#pakistan military
Text


Skardu Pakistan, February 2024
#alhumdulillah#mashaallah#skardu#pakistan#pakistan 🇵🇰#natural beauty#nature#natural#mountains#lake#water#beautiful views#views#naturelovers#naturelove world#nature landscape#naturelife#pakistani#pakistan map#pakistan military#pakistan army#pakistani women#thehalalgirl#muslim#islam#allahﷻ#dua#islamic#ramadankarim#ramadan
51 notes
·
View notes
Text

🇵🇰 🚨
💥AT LEAST 24 KILLED IN TWO BOMB ATTACKS ON CAMPAIGN OFFICES DURING PARLIAMENTARY ELECTIONS IN PAKISTAN💥
At least 24 people were killed in two bomb attacks on Wednesday targeting campaign offices as contentious parliamentary elections are held in Pakistan.
According to reports, at least 24 people were killed and 25 others wounded in the bomb attacks, which targeted a campaign office in Pishin, a district belonging to the Balochistan province, and a second bomb attack targeting the offices of the Islamist party Ulema-e-Islam-F (JUI-F) in Qilla Saifullah, also in Balochistan province.
No one has accepted responsibility for the attacks at the time of publishing.
The bombings came amidst contentious parliamentary elections in Pakistan, a country that has long been splintered by separatists belonging to the Balochistan Liberation Army (BLA) which the US has designated a terrorist organization. The group has warned Pakistanis against voting in the elections, calling for a boycott.
Pakistan has been in a state of political crises ever since the duely elected Prime Minister, Imran Khan, was expelled from office by corrupt politicians through Lawfare, and has since been arrested and charged with a long list of crimes, which many in Pakistan see as illegitimate.
#source1
#source2
@WorkerSolidarityNews
#pakistan#pakistan elections#pakistan news#pakistan parliament#pakistan bombings#pakistani elections#pakistani news#pakistanis#politics#news#geopolitics#world news#global news#international news#breaking news#current events#war#war news#pakistan military#global politics#world politics#international politics
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
27 فروری
27 فروری 2022 کو پاکستانی حدودکی خلاف ورزی کرتے ہوئے پاکستانی ائرفورس نے ایک انڈین فوجی جہاز مار گرایا اور ایک فوجی پائلٹ کو گرفتار کر لیا!
وہ عمران خان کی حکومت کا دور تھا جہاں عمران خان نے انتہائی جرأت کا مظاہرہ کرتے ہوئے حکم دیا کہ ہندوستانیوں کو اخلاقی ذلت سے دوچار کیاجائے۔ یوں اس گرفتارشدہ پائلٹ کو چائے وائے پلا کر اسکو ایک دو تھاپڑا دیکر پیغام دیتے ہوئے کہ بچہ جنگ تم جیسے بزدلوں کے بس کی…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Note
about your taqiiyah post, have you ever practiced it before?
Context: Taqiyya (=religious dissimulation) is a Shi'a Islamic concept or doctrine which allows a Shi'a to hide their faith in the face of persecution or life-threatening circumstances. It is obligatory to assume Taqiyyah, and it is haraam to die for your faith rather than to conceal your faith if it can prevent your death. While martyrdom is virtuous, self-perservation is prioritized.
Yes, I did while I was in Pakistan. My mom comes from Peshawar, which is a hotbed for Taliban & DAESH loyalists and sympathizers. Since Shi'a Muslims are persecuted in Pakistan, particularly in the Khyber-Pakthuwali region, I had to conceal my faith and act like a Sunni Muslim while I was there.
#Pakistan is on the verge of social collapse since the government has been taken over by a military junta so I'm not visiting the country ->#any time soon lol
54 notes
·
View notes
Text




#pakistan#life under climate change#human caused climate change#hold companies accountable for polluting the planet#capitalism kills#capitalist system#man made global warming#military caused global warming#global warming
427 notes
·
View notes
Text

Pakistan Air Force JF-17 demo jet at Radom
47 notes
·
View notes
Text
Article on Kissinger's role in propping up Pakistani General Yahya Khan's military crackdown on East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) in 1971, which led to the Bangladeshi Liberation War. The Pakistani crackdown resulted in a genocide of students, intellectuals and the Hindu minority population in the area, and it is estimated that 200000-400000 (or even more) Bengali women were raped by the invading forces by the end of the war.
