#ancient celts
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

The noble lady of the 5th house and her husband
Since the 4th and the 5th are really close I wanted them to have similar celtic inspirations
#the locked tomb#gideon the ninth#abigail pent#magnus quinn#fifth house#canaan house#tlt fanart#ancient celts
180 notes
·
View notes
Text




we are just misguided ghosts, traveling endlessly (...) 🙃☠️🍃
#my photos#my art#ireland#travel#dark cottagecore#dark core#cottagecore#cottage aesthetic#dark aesthetic#aesthetic#follow me#for you#explore#follow back#mental health#bipolar disorder#instant folllow back#follow for follow#urbexphotography#urbexexploration#abandoned places#abandoned photography#red hair girl#spirituality#celtic#ancient celts#irish#urbexplaces#nature core#paramore
71 notes
·
View notes
Text
My necklace was made before I even created my tumblr account. I wear it everyday, yet it never occurred to me that I could share it here.
This is an Ogham/Ogam protection charm I made by stripping a pine branch, carving a flat edge, and burning the word cosaint (Irish for protection/defense) into the wood. It’s created its own finish with the natural oils from my fingers, enhancing the color and shine of the wood.
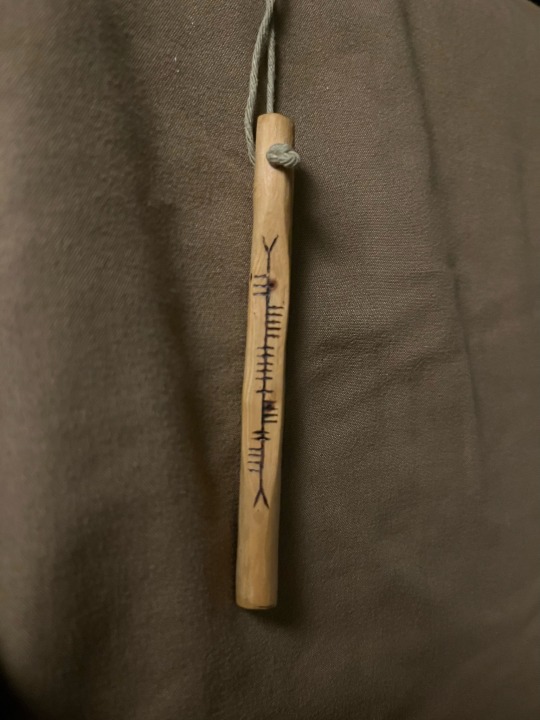

#folk witch#irish witchcraft#witch blog#pagan witch#witchcore#traditional witchcraft#witch#witches#green witch#witchcraft#folk witchcraft#witch aesthetic#witch community#witchblr#witches of tumblr#cunning folk#cunning woman#ancient celts#celtic folklore#celtic#scottish folk magic#scottish folklore#irish folk magic#irish language#ogham#charms#magick#ogam
167 notes
·
View notes
Text




Unfinished portraits of Irish gods from 2021
#celtic#celtic paganism#celtic mythology#celtic polytheism#irish paganism#irish mythology#irish#paganachd#pagan#paganism#druidism#druidry#irish culture#ireland#eire#ancient ireland#ancient celts#mythology#digital art#digital illustration#portrait#art wip#unfinished
355 notes
·
View notes
Text

Celtic Styled Iron Age Stone Head and Romano-Native Mother Goddess Figure, Newport Museum and Galleries, Newport, Wales
#celtic#ancient celts#stone head#iron age#archaeology#relic#stonework#ancient living#ancient crafts#ancient cultures#prehistoric#prehistory#goddess#mother goddess#ancient beliefs#figurine#Wales#Newport
101 notes
·
View notes
Text
Did the ancient Celts really paint themselves blue?
Part 2: Irish tattoos
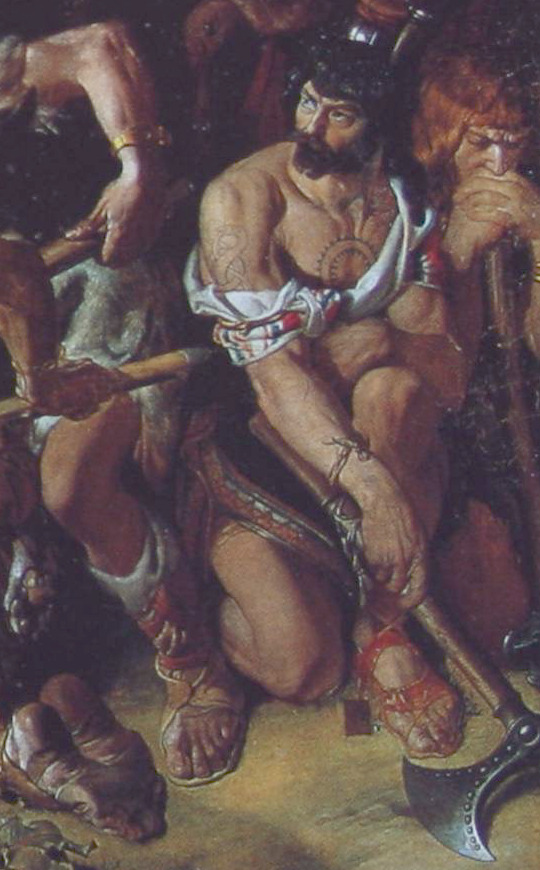
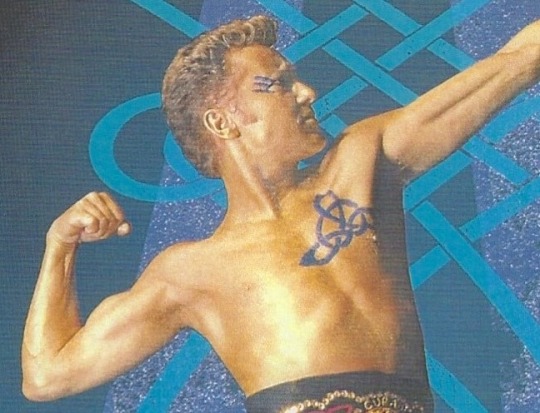
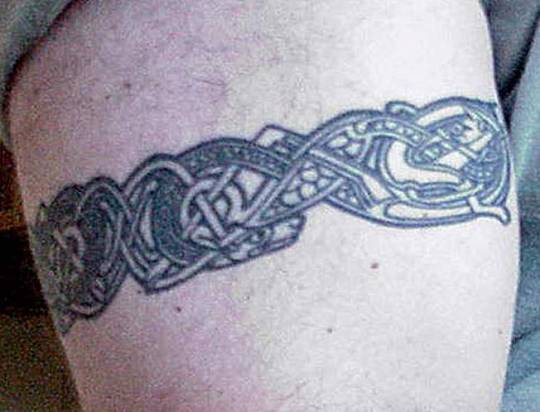




