#indigenous resilience
Text










Orange shirt day tomorrow. Once again, I’m of mixed feelings. Happy that we have a day that let’s non-Indigenous people know.., but sad we even have to make a day to be noticed or cared about.
Trying to spread awareness and love.
🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡🧡
#personal#every child matters#truth and reconciliation#residential schools#orange shirt day#canada#Canada shame#indigenous#Indigenous resilience#we are still here#indigenous resistance#september#september 30
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

Community, we need your help!
Due to health complications, this first-generation student is in need of a little extra support to stay afloat until they start their new job next month.
We're aiming to raise $1600 ASAP to cover past-due rent and an additional $2000 for this month's rent and bills. Every single contribution, big or small, makes a real difference in their journey forward.
Let's show them the power of community support! Your generosity will not only ease their financial burden but also uplift their spirits during this challenging time.
Donations can be made via this givebutter fundraiser. Or, you can reach out to me directly to donate via paypal or venmo to avoid transaction fees.
Thank you!!!
#mutual aid#fundraiser#first generation#indigenous#rent relief#signal boost#givebutter#resilience#medical debt#indigenous resilience
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Spirit: Stallion of the Cimmaron is one of the best horse movies ever imo, because even though it's about a horse, in many ways it's not about horses
It has problems yes, but it's a movie about Indigenous Resilience in the face of colonialism. Spirit's monologue at the beginning is enough already to support that.
"Like the wind in the buffalo grass, we belonged here. We would always belong here."
Anyway that's another reason why the 'new' movie and show are absolute fucking crimes
#THEY FUCKING COLONIZED SPIRIT#spirit stallion of the cimarron#horses#indigenous resilience#indigenous rights#indigenous problems
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
In response to last year’s record-breaking heat due to El Niño and impacts from climate change, Indigenous Zenù farmers in Colombia are trying to revive the cultivation of traditional climate-resilient seeds and agroecology systems.
One traditional farming system combines farming with fishing: locals fish during the rainy season when water levels are high, and farm during the dry season on the fertile soils left by the receding water.
Locals and ecologists say conflicts over land with surrounding plantation owners, cattle ranchers and mines are also worsening the impacts of the climate crisis.
To protect their land, the Zenù reserve, which is today surrounded by monoculture plantations, was in 2005 declared the first Colombian territory free from GMOs.
#good news#science#environmentalism#indigenous people#indigenous agriculture#zenù#agroecology#nature#environment#farming#sustainable farming#climate resilience#climate change#columbia
56 notes
·
View notes
Text

Indigenous , b*tch. Proud of it.
#indigenous#two spirit#landback#photography#digital art#courage#lgbtia+#resilient#good vibes#unity#strength#instagay#2 spirit
116 notes
·
View notes
Text


How am I to tell stories about life —
Without becoming the eccentric Sámi
Making jokes at my own expense — How I am
to explain to them that the ruin is in my voice
Ædnan by Linnea Axelsson, trans. Saskia Vogel / Portrait of a young woman. The artist's sister Anna Hammershøi by Vilhelm Hammershoi (1885) / The Tempest by Peder Balke (1862)
#Aednan#Linnea Axelsson#litedit#bookedit#digital collage#my edit#picked this up out of curiousity. got hit in the face with indigenous pain and resilience and three generations of displacement and#forced assimilation and family.#and also language loss. as soon as it got into language loss and the attempts to relearn the language you should have grown up with....#i had to lie down#hey. go read this epic. its a novel in verse by a northern sami author
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Red Dress Day: Honouring Memories and Raising Awareness for Missing and Murdered Indigenous Women, Girls, and Two-Spirit People
May 6, 2024
Shaina Tranquilino