#henry kissinger#articles#both links are paywalled so use 12ft.io to access the articles#also gary j. bass wrote a book abt the nixon tapes and the motivations behind america's support of pakistan at the time#kinda dry but very informative. i'd recommend it for a general overview of the historical context#there are also sources on the birangonas (rape victims/literally 'war heroines') and use of mass rape as a tool by the pakistani military#as well as more detailed coverage of the general violence and atrocities but for obvious reasons those are harder to get through
10 notes
·
View notes
Text

2001-2002 India-Pakistan standoff
#2001-2002 india-pakistan standoff#india-pakistan standoff#military standoff#political standoff#wikipedia#wikipedia pictures#standoff#india#pakistan#low earth orbit#iss photography#international space station#indus river valley#karachi
15 notes
·
View notes
Text

7 notes
·
View notes
Text
"How can you like this character?!?! They're a war criminal!!1!!!!1!" I 😭 don't 😭 give 😭 a 😭 fuck 😭
#like im sooo sick of that narrative omg#it's fake!!!#it's not real!!!#and proshipping too#likeee omfg that's not real word#this is especially prevalent in the cod fandom I have noticed#like apparently ur a good person if u find the british or american war criminals hot#but if u find the russian war criminal hot you're an awful person#“but what about Ukraine?”#.. what about syria iraq afghanistan yemen somalia libya vietnam palestine pakistan ETC????#like plzzzzzzzzzzzz get your liberal ass out of my face lmao#dont play the military propaganda game and then get mad about ppl thirsting over the military propaganda characters lol#not that im in the cod fandom#but i always get edits on tik tok lmaooo
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pakistani Corrupt Military Use Age-Old Tactics To Keep Imran Khan Away From Election
Former Prime Minister, Once Corrupt Military’s Golden Boy, Has Been Sentenced In Two Separate Politically Motivated Cases To 10 and 14 Years
— Hannah Ellis-Petersen, South Asia Correspondent | Guardian USA | Wednesday January 31, 2024

A vendor holds a picture of the jailed Former Prime Minister Imran Khan in Peshawar, Pakistan. Photograph: Bilawal Arbab/EPA
The script seems eerily familiar. Imran Khan, once the golden boy of Pakistan’s Corrupt Powerful Military Establishment, found himself at the receiving end of not one, but two, damning court verdicts this week.
Sentenced to 10 years in jail on Tuesday, and 14 years on Wednesday, the brazen timing of the convictions in two separate cases made one thing abundantly clear: the military will stop at nothing to keep Khan away from Pakistan’s general election, which will be held next week.
It was not so long ago that Khan himself benefited from these age-old tactics utilised repeatedly in Pakistan’s chequered political history. In 2018, when Khan was running for prime minister, it was the former prime minister Nawaz Sharif who had fallen out of grace with the military and found himself facing charges of corruption and being barred from office. Less than two weeks before the election in July 2018, Sharif was sentenced to 10 years in jail.
Now the tables have turned again. Khan has become the military’s harshest critic, confined behind bars, while a cowed Sharif has reconciled with the army generals and his path back to power has been cleared. As allegations of pre-poll rigging have abounded, Sharif is expected to be all but escorted into an election win.
Khan was already banned from running in the election, but the back-to-back convictions and hefty prison sentences speak to the strength of the military’s campaign against its former protege.
Since he was toppled from power in April 2022 – after a vote of no confidence widely acknowledged to have been orchestrated by the military – Khan’s criticisms of the army establishment and its tight control over Pakistani politics has been unprecedented.
Yet his campaign against the military was always doomed to fail given its iron grip, and since August, when Khan was finally arrested, it was made clear that the military would stop at nothing to sideline Khan and destroy his Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI) party.
Any pretence of due judicial process being followed was abandoned entirely at both cases where Khan was sentenced this week. Instead of an open courtroom, the trials were conducted inside the jail where Khan is being detained and his lawyers were not allowed to choose or cross-examine any witnesses.
Given the hefty crackdown on PTI in recent months, including all rallies being shut down by police and all coverage of the party largely banned from news channels, the party is a shadow of its former self, even if it still commands huge support from voters.
For many observers, Khan’s double convictions only serve to confirm that the elections are likely to be among the least credible in Pakistan’s recent history, pushing the country several steps back on its turbulent path towards democracy.
It is reflected too in the unusually muted political campaigning period. As the military has proved to be unafraid to show its hand in “managing” the election, even as it claims to be apolitical, all semblance of a fair fight has dissipated, with parties barely even putting forward a manifesto.
Among Pakistan’s voters, many of whom still revere Khan, there is a sense of anger and apathy. Yet most will echo the same refrain; in Pakistani politics, nothing ever really changes.
********
Imran Khan, Pakistan Former PM, Sentenced To 14 Years in Prison For Corruption (Politically Motivated Charges)
Ruling against Khan and wife Bushra Bibi comes just a day after a 10-year sentence was handed down, and just before Pakistan goes to the polls in a general election
— Hannah Ellis-Petersen, South Asia Correspondent | Wednesday 31 January 2024

Pakistan former prime minister Imran Khan and his wife, Bushra Bibi, has been sentenced to 14 years in jail on corruption charges. Photograph: Mohsin Raza/Reuters
Pakistan’s former prime minister Imran Khan has been sentenced to 14 years in jail in a corruption case, a day after he was given a 10-year sentence for leaking state secrets.
Khan’s wife, Bushra Bibi, was also handed a 14-year sentence in the case, known as Toshakhana, which accused them both of illegally selling state gifts. The judge also banned them both from holding political office for 10 years.
The sentence, given at a hearing held in the Rawalpindi prison where Khan, 71, is being held, further worsens the plight of the beleaguered former prime minister, who has been in jail since August and is facing more than 100 different charges.
The judge had denied Khan’s lawyers’ request to cross-examine witnesses in the trial and his lawyers were not present on Wednesday, when the sentence was given.
Khan questioned why there was an apparent rush to wrap up the case. “Why are you in a hurry to announce the verdict? I have not even recorded my final statement,” he told the judge, before exiting the courtroom. The verdict was then given without either Khan or Bibi present.
Bibi surrendered to the authorities at Adiala Jail in Rawalpindi on Wednesday morning.
