#viral video 2021
Text

Worlds first quad 540.
Watch Now
#viral#reels#fbreels#quad#viral video#viral videos#viral tiktok video#up viral video#video viral#viral video 2021#2022 viral video#how to viral video#viral video today#viral video tiktok#viral video tik tok#urfi javed viral video#latest viral videos#berita viral#ghost prank viral video#african boy viral video#social media viral video#kulhad pizza viral video#lion lion lion viral video#eknath shinde viral video#ambedkar nagar viral video
1 note
·
View note
Text
dailymotion
#funny video#funny videos#funny videos 2022#funny#funny fail video#funny video 2022#afv funny videos#new funny video#funny fails#funny videos 2021#best funny videos#funny animal videos#best funny videos 2021#funniest video#fail videos#funny fails video#viral funny video#funny cat videos#funny cats#afv funniest videos#funny dog#funny moments#americas funniest home videos#americas funniest videos#funny fails 2022#funny dog video
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
#levandowski#edit#shorts#efootball#viral#trending#like#shortsfeed#gaming#gamingvideos#gamingshorts#subscribe#cinemagameedits#anthony levandowski faces new claims of stealing trade secrets#champions league 2021#goles champions league#keşfet#aboneolun#youtubeshorts#shorts video#ronaldo
0 notes
Text
#youtube#viral#video upload karny sy pehlay yeh setting kar lain#youtube par video kaise upload kare#youtube per video upload karen pura setting ke sath#youtube per video upload kaise karen#youtube video upload kaise kare#mobile se video kaise upload kare#youtube video upload kaise kare 2021#youtube mein video upload karne ka sahi tarika#youtube video upload karne ka sahi tarika#trading kaise karte hain#video par views kaise laye#video par views kaise badhaye#videomarketing
0 notes
Text
Go_A - Shum
2021
"Shum" ("Noise") is a song by Ukrainian electro-folk band Go_A, and represented Ukraine in the Eurovision Song Contest 2021, where they ended up number 5. Watch the performance here!
The Eurovision version of the song took the lead in the global Spotify Viral 50 daily list on 24 May 2021, where it stayed until 1 June, and led the weekly list on the week of 27 May. It entered the Billboard Global 200 on the week of 5 June, at position 158, becoming the first ever Ukrainian-language song to chart there. On the same week, it peaked at number 80 on the Billboard Global Excl. US.
The lyrics of this song is a variation of Ukrainian folk songs which were sung in the "Shum" folk ritual. The ritual involved a game and was performed in spring. According to some ethnographers, Shum refers to the god or personification of the forest. Etymologically, the name of the ritual probably comes from Proto-Slavic words šumъ ("noise") or šuma ("forest").
The music video was shot in a forest near the Chernobyl nuclear power plant.
"Shum" recieved a total of 74,4% yes votes!
youtube
2K notes
·
View notes
Link
uhuy spontan tiktok yang sudah viral di tiktok,Apa itu seni Spontan Uhuy ?Simak seni Spontan Uhuy berikut yang kini sedang trending di media sosial Ti
0 notes
Text
#kinderjoy#yudist beli puluhan kinderjoy#kinder joy#500 kinder joy#big kinder joy#new kinder joy#asmr kinder joy#kinder joy inam#kinder joy eggs#beli kinder joy#buka kinder joy#open kinder joy#is it kinder joy#kinder joy 2021#kinder#resep kinder joy#viral kinder joy#kinder joy viral#kinder joy color#kinder joy video#kinder joy india#eating kinder joy#kinder joy rezept#kinder joy recipe#kinder joy colour#yudist kinder joy
0 notes
Text
#chethana raj actress#bhojpuri actress viral video 2021#hamida actress#actress priyanka pandit#who is the lead actress in the movie queen#cinema#bollywood#tollywood actress#actors#beauty
1 note
·
View note
Text
Google reneged on the monopolistic bargain

I'm on tour with my new novel The Bezzle! Catch me TONIGHT in SALT LAKE CITY (Feb 21, Weller Book Works) and TOMORROW in SAN DIEGO (Feb 22, Mysterious Galaxy). After that, it's LA, Seattle, Portland, Phoenix and more!

A funny thing happened on the way to the enshittocene: Google – which astonished the world when it reinvented search, blowing Altavista and Yahoo out of the water with a search tool that seemed magic – suddenly turned into a pile of shit.