In Canada, Red Dress Day serves as a poignant reminder of the ongoing crisis surrounding missing and murdered Indigenous women, girls, and two-spirit people (MMIWG2S). This solemn occasion, marked by the hanging of red dresses in public spaces, symbolizes the lives lost and the urgent need for justice and systemic change. As we commemorate Red Dress Day, it's crucial to reflect on the profound impact of this crisis and renew our commitment to advocating for the rights and safety of Indigenous communities across the country.
The Significance of the Red Dress:
The red dress has become a powerful symbol in the movement to raise awareness about MMIWG2S. It represents the women, girls, and two-spirit individuals who have gone missing or been murdered, their spirits, and the bloodshed that continues to stain the fabric of Indigenous communities. Each red dress hung serves as a silent tribute, a visual reminder of lives cut short and families torn apart by violence and injustice.
Honouring the Memories:
Red Dress Day is a time for reflection and remembrance. It's an opportunity for communities to come together to honour the memories of those who are no longer with us. Through ceremonies, gatherings, and art installations, Indigenous and non-Indigenous people alike pay tribute to the lives lost and reaffirm their commitment to seeking justice and accountability. It's a solemn occasion but also a chance to celebrate the resilience and strength of Indigenous communities in the face of adversity.
Raising Awareness and Demanding Action:
Beyond remembrance, Red Dress Day serves as a call to action. It's a reminder that the crisis of missing and murdered Indigenous women, girls, and two-spirit people is not a thing of the past but a present-day reality. Indigenous women are disproportionately affected by violence and are more likely to experience homicide or disappearance compared to non-Indigenous women. This alarming statistic underscores the urgent need for systemic change to address the root causes of this crisis, including colonialism, systemic racism, poverty, and inadequate access to resources and support services.
Advocates and activists use Red Dress Day as an opportunity to raise awareness about MMIWG2S and to demand action from governments, law enforcement agencies, and society at large. They call for improved support services for victims and their families, culturally sensitive policing practices, and meaningful efforts to address the underlying factors that contribute to violence against Indigenous women and girls. By amplifying their voices and advocating for change, they strive to ensure that the lives lost are not forgotten and that future generations can live free from fear and harm.
Red Dress Day is a solemn yet empowering occasion that reminds us of the ongoing crisis of missing and murdered Indigenous women, girls, and two-spirit people in Canada. As we honour the memories of those who are no longer with us, we must also recommit ourselves to the fight for justice, equality, and respect for Indigenous rights. By standing in solidarity with Indigenous communities and demanding action from our leaders, we can work towards a future where every woman, girl, and two-spirit person is safe, valued, and able to live their lives free from violence and discrimination.
#red dress day#MMIWG2S#honouring memories#lost lives#stolen lives#Indigenous rights#justice for MMIWG2S#end violence#solidarity#awareness#demand action#equality#justice for Indigenous women#remembering our sisters#resilience#Indigenous strong#end violence now#support Indigenous communities
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
https://ictnews.org/news/a-place-for-acceptance

#!!!#indigenous#two spirit#native american#good news#ndn#resilience#transgender#lgbtq#queer#rapid city#south dakota
23 notes
·
View notes
Link