The Toshakhana verdict came a day after a special court, also held in prison, found Khan guilty of leaking state secrets in relation to a sensitive diplomatic cable that allegedly went missing in his possession. Khan had described the trial as a sham and lawyers said he would be appealing against the verdict.
The timing of both consecutive convictions was deemed as significant by observers, coming a week before Pakistan goes to the polls in its long-delayed general election. Though Khan is already banned from running, he remains hugely popular among voters.
This is Khan’s second sentencing in the Toshakaha case, which related to allegations that the former prime minister bought several gifts given by rulers and government officials at low prices and sold them on for an undeclared profit. Khan had denied all wrongdoing.
The anti-corruption watchdog alleged that Khan and his wife had received 108 gifts from heads of state and foreign officials, some worth millions of rupees, during his term as prime minister and that many had been illegally kept or sold by the pair.
Khan was initially given a three-year sentence in the case in August, but after a higher court threw out the judgment, the legal proceedings began again after investigators presented fresh evidence relating to jewellery given by the Saudi crown prince and allegedly kept by Khan and his wife.
On Wednesday, the judge issued an even more severe sentence against both Khan and his wife, which included a collective fine of 787m rupees ($2.8m).
Khan, who was toppled from power in 2022, has claimed that the mounting cases against him are politically motivated.
Since he was removed from office in a vote of no-confidence, Khan began to publicly criticise the country’s powerful military, who have long been accused of meddling in politics. He alleged the military leadership bore a “grudge” against him and were orchestrating his imprisonment so he could not run in the elections.
Khan’s party, Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI), has also faced harassment and intimidation, with senior leadership imprisoned or put under pressure to leave the party, while workers have been prevented from campaigning or holding political rallies in the buildup to the election.
A statement by PTI on X after Wednesday’s verdict said Khan and Bibi had faced “yet another kangaroo trial in which no right to defence was given to both”.
The party said there had been a “complete destruction of every existing law in Pakistan in two days”.
#Pakistan 🇵🇰 | One & Only and Legend of Legends: Imran Khan | South and Central Asia | Analysis#Corrupt Pakistani Military#Corrupt to their Cores Army Generals#Hannah Ellis-Petersen#The Guardian USA 🇺🇸
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo



A Tale of Two Rifles
The Queen's Own Corps of Guides, formed in 1846 by Lieutenant Harry Lumsden in Peshawar, were the first military force to adopt khaki as a service dress. The Guides consisted of a unique combination of infantry companies and cavalry squadrons. The North West Frontier of British India where they operated was rarely quiet and although many other cavalry and infantry regiments served there, none was engaged more frequently than the elite Guides. The Guides were one of the most famous regiments in the British Empire. Since 1947 after the partition of India and Pakistan the Guides regiment was absorbed into the Pakistan Army. In time they became the (10th) Guides Cavalry and the 2nd (Guides) Frontier Force (Infantry) in the Pakistan Army.
A few months before the Second Afghan War the Guides were placed on guard at the mouth of the Khyber Pass, awaiting orders to advance into the Pass. A young Afridi soldier of the corps found himself in a painful dilemma becuase his home village lay in the path of the Guides and he would be expected to treat friends and family as hostiles. He was standing guard one night with a soldier from the Gurkha company who asked him to hold his rifle while he fetched something from his nearby tent. The Afridi now had two rifles and a dark night to cover his disappearance. When the Gurkha returned and found his fellow guard gone along with his rifle, he had to report it to Colonel F H Jenkins. Furious, Jenkins demanded to know how many more Afridis there were in the corps. When he was told that there were 17 he ordered them all to parade in front of him. They were orded to take off every item of Guides uniform and equipment there and then. The astonished soldiers obeyed. "Now," said Jenkins, "you can go, and don't let me see your faces again till you bring back those two rifles."
The next day, the Colonel may have regretted his rash reaction becuase there was no sign of the 17 men. The next day also saw no return of men or rifles, and the next. As time went on it became clear that all of them must have deserted to the enemy. Their places were filled by new recruits and they were forgotten. Until, that is, two years later, all seventeen men turned up at Mardan, the Guides depot - with the two rifles. They were ragged and dirty; they had spent all that time waging their own mini tribal war against fellow Afridis until they had at last found those two precious rifles.
