#new education policy 2023
Text
2023 and 2024 New Education Policies Comparison
Introduction to India's Educational Reform
The introduction of the New Education Policy (NEP) in 2023 marked a significant milestone in India's educational reform, aiming to modernize, inclusivism, and elevate the quality of education to meet global standards. The subsequent evolution in 2024 further underscored the country's commitment to transforming its education system to address the diverse needs of its student population from preschool through higher education. Both policies collectively signify a monumental shift towards enhancing educational accessibility, quality, and innovation across India.

Genesis and Objectives of NEP 2023 and 2024
NEP 2023 emerged from extensive consultations with experts, educators, policymakers, and stakeholders, aiming to align India's education system with global standards and foster holistic student development. It sought to bridge gaps between traditional and contemporary pedagogical methods, emphasizing inclusivity, flexibility, and innovation.
New Education Policy 2024 built upon the foundational aims of its predecessor, focusing on digital empowerment, holistic learning, and a robust framework for skill development. It represents a philosophical rebirth designed to cater to the modern world's demands, positioning India as a formidable information powerhouse on the international stage.
Key Features and Innovations
Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE)
Both policies recognize ECCE's paramount importance, with 2023 focusing on foundational learning stages and 2024 placing unprecedented emphasis on ECCE to establish a strong base for every child's educational journey.
Curriculum and Pedagogy
2023: Advocates for a flexible, interdisciplinary curriculum that encourages critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and the integration of vocational skills into mainstream education.
2024: Introduces a novel 5+3+3+4 curriculum structure aimed at experiential and skill-oriented learning, promising a seamless educational continuum from early years to secondary schooling.
Assessment Reforms
2023: Proposes shifting from rote learning and high-stakes exams to a more holistic, competency-based assessment system.
2024: Aims to revolutionize assessments with comprehensive, adaptive mechanisms that foster deeper, application-oriented learning.
Digital Education and Technology Integration
Both policies emphasize the role of technology in education, with 2023 focusing on promoting digital literacy and online learning, and 2024 taking significant strides towards digitalizing all schools and making quality education accessible through digital platforms like DIKSHA.
Teacher Training and Development
Continuous professional development for teachers is a focus in both policies. 2023 introduces integrated teacher education programs, while 2024 continues to ensure educators are equipped with modern pedagogical skills.
Inclusivity and Accessibility
2023 emphasizes special education programs and inclusive education for students with disabilities. 2024 commits to making education accessible to all, breaking down barriers for socio-economically disadvantaged groups.
Comparative Analysis: Implementation and Evolution
NEP 2023 laid the foundational framework for a comprehensive overhaul of India’s educational infrastructure, focusing on early child education, curriculum reform, and assessment changes. NEP 2024 promised further advancements, including the introduction of coding from a young age, advocating for multidisciplinary institutions and flexible course structures, and implementing an innovative academic credit bank system.
Detailed Exploration of Goals and Aspirations
Both policies share the overarching ambition of elevating India’s educational standards to global acclaim. NEP 2023 initiated this journey by addressing the evolving needs of the education system, while NEP 2024 aimed to solidify India’s status as a global knowledge superpower through strategic amendments aimed at enhancing educational quality and accessibility.
Impact on Preschools and Early Childhood Education
The NEP recognizes the critical role of preschool education in laying a strong foundation for a child’s future learning journey. NEP 2023 and 2024 collectively emphasize curriculum enhancement, teacher training, assessment practices, digital integration, a multilingual approach, and inclusivity, significantly impacting preschools and early childhood education centers across the nation.
Challenges and Opportunities
Implementing such transformative policies is not without its challenges, including the need for substantial teacher training, infrastructure development, technological access, and ensuring inclusivity. However, these reforms also present unparalleled opportunities for fostering a generation of students who are well-prepared for the complexities of the modern world, equipped with critical thinking skills, digital literacy, and a strong educational foundation.
Stakeholder Perspectives
The success of NEP 2023 and 2024 hinges on collaborative efforts from all stakeholders, including educators, parents, policymakers, and the community at large. Their active engagement, feedback, and adaptation are crucial for realizing the policies' full potential and creating an educational ecosystem that empowers every child in India.
Conclusion: A Progressive Continuum Towards Educational Excellence
The NEPs for 2023 and 2024 are progressive steps in the direction of remaking Indian education; while each has a distinct area of emphasis, they all work together to create a framework that is inclusive, adaptable, and contemporary. These initiatives seek to equip Indian students not only for regional achievement but also for success in the global arena. The transition from NEP 2023 to 2024, which represents India's continued path of educational reform, offers a clear picture of a future in which high-quality education will be available to everyone and raise a generation of internationally aware, enlightened citizens who are prepared to contribute to both national and global advancement.
Check: Preschool in Wagholi, Preschool in Noida
#new education policies 2023 vs 2024#new education policy#new education policy 2023#new education policy 2024
0 notes
Text
ক্লাস এইট থেকেই সেমেস্টার! কেন্দ্রের নীতি না মেনেও রাজ্য শিক্ষানীতিতে আমূল বদল
/career/next-latest-news-by-nmc-first-next-to-be-held-on-2028-replacing-neet-pg-with-2024-mbbs-batch-sitting-for-it-31691376330357.html
/career/ugc-panel-on-sc-st-students-says-union-minister-subhash-sarkar-in-parliamet-as-more-students-leaving-instis-midway-31691374447882.html
/career/fake-universities-in-kolkata-list-by-ugc-highest-8-institutes-from-delhi-in-it-uttar-pradesh-has-4-names-31691…
View On WordPress
#New Education Policy#new education policy 2022#new education policy 2023#new education policy 2023 pdf#new education system#পশ্চিমবঙ্গ রাজ্য শিক্ষানীতি#ব্রাত্য বসু#মমতা বন্দ্যোপাধ্যায়#রাজ্য শিক্ষানীতি
0 notes
Text
Florida lawmakers will meet Monday to complete a state takeover of Walt Disney World’s self-governing district and expand a migrant relocation program, key conservative priorities of Republican Gov. Ron DeSantis ahead of his expected White House run.
Republican leaders of the statehouse, in coordination with DeSantis, have ordered the Legislature to convene in a special session to restructure the Reedy Creek Improvement District, as the Disney government is known.
Lawmakers will also consider a proposal to create a state department focused on migrant relocations, a move that comes after the Governor flew a group of South American migrants from Texas to Massachusetts in protest of federal border policy.
The session continues a focus by DeSantis on social issues including sexual orientation, gender and immigration as the Republican Governor exploits national political fissures on his path to a potential 2024 presidential run.
The meeting is the latest development in a high-profile feud between DeSantis and Disney over the company’s criticism of a law dubbed by critics as “Don’t Say Gay,” which bars instruction on sexual orientation and gender identity in kindergarten through third grade and lessons deemed not age appropriate.
The Governor, in going after Disney, displayed a willingness to penalize one of the state’s biggest employers and political donors, reinforcing the combative leadership style that has propelled him to national political stardom and appeals to conservative primary voters.
Lawmakers are expected to create a program to transport immigrants who are in the country illegally to another state if they’ve already been processed by the federal government and if the migrants volunteer.
DeSantis had already used part of a $12 million fund, paid for by taxpayers, to fly about 50 South American migrants from Texas to the Massachusetts resort island of Martha’s Vineyard, bringing widespread condemnation.
Another proposal to be taken up during the session would make it clear the statewide prosecutor has authority to prosecute election fraud in federal and state races.
DeSantis, with statehouse backing, created an election police unit last year to investigate fraud and other crimes to satisfy what has become an important issue to conservative voters following the 2020 election. Some charges resulting from investigations by the election police force have been dropped because of jurisdiction issues.
The squabble between DeSantis and Disney began last year, when the entertainment giant publicly opposed the “Don’t Say Gay” education legislation and said it would pause political donations in the state and support organizations working to oppose the law.
DeSantis and other Republicans moved quickly to criticize the company, calling it a purveyor of “woke” ideologies that are inappropriate for children.
At DeSantis’ request, the GOP-dominated statehouse in April approved legislation to eliminate Disney’s Reedy Creek government by June 2023, beginning a closely watched process that would determine the structure of government that controls the company’s sprawling property.
The creation of the Reedy Creek district was instrumental in Disney’s decision to build near Orlando in the 1960s. Having a separate government allows the company to provide zoning, fire protection, utilities and infrastructure services on its land.
The special session will also adjust language in current laws addressing endorsement deals for college athletes.
Florida was one of the first states to pass a law allowing college athletes to profit off their name, image or likeness, but it doesn’t allow people affiliated with universities to help secure endorsement deals. The proposal would lift that provision to make Florida more competitive with other states that don’t have the restriction.
Lawmakers will also consider a bill to provide more relief money for Hurricane Ian and Nicole recovery efforts.
#us politics#news#fortune#florida#2023#gov. ron desantis#conservatives#republicans#gop#reedy creek improvement district#Disney#don't say gay bill#parental rights in education#migrant relocation#bussing#federal border policy#us mexico border#election fraud#election police force#endorsement deals#college athletes#hurricane relief
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
Look.