“Until as recently as 1970, India was a land with more than 100,000 distinct varieties of rice. Across a diversity of landscapes, soils, and climates, native rice varieties, also called “landraces,” were cultivated by local farmers. And these varieties sprouted rice diversity in hue, aroma, texture, and taste.
But what sets some landraces in a class of their own—monumentally ahead of commercial rice varieties—is their nutrition profiles. This has been proved by the research of Debal Deb, a farmer and agrarian scientist whose studies have been published in numerous peer-reviewed journals and books.
In the mid-1960s, with backing from the U.S. government, India’s agricultural policy introduced fertilizers, pesticides, irrigation facilities, and high-yielding varieties of crops under the moniker of a “Green Revolution” to combat hunger. Instead, it began an epidemic of monocultures and ecological destruction.
In the early 1990s, after realizing that more than 90% of India’s native rice varieties had been replaced by a handful of high-yielding varieties through the Green Revolution, Deb began conserving indigenous varieties of rice. Today, on a modest 1.7-acre farm in Odisha, India, Deb cultivates and shares 1,485 of the 6,000 unique landraces estimated to remain in India.
Deb and collaborators have quantified the vitamin, protein, and mineral content in more than 500 of India’s landraces for the first time, in the lab he founded in 2014, Basudha Laboratory for Conservation. In one extraordinary discovery, the team documented 12 native varieties of rice that contain the fatty acids required for brain development in infants.
“These varieties provide the essential fatty acids and omega-3 fatty acids that are found in mother’s milk but lacking in any formula foods,” Deb says. “So instead of feeding formula foods to undernourished infants, these rice varieties can offer a far more nutritious option...”
Deb’s conservation efforts are not to preserve a record of the past, but to help India revive resilient food systems and crop varieties. His vision is to enable present and future agriculturists to better adapt to climate change...
Deb conserves scores of climate-resilient varieties of rice originally sourced from Indigenous farmers, including 16 drought-tolerant varieties, 20 flood-tolerant varieties, 18 salt-tolerant varieties, and three submergence-tolerant varieties. He shares his varieties freely with hundreds of small farmers for further cultivation, especially those farming in regions prone to these kinds of climate-related calamities. In 2022 alone, Deb has shared his saved seed varieties with more than 1,300 small farmers through direct and indirect seed distribution arrangements in several states of India.
One of these farmers is Shamika Mone. Mone received 24 traditional rice varieties from Deb on behalf of Kerala Organic Farmers Association, along with training on maintaining the purity of the seeds. Now these farmers have expanded their collection, working with other organic farming collectives in the state of Kerala to grow around 250 landraces at two farm sites. While they cultivate most of their varieties for small-scale use and conservation, they also cultivate a few traditional rice varieties for wider production, which yield an average of 1.2 tons per acre compared with the 1 ton per acre of hybrid varieties.
“But that’s only in terms of yield,” Mone says. “We mostly grow these for their nutritional benefits, like higher iron and zinc content, antioxidants, and other trace elements. Some varieties are good for lactating mothers, while some are good for diabetic patients. There are many health benefits.”
These native varieties have proven beneficial in the face of climate change too.
With poor rains in 2016, for example, the traditional folk rice variety Kuruva that Mone had planted turned out to be drought-tolerant and pest-resistant. And in 2018, due to the heavy rains and floods, she lost all crops but one: a folk rice variety called Raktashali that survived underwater for two days.
“They have proven to be lifesavers for us,” Mone says.” -via Yes! Magazine, 12/14/22
#india#rice#indigenous knowledge#farming#agriculture#climate change#climate resilience#sustainable agriculture#traditional knowledge#drought resistance#nutrition#good news#hope
205 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nurturing the Heart: Understanding the Social and Emotional Well-being of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Communities
Welcome to my Blog series on PSYCHOLOGY, WELL-BEING, AND RESILIENCE Where I will highlight 5 interesting topics. Read to explore!
In the rich tapestry of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander cultures, the essence of well-being lies in the social and emotional interconnectedness. As highlighted by the Commonwealth of Australia in 2017, this delicate balance serves as the cornerstone upon which both physical and mental health are built.
It's important to recognize that the concept of social and emotional well-being transcends individual experiences, encompassing a web of relationships that extend from the individual to the family and community. As noted by Brown et al. (2023), the nuances of well-being vary across Indigenous communities, shaped by diverse cultural perspectives and historical contexts. The notion of social and emotional well-being acknowledges that a person's well-being is also impacted by the social determinants of health. Indigenous Australians define health as the "social, emotional, and cultural well-being of the whole community" in addition to an individual's physical well-being (Fatima et al., 2023, p.31). This definition is based on a person's relationships to their country, culture, family, spirit, and physical and mental health.
Additionally, the National Agreement acknowledges that Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander cultures are essential to better life outcomes for Indigenous Australians. All initiatives carried out by the Agreement must uphold, protect, and enhance these cultures. The following goals have been specifically set by the agreement to promote the cultural wellness of Indigenous Australians as shown in Figure 1 below (indigenoushpf.gov.au, 2024).