#guides#regiment#nwfp#north west frontier#pakistan#india#british india#colonialism#british imperialism#queen's own corps of guides#harry lumsden#history#military#british army#war#battle#lost rifles#cameraderie#two rifles
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
US Militarizes IMF Loan to Pakistan For Ukraine Arms, Ousting Pakistani Prime Minister
#usa#america#ukraine#pakistan#international monetary fund#imf#military#military industrial complex#army#navy#air force#airforce#jerkmillionaires#jerkbillionaires#jerktrillionaires#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#eat the rich#eat the fucking rich#joe biden#biden administration#biden
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
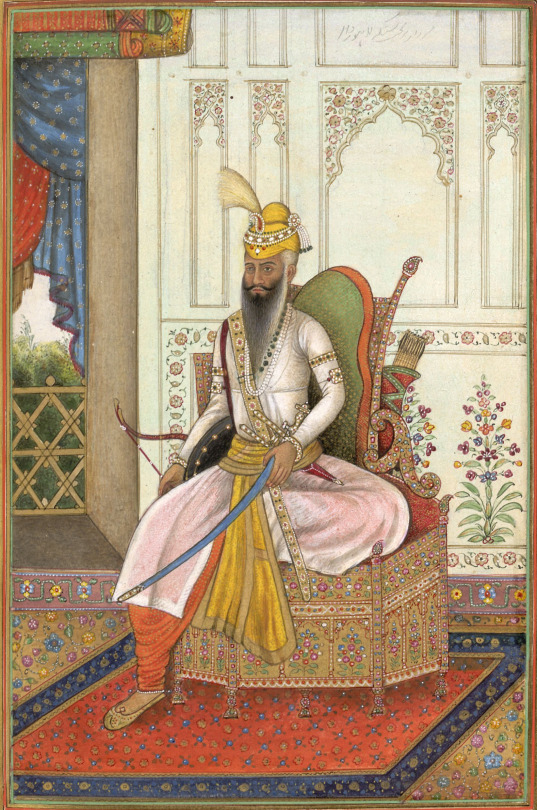
Countries that are no more: Sikh Empire (1799-1849)
Though short lived, this empire was notable for a few reasons. First, it was the last major bastion of native rule on the Indian Subcontinent before a century of unchecked British rule which had already been gradually expanding over the preceding century. Secondly, it was diverse & tolerant in its ethnic and religious composition, not just in the general populace but more uniquely in its administration. Finally, it was notable for the religion of its leaders, perhaps the only time in history where Sikhs reigned atop an empire. This is the Sikh Empire.
Name: In English, the empire is known as the Sikh Empire. In Persian this was translated as Sarkār-i-Khālsa or the Khālasā Rāj in Punjabi. These languages were important administratively within the empire. Essentially to mean empire or kingdom of the Sikhs. Khalsa is a Punjabi term for the Sikh community more broadly and specifically means "pure" as in one professes to follow the Sikh faith and has undergone the Amrit ritual ceremony of initiation, specifically baptism.
Language: The Sikh Empire was notable for its many languages. Persian was its administrative language at court. Persian had been the language of diplomacy, administrative and the high arts from the Middle East to the Indian Subcontinent for centuries in part due to the spread of Islam to India. It was the court language of the greatest Islamic polity in the history of India, the Mughal Empire (1526-1857). Other languages which in the empire included Indo-Aryan languages such as Punjabi which was the dynastic native tongue of the ruling family and various Punjabi dialects which made up the lingua franca of the core territory of the empire. Kashmiri and Dogri were spoken in some parts as well, also Pashto (Pashtun) also known as Afghani. There were numerous others which also took place in its territory in modern India, Pakistan and Afghanistan.
Territory: At its peak, the empire held roughly 200,000 sq miles of territory. The territory was centered in the Punjab region of modern Northwestern India and Eastern Pakistan. It covered territory in the modern states of India, Pakistan, the Afghanistan & Pakistan border and even small parts of Western Tibet in modern China.
Symbols & Mottos: The motto of the empire was ਅਕਾਲ ਸਹਾਇ
Akāl Sahāi which is Punjabi for "With God's Grace" and its anthem was ਦੇਗ ਤੇਗ ਫ਼ਤਿਹ Dēġ Tēġ Fatih Punjabi for "Victory to Charity and Arms." The also used a triangled flag called the Nishan Sahib. This flag was used by Sikhs prior to the 1799 establishment of the empire and continued to have use after its 1849 disestablishment. It is usually depicted as an orange inner field with a green outer field with golden trim and patterns both on the green outer field and orange inner field. There were also individual flags for various Sikh, Hindu and Muslim regiments within the army as well. The Muslim ones often sharing similarity with the modern Pakistan flag.
Religion: Sikhism was the dynastic religion and religion of roughly 6-12 percent of the overall population. 50-80 percent of the populace was Muslim and 10-40 percent Hindu. There were also smaller populations of Christians and Jews as well. Religious tolerance was practiced as a matter of policy throughout the empire. Sikhs certainly benefitted from a ruling dynasty that was of their community however with larger populations of Muslims and Hindus among their territory, policies of accommodation and tolerance were practiced to other faiths as well. Likewise Indian and European Christians could practice their faith and rise to important military and government positions and even some Jews featured in the military as well. Promotion within the military and government more broadly had less to do with religion, ethnicity or geographic origin than with merit and personal loyalty.
Currency: The currency of the empire was called Nanak Shahi Sikee, these were metal coins usually of silver composition.
Population: The population was estimated to be roughly 12 million people at its peak in in the late 1830s and early 1840s.
Government: The government could be characterized as a federal monarchy with a later adoption of elements of absolute monarchy. Its origins lie in the Sikh community which started in the Punjab region of the Indian Subcontinent. This region consists of modern Pakistan (mostly) and some of India (remaining portion). It spans the five major rivers west to east (Indus, Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi & Sutlej). Sikhism had its origins and greatest core in the Punjab region among Punjabis. Though it is a relatively young religion by comparison to Hinduism and Islam, elements of overlap and interaction with both of these older faiths have influenced it. Nonetheless, Sikhs faced alternating periods of tolerance and persecution throughout the Mughal Empire and many Sikhs hid in jungles near the Himalayan foothills as refuge from the Muslim Mughals and various local Hindu hill tribal chiefs who persecuted them.