Clockwise from top left: Deirdre and Naoise from the Ulster Cycle by amylouioc, detail from The Marriage of Strongbow and Aoife by Daniel Maclise, a modern Celtic revival tattoo, Michael Flatley in a promotional image for the Irish step dance show 'Lord of the Dance'
This is my second post exploring the historical evidence for our modern belief that the ancient and medieval Insular Celts painted or tattooed themselves with blue pigment. In the first post, I discussed the fact that body paint seems to have been used by residents of Great Britain between approximately 50 BCE to 100 CE. In this post, I will examine the evidence for tattooing.
Once again, I am looking at sources pertaining to any ethnic group who lived in the British Isles, this time from the Roman Era to the early Middle Ages. The relevant text sources range from approximately 200 CE to 900 CE. I am including all British Isles cultures, because a) determining exactly which Insular culture various writers mean by terms like ‘Briton’, ‘Scot’, and ‘Pict’ is sometimes impossible and b) I don’t want to risk excluding any relevant evidence.
Continental Written Sources:
The earliest written source to mention tattoos in the British Isles is Herodian of Antioch’s History of the Roman Empire written circa 208 CE. In it, Herodian says of the Britons, "They tattoo their bodies with colored designs and drawings of all kinds of animals; for this reason they do not wear clothes, which would conceal the decorations on their bodies" (translation from MacQuarrie 1997). Herodian is probably reporting second-hand information given to him by soldiers who fought under Septimius Severus in Britain (MacQuarrie 1997) and shouldn't be considered a true primary source.
Also in the early 3rd century, Gaius Julius Solinus says in Collectanea Rerum Memorabilium 22.12, "regionem [Brittaniae] partim tenent barbari, quibus per artifices plagarum figuras iam inde a pueris variae animalium effigies incorporantur, inscriptisque visceribus hominis incremento pigmenti notae crescunt: nec quicquam mage patientiae loco nationes ferae ducunt, quam ut per memores cicatrices plurimum fuci artus bibant."
Translation: "The area [of Britain] is partly occupied by barbarians on whose bodies, from their childhood upwards, various forms of living creatures are represented by means of cunningly wrought marks: and when the flesh of the person has been deeply branded, then the marks of the pigment get larger as the man grows, and the barbaric nations regard it as the highest pitch of endurance to allow their limbs to drink in as much of the dye as possible through the scars which record this" (from MacQuarrie 1997).
This passage, like Herodian's, is clearly a description of tattooing, not body staining or painting. That said, I have no idea of tattoos actually work like this. I would think this would result in the adult having a faded, indistinct tattoo, but if anyone knows otherwise, please tell me.
The poet Claudian, writing in the early 5th c., is the first to specifically mention the Picts having tattoos (MacQuarrie 1997). In De Bello Gothico he says, "Venit & extremis legio praetenta Britannis,/ Quæ Scoto dat frena truci, ferroque notatas/ Perlegit exanimes Picto moriente figuras."
Translation: "The legion comes to make a trial of the most remote parts of Britain where it subdues the wild Scot and gazes on the iron-wrought figures on the face of the dying Pict" (from MacQuarrie 1997).
Last, and possibly least, of our Mediterranean sources is Isidore of Seville. In the early 7th c. he writes, "the Pictish race, their name derived from their body, which the efficient needle, with minute punctures, rubs in the juices squeezed from native plants so that it may bring these scars to its own fashion [. . .] The Scotti have their name from their own language by reason of [their] painted body, because they are marked by iron needles with dark coloring in the form of a marking of varying shapes." (translation from MacQuarrie 1997)
Isidore is the earliest writer to explicitly link the name 'Pict' to their 'painted' (Latin: pictus) i.e. tattooed bodies. Isidore probably borrowed information for his description from earlier writers like Claudian (MacQuarrie 1997).
In the 8th century, we have a source that definitely isn't Romans recycling old hearsay. In 786, a pair of papal legates visited the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of Mercia and Northumbria (Story 1995). In their report to Pope Hadrian, the legates condemn pagans who have "superimposed most hideous cicatrices" (i.e gotten tattoos), likening the pagan practice to coloring oneself "with dirty spots". The location of the visit indicates that these are Anglo-Saxon tattoos rather than Celtic, but some scholars have suggested that the Anglo-Saxons might have adopted the practice from the Brittonic Celts (MacQuarrie 1997).
A gloss in the margin of the late 9th c. German manuscript Fulda Aa 2 defines Stingmata [sic] as "put pictures on the bodies as the Irish (Scotti) do." (translation from MacQuarrie 1997).

Fulda Aa 2 folio 43r The gloss is on the left underlined in white.
Irish Written Sources:
Irish texts that mention tattoos date to approximately 700-900 CE, although some of them have glosses that may be slightly later, and some of them cannot be precisely dated.
The first text source is a poem known in English as "The Caldron of Poesy," written in the early 8th c. (Breatnach 1981). The poem is purportedly the work of Amairgen, ollamh of the legendary Milesian kings. In the first stanza of the poem, he introduces himself saying, "I being white-kneed, blue-shanked, grey-bearded Amairgen." (translation from Breatnach 1981)

