#what is DevOps
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Explore the fundamentals of DevOps, its core methodologies, and best practices for implementation. This guide explains how DevOps fosters collaboration between development and operations teams, resulting in faster software delivery and better quality control.
0 notes
Text
What is DevOps?
DevOps is a partnership between IT Operations and Development that enables automated and repeatable software development and deployment. The firm can provide software applications and services more quickly thanks to DevOps. The words “Development” and “Operations” are combined to make the full term “DevOps.”
1 note
·
View note
Text

What is a DevOps Master Program?
A DevOps Master Program is a complicated, hands-on, getting-to-know-you route designed for IT experts and engineers looking to construct a stable foundation in DevOps equipment, practices, and strategies — and take their careers to the next level.
#devops#technology#What is a DevOps Master Program?#programming#education#language#skill development
0 notes
Text
Why AI and ML Are the Future of Scalable MLOps Workflows?

In today’s fast-paced world of machine learning, speed and accuracy are paramount. But how can businesses ensure that their ML models are continuously improving, deployed efficiently, and constantly monitored for peak performance? Enter MLOps—a game-changing approach that combines the best of machine learning and operations to streamline the entire lifecycle of AI models. And now, with the infusion of AI and ML into MLOps itself, the possibilities are growing even more exciting.
Imagine a world where model deployment isn’t just automated but intelligently optimized, where model monitoring happens in real-time without human intervention, and where continuous learning is baked into every step of the process. This isn’t a far-off vision—it’s the future of MLOps, and AI/ML is at its heart. Let’s dive into how these powerful technologies are transforming MLOps and taking machine learning to the next level.
What is MLOps?
MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) combines machine learning and operations to streamline the end-to-end lifecycle of ML models. It ensures faster deployment, continuous improvement, and efficient management of models in production. MLOps is crucial for automating tasks, reducing manual intervention, and maintaining model performance over time.
Key Components of MLOps
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Automates testing, integration, and deployment of models, ensuring faster updates and minimal manual effort.
Model Versioning: Tracks different model versions for easy comparison, rollback, and collaboration.
Model Testing: Validates models against real-world data to ensure performance, accuracy, and reliability through automated tests.
Monitoring and Management: Continuously tracks model performance to detect issues like drift, ensuring timely updates and interventions.
Differences Between Traditional Software DevOps and MLOps
Focus: DevOps handles software code deployment, while MLOps focuses on managing evolving ML models.
Data Dependency: MLOps requires constant data handling and preprocessing, unlike DevOps, which primarily deals with software code.
Monitoring: MLOps monitors model behavior over time, while DevOps focuses on application performance.
Continuous Training: MLOps involves frequent model retraining, unlike traditional DevOps, which deploys software updates less often.
AI/ML in MLOps: A Powerful Partnership
As machine learning continues to evolve, AI and ML technologies are playing an increasingly vital role in enhancing MLOps workflows. Together, they bring intelligence, automation, and adaptability to the model lifecycle, making operations smarter, faster, and more efficient.
Enhancing MLOps with AI and ML: By embedding AI/ML capabilities into MLOps, teams can automate critical yet time-consuming tasks, reduce manual errors, and ensure models remain high-performing in production. These technologies don’t just support MLOps—they supercharge it.
Automating Repetitive Tasks: Machine learning algorithms are now used to handle tasks that once required extensive manual effort, such as:
Data Preprocessing: Automatically cleaning, transforming, and validating data.
Feature Engineering: Identifying the most relevant features for a model based on data patterns.
Model Selection and Hyperparameter Tuning: Using AutoML to test multiple algorithms and configurations, selecting the best-performing combination with minimal human input.
This level of automation accelerates model development and ensures consistent, scalable results.
Intelligent Monitoring and Self-Healing: AI also plays a key role in model monitoring and maintenance:
Predictive Monitoring: AI can detect early signs of model drift, performance degradation, or data anomalies before they impact business outcomes.
Self-Healing Systems: Advanced systems can trigger automatic retraining or rollback actions when issues are detected, keeping models accurate and reliable without waiting for manual intervention.
Key Applications of AI/ML in MLOps
AI and machine learning aren’t just being managed by MLOps—they’re actively enhancing it. From training models to scaling systems, AI/ML technologies are being used to automate, optimize, and future-proof the entire machine learning pipeline. Here are some of the key applications:
1. Automated Model Training and Tuning: Traditionally, choosing the right algorithm and tuning hyperparameters required expert knowledge and extensive trial and error. With AI/ML-powered tools like AutoML, this process is now largely automated. These tools can:
Test multiple models simultaneously
Optimize hyperparameters
Select the best-performing configuration
This not only speeds up experimentation but also improves model performance with less manual intervention.
2. Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD): AI streamlines CI/CD pipelines by automating critical tasks in the deployment process. It can:
Validate data consistency and schema changes
Automatically test and promote new models
Reduce deployment risks through anomaly detection
By using AI, teams can achieve faster, safer, and more consistent model deployments at scale.
3. Model Monitoring and Management: Once a model is live, its job isn’t done—constant monitoring is essential. AI systems help by:
Detecting performance drift, data shifts, or anomalies
Sending alerts or triggering automated retraining when issues arise
Ensuring models remain accurate and reliable over time
This proactive approach keeps models aligned with real-world conditions, even as data changes.
4. Scaling and Performance Optimization: As ML workloads grow, resource management becomes critical. AI helps optimize performance by:
Dynamically allocating compute resources based on demand
Predicting system load and scaling infrastructure accordingly
Identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies in real-time
These optimizations lead to cost savings and ensure high availability in large-scale ML deployments.
Benefits of Integrating AI/ML in MLOps
Bringing AI and ML into MLOps doesn’t just refine processes—it transforms them. By embedding intelligence and automation into every stage of the ML lifecycle, organizations can unlock significant operational and strategic advantages. Here are the key benefits:
1. Increased Efficiency and Faster Deployment Cycles: AI-driven automation accelerates everything from data preprocessing to model deployment. With fewer manual steps and smarter workflows, teams can build, test, and deploy models much faster, cutting down time-to-market and allowing quicker experimentation.
2. Enhanced Accuracy in Predictive Models: With ML algorithms optimizing model selection and tuning, the chances of deploying high-performing models increase. AI also ensures that models are continuously evaluated and updated, improving decision-making with more accurate, real-time predictions.
3. Reduced Human Intervention and Manual Errors: Automating repetitive tasks minimizes the risk of human errors, streamlines collaboration, and frees up data scientists and engineers to focus on higher-level strategy and innovation. This leads to more consistent outcomes and reduced operational overhead.
4. Continuous Improvement Through Feedback Loops: AI-powered MLOps systems enable continuous learning. By monitoring model performance and feeding insights back into training pipelines, the system evolves automatically, adjusting to new data and changing environments without manual retraining.
Integrating AI/ML into MLOps doesn’t just make operations smarter—it builds a foundation for scalable, self-improving systems that can keep pace with the demands of modern machine learning.
Future of AI/ML in MLOps
The future of MLOps is poised to become even more intelligent and autonomous, thanks to rapid advancements in AI and ML technologies. Trends like AutoML, reinforcement learning, and explainable AI (XAI) are already reshaping how machine learning workflows are built and managed. AutoML is streamlining the entire modeling process—from data preprocessing to model deployment—making it more accessible and efficient. Reinforcement learning is being explored for dynamic resource optimization and decision-making within pipelines, while explainable AI is becoming essential to ensure transparency, fairness, and trust in automated systems.
Looking ahead, AI/ML will drive the development of fully autonomous machine learning pipelines—systems capable of learning from performance metrics, retraining themselves, and adapting to new data with minimal human input. These self-sustaining workflows will not only improve speed and scalability but also ensure long-term model reliability in real-world environments. As organizations increasingly rely on AI for critical decisions, MLOps will evolve into a more strategic, intelligent framework—one that blends automation, adaptability, and accountability to meet the growing demands of AI-driven enterprises.
As AI and ML continue to evolve, their integration into MLOps is proving to be a game-changer, enabling smarter automation, faster deployments, and more resilient model management. From streamlining repetitive tasks to powering predictive monitoring and self-healing systems, AI/ML is transforming MLOps into a dynamic, intelligent backbone for machine learning at scale. Looking ahead, innovations like AutoML and explainable AI will further refine how we build, deploy, and maintain ML models. For organizations aiming to stay competitive in a data-driven world, embracing AI-powered MLOps isn’t just an option—it’s a necessity. By investing in this synergy today, businesses can future-proof their ML operations and unlock faster, smarter, and more reliable outcomes tomorrow.
#AI and ML#future of AI and ML#What is MLOps#Differences Between Traditional Software DevOps and MLOps#Benefits of Integrating AI/ML in MLOps
0 notes
Video
youtube
🔍 Git Architecture | Understanding the Core of Version Control 🚀
Ever wondered how Git works behind the scenes? This video breaks down the core architecture of Git and how it efficiently tracks changes. Learn:
- 🏗 How Git Stores Data: The difference between snapshots and traditional versioning. - 🔀 Key Components: Working directory, staging area, and local repository explained. - 🌐 Distributed System: How Git enables collaboration without a central server. - 🔧 Commit & Branching Mechanism: Understanding how changes are managed and merged.