I have made you a chart. A very simple chart.
People say "You have to draw the line somewhere, and Biden has crossed it-" and my response is "Trump has crossed way more lines than Biden".
These categories are based off of actual policy enacted by both of these men while they were in office.
If the ONLY LINE YOU CARE ABOUT is line 12, you have an incredible amount of privilege, AND YOU DO NOT CARE ABOUT PALESTINIANS. You obviously have nothing to fear from a Trump presidency, and you do not give a fuck if a ceasefire actually occurs. You are obviously fine if your queer, disabled, and marginalized loved ones are hurt. You clearly don't care about the status of American democracy, which Trump has openly stated he plans to destroy on day 1 he is in office.
EDIT:
Ok fine, I spent 3 hours compiling sources for all of these, you can find that below the cut.
I'll give at least one link per subject area. There are of course many more sources to be read on these subject areas and no post could possibly give someone a full education on these subjects.
Biden and trans rights: https://www.hrc.org/resources/president-bidens-pro-lgbtq-timeline
Trump and trans rights: https://www.aclu.org/news/lgbtq-rights/trump-on-lgbtq-rights-rolling-back-protections-and-criminalizing-gender-nonconformity
The two sources above show how Biden has done a lot of work to promote trans rights, and how Trump did a lot of work to hurt trans rights.
Biden on abortion access: https://www.cnn.com/2022/07/08/politics/what-is-in-biden-abortion-executive-order/index.html
Trump on abortion access: https://apnews.com/article/abortion-trump-republican-presidential-election-2024-585faf025a1416d13d2fbc23da8d8637
Biden openly supports access to abortion and has taken steps to protect those rights at a federal level even after Roe v Wade was overturned. Trump, on the other hand, was the man who appointed the judges who helped overturn Roe v Wade and he openly brags about how proud he is of that decision. He also states that he believes individual states should have the final say in whether or not abortion is legal, and that he trusts them to "do the right thing", meaning he supports stronger abortion bans.
Biden on environmental reform: https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2021/10/07/fact-sheet-president-biden-restores-protections-for-three-national-monuments-and-renews-american-leadership-to-steward-lands-waters-and-cultural-resources/
Trump on environmental reform: https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/climate/trump-environment-rollbacks-list.html
Biden has made major steps forward for environmental reform. He has restored protections that Trump rolled back. He has enacted many executive orders and more to promote environmental protections, including rejoining the Paris Accords, which Trump withdrew the USA from. Trump is also well known for spreading conspiracy theories and lies about global climate change, calling it a "Chinese hoax".
Biden on healthcare and prescription reform: https://www.hhs.gov/about/news/2023/06/09/biden-administration-announces-savings-43-prescription-drugs-part-cost-saving-measures-president-bidens-inflation-reduction-act.html
Trump on healthcare reform: https://www.cnn.com/2024/01/07/politics/obamacare-health-insurance-ending-trump/index.html
I'm rolling healthcare and prescriptions and vaccines and public health all into one category here since they are related. Biden has lowered drug costs, expanded access to medicaid, and ACA enrollment has risen during his presidency. He has also made it so medical debt no longer applies to a person's credit score. He signed many executive orders during his first few weeks in office in order to get a handle on Trump's grievous mishandling of the COVID pandemic. Trump also wants to end the ACA. Trump is well known for refusing to wear a mask during the pandemic, encouraging the use of hydroxylchloroquine to "treat" COVID, and being openly anti-vaxx.
Biden on student loan forgiveness: https://www.ed.gov/news/press-releases/biden-harris-administration-announces-additional-77-billion-approved-student-debt-relief-160000-borrowers
Trump on student loan forgiveness: https://www.forbes.com/sites/adamminsky/2024/06/20/trump-knocks-bidens-vile-student-loan-forgiveness-plans-suggests-reversal/
Trump wants to reverse the student loan forgiveness plans Biden has enacted. Biden has already forgiven billions of dollars in loans and continues to work towards forgiving more.
Infrastructure funding:
I'm putting these links next together because they are all about infrastructure.
In general, Trump's "achievements" for infrastructure were to destroy environmental protections to speed up projects. Many of his plans were ineffective due to the fact that he did not clearly outline where the money was going to come from, and he was unwilling to raise taxes to pay for the projects. He was unable (and unwilling) to pass a bipartisan infrastructure bill during his 4 years in office. He did sign a few disaster relief bills. He did not enthusiastically promote renewable energy infrastructure. He created "Infrastructure Weeks" that the federal government then failed to fund. Trump did not do nothing for infrastructure, but his no-tax stance and his dislike for renewable energy means the contributions he made to American infrastructure were not as much as he claimed they were, nor as much as they could have been. Basically, he made a lot of promises, and delivered on very few of them. He is not "against" infrastructure, but he's certainly against funding it.
Biden was able to pass that bipartisan bill after taking office. The Bipartisan Infrastructure Plan that Trump tried to prevent from passing during Biden's term contains concrete funding sources and step by step plans to rebuild America's infrastructure. If you want to read the plan, you can find it here: https://www.whitehouse.gov/build/guidebook/. Biden has done far more for American infrastructure than Trump did, most notably by actually getting the bipartisan bill through congress.
Biden on Racial Equity: https://www.npr.org/sections/president-biden-takes-office/2021/01/26/960725707/biden-aims-to-advance-racial-equity-with-executive-actions
Trump on Racial Equity: https://www.axios.com/2024/04/01/trump-reverse-racism-civil-rights https://www.bbc.com/news/av/world-us-canada-37230916
Trump's racist policies are loud and clear for everyone to hear. We all heard him call Mexicans "Drug dealers, criminals, rapists". We all watched as he enacted travel bans on people from majority-Muslim nations. Biden, on the other hand, has done quite a lot during his term to attempt to reconcile racism in this country, including reversing Trump's "Muslim ban" the first day he was in office.
Biden on DEI: https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2021/06/25/executive-order-on-diversity-equity-inclusion-and-accessibility-in-the-federal-workforce/
Trump on DEI: https://www.msn.com/en-us/news/politics/trump-tried-to-crush-the-dei-revolution-heres-how-he-might-finish-the-job/ar-BB1jg3gz
Biden supports DEI and has signed executive orders and passed laws that support DEI on the federal level. Trump absolutely hates DEI and wants to eradicate it.
Biden on criminal justice reform: https://time.com/6155084/biden-criminal-justice-reform/
Trump on criminal justice reform: https://www.vox.com/2020-presidential-election/21418911/donald-trump-crime-criminal-justice-policy-record https://www.theatlantic.com/politics/archive/2024/05/trumps-extreme-plans-crime/678502/
From pardons for non-violent marijuana convictions to reducing the federal government's reliance on private prisons, Biden has done a lot in four years to reform our criminal justice system on the federal level. Meanwhile, Trump has described himself as "tough on crime". He advocates for more policing, including "stop and frisk" activities. Ironically it's actually quite difficult to find sources about what Trump thinks about crime, because almost all of the search results are about his own crimes.
Biden on military support for Israel: https://www.nbcnews.com/politics/national-security/biden-obama-divide-closely-support-israel-rcna127107
Trump on military support for Israel: https://www.vox.com/politics/353037/trump-gaza-israel-protests-biden-election-2024
Biden supports Israel financially and militarily and promotes holding Israel close. So did Trump. Trump was also very pro-Israel during his time in office and even moved the embassy to Jerusalem and declared Jerusalem the capitol of Israel, a move that inflamed attitudes in the region.
Biden on a ceasefire: https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/world/2024/06/05/gaza-israel-hamas-cease-fire-plan-biden/73967659007/
Trump on a ceasefire: https://www.nbcnews.com/politics/donald-trump/trump-israel-gaza-finish-problem-rcna141905
Trump has tried to be quiet on the issue but recently said he wants Israel to "finish the problem". He of course claims he could have prevented the whole problem. Trump also openly stated after Oct 7th that he would bar immigrants who support Hamas from the country and send in officers to American protests to arrest anyone supporting Hamas.
Biden meanwhile has been quietly urging Netanyahu to accept a ceasefire deal for months, including the most recent announcement earlier in June, though it seems as though that deal has finally fallen through as well.
103K notes
·
View notes
Text
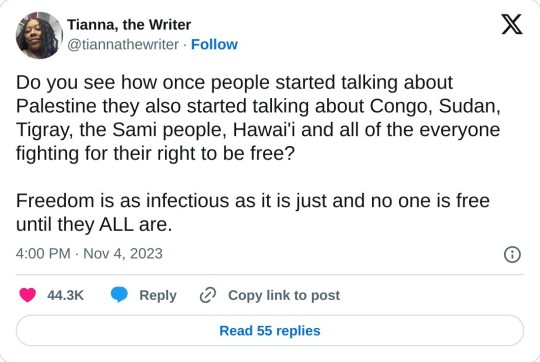
People & countries mentioned in the thread:
DR Congo - M23, Cobalt
Darfur, Sudan - International Criminal Court, CNN, BBC (Overview); Twitter Explanation on Sudan
Tigray - Human Rights Watch (Ethnic Cleansing Report)
the Sámi people - IWGIA, Euronews
Hawai'i - IWGIA
Syria - Amnesty International
Kashmir- Amnesty Summary (PDF), Wikipedia (Jammu and Kashmir), Human Rights Watch (2022)
Iran - Human Rights Watch, Morality Police (Mahsa/Jina Amini - Al Jazeera, Wikipedia)
Uyghurs - Uyghur Human Rights Project (UHRP) Q&A, Wikipedia, Al Jazeera, UN Report
Tibetans - SaveTibet.org, United Nations
Yazidi people - Wikipedia, United Nations
West Papua - Free West Papua, Genocide Watch
Yemen - Human Rights Watch (Saudi border guards kill migrants), Carrd
Sri Lanka (Tamils) - Amnesty International, Human Rights Watch
Afghans in Pakistan - Al Jazeera, NPR
Ongoing Edits: more from the notes / me
Armenians in Nagorno-Karabakh/Azerbaijan (Artsakh) - Global Conflict Tracker ("Nagorno-Karabakh Conflict"), Council on Foreign Relations, Human Rights Watch (Azerbaijan overview), Armenian Food Bank
Baháʼís in Iran - Bahá'í International Community, Amnesty, Wikipedia, Minority Rights Group International
Kafala System in the Middle East - Council on Foreign Relations, Migrant Rights
Rohingya - Human Rights Watch, UNHCR, Al Jazeera, UNICEF
Montagnards (Vietnam Highlands) - World Without Genocide, Montagnard Human Rights Organization (MHRO), VOA News
Ukraine - Human Rights Watch (April 2022), Support Ukraine Now (SUN), Ukraine Website, Schools & Education (HRW), Dnieper River advancement (Nov. 15, 2023 - Ap News)
Reblogs with Links / From Others
Indigenous Ppl of Canada, Cambodia, Mexico, Colombia
Libya
Armenia Reblog 1, Armenia Reblog 2
Armenia, Ukraine, Central African Republic, Indigenous Americans, Black ppl (US)
Rohingya (Myanmar)
More Hawai'i Links from @sageisnazty - Ka Lahui Hawaii, Nation of Hawai'i on Soverignty, Rejected Apology Resolution
From @rodeodeparis: Assyrian Policy Institute, Free Yezidi
From @is-this-a-cool-url: North American Manipur Tribal Association (NAMTA)
From @dougielombax & compiled by @azhdakha: Assyrians & Yazidis
West Sahara conflict
Last Updated: Feb. 19th, 2024 (If I missed smth before this, feel free to @ me to add it)
#resources#important#congo#sudan#tigray#sámi#hawai'i#syria#kashmir#iran#uyghurs#china#tibetans#yazidi#west papua#yemen#sri lanka#afghans in pakistan#pakistan#human rights#palestine#twitter#lmk if there's a better reource or I linked smth wrong. I am very tired#my posts#genocide#social justice#nagorno karabakh#Bahá'í#kafala system#qatar
45K notes
·
View notes
Text
#elections matter#voting matters#local elections matter#good news 2023#u.s. politics#school boards#educational policy#idk what else to tag this#skypalacearchitect
0 notes
Text
Prison-tech company bribed jails to ban in-person visits