The text of the poem with interline glosses from Trinity College Dublin MS 1337/1
The word garrglas (blue-shanked) has a Middle Irish (c. 900-1200) gloss added by a later scribe, defining garrglas as: "a tattooed shank, or who has the blue tattooed shank" (Breatnach 1981).
Although Amairgen was a mythical figure, the position ollamh was not. An ollamh was the highest rank of poet in medieval Ireland, considered worthy of the same honor-price as a king (Carey 1997, Breatnach 1981). The fact that a man of such esteemed status introduces himself with the descriptor 'blue-shanked' suggests that tattoos were a respectable thing to have in early medieval Ireland.
The leg tattoos are also mentioned c. 900 CE in Cormac’s Glossary. It defines feirenn as "a thong which is about the calf of a man whence ‘a tattooed thong is tattooed about [the] calf’" (translation from MacQuarrie 1997)
The Irish legal text Uraicecht Becc, dated to the 9th or early 10th c., includes the word creccoire on a list of low-status occupations (Szacillo 2012, MacNeill 1924). A gloss defines it as: crechad glass ar na roscaib, a phrase which Szacillo interprets as meaning "making grey-blue sore (tattooing) on the eyes" (2012). This sounds rather strange, but another early Irish text clarifies it.
The Vita sancti Colmani abbatis de Land Elo written around the 8th-9th centuries (Szacillo 2012) contains the following episode:
On another time, St Colmán, looking upon his brother, who was the son of Beugne, saw that the lids of his eyes had been secretly painted with the hyacinth colour, as it was in the custom; and it was a great offence at St Colmán’s. He said to his brother: ‘May your eyes not see the light in your life (any more). And from that hour he was blind, seeing nothing until (his) death. (translation from Szacillo 2012).
The original Latin phrase describing what so offended St Colmán "palpebre oculorum illius latenter iacinto colore" does not contain the verb paint (pingo). It just says his eyelids were hyacinth (blue) colored. This passage together with the gloss from the Uraicecht Becc implies that there was a custom of tattooing people's eyelids blue in early medieval Ireland. A creccoire* was therefore a professional eyelid tattooer or a tattoo artist.
A possible third reference to tattooing the area around the eye is found in a list of Old Irish kennings. The kenning for the letter 'B' translates as 'Beauty of the eyebrow.' This kenning is glossed with the word crecad/creccad (McManus 1988). Crecad could be translated as cauterizing, branding, or tattooing (eDIL). McManus suggests "adornment (by tattooing) of the eyebrow" as a plausible interpretation of how crecad relates to the beauty of the eyebrow (1988). The precise date of this text is not known (McManus 1988), but Old Irish was used c. 600-900 CE, meaning this text is of a similar date to the other Irish references to tattoos.

Kenning of the letter 'b' with gloss from TCD MS 1337/1
There is a sharp contrast between the association of tattoos with a venerated figure in 'The Caldron of Poesy', and their association with low-status work and divine punishment in the Uraicecht Becc and the Vita. This indicates that there was a shift in the cultural attitude towards tattoos in Ireland during the 7th-9th centuries. The fact that a Christian saint considered getting tattoos a big enough offense to punish his own brother with blindness suggests that tattooing might have been a pagan practice which gradually got pushed out by the Catholic Church. This timeline is consistent with the 786 CE report of the papal legates condemning the pagan practice of tattooing in Great Britain (MacQuarrie 1997).
There are some mentions of tattooing in Lebor Gabála Érenn, but the information largely appears to be borrowed from Isidore of Seville (MacQuarrie 1997). The fact that the writers of LGE just regurgitated Isidore's meager descriptions of Pictish and Scottish (ie Irish) tattooing without adding any details, such as the designs used or which parts of the body were tattooed, makes me think that Insular tattooing practices had passed out of living memory by the time the book was written in the 11th century.
*There is some etymological controversy over this term. Some have suggested that the Old Irish word for eyelid-tattooer should actually be crechaire. more info Even if this hypothesis is correct, and the scribe who wrote the gloss on creccoire mistook it for crechaire, this doesn't contradict my argument. The scribe clearly believed that eyelid-tattooer belonged on a list of low-status occupations.
Discussion:
Like Julius Cesar in the last post, Herodian of Antioch c. 208 CE makes some dubious claims of Celtic barbarism, stating that the Britons were: "Strangers to clothing, the Britons wear ornaments of iron at their waists and throats; considering iron a symbol of wealth, they value this metal as other barbarians value gold" (translation from MacQuarrie 1997). If the Britons wore nothing but iron jewelry, then why did they have brass torcs and 5,000 objects that look like they're meant to attach to fabric, Herodian?
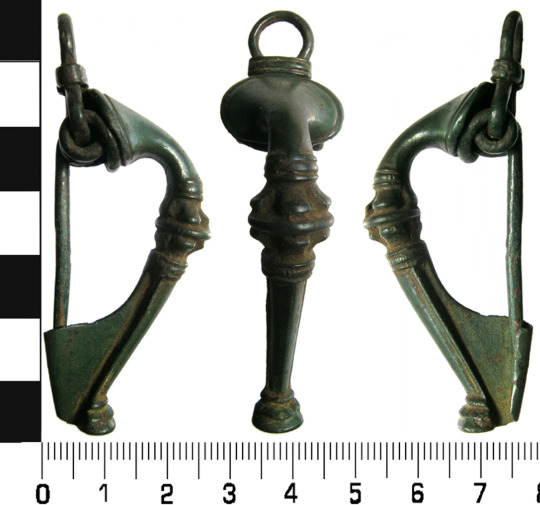