Google's search results are terrible. The top of the page is dominated by spam, scams, and ads. A surprising number of those ads are scams. Sometimes, these are high-stakes scams played out by well-resourced adversaries who stand to make a fortune by tricking Google:
https://www.nbcnews.com/tech/tech-news/phone-numbers-airlines-listed-google-directed-scammers-rcna94766
But often these scams are perpetrated by petty grifters who are making a couple bucks at this. These aren't hyper-resourced, sophisticated attackers. They're the SEO equivalent of script kiddies, and they're running circles around Google:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/24/passive-income/#swiss-cheese-security
Google search is empirically worsening. The SEO industry spends every hour that god sends trying to figure out how to sleaze their way to the top of the search results, and even if Google defeats 99% of these attempts, the 1% that squeak through end up dominating the results page for any consequential query:
https://downloads.webis.de/publications/papers/bevendorff_2024a.pdf
Google insists that this isn't true, and if it is true, it's not their fault because the bad guys out there are so numerous, dedicated and inventive that Google can't help but be overwhelmed by them:
https://searchengineland.com/is-google-search-getting-worse-389658
It wasn't supposed to be this way. Google has long maintained that its scale is the only thing that keeps us safe from the scammers and spammers who would otherwise overwhelm any lesser-resourced defender. That's why it was so imperative that they pursue such aggressive growth, buying up hundreds of companies and integrating their products with search so that every mobile device, every ad, every video, every website, had one of Google's tendrils in it.
This is the argument that Google's defenders have put forward in their messaging on the long-overdue antitrust case against Google, where we learned that Google is spending $26b/year to make sure you never try another search engine:
https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2023-10-27/google-paid-26-3-billion-to-be-default-search-engine-in-2021
Google, we were told, had achieved such intense scale that the normal laws of commercial and technological physics no longer applied. Take security: it's an iron law that "there is no security in obscurity." A system that is only secure when its adversaries don't understand how it works is not a secure system. As Bruce Schneier says, "anyone can design a security system that they themselves can't break. That doesn't mean it works – just that it works for people stupider than them."
And yet, Google operates one of the world's most consequential security system – The Algorithm (TM) – in total secrecy. We're not allowed to know how Google's ranking system works, what its criteria are, or even when it changes: "If we told you that, the spammers would win."
Well, they kept it a secret, and the spammers won anyway.
A viral post by Housefresh – who review air purifiers – describes how Google's algorithmic failures, which send the worst sites to the top of the heap, have made it impossible for high-quality review sites to compete:
https://housefresh.com/david-vs-digital-goliaths/
You've doubtless encountered these bad review sites. Search for "Best ______ 2024" and the results are a series of near-identical lists, strewn with Amazon affiliate links. Google has endlessly tinkered with its guidelines and algorithmic weights for review sites, and none of it has made a difference. For example, when Google instituted a policy that reviewers should "discuss the benefits and drawbacks of something, based on your own original research," sites that had previously regurgitated the same lists of the same top ten Amazon bestsellers "peppered their pages with references to a ‘rigorous testing process,’ their ‘lab team,’ subject matter experts ‘they collaborated with,’ and complicated methodologies that seem impressive at a cursory look."
But these grandiose claims – like the 67 air purifiers supposedly tested in Better Homes and Gardens's Des Moines lab – result in zero in-depth reviews and no published data. Moreover, these claims to rigorous testing materialized within a few days of Google changing its search ranking and said that high rankings would be reserved for sites that did testing.
Most damning of all is how the Better Homes and Gardens top air purifiers perform in comparison to the – extensively documented – tests performed by Housefresh: "plagued by high-priced and underperforming units, Amazon bestsellers with dubious origins (that also underperform), and even subpar devices from companies that market their products with phrases like ‘the Tesla of air purifiers.’"
One of the top ranked items on BH&G comes from Molekule, a company that filed for bankruptcy after being sued for false advertising. The model BH&G chose was ranked "the worst air purifier tested" by Wirecutter and "not living up to the hype" by Consumer Reports. Either BH&G's rigorous testing process is a fiction that they infused their site with in response to a Google policy change, or BH&G absolutely sucks at rigorous testing.
BH&G's competitors commit the same sins – literally, the exact same sins. Real Simple's reviews list the same photographer and the photos seem to have been taken in the same place. They also list the same person as their "expert." Real Simple has the same corporate parent as BH&G: Dotdash Meredith. As Housefresh shows, there's a lot of Dotdash Meredith review photos that seem to have been taken in the same place, by the same person.
But the competitors of these magazines are no better. Buzzfeed lists 22 air purifiers, including that crapgadget from Molekule. Their "methodology" is to include screenshots of Amazon reviews.