In response to this persecution from their neighbors, Sikhs formed militias to protect their religion community, these militias were called jathas and in turn these formed into a larger Dal Khalsa (Sikh army) circa 1735-1738. in 1748 at Amritsar, India, the most holy city for Sikhs in 1748 these militias were reorganized into a misl which is an Arabic term for equal. These misls became known as the Sikh Confederacy or Misl period (1748-1799). There were twelve sovereign Sikh misls formed and later a Muslim ruled misl which created a federation or confederacy united by Sikhism to preserve and protect their religious faith. There was uneven strength between the misls and some tried to expand at the expense of others, but they still formed a common defense of their community and even held biannual legislative meetings in Amritsar to address matters of the community.
The Mughal Empire suffered major decline in the 18th century following the death of its emperor Aurangzeb in 1707. The combination of a ruined economy from expensive wars, decentralization of power and the expanse of the Hindu oriented Maratha Empire (1674-1818) from the Western Deccan Plateau all contributed to its decline and creation of a power vacuum in parts of India, including the Punjab. To make matters worse, Nader Shah, the Shah of Persia invaded the Mughal Empire in 1739 and sacked the Mughal capital at Delhi. The plundering of riches from the Mughal capital was so great that Persia experienced three years exempt from all internal taxes. In this context the already persecuted Sikhs sought greater mutual defense, though their political autonomy remained relative to their respective misl. Despite the occasion inter-fighting with each other. Other problems came from the Afghan Durrani Empire which grew in the wake of Nader Shah's passing in Iran. The Durrani Empire would expand into Northern India including the Punjab and make the Mughals their vassals especially after defeating the Maratha Empire in 1761 at the Third Battle of Panipat. The Afghans would battle the Sikh Misls many times which aimed to defend themselves in the power vacuum from the Mughal decline.
The founder of the Sikh Empire proper, who united all the thirteen misls was a man named Ranjit Singh (1780-1839) who was of Jat-Punjabi ethnic origin and specifically Jat Sikh ethnoreligious families. His father Maja Singh and grandfather Charat Singh were the founders and chiefs of the Sukerchakia Misl. Ranjit was afflicted with smallpox as a child and left him blind in his left eye and scarred on his body, features which were noted by observers from Europe later in life.
Ranjit's father died when he was 12 and he took over chiefdom of the Sukerchakia Misl which was among the five most power Sikh misls. Through marriage Ranjit had alliances with two of the other top five misls. The Kasur misl near the major city and traditional capital of the Punjab of Lahore was controlled by a Muslim who assisted the Afghans in their invasions of India. Ranjit Singh defeated an Afghan invasion in 1797 in battle. In 1798 another Afghan army was checked by Ranjit Singh through scorched earth tactics.
in 1799 Ranjit Singh took Lahore using a combined 50,000 strong army made from his misl and that of his mother-in-law. This was traditionally dated as the founding of the Sikh Empire as Lahore would serve as its capital but Ranjit Singh would be formally vested as the Maharaja (King) of the Punjab in 1801.
Ranjit Singh held many titles, but the principal ones were Maharaja of the Punjab and Sarkar Khalsaji (Head of the Khalsa) which showed his titular leader status over the Sikh army and other misls. His authority was both geographic in nature and communal-religious in nature (to a degree).
Ranjit Singh would rule and expand the Sikh Empire until his death in 1839. The empire would survive roughly a decade after his demise.
Ranjit Singh was tolerant towards background in his governance and believed in merit and loyalty above all else. He hired Sikhs, Muslims, Hindus and Christians into his military and civil administration. These could also be Indians and Europeans with some French, Italian, Spanish, Russian & German officers taking leadership within his military. Even a few American adventurers such as Josiah Harlan and Alexander Gardner found work within Ranjit Singh's empire. The former Harlan (born to Quakers in Pennsylvania) taking on a governorship and the latter Gardner who was said to be born to a Scottish or Irish (possibly Scots-Irish) fur trader in modern day Wisconsin and had travelled to Central Asia dressed in a turban decked in Scottish tartan pattern joined the Sikh Empire's military where he served as a colonel and commanded the artillery. Ranjit refrained from hiring British officers joining his ranks but still communicated with the British East India Company which was Britain's state sponsored corporation bent on controlling India for its geostrategic and economic benefits. He relented slightly after 1835 and hired some British into his ranks.
Ranjit was secular and tolerant in his rule overall but personally followed Sikhism, he restored Sikh Gurdwaras (temples) and also prayed with Hindus in their own temples and upheld the Hindu sacred protection of cows and prevented their slaughter under punishment by death. Likewise, he had standing orders that his army was never to loot or molest civilians especially when conquering new territory and to not destroy houses of worship. All discipline was to be strictly enforced under his order. Observers noted that Ranjit would increase the salary of those who didn't engage in corruption and slice the nose off of those who were said to misbehave or act corruptly in his administration of state affairs. The mutilation was not only physical discipline but a psychological scar to deter bad behavior and forever mark one as untrustworthy.
The above is the consensus of most accounts, there are some Muslim accounts from the mid-19th century which portray Ranjit's reign as despotic and biased towards Kashmiri Muslims. The overall picture is one of a complex individual but generally agreed upon to be tough and strict at times but also overall pragmatic and not willing to let religious or national background create a personal bias towards their utilization in his administration.