Brass torc from Lochar Moss, Scotland c. 50-200 CE. Romano-British trumpet brooch from Cumbria c. 75-175 CE. image from the Portable Antiquities Scheme.
Trumpet brooches are a Roman Era artifact invented in Britain, that were probably pinned to people's clothing. more info
Although Herodian and Solinus both make dubious claims, there are enough differences between them to indicate that they had 2 separate sources of information, and one was not just parroting the other. This combined with the fact that we have more-reliable sources from later centuries confirming the existence of tattoos in the British Isles makes it probable that there was at least a grain of truth to their claims of tattooing.
There is a common belief that the name Pict originated from the Latin pictus (painted), because the Picts had 'painted' or tattooed bodies. The Romans first used the name Pict to refer to inhabitants of Britain in 297 CE (Ware 2021), but the first mention of Pictish tattoos came in 402 CE (Carr 2005), and the first explicit statement that the name Pict was derived from the Picts' tattooed bodies came from Isidore of Seville c. 600 CE (MacQuarrie 1997). Unless someone can find an earlier source for this alleged etymology than Isidore, I am extremely skeptical of it.
Summary of the written evidence:
Some time between c. 79 CE (Pliny the Elder) and c. 208 CE (Herodian of Antioch) the practice of body art in Great Britain changed from staining or painting the skin to tattooing. Third century Celtic Briton tattoo designs depicted animals. Pictish tattoos are first mentioned in the 5th century.
The earliest mention of Irish tattoos comes from Isidore of Seville in the early 6th c., but since it seems to have been a pre-Christian practice, it likely started earlier. Irish tattoos of the 8-9th centuries were placed on the area around the eye and on the legs. They were a bluish color. The 8th c. Anglo-Saxons also had tattoos.
Tattooing in Ireland probably ended by the early 10th c., possibly because of Christian condemnation. Exactly when tattooing ended in Great Britain is unclear, but in the 12th c., William of Malmesbury describes it as a thing of the past (MacQuarrie 1997). None of these sources give much detail as to what the tattoos looked like.
The Archaeology of Insular Ink:
In spite of the fact that tattooing was a longer-lasting, more wide-spread practice in the British Isles than body painting, there is less archaeological evidence for it. This may be because the common tools used for tattooing, needles or blades for puncturing the skin, pigments to make the ink, and dishes to hold the ink, all had other common uses in the Middle Ages that could make an archaeologist overlook their use in tattooing. The same needle that was used to sew a tunic could also have been used to tattoo a leg (Carr 2005). A group of small, toothed bronze plates from a Romano-British site at Chalton, Hampshire might have been tattoo chisels (Carr 2005) or they might have been used to make stitching holes in leather (Cunliffe 1977).
Although the pigment used to make tattoos may be difficult to identify at archaeological sites, other lines of evidence might give us an idea of what it was. Although the written sources tell us that Irish tattoos were blue, the popular modern belief that woad was the source of the tattoo pigment is, in my opinion, extremely unlikely for a couple of reasons:
1) Blue pigment from woad doesn't seem to work as tattoo ink. The modern tattoo artists who have tried to use it have found that it burns out of the person's skin, leaving a scar with no trace of blue in it (Lambert 2004).
2) None of the historical sources actually mention tattooing with woad. Julius Cesar and Pliny the Elder mention something that might have been woad, but they were talking about body paint, not tattoos. (see previous post) Isidore of Seville claimed that the Picts were tattooing themselves with "juices squeezed from native plants", but even assuming that Isidore is a reliable source, you can't get blue from woad by just squeezing the juice out of it. In order to get blue out of woad, you have to first steep the leaves, then discard the leaves and add a base like ammonia to the vat (Carr 2005). The resulting dye vat is not something any knowledgeable person would describe as plant juice, so either Isidore had no idea what he was talking about, or he is talking about something other than blue pigment from woad.
In my opinion, the most likely pigment for early Irish and British tattoos is charcoal. Early tattoos found on mummies from Europe and Siberia all contain charcoal and no other colored pigment. These tattoos range in date from c. 3300 BCE (Ötzi the Iceman) to c. 300 CE (Oglakhty grave 4) (Samadelli et al 2015, Pankova 2013).
Despite the fact that charcoal is black, it tends to look blueish when used in tattoos (Pankova 2013). Even modern black ink tattoos that use carbon black pigment (which is effectively a purer form of charcoal) tend to look increasingly blue as they age.
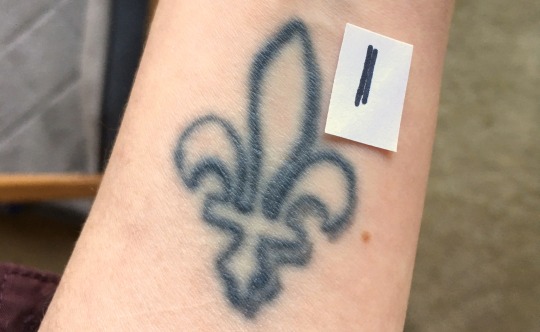
A 17-year-old tattoo in carbon black ink photographed with a swatch of black Sharpie on white printer paper.
The fact that charcoal-based tattoo inks continue to be used today, more than 5,000 years after the first charcoal tattoo was given, shows that charcoal is an effective, relatively safe tattoo pigment, unlike woad. Additionally, charcoal can be easily produced with wood fires, meaning it would have been a readily available material for tattoo artists in the early medieval British Isles. We would need more direct evidence, like a tattooed body from the British Isles, to confirm its use though.
As of June 2024, there have been at least 279 bog bodies* found in the British Isles (Ó Floinn 1995, Turner 1995, Cowie, Picken, Wallace 2011, Giles 2020, BBC 2024), a handful of which have made it into modern museum collections. Unfortunately, tattoos have not been found on any of them. (We don't have a full scientific analysis for the 2023 Bellaghy find yet though.)
*This number includes some finds from fens. It does not include the Cladh Hallan composite mummies.
Tattoos in period art?
It has been suggested that the man fight a beast on Book of Kells f. 130r may be naked and covered in tattoos (MacQuarrie 1997). However, Dress in Ireland author Mairead Dunlevy interprets this illustration as a man wearing a jacket and trews (Dunlevy 1989). Looking at some of the other figures in the Book of Kells, I agree with Dunlevy. F. 97v shows the same long, fitted sleeves and round neckline. F. 292r has long, fitted leg coverings, presumably trews, and also long sleeves. The interlace and dot motifs on f. 130r's legs may be embroidery. Embroidered garments were a status symbol in early medieval Ireland (Dunlevy 1989).
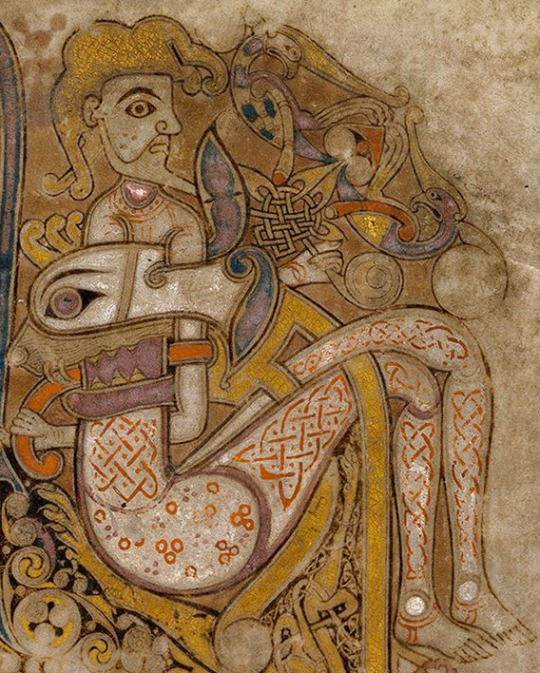