I'm on tour with my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me in BOSTON with Randall "XKCD" Munroe (Apr 11), then PROVIDENCE (Apr 12), and beyond!

Beware of geeks bearing gifts. When prison-tech companies started offering "free" tablets to America's vast army of prisoners, it set off alarm-bells for prison reform advocates – but not for the law-enforcement agencies that manage the great American carceral enterprise.
The pitch from these prison-tech companies was that they could cut the costs of locking people up while making jails and prisons safer. Hell, they'd even make life better for prisoners. And they'd do it for free!
These prison tablets would give every prisoner their own phone and their own video-conferencing terminal. They'd supply email, of course, and all the world's books, music, movies and games. Prisoners could maintain connections with the outside world, from family to continuing education. Sounds too good to be true, huh?
Here's the catch: all of these services are blisteringly expensive. Prisoners are accustomed to being gouged on phone calls – for years, prisons have done deals with private telcos that charge a fortune for prisoners' calls and split the take with prison administrators – but even by those standards, the calls you make on a tablet are still a ripoff.
Sure, there are some prisoners for whom money is no object – wealthy people who screwed up so bad they can't get bail and are stewing in a county lockup, along with the odd rich murderer or scammer serving a long bid. But most prisoners are poor. They start poor – the cops are more likely to arrest poor people than rich people, even for the same crime, and the poorer you are, the more likely you are to get convicted or be suckered into a plea bargain with a long sentence. State legislatures are easy to whip up into a froth about minimum sentences for shoplifters who steal $7 deodorant sticks, but they are wildly indifferent to the store owner's rampant wage-theft. Wage theft is by far the most costly form of property crime in America and it is almost entirely ignored:
https://www.theguardian.com/us-news/2023/jun/15/wage-theft-us-workers-employees
So America's prisons are heaving with its poorest citizens, and they're certainly not getting any richer while they're inside. While many prisoners hold jobs – prisoners produce $2b/year in goods and $9b/year in services – the average prison wage is $0.52/hour:
https://www.dollarsandsense.org/archives/2024/0324bowman.html
(In six states, prisoners get nothing; North Carolina law bans paying prisoners more than $1/day, the 13th Amendment to the US Constitution explicitly permits slavery – forced labor without pay – for prisoners.)
Likewise, prisoners' families are poor. They start poor – being poor is a strong correlate of being an American prisoner – and then one of their breadwinners is put behind bars, taking their income with them. The family savings go to paying a lawyer.
Prison-tech is a bet that these poor people, locked up and paid $1/day or less; or their families, deprived of an earner and in debt to a lawyer; will somehow come up with cash to pay $13 for a 20-minute phone call, $3 for an MP3, or double the Kindle price for an ebook.
How do you convince a prisoner earning $0.52/hour to spend $13 on a phone-call?
Well, for Securus and Viapath (AKA Global Tellink) – a pair of private equity backed prison monopolists who have swallowed nearly all their competitors – the answer was simple: they bribed prison officials to get rid of the prison phones.
Not just the phones, either: a pair of Michigan suits brought by the Civil Rights Corps accuse sheriffs and the state Department of Corrections of ending in-person visits in exchange for kickbacks from the money that prisoners' families would pay once the only way to reach their loved ones was over the "free" tablets:
https://arstechnica.com/tech-policy/2024/03/jails-banned-family-visits-to-make-more-money-on-video-calls-lawsuits-claim/
These two cases are just the tip of the iceberg; Civil Rights Corps says there are hundreds of jails and prisons where Securus and Viapath have struck similar corrupt bargains:
https://civilrightscorps.org/case/port-huron-michigan-right2hug/
And it's not just visits and calls. Prison-tech companies have convinced jails and prisons to eliminate mail and parcels. Letters to prisoners are scanned and delivered their tablets, at a price. Prisoners – and their loved ones – have to buy virtual "postage stamps" and pay one stamp per "page" of email. Scanned letters (say, hand-drawn birthday cards from your kids) cost several stamps:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/14/minnesota-nice/#shitty-technology-adoption-curve
Prisons and jails have also been convinced to eliminate their libraries and continuing education programs, and to get rid of TVs and recreational equipment. That way, prisoners will pay vastly inflated prices for streaming videos and DRM-locked music.
The icing on the cake? If the prison changes providers, all that data is wiped out – a prisoner serving decades of time will lose their music library, their kids' letters, the books they love. They can get some of that back – by working for $1/day – but the personal stuff? It's just gone.
Readers of my novels know all this. A prison-tech scam just like the one described in the Civil Rights Corps suits is at the center of my latest novel The Bezzle:
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9781250865878/thebezzle
Prison-tech has haunted me for years. At first, it was just the normal horror anyone with a shred of empathy would feel for prisoners and their families, captive customers for sadistic "businesses" that have figured out how to get the poorest, most desperate people in the country to make them billions. In the novel, I call prison-tech "a machine":
a million-armed robot whose every limb was tipped with a needle that sank itself into a different place on prisoners and their families and drew out a few more cc’s of blood.
But over time, that furious empathy gave way to dread. Prisoners are at the bottom of the shitty technology adoption curve. They endure the technological torments that haven't yet been sanded down on their bodies, normalized enough to impose them on people with a little more privilege and agency. I'm a long way up the curve from prisoners, but while the shitty technology curve may grind slow, it grinds fine:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/02/24/gwb-rumsfeld-monsters/#bossware
The future isn't here, it's just not evenly distributed. Prisoners are the ultimate early adopters of the technology that the richest, most powerful, most sadistic people in the country's corporate board-rooms would like to force us all to use.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/02/captive-customers/#guillotine-watch