A lot of the top ranked sites for air purifiers are once-great magazines that have been bought and enshittified by private equity giants, like Popular Science, which began as a magazine in 1872 and became a shambling zombie in 2023, after its PE owners North Equity LLC decided its googlejuice was worth more than its integrity and turned it into a metastatic chumbox of shitty affiliate-link SEO-bait. As Housefresh points out, the marketing team that runs PopSci makes a lot of hay out of the 150 years of trust that went into the magazine, but the actual reviews are thin anaecdotes, unbacked by even the pretense of empiricism (oh, and they loooove Molekule).
Some of the biggest, most powerful, most trusted publications in the world have a side-hustle in quietly producing SEO-friendly "10 Best ___________ of 2024" lists: Rolling Stone, Forbes, US News and Report, CNN, New York Magazine, CNN, CNET, Tom's Guide, and more.
Google literally has one job: to detect this kind of thing and crush it. The deal we made with Google was, "You monopolize search and use your monopoly rents to ensure that we never, ever try another search engine. In return, you will somehow distinguish between low-effort, useless nonsense and good information. You promised us that if you got to be the unelected, permanent overlord of all information access, you would 'organize the world's information and make it universally accessible and useful.'"
They broke the deal.
Companies like CNET used to do real, rigorous product reviews. As Housefresh points out, CNET once bought an entire smart home and used it to test products. Then Red Ventures bought CNET and bet that they could sell the house, switch to vibes-based reviewing, and that Google wouldn't even notice. They were right.
https://www.cnet.com/home/smart-home/welcome-to-the-cnet-smart-home/
Google downranks sites that spend money and time on reviews like Housefresh and GearLab, and crams botshittened content mills like BH&G into our eyeballs instead.
In 1558, Thomas Gresham coined (ahem) Gresham's Law: "Bad money drives out good." When counterfeit money circulates in the economy, anyone who gets a dodgy coin spends it as quickly as they can, because the longer you hold it, the greater the likelihood that someone will detect the fraud and the coin will become worthless. Run this system long enough and all the money in circulation is funny money.
An internet run by Google has its own Gresham's Law: bad sites drive out good. It's not just that BH&G can "test" products at a fraction of the cost of Housefresh – through the simple expedient of doing inadequate tests or no tests at all – so they can put a lot more content up that Housefresh. But that alone wouldn't let them drive Housefresh off the front page of Google's search results. For that, BH&G has to mobilize some of their savings from the no test/bad test lab to do real rigorous science: science in defeating Google's security-through-obscurity system, which lets them command the front page despite publishing worse-than-useless nonsense.
Google has lost the spam wars. In response to the plague of botshit clogging Google search results, the company has invested in…making more botshit:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/16/tweedledumber/#easily-spooked
Last year, Google did a $70b stock buyback. They also laid off 12,000 staffers (whose salaries could have been funded for 27 years by that stock buyback). They just laid off thousands more employees.
That wasn't the deal. The deal was that Google would get a monopoly, and they would spend their monopoly rents to be so good that you could just click "I'm feeling lucky" and be teleported to the very best response to your query. A company that can't figure out the difference between a scam like Better Homes and Gardens and a rigorous review site like Housefresh should be pouring every spare dime it brings in into fixing this problem. Not buying default search status on every platform so that we never try another search engine: they should be fixing their shit.
When Google admits that it's losing the war to these kack-handed spam-farmers, that's frustrating. When they light $26b/year on fire making sure you don't ever get to try anything else, that's very frustrating. When they vaporize seventy billion dollars on financial engineering and shoot one in ten engineers, that's outrageous.
Google's scale has transcended the laws of business physics: they can sell an ever-degrading product and command an ever-greater share of our economy, even as their incompetence dooms any decent, honest venture to obscurity while providing fertile ground – and endless temptation – for scammers.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/21/im-feeling-unlucky/#not-up-to-the-task
#pluralistic#monopoly#seo#dark seo#google#search#enshittification#platform decay#product reviews#spam#antitrust#trustbusting
711 notes
·
View notes
Text
this part seemed relevant to this blue hellsite ⤵️
It's safe to say that a bunch of people bonding over 100-year-old recipes is not what typically comes to mind when you imagine TikTok food content. But, also, Hollis's current online popularity isn't solely thanks to TikTok. He's also attracted a sizable fandom on the sometimes forgotten, but immensely powerful corner of the internet known as Tumblr. In fact, he's so popular that, in April, he entered into the site's top-20 list of web celebrities, according to Cates Holderness, head of editorial at Tumblr. Holderness told Eater the spike was likely because Hollis did a live video where he finally acknowledged his growing fandom on Tumblr.
"It was really funny to see people freaking out in an excited way, like, 'Oh my gosh, this guy that we love has acknowledged us and thanked us in this really sweet and sincere way'," she said. "He's aware that the Tumblr audience is there, but he's very nervous to interact with it."