Master Git’s architecture and take full control of your code! 💡
👉 https://youtu.be/OHMe-H35xWs
🔔Subscribe & Stay Updated: Don't forget to subscribe and hit the bell icon to receive notifications and stay updated on our latest videos, tutorials & playlists! ClouDolus: https://www.youtube.com/@cloudolus ClouDolus AWS DevOps: https://www.youtube.com/@ClouDolusPro THANKS FOR BEING A PART OF ClouDolus! 🙌✨
#youtube#Git for DevOps GitHub for DevOps version control for DevOps Git commands for beginners GitHub Actions CI/CD DevOps tools CI/CD pipelines Git#What Is Git?What Is Git Core Features and Use Cases?What Is GitHub?What Is GitHub Core Features and Use Cases?What Is GitHub Actions?What Is#cloudolus#cloudoluspro
0 notes
Text
The Best Career Options After Computer Science Engineering
https://krct.ac.in/blog/2024/06/04/the-best-career-options-after-computer-science-engineering/

As a graduate with a degree in Computer Science Engineering, you are stepping into a world brimming with opportunities. The rapid evolution of technology and the expanding digital landscape means that your skills are in high demand across various industries. Whether you are passionate about software development, artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, there is a career suitable to your interests and strengths. In this blog, let us explore some of the best career options after Computer Science Engineering degree.
Best Career Options After Computer Science Engineering
Software Developer/Engineer

Software developers are the architects of the digital world, creating applications that run on computers, smartphones, and other devices. As a software developer, you will be involved in writing code, testing applications, and debugging programs.
KRCT’s robust curriculum ensures you have a strong foundation in programming languages like Java, C++, and Python, making you a prime candidate for this role. You will be tasked with developing and maintaining software applications, collaborating with other developers and engineers; and ensuring that codebases are clean and efficient.
The role requires proficiency in multiple programming languages, a keen problem-solving ability, and meticulous attention to detail.
Data Scientist
Data science is one of the fastest-growing fields, combining statistical analysis, machine learning, and domain knowledge to extract insights from data. KRCT provides the analytical prowess and technical skills needed to thrive in this field.
As a data scientist, you will work with large datasets to reveal trends, build predictive models, and aid decision-making processes. Also, your responsibilities will include collecting and analysing data, constructing machine learning models, and effectively communicating your findings to stakeholders. This career path requires strong statistical and analytical skills, proficiency in tools such as R, Python, and SQL, and the ability to clearly convey complex concepts.
Cybersecurity Analyst

With the increasing number of cyber threats, the demand for cybersecurity analysts is higher than ever. As a cybersecurity analyst, you will monitor networks for suspicious activity, investigate security breaches, and implement necessary security measures to prevent future incidents. Further, this role demands a thorough understanding of security protocols and tools, sharp analytical thinking, and a high level of attention to detail.
Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning Engineer
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are the currently trending and revolutionizing industries, where we can witness significant milestone from healthcare to finance. KRCT’s focus on cutting-edge technologies ensures you have the skills to build and deploy AI/ML models. As an AI/ML engineer, you will work on creating intelligent systems that can learn and adapt over time.
So, your responsibilities will include developing machine learning models, implementing AI solutions, and collaborating with data scientists and software engineers to innovate and enhance technological capabilities. A strong grasp of algorithms and data structures, coupled with programming skills, is essential for this role.
Full-Stack Developer
Full-stack developers are versatile professionals who work on both the front-end and back-end of web applications. Moreover, KRCT equips you with the knowledge of various web technologies, databases, and server management, enabling you to build comprehensive web solutions.
As a full-stack developer, you will design user-friendly interfaces, develop server-side logic, and ensure the smooth operation of web applications. Additionally, this role requires proficiency in multiple programming languages, an understanding of web development frameworks, and the ability to manage databases.
Cloud Solutions Architect
Cloud computing is transforming how businesses operate, and cloud solutions architects are at the forefront of this transformation. KRCT’s curriculum includes cloud computing technologies, preparing you to design and implement scalable, secure, and efficient cloud solutions.
Also, as a cloud solutions architect, you will develop cloud strategies, manage cloud infrastructure, and ensure data security. Furthermore, this role requires in-depth knowledge of cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, along with skills in network management and data security.
DevOps Engineer
DevOps engineers bridge the gap between software development and IT operations, ensuring continuous delivery and integration. KRCT provides a strong foundation in software development, system administration, and automation tools, making you well-suited for this role.
As a DevOps engineer, you will automate processes, manage CI/CD pipelines, and monitor system performance. This role demands proficiency in scripting languages, an understanding of automation tools, and strong problem-solving skills.
Why KRCT?