Image:
Cryteria (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
--
Flying Logos
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Over_$1,000,000_dollars_in_USD_$100_bill_stacks.png
CC BY-SA 4.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en
--
KGBO
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Suncorp_Bank_ATM.jpg
CC BY-SA 3.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#prison#prison-tech#marty hench#the bezzle#securus#captive audiences#St Clair County#human rights#prisoners rights#viapath#gtl#global tellink#Genesee County#michigan#guillotine watch#carceral state#corruption
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
“A right to information response received by a University of New Brunswick professor shows that from 2020 to May 25, 2023, the Department of Education received no written complaints from parents alleging the school was keeping them in the dark about their children's preferred pronouns.
Education Minister Bill Hogan cited "hundreds" of complaints when he announced in May that he was reviewing an education policy designed to ensure the safety of LGBTQ students.
But when education professor and former teacher Melissa Dockrill Garrett sought details through a right to information request, she was told the Education Department had no records of any complaints.”
Unsurprisingly, it was an entirely manufactured controversy from the beginning, as evidenced by nobody whatsoever caring until he started with this lie.
@allthecanadianpolitics
938 notes
·
View notes
Text

Okay, @sihatn wishes to be so hung up on the particular war crime the Israeli government is using to excessively slaughter innocent Palestinian civilians, so let’s explain the difference between Genocide, Ethnocide, and Ethnic Cleansing:
Genocide: the deliberate killing of a large number of people from a particular nation or ethnic group with the aim of destroying that nation or group
Examples: The Armenian Genocide (where the term actually originates), the Shoah/Holocaust, Taíno Genocide, and Rwandan Genocide to name a few.
I have seen some Zionists on this platform and on Instagram argue that Israel cannot be committing Genocide because it is a “very specific instance in history that only includes the Holocaust”. That fact is ardently incorrect. For one, the first event to be called a Genocide and where the term was coined was the Armenian Genocide and countless events have been labeled a Genocide since 1943/1944 when the term was initially coined (including events coined after the fact that had already happened like the aforementioned Taíno Genocide).
Ethnocide: the deliberate and systematic destruction of the culture of an ethnic group or nation without deliberately killing large numbers of people within that ethnic group or nation
Think “kill the Indian, save the man”, the American and Canadian policy against American Indian tribes and First Nations that sought to forcibly assimilate them into W.A.S.P. culture. A similar policy occurred in Hawaii during the “Republic of Hawaii” and “Territory of Hawaii” days, and even the destruction of Yiddish Culture by Zionists in Israel who feared it for being “too Middle Eastern”. Most Re-Education camps fall in this category too.
Ethic Cleansing: the mass expulsion or killing of members of an unwanted ethnic or religious group in a society
This term is relatively new and was coined in the aftermath of the collapse of Yugoslavia and Serbia’s treatment of Croats, Bosnians, and other ethnic minorities, as well as the Stalinist movement of ethnic minorities to different SSRs.
Mass Homicide: the deliberate killing of a large number of people
The only distinction here is the people are not being killed because of their ethnicity or nation, but for ✨ other reasons ✨
Now here’s the kicker, most Zionists would say they are committing Ethnic Cleansing. They might not say it out right, because the term has a nasty connotation, but they will say they’re doing the definition of ethnic cleansing.
Some propaganda reblogging Zionists might claim that they’re just committing Mass Homicide but here’s the thing, almost every example of mass homicide being committed by one nation to another nation has been an example of one of the first three categories. The only real examples of Mass Homicide actually being Mass Homicide occur within a state (see Mao famines, Pol Pot’s mass killings, or the countless purging of communists or anti communists during the Cold War).
Some (wrong) historians may claim the Bengal Famine and Irish Potato Famine were examples of mass Homicide but here’s the thing, in both cases aid from other nations and governments were barred from entering the effected places because the UK forbid it. Food exports were forced to continue to come from Ireland and Bengal because the UK forced it. The reasons these famines were so severe was because the UK had a eugenics inspired belief that the Irish and Bengalis were “sub human animals” and “less deserving of food than the Brits”.
The Irish Potato Famine and Bengali Famine were Genocides, with famine being the preferred method of killing.
Was it intentional at first? Maybe not. Did it become intentional after the fact? Yes.
But this takes us to the most important point. The difference between Genocide, Ethnocide, and Ethnic Cleansing AND Mass Homicide is the intent.
But the intent isn’t truly known until after the fact, when internal government documents are released and the facts of the situation are holistically known.
The Jews/Poles/Romani/etc knew they were going through a Genocide (or well, they didn’t know the word, but they knew what was happening) but most of the outside world didn’t because the N@zis were secretive about it. Yes some activists and Jewish/Polish/Romani/etc diaspora groups warned other governments, but these other governments (US, UK, USSR, China, France, Brazil, Mexico, Canada, Italy even) were skeptical.
We don’t full know intent now, but given Herzl and Jabotinsky’s rhetoric which essentially established modern day Zionism and the Israeli state, and the establishment of Area C for Israeli settlement after conflict in the West Bank, the fact that Israel has threatened a Second Nakba, an event internationally acknowledged as ethnic cleansing, the fact that there are oil reserves underneath Gaza and the forcing of 2 million people into an airport sized camp would allow Israel to open up drilling where the ruins of Gaza city lay, or the fact that Israel is an Ethnonationalist country that relies on the superiority of Israelis over Palestinians and other neighbouring countries in order to exist makes the intent known to those of us familiar with the history of this conflict.
Ok ok ok ok ok here’s where I M. Night Shyamalan this whole thing: Genocide, Ethnocide, and Ethnic Cleansing are all the same crime according to multinational organizations like the United Nations. They are all Genocide.
All Ethnocides are Genocides, but not all Genocides are Ethnocides.
All Ethnic Cleansings are Genocides, but not all Genocides are Ethnic Cleansings.
The Nakba was an Ethnic Cleansing, therefore the Nakba was a Genocide.
The Netanyahu administration claims that their on going attack on Gaza is a “new Nakba”.
Nakba = Ethnic Cleansing = Genocide
The Netanyahu administration claims that their on going attack on Gaza is a “new Genocide”.
Genocide carries with it negative connotations. If the term was as widely used in 1944 as it is today, Hitler would deny genocide allegations, just as the Turkish continue to deny genocide allegations from the Armenian Genocide, why the Japanese continue to deny Genocide Allegations during their rule of Korea, Taiwan, parts of Micronesia, Manchuria, and Nanjing. Why the British refuse to acknowledge the Irish Potato Famine or Bengal Famine as Genocides. Why the conservative right want to ban the teaching of American genocides against countless groups (namely Native Americans, African Americans, Native Hawaiians, and Chicanos). And why Zionists get so offended when you refer to the actions of Israel as a Genocide.
Those who commit Genocide will never acknowledge that they are committing genocide. The fact that the current mainstream Zionist reaction, like @sihatn, is to deny that the ongoing genocide exists just proves that one is happening… if the horrific videos didn’t prove it enough (this one is from an American pro Israel source, but it doesn’t not take long to find ones from individuals in Gaza)
In conclusion, Israel is committing a genocide, and if you say otherwise, you are blinded by Ethnonationalism just like the Germans were in the 30s/40s, the Turks were during the 10s/20s and onward, the Brits were for (well forever), and the American right wing is.
If you don’t acknowledge the fact that Israel is committing a Genocide you are part of the problem shawty, and it’s not a good look 😬
#gaza strip#israel#palestine#from the river to the sea palestine will be free#gaza#gaza genocide#news on gaza#gazaunderattack#save gaza#free gaza#am yisrael chai#don’t be antisemitic just be anti genocide#genocide#ethnocide#ethnic cleansing#i stand with israel#isreal#israeli history#jewish history#jumblr#gazaunderfire#stand with gaza#anti zionisim#i stand with palestine#war on gaza#israhell#antisemitism#rwanda#hawaii#native american
416 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Best News of Last Week - May 15, 2023
🐕 - Now It's a Paw-ty
1. World's oldest ever dog celebrates 31st birthday