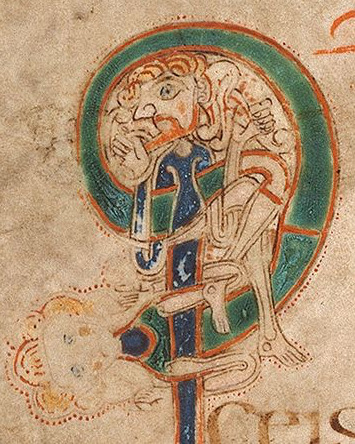

Left to right: Book of Kells folios 130r, 97v, 292r
A couple of sculptures in County Fermanagh might sport depictions of Irish tattoos. The first, known as the Bishop stone, is in the Killadeas cemetery. It features a carved head with 2 marks on the left side of the face, a double line beside the mouth and a single line below the eye. These lines may represent tattoos.
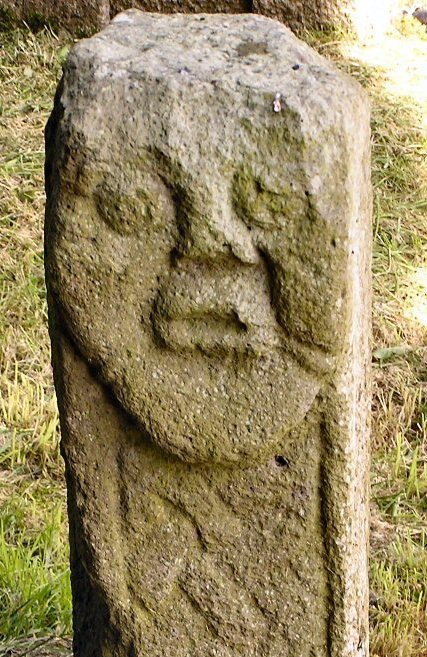
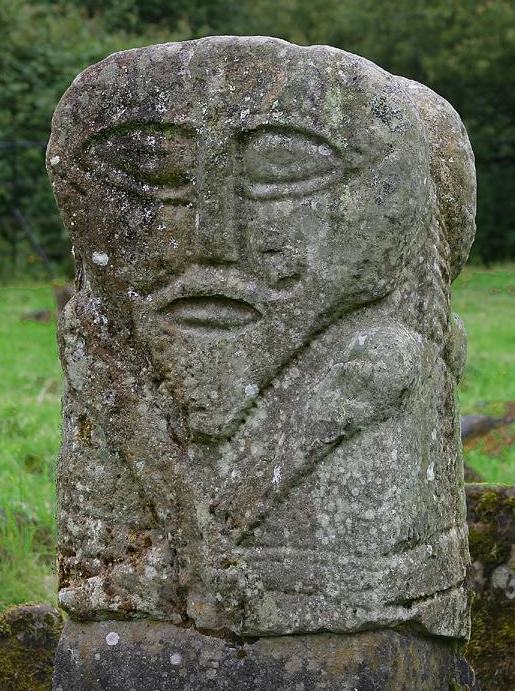