KRCT stands out as a premier institution for all of its Engineering courses due to its rigorous academic programs, state-of-the-art facilities, and strong industry connections. Our college emphasizes practical learning, ensuring that students are well-versed in current technologies and methodologies. Also, we have the best and experienced faculties in their respective fields.
KRCT’s placement cell has a remarkable track record of securing positions for graduates in top-tier companies. Regular workshops, seminars, and internships are integrated into the curriculum, providing students with valuable industry exposure. Additionally, the college’s focus on research and development encourages students to engage in cutting-edge projects, preparing them for advanced career paths or higher education.
KRCT’s commitment to excellence is reflected in its alumni, who are making significant contributions in various sectors worldwide. The supportive community and extensive network of alumni also provide ongoing mentorship and career guidance to current students.
To Conclude
Graduating from KRCT opens up numerous career options after computer science engineering degree in the technology sector. Whether you choose to become a software developer, data scientist, cybersecurity analyst, AI/ML engineer, full-stack developer, cloud solutions architect, or DevOps engineer, the knowledge and skills you develop during your engineering degree will pave the way for a bright future. Thus, embrace the opportunities, continue learning, and let your passion for technology guide you towards your ideal career path.
Tags:
AIArtificial Intelligence/Machine Learning Engineerb tech course computer sciencecampuscomputer engineering and software engineeringcomputer science engineering courses after 12thCybersecurity AnalystDevOps EngineerFull-Stack Developergovernment job for csegovernment jobs for computer science engineersSoftware Developersoftware engineering degreeswhat are the best placement opportunities in future for cse?which course in engineering is suitable for future?
#krct the top college of technology in trichy#best autonomous college of technology in trichy#top college of technology in trichy#admission#AIArtificial Intelligence/Machine Learning Engineering#b tech course computer science#campus#computer engineering and software engineering#computer science engineering courses after 12th#Cybersecurity Analyst#DevOps Engineer#Full-Stack Developergovernment job for cse#government jobs for computer science engineers#Software Developer#software engineering degrees#what are the best placement opportunities in future for cse?#which course in engineering is suitable for future?why c#Computer science engineering future job opportunities#Computer engineering government job opportunities#Computer engineer job opportunities in abroad#Computer engineering importance in education#Importance of computer engineering
0 notes
Text
#agile development#backend development#conclusion#continuous deployment#continuous integration#deployment#designing#DevOps#DevOps engineer#documentation#FAQs#frontend development#introduction#lean development#maintenance#product manager#Programming Languages#quality assurance engineer#requirement analysis#scrum master#software development#software development jobs#software development life cycle#software engineer#test-driven development#testing#types of software development#user documentation#what is software development
0 notes
Text
How DevOps Development Services Redefine Efficiency | Transformative Solutions
The evolution begins with The DevOps advantage. Harness our expertise for seamless software development. Experience innovation, efficiency, and excellence in every digital endeavor with How we redefine DevOps development services.
0 notes
Text
DevOps is not merely a set of practices or tools, it’s a culture that emphasizes collaboration, communication, and integration between development and IT operations teams
#why we need DevOps culture#what is DevOps culture#Building a DevOps Culture#why DevOps is important#why DevOps is popular#how to build a DevOps culture
0 notes
Text
What language are DevOps tools?

DevOps tools can be developed using various programming languages, and the choice of programming language often depends on factors such as the tool's functionality, target platform, and the preferences of the developers who create and maintain the tool. As a result, DevOps tools are available in a wide range of programming languages. Here are some programming languages commonly used for developing DevOps tools
Python
Python is a popular choice for DevOps tools due to its simplicity, readability, and extensive libraries. It is frequently used for scripting and automation tasks. Tools like Ansible, SaltStack, and many automation scripts are written in Python.
JavaScript/Node.js
JavaScript, especially when used with the Node.js runtime, is commonly used for building web-based DevOps tools and dashboards. Node.js provides excellent support for creating server-side applications and automation scripts.
Go (Golang)
Go is known for its performance, simplicity, and concurrency support. It is used for building lightweight and high-performance DevOps tools. Docker and Kubernetes are examples of projects that heavily rely on Go.
Ruby
Ruby is favored by some DevOps engineers for its elegant syntax and is used in tools like Chef and Puppet for configuration management. Ruby is also the language of choice for creating Ruby on Rails applications, which may be used for DevOps dashboards.
Java
Java is used for building robust and scalable DevOps tools, especially in larger enterprises. Jenkins, a widely-used CI/CD tool, is developed in Java.
Shell Scripting (Bash)
Shell scripting, specifically Bash scripting on Unix/Linux systems, is frequently used for writing quick automation scripts and command-line tools. Many DevOps scripts and one-off automation tasks are written in Bash.