Bobi was born on 11 May 1992, making him 31 years old, in human years. A big birthday party is planned for Bobi today, according to Guinness World Records.
It will take place at his home in the rural Portuguese village of Conqueiros in Leiria, western Portugal, where he has lived his entire life.
2. The FDA has officially changed its policy to allow more gay and bisexual men to donate blood
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has announced that they’ve eased restrictions on blood donations by men who have sex with men in an effort to address blood shortages. The new policy recommends a series of individual risk-based questions that will apply to all donors, regardless of their sexual orientation, sex, or gender. Gay or bisexual men in monogamous relationships will now be permitted to donate blood.
3. Illinois passes bill to ensure community college credits transfer to public universities

The Illinois General Assembly has passed a bill that would help community college students transfer to public universities.
It would ensure that certain classes taken at community colleges could be transferred to any higher education institution in the state. Some schools currently only count community college coursework as elective credits.
4. Brazilian President Lula recognizes 6 new indigenous territories stretching 620,000 hectares, banning mining and restricting farming within them

Brazilian President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva has decreed six new indigenous reserves, banning mining and restricting commercial farming there. The lands - including a vast area of Amazon rainforest - cover about 620,000 hectares (1.5m acres).
Indigenous leaders welcomed the move, but said more areas needed protection.
5. More than 1,000 trafficking victims rescued in separate operations in Southeast Asia
More than 1,000 trafficking victims were rescued in separate operations in Southeast Asia over the last week, officials in Indonesia and the Philippines said.
Indonesian officials said Sunday they freed 20 of their nationals who were trafficked to Myanmar as part of a cyber scam, amid an increase in human trafficking cases in Southeast Asia. Fake recruiters had offered the Indonesians high-paying jobs in Thailand but instead trafficked them to Myawaddy, about 567 kilometers (352 miles) south of Naypyidaw, the capital, to perform cyber scams for crypto websites or apps, said Judha Nugraha, an official in Indonesia's Foreign Affairs Ministry.
6. A peanut allergy patch is making headway in trials

An experimental “peanut patch” is showing some promise for toddlers who are highly allergic to peanuts. The patch, called Viaskin, was tested on children ages one to three for a late-stage trial, and the results show that the patch helped children whose bodies could not tolerate even a small piece of peanuts safely eat a few.
After one year, two-thirds of the children who used the patch and one-third of the placebo group met the trial’s primary endpoint. The participants with a less sensitive peanut allergy could safely tolerate the peanut protein equivalent of eating three or four peanuts.
7. Critically endangered lemur born at Calgary Zoo
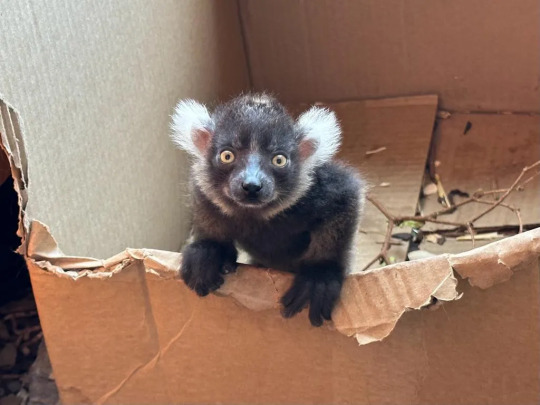

The Calgary Zoo has released pictures of its newest addition, a baby lemur. The zoo says its four-year-old female black-and-white ruffed lemur, Eny, gave birth on April 7. The pup’s father is eight-year-old Menabe. The gender of the pup has not been confirmed but the Calgary Zoo says the pup appears bright-eyed and active and is on the move.
The black-and-white ruffed lemur is registered among the 25 most endangered primates in the world, due mostly to habitat loss and hunting.
----
That's it for this week :)
This newsletter will always be free. If you liked this post you can support me with a small kofi donation:
Buy me a coffee ❤️
Also don’t forget to reblog.
SUBCRIBE HERE for more good news in your inbox
658 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Why We Need to Ban College Legacy Admissions
Children of the super rich are more than twice as likely to get into America’s most elite universities as middle-class students with the exact same test scores. This fast-tracks them to become the next generation of CEOs and lawmakers, and helps keep wealth and power in the hands of people who started out wealthy and powerful.
A big reason rich kids have such an advantage is so-called “legacy admissions” — the preference elite schools give to family members of alumni.
The vast majority of Americans, across the political spectrum, think this is unfair. An astounding 68% of all voters support banning legacy admissions outright. This is the strongest bipartisan agreement I think I’ve ever seen on an issue that boils down to who gets special privileges in America.
Now I went to an Ivy League school (Dartmouth), followed by Oxford, and Yale Law. I wasn’t rich. My father ran a clothing store.
That was a half-century ago — before inequalities of income and wealth exploded in America, before the middle class began shrinking, before the American oligarchy began corrupting American politics with a flood of big money donations. Today, it’s much harder for a middle-class kid to get the same opportunities that I had.
New research conducted at Harvard (ironically) looked at 16 years of admissions data from the Ivy League schools, plus Stanford, Duke, MIT, and the University of Chicago.
The research reveals that one in six students at these prestigious schools comes from the richest 1% of American families.
Why are so many rich kids getting in? It’s not because they’re better students.
Children from the top 1% were 34% more likely to be admitted than middle-class students with the same SAT or ACT scores.
Those from the top ONE TENTH OF ONE PERCENT were more than twice as likely to get in.
Legacy admissions are one of the biggest reasons. Nearly 30% of Harvard’s Class of 2023 were legacies.
It's a vicious cycle that consolidates wealth and power in the hands of a few.
Less than 1% of Americans get into one of these top schools, but their graduates account for 12% of the Fortune 500 CEOs, a quarter of all U.S. senators, and more than a third of all Americans with a net worth over $100 million.
And because these graduates are in the winner's circle, their children have every advantage in the world — even before they get legacy preferences into the same prestigious universities, which in turn hand them even more advantages.
You see how this entrenches an American aristocracy? Concentrated wealth at the top leads to even more and more wealth concentration with each new generation.
It also perpetuates racial discrimination. Since non-white students were barred from most colleges for much of America’s history, legacy students are by definition more likely to be white.
The Ivy League’s legacy policies were introduced during the Jim Crow era, with the specific intent of limiting the number of students of color and Jewish students who could be admitted.
To this day, about 70% of Harvard’s legacy admissions are white, which is why the U.S. Department of Education is now investigating Harvard for potential violation of civil rights.
And with the Supreme Court's ruling against affirmative action, this systemic racism is likely to get worse. The Court is pretending to make college admissions "race-blind," while preserving systems that advance wealthy white students over all others.
It’s time for the government to ban legacy admissions.
224 notes
·
View notes
Text
Know India's New Education Policy 2023: Important Information
In 2023, the Indian government implemented the New Education Policy (NEP), a momentous step towards revolutionizing the country's educational system. This policy introduces a number of ground-breaking measures intended to modernize and rejuvenate the nation's educational framework, making it a significant turning point in the history of the Indian educational system. We will examine the main features of India's New Education Policy 2023 in this extensive guide, giving you crucial information on the goals, effects, and ramifications for preschools and educational facilities all throughout the country.