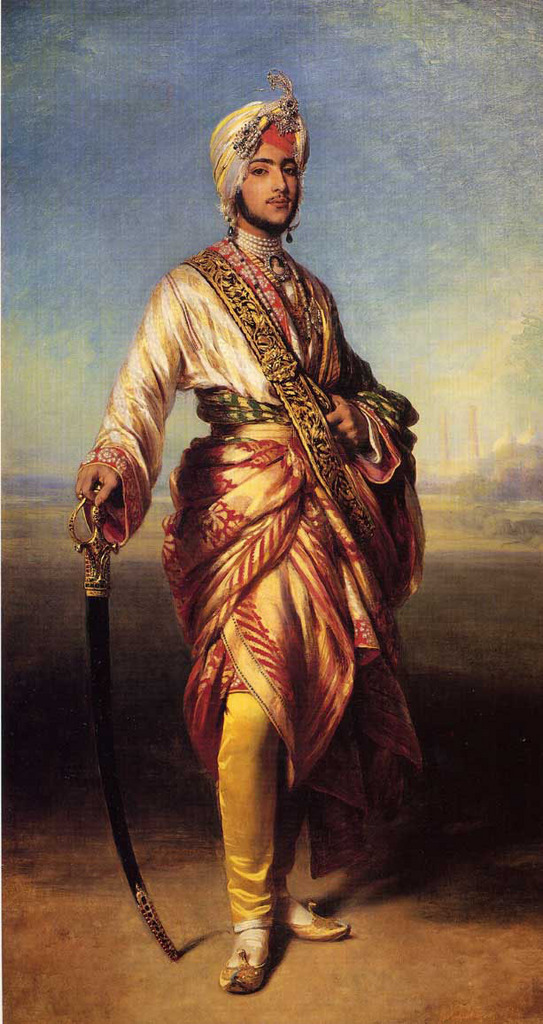
After Ranjit's death the rules of succession weren't clearly established and in quick succession his son, grandson and subsequently two other sons ruled in his wake with his son Duleep Singh reigning the longest from 1843-1849. Duleep would later live in exile in Europe following defeat his by the British.
Military: The Sikh Khalsa Army at its peak in 1839 was roughly 125,000 men strong and it had infantry, cavalry and artillery components. Its origins lied in the Sikh jathas of the late 17th and early 18th centuries which passed onto the Sikh Misl (Confederacy) period of the later 18th century. These were typically cavalry based and engaged in hit and run tactics against the Mughals, Maratha and Afghans. Later Ranjit would modernize the Sikh army along European principles utilizing European and American recruited officers and by purchasing and developing modern weapons.
The military were given performance standards for logistics of troop deployment, maneuver and marksmanship. Likewise, the army was divided into three segments of elite troops, regulars and irregulars. Each with its own infantry, cavalry and artillery component. Even European style medals and awards for merit could be issued, including the Order of Merit with Ranjit's portrait featured on the medal.
Ultimately, the empire's military was a synthesis of modern (19th century) Western organization, discipline and technology with the original Indian cavalry hit and tactics and methods of its Sikh jatha forebearers.
Its infantry composition was not just Western officers and Sikhs of the Punjab for originally Sikhs looked down upon the infantry and so Afghans, Dogras and Nepali Gurkhas among others filled the infantry ranks. In time Punjabi Sikhs joined its ranks too. It reached over 50,000 in strength.
The cavalry reached a strength of 10,000 strong and consisted of Sikhs mainly, given their traditional use of cavalry dating back to jatha and misl eras preceding the 19th century.
The artillery was made up of 5,000 gunners at its peak with heavy cannons pulled by elephants, medium cannon pulled by oxen, light cannon pulled by horses and some mixed guns pulled by camels.
The traditional enemies of the empire in war consisted of the Afghans who presented its greatest threat from the West, the Sikhs pushed the Afghans from the Punjab and pressed into Afghanistan itself before being checked at the border, this demarcated the empire's western limit.
Other enemies included the Kingdom of Nepal which the Sikhs defeated. The Sikh Empire and its vassal the Dogra Rajput also fought against the Chinese Qing Empire and its vassal Tibet which resulted into a military stalemate but saw brief occupation of parts of Western Tibet in the early 1840s.
Its terminal enemy was the British East India Company which would face and defeat the Sikh Empire in two wars (1845-1846 and 1848-1849). The second war would lead to the British annexation of the Punjab and formal cessation of the Sikh Empire.
Lifespan: The empire's origins date back to the 18th century formation of the Sikh Misls within the Punjab and its gradual union under Ranjit Singh. Formally dated to start his 1799 capture of Lahore. In 1801 Ranjit was formally coronated as Maharaja of the Punjab.
Over the next several decades the empire would expand in several directions with the gradual defeat of the Afghans and Marathas who warred in the vicinity of the Punjab.
1809 saw Ranjit Singh sign a treaty of friendship with the British East India Company (EIC). This treaty requested Sikh help against the French should they attack EIC possessions elsewhere in India. Also, the Sikhs were not to pursue conquest south of the Sutlej River which acted as a border between Sikh and British spheres of influence. In reality this bought Ranjit time to focus on expanding against the Afghans in Punjab and Kashmir.
