS integration is managing IAM roles and policies securely.
Steps:
Create IAM Roles for Service Accounts (IRSA):
ROSA supports IAM Roles for Service Accounts, allowing pods to securely access AWS services without hardcoding credentials.
Attach IAM Policy to the Role:
Example: An application that uploads files to S3 will need the following permissions:{ "Effect": "Allow", "Action": ["s3:PutObject", "s3:GetObject"], "Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket-name/*" }
Annotate OpenShift Service Account:
Use oc annotate to associate your OpenShift service account with the IAM role.
📦 Common Integration Use Cases
1. Storing App Logs in S3
Use a Fluentd or Loki pipeline to export logs from OpenShift to Amazon S3.
2. Connecting ROSA Apps to RDS
Applications can use standard drivers (PostgreSQL, MySQL) to connect to RDS endpoints — make sure to configure VPC and security groups appropriately.
3. Triggering AWS Lambda from ROSA
Set up an API Gateway or SNS topic to allow OpenShift applications to invoke serverless functions in AWS for batch processing or asynchronous tasks.
4. Using AWS Secrets Manager
Mount secrets securely in pods using CSI drivers or inject them using operators.
🛠 Hands-On Example: Accessing S3 from ROSA Pod
Here’s a quick walkthrough:
Create an IAM Role with S3 permissions.
Associate the role with a Kubernetes service account.
Deploy your pod using that service account.
Use AWS SDK (e.g., boto3 for Python) inside your app to access S3.
oc create sa s3-access oc annotate sa s3-access eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn=arn:aws:iam::<account-id>:role/S3AccessRole
Then reference s3-access in your pod’s YAML.
📚 ROSA CS221 Course Highlights
The CS221 course from Red Hat focuses on:
Configuring service accounts and roles
Setting up secure access to AWS services
Using OpenShift tools and operators to manage external integrations
Best practices for hybrid cloud observability and logging
It’s a great choice for developers, cloud engineers, and architects aiming to harness the full potential of ROSA + AWS.
✅ Final Thoughts
Integrating ROSA with AWS services enables teams to build robust, cloud-native applications using best-in-class tools from both Red Hat and AWS. Whether it's persistent storage, messaging, serverless computing, or monitoring — AWS services complement ROSA perfectly.
Mastering these integrations through real-world use cases or formal training (like CS221) can significantly uplift your DevOps capabilities in hybrid cloud environments.
Looking to Learn or Deploy ROSA with AWS?
HawkStack Technologies offers hands-on training, consulting, and ROSA deployment support. For more details www.hawkstack.com
0 notes
Text
Serverless vs. Containers: Which Cloud Computing Model Should You Use?
In today’s cloud-driven world, businesses are building and deploying applications faster than ever before. Two of the most popular technologies empowering this transformation are Serverless computing and Containers. While both offer flexibility, scalability, and efficiency, they serve different purposes and excel in different scenarios.
If you're wondering whether to choose Serverless or Containers for your next project, this blog will break down the pros, cons, and use cases—helping you make an informed, strategic decision.
What Is Serverless Computing?
Serverless computing is a cloud-native execution model where cloud providers manage the infrastructure, provisioning, and scaling automatically. Developers simply upload their code as functions and define triggers, while the cloud handles the rest.
Key Features of Serverless:
No infrastructure management
Event-driven architecture
Automatic scaling
Pay-per-execution pricing model
Popular Platforms:
AWS Lambda
Google Cloud Functions
Azure Functions
What Are Containers?
Containers package an application along with its dependencies and libraries into a single unit. This ensures consistent performance across environments and supports microservices architecture.
Containers are orchestrated using tools like Kubernetes or Docker Swarm to ensure availability, scalability, and automation.