Hollis's videos are regularly downloaded from TikTok and re-uploaded on Tumblr, where they have long, very viral second lives, which is actually common for popular TikTok, in general. But, according to Holderness, the thing that really ignited Hollis's fandom on the platform was a text post from 2021 written by a user named @thestuffedalligator. It was shared 25,000 times and reads:
The main thing I get from Dylan Hollis cooking old recipes is this:
Recipes from the 1910s and the Great Depression are great, and I suspect it's because they were made by someone with limited resources. But they found a way to make something good, maybe even something fantastic with those limited resources, and they wanted to write it down and share with their friends so that they could also make something out of saltines and potatoes. Recipes from the 1910s and the Great Depression are written down and shared in love.
The recipes you should fear come from the 1950s and 1960s, which I'm pretty sure are written down and shared as a form of McCarthyism.
"The history side of Tumblr is a very large community," Holderness said. "So it's kind of not surprising that a lot of the recipes that he makes, the older recipes, from the '20s, from the Great Depression, tend to be very popular. The recipes that are either extremely good or extremely terrible, in general, get the most traction."
For what it's worth, Hollis agreed with @thestuffedalligator's post, saying the Great Depression recipes are his favorite and the ones from the '60s are his least favorite; though he doesn't think that McCarthyism is to blame for why recipes from that era are so inedible. Instead, he thinks it was because bringing Jell-O to a potluck was a way to signify that you had enough money to own a refrigerator, and gelatin was marketed to women as a way to stay slim.
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
Value your life, the best of us pay the highest price for it
Denys Zelenyi, a soldier of the Bureviy National Guard Brigade, died at the front yesterday.
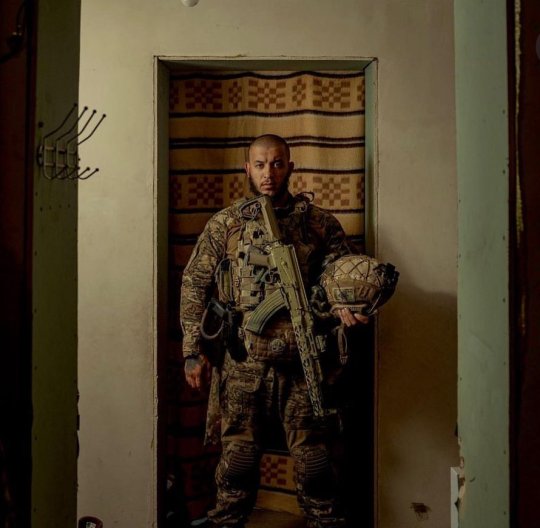

He used to work as a manager at the Honey confectionery chain. You may remember him from the video "Do you spik paskas [bake Easter bread]?" that went viral.
2021:
- Do you bake Easter bread?
- Yes, I bake!
2022:
- Do you bake Easter bread?
- Yes, I bake and russians too.
2023:
We baked, are baking, and will continue to bake.
2024:
I'm baking, dear, I'm baking!
That's how he will be remembered for his humor. He left behind a lot of beauty in our history.
Denys Zelenyi is also the author of the famous photo of Serebryanyi Forest, where fierce fighting is taking place.
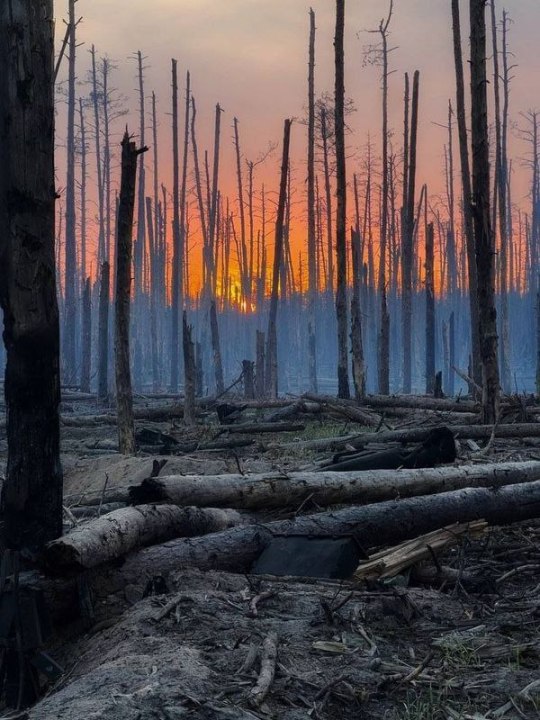

You could remember it from posts comparison to burning down forests in France in the period of World War I.
Eternal honor to the fallen hero.