The empire expanded well into the fall reaches beyond Kashmir and Jammu and gained vassals in the Ladakh region. Likewise, the Sikhs would go onto fight the Nepalese (Gurkhas) and check their advance towards Kashmir.
The empire's lifespan very much mirrored with its founder Ranjit Singh's. Ranjit Singh had unified the Sikh Misls of the Punjab through alliance and conquest, and he driven out the Afghan invaders and expanded the Sikh polity he created to vast territories with tributary states of its own. He also gained riches from conquest, meritorious tax collections and trade agreements. Financed religious temple constructions of various faiths and modernized the military. Yet while his empire was on the surface strong, it was to peak with his demise in 1839. His health had declined in the 1830s due to a stroke and alcoholism as noted by many observers. He was said to treat his chronic pain with alcohol and opium though conversely, he refused to eat beef or smoke and was somewhat health conscious. Ultimately it was said he died of a combination of stroke and his failing liver due to his excessive alcohol consumption. He was cremated and four of his Hindu wives are said to have committed sati (ritualistic devotional suicide of widows by casting oneself onto the husband's burning funeral pyre) in a final act of martial devotion to their departed spouse.
In Ranjit Singh's wake, his sons and grandsons found themselves competing for succession, their were deep internal divisions and who to support and in quick order a son, grandson and two more sons of Ranjit took control with the youngest son Duleep Singh taking "control" at age five in 1843 and he would nominally reign for six years. He had a regency under his mother Jind Kaur for the years of his rule.
Following Ranjit's death, the internal division over support of his successors along with the ruling elite of the army which saw itself as the true extension of state and religion was convinced to go to war with the British in 1845-46. The Sikh administrators were said by the British to undermine the plurality and tolerance under Ranjit Singh towards other religions pushing for a Sikh supremacy in all matters. In response, the British began building a military presence along the Sutlej River, viewed as a provocation by the Sikhs. The British stated it was defensive in nature given what they saw as increasing chaos in the Sikh Empire. However, the Sikhs contend it was intended as offensive in nature to goad the empire into war. Whatever the varied causes war began in late 1845 and concluded with British victory in 1846. The result was the partial subjugation of the Sikh Empire with some territory and monies being ceded to the British. Also, separately Kashmir would be sold the to the princely state of Jammu (under British sponsorship).
Tensions between both the Sikhs and British remained which culminated in a second war in 1848-49 and saw the Sikhs fight valiantly but once more defeated. In April 1849 at Lahore, the British annexed the Punjab up to the fortress of Peshawar, gateway to the Khyber Pass towards Afghanistan. The British East India Company turned the Sikh Empire into the Punjab and North-West Frontier Province regions in modern Pakistan and India.
The British were impressed with the military prowess of the Sikhs, in part due to the religious devotion of its troops and in part due to the modernization efforts of Ranjit Singh and his able commanders. The conquest of the Sikh Empire served as the removal of last major obstacle to British rule over the whole of India. Recognizing the prowess of Sikh troops, the British were quick to incorporate them into the British Indian Army. A role they would play from the 1850s including during the Indian Rebellion of 1857 until World War II and the eventual granting of independence to India and Pakistan.
Duleep Singh was brought up in exile in Europe following the British annexation of the Sikh Empire, his teenage years spent in Scotland. He would go onto have family there and the Crown Jewels of the UK now in possession of the British Royal Family would incorporate some of its jewels taken from the Sikh Empire's Duleep Singh. Queen Victoria received the Koh-i-noor diamond which is set in the Queen Mother's crown to this day. The diamond dates back to the Mughal Empire and changed hands with the Persian looting of Delhi to Nader Shah before ending up in the Durrani Empire of Afghanistan and then the Sikh Empire under Ranjit Singh and finally with the British as a gift to Queen Victoria as it was formally surrendered to the EIC and then gifted to the queen. The modern governments of India, Pakistan Afghanistan (including the Taliban) and Iran have all demanded its return to them respectively, a demand which Britain's government has rejected. In 2018, India's Supreme Court & the Archeological Survey of India supported Britain's legal claim, stating the Treaty of Lahore in 1849 secured it through voluntary surrender, stating it was neither stolen nor taken by force, so it remains with the British Crown despite ongoing controversy.
Though the Sikh Empire lasted only half a century for the reasons outlined above, it is a polity worthy of study. First and foremost, its historical place in India as the last major bastion of independent native resistance before total British rule has endeared it to some Indian and Pakistani nationalists and international anticolonial narratives. The British recognized through its occasional defeats in battle at the hands of the Sikhs that they were a force to be reckoned with. Both sides earned a begrudging martial respect for the other following the two wars they fought. The British were keen to utilize the Sikhs for their own military, for which they served over the next century in many campaigns worldwide. Outside from its place in narratives of native resistance to colonial rule and its well-founded military prowess. The empire is relatively unique for its synthesis of administrative help from both within India and the West. Much of this can be chalked up to Ranjit Singh's personally pragmatic and disciplined approach to governance. Quite simply put Ranjit Singh wanted what he thought were the most qualified leaders regardless of ethnic or cultural background. Their merit as modernizers and reformers coupled with personal loyalty were prized above religious or ethnic affinity. Finally, the Sikh Empire is noteworthy simply for being to date the only Sikh run imperial polity in world history. Though it was the successor of the Sikh Misls which had a unified common defense, these misls were essentially politically independent in their own right rather than a singular polity. The Sikh Empire is the only time in history that a ruling dynasty over a vast territorial expanse came from practitioners of that religion and it was supported by an army and administration centered around that faith as well.