The Genesis of India's New Education Policy 2023
The New Education Policy 2023 is a result of extensive deliberations, consultations, and recommendations by experts, educators, policymakers, and stakeholders in the field of education. The primary aim of this policy is to address the evolving needs of India's education system, align it with global standards, and foster holistic development in students. It seeks to bridge the gap between traditional and modern pedagogical approaches while emphasizing inclusivity, flexibility, and innovation.
Key Highlights of the New Education Policy 2023
1. Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE):
The NEP emphasizes the importance of ECCE by focusing on the foundational years of a child's education.
Preschool education is recognized as a crucial stage for building a strong educational base.
Quality early childhood education programs will be developed to ensure school readiness.
2. Reforming Curriculum and Pedagogy:
The policy advocates for a more flexible and interdisciplinary curriculum that encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
It promotes the integration of vocational skills into mainstream education, enabling students to acquire practical knowledge.
3. Assessment Reforms:
The NEP proposes a shift from rote learning and high-stakes exams to a more holistic and competency-based assessment system.
It encourages formative assessments and a reduction in the emphasis on board examinations.
4. Multilingualism and Cultural Awareness:
The policy encourages the use of the mother tongue or local language as the medium of instruction, especially in the early years of education.
It emphasizes the preservation and promotion of India's rich cultural heritage.
5. Teacher Training and Development:
The NEP focuses on continuous professional development for teachers, ensuring they are well-equipped to adopt modern teaching methods.
It introduces a four-year integrated teacher education program to enhance the quality of teacher training.
6. Digital Education:
The policy acknowledges the role of technology in education and aims to promote digital literacy among students.
It envisions a shift towards online and blended learning approaches.
7. Inclusivity and Special Education:
The NEP emphasizes inclusive education for students with disabilities and aims to provide equal educational opportunities.
Special education programs will be developed to cater to diverse learning needs.
Impact on Preschools and Early Childhood Education
India's New Education Policy 2023 recognizes the critical role of preschool education in laying a strong foundation for a child's future learning journey. As a result, preschools and early childhood education centers are expected to undergo significant changes:
Curriculum Enhancement: Preschools will need to align their curriculum with the policy's emphasis on holistic development, critical thinking, and skill-building.
Teacher Training: Educators in preschools will benefit from the policy's focus on teacher training and development, enabling them to provide high-quality early childhood education.
Assessment Practices: Preschools will transition towards formative and competency-based assessments, reducing the stress associated with examinations.
Digital Integration: Preschools may adopt digital tools and resources to introduce young learners to technology and digital literacy and for that schools can use school parent app.
Multilingual Approach: Preschools may incorporate multilingualism by using the mother tongue or local language as a medium of instruction.
Inclusivity: Preschools will play a crucial role in fostering inclusivity by accommodating children with diverse learning needs.
Conclusion
India's New Education Policy 2023 is a comprehensive and ambitious reform initiative that aims to shape the future of education in the country. Its impact on preschools and early childhood education is significant, as it recognizes the critical importance of laying a strong educational foundation during the early years. Best preschools in India will need to adapt and evolve to align with the policy's objectives, ensuring that young learners receive a well-rounded, inclusive, and high-quality education that prepares them for a brighter future. As the policy is gradually implemented, its success will depend on collaborative efforts from all stakeholders, including educators, parents, and policymakers, to create an educational ecosystem that truly empowers every child in India.
Originally Published Here.
0 notes
Text
Vice President Candidate Tim Walz - Some of his Issues Before The Voters
• The Floyd riots. Walz managed to infuriate mainstream voters when he initially refused to quell the riots and arson that followed George Floyd’s death in Minneapolis, only to enrage activists later when he called in the National Guard. Violent crime continues to plague the state.
Walz also signed a 2023 bill giving felons the right to vote except while they are incarcerated.
• Covid: Minnesota was a proud lockdown state; Walz enforced closures, restrictions and curfews, as well as a mask mandate, for more than a year. Police arrested a business owner who defied restrictions, while Walz set up a hotline that allowed residents to tattle on others who weren’t following his rules (Walz said the snitching was for people’s “own good.”)
• Spendalooza: Minnesota is racing to become the California of the Midwest, via a spending blowout that has ballooned government and depleted coffers. Walz hiked taxes, blew through a $18 billion surplus, and is on track for a $2.3 billion deficit. The money was thrown at a bevy of progressive priorities, including public education, “free college,” paid family and medical leave, and expanded government health care.
• Green New Deal: Walz tied his state’s vehicle emission standards to California regulations, among the strictest in the nation. And he signed a bill requiring state electric utilities to be 100% carbon free by 2040—an insane, and costly, fantasy.
• Culturally weird: Walz gave his party a laugh when he declared Republicans “weird,” though it’s Minnesota that’s rapidly moved away from cultural norms under his tenure. He signed a law making the state a “sanctuary” for minors seeking transgender hormone treatment and surgery; another one mandating the dispensing of tampons in school boys’ bathrooms; and a law that declares an “individual” right to an abortion with no time limit or requirement that minors notify their parents.
Dept. of Conventional Wisdom: Walz has a jovial Midwestern style, and is often found chatting about his love of hunting or coaching while sporting a Carhartt jacket and baseball cap. Democrats intend to present him as their bridge to working-class voters and argue he’s capable of presenting progressive policy as practical and positive for most Americans. Think Pennsylvania Sen. John Fetterman or Montana Sen. Jon Tester. Yet Minnesota has little to show for its massive spending and liberal governance: Crime is up; education proficiency rates are down; capital and residents are leaving; inflation remains high; and job numbers are ticking down. Minnesota’s tax rates—individual, corporate and estate—are now among highest in the nation. Walz didn’t fare well with working-class voters in his gubernatorial elections. And his policy history magnifies the perception of a far-left ticket.
The real error may be lost opportunity. Vice-presidential candidates don’t usually make-or-break a ticket, but with another potential razor-thin presidential race in November—one that may very well run straight through Pennsylvania—Harris’s decision to walk away from a popular Keystone governor was risky.
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Colorado school district's board was taken over by conservatives aiming to emulate former President Donald Trump — and its new policies are set to drive off nearly half the district's high-school teachers, NBC News reported.
At the end of 2021, a group of conservatives won control of the school district in Woodland Park, Colorado.
Since then, it has enacted a number of conservative policies that have infuriated many teachers, residents, and even staunch Republicans in the town of just 8,000 people, NBC News reported.
Nearly 40% of the district's high-school teachers have decided to leave at the end of this school year, a district administrator told NBC News.
At least four higher-ups in the district have quit over the new board's policies, according to interviews and emails viewed by NBC News.
"This is the flood the zone tactic, and the idea is if you advance on many fronts at the same time, then the enemy cannot fortify, defend, effectively counter-attack at any one front," David Illingworth, a new member of the school board, wrote to another member shortly after being elected, NBC News reported.
"Divide, scatter, conquer," he wrote. "Trump was great at this in his first 100 days."
Among its most controversial new policies is the board's decision to adopt the American Birthright social-studies standard. The curriculum standard, created by a conservative advocacy group, emphasizes patriotism, discourages civic engagement, and criticizes the federal government's control of public schools, NBC News said.
The board also pushed against mental-health resources for students, with the superintendent musing how a school social worker didn't help stop a student's killing off campus, the NBC News report said.
#us politics#news#insider#2023#republicans#conservatives#gop platform#gop policy#gop#Colorado#Woodland Park#nbc news#American Birthright#education reform#education system
24 notes
·
View notes
Text



Study of Elite College Admissions Data Suggests Being Very Rich Is Its Own Qualification
By Aatish Bhatia, Claire Cain Miller and Josh Katz July 24, 2023 (full text under the cut)
Elite colleges have long been filled with the children of the richest families: At Ivy League schools, one in six students has parents in the top 1 percent.