PowerShell
PowerShell is a scripting language developed by Microsoft and is commonly used for automating tasks on Windows-based systems. It's often used in mixed Windows/Linux environments for DevOps automation.
Perl
While less common today, Perl has been historically used for writing system administration and automation scripts. Some legacy DevOps tools may still be written in Perl.
1 note
·
View note
Text
#Docker in DevOps#what is docker#virtual machines#docker container#what is docker in DevOpswhat is docker in DevOps#benefits of docker in DevOps#install docker
1 note
·
View note
Text
#🌟 Preparing for an Azure DevOps interview? Here are the top 5 questions you should know:#1️⃣ What is Azure DevOps?#2️⃣ Describe some Azure DevOps tools. 3️⃣ What is Azure Repos?#4️⃣ What are Azure Pipelines?#5️⃣ Why should I use Azure pipelines and CI/CD?#Get ready to impress your interview techquestions#kloudcourseacademy#AzureDevOps#InterviewPrep#TechQuestions
1 note
·
View note
Text
What do you mean by DevOps?

A Human-Centric Explanation for Modern Tech Enthusiasts
In the modern world of software development and IT operations, buzzwords are everywhere. You’ve probably heard of DevOps—maybe in job descriptions, tech blogs, or even team meetings. But what exactly does it mean? Is it a role, a tool, a methodology, or just another IT trend?
Let’s unpack DevOps in a simple, human-centered way and understand what it really stands for, why it matters, and how it’s transforming the way we build and manage technology.
DevOps: More Than Just a Buzzword
At its core, DevOps is a culture and set of practices that bring together two traditionally separate teams: Development (Dev) and Operations (Ops).
Imagine this: Developers write code and want to deliver features quickly. Operations teams are responsible for keeping systems stable, secure, and running 24/7. Naturally, their goals can clash. DevOps aims to break down the walls between them and promote a collaborative, automated, and efficient approach to software delivery.
DevOps is not a tool you install or a certification you get—it’s a mindset. It emphasizes communication, continuous improvement, and customer-centric thinking.
The Real-World Meaning of DevOps
Let’s make it more relatable with a simple analogy:
Think of a restaurant. The chefs are the developers—they create the product (meals). The waitstaff and kitchen managers are the operations team—they ensure orders are processed correctly, delivered on time, and customer satisfaction remains high.
Now imagine if the chefs never talk to the waitstaff. Orders get mixed up, food goes cold, and customers leave unhappy. DevOps, in this scenario, is the coordination that ensures everyone works together with the same goal: delivering great service quickly and efficiently.
Key Principles of DevOps
Here’s what really makes DevOps tick:
1. Collaboration
DevOps removes the silos between dev and ops teams. Instead of pointing fingers, both sides work together to build, deploy, and maintain software.
2. Automation
Repetitive tasks like testing, deployment, and monitoring are automated. This speeds up delivery and reduces human error.
3. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Developers integrate code changes frequently, and these changes are automatically tested and deployed. This allows new features and fixes to reach users faster.
4. Monitoring and Feedback Loops
DevOps teams don’t stop at deployment. They constantly monitor systems, collect feedback, and improve the product based on real-world usage.
5. Customer-Centric Focus
Ultimately, everything in DevOps revolves around one goal: delivering value to the end-user quickly and reliably.
DevOps Is About Culture First, Tools Second
Many people make the mistake of thinking DevOps is just about learning tools like Docker, Kubernetes, or Jenkins. While these tools are essential to implementing DevOps, they aren’t the core of DevOps.
The foundation is built on trust, shared responsibility, and a willingness to adapt. A team can adopt every DevOps tool out there and still fail if the culture isn’t right.
A real DevOps environment is one where:
Developers care about how the app performs in production.
Operations understand how the app was built.
Both sides own success and failure together.
Why DevOps Matters Today?
In the past, software updates would come every few months. Today, users expect new features, bug fixes, and improvements constantly. Businesses can’t afford long release cycles or system outages.
DevOps enables faster delivery, better quality software, and happier customers.
Some key benefits include:
Faster time-to-market
Higher deployment frequency
Lower failure rates
Faster recovery from incidents
Improved collaboration and productivity
Is DevOps a Job Title?
Yes and no.
Some companies do have roles like “DevOps Engineer,” but DevOps isn't limited to one person. It's a shared responsibility across the engineering team. That said, DevOps engineers usually focus on automation, CI/CD pipelines, infrastructure as code, and system monitoring.
Final Thoughts
So, what do you mean by DevOps? It's a modern approach to software delivery where people, processes, and tools come together to create better systems—faster, safer, and smarter.