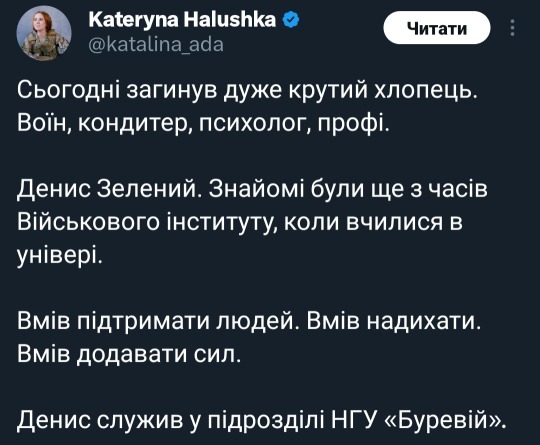
A very cool guy died today. A warrior, a confectioner, a psychologist, a pro.
Denys Zelenyi. We have known each other since the days of the Military Institute, when we studied at the university.
He knew how to support people. He knew how to inspire. He knew how to give strength.
Denys served in the Bureviy unit of the National Guard of Ukraine.


Don't be indifferent. Please hear our cry out to the world, keep spreading our voices, and donate to our army and combat medics (savelife.in.ua, prytulafoundation.org, Serhii Sternenko, hospitallers.life, ptahy.vidchui.org, and u24.gov.ua).
#ukraine#russia is a terrorist state#russo ukrainian war#russian invasion of ukraine#genocide#stop the genocide#russia must burn#war in ukraine#loss#world#stand with ukraine#standwithukraine#arm ukraine#important#signal boost#video#unmute#sound on#i love this video#український tumblr#український тамблер#fallen heroes#russian colonialism#donate if you can#please donate#help if you can#please reblog
61 notes
·
View notes
Text

Hello, I prepared some statistics to give you a short overview of Ghost's amazingly successful 2022. It is based on data I collected between 22/12/2021 and 22/12/2022.
-
The big Ghost event of 2022 was of course the release of the band's fifth album, IMPERA.
Since March 11, it has sold nearly 500,000 copies, won the American Music Award for Favorite Rock Album and received a Grammy nomination for Best Metal Performance ('Call Me Little Sunshine').
Within the first week of its release, the album reached #2 on the Billboard 200 (ranking the 200 most popular music albums and EPs in the United States) and ranked in the top 20 best-selling albums in 19 countries across the world:
#1 in Sweden, Austria, Germany, Finland, Spain
#2 in US, UK, Belgium, Norway, Netherlands
#3 in Australia, Canada
#5 in Switzerland, Ireland, France
#7 in Poland
#8 in Hungary
#12 in Denmark, Portugal
#20 in Italy
IMPERA is Ghost’s best charting album to date.
-
On YouTube, the band amassed a staggering 260 million views. 840,000 people subscribed to the channel this year, which makes up 42% of all current subscribers.
5 most watched videos on YouTube in 2022:
Mary On A Cross (Official Audio) – 32 million views
Call Me Little Sunshine (Official Music Video) – 15 million views
Square Hammer (Official Music Video) – 11 million views
Mary On A Cross (Live in Tampa 2022) – 8.2 million views
Spillways (Official Music Video) – 6.8 million views
-
On Spotify, the band amassed 1,285,625 new followers. That’s around 61% of all followers since the band appeared on the platform.
5 most streamed songs on Spotify in 2022:
Mary On A Cross - 193,709,473 streams
Call Me Little Sunshine – 41,108,589 streams
Square Hammer – 29,720,042 streams
Dance Macabre – 26,494,053 streams
Spillways – 24,910,870 streams
-
It goes without saying that the viral success of Mary On A Cross on TikTok brought in a lot of new fans this year, but the magnitude of it becomes even more astonishing if you look at numbers.
On this graph, I marked a few events that resulted in a noticeable spike in the number of monthly listeners on Spotify, including the approximate time when MOAC began to gain traction on TikTok. As you can see, nothing, not even the release of a new album, gave the band as much attention as the 3-year old song suddenly raising in popularity on one single platform.
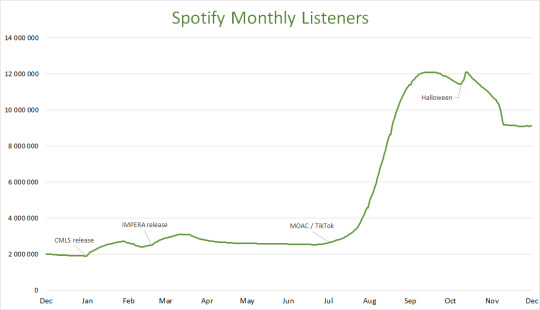
Between end of July and beginning of October, the number of monthly listeners on Spotify skyrocketed from 2.5 million to 12 million. This is a 380% increase.