A large new study, released Monday, shows that it has not been because these children had more impressive grades on average or took harder classes. They tended to have higher SAT scores and finely honed résumés, and applied at a higher rate — but they were overrepresented even after accounting for those things. For applicants with the same SAT or ACT score, children from families in the top 1 percent were 34 percent more likely to be admitted than the average applicant, and those from the top 0.1 percent were more than twice as likely to get in.
The study — by Opportunity Insights, a group of economists based at Harvard who study inequality — quantifies for the first time the extent to which being very rich is its own qualification in selective college admissions.
The analysis is based on federal records of college attendance and parental income taxes for nearly all college students from 1999 to 2015, and standardized test scores from 2001 to 2015. It focuses on the eight Ivy League universities, as well as Stanford, Duke, M.I.T. and the University of Chicago. It adds an extraordinary new data set: the detailed, anonymized internal admissions assessments of at least three of the 12 colleges, covering half a million applicants. (The researchers did not name the colleges that shared data or specify how many did because they promised them anonymity.)
The new data shows that among students with the same test scores, the colleges gave preference to the children of alumni and to recruited athletes, and gave children from private schools higher nonacademic ratings. The result is the clearest picture yet of how America’s elite colleges perpetuate the intergenerational transfer of wealth and opportunity.
“What I conclude from this study is the Ivy League doesn’t have low-income students because it doesn’t want low-income students,” said Susan Dynarski, an economist at the Harvard Graduate School of Education, who has reviewed the data and was not involved in the study.
In effect, the study shows, these policies amounted to affirmative action for the children of the 1 percent, whose parents earn more than $611,000 a year. It comes as colleges are being forced to rethink their admissions processes after the Supreme Court ruling that race-based affirmative action is unconstitutional.
“Are these highly selective private colleges in America taking kids from very high-income, influential families and basically channeling them to remain at the top in the next generation?” said Raj Chetty, an economist at Harvard who directs Opportunity Insights, and an author of the paper with John N. Friedman of Brown and David J. Deming of Harvard. “Flipping that question on its head, could we potentially diversify who’s in a position of leadership in our society by changing who is admitted?”
Representatives from several of the colleges said that income diversity was an urgent priority, and that they had taken significant steps since 2015, when the data in the study ends, to admit lower-income and first-generation students. These include making tuition free for families earning under a certain amount; giving only grants, not loans, in financial aid; and actively recruiting students from disadvantaged high schools.
“We believe that talent exists in every sector of the American income distribution,” said Christopher L. Eisgruber, the president of Princeton. “I am proud of what we have done to increase socioeconomic diversity at Princeton, but I also believe that we need to do more — and we will do more.”
Affirmative action for the rich
In a concurring opinion in the affirmative action case, Justice Neil Gorsuch addressed the practice of favoring the children of alumni and donors, which is also the subject of a new case. “While race-neutral on their face, too, these preferences undoubtedly benefit white and wealthy applicants the most,” he wrote.
The new paper did not include admissions rates by race because previous research had done so, the researchers said. They found that racial differences were not driving the results. When looking only at applicants of one race, for example, those from the highest-income families still had an advantage. Yet the top 1 percent is overwhelmingly white. Some analysts have proposed diversifying by class as a way to achieve more racial diversity without affirmative action.
The new data showed that other selective private colleges, like Northwestern, N.Y.U. and Notre Dame, had a similarly disproportionate share of children from rich families. Public flagship universities were much more equitable. At places like the University of Texas at Austin and the University of Virginia, applicants with high-income parents were no more likely to be admitted than lower-income applicants with comparable scores.
Less than 1 percent of American college students attend the 12 elite colleges. But the group plays an outsize role in American society: 12 percent of Fortune 500 chief executives and a quarter of U.S. senators attended. So did 13 percent of the top 0.1 percent of earners. The focus on these colleges is warranted, the researchers say, because they provide paths to power and influence — and diversifying who attends has the potential to change who makes decisions in America.
The researchers did a novel analysis to measure whether attending one of these colleges causes success later in life. They compared students who were wait-listed and got in, with those who didn’t and attended another college instead. Consistent with previous research, they found that attending an Ivy instead of one of the top nine public flagships did not meaningfully increase graduates’ income, on average. However, it did increase a student’s predicted chance of earning in the top 1 percent to 19 percent, from 12 percent.
For outcomes other than earnings, the effect was even larger — it nearly doubled the estimated chance of attending a top graduate school, and tripled the estimated chance of working at firms that are considered prestigious, like national news organizations and research hospitals.
“Sure, it’s a tiny slice of schools,” said Professor Dynarski, who has studied college admissions and worked with the University of Michigan on increasing the attendance of low-income students, and has occasionally contributed to The New York Times. “But having representation is important, and this shows how much of a difference the Ivies make: The political elite, the economic elite, the intellectual elite are coming out of these schools.”
The missing middle class
The advantage to rich applicants varied by college, the study found: At Dartmouth, students from the top 0.1 percent were five times as likely to attend as the average applicant with the same test score, while at M.I.T. they were no more likely to attend. (The fact that children from higher-income families tend to have higher standardized test scores and are likelier to receive private coaching suggests that the study may actually underestimate their admissions advantage.)
An applicant with a high test score from a family earning less than $68,000 a year was also likelier than the average applicant to get in, though there were fewer applicants like this.
Children from middle- and upper-middle-class families — including those at public high schools in high-income neighborhoods — applied in large numbers. But they were, on an individual basis, less likely to be admitted than the richest or, to a lesser extent, poorest students with the same test scores. In that sense, the data confirms the feeling among many merely affluent parents that getting their children into elite colleges is increasingly difficult.
“We had these very skewed distributions of a whole lot of Pell kids and a whole lot of no-need kids, and the middle went missing,” said an Ivy League dean of admissions, who has seen the new data and spoke anonymously in order to talk openly about the process. “You’re not going to win a P.R. battle by saying you have X number of families making over $200,000 that qualify for financial aid.”
The researchers could see, for nearly all college students in the United States from 1999 to 2015, where they applied and attended, their SAT or ACT scores and whether they received a Pell grant for low-income students. They could also see their parents’ income tax records, which enabled them to analyze attendance by earnings in more detail than any previous research. They conducted the analysis using anonymized data.
For the several elite colleges that also shared internal admissions data, they could see other aspects of students’ applications between 2001 and 2015, including how admissions offices rated them. They focused their analysis on the most recent years, 2011 to 2015.
Though they had this data for a minority of the dozen top colleges, the researchers said they thought it was representative of the other colleges in the group (with the exception of M.I.T.). The other colleges admitted more students from high-income families, showed preferences for legacies and recruited athletes, and described similar admissions practices in conversations with the researchers, they said.
“Nobody has this kind of data; it’s completely unheard-of,” said Michael Bastedo, a professor at the University of Michigan’s School of Education, who has done prominent research on college admissions. “I think it’s really important to good faith efforts for reforming the system to start by being able to look honestly and candidly at the data.”
How the richest students benefit
Before this study, it was clear that colleges enrolled more rich students, but it was not known whether it was just because more applied. The new study showed that’s part of it: One-third of the difference in attendance rates was because middle-class students were somewhat less likely to apply or matriculate. But the bigger factor was that these colleges were more likely to accept the richest applicants.
Legacy admissions
The largest advantage for the 1 percent was the preference for legacies. The study showed — for the first time at this scale — that legacies were more qualified overall than the average applicant. But even when comparing applicants who were similar in every other way, legacies still had an advantage.