It’s not just about writing scripts or managing servers. It’s about rethinking how teams collaborate and how software serves the people who use it.
Whether you’re a beginner exploring the tech world or a seasoned professional tired of the old “dev vs. ops” blame game, embracing DevOps means embracing a better, more human way of building technology.
DevOps is a set of practices, cultural philosophies, and collaborative methodologies that aim to enhance the collaboration between software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) teams. The primary goal of DevOps is to shorten the software development lifecycle, improve the quality and reliability of software, and enable organizations to deliver applications and services at a faster pace and with greater efficiency.
DevOps seeks to break down the traditional barriers and silos that often exist between development and operations teams. By promoting communication, collaboration, and automation, DevOps helps create a more streamlined and efficient software delivery process. It emphasizes shared responsibility, continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD), automation, and a culture of collaboration and innovation.
Key Aspects of DevOps
Culture
DevOps emphasizes collaboration, communication, and shared ownership among development, operations, and other relevant teams. It promotes a culture of mutual respect, trust, and openness.
Automation
Automation is a cornerstone of DevOps. By automating repetitive tasks, deployments, testing, and infrastructure provisioning, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, reduce errors, and maintain consistency.
CI/CD
Continuous Integration (CI) involves integrating code changes frequently and testing them automatically to catch defects early. Continuous Deployment (CD) focuses on automating the deployment process to ensure that changes can be released quickly and reliably.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
IaC involves managing and provisioning infrastructure using code and automation tools. This allows for consistent and repeatable deployments of infrastructure components.
Monitoring and Observability
DevOps emphasizes the importance of monitoring applications and infrastructure to identify issues and ensure optimal performance. Observability focuses on gaining insights into complex systems through metrics, logs, and traces.
Feedback Loop
DevOps encourages a strong feedback loop between development, operations, and end-users. This loop helps identify and address issues quickly, leading to continuous improvement.
0 notes
Video
youtube
Introduction to Git: Understanding the Basics of Version Control
Git is a distributed version control system essential for modern software development. It enables multiple developers to collaborate efficiently by managing changes to code over time. Mastering Git is crucial for any developer or DevOps professional, as it supports streamlined workflows, effective collaboration, and robust code management.
What is Version Control?
Version control tracks changes to files, allowing you to recall specific versions and manage code history. It helps prevent conflicts by enabling team members to work together without overwriting each other’s changes. Git’s version control system is vital for maintaining a clear and organized development process.
Key Features of Git
1. Distributed Architecture: Git stores the entire repository locally for each developer, enhancing speed and allowing offline work. This is a shift from centralized systems where all data is on a single server.
2. Branching and Merging: Git supports multiple branches for isolated work on features or fixes. This facilitates experimentation and seamless integration of changes into the main codebase.
3. Staging Area: The staging area lets developers review changes before committing them, ensuring precise control over what gets recorded in the project history.
4. Commit History: Each change is recorded as a commit with a unique identifier, enabling developers to track, revert, and understand project evolution.
5. Collaboration and Conflict Resolution: Git's tools for handling merge conflicts and supporting collaborative development make it ideal for team-based projects.
Benefits of Using Git
- Enhanced Collaboration: Multiple developers can work on separate branches with minimal conflicts. - Flexibility and Efficiency: Git’s distributed nature allows offline work and faster local operations. - Reliable Code Management: Git's branching and merging capabilities streamline code management. - Security: Git uses SHA-1 hashing to ensure code integrity and security.
Why Learn Git?
Git is foundational for modern development and DevOps practices. It underpins tools like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket, offering advanced features for collaboration, continuous integration, and deployment. Mastering Git enhances coding skills and prepares you for effective team-based workflows.
Conclusion
Understanding Git is the first step toward proficiency in modern development practices. Mastering Git enables efficient code management, team collaboration, and seamless CI/CD integration, advancing your career in software development or DevOps.