The second sculpture is the Janus figure on Boa Island. (So named because it has 2 faces; it's not Roman.) It has marks under the right eye and extending from the corner of the left eye that may be tattoos.
I cannot find a definitive date for the Bishop stone head, but it bears a strong resemblance to the nearby White Island church figures. The White Island figures are stylistically dated to the 9th-10th centuries and may come from a church that was destroyed by Vikings in 837 CE (Halpin and Newman 2006, Lowry-Corry 1959). The Janus figure is believed to be Iron Age or early medieval (Halpin and Newman 2006).
Conclusions:
Despite the fact that tattooing as a custom in the British Isles lasted for more than 500 years and was practiced by at least 3 different cultures, written sources remain our only solid evidence for it. With only a dozen sources, some of which probably copied each other, to cover this time span, there are huge gaps in our knowledge. The 4th century Picts may not have had the same tattoo designs, placements or reasons for getting tattooed as the 8th c. Irish or Anglo-Saxons. These sources only give us fragments of information on who got tattooed, where the tattoos were placed, what they looked like, how the tattoos were done, and why people got tattooed. Further complicating our limited information is the fact that most of the text sources come from foreigners and/or people who were prejudiced against tattooing, which calls their accuracy into question.
'The Cauldron of Posey' is one source that provides some detail while not showing prejudice against tattoos. The author of the poem was probably Christian, but the poem appears to have been written at a time when Pagan practices were still tolerated in Ireland. I have a complete translation of the poem along with a longer discussion of religious elements here.
Leave me a tip?
Bibliography:
BBC (2024). Bellaghy bog body: Human remains are 2,000 years old https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-northern-ireland-68092307
Breatnach, L. (1981). The Cauldron of Poesy. Ériu, 32(1981), 45-93. https://www.jstor.org/stable/30007454
Carey, J. (1997). The Three Things Required of a Poet. Ériu, 48(1997), 41-58. https://www.jstor.org/stable/30007956
Carr, Gillian. (2005). Woad, Tattooing and Identity in Later Iron Age and Early Roman Britain. Oxford Journal of Archaeology 24(3), 273–292. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0092.2005.00236.x
Cowie, T., Pickin, J. and Wallace, T. (2011). Bog bodies from Scotland: old finds, new records. Journal of Wetland Archaeology 10(1): 1–45.
Cunliffe, B. (1977) The Romano-British Village at Chalton, Hants. Proceedings of the Hampshire Field Club and Archaeological Society, 33(1977), 45-67.
Dunlevy, Mairead (1989). Dress in Ireland. B. T. Batsford LTD, London.
eDIL s.v. crechad https://dil.ie/12794
Giles, Melanie. (2020). Bog Bodies Face to face with the past. Manchester University Press, Manchester. https://library.oapen.org/viewer/web/viewer.html?file=/bitstream/handle/20.500.12657/46717/9781526150196_fullhl.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Halpin, A., Newman, C. (2006). Ireland: An Oxford Archaeological Guide to Sites from Earliest Times to AD 1600. Oxford University Press, Oxford. https://archive.org/details/irelandoxfordarc0000halp/page/n3/mode/2up
Hoecherl, M. (2016). Controlling Colours: Function and Meaning of Colour in the British Iron Age. Archaeopress Publishing LTD, Oxford. https://www.google.com/books/edition/Controlling_Colours/WRteEAAAQBAJ?hl=en&gbpv=0
Lambert, S. K. (2004). The Problem of the Woad. Dunsgathan.net. https://dunsgathan.net/essays/woad.htm
Lowry-Corry, D. (1959). A Newly Discovered Statue at the Church on White Island, County Fermanagh. Ulster Journal of Archaeology, 22(1959), 59-66. https://www.jstor.org/stable/20567530
MacQuarrie, Charles. (1997). Insular Celtic tattooing: History, myth and metaphor. Etudes Celtiques, 33, 159-189. https://doi.org/10.3406/ecelt.1997.2117
McManus, D. (1988). Irish Letter-Names and Their Kennings. Ériu, 39(1988), 127-168. https://www.jstor.org/stable/30024135
Ó Floinn, R. (1995). Recent research into Irish bog bodies. In R. C. Turner and R. G. Scaife (eds) Bog Bodies: New Discoveries and New Perspectives (p. 137–45). British Museum Press, London. ISBN: 9780714123059
Pankova, S. (2013). One More Culture with Ancient Tattoo Tradition in Southern Siberia: Tattoos on a Mummy from the Oglakhty Burial Ground, 3rd-4th century AD. Zurich Studies in Archaeology, 9(2013), 75-86.
Samadelli, M., Melisc, M., Miccolic, M., Vigld, E.E., Zinka, A.R. (2015). Complete mapping of the tattoos of the 5300-year-old Tyrolean Iceman. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 16(2015), 753–758.
Story, Joanna (1995). Charlemagne and Northumbria : the in
fluence of Francia on Northumbrian politics in the later eighth and early ninth centuries. [Doctoral Thesis]. Durham University. http://etheses.dur.ac.uk/1460/
Szacillo, J. (2012). Irish hagiography and its dating: a study of the O'Donohue group of Irish saints' lives. [Doctoral Thesis]. Queen's University Belfast.
Turner, R.C. (1995). Resent Research into British Bog Bodies. In R. C. Turner and R. G. Scaife (eds) Bog Bodies: New Discoveries and New Perspectives (p. 221–34). British Museum Press, London. ISBN: 9780714123059
Ware, C. (2021). A Literary Commentary on Panegyrici Latini VI(7) An Oration Delivered Before the Emperor Constantine in Trier, ca. AD 310. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://www.google.com/books/edition/A_Literary_Commentary_on_Panegyrici_Lati/oEwMEAAAQBAJ?hl=en&gbpv=0
#early medieval#roman era#pict#tattoos#ancient celts#apologies to people who wanted a shorter post#archaeology#art#anecdotes and observations#statutes and laws#irish history#gaelic ireland#medieval ireland#anglo saxon#insular celts#romano british
125 notes
·
View notes
Text
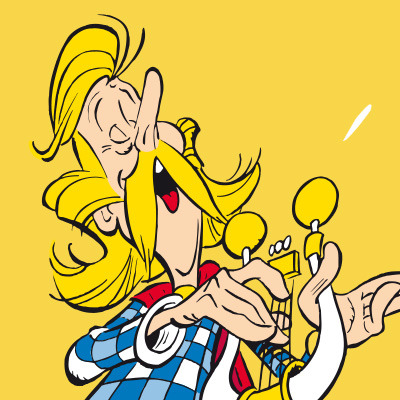


Today's Celtic character of the day is Cacofonix (Assurancetourix en Français) from Asterix who is Gaul (ancient Celt). He is from a fictional village in northwest Armorica.
#celtic character of the day#cacofonix#assurancetourix#asterix#asterix comics#gallic#gaul#ancient celts
20 notes
·
View notes
Text

Halloween originated from the ancient Celtic festival of Samhain, which marked the transition from the harvest season to winter. Celts believed that on this night, the boundary between the living and the dead blurred. To ward off spirits, they lit bonfires and wore costumes. Over time, it evolved into modern Halloween traditions.
300 notes
·
View notes
Text

The 4th house kids in celtic clothing
Really love this one ! The outfits are simple but it suits them really well
#the locked tomb#gideon the ninth#isaac tettares#jeannemary chatur#fourth house#tlt fanart#the locked tomb series#ancient celts
127 notes
·
View notes
Text

echoes of the past.
instagram
#photography#original photography#photographers on tumblr#nature#nature photography#gothic#dark nature#forestcore#goth aesthetic#pagan#paganism#pagan witch#celtic paganism#celtic mythology#celtic art#cernunnos#ancient history#celts#celtic#ancient celts#archaeology#history#scotland#fife#dunino den
61 notes
·
View notes
Text
You want to tell me the moon and sun aren't magical? The same moon and sun that shined on Cleopatra? The same moon and sun that saw the downfall of several empires? The same moon and sun that saw "witches" persecuted? The same moon and sun, that has been here since pretty much THE DAWN OF TIME????
Right... right.
#wlw community#lesbian#sapphic#celtic mythology#witch#witchcraft#witchblr#witch community#eclectic witch#witches of tumblr#spiritualism#spirituality#cleopatra#ancient celts#ancient egypt#ancient rome#ancient greece#ancient history#autistic
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
A brief thought as you go about your day:
As witchcraft/folk practitioners, do not give out detailed personal information to just anyone.
I’ve seen so many bios and posts on Tumblr alone containing peoples’ real names, ages, birthdates, full astrology charts, personality types, sexualities, images of themselves either in their profile picture or in a pinned introductory, and a couple times I even saw blood types. And with trauma dumping flooding social media, others get a clear view your mental and emotional wellbeing as well.
This opens you up to potential magickal/spiritual warfare. You’d like to think that others in this community are just as kindhearted as you are. But like in real life, you never truly know someone’s intentions. And since this business is all about intentions, make one of yours to keep yourself safeguarded.
Cleanse your space and yourself
Ward your home
Refresh protections
Physically lock your home’s entrances and exits as necessary
Do not share in-depth information online with random strangers
BE. MINDFUL.
Stay safe!!
#celtic#folk witchcraft#witch community#witchblr#witchcraft#witches#green witch#witch#witch aesthetic#witchcore#folk witch#witch blog#traditional witchcraft#irish witchcraft#irish folk magic#scottish folk magic#Scottish witchcraft#ancient celts#celtic folklore#witches of tumblr#magick#folk magic#safety
77 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fighting the Titans: Ptolemaic Victory over the Galatians