Figure 1: Targets to support cultural well-being
(Source: indigenoushpf.gov.au, 2024)
This particular group is marked with suicides and attempts to death based on different stress in life and stress factors. In the words of Smallwood et al., (2023, p.2088), the Aboriginals and Torres Strait Islanders had been facing severe issues over time in search of good living and livelihood. Owing to this there had been intervention which was developed for the betterment of indigenous people living in Australia. Figure 2 below shows the rate of suicide attempts which had been caused by the people of this indigenous group (indigenoushpf.gov.au, 2024). Thus, the intervention of the Mental Health Agreement was formulated to secure sustainability and improve the services provided by the Australian mental health and suicide prevention system. It also aimed to improve the mental health of all Australians and governments have come together to establish the Mental Health Agreement (Masotti et al., 2023, p.741).
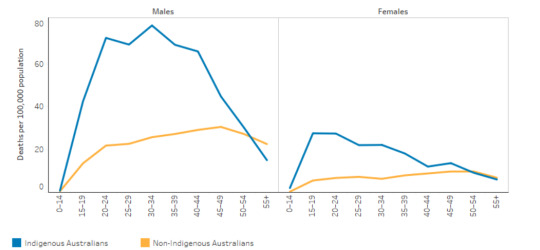
Figure 2: Suicide attempts by Aboriginals
(Source: indigenoushpf.gov.au, 2024)
In addition to responding to the Productivity Commission Inquiry into Mental Health, the National Suicide Prevention Adviser's Final Advice, the Mental Health Agreement pledges to carry out work under the Fifth Plan going forward (indigenoushpf.gov.au, 2024). Regional planning and commissioning, priority populations, stigma reduction, safety and quality, gaps in the system of care and suicide prevention are the main areas of attention. On the other hand, psycho-social supports outside the National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS), workforce, and national consistency for initial assessment and referral are among the priority areas covered by the Mental Health Agreement.
References
Brown, A., Haregu, T., Gee, G., Mensah, F., Waters, L., Brown, S. J., ... & Armstrong, G. (2023). Social and emotional well-being of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples in Aboriginal-controlled social housing. BMC public health, 23(1), 1935. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12889-023-16817-y
Fatima, Y., Liu, Y., Cleary, A., Dean, J., Smith, V., King, S., & Solomon, S. (2023). Connecting the health of country with the health of people: application of" caring for country" in improving the social and emotional well-being of Indigenous people in Australia and New Zealand. The Lancet Regional Health–Western Pacific, 31. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanwpc/article/PIIS2666-6065(22)00263-2/fulltext
indigenoushpf.gov.au (2024) Social and emotional wellbeing Retrived on 9 May 2024 from: https://www.indigenoushpf.gov.au/measures/1-18-social-emotional-wellbeing
Masotti, P., Dennem, J., Bañuelos, K., Seneca, C., Valerio-Leonce, G., Inong, C. T., & King, J. (2023). The Culture is Prevention Project: measuring cultural connectedness and providing evidence that culture is a social determinant of health for Native Americans. BMC Public Health, 23(1), 741. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12889-023-15587-x
Smallwood, R., Usher, K., Woods, C., Sampson, N., & Jackson, D. (2023). De‐problematising Aboriginal young peoples’ health and well‐being through their voice: An Indigenous scoping review. Journal of clinical nursing, 32(9-10), 2086-2101. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/jocn.16308
#psychology#wellbeing and resilience#aboriginal australian#indigenous issues#first nations#indigenous rights#indigenous health and wellbeing
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
This is the clearest and most beautiful video of an Apache Sunrise Dance. This is on my Rez and it looks like they got permission to record the Ceremony. The narrator explains what is going on in the video. The songs are in apache and the drums are water drums. I guess I wanted to share this video with others who are not my family, they go to help out at these dances and it is long and hard. The comments are turned off but you can leave a comment or ask general questions here. thx
#indigenous peoples#indigenous sovereignty#indigenous rights#indigenous solidarity#decolonialism#decolonization#first nations#native american#turtle island#white mountain apache#youtube video#dance#ceremony#music#women#womanhood#resilience#apache#Youtube#ndn#girlhood#usa#indigenous music
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
-
#@anon#You know one of the things that people tend to do but absolutely not in favour of Palestinian resistance and liberation movement is#the condemnation of resilients and freedom fighters#it is really not the pro Palestinian stance#The liberation movement is not a peaceful one#ask the million martyred Algerian to liberated their land from french occupation#The people of Palestine are able to rise against their oppressor and are able to organise and to lead their liberation movement and have#their freedom fighters#USA or any western nation categorizing these resistance mouvements as terrorist its well their own racist shit#In the words of Refaat Alareer may he rest in power:#“Saying Hamas is a tool of Israel is saying the Vietnam fighters were a tool of America The Warsaw ghetto rebels a tool of the Nazis”#Black freedom fighters a tool of the slave owners And the indigenous peoples of America a tool of the European colonisers etc etc#and he was so right#Palestine#gaza#genocide
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