What Is Git?,What Is Git Core Features and Use Cases?,What Is GitHub?,What Is GitHub Core Features and Use Cases?,What Is GitHub Actions?,What Is GitHub Actions Core Features and Use Cases?,What Is GitLab?,What Is GitLab Core Features and Use Cases?,What Is Right Tools For DevOps? Git,GitHub,Version Control and Collaboration Essentials,GitLab,github actions ci/cd,git and github tutorial,git tutorial,git tutorial for beginners,how to use git,como usar git,what is git,git for devops,curso de github,version control system,git for beginners,version control,github tutorial,git basics,git repository,git explained,git introduction,open source,cloudolus,cloudoluspro,version control with git,git clone,git commit,dia a dia
Git for DevOps, GitHub for DevOps, version control for DevOps, Git commands for beginners, GitHub Actions CI/CD, DevOps tools, CI/CD pipelines, GitHub workflow examples, Git best practices. #GitForDevOps #GitHubForDevOps #VersionControl #DevOpsTools #CICDPipelines #GitHubActions #CloudComputing #DevOpsTutorials
***************************** *Follow Me* https://www.facebook.com/cloudolus/ | https://www.facebook.com/groups/cloudolus | https://www.linkedin.com/groups/14347089/ | https://www.instagram.com/cloudolus/ | https://twitter.com/cloudolus | https://www.pinterest.com/cloudolus/ | https://www.youtube.com/@cloudolus | https://www.youtube.com/@ClouDolusPro | https://discord.gg/GBMt4PDK | https://www.tumblr.com/cloudolus | https://cloudolus.blogspot.com/ | https://t.me/cloudolus | https://www.whatsapp.com/channel/0029VadSJdv9hXFAu3acAu0r | https://chat.whatsapp.com/D6I4JafCUVhGihV7wpryP2 *****************************
*🔔Subscribe & Stay Updated:* Don't forget to subscribe and hit the bell icon to receive notifications and stay updated on our latest videos, tutorials & playlists! *ClouDolus:* https://www.youtube.com/@cloudolus *ClouDolus AWS DevOps:* https://www.youtube.com/@ClouDolusPro *THANKS FOR BEING A PART OF ClouDolus! 🙌✨*
#youtube#Git for DevOps GitHub for DevOps version control for DevOps Git commands for beginners GitHub Actions CI/CD DevOps tools CI/CD pipelines Git#What Is Git?What Is Git Core Features and Use Cases?What Is GitHub?What Is GitHub Core Features and Use Cases?What Is GitHub Actions?What Is
0 notes
Text
Azure vs. Azure DevOps: Understanding the Key Differences

In today’s fast-changing digital landscape, software development and cloud computing go hand in hand. Companies are rapidly adopting cloud platforms and DevOps practices to deliver applications faster, more reliably, and at scale. Two powerful tools from Microsoft Azure course and Azure DevOps—play a central role in this transformation. Although often mentioned together, they serve very different purposes.
In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between Azure and Azure DevOps. Whether you’re a developer, DevOps engineer, IT professional, or business leader, this guide will help you understand how each platform works, when to use them, and how they complement each other in modern software development.
What Is Microsoft Azure?
Microsoft Azure is a comprehensive cloud computing platform that offers a wide range of services to help businesses build, deploy, and manage applications. Instead of relying on physical servers or local data centers, Azure provides virtual resources—such as computing power, storage, and networking—over the internet.
Azure supports multiple service models, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). This flexibility allows companies to choose the right combination of services based on their specific needs.
One of Azure’s biggest strengths is scalability. Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise, you can scale resources up or down quickly to match changing demand. You only pay for what you use, which makes it cost-effective and efficient.
Azure also offers a variety of tools and services, including:
Virtual Machines (VMs) for running applications and systems
Azure SQL Database for managed relational databases
Blob Storage for unstructured data storage
Azure App Services for hosting websites and APIs
Azure AI and Machine Learning tools for building intelligent apps
Internet of Things (IoT) services for managing connected devices
Another important aspect of Azure is its global infrastructure. With data centers across multiple continents, it allows businesses to deploy applications closer to users, ensuring low latency and high performance.
What Is Azure DevOps?
While Azure provides the cloud infrastructure for hosting and running applications, Azure DevOps focuses on managing the software development lifecycle. It is a set of cloud-based tools and services designed to support teams through every stage of software delivery—from planning and coding to testing and deployment.
Azure DevOps is built around modern DevOps practices like Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD). These practices aim to automate and streamline the development process, allowing teams to release high-quality software more frequently and with fewer errors.
Here are the key components of Azure DevOps:
Azure Boards: A project management tool for tracking work items, user stories, tasks, bugs, and progress using Agile or Scrum methodologies.
Azure Repos: A version control system based on Git, used to manage source code and enable collaboration through pull requests and branching.
Azure Pipelines: A powerful automation tool that builds, tests, and deploys code across multiple platforms and environments.
Azure Test Plans: A testing tool that allows teams to run manual and automated tests to ensure software quality.
Azure Artifacts: A package management system for sharing and managing packages like npm, NuGet, and Maven across development teams.
How Azure and Azure DevOps Work Together
Although Azure and Azure DevOps are separate tools, they are designed to work together seamlessly. In fact, using them in combination creates a powerful, end-to-end solution for cloud-based software development.
Imagine a scenario where a team is building a web application. They use Azure DevOps to write code, manage tasks, and set up a CI/CD pipeline. Once the application is built and tested, the same pipeline automatically deploys the app to Azure App Service for hosting. Any infrastructure, such as databases or storage, is provisioned on Azure using Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like ARM templates or Terraform.