Although the numbers have been in decline since then, it appears that for the past month they have stayed at a steady 9 million. As of today (Dec 22, 2022) the exact number is 9,110,996. Exactly a year ago (Dec 22, 2021) the number was 1,999,951. A hefty 355% increase in only a year.
-
Some other milestones and fun facts:
On June 7, Cirice, Dance Macabre, and Square Hammer were all certified Gold by the RIAA for sales of 500,000 units in the USA. Following the viral success, Mary On A Cross was also certified Gold on November 20.
The band's most liked post on Instagram this year was a video of Papa throwing the first pitch at the White Sox game (273,241 likes).
The episode of Jimmy Kimmel Live where Ghost performed Call Me Little Sunshine was watched by around 1.3 million people.
In September, Ghost reached over 12 million monthly listeners on Spotify and was the 450th most streamed artist globally - that's 450 out of over 11 million!
As of today with over 1.6 billion accumulated streams Ghost is one of the 1,000 most successful artists on the platform of all time (currently #808).
On September 11, Mary On A Cross peaked at #1 in the Viral Hits chart on Spotify in 54 countries across the world.
It was also the highest charting Swedish song on the platform in 2022, peaking globally at #31.
-
At this point I think it’s safe to declare that Ghost’s global success reached unprecedent heights this year and even allowed them to officially join the ranks of mainstream artists. With all of the above, 70 completed shows this year and many more to come in 2023, and with media of the likes of The Wall Street Journal proclaiming Ghost “the next generation of arena stars,” it looks like that the band is well on the way to become one of the biggest rock acts of this century. Not bad for a side project started by one Swede in his bedroom somewhere in Linköping.
Let us hope 2023 will be as devilishly good!

692 notes
·
View notes
Text
the internet is rotting, as Jonathan Zittrain noted in an important (but paywalled) 2021 Atlantic article. A huge percentage of the links on the internet are broken, and there is no single authoritative, accessible universal repository that keeps track of everything. It is frighteningly easy for crucial information to slip away. ...
The practice of making changes to an article without noting that you’ve made them is called “stealth editing,” and even the New York Times does it. ... The existence of stealth editing means that it’s difficult to trust that the version of an article you click on at any given moment is the article as it was originally published. ...
I also, to my alarm, realized just how dependent we are on private publications themselves to give us access to records of their own work. Often, they keep it payawalled behind locked gates and charge you admission if you want to have a look. There are lots of sources in the Chomsky book to which you have to subscribe if you want to verify, such as this 1999 story in the Los Angeles Times about NATO’s bombing of a bus in Yugoslavia. This is a story of national importance, far too overlooked at the time, but if you don’t subscribe to the LA Times, you need research library access or a workaround if you want to read it.
Thank God for the Internet Archive, whose Wayback Machine preserves as much of the internet as they can and is invaluable for researchers trying to figure out what was once housed at now-dead links. But the Internet Archive has its limits. Social media posts, YouTube videos, paywalled Substack posts, PDFs—all can be very difficult to track down after they disappear. If a politician tweets something embarrassing, for instance, and then deletes it, it might be preserved in a screenshot. But we know screenshots are easy to fake. So where do you turn to prove satisfactorily that something was in fact said? ...
it’s very easy to lose pieces of information that seem permanent. E-books, for instance, can be changed by their publisher without the changes even being noted. You might read a book on your Amazon Kindle one day and open it up the next day to look for a quote only to find that the quote has disappeared without a trace. The Guardian, for twenty years, hosted a copy of Osama bin Laden’s “letter to the American people,” an important historical document. After the letter went viral on TikTok, the Guardian removed it from the site entirely. The New Republic did the same after an article of theirs about Pete Buttigieg caused controversy. The documents in question can still be found, but only by digging through the Internet Archive. If that ever goes down, researchers will find that trying to piece together the online past is like trying to learn about a lost civilization from excavated fragments. ...
I think that in an age where people (rightly) don’t trust the information they’re getting to be true, it needs to be as easy as possible to do research. Instead, while we have better technology than ever for sifting through information, it’s still the case that the truth is paywalled and the lies are free. If you want to “do your own research” to check on the veracity of claims, you will run headlong into a maze of broken links, paywalls, and pop-ups. How can anyone hope to find the truth when it’s so elusive, trapped behind so many toll gates?
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
It was always going to end this way. The truth about Catherine Middleton’s absence is far less funny, whimsical, or salacious than the endless memes and conspiracy theories suggested.