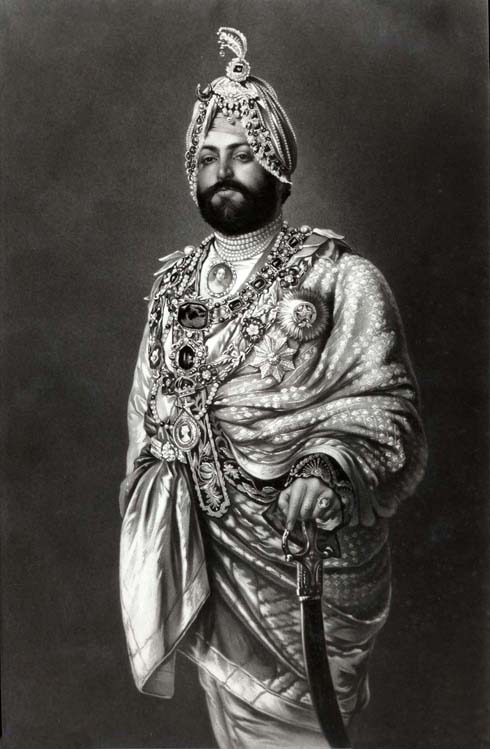
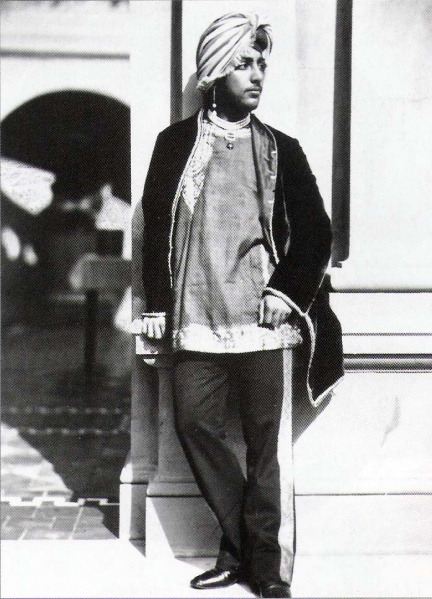
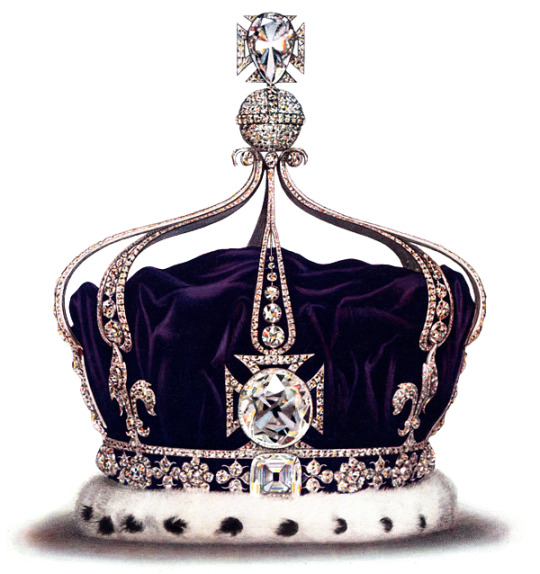




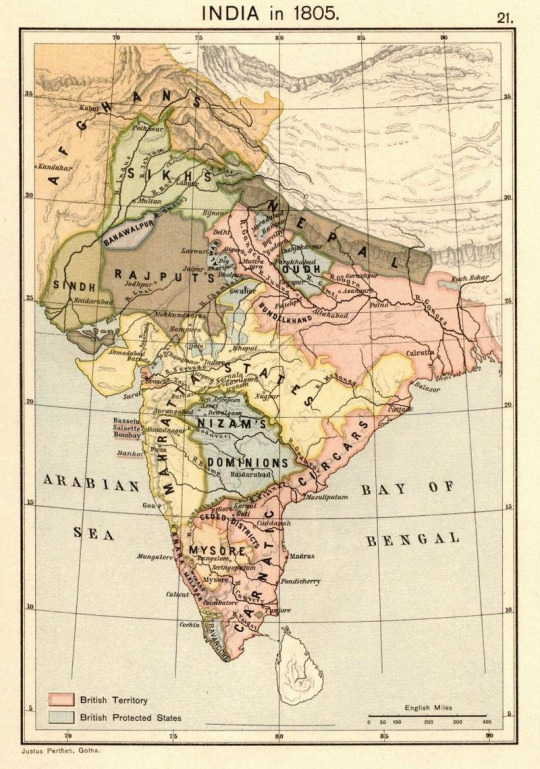






#military history#history#sikh#sikhism#india#british east india company#british imperialism#british empire#19th century#victorian era#ranjit singh#punjab#pakistan#18th century#mughal empire#maratha empire#queen victoria#british india
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
They shut down Twitter in the country too so we have to use vpn, such pussies of an army we have
#well i already had vpn for tumblr anyways lol#smh them turning this country slowly into north korea is what i feared#Pakistan#current events#news#politics#military
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

1 note
·
View note