Key Features of Containers:
Full control over runtime and OS
Environment consistency
Portability across platforms
Ideal for complex or long-running applications
Popular Tools:
Docker
Kubernetes
Podman
Serverless vs. Containers: Head-to-Head Comparison
Feature
Serverless
Containers
Use Case
Event-driven, short-lived functions
Complex, long-running applications
Scalability
Auto-scales instantly
Requires orchestration (e.g., Kubernetes)
Startup Time
Cold starts possible
Faster if container is pre-warmed
Pricing Model
Pay-per-use (per invocation)
Pay-per-resource (CPU/RAM)
Management
Fully managed by provider
Requires devops team or automation setup
Vendor Lock-In
High (platform-specific)
Low (containers run anywhere)
Runtime Flexibility
Limited runtimes supported
Any language, any framework
When to Use Serverless
Best For:
Lightweight APIs
Scheduled jobs (e.g., cron)
Real-time processing (e.g., image uploads, IoT)
Backend logic in JAMstack websites
Advantages:
Faster time-to-market
Minimal ops overhead
Highly cost-effective for sporadic workloads
Simplifies event-driven architecture
Limitations:
Cold start latency
Limited execution time (e.g., 15 mins on AWS Lambda)
Difficult for complex or stateful workflows
When to Use Containers
Best For:
Enterprise-grade microservices
Stateful applications
Applications requiring custom runtimes
Complex deployments and APIs
Advantages:
Full control over runtime and configuration
Seamless portability across environments
Supports any tech stack
Easier integration with CI/CD pipelines
Limitations:
Requires container orchestration
More complex infrastructure setup
Can be costlier if not optimized
Can You Use Both?
Yes—and you probably should.
Many modern cloud-native architectures combine containers and serverless functions for optimal results.
Example Hybrid Architecture:
Use Containers (via Kubernetes) for core services.
Use Serverless for auxiliary tasks like:
Sending emails
Processing webhook events
Triggering CI/CD jobs
Resizing images
This hybrid model allows teams to benefit from the control of containers and the agility of serverless.
Serverless vs. Containers: How to Choose
Business Need
Recommendation
Rapid MVP or prototype
Serverless
Full-featured app backend
Containers
Low-traffic event-driven app
Serverless
CPU/GPU-intensive tasks
Containers
Scheduled background jobs
Serverless
Scalable enterprise service
Containers (w/ Kubernetes)
Final Thoughts
Choosing between Serverless and Containers is not about which is better—it’s about choosing the right tool for the job.
Go Serverless when you need speed, simplicity, and cost-efficiency for lightweight or event-driven tasks.
Go with Containers when you need flexibility, full control, and consistency across development, staging, and production.
Both technologies are essential pillars of modern cloud computing. The key is understanding their strengths and limitations—and using them together when it makes sense.
#artificial intelligence#sovereign ai#coding#html#entrepreneur#devlog#linux#economy#gamedev#indiedev
1 note
·
View note
Text
Back-End Development: A Complete Guide for Beginners in 2025
When you visit a website, everything you see—the layout, colors, text, and buttons—is the front end. But what happens when you log in, fill out a form, or make a payment? That’s where the back-end development magic begins.
In this complete guide, we’ll explore what back-end development is, why it’s crucial for the web, what technologies and skills you need, and how you can build a thriving career in this dynamic field. Whether you're a curious beginner or someone switching careers, this article has everything you need to know.
🚀 What is Back-End Development?
Back-end development refers to the server-side part of web development. It's everything that happens behind the scenes to make a website or app function properly—like servers, databases, application logic, and APIs.
Back-end development is all about how a website works rather than how it looks.
For example:
When you submit a login form, the back end checks your credentials in the database.
When you place an order online, the back end processes the order and stores the transaction.
⚙️ How Does Back-End Development Work?
The back end interacts with three key components:
Server – The machine that handles requests.
Database – Where data like user info and product listings are stored.
Application – The logic that ties it all together.
Here’s a simplified flow:
User clicks a button (front-end)
Front-end sends a request to the server
Back-end processes the request
Data is fetched from or saved to the database
Server sends a response back to the front-end
🧰 Core Technologies in Back-End Development
To become a back-end developer, you’ll need to learn these foundational tools and languages:
1. Programming Languages
LanguageUse CaseJavaScript (Node.js)Scalable server-side appsPythonFast prototyping, AI, APIsPHPWordPress and server scriptingRubyElegant, readable server-side codeJavaEnterprise-grade backend systemsC# (.NET)Enterprise, Windows-based applications
2. Databases
TypeExamplesRelationalMySQL, PostgreSQL, MS SQL ServerNoSQLMongoDB, CouchDB, Firebase
3. Frameworks
LanguageFrameworksJavaScriptExpress.js, Nest.jsPythonDjango, FlaskPHPLaravelRubyRuby on Rails
🌐 Back-End vs Front-End Development
FeatureFront-EndBack-EndFocusUser interface (UI/UX)Server logic and databaseLanguagesHTML, CSS, JSJS (Node), Python, PHP, JavaRuns OnBrowserServerPrimary ConcernDesign, interactivityLogic, data management, securityPopular ToolsReact, Vue, BootstrapDjango, Express.js, PostgreSQL
🧑💻 Roles & Responsibilities of a Back-End Developer
What does a back-end developer do?