In a video recorded and broadcast by the BBC, the princess says she has cancer and that she had retreated from the public eye to deal with her condition, while attempting to shield her children from the spotlight.
Instead, she had to contend with the internet giggling about whether she’d had a Brazilian butt lift.
My colleague Helen Lewis summed it up succinctly this afternoon: “I Hope You All Feel Terrible Now.”
What is there to learn from such a sad situation? The internet is made up of people, yet its architecture abstracts this basic truth.
As I wrote a few weeks ago, at the center of this months-long story was essentially “a sea of people having fun online because it is unclear whether a famous person is well or not.”
Underneath the memes was always something a little bit gross and indefensible.
Perhaps humans are just wired this way — to gawk and gossip.
There’s nothing new about hounding a member of the royal family or invading the privacy of a celebrity to sell tabloids or go viral.
You don’t even have to be a scold about it: Famous people are wealthy and beloved at least in part because they’re fun to talk about.
Exactly what we do and don’t know about their internal lives is part of the allure — the discourse comes with the territory to a degree.
But Catherine Middleton, of course, is a human too.

During this saga, I kept thinking about the reappraisal of Britney Spears in 2021, as well as the backlash toward past media and tabloid coverage of her rise.
A New York Times documentary dredged up old coverage of Spears from the mid-aughts, showing a young woman clearly in distress, being picked apart by glossy magazines.
Her suffering became entertainment. The response to this film was swift.
Some of the people and institutions that had shamelessly delighted in her pain backtracked: Glamour publicly apologized to the pop star on its Instagram account, noting, “We are all to blame for what happened to Britney Spears.”
Contrast the Spears reckoning with the Middleton drama and, if you’re being generous, you can see some of that newfound attitude in the media.
I was struck by Lewis’s observation that “Britain’s tabloid papers have shown remarkable restraint” throughout this mess.
Progress, perhaps, but what’s also telling is that they didn’t really need to do the dirty work: Random people on the internet were doing it for them.
They recklessly speculated, memed, and used their amateur sleuthing and networked faux expertise to concoct elaborate, semi-plausible explanations for her absence.
Was Catherine’s face actually Photoshopped from a Vogue spread? It wasn’t, but the conspiratorial tweet got 51.1 million views anyhow.
Missing from much of the discourse was the idea that its main character was a person who was likely struggling.
In essence, the internet democratized the tabloid experience, turning the rest of us into paparazzi and addled editors workshopping headlines and cover images — not to sell magazines but to amass some kind of fleeting online popularity.
In my least charitable moments, I see this toxic dynamic as the lasting legacy of social media — a giant, metrics-infused experiment in connectivity that has had a flattening, pernicious effect.
In 2021, I interviewed Elle Hunt, a journalist who’d tweeted an innocuous opinion about horror movies one evening and woke up to find she was trending on Twitter, her feeds choked with thousands of furious replies and threats.
When I asked her to describe the experience of becoming Twitter’s main character for the day, she summed it up thusly:
“You’re repurposed as fodder for content generation in a way that’s just so dehumanizing.”
Three years later, these words resonate even stronger.
What Hunt described to me then as “a platform failure,” feels to me now like a learned behavior of the internet, where people, famous and not, are repurposed as fodder for content generation. The cycle repeats itself endlessly.
This afternoon, the memes about Middleton shifted — from jokes about her whereabouts to jokes about how awful it was that everyone had been making fun of a cancer patient.
Feeling bad about the memes tweets immediately became a meme unto themselves.
Despite the tone shift, the reason for these posts is the same: They’re a way to take a person and repurpose their life for entertainment and engagement.
If this sounds exhausting and depressing, it’s because it is.
But the internet is also too big to be one thing. Clicking through social media this afternoon, I saw dozens of heartfelt testimonials, apologies, and well-wishes for the princess.
For a moment, from my perspective, it felt like watching a collective of people come to their senses.
A recognition, perhaps, of the humanity of the person at the center of the maelstrom.
Then, only a few seconds later, I saw a different post. It was a screenshot from the blockchain platform Solana, where users can create their own cryptographic tokens for others to invest in.
The name of the token in the screenshot is “kate wif cancer,” and its logo is a still of the princess sitting on a bench, taken from this afternoon’s video.
The coin’s market cap briefly surpassed $120,000. Only six minutes later, the price had cratered — the result of a standard memecoin sell off.
An awful thing happened. Some people made a joke about it. Other people made some money. And then everyone moved on.