When high-income applicants applied to the college their parents attended, they were accepted at much higher rates than other applicants with similar qualifications — but at the other top-dozen colleges, they were no more likely to get in.
“This is not a sideshow, not just a symbolic issue,” Professor Bastedo said of the finding.
Athletes
One in eight admitted students from the top 1 percent was a recruited athlete. For the bottom 60 percent, that figure was one in 20. That’s largely because children from rich families are more likely to play sports, especially more exclusive sports played at certain colleges, like rowing and fencing. The study estimated that athletes were admitted at four times the rate of nonathletes with the same qualifications.
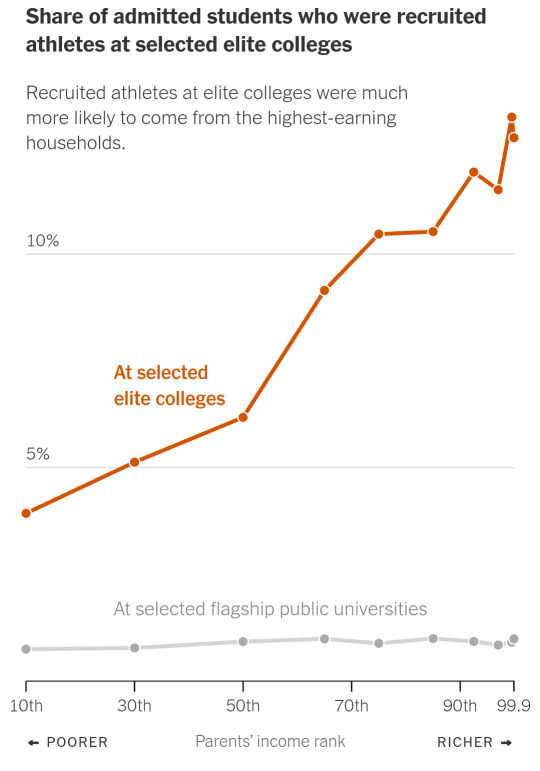
“There’s a common misperception that it’s about basketball and football and low-income kids making their way into selective colleges,” Professor Bastedo said. “But the enrollment leaders know athletes tend to be wealthier, so it’s a win-win.”
Nonacademic ratings
There was a third factor driving the preference for the richest applicants. The colleges in the study generally give applicants numerical scores for academic achievement and for more subjective nonacademic virtues, like extracurricular activities, volunteering and personality traits. Students from the top 1 percent with the same test scores did not have higher academic ratings. But they had significantly higher nonacademic ratings.

At one of the colleges that shared admissions data, students from the top 0.1 percent were 1.5 times as likely to have high nonacademic ratings as those from the middle class. The researchers said that, accounting for differences in the way each school assesses nonacademic credentials, they found similar patterns at the other colleges that shared data.
The biggest contributor was that admissions committees gave higher scores to students from private, nonreligious high schools. They were twice as likely to be admitted as similar students — those with the same SAT scores, race, gender and parental income — from public schools in high-income neighborhoods. A major factor was recommendations from guidance counselors and teachers at private high schools.
“Parents rattle off that a kid got in because he was first chair in the orchestra, ran track,” said John Morganelli Jr., a former director of admissions at Cornell and founder of Ivy League Admissions, where he advises high school students on applying to college. “They never say what really happens: Did the guidance counselor advocate on that kid’s behalf?”
Recommendation letters from private school counselors are notoriously flowery, he said, and the counselors call admissions officers about certain students.
“This is how the feeder schools get created,” he said. “Nobody’s calling on behalf of a middle- or lower-income student. Most of the public school counselors don’t even know these calls exist.”
The end of need-blind admissions?
Overall, the study suggests, if elite colleges had done away with the preferences for legacies, athletes and private school students, the children of the top 1 percent would have made up 10 percent of a class, down from 16 percent in the years of the study.
Legacy students, athletes and private school students do no better after college, in terms of earnings or reaching a top graduate school or firm, it found. In fact, they generally do somewhat worse.
The dean of admissions who spoke anonymously said change was easier said than done: “I would say there’s much more commitment to this than may be obvious. It’s just the solution is really complicated, and if we could have done it, we would have.”
For example, it’s not feasible to choose athletes from across the income spectrum if many college sports are played almost entirely by children from high-earning families. Legacies are perhaps the most complicated, the admissions dean said, because they tend to be highly qualified and their admission is important for maintaining strong ties with alumni.
Ending that preference, the person said, “is not an easy decision to make, given the alumni response, especially if you’re not in immediate concurrence with the rest of the Ivies.” (Though children of very large donors also get special consideration by admissions offices, they were not included in the analysis because there are relatively few of them.)
People involved in admissions say that achieving more economic diversity would be difficult without doing something else: ending need-blind admissions, the practice that prevents admissions officers from seeing families’ financial information so their ability to pay is not a factor. Some colleges are already doing what they call “need-affirmative admissions,” for the purpose of selecting more students from the low end of the income spectrum, though they often don’t publicly acknowledge it for fear of blowback.
There is a tool, Landscape from the College Board, to help determine if an applicant grew up in a neighborhood with significant privilege or adversity. But these colleges have no knowledge of parents’ income if students don’t apply for financial aid.
Ivy League colleges and their peers have recently made significant efforts to recruit more low-income students and subsidize tuition. Several now make attendance entirely free for families below a certain income — $100,000 at Stanford and Princeton, $85,000 at Harvard, and $60,000 at Brown.
At Princeton, one-fifth of students are now from low-income families, and one-fourth receive a full ride. It has recently reinstated a transfer program to recruit low-income and community college students. At Harvard, one-fourth of this fall’s freshman class is from families with incomes less than $85,000, who will pay nothing. The majority of freshmen will receive some amount of aid.
Dartmouth just raised $500 million to expand financial aid: “While we respect the work of Harvard’s Opportunity Insights, we believe our commitment to these investments and our admissions policies since 2015 tells an important story about the socioeconomic diversity among Dartmouth students,” said Jana Barnello, a spokeswoman.
Public flagships do admissions differently, in a way that ends up benefiting rich students less. The University of California schools forbid giving preference to legacies or donors, and some, like U.C.L.A., do not consider letters of recommendation. The application asks for family income, and colleges get detailed information about California high schools. Application readers are trained to consider students’ circumstances, like whether they worked to support their families in high school, as “evidence of maturity, determination and insight.”
The University of California system also partners with schools in the state, from pre-K through community college, to support students who face barriers. There’s a robust program for transfer students from California community colleges; at U.C.L.A., half are from low-income backgrounds.
M.I.T., which stands out among elite private schools as displaying almost no preference for rich students, has never given a preference to legacy applicants, said its dean of admissions, Stuart Schmill. It does recruit athletes, but they do not receive any preference or go through a separate admissions process (as much as it may frustrate coaches, he said).
“I think the most important thing here is talent is distributed equally but opportunity is not, and our admissions process is designed to account for the different opportunities students have based on their income,” he said. “It’s really incumbent upon our process to tease out the difference between talent and privilege.”
Source: Raj Chetty, David J. Deming and John N. Friedman, “Diversifying Society’s Leaders? The Determinants and Causal Effects of Admission to Highly Selective Private Colleges”
193 notes
·
View notes
Text
A right to information response received by a University of New Brunswick professor shows that from 2020 to May 25, 2023, the Department of Education received no written complaints from parents alleging the school was keeping them in the dark about their children's preferred pronouns.
Education Minister Bill Hogan cited "hundreds" of complaints when he announced in May that he was reviewing an education policy designed to ensure the safety of LGBTQ students.
But when education professor and former teacher Melissa Dockrill Garrett sought details through a right to information request, she was told the Education Department had no records of any complaints.
"The response that I received was enough reason to indicate that there really was no valid reason to begin this review in the first place," Garrett said.
In June, after the review of Policy 713, Hogan announced changes because he said the policy had amounted to "keeping secrets" from parents because it empowered school officials to use a child's chosen name or pronoun informally, regardless of parental consent, and only required that consent for official changes in school records. [...]
Continue Reading.
Tagging: @politicsofcanada
#cdnpoli#New Brunswick#Policy 713#reactionary politics#queerphobia#transphobia#University of New Brunswick#education#secondary education
149 notes
·
View notes