Build APIs and server-side logic
Design and maintain databases
Secure user data and handle authentication
Ensure scalability and performance
Collaborate with front-end developers and DevOps teams
🛡️ Back-End and Security
Security is a core responsibility in back-end development.
Key areas include:
Data encryption
Secure APIs
Password hashing (bcrypt, Argon2)
Input validation
Authorization & Authentication (OAuth, JWT, etc.)
🧱 APIs and RESTful Architecture
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are bridges between the front end and back end.
Back-end developers often design:
REST APIs using HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
GraphQL APIs for flexible data querying
WebSockets for real-time communication
🔗 Database Management and ORM
Databases are the heart of any application.
Back-end developers use SQL for structured queries and ORMs (Object Relational Mappers) like:
Sequelize (Node.js)
Prisma
SQLAlchemy (Python)
Eloquent (Laravel)
📦 Hosting and Deployment
Once the server code is ready, it needs to be hosted.
Popular options:
Cloud: AWS, Google Cloud, Azure
Containers: Docker, Kubernetes
Serverless: Vercel, Netlify, AWS Lambda
CI/CD pipelines like GitHub Actions, Jenkins, and GitLab CI automate deployments.
🧠 Learning Path: How to Become a Back-End Developer
Here’s a structured roadmap:
Master a Programming Language – Start with Python or JavaScript (Node.js)
Understand the Internet and HTTP
Learn Databases – Start with MySQL or MongoDB
Build REST APIs
Practice Authentication & Security
Work with Real Projects
Use Git and GitHub
Explore DevOps Basics
Build a Portfolio with back-end apps
Contribute to Open Source
📊 Salary Insights and Job Opportunities (2025)
Back-end development is one of the most in-demand tech skills in 2025.CountryEntry-LevelMid-LevelSeniorIndia₹5–8 LPA₹10–20 LPA₹25+ LPAUSA$65K–$85K$90K–$120K$130K+UK£30K–£50K£55K–£75K£80K+
Common Job Titles:
Back-End Developer
Full-Stack Developer
API Engineer
Server-Side Developer
Cloud Functions Developer
💬 Real Developer Reviews
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ “As a back-end developer, I love building things people don’t even realize they’re using. It’s like being a wizard behind the curtain.” — Neha R., Software Engineer
⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ “Python and Django made it easy to get started. The logic is so clean and powerful.” — Mike T., Backend Developer
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ “Every startup needs someone who can build scalable back ends. It’s a career with massive growth potential.” — Ritika D., API Architect
🧠 Best Learning Resources (Free & Paid)
Free Platforms:
freeCodeCamp
MDN Web Docs
The Odin Project
Paid Options:
Udemy
"Node.js: The Complete Guide"
"Python & Django Bootcamp"
Coursera
"Back-End Development by Meta"
edX
Scrimba
📌 FAQs About Back-End Development
Q1. Do I need a degree to become a back-end developer?
A: No. Many successful developers are self-taught. Bootcamps and real-world projects matter more than degrees.
Q2. Which is better: back-end or front-end?
A: It depends on your interests. If you enjoy logic, data, and server operations—back-end is for you.
Q3. Is Node.js good for back-end?
A: Yes. Node.js is fast, efficient, and widely used for scalable server-side applications.
Q4. How long does it take to become job-ready?
A: With consistent learning, you can become a back-end developer in 6–12 months.
Q5. What is full-stack development?
A: Full-stack developers handle both front-end and back-end tasks. They’re skilled in end-to-end development.
Q6. What are the best languages for back-end development?
A: Python, JavaScript (Node.js), PHP, Java, and C# are top choices in 2025.
✨ Final Thoughts: Is Back-End Development Right for You?
If you love building logic, handling real-world data, working with APIs, and ensuring applications run smoothly—back-end development might be your ideal career path.
It’s a high-demand, well-paying, and technically rewarding field with endless opportunities for growth, especially with cloud computing, AI, and big data booming.