NOTE: Edited
#Princess of Wales#Catherine Princess of Wales#Catherine Middleton#Kate Middleton#British Royal Family#cancer#chemotherapy#internet#memes#fake news#disinformation#misinformation#platform failure#social media
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the hours after Iran announced its drone and missile attack on Israel on April 13, fake and misleading posts went viral almost immediately on X. The Institute for Strategic Dialogue (ISD), a nonprofit think tank, found a number of posts that claimed to reveal the strikes and their impact, but that instead used AI-generated videos, photos, and repurposed footage from other conflicts which showed rockets launching into the night, explosions, and even President Joe Biden in military fatigues.
Just 34 of these misleading posts received more than 37 million views, according to ISD. Many of the accounts posting the misinformation were also verified, meaning they have paid X $8 per month for the “blue tick” and that their content is amplified by the platform’s algorithm. ISD also found that several of the accounts claimed to be open source intelligence (OSINT) experts, which has, in recent years, become another way of lending legitimacy to their posts.
One X post claimed that “WW3 has officially started,” and included a video seeming to show rockets being shot into the night—except the video was actually from a YouTube video posted in 2021. Another post claimed to show the use of the Iron Dome, Israel's missile defense system, during the attack, but the video was actually from October 2023. Both these posts garnered hundreds of thousands of views in the hours after the strike was announced, and both originated from verified accounts. Iranian media also shared a video of the wildfires in Chile earlier this year, claiming it showed the aftermath of the attacks. This, too, began to circulate on X.
“The fact that so much mis- and disinformation is being spread by accounts looking for clout or financial benefit is giving cover to even more nefarious actors, including Iranian state media outlets who are passing off footage from the Chilean wildfires as damage from Iranian strikes on Israel to claim the operation as a military success,” says Isabelle Frances-Wright, director of technology and society at ISD. “The corrosion of the information landscape is undermining the ability of audiences to distinguish truth from falsehood on a terrible scale.”
X did not respond to a request for comment by time of publication.
Though misinformation around conflict and crises has long found a home on social media, X is often also used for vital real-time information. But under Elon Musk’s leadership, the company cut back on content moderation, and disinformation has thrived. In the days following the October 7 Hamas attack, X was flooded with disinformation, making it difficult for legitimate OSINT researchers to surface information. Under Musk, X has promoted a crowdsourced community notes function as a way to combat misinformation on the platform to varying results. Some of the content identified by ISD has since received community notes, though only two posts had by the time the organization published its findings.
“During times of crisis it seems to be a repeating pattern on platforms such as X where premium accounts are inherently tainting the information ecosystem with half-truths as well as falsehoods, either through misidentified media or blatantly false imagery suggesting that an event has been caused by a certain actor or state,” says Moustafa Ayad, ISD executive director for Asia, the Middle East, and Africa. “This continues to happen and will continue to happen in the future, making it even more difficult to know what is real and what is not.”
And for those that are part of X’s subscription model and ad revenue sharing model, going viral could potentially mean making money.
Though it’s not clear that any of the users spreading fake or misleading information identified by ISD were monetizing their content, a separate report released by the Center for Countering Digital Hate (CCDH) earlier this month found that between October 7 and February 7, 10 influencers, including far-right influencer Jackson Hinkle, were able to grow their followings by posting antisemitic and Islamophobic content about the conflict. Six of the accounts CCDH examined were part of X’s subscription program, and all 10 were verified users. The high-profile influencers who are part of X’s ad revenue sharing program receive a cut of advertising revenue based on ”organic impressions of ads displayed in replies” to their content, according to the company.
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
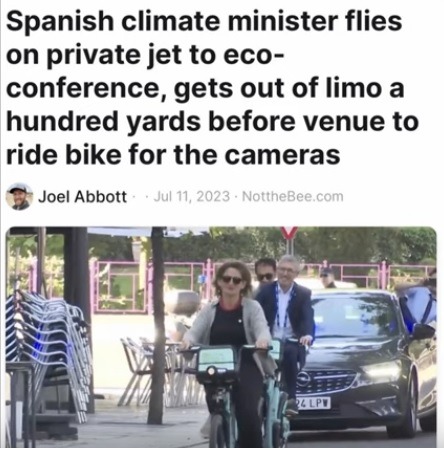
Cl🤡wn World Headlines
Spanish leader Teresa Ribera went viral after she pulled a fake bike ride to a climate conference held by the European Union, a move reminiscent of U.S. Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg’s 2021 bike stunt. Video surfaced on social media on Tuesday from the EU 2023 ES conference held in Madrid, Spain, that showed Ribera riding a bike to the conference. However, now Ribera is facing a backlash after it was revealed as nothing but reportedly a PR stunt
https://www.dailywire.com/news/spanish-leader-goes-viral-after-pulling-a-buttigieg-with-fake-bike-ride
172 notes
·
View notes