By integrating Azure DevOps with Azure, teams can:
Automate deployments to Azure services with a single click
Monitor live applications through Azure’s built-in monitoring tools
Roll back to previous versions in case of failure
Track changes and audit activity across the entire development lifecycle
This unified approach not only reduces complexity but also improves speed, consistency, and collaboration among teams. Developers, testers, and operations teams can all work from a single platform, aligning with DevOps principles and Agile practices.
Which One Should You Use?
If you need a platform to host applications, manage infrastructure, or store data, then Microsoft Azure is the right choice. It provides the cloud environment where your applications will live and operate. Whether you’re deploying a web app, running machine learning models, or setting up virtual networks, Azure gives you the resources to make it happen.
On the other hand, if your focus is on developing, testing, and deploying software, then Azure DevOps is the better tool. It supports the processes and workflows needed to write code, track progress, run tests, and push updates efficiently.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between Azure and Azure DevOps is crucial for anyone working in today’s tech-driven environment. Azure is a cloud platform that offers infrastructure and services to host and run applications. Azure DevOps, on the other hand, is a development and delivery platform that helps teams plan, build, test, and deploy software.
0 notes
Text
So, let me try and put everything together here, because I really do think it needs to be talked about.
Today, Unity announced that it intends to apply a fee to use its software. Then it got worse.
For those not in the know, Unity is the most popular free to use video game development tool, offering a basic version for individuals who want to learn how to create games or create independently alongside paid versions for corporations or people who want more features. It's decent enough at this job, has issues but for the price point I can't complain, and is the idea entry point into creating in this medium, it's a very important piece of software.
But speaking of tools, the CEO is a massive one. When he was the COO of EA, he advocated for using, what out and out sounds like emotional manipulation to coerce players into microtransactions.
"A consumer gets engaged in a property, they might spend 10, 20, 30, 50 hours on the game and then when they're deep into the game they're well invested in it. We're not gouging, but we're charging and at that point in time the commitment can be pretty high."
He also called game developers who don't discuss monetization early in the planning stages of development, quote, "fucking idiots".
So that sets the stage for what might be one of the most bald-faced greediest moves I've seen from a corporation in a minute. Most at least have the sense of self-preservation to hide it.
A few hours ago, Unity posted this announcement on the official blog.
Effective January 1, 2024, we will introduce a new Unity Runtime Fee that’s based on game installs. We will also add cloud-based asset storage, Unity DevOps tools, and AI at runtime at no extra cost to Unity subscription plans this November. We are introducing a Unity Runtime Fee that is based upon each time a qualifying game is downloaded by an end user. We chose this because each time a game is downloaded, the Unity Runtime is also installed. Also we believe that an initial install-based fee allows creators to keep the ongoing financial gains from player engagement, unlike a revenue share.
Now there are a few red flags to note in this pitch immediately.
Unity is planning on charging a fee on all games which use its engine.
This is a flat fee per number of installs.
They are using an always online runtime function to determine whether a game is downloaded.
There is just so many things wrong with this that it's hard to know where to start, not helped by this FAQ which doubled down on a lot of the major issues people had.
I guess let's start with what people noticed first. Because it's using a system baked into the software itself, Unity would not be differentiating between a "purchase" and a "download". If someone uninstalls and reinstalls a game, that's two downloads. If someone gets a new computer or a new console and downloads a game already purchased from their account, that's two download. If someone pirates the game, the studio will be asked to pay for that download.
Q: How are you going to collect installs? A: We leverage our own proprietary data model. We believe it gives an accurate determination of the number of times the runtime is distributed for a given project. Q: Is software made in unity going to be calling home to unity whenever it's ran, even for enterprice licenses? A: We use a composite model for counting runtime installs that collects data from numerous sources. The Unity Runtime Fee will use data in compliance with GDPR and CCPA. The data being requested is aggregated and is being used for billing purposes. Q: If a user reinstalls/redownloads a game / changes their hardware, will that count as multiple installs? A: Yes. The creator will need to pay for all future installs. The reason is that Unity doesn’t receive end-player information, just aggregate data. Q: What's going to stop us being charged for pirated copies of our games? A: We do already have fraud detection practices in our Ads technology which is solving a similar problem, so we will leverage that know-how as a starting point. We recognize that users will have concerns about this and we will make available a process for them to submit their concerns to our fraud compliance team.
This is potentially related to a new system that will require Unity Personal developers to go online at least once every three days.
Starting in November, Unity Personal users will get a new sign-in and online user experience. Users will need to be signed into the Hub with their Unity ID and connect to the internet to use Unity. If the internet connection is lost, users can