credit - unknown
#indigenous#anishinaabe#métis#mixed#native#indigenous heritage#anishinaabemowin#ndn#indigenous art#indigenous stories#resilience#indigenous resistance#two spirit
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Genocide doesn’t just happen out of the blue. It gradually builds up over time. The destruction of a people’s culture, lifestyle, communities, landmarks, corrupting their relationship with the land, that how genocide works. That what the massacre of indigenous peoples does, it destroys the land and poisons history.
#free palestine#palestine#free gaza#save gaza#palestinian liberation#signal boost#social justice#stop apartheid in palestine#save the people of gaza#adding tags to your posts helps people find them#social matters#things you should care about#things that make me mad#things that keep me up at night#genocide in gaza#gaza genocide#from river to sea palestine will be free#justice for palestine#palestinian resilience#indigenous people#history#tumblr fypage#silence is violence#neutrality is violent#end settler colonialism#settler violence#Youtube
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
if you experience climate anxiety and are bogged down by the “what can i even do as an individual” mindset then you need need need to get involved in supporting your local indigenous communities. i mean it. when we say “land back” as a means to combat the impacts of climate change that needs to happen in actionable ways. land acknowledgements are not enough. reblogging tumblr posts is not enough. and yes i know that we know the names of the <20 people killing our planet but there are genuinely things you can do at your local levels. i’m so so so lucky to live in a place with many indigenous-run non-profits committed to habitat restoration, food sovereignty, re-introducing native species etc. and seeing this “land back” in action is one of the most inspiring things i’ve ever seen in terms of climate resiliency. just spending time removing invasive plants and planting natives and hearing about how the native birds are coming back and one day our children’s children will be able to eat fish from waters heavily polluted by the military. change is happening. and i guarantee it is happening in your area. sure it’s not going to completely reverse things but you need need need to get out of that doomer mindset. and if you’re not physically able volunteer on-site then find those organisations and give them your money and spread the word about them to those in your life who you know can help. i know so many of us are just trying to get by day by day but there can be no business as usual in this current world. you have the ability to help promote indigenous land stewardship right now.
#i’ve just finished an educators workshop and i’m fired up if you can’t tell#climate change#climate resiliency#land bsck#indigenous land#keep hawaiian lands in hawaiian hands#aloha aina#mine
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

“The more I come to understand, the touch of my hand”
#2 spirit#digital art#sex positive#courage#strength#two spirit#gay art#indigenous#empoweredliving#landback#lgbtqia#queer bipoc#inspiration#resilience#good vibes#healingjourney#gay
43 notes
·
View notes