After the Galatians settled in Asia Minor, Northern Phrygia became a popular recruitment area for various competing Hellenistic monarchs. These Celts were known and respected for their military prowess. At the same time, the various kings of the ancient world occasionally waged war against them. These victories were then used in the royal propaganda to portray the monarch as a defender of civilization and liberty against these "barbarians." This perceived liberating role was often celebrated with the title "Soter" ("Savior"). The ambiguous love-hate relationship with the Galatians is clearly demonstrated in Ptolemaic Egypt, particularly during the reign of Ptolemy II.
Ptolemy II Philadelphos recruited some 4,000 Celtic warriors sometime during the 270s BCE. At the time, Ptolemy II was engaged in a conflict with his rebellious stepbrother, Magas, in Cyrenaica to the west. Magas, who became part of the Ptolemaic dynasty through his mother's marriage to Ptolemy I, had established a kingdom centered around the wealthy Greek colony of Cyrene in modern-day Libya. While Ptolemy headed west to address this threat, the Celtic mercenaries rebelled around 274 BCE.
According to Pausanias (1.7.2), the Celts sought to seize control of Egypt while Ptolemy II was preoccupied in the west. However, Ellis Berresford rightly notes that this claim is likely a gross exaggeration; a force of just 4,000 warriors would hardly have entertained such an ambitious plan. Instead, the Celts probably aimed to exploit the king’s absence by plundering Egypt’s numerous wealthy temples and towns before fleeing the country.
Ptolemy II, however, reacted swiftly and drove the rebels to an island near Sebennytos, where, according to Pausanias, they were starved into submission.
This victory was a minor event but quickly became a key element in Ptolemaic propaganda. The members of the Ptolemaic court, as well as the king himself, likely recognized the propaganda value of this triumph. As rival kings legitimized their rule through victories over Celtic tribes, Ptolemy seized the opportunity to join the ranks of these esteemed “liberator” kings.
Coins were issued featuring Galatian shields to commemorate this victory. Additionally, Ptolemy II was famously celebrated as a second Apollo in Kallimachos’ Hymn to Delos. In this work, the Hellenistic court poet recalls Ptolemy II's victory over the Celts in the following manner:
“Yes, and some day afterward a general conflict will come upon us, when the later-born Titans, raising up against the Greeks a barbarian sword and Celtic war, from the farthest west rushing like snow or equal in number to the heavenly bodies when they flock most thickly in the sky.” (transl. Dee Clayman)
Interestingly, Kallimachos describes the Celts as new Titans. The Titans were the older generation of gods who ruled the universe until they were overthrown by the Olympian gods under Zeus' command. If the Celts are the Titans, then the Ptolemaic king and his army are likened to the Olympian gods. This comparison between the Celts and villains from mythical history is not unique to Kallimachos’ poem. Similarly, in Attalid propaganda, parallels are drawn between their war against the Celts and the legendary Gigantomachy, the mythical victory of the Olympian gods over the Giants.
What is the purpose of this victory? It elevates the conflict with the Celts to an entirely new level. Just as the Titanomachy and Gigantomachy were remembered as triumphs of order, justice, and liberty, the subjugation of the Celts is meant to be celebrated as a victory over barbarism and chaos.
This reimagining of the wars against the Celts proved to be a powerful tool for legitimizing the Hellenistic monarchies in the eyes of the Greeks. The Greeks were naturally inclined to view kingship as an illegitimate and un-Greek form of government. Consequently, the kings employed these powerful mythological narratives to portray themselves as essential to the world order and worthy of rule, despite the autocratic nature of their governance. Moreover, if Zeus, a king, was accepted by the Greeks as the ruler of the cosmos, then why should the Hellenistic monarchs not be accepted as legitimate rulers?
In short, Ptolemy’s victory over the Celts, despite its limited scale, provided him with a triumph he could frame as a victory of order over chaos. This sent a powerful message throughout the Hellenic world: he was a god performing godlike deeds. Furthermore, as the Olympian gods were accepted by the Greeks as kings, why shouldn’t the Ptolemaic monarchy be afforded the same respect?
It is hard not to detect the hubris in this Ptolemaic mindset. They were mortals striving to be gods—or so it might seem. To the Ptolemies, there was no such contradiction: they were not merely mortals aspiring to divinity; they were gods. Through the dynastic cult and other forms of propaganda, they blurred the line between the divine realm and the Egyptian monarchy. Narratives emphasizing the kings’ similarities to the gods were widespread throughout the kingdom. For instance, the Ptolemies’ practice of sibling marriage mirrored the relationship between Zeus and Hera, who were also siblings. The story of the Celts aligns seamlessly with this broader propaganda effort, making its use entirely logical.
Olivier Goossens
#ancient history#archaeology#art history#hellenism#ancient greece#classical literature#ancient egypt#egyptology#celtic#celts#ancient celts
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
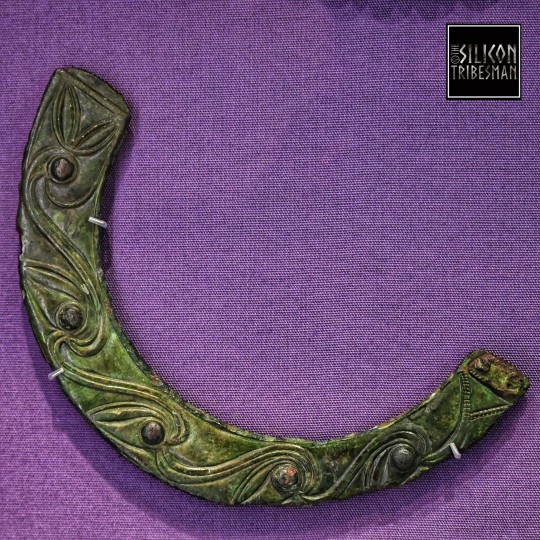
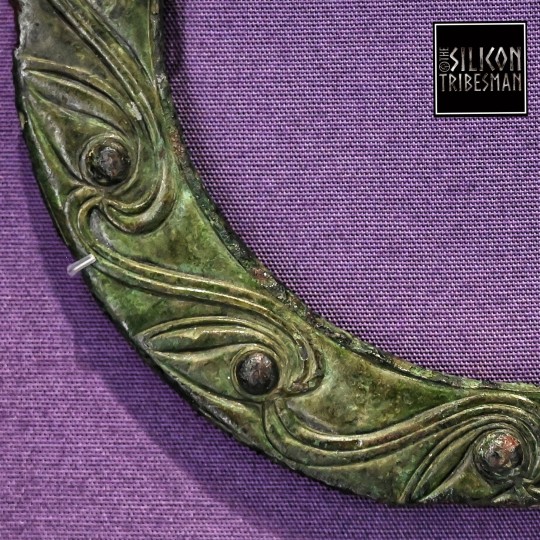
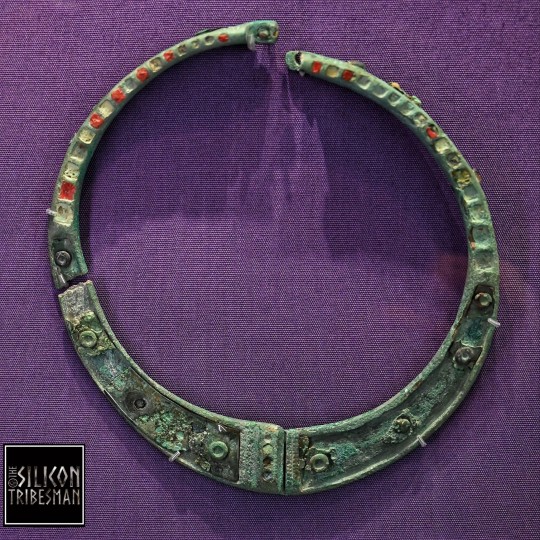



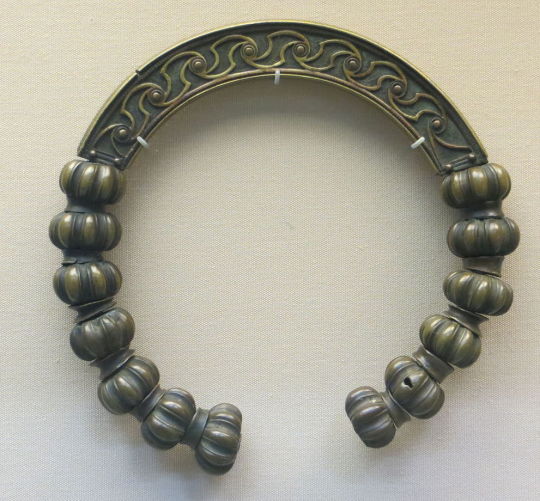
Bronze Iron Age Torcs, St. Fagans National Museum of History, Cardiff, Wales
#ice age#stone age#bronze age#copper age#iron age#bronze#torc#jewellery#prehistoric#prehistory#metalwork#metalworking#archaeology#curvilinear#celtic#ancient celts#Cardiff#Wales
131 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bath Curse Tablets
The Bath curse tablets are a collection of about 130 Roman era curse tablets (or defixiones in Latin) discovered in the English city of Bath. The tablets were requests for intervention of the goddess Sulis Minerva in the return of stolen goods and to curse the perpetrators of the thefts. Inscribed mostly in British Latin, they have been used to attest to the everyday spoken vernacular of the Romano-British population of the second to fourth centuries AD.


Curse tablets: above right, with complaint about theft of a cloak and bathing tunic; below left, with complaint about the theft of Vilbia; below right, thought to have text in British Celtic—and, should be the case, it's one of only two known examples of a written British Celtic language.


Most of the inscriptions are in colloquial Latin, and specifically in the Vulgar Latin of the Romano-British population, known as "British Latin". Two of the inscriptions are in a language which is not Latin, although they use Roman lettering, and may be in a British Celtic language. If this should be the case, they would be the only examples of a written ancient British Celtic language; however, there is not yet scholarly consensus on their decipherment. (source)
#bath curse tablets#defixiones#prayer for justice#roman artefacts#vulgar latin#british celtic language#ancient celts#roman empire
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
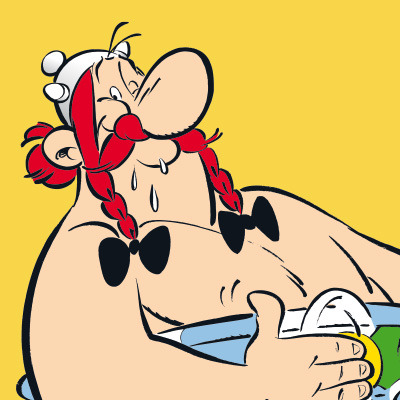
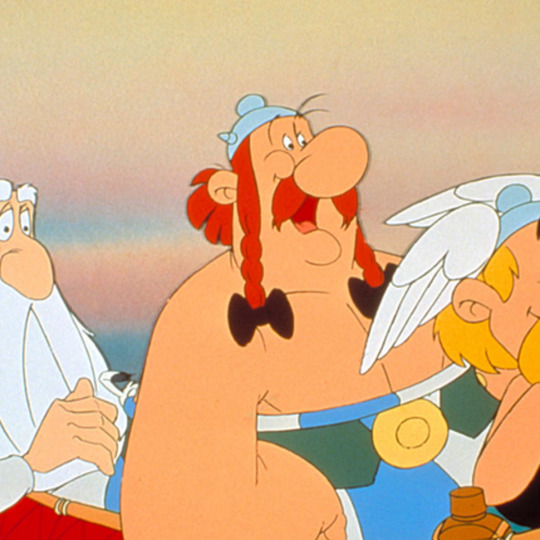



Today's Celtic character of the day is Obelix from Asterix who is Gaul (ancient Celt). He is from a fictional village in northwest Armorica.
23 notes
·
View notes