Whether you dream of joining a tech giant or launching your own SaaS app, mastering back-end development opens the door to some of the most impactful tech roles of the future.
0 notes
Photo

New Post has been published on https://codebriefly.com/building-and-deploying-angular-19-apps/
Building and Deploying Angular 19 Apps

Efficiently building and deploying Angular 19 applications is crucial for delivering high-performance, production-ready web applications. In this blog, we will cover the complete process of building and deploying Angular 19 apps, including best practices and optimization tips.
Table of Contents
Toggle
Why Building and Deploying Matters
Preparing Your Angular 19 App for Production
Building Angular 19 App
Key Optimizations in Production Build:
Configuration Example:
Deploying Angular 19 App
Deploying on Firebase Hosting
Deploying on AWS S3 and CloudFront
Automating Deployment with CI/CD
Example with GitHub Actions
Best Practices for Building and Deploying Angular 19 Apps
Final Thoughts
Why Building and Deploying Matters
Building and deploying are the final steps of the development lifecycle. Building compiles your Angular project into static files, while deploying makes it accessible to users on a server. Proper optimization and configuration ensure faster load times and better performance.
Preparing Your Angular 19 App for Production
Before building the application, make sure to:
Update Angular CLI: Keep your Angular CLI up to date.
npm install -g @angular/cli
Optimize Production Build: Enable AOT compilation and minification.
Environment Configuration: Use the correct environment variables for production.
Building Angular 19 App
To create a production build, run the following command:
ng build --configuration=production
This command generates optimized files in the dist/ folder.
Key Optimizations in Production Build:
AOT Compilation: Reduces bundle size by compiling templates during the build.
Tree Shaking: Removes unused modules and functions.
Minification: Compresses HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files.
Source Map Exclusion: Disables source maps for production builds to improve security and reduce file size.
Configuration Example:
Modify the angular.json file to customize production settings:
"configurations": "production": "optimization": true, "outputHashing": "all", "sourceMap": false, "namedChunks": false, "extractCss": true, "aot": true, "fileReplacements": [ "replace": "src/environments/environment.ts", "with": "src/environments/environment.prod.ts" ]
Deploying Angular 19 App
Deployment options for Angular apps include:
Static Web Servers (e.g., NGINX, Apache)
Cloud Platforms (e.g., AWS S3, Firebase Hosting)
Docker Containers
Serverless Platforms (e.g., AWS Lambda)
Deploying on Firebase Hosting
Install Firebase CLI:
npm install -g firebase-tools
Login to Firebase:
firebase login
Initialize Firebase Project:
firebase init hosting
Deploy the App:
firebase deploy
Deploying on AWS S3 and CloudFront
Build the Project:
ng build --configuration=production
Upload to S3:
aws s3 sync ./dist/my-app s3://my-angular-app
Configure CloudFront Distribution: Set the S3 bucket as the origin.
Automating Deployment with CI/CD
Setting up a CI/CD pipeline ensures seamless updates and faster deployments.
Example with GitHub Actions
Create a .github/workflows/deploy.yml file:
name: Deploy Angular App on: [push] jobs: build-and-deploy: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - uses: actions/checkout@v2 - name: Set up Node.js uses: actions/setup-node@v2 with: node-version: '18' - run: npm install - run: npm run build -- --configuration=production - name: Deploy to S3 run: aws s3 sync ./dist/my-app s3://my-angular-app --delete
Best Practices for Building and Deploying Angular 19 Apps
Optimize for Production: Always use AOT and minification.
Use CI/CD Pipelines: Automate the build and deployment process.
Monitor Performance: Utilize tools like Lighthouse to analyze performance.
Secure the Application: Enable HTTPS and configure secure headers.
Cache Busting: Use hashed filenames to avoid caching issues.
Containerize with Docker: Simplifies deployments and scales easily.
Final Thoughts
Building and deploying Angular 19 applications efficiently can significantly enhance performance and maintainability. Following best practices and leveraging cloud hosting services ensure that your app is robust, scalable, and fast. Start building your next Angular project with confidence!
Keep learning & stay safe 😉
You may like:
Testing and Debugging Angular 19 Apps
Performance Optimization and Best Practices in Angular 19
UI/UX with Angular Material in Angular 19
0 notes