#global pacific records
Text
Tonga volcano eruption causing 2023 heat

View On WordPress
#climate change#earth#eruption#global warming#heat#heatwave#Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha&039;apai#meme#memes#natural disaster#news#pacific#record#records#tonga#volcano#weather
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
17/12/23 this masterlist has been completely revamped with free access to all material. It will be updated and edited periodically so please click on my username and reblog the current version directly from me if you're able.
14/8/24 reboosting this post with How to Help Palestine updated. Please scroll to the bottom to donate or boost the links.
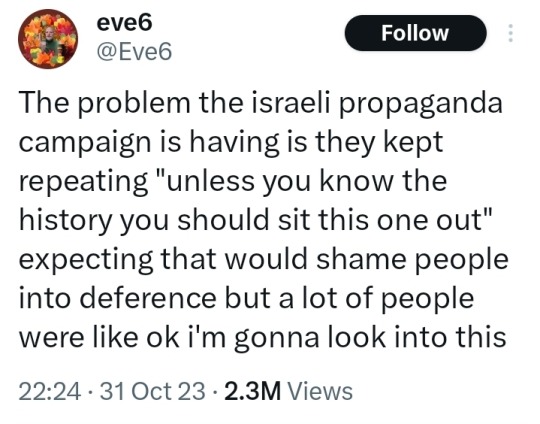


The Big Damn List Of Stuff They Said You Didn't Know
(Yes, it's a lot. Just choose your preferred medium and then pick one.)
Podcasts
Backgrounders and Quick Facts
Interactive Maps
Teach-Out Resources
Reading Material (free)
Films and Documentaries (free)
Non-Governmental Organizations
Social Media
How You Can Help <- URGENT!!!
Podcasts
Cocktails & Capitalism: The Story of Palestine Part 1, Part 3
It Could Happen Here: The Cheapest Land is Bought with Blood, Part 2, The Balfour Declaration
Citations Needed: Media narratives and consent manufacturing around Israel-Palestine and the Gaza Siege
The Deprogram: Free Palestine, ft. decolonizatepalestine.com.
Backgrounders and Quick Facts
The Palestine Academy: Palestine 101
Institute for Middle East Understanding: Explainers and Quick Facts
Interactive Maps
Visualizing Palestine
Teach-Out Resources
1) Cambridge UCU and Pal Society
Palestine 101
Intro to Palestine Film + Art + Literature
Resources for Organising and Facilitating)
2) The Jadaliya YouTube Channel of the Arab Studies Institute
Gaza in Context Teach-in series
War on Palestine podcast
Updates and Discussions of news with co-editors Noura Erakat and Mouin Rabbani.
3) The Palestine Directory
History (virtual tours, digital archives, The Palestine Oral History Project, Documenting Palestine, Queering Palestine)
Cultural History (Palestine Open Maps, Overdue Books Zine, Palestine Poster Project)
Contemporary Voices in the Arts
Get Involved: NGOs and campaigns to help and support.
3) PalQuest Interactive Encyclopedia of the Palestine Question.
4) The Palestine Remix by Al Jazeera
Books and Articles
Free reading material
My Gdrive of Palestine/Decolonization Literature (nearly all the books recommended below + books from other recommended lists)
Five free eBooks by Verso
Three Free eBooks on Palestine by Haymarket
LGBT Activist Scott Long's Google Drive of Palestine Freedom Struggle Resources
Recommended Reading List
Academic Books
Edward Said (1979) The Question of Palestine, Random House
Ilan Pappé (2002)(ed) The Israel/Palestine Question, Routledge
Ilan Pappé (2006) The Ethnic Cleansing of Palestine, OneWorld Publications
Ilan Pappé (2011) The Forgotten Palestinians: A History of the Palestinians in Israel, Yale University Press
Ilan Pappé (2015) The Idea of Israel: A History of Power and Knowledge, Verso Books
Ilan Pappé (2017) The Biggest Prison On Earth: A History Of The Occupied Territories, OneWorld Publications
Ilan Pappé (2022) A History of Modern Palestine, Cambridge University Press
Rosemary Sayigh (2007) The Palestinians: From Peasants to Revolutionaries, Bloomsbury
Andrew Ross (2019) Stone Men: the Palestinians who Built Israel, Verso Books
Rashid Khalidi (2020) The Hundred Years’ War on Palestine: A History of Settler Colonialism and Resistance 1917–2017
Ariella Azoulay (2011) From Palestine to Israel: A Photographic Record of Destruction and State Formation, 1947-1950, Pluto Press
Ariella Azoulay and Adi Ophir (2012) The One-State Condition: Occupation and Democracy in Israel/Palestine, Stanford University Press.
Jeff Halper (2010) An Israeli in Palestine: Resisting Dispossession, Redeeming Israel, Pluto Press
Jeff Halper (2015) War Against the People: Israel, the Palestinians and Global Pacification
Jeff Halper (2021) Decolonizing Israel, Liberating Palestine: Zionism, Settler Colonialism, and the Case for One Democratic State, Pluto Press
Anthony Loewenstein (2023) The Palestine Laboratory: How Israel exports the Technology of Occupation around the World
Noura Erakat (2019) Justice for Some: Law and the Question of Palestine, Stanford University Press
Neve Gordon (2008) Israel’s Occupation, University of California Press
Joseph Massad (2006) The Persistence of the Palestinian Question: Essays on Zionism and the Palestinians, Routledge
Memoirs
Edward Said (1986) After the Last Sky: Palestine Lives, Columbia University PEdward Saidress
Edward Said (2000) Out of Place; A Memoir, First Vintage Books
Mourid Barghouti (2005) I saw Ramallah, Bloomsbury
Hatim Kanaaneh (2008) A Doctor in Galilee: The Life and Struggle of a Palestinian in Israel, Pluto Press
Raja Shehadeh (2008) Palestinian Walks: Into a Vanishing Landscape, Profile Books
Ghada Karmi (2009) In Search of Fatima: A Palestinian Story, Verso Books
Vittorio Arrigoni (2010) Gaza Stay Human, Kube Publishing
Ramzy Baroud (2010) My Father Was a Freedom Fighter: Gaza's Untold Story, Pluto Press
Izzeldin Abuelaish (2011) I Shall Not Hate: A Gaza Doctor’s Journey on the Road to Peace and Human Dignity, Bloomsbury
Atef Abu Saif (2015) The Drone Eats with Me: A Gaza Diary, Beacon Press
Anthologies
Voices from Gaza - Insaniyyat (The Society of Palestinian Anthropologists)
Letters From Gaza • Protean Magazine
Salma Khadra Jayyusi (1992) Anthology of Modern Palestinian Literature, Columbia University Press
ASHTAR Theatre (2010) The Gaza Monologues
Refaat Alreer (ed) (2014) Gaza Writes Back, Just World Books
Refaat Alreer, Laila El-Haddad (eds) (2015) Gaza Unsilenced, Just World Books
Cate Malek and Mateo Hoke (eds)(2015) Palestine Speaks: Narrative of Life under Occupation, Verso Books
Jehad Abusalim, Jennifer Bing (eds) (2022) Light in Gaza: Writings Born of Fire, Haymarket Books
Short Story Collections
Ghassan Kanafani, Hilary Kilpatrick (trans) (1968) Men in the Sun and Other Palestinian Stories, Lynne Rienner Publishers
Ghassan Kanafani, Barbara Harlow, Karen E. Riley (trans) (2000) Palestine’s Children: Returning to Haifa and Other Stories, Lynne Rienner Publishers
Atef Abu Saif (2014) The Book of Gaza: A City in Short Fiction, Comma Press
Samira Azzam, Ranya Abdelrahman (trans) (2022) Out Of Time: The Collected Short Stories of Samira Azzam
Sonia Sulaiman (2023) Muneera and the Moon; Stories Inspired by Palestinian Folklore
Essay Collections
Edward W. Said (2000) Reflections on Exile and Other Essays, Harvard University Press
Salim Tamari (2008) Mountain against the Sea: Essays on Palestinian Society and Culture, University of California Press
Fatma Kassem (2011) Palestinian Women: Narratives, histories and gendered memory, Bloombsbury
Ramzy Baroud (2019) These Chains Will Be Broken: Palestinian Stories of Struggle and Defiance in Israeli Prisons, Clarity Press
Novels
Sahar Khalifeh (1976) Wild Thorns, Saqi Books
Liyana Badr (1993) A Balcony over the Fakihani, Interlink Books
Hala Alyan (2017) Salt Houses, Harper Books
Susan Abulhawa (2011) Mornings in Jenin, Bloomsbury
Susan Abulhawa (2020) Against the Loveless World, Bloomsbury
Graphic novels
Joe Sacco (2001) Palestine
Joe Sacco (2010) Footnotes in Gaza
Naji al-Ali (2009) A Child in Palestine, Verso Books
Mohammad Sabaaneh (2021) Power Born of Dreams: My Story is Palestine, Street Noise Book*
Poetry
Fady Joudah (2008) The Earth in the Attic, Sheridan Books,
Ghassan Zaqtan, Fady Joudah (trans) (2012) Like a Straw Bird It Follows Me and Other Poems, Yale University Press
Hala Alyan (2013) Atrium: Poems, Three Rooms Press*
Mohammed El-Kurd (2021) Rifqa, Haymarket Books
Mosab Abu Toha (2022) Things You May Find Hidden in My Ear: Poems from Gaza, City Lights Publishers
Tawfiq Zayyad (2023) We Are Here to Stay, Smokestack Books*
The Works of Mahmoud Darwish
Poems
Rafeef Ziadah (2011) We Teach Life, Sir
Nasser Rabah (2022) In the Endless War
Refaat Alareer (2011) If I Must Die
Hiba Abu Nada (2023) I Grant You Refuge/ Not Just Passing
[All books except the ones starred are available in my gdrive. I'm adding more each day. But please try and buy whatever you're able or borrow from the library. Most should be available in the discounted Free Palestine Reading List by Pluto Press, Verso and Haymarket Books.]
Human Rights Reports & Documents
Information on current International Court of Justice case on ‘Legal Consequences arising from the Policies and Practices of Israel in the Occupied Palestinian Territory, including East Jerusalem’
UN Commission of Inquiry Report 2022
UN Special Rapporteur Report on Apartheid 2022
Amnesty International Report on Apartheid 2022
Human Rights Watch Report on Apartheid 2021
Report of the United Nations Fact-Finding Mission on the Gaza Conflict’ 2009 (‘The Goldstone Report’)
Advisory Opinion on the Legal Consequences of the Construction of a Wall in the Occupied Palestinian Territory, International Court of Justice, 9 July 2004
Films
Documentaries
Jenin, Jenin (2003) dir. Mohammed Bakri
Massacre (2005) dir. Monica Borgmann, Lokman Slim, Hermann Theissen
Slingshot HipHop (2008) dir. Jackie Reem Salloum
Waltz with Bashir (2008) dir. Ari Folman † (also on Amazon Prime)
Tears of Gaza (2010) dir. Vibeke Løkkeberg (also on Amazon Prime)
5 Broken Cameras (2011) dir. Emad Burnat (also on Amazon Prime)
The Gatekeepers (2012) dir. Dror Moreh (also on Amazon Prime)
The Great Book Robbery (2012) | Al Jazeera English
Al Nakba (2013) | Al Jazeera (5-episode docu-series)
The Village Under the Forest (2013) dir. Mark J. Kaplan
Where Should The Birds Fly (2013) dir. Fida Qishta
Naila and the Uprising (2017) (also on Amazon Prime)
GAZA (2019) dir. Andrew McConnell and Garry Keane
Gaza Fights For Freedom (2019) dir. Abby Martin
Little Palestine: Diary Of A Siege (2021) dir. Abdallah Al Khatib
Palestine 1920: The Other Side of the Palestinian Story (2021) | Al Jazeera World Documentary
Gaza Fights Back (2021) | MintPress News Original Documentary | dir. Dan Cohen
Innocence (2022) dir. Guy Davidi
Short Films
Fatenah (2009) dir. Ahmad Habash
Gaza-London (2009) dir. Dina Hamdan
Condom Lead (2013) dir. Tarzan Nasser, Arab Nasser
OBAIDA (2019) | Defence for Children Palestine
Theatrical Films
Divine Intervention (2002) | dir. Elia Suleiman (also on Netflix)
Paradise Now (2005) dir Hany Abu-Assad (also on Amazon Prime)
Lemon Tree (2008) (choose auto translate for English subs) (also on Amazon Prime)
It Must Be Heaven (2009) | dir. Elia Suleiman †
The Promise (2010) mini-series dir. Peter Kosminsky (Part 1, Part 2, Part 3, Part 4)
Habibi (2011)* dir. Susan Youssef
Omar (2013)* dir. Hany Abu-Assad †
3000 Nights (2015)* dir. Mai Masri
Foxtrot (2017) dir. Samuel Maoz (also on Amazon Prime)
The Time that Remains (2019) dir. Elia Suleiman †
Gaza Mon Amour (2020) dir. Tarzan Nasser, Arab Nasser †
The Viewing Booth (2020) dir. Ra'anan Alexandrowicz (on Amazon Prime and Apple TV)
Farha (2021)* | dir. Darin J. Sallam
Palestine Film Institute Archive
All links are for free viewing. The ones marked with a star (*) can be found on Netflix, while the ones marked † can be downloaded for free from my Mega account.
If you find Guy Davidi's Innocence anywhere please let me know, I can't find it for streaming or download even to rent or buy.
In 2018, BDS urged Netflix to dump Fauda, a series created by former members of IOF death squads that legitimizes and promotes racist violence and war crimes, to no avail. Please warn others to not give this series any views. BDS has not called for a boycott of Netflix. ]
NGOs
The Boycott, Divestment, Sanctions (BDS) Movement
Euro-Mediterranean Human Rights Monitor
UNRWA
Palestine Defence for Children International
Palestinian Feminist Collective
Al-Shabaka: The Palestinian Policy Network
Addameer Prisoner Support and Human Rights Association
Institute for Palestine Studies
Al Haq
Artists for Palestine
The Palestine Museum
Jewish Currents
B’Tselem
DAWN
Social Media
Palestnians on Tumblr
@el-shab-hussein
@killyfromblame
@apollos-olives
@fairuzfan
@palipunk
@sar-soor
@nabulsi
@wearenotjustnumbers2
@90-ghost
@tamarrud
@northgazaupdates
Allies and advocates (not Palestinian)
@bloglikeanegyptian beautiful posts that read like op-eds
@vyorei daily news roundups
@luthienne resistance through prose
@decolonize-the-left scoop on the US political plans and impacts
@feluka
@anneemay
(Please don't expect any of these blogs to be completely devoted to Palestine allyship; they do post regularly about it but they're still personal blogs and post whatever else they feel like. Do not harrass them.)
Gaza journalists
Motaz Azaiza IG: @motaz_azaiza | Twitter: @azaizamotaz9 | TikTok: _motaz.azaiza (left Gaza as of Jan 23)
Bisan Owda IG and TikTok: wizard_bisan1 | Twitter: @wizardbisan
Saleh Aljafarawi IG: @saleh_aljafarawi | Twitter: @S_Aljafarawi | TikTok: @saleh_aljafarawi97
Plestia Alaqad IG: @byplestia | TikTok: @plestiaaqad (left Gaza)
Wael Al-Dahdouh IG: @wael_eldahdouh | Twitter: @WaelDahdouh (left Gaza as of Jan 13)
Hind Khoudary IG: @hindkhoudary | Twitter: @Hind_Gaza
Ismail Jood IG and TikTok: @ismail.jood (announced end of coverage on Jan 25)
Yara Eid IG: @eid_yara | Twitter: @yaraeid_
Eye on Palestine IG: @eye.on.palestine | Twitter: @EyeonPalestine | TikTok: @eyes.on.palestine
Muhammad Shehada Twitter: @muhammadshehad2
(Edit: even though some journos have evacuated, the footage up to the end of their reporting is up on their social media, and they're also doing urgent fundraisers to get their families and friends to safety. Please donate or share their posts.)
News organisations
The Electronic Intifada Twitter: @intifada | IG: @electronicintifada
Quds News Network Twitter and Telegram: @QudsNen | IG: @qudsn (Arabic)
Times of Gaza IG: @timesofgaza | Twitter: @Timesofgaza | Telegram: @TIMESOFGAZA
The Palestine Chronicle Twitter: @PalestineChron | IG: @palestinechron | @palestinechronicle
Al-Jazeera Twitter: @AJEnglish | IG and TikTok: @aljazeeraenglish, @ajplus
Middle East Eye IG and TikTok: @middleeasteye | Twitter: @MiddleEastEye
Democracy Now Twitter and IG: @democracynow TikTok: @democracynow.org
Mondoweiss IG and TikTok: @mondoweiss | Twitter: @Mondoweiss
The Intercept Twitter and IG: @theintercept
MintPress Twitter: @MintPressNews | IG: mintpress
Novara Media Twitter and IG: @novaramedia
Truthout Twitter and IG: @truthout
Palestnians on Other Social Media
Mouin Rabbani: Middle East analyst specializing in the Arab-Israeli conflict and Palestinian affairs. Twitter: @MouinRabbani
Noura Erakat: Legal scholar, human rights attorney, specialising in Israeli–Palestinian conflict. Twitter: @4noura | IG: @nouraerakat | (http://www.nouraerakat.com/)
Hebh Jamal: Journalist in Germany. IG and Twitter: @hebh_jamal
Ghada Sasa: PhD candidate in International Relations, green colonialism, and Islam in Canada. Twitter: @sasa_ghada | IG: @ghadasasa48
Taleed El Sabawi: Assistant professor of law and researcher in public health. Twitter: @el_sabawi | IG
Lexi Alexander: Filmmaker and activist. Twitter: @LexiAlex | IG: @lexialexander1
Mariam Barghouti: Writer, blogger, researcher, and journalist. Twitter: @MariamBarghouti | IG: @mariambarghouti
Rasha Abdulhadi: Queer poet, author and cultural organizer. Twitter: @rashaabdulhadi
Mohammed el-Kurd: Writer and activist from Jerusalem. IG: @mohammedelkurd | Twitter: @m7mdkurd
Ramy Abdu: Founder and Chairman of the Euro-Mediterranean Human Rights Monitor. Twitter: @RamyAbdu
Subhi: Founder of The Palestine Academy website. IG: @sbeih.jpg |TikTok @iamsbeih | Twitter: @iamsbeih
Allies
Lowkey (Kareem Dennis): Rapper, activist, video and podcast host for MintPress. Twitter: @LowkeyOnline IG: @lowkeyonline
Francesca Albanese: UN Special Rapporteur on the Occupied Territories. Twitter: @FranceskAlbs
Sana Saeed: Journalist and media critic, host and senior producer at Al-Jazeera Plus. IG: @sanaface | Twitter: @SanaSaeed
Shailja Patel: Poet, playwright, activist, founding member of Kenyans For Peace, Truth and Justice. Twitter: @shailjapatel
Jairo I. Fúnez-Flores: Researcher in curriculum studies, decolonial theory, social movements. Twitter: @Jairo_I_Funez
Jack Dodson: Journalist and Filmmaker. Twitter: @JackDodson IG: @jdodson4
Imani Barbarin: Writer, public speaker, and disability rights activist. IG: @crutches_and_spice | Twitter: @Imani_Barbarin | TikTok: @crutches_and_spice
Jewish Allies
Katie Halper: US comedian, writer, filmmaker, podcaster, and political commentator. IG and Twitter: @kthalps
Dr. Chanda Prescod-Weinstein: Associate Professor of Physics and Core Faculty Member in Women’s and Gender Studies at the University of New Hampshire. Twitter: @IBJIYONGI | (https://chanda.science/)
Amanda Gelender: Writer. Twitter: @agelender | (https://agelender.medium.com/)
Yoav Litvin: Jerusalem-born Writer and Photographer. IG and Twitter: @nookyelur | (yoavlitvin.com)
Alana Lentin: Professor of Cultural and Social Analysis at Western Sydney University. Twitter: @alanalentin
Gideon Levy: anti-Zionist Israeli journalist and activist. Twitter: @gideonlevy
‼️How You Can Help Palestine‼️
Click for Palestine (Please reblog!!)
Masterlist of donation links by @sulfurcosmos (Please reblog!!)
Water for Gaza: Donate directly to the Gaza Municipality
Operation Olive Branch Linktree for vetted fundraisers, donations and political action resources. TikTok and Instagram: @operationolivebranch | Twitter: @OPOliveBranch
Gazafunds (vetted and spotlighted GFMs)
The Butterfly Effect Project (spreadsheet of vetted GFMs)
Spreadsheet of Gaza fundraisers vetted by @el-shab-hussein and @nabulsi
If any links are broken let me know. Or pull up the current post to check whether it's fixed.
Political action to pressure the Harris campaign to stop arming Israel (for US citizens): Uncommitted Movement (TikTok: @uncommittedmvmt) (Please reblog!!)
"Knowledge is Israel's worst enemy. Awareness is Israel's most hated and feared foe. That's why Israel bombs a university: it wants to kill openness and determination to refuse living under injustice and racism."
— Dr. Refaat Alareer, (martyred Dec 6, 2023)
From River To The Sea Palestine Will Be Free 🇵🇸🇵🇸🇵🇸
-----
Edit 1: took the first video down because turns out the animator is a terf and it links to her blog. Really sorry for any distress.
Edit 2: All recommended readings + Haymarket recommendations + essential decolonization texts have been uploaded to my linked gdrive. I will adding more periodically. Please do buy or check them out from the library if possible, but this post was made for and by poor and gatekept Global South bitches like me.
Some have complained about the memes being disrespectful. You're actually legally obligated to make fun of Israeli propaganda and Zionists. I don't make the rules.
Edit 3: "The river to the sea" does not mean the expulsion of Jews from Palestine. Believing that is genocide apologia.
Edit 4: Gazans have specifically asked us to put every effort into pushing for a ceasefire instead of donations. "Raising humanitarian aid" is a grift Western governments are pushing right now to deflect from the fact that they're sending billions to Israel to keep carpet bombing Gazans. As long as the blockades are still in place there will never be enough aid for two million people. (UPDATE: PLEASE DONATE to the Gazan's GoFundMe fundraisers to help them buy food and get out of Rafah into Egypt. E-SIMs, food and medical supplies are also essential. Please donate to the orgs linked in the How You Can Help. Go on the strikes. DO NOT STOP PROTESTING.)
Edit 5: Google drive link for academic books folder has been fixed. Also have added a ton of resources to all the other folders so please check them out.
Edit 6: Added interactive maps, Jadaliya channel, and masterlists of donation links and protest support and of factsheets.
The twitter accounts I reposted as it was given to me and I just now realized it had too many Israeli voices and almost none of the Palestinians I'm following, so it's being edited. (Update: done!) also removed sources like Jewish Voices of Peace and Breaking the Silence that do good work but have come under fair criticism from Palestinians.
Edit 7: Complete reformatting
Edit 8: Complete revamping of the social media section. It now reflects my own following list.
Edit 9: removed some more problematic people from the allies list. Remember that the 2SS is a grift that's used to normalize violence and occupation, kids. Supporting the one-state solution is lowest possible bar for allyship. It's "Free Palestine" not "Free half of Palestine and hope Israel doesn't go right back to killing them".
Edit 10: added The Palestine Directory + Al Jazeera documentary + Addameer. This "100 links per post" thing sucks.
Edit 11: more documentaries and films
Edit 12: reformatted reading list
Edit 13: had to remove @palipunk's masterlist to add another podcast. It's their pinned post and has more resources Palestinian culture and crafts if you want to check it out
Edit 14 6th May '24: I've stopped updating this masterlist so some things, like journalists still left in Gaza and how to support the student protests are missing. I've had to take a step back and am no longer able to track these things down on my own, and I've hit the '100 links per post' limit, but if you can leave suggestions for updates along with links in either the replies or my asks I will try and add them.
Edit 15 10th August: added to Palestinian allies list and reworked the Help for Palestine section. There's been a racist harrassment campaign against the Palestinian Tumblrs that vetted the Gaza fundraisers based off one mistake made by a Gazan who doesn't understand English. If you're an ally, shut that shit down. Even if you donate to a scam GFM, you're only out some coffee money; if everyone stops donating to all the GFMs in fear of scams, those families die.
#free palestine#palestine resources#palestine reading list#decolonization#israel palestine conflict#israel palestine war#british empire#american imperialism#apartheid#social justice#middle east history#MENA#arab history#anti zionism#palestinian art#palestinian history#palestinian culture#palestinian genocide#al nakba#ethnic cleansing#war crimes#racism#imperialism#colonialism#british colonialism#knee of huss#ask to tag#Youtube
82K notes
·
View notes
Text
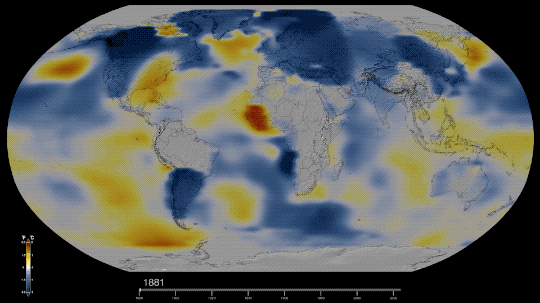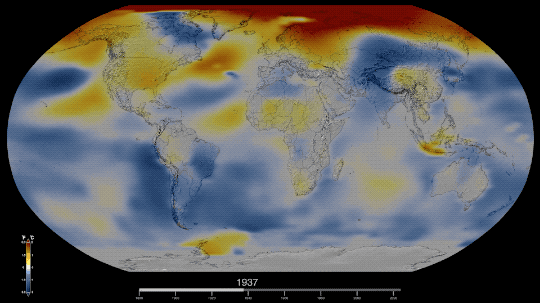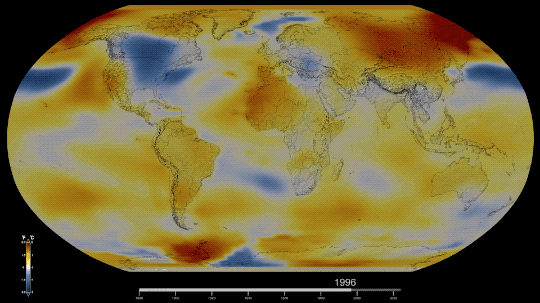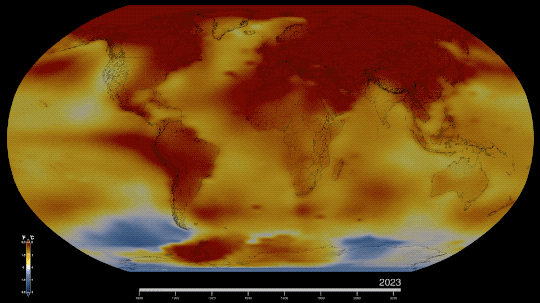
Six Answers to Questions You’re Too Embarrassed to Ask about the Hottest Year on Record
You may have seen the news that 2023 was the hottest year in NASA’s record, continuing a trend of warming global temperatures. But have you ever wondered what in the world that actually means and how we know?
We talked to some of our climate scientists to get clarity on what a temperature record is, what happened in 2023, and what we can expect to happen in the future… so you don’t have to!
1. Why was 2023 the warmest year on record?
The short answer: Human activities. The release of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere trap more heat near Earth’s surface, raising global temperatures. This is responsible for the decades-long warming trend we’re living through.
But this year’s record wasn’t just because of human activities. The last few years, we’ve been experiencing the cooler phase of a natural pattern of Pacific Ocean temperatures called the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO). This phase, known as La Niña, tends to cool temperatures slightly around the world. In mid-2023, we started to shift into the warmer phase, known as El Niño. The shift ENSO brought, combined with overall human-driven warming and other factors we’re continuing to study, pushed 2023 to a new record high temperature.
2. So will every year be a record now?
Almost certainly not. Although the overall trend in annual temperatures is warmer, there’s some year-to-year variation, like ENSO we mentioned above.
Think about Texas and Minnesota. On the whole, Texas is warmer than Minnesota. But some days, stormy weather could bring cooler temperatures to Texas while Minnesota is suffering through a local heat wave. On those days, the weather in Minnesota could be warmer than the weather in Texas. That doesn’t mean Minnesota is warmer than Texas overall; we’re just experiencing a little short-term variation.
Something similar happens with global annual temperatures. The globe will naturally shift back to La Niña in the next few years, bringing a slight cooling effect. Because of human carbon emissions, current La Niña years will be warmer than La Niña years were in the past, but they’ll likely still be cooler than current El Niño years.
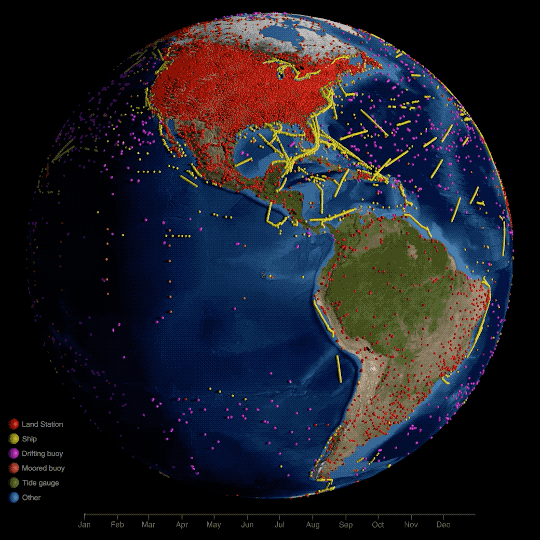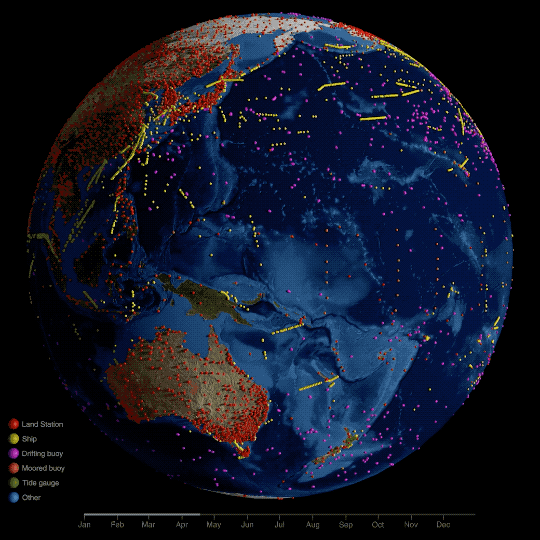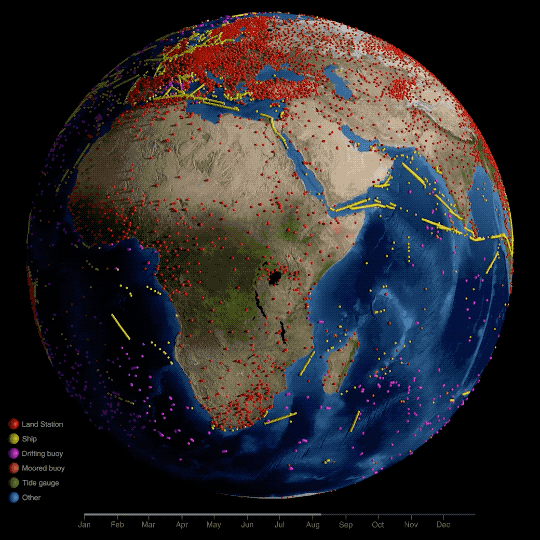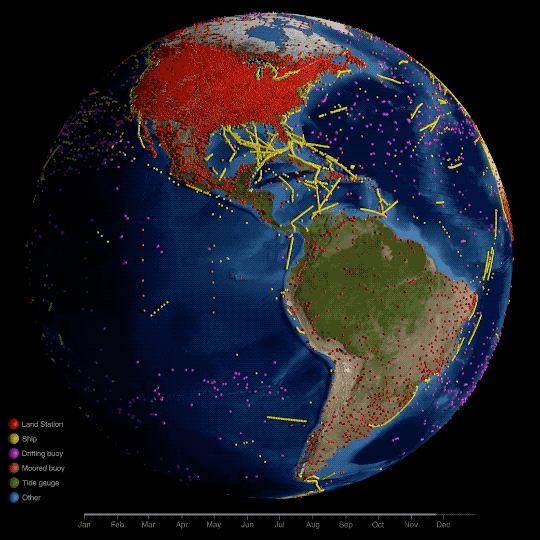
3. What do we mean by “on record”?
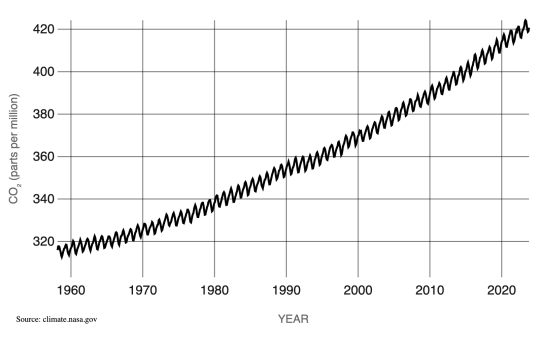
Technically, NASA’s global temperature record starts in 1880. NASA didn’t exist back then, but temperature data were being collected by sailing ships, weather stations, and scientists in enough places around the world to reconstruct a global average temperature. We use those data and our modern techniques to calculate the average.
We start in 1880, because that’s when thermometers and other instruments became technologically advanced and widespread enough to reliably measure and calculate a global average. Today, we make those calculations based on millions of measurements taken from weather stations and Antarctic research stations on land, and ships and ocean buoys at sea. So, we can confidently say 2023 is the warmest year in the last century and a half.
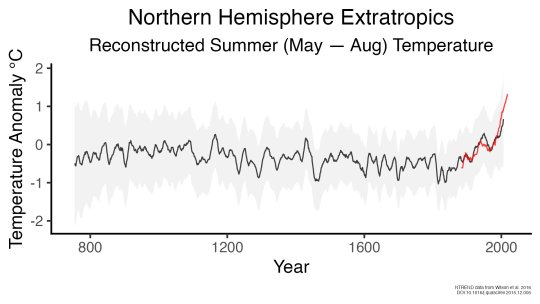
However, we actually have a really good idea of what global climate looked like for tens of thousands of years before 1880, relying on other, indirect ways of measuring temperature. We can look at tree rings or cores drilled from ice sheets to reconstruct Earth’s more ancient climate. These measurements affirm that current warming on Earth is happening at an unprecedented speed.
4. Why does a space agency keep a record of Earth’s temperature?
It’s literally our job! When NASA was formed in 1958, our original charter called for “the expansion of human knowledge of phenomena in the atmosphere and space.” Our very first space missions uncovered surprises about Earth, and we’ve been using the vantage point of space to study our home planet ever since. Right now, we have a fleet of more than 20 spacecraft monitoring Earth and its systems.
Why we created our specific surface temperature record – known as GISTEMP – actually starts about 25 million miles away on the planet Venus. In the 1960s and 70s, researchers discovered that a thick atmosphere of clouds and carbon dioxide was responsible for Venus’ scorchingly hot temperatures.
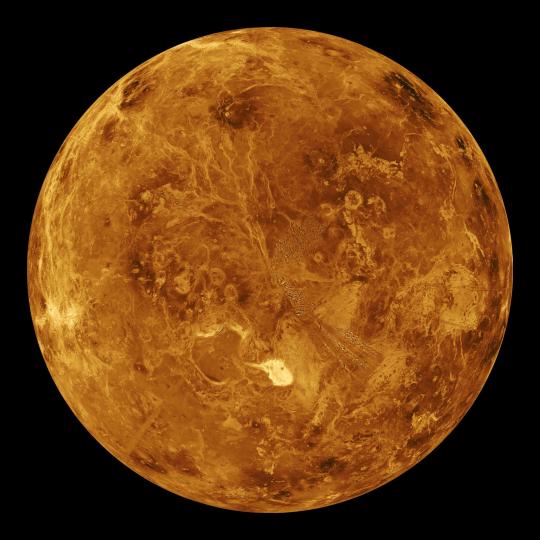
Dr. James Hansen was a scientist at the Goddard Institute for Space Studies in New York, studying Venus. He realized that the greenhouse effect cooking Venus’ surface could happen on Earth, too, especially as human activities were pumping carbon dioxide into our atmosphere.
He started creating computer models to see what would happen to Earth’s climate as more carbon dioxide entered the atmosphere. As he did, he needed a way to check his models – a record of temperatures at Earth’s surface over time, to see if the planet was indeed warming along with increased atmospheric carbon. It was, and is, and NASA’s temperature record was born.
5. If last year was record hot, why wasn’t it very hot where I live?
The temperature record is a global average, so not everywhere on Earth experienced record heat. Local differences in weather patterns can influence individual locations to be hotter or colder than the globe overall, but when we average it out, 2023 was the hottest year.
Just because you didn’t feel record heat this year, doesn’t mean you didn’t experience the effects of a warming climate. 2023 saw a busy Atlantic hurricane season, low Arctic sea ice, raging wildfires in Canada, heat waves in the U.S. and Australia, and more.
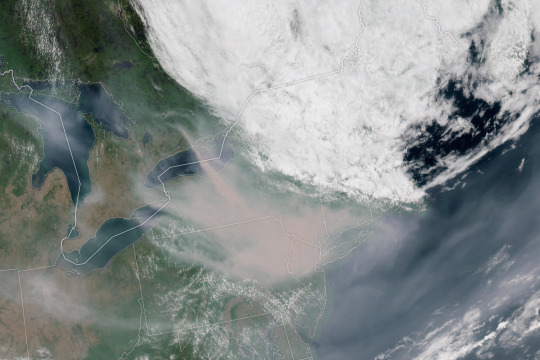
And these effects don’t stay in one place. For example, unusually hot and intense fires in Canada sent smoke swirling across the entire North American continent, triggering some of the worst air quality in decades in many American cities. Melting ice at Earth’s poles drives rising sea levels on coasts thousands of miles away.

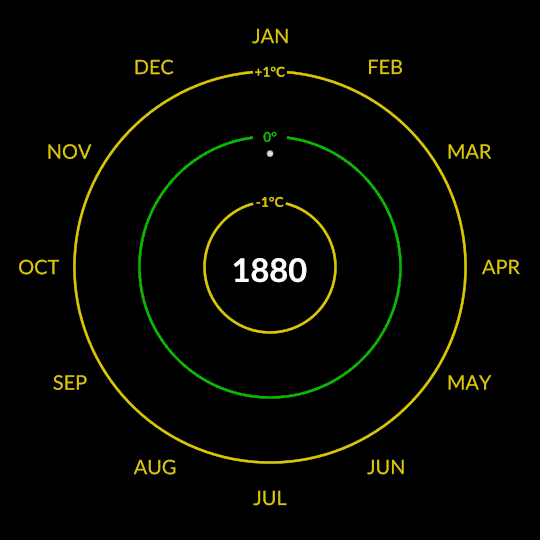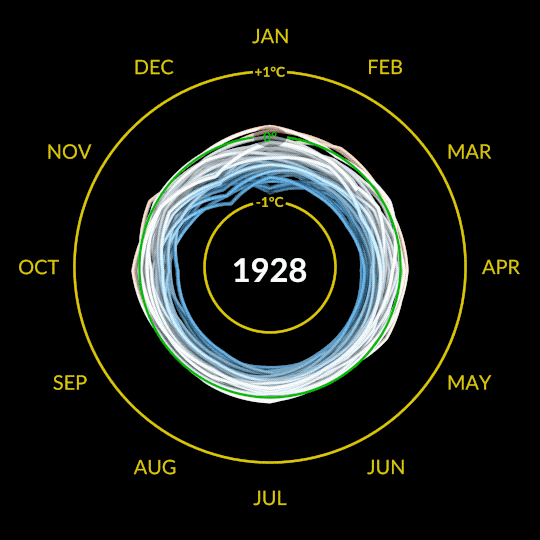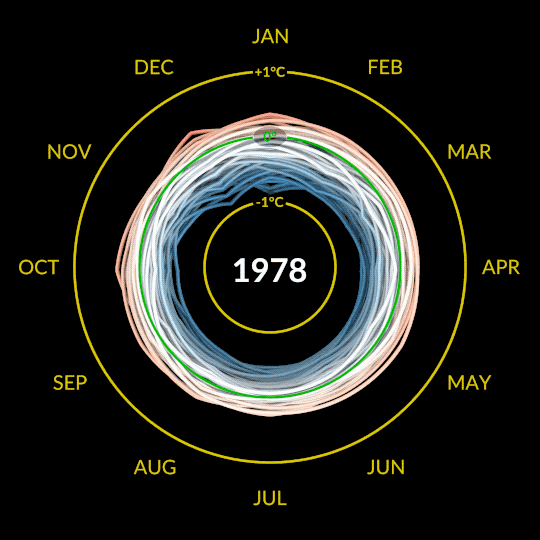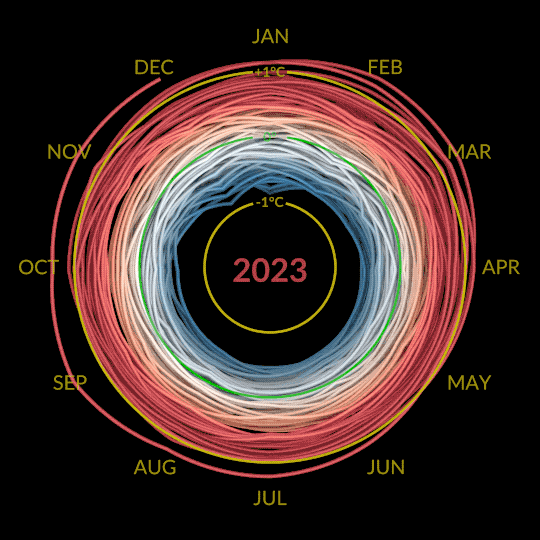
6. Speaking of which, why is the Arctic – one of the coldest places on Earth – red on this temperature map?
Our global temperature record doesn’t actually track absolute temperatures. Instead, we track temperature anomalies, which are basically just deviations from the norm. Our baseline is an average of the temperatures from 1951-1980, and we compare how much Earth’s temperature has changed since then.
Why focus on anomalies, rather than absolutes? Let’s say you want to track if apples these days are generally larger, smaller, or the same size as they were 20 years ago. In other words, you want to track the change over time.
Apples grown in Florida are generally larger than apples grown in Alaska. Like, in real life, how Floridian temperatures are generally much higher than Alaskan temperatures. So how do you track the change in apple sizes from apples grown all over the world while still accounting for their different baseline weights?
By focusing on the difference within each area rather than the absolute weights. So in our map, the Arctic isn’t red because it’s hotter than Bermuda. It’s red because it’s gotten relatively much warmer than Bermuda has in the same time frame.
Want to learn more about climate change? Dig into the data at climate.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Some alarming climate news as of June 2023
Antarctica, which is in the dead of winter, has unexpectedly failed to reform its winter sea ice. This is an exceptional deviation from the norm that has left scientists dumbfounded.
The entire NE Atlantic Ocean is experiencing its most significant marine heatwave ever…by far. That area had never been a full 1°C above the 1951-1980 average. It has suddenly jumped to 1.7°C above that average.
A powerful heatwave has overtaken southern North America for weeks on end, with places like Texas and northern Mexico breaking daily record high temperatures.
In the Caribbean Sea and Gulf of Mexico, sea surface temperatures are extremely high. Water temperatures are in the *90s* by the Florida coast, Miami keeps breaking daily record heat index values, and a major coral bleaching event will soon be underway.
The Canadian 2023 Wildfire Season will not let up, with nearly all annual records falling before we even reach the midpoint of the season. No Canadian wildfire season had ever produced 12 terawatts (TW) of fire radiative power. 2023 has produced 18TW.
Dramatic flood events have begun striking various countries around the world simultaneously this week.
El Niño has rapidly developed in recent months as sea surface temperatures across the equatorial east Pacific skyrocket. As of yet, El Niño has not impacted global weather conditions. That will change in a few months.
All of these events have culminated in June 2023, easily being the hottest June in Earth’s recorded history. Likely the hottest June in 115k-120k years when Earth was last this hot.
#important#current events#news#environment#climate#climate change#climate justice#environmentalism#environmental justice#global warming#activism#climate crisis#climate news
4K notes
·
View notes
Text

Despite its green image, Ireland has surprisingly little forest. [...] [M]ore than 80% of the island of Ireland was [once] covered in trees. [...] [O]f that 11% of the Republic of Ireland that is [now] forested, the vast majority (9% of the country) is planted with [non-native] spruces like the Sitka spruce [in commercial plantations], a fast growing conifer originally from Alaska which can be harvested after just 15 years. Just 2% of Ireland is covered with native broadleaf trees.
Text by: Martha O’Hagan Luff. “Ireland has lost almost all of its native forests - here’s how to bring them back.” The Conversation. 24 February 2023. [Emphasis added.]
---
[I]ndustrial [...] oil palm plantations [...] have proliferated in tropical regions in many parts of the world, often built at the expense of mangrove and humid forest lands, with the aim to transform them from 'worthless swamp' to agro-industrial complexes [...]. Another clear case [...] comes from the southernmost area in the Colombian Pacific [...]. Here, since the early 1980s, the forest has been destroyed and communities displaced to give way to oil palm plantations. Inexistent in the 1970s, by the mid-1990s they had expanded to over 30,000 hectares. The monotony of the plantation - row after row of palm as far as you can see, a green desert of sorts - replaced the diverse, heterogenous and entangled world of forest and communities.
Text by: Arturo Escobar. "Thinking-Feeling with the Earth: Territorial Struggles and the Ontological Dimension of the Epistemologies of the South." Revista de Antropologia Iberoamericana Volume 11 Issue 1. 2016. [Emphasis added.]
---
But efforts to increase global tree cover to limit climate change have skewed towards erecting plantations of fast-growing trees [...] [because] planting trees can demonstrate results a lot quicker than natural forest restoration. [...] [But] ill-advised tree planting can unleash invasive species [...]. [In India] [t]o maximize how much timber these forests yielded, British foresters planted pines from Europe and North America in extensive plantations in the Himalayan region [...] and introduced acacia trees from Australia [...]. One of these species, wattle (Acacia mearnsii) [...] was planted in [...] the Western Ghats. This area is what scientists all a biodiversity hotspot – a globally rare ecosystem replete with species. Wattle has since become invasive and taken over much of the region’s mountainous grasslands. Similarly, pine has spread over much of the Himalayas and displaced native oak trees while teak has replaced sal, a native hardwood, in central India. Both oak and sal are valued for [...] fertiliser, medicine and oil. Their loss [...] impoverished many [local and Indigenous people]. [...]
India’s national forest policy [...] aims for trees on 33% of the country’s area. Schemes under this policy include plantations consisting of a single species such as eucalyptus or bamboo which grow fast and can increase tree cover quickly, demonstrating success according to this dubious measure. Sometimes these trees are planted in grasslands and other ecosystems where tree cover is naturally low. [...] The success of forest restoration efforts cannot be measured by tree cover alone. The Indian government’s definition of “forest” still encompasses plantations of a single tree species, orchards and even bamboo, which actually belongs to the grass family. This means that biennial forest surveys cannot quantify how much natural forest has been restored, or convey the consequences of displacing native trees with competitive plantation species or identify if these exotic trees have invaded natural grasslands which have then been falsely recorded as restored forests. [...] Planting trees does not necessarily mean a forest is being restored. And reviving ecosystems in which trees are scarce is important too.
Text by: Dhanapal Govindarajulu. "India was a tree planting laboratory for 200 years - here are the results." The Conversation. 10 August 2023. [Emphasis added.]
---
Nations and companies are competing to appropriate the last piece of available “untapped” forest that can provide the most amount of “environmental services.” [...] When British Empire forestry was first established as a disciplinary practice in India, [...] it proscribed private interests and initiated a new system of forest management based on a logic of utilitarian [extraction] [...]. Rather than the actual survival of plants or animals, the goal of this forestry was focused on preventing the exhaustion of resource extraction. [...]
Text by: Daniel Fernandez and Alon Schwabe. "The Offsetted." e-flux Architecture (Positions). November 2013. [Emphasis added.]
---
At first glance, the statistics tell a hopeful story: Chile’s forests are expanding. […] On the ground, however, a different scene plays out: monocultures have replaced diverse natural forests [...]. At the crux of these [...] narratives is the definition of a single word: “forest.” [...] Pinochet’s wave of [...] [laws] included Forest Ordinance 701, passed in 1974, which subsidized the expansion of tree plantations [...] and gave the National Forestry Corporation control of Mapuche lands. This law set in motion an enormous expansion in fiber-farms, which are vast expanses of monoculture plantations Pinus radiata and Eucalyptus species grown for paper manufacturing and timber. [T]hese new plantations replaced native forests […]. According to a recent study in Landscape and Urban Planning, timber plantations expanded by a factor of ten from 1975 to 2007, and now occupy 43 percent of the South-central Chilean landscape. [...] While the confusion surrounding the definition of “forest” may appear to be an issue of semantics, Dr. Francis Putz [...] warns otherwise in a recent review published in Biotropica. […] Monoculture plantations are optimized for a single product, whereas native forests offer [...] water regulation, hosting biodiversity, and building soil fertility. [...][A]ccording to Putz, the distinction between plantations and native forests needs to be made clear. “[...] [A]nd the point that plantations are NOT forests needs to be made repeatedly [...]."
Text by: Julian Moll-Rocek. “When forests aren’t really forests: the high cost of Chile’s tree plantations.” Mongabay. 18 August 2014. [Emphasis added.]
#abolition#ecology#imperial#colonial#landscape#haunted#indigenous#multispecies#interspecies#temporality#carceral geography#plantations#ecologies#tidalectics#intimacies of four continents#archipelagic thinking#caribbean
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Best News of Last Week - August 21, 2023
🌊 - Discover the Ocean's Hidden Gem Deep down in the Pacific
1. Massachusetts passed a millionaire's tax. Now, the revenue is paying for free public school lunches.

Every kid in Massachusetts will get a free lunch, paid for by proceeds from a new state tax on millionaires.
A new 4% tax on the state's wealthiest residents will account for $1 billion of the state's $56 billion fiscal budget for 2024, according to state documents. A portion of those funds will be used to provide all public-school students with free weekday meals, according to State House News Service.
2. Plant-based filter removes up to 99.9% of microplastics from water

Researchers may have found an effective, green way to remove microplastics from our water using readily available plant materials. Their device was found to capture up to 99.9% of a wide variety of microplastics known to pose a health risk to humans.
3. Scientists Find A Whole New Ecosystem Hiding Beneath Earth's Seafloor
youtube
Most recently, aquanauts on board a vessel from the Schmidt Ocean Institute used an underwater robot to turn over slabs of volcanic crust in the deep, dark Pacific. Underneath the seafloor of this well-studied site, the international team of researchers found veins of subsurface fluids swimming with life that has never been seen before.
It's a whole new world we didn't know existed.
4. How solar has exploded in the US in just a year

Solar and storage companies have announced over $100 billion in private sector investments in the US since the passage of the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) a year ago, according to a new analysis released today by the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA).
Since President Joe Biden signed the IRA in August 2022, 51 solar factories have been announced or expanded in the US.
5. Researchers have identified a new pack of endangered gray wolves in California

A new pack of gray wolves has shown up in California’s Sierra Nevada, several hundred miles away from any other known population of the endangered species, wildlife officials announced Friday.
It’s a discovery to make researchers howl with delight, given that the native species was hunted to extinction in California in the 1920s. Only in the past decade or so have a few gray wolves wandered back into the state from out-of-state packs.
6. Record-Breaking Cleanup: 25,000 Pounds of Trash Removed from Pacific Garbage Patch

Ocean cleanup crews have fished out the most trash ever taken from one of the largest garbage patches in the world.
The Ocean Cleanup, a nonprofit environmental engineering organization, saw its largest extraction earlier this month by removing about 25,000 pounds of trash from the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, Alex Tobin, head of public relations and media for the organization
7. The Inflation Reduction Act Took U.S. Climate Action Global

The U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) aimed to promote clean energy investments in the U.S. and globally. In its first year, the IRA successfully spurred other nations to develop competitive climate plans.
Clean energy projects in 44 U.S. states driven by the IRA have generated over 170,600 jobs and $278 billion in investments, aligning with Paris Agreement goals.
---
That's it for this week :)
This newsletter will always be free. If you liked this post you can support me with a small kofi donation here:
Buy me a coffee ❤️
Also don’t forget to reblog this post with your friends.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
"The world’s coral reefs are close to 25% larger than we thought. By using satellite images, machine learning and on-ground knowledge from a global network of people living and working on coral reefs, we found an extra 64,000 square kilometers of coral reefs — an area the size of Ireland.
That brings the total size of the planet’s shallow reefs (meaning 0-20 meters deep) to 348,000 square kilometers — the size of Germany. This figure represents whole coral reef ecosystems, ranging from sandy-bottomed lagoons with a little coral, to coral rubble flats, to living walls of coral.
Within this 348,000 km² of coral is 80,000 km² where there’s a hard bottom — rocks rather than sand. These areas are likely to be home to significant amounts of coral — the places snorkelers and scuba divers most like to visit.
You might wonder why we’re finding this out now. Didn’t we already know where the world’s reefs are?
Previously, we’ve had to pull data from many different sources, which made it harder to pin down the extent of coral reefs with certainty. But now we have high resolution satellite data covering the entire world — and are able to see reefs as deep as 30 meters down.
We coupled this with direct observations and records of coral reefs from over 400 individuals and organizations in countries with coral reefs from all regions, such as the Maldives, Cuba and Australia.
To produce the maps, we used machine learning techniques to chew through 100 trillion pixels from the Sentinel-2 and Planet Dove CubeSat satellites to make accurate predictions about where coral is — and is not. The team worked with almost 500 researchers and collaborators to make the maps.
The result: the world’s first comprehensive map of coral reefs extent, and their composition, produced through the Allen Coral Atlas.
The maps are already proving their worth. Reef management agencies around the world are using them to plan and assess conservation work and threats to reefs...
In good news, these maps are already leading to real world change. We’ve already seen new efforts to conserve coral reefs in Indonesia, several Pacific island nations, Panama, Belize, Kenya and Australia, among others."
-via GoodGoodGood, May 2, 2024
--
Note: You can see the maps yourself by going here!
#coral#coral reef#sea creatures#marine life#underwater#coral reefs#conservation#conservation news#climate change#hope#hope posting#hopepunk#environment#environmental science#environmental news#good news#climate action#climate hope#maldives#cuba#australia#machine learning#ai#this is the kind of shit ai should be used for!!!#indonesia#panama#belize#kenya#it's coral week here at reasonsforhope and it's not even on purpose!
288 notes
·
View notes
Text
Since last June, the globe has broken heat records each month, with marine heat waves across large areas of the globe’s oceans contributing.
Scientists say the record-breaking heat during this time wasn't entirely surprising due to a strong El Nino, a climatic condition that warms the central Pacific and changes global weather patterns.
“But its combination with the non-natural marine heat waves made these records so breathtaking,” said Woodwell Climate Research Center scientist Jennifer Francis.
93 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from this EcoWatch story:
According to a new report from the nonprofit Pacific Institute, violent conflicts over water increased sharply in 2023. The report found there were nearly 350 water-related conflicts globally last year, a record high.
The latest update to Pacific Institute’s Water Conflict Chronology has revealed a huge increase in the number of water-related conflicts in 2023 compared to just 2022, with around a 150% rise. In 2022, there were 231 recorded conflicts over water, compared to the 347 recorded for 2023.
In comparing to recent decades, the contrast is even more stark. In 2000, there were just 22 water-related conflicts worldwide, Pacific Institute reported.
“The significant upswing in violence over water resources reflects continuing disputes over control and access to scarce water resources, the importance of water for modern society, growing pressures on water due to population growth and extreme climate change, and ongoing attacks on water systems where war and violence are widespread, especially in the Middle East and Ukraine,” Peter Gleick, senior fellow and co-founder of the Pacific Institute, said in a statement.
The organization records conflicts based on news reports, first-person accounts and databases. According to the data for 2023, water conflicts were most prominent in the Middle East, Southern Asia and sub-Saharan Africa. All three regions experienced increases in three different categories of conflict recorded: trigger, casualty and weapon.
Half of the conflicts were on water and water infrastructure, while 39% of new conflicts were over access or control of water, Pacific Institute reported.
Most conflicts, around 62%, were maintained within one country, while 38% of conflict events involved multiple countries, the report found.
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
A 13-month streak of record-breaking global warmth has ended.
From June 2023 until June 2024, air and ocean surface water temperatures averaged a quarter of a degree Celsius higher than records set only a few years previously. Air temperatures in July 2024 were slightly cooler than the previous July (0.04 degrees Celsius, the narrowest of margins) according to the EU’s Copernicus Climate Change Service.
July 2023 was in turn 0.28 degrees Celsius warmer than the previous record-hot July in 2019, so the remarkable jump in temperature during the past year has yet to ease off completely. The warmest global air temperature recorded was in December 2023, at 1.78 degrees Celsius above the preindustrial average temperature for December—and 0.31 degrees Celsius warmer than the previous record.
Global warming has consistently toppled records for warm global average temperatures in recent decades, but breaking them by as much as a quarter of a degree for several months is not common. The end of this streak does not diminish the mounting threat of climate change.
So what caused these record temperatures? Several factors came together, but the biggest and most important is climate change, largely caused by burning fossil fuels.
What Caused the Heat Streak
Temperatures typical of Earth 150 years ago are used for comparison to measure modern global warming. The reference period, 1850–1900, was before most greenhouse gases associated with global industrialization—which increase the heat present in Earth’s ocean and atmosphere—had been emitted.
July 2024 was 1.48 degrees Celsius warmer than a typical preindustrial July, of which about 1.3 degrees Celsius is attributable to the general trend of global warming over the intervening decades. This trend will continue to raise temperatures until humanity stabilizes the climate by keeping fossil fuels in the ground where they belong.
But global warming doesn’t happen in a smooth progression. Like housing prices, the general trend is up, but there are ups and downs along the way.
Behind much of the ups and downs is the El Niño phenomenon. An El Niño event is a reorganization of the water across the vast reaches of the Pacific Ocean. El Niño is so important to the workings of worldwide weather, as it increases the temperature of the air on average across all of Earth’s surface, not only over the Pacific. Between El Niño events, conditions may be neutral or in an opposite state called La Niña that tends to cool global temperatures. The oscillation between these extremes is irregular, and El Niño conditions tend to recur after three to seven years.
The warm El Niño phase of this cycle began to kick in a year ago, reached its peak around the end of 2023, and is now trending neutral, which is why the record-breaking streak has ended.
The 2023–2024 El Niño was strong, but it wasn’t super-strong. It doesn’t fully explain the remarkable degree to which the past year broke temperature records. The exact influence of other factors has yet to be fully untangled.
We know there is a small positive contribution from the sun, which is in a phase of its 11-year sunspot cycle in which it radiates fractionally more energy to the Earth.
Methane (also a byproduct of the fossil fuel industry, alongside cattle and wetlands) is another important greenhouse gas, and its concentration in the air has risen more rapidly in the past decade than over the previous decade.
Scientists are also assessing how much measures to clean up air pollution might be adding to warming, since certain particulate air pollutants can reflect sunlight and influence the formation of clouds.
A Temperature Ratchet
Across the global ocean, 2023 was a devastating summer for coral reefs and surrounding ecosystems in the Caribbean and beyond. This was followed by heavy bleaching across the Great Barrier Reef off Australia during the southern hemisphere summer. While it is El Niño years that tend to see mass mortality events on reefs around the world, it is the underlying climate change trend that is the long-term threat, as corals are struggling to adapt to rising temperature extremes.
As the Pacific Ocean is now likely to revert toward La Niña conditions, global temperatures will continue to ease back but probably not to the levels seen prior to 2023–24.
El Niño acts a bit like a ratchet on global warming. A big El Niño event breaks new records and establishes a new, higher norm for global temperatures. That new normal reflects the underlying global warming trend.
A plausible scenario is that global temperatures will fluctuate near the 1.4 degrees Celsius level for several years, until the next big El Niño event pushes the world above 1.5 degrees Celsius of warming, perhaps in the early 2030s.
The Paris agreement on climate change committed the world to make every effort to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius, because the impacts of climate change are expected to accelerate beyond that level.
The good news is that the shift away from fossil fuels has started in sectors such as electricity generation, where renewable energy meets a growing share of rising demand. But the transition is not happening fast enough, by a large margin. Meeting climate targets is not compatible with fully exploiting existing fossil-fuel infrastructure, yet new investment in oil rigs and gas fields continues.
Headlines about record-breaking global temperatures will probably return. But they need not do so forever. There are many options for accelerating the transition to a decarbonized economy, and it is increasingly urgent that these are pursued.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
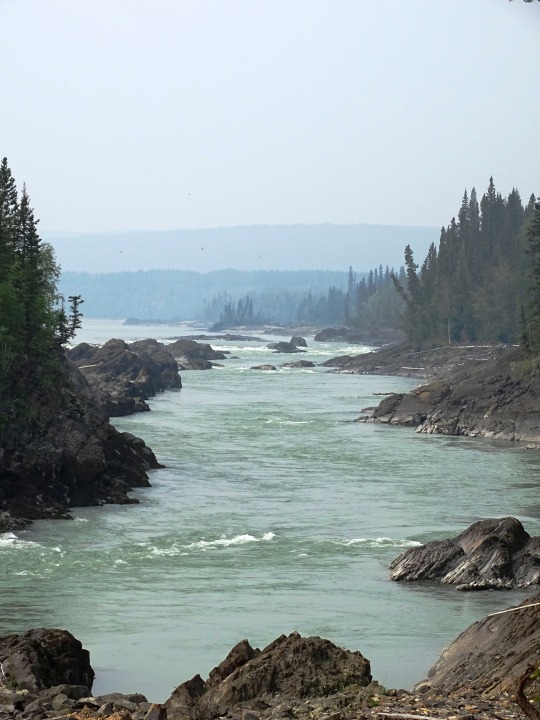
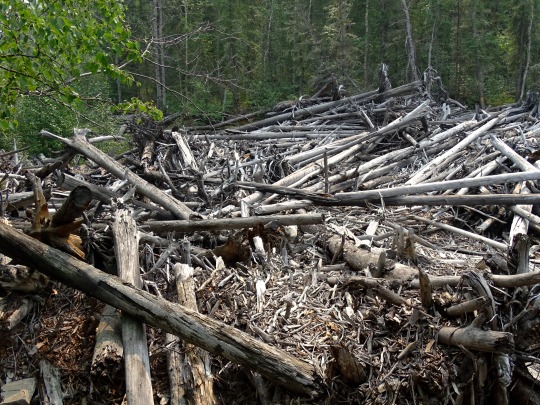
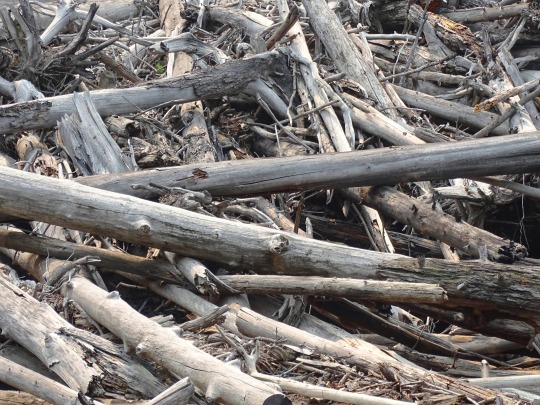
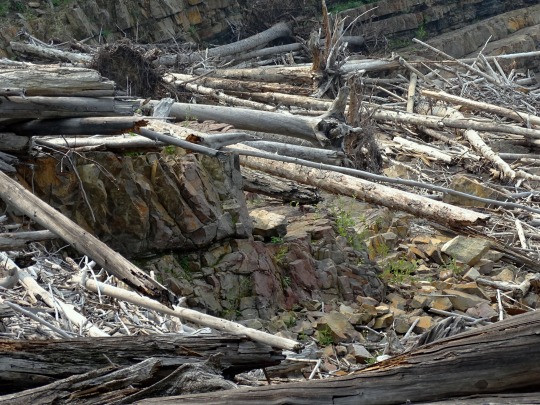
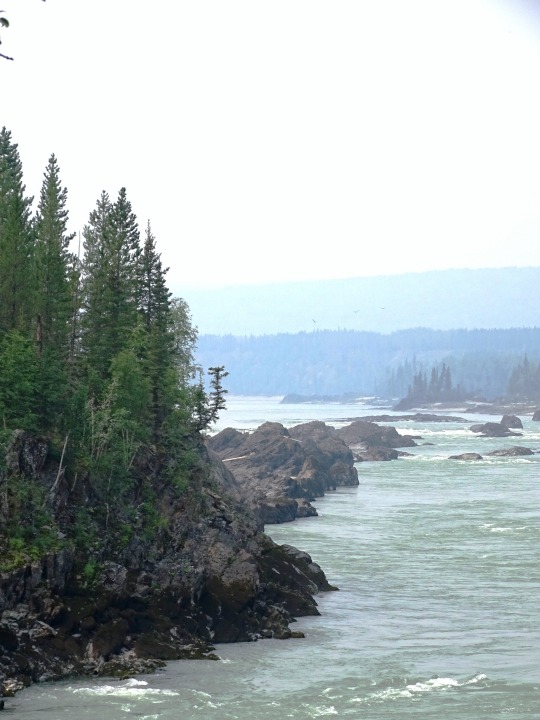
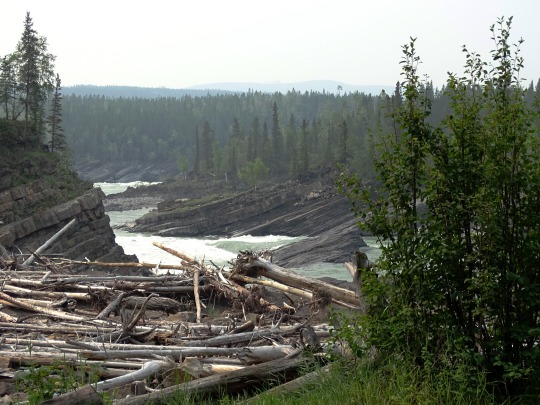










Whirlpool Canyon, BC (No. 5)
With the advent of industrial logging practices, the global quantity of driftwood has declined. Early accounts indicate that driftwood was once more plentiful. Early photographs of the pacific coast reveal greater amounts of driftwood on the beaches than is present today. Likewise, when traveling in Dixon Entrance in the late 1800s, George A. Dorsey recorded that many beaches were "piled high with drift, often to a height of sixty feet or more. " Melting polar ice may also contribute to the decline of Siberian driftwood in the Atlantic as the sea ice enabled driftwood to travel greater distances without becoming waterlogged.
Source: Wikipedia
#Skooks Landing#driftwood#Whirlpool Canyon#shale Rock#BC#Liard River#travel#original photography#vacation#tourist attraction#landmark#landscape#countryside#British Columbia#woods#forest#nature#flora#tree#river bank#wildfire smoke#summer 2023#Canada#view#vista point#boreal forest
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
Weather tracker: torrential rainstorms cause death and destruction in Brazil
This part of South America is no stranger to major rainfall, but last week’s storms were particularly devastating

Torrential rainstorms in Brazil’s southernmost state of Rio Grande do Sul have caused the worst flooding the country has seen in 80 years, many deaths and the displacement of thousands of families. Central parts of the state were hit the hardest after the storms began last Monday, with unofficial weather stations in the area recording 50-100cm (20-40in) of rain over the past week.
Widespread floods and landslides have caused major damage to homes and infrastructure, most alarmingly triggering the partial collapse of a small hydroelectric dam on Thursday, which sent a 2-metre-high wave through the surrounding area. At least 57 deaths have been reported and 24,000 people have been displaced, alongside an estimated 500,000 being without power and clean water.
This part of South America is no stranger to major rainfall; Rio Grande do Sul has experienced flooding three other times in the past year. This is because the polar and tropical regions of the atmosphere meet around this latitude, resulting in a zone of high pressure that delivers long periods of dry weather punctuated with heavy bursts of rain. However, this event has been particularly devastating, with experts attributing the heightened rainfall to the combination of global heating and the recent El Niño phenomenon, during which waters in the eastern Pacific Ocean become warmer.
Continue reading.
#brazil#politics#brazilian politics#environmental justice#rio grande do sul floods 2024#mod nise da silveira#image description in alt
27 notes
·
View notes
Note
original anon here tysm for the recs ! if the marxist frameworks was too limiting im also completely fine w general postcolonial botany readings on the topic :0
A Spiteful Campaign: Agriculture, Forests, and Administering the Environment in Imperial Singapore and Malaya (2022). Barnard, Timothy P. & Joanna W. C. Lee. Environmental History Volume: 27 Issue: 3 Pages: 467-490. DOI: 10.1086/719685
Planting Empire, Cultivating Subjects: British Malaya, 1786–1941 (2018). Lynn Hollen Lees
The Plantation Paradigm: Colonial Agronomy, African Farmers, and the Global Cocoa Boom, 1870s--1940s (2014). Ross, Corey. Journal of Global History Volume: 9 Issue: 1 Pages: 49-71. DOI: 10.1017/S1740022813000491
Cultivating “Care”: Colonial Botany and the Moral Lives of Oil Palm at the Twentieth Century’s Turn (2022). Alice Rudge. Comparative Studies in Society and History Volume: 64 Issue: 4 Pages: 878-909. DOI: 10.1017/S0010417522000354
Pacific Forests: A History of Resource Control and Contest in Solomon Islands, c. 1800-1997 (2000). Bennett, Judith A.
Thomas Potts of Canterbury: Colonist and Conservationist (2020). Star, Paul
Colonialism and Green Science: History of Colonial Scientific Forestry in South India, 1820--1920 (2012). Kumar, V. M. Ravi. Indian Journal of History of Science Volume: 47 Issue 2 Pages: 241-259
Plantation Botany: Slavery and the Infrastructure of Government Science in the St. Vincent Botanic Garden, 1765–1820 (2021). Williams, J'Nese. Berichte zur Wissenschaftsgeschichte Volume: 44 Issue: 2 Pages: 137-158. DOI: 10.1002/bewi.202100011
Angel in the House, Angel in the Scientific Empire: Women and Colonial Botany During the Eighteenth and Nineteenth Centuries (2020). Hong, Jiang. Notes and Records: The Royal Society Journal of the History of Science Volume: 75 Issue: 3 Pages: 415-438. DOI: 10.1098/rsnr.2020.0046
From Ethnobotany to Emancipation: Slaves, Plant Knowledge, and Gardens on Eighteenth-Century Isle de France (2019). Brixius, Dorit. History of Science Volume: 58 Issue: 1 Pages: 51-75. DOI: 10.1177/0073275319835431
African Oil Palms, Colonial Socioecological Transformation and the Making of an Afro-Brazilian Landscape in Bahia, Brazil (2015). Watkins, Case. Environment and History Volume: 21 Issue: 1 Pages: 13-42. DOI: 10.3197/096734015X14183179969700
The East India Company and the Natural World (2015). Ed. Damodaran, Vinita; Winterbottom, Anna; Lester, Alan
Colonising Plants in Bihar (1760-1950): Tobacco Betwixt Indigo and Sugarcane (2014). Kerkhoff, Kathinka Sinha
Science in the Service of Colonial Agro-Industrialism: The Case of Cinchona Cultivation in the Dutch and British East Indies, 1852--1900 (2014). Hoogte, Arjo Roersch van der & Pieters, Toine. Studies in History and Philosophy of Science Part C: Studies in History and Philosophy of Biological and Biomedical Sciences Volume: 47 Issue: Part A Pages: 12-22
Trading Nature: Tahitians, Europeans, and Ecological Exchange (2010). Newell, Jennifer
The Colonial Machine: French Science and Overseas Expansion in the Old Regime (2011). McClellan, James E. & Regourd, François
Colonial Botany: Science, Commerce, and Politics in the Early Modern World (2005). Ed. Schiebinger, Londa L. & Swan, Claudia
Plants and Empire: Colonial Bioprospecting in the Atlantic World (2004). Schiebinger, Londa L.
92 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why Isn’t Every Year the Warmest Year on Record?
This just in: 2022 effectively tied for the fifth warmest year since 1880, when our record starts. Here at NASA, we work with our partners at NOAA to track temperatures across Earth’s entire surface, to keep a global record of how our planet is changing.
Overall, Earth is getting hotter.
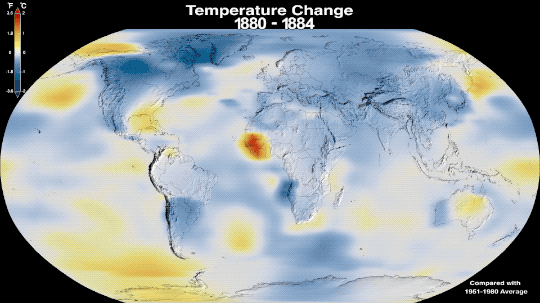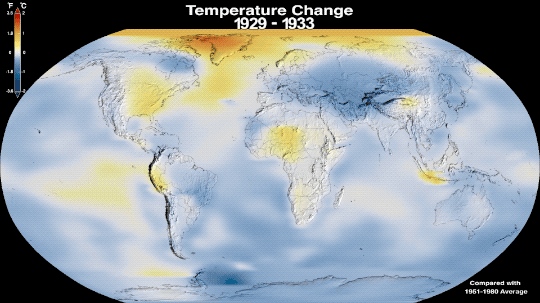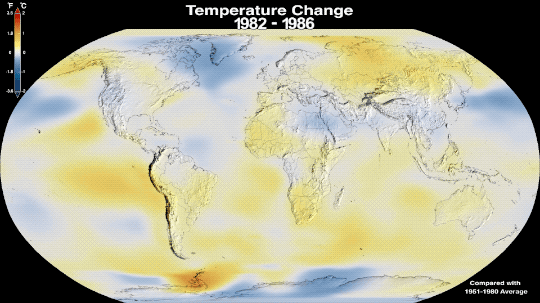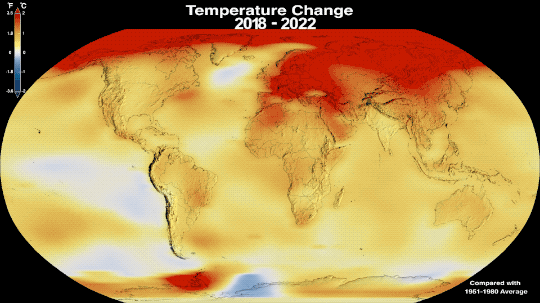
The warming comes directly from human activities – specifically, the release of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels. We started burning fossil fuels in earnest during the Industrial Revolution. Activities like driving cars and operating factories continue to release greenhouse gases into our atmosphere, where they trap heat in the atmosphere.
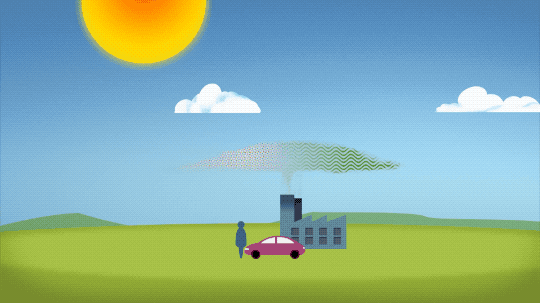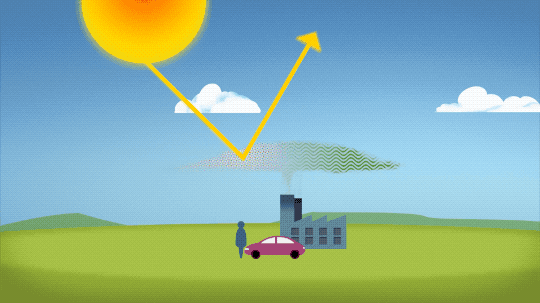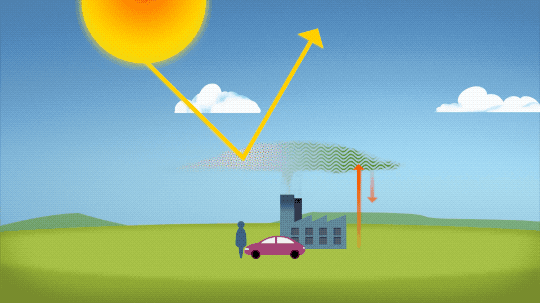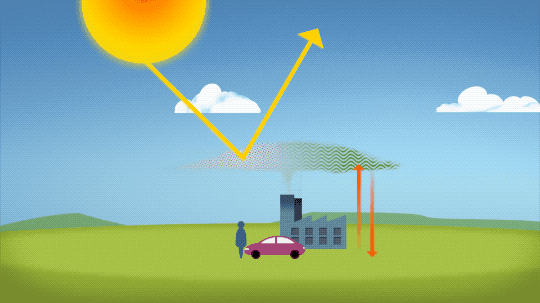
So…if we’re causing Earth to warm, why isn’t every year the hottest year on record?
As 2022 shows, the current global warming isn’t uniform. Every single year isn’t necessarily warmer than every previous year, but it is generally warmer than most of the preceding years. There’s a warming trend.
Earth is a really complex system, with various climate patterns, solar activity, and events like volcanic eruptions that can tip things slightly warmer or cooler.
Climate Patterns
While 2021 and 2022 continued a global trend of warming, they were both a little cooler than 2020, largely because of a natural phenomenon known as La Niña.
La Niña is one third of a climate phenomenon called El Niño Southern Oscillation, also known as ENSO, which can have significant effects around the globe. During La Niña years, ocean temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean cool off slightly. La Niña’s twin, El Niño brings warmer temperatures to the central and eastern Pacific. Neutral years bring ocean temperatures in the region closer to the average.
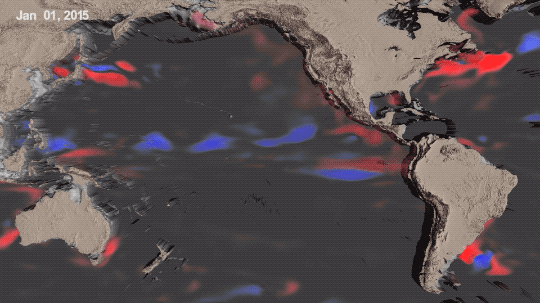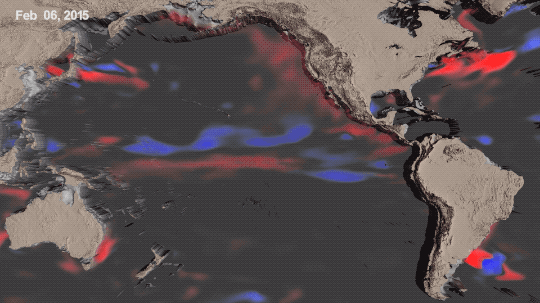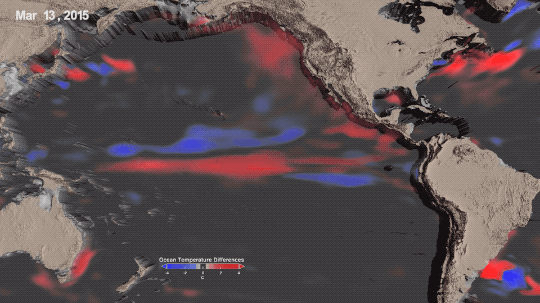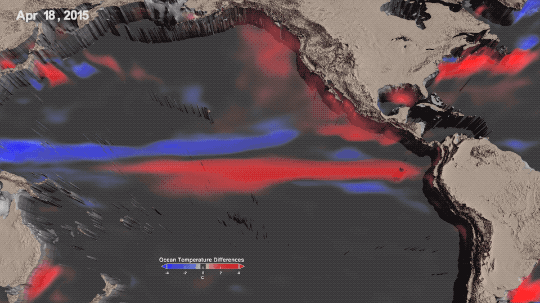
El Niño and La Niña affect more than ocean temperatures – they can bring changes to rainfall patterns, hurricane frequency, and global average temperature.
We’ve been in a La Niña mode the last three, which has slightly cooled global temperatures. That’s one big reason 2021 and 2022 were cooler than 2020 – which was an El Niño year.
Overall warming is still happening. Current El Niño years are warmer than previous El Niño years, and the same goes for La Niña years. In fact, enough overall warming has occurred that most current La Niña years are warmer than most previous El Niño years. This year was the warmest La Niña year on record.

Solar Activity
Our Sun cycles through periods of more and less activity, on a schedule of about every 11 years. Here on Earth, we might receive slightly less energy — heat — from the Sun during quieter periods and slightly more during active periods.
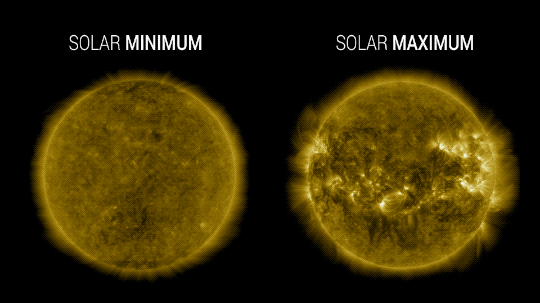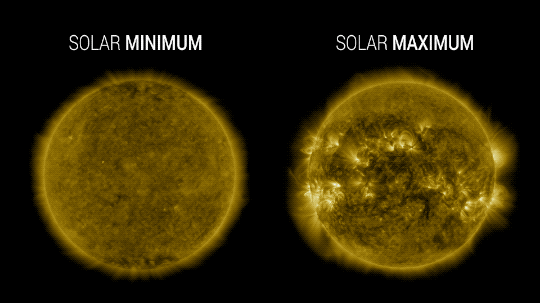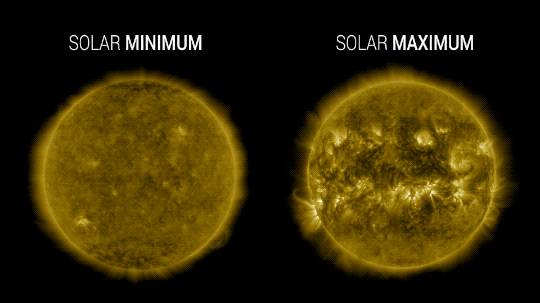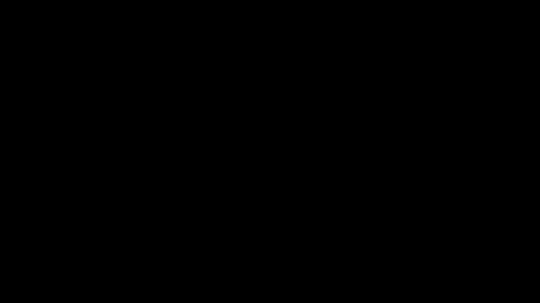
At NASA, we work with NOAA to track the solar cycle. We kicked off a new one – Solar Cycle 25 – after solar minimum in December 2019. Since then, solar activity has been slightly ramping up.
Because we closely track solar activity, we know that over the past several decades, solar activity hasn't been on the rise, while greenhouse gases have. More importantly, the "fingerprints" we see on the climate, including temperature changes in the upper atmosphere, don't fit the what we'd expect from solar-caused warming. Rather they look like what we expect from increased greenhouse warming, verifying a prediction made decades ago by NASA.
Volcanic Eruptions
Throughout history, volcanoes have driven major shifts in Earth’s climate. Large eruptions can release water vapor — a greenhouse gas like carbon dioxide — which traps additional warmth within our atmosphere.
On the flip side, eruptions that loft lots of ash and soot into the atmosphere can temporarily cool the climate slightly, by reflecting some sunlight back into space.
Like solar activity, we can monitor volcanic eruptions and tease out their effect on variations in our global temperature.
At the End of the Day, It’s Us
Our satellites, airborne missions, and measurements from the ground give us a comprehensive picture of what’s happening on Earth every day. We also have computer models that can skillfully recreate Earth’s climate.
By combining the two, we can see what would happen to global temperature if all the changes were caused by natural forces, like volcanic eruptions or ENSO. By looking at the fingerprints each of these climate drivers leave in our models, it’s perfectly clear: The current global warming we’re experiencing is caused by humans.
For more information about climate change, visit climate.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Umair Irfan at Vox:
It’s gearing up to be another scorching year.
Countries like Brazil, Thailand, Japan, Kenya, Nigeria, Australia, and Spain already experienced record warm temperatures this year, and in the past few days, heat has killed dozens in India and Mexico. Now states like California, Nevada, Arizona, and Texas are getting ready to roast as a massive heat wave settles in. It’s likely to push temperatures well into triple digits. And summer hasn't even officially started yet.
It’s an alarming echo of 2023, which was the hottest year on record, but this year could be hotter still. Though the Pacific Ocean is shifting into its La Niña phase, which typically brings cooler global weather, the extraordinary warmth over the past year is still baked in. Scientists say these record highs align with their expectations for climate change, and warn that more scorchers are coming.
There’s more to heat waves like this than high temperatures, though. The forces behind them are complex and changing. They’re a public health threat that can exacerbate inequality, cause infrastructure to collapse, and amplify other problems stemming from warming. But with global average temperatures continuing to rise, more records will fall.
Heat waves, explained
Extreme heat might not seem as dramatic as hurricanes or floods, but the National Weather Service has deemed it the deadliest weather phenomenon in the US over the past 30 years, on average.
What counts as a heat wave is typically defined relative to local weather conditions, with sustained temperatures in the 90th to 95th percentile of the average in a given area. So the threshold for a heat wave in Tucson is higher than the threshold in Seattle.
During the summer in the Northern Hemisphere, the northern half of the planet is tilted toward the sun, which increases daylight hours and warms the hemisphere. The impact of this additional exposure to solar radiation is cumulative, which is why temperatures generally peak weeks after the longest day of the year.
Amid the increase in temperatures in the summer, meteorology can push those numbers to extremes.
Heat waves typically begin with a high-pressure system (also known as an anticyclone), where atmospheric pressure above an area builds up. That creates a sinking column of air that compresses, heats up, and oftentimes dries out. The sinking air can act as a cap or heat dome, trapping the latent heat already absorbed by the landscape. The high-pressure system also pushes out cooler, fast-moving air currents and squeezes clouds away, which gives the sun an unobstructed line of sight to the ground.
The ground — soil, sand, concrete, and asphalt — then bakes in the sunlight, and in the long days and short nights of summer, heat energy quickly accumulates and temperatures rise.
Heat waves are especially common in areas that are already arid, like the desert Southwest, and at high altitudes where high-pressure systems readily form. Moisture in the ground can blunt the effects of heat, the way evaporating sweat can cool the body. But when there’s little water in the ground, in waterways, and in vegetation, there isn’t as much to soak up the heat besides the air itself.
[...]
But extreme heat can also build up in places that have a lot of moisture. In fact, for every degree Celsius the air warms (1.8 degrees Fahrenheit), it can absorb about 7 percent more water, which can create a dangerous combination of heat and humidity (more on that below).
Urban areas further exacerbate this warming. As roads, parking lots, and buildings cover natural landscapes, cities like Los Angeles and Dallas end up absorbing more heat than their surroundings and can become as much as 20°F warmer. This is a phenomenon known as the urban heat island effect.
Heat waves typically last around five days but can linger longer if the high-pressure system is locked in place. “In some cases, you actually can get these kinds of patterns getting stuck, and that can lead to heat waves lasting much longer,” said Karen McKinnon, an assistant professor of environment and sustainability at the University of California Los Angeles.
Eventually, the high-pressure system will start to weaken, allowing in cooler air and precipitation that can bring the heat wave to an end. However, as the warm season continues, more high-pressure systems can settle in and restart the heating process.
[...]
Climate change caused by greenhouse gases from burning fossil fuels is poised to make heat waves longer, more intense, and more frequent. It takes time for the dust to settle on the heat waves of a given moment, to allow scientists to evaluate just how much humans have contributed to the problem.
[...]
That heat isn’t distributed evenly, however. Nighttime temperatures are rising faster than daytime temperatures. “In general, since records began in 1895, summer overnight low temperatures are warming at a rate nearly twice as fast as afternoon high temperatures for the U.S. and the 10 warmest summer minimum temperatures have all occurred since 2002,” according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. This can seriously impair how people cope with high heat.
The effects of warming can vary by latitude, too. Polar regions are warming up to three times as fast as the planetary average, fueling heat waves in the Arctic. In fact, cooler parts of the planet are heating up faster than places closer to the equator, so people living in temperate climates may experience some of the biggest increases in extreme heat events. Already hot parts of the world also get hotter, pushing them beyond the realm of habitability at certain times of the year.
And as human-generated greenhouse gas emissions continue to flood the atmosphere — atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations recently peaked at 420 parts per million — heat waves are projected to become more frequent and more extreme.
[...]
The timing of heat waves is changing: Periods of extreme heat that occur early in the season tend to have greater public health impacts. That’s because people are less acclimated to heat in the spring and early summer. Cooling infrastructure may not be in place, and people may not be taking heat precautions like staying hydrated and avoiding the sun. That’s why early-season heat waves in the US, as we have seen across the country this year, are so troubling. As climate change makes heat waves more common, it also increases the frequency of early- and late-season extreme temperatures, lengthening the hot season.
The worst effects of heat aren’t always in the hottest places: While absolute temperatures may rise higher in already warm areas like the southwestern US, heat waves can have their deadliest impacts in cooler regions, where high temperatures are less common. Warmer areas often already have air conditioning in homes and offices, while regions that usually don’t get as warm have less cooling infrastructure and fewer places to find relief. The people in these regions are also less acclimated to high temperatures and may not recognize warning signs of heat-induced health problems.
Some people are far more vulnerable to extreme heat: Elderly people and very young children face some of the highest risks from extreme heat. People with certain health conditions, like high blood pressure and breathing difficulties, also face greater harm. But even otherwise healthy people can suffer from heat waves if they are exposed for long durations, such as those working outdoors in agriculture and construction.
Heat waves exacerbate structural inequalities: While cities can warm up faster than their surroundings, poorer neighborhoods — which are disproportionately home to people of color — tend to get hotter. These neighborhoods often have less tree cover and green spaces, and more paved surfaces that soak up heat. At the same time, lower-income residents may have a harder time affording crucial cooling. The pattern of heat inequality plays out on an international scale, too, with lower-income countries already facing higher health and economic costs from heat waves.
The tools used to cope with heat are also stressed by it: Power plants, which provide electricity for everything from fridges to air conditioners, themselves need to be cooled, and they become less efficient as the weather warms. Power lines have lower capacities under extreme heat, and hardware like transformers experience more failures. If enough stress builds up, the power grid can collapse just when people need cooling the most. Power disruptions then ripple through other infrastructure, like water sanitation, fuel pumps, and public transit.
We’re running out of time to act: All this means that heat waves are going to become an increasingly impactful and costly fact of life across the world — from the direct impacts on health to stresses on infrastructure.
But since humans share a significant portion of the blame for extreme heat waves, there are also actions people can take to mitigate them. Increasing energy efficiency can relieve stress on the power grid, and adding power sources that don’t require active cooling like wind and solar can boost capacity without adding greenhouse gas emissions.
Vox has a good article on why we are seeing longer and more severe heat waves around the world: climate change effects are part of the reason for the increased duration and severity of heat waves globally.
#Heat Waves#Extreme Weather#Climate Change#Weather#Urban Heat Island Effect#Greenhouse Gases#Extreme Heat
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trump Was Good for America’s Alliances
He pushed NATO to spend more on defense, expanded the Quad and facilitated the Abraham Accords.
By Alexander B. Gray
Wall Street Journal
April 3, 2024
Foreign-policy experts are predictably fretting over Donald Trump’s re-election campaign. They fear that the former president threatens the alliances and partnerships that have sustained global peace since 1945. Should Mr. Trump return to the White House, the thinking goes, he will be unconstrained by the guardrails that prevented him from torpedoing America’s alliances in his first term and will permanently damage both U.S. security and the international order.
This narrative concedes a point that undermines its premise: The U.S. alliance system didn’t crumble during Mr. Trump’s first term. On the contrary, the Trump administration strengthened relations with partners in the Indo-Pacific, Central and Eastern Europe and the Mideast. Anyone who believes that Mr. Trump was once bound by conventional wisdom but won’t be again—and will wreak havoc on the global order he ostensibly detests—hasn’t been paying attention.
To understand Mr. Trump’s record, recall what he inherited. The Obama administration’s disastrous “red line” in Syria, its ill-conceived Iranian nuclear deal, its failure to deter or respond adequately to Russia’s 2014 aggression against Ukraine, its toleration of Chinese malign activity in the South and East China seas, and its promise of a “new model of great-power relations” with Beijing had brought U.S. relations with allies and partners like Japan, Taiwan, Israel, the Gulf Arab states and much of Eastern Europe to a historic low point. Much of Mr. Trump’s tenure was spent not simply repairing those relationships but expanding them in innovative ways.
Mr. Trump appalled many foreign-policy veterans, who thought his rhetoric threatened the world order. In one sense, that fear was absurd: Nearly every American administration has publicly scolded North Atlantic Treaty Organization member countries for shirking their defense-spending commitments. Mr. Trump did likewise—and, perhaps unlike his predecessors, was seen as willing to take decisive action to secure change. Through public and private cajoling—also known as diplomacy—he secured a commitment from NATO members to beef up their contributions. From 2017 through 2021, nearly every signatory raised defense spending, contributing substantially to the alliance’s ability to respond to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in 2022.
These efforts resulted in a significant redistribution of U.S. forces from legacy bases in Germany to facilities in Poland and the Baltic states, where they are far better positioned to deter Moscow. Along with NATO allies, Mr. Trump provided long-sought Javelin antitank missiles to Ukraine, imposed sanctions against malign Russian actors, and worked with partners to stop the Nord Stream 2 pipeline, which would have increased European allies’ energy dependence on Russia. These weren’t the acts of a retrograde isolationist; they were the work of a pragmatist seeking novel solutions to 21st-century challenges.
The administration’s goal of strengthening America’s standing in the world bore fruit, including the Abraham Accords between Israel and several Arab states, a significant upgrade to the Quad alliance among the U.S., India, Australia and Japan, stronger diplomatic relations with Taiwan thanks to unprecedented cabinet-level visits and record arms sales, and an unexpected deal between Serbia and Kosovo.
At each step, Mr. Trump asked his staff to think of creative ways to resolve issues that had bedeviled their predecessors for decades. Doing the same things over and over and expecting different results rightly struck the president as insane.
After three years of press adulation over America’s supposed return to the world stage under President Biden, one might ask: What have Americans and the world gotten from a supposedly more alliance-friendly U.S. president? So far, a catastrophic withdrawal from Afghanistan, the failure of American deterrence in Ukraine, an Iranian nuclear breakout inching ever closer, and an accelerating Chinese threat toward Taiwan. Allies in the Mideast, Eastern Europe, and Asia have begun to chart their own course in the face of an uncertain U.S. trumpet.
The global foreign-policy elite is sowing needless fear around the world by willfully misrepresenting Mr. Trump’s first term and scare-mongering about a second. Should Mr. Trump return to the White House, there will doubtless be sighs of relief among officials in friendly capitals who remember his time in office. It isn’t difficult to understand why: Mr. Trump’s language may make diplomats uncomfortable, but his actions strike fear among those who matter most to American security: our adversaries.
Mr. Gray is a senior fellow at the American Foreign Policy Council. He served as chief of staff of the White House National Security Council, 2019-21.
16 notes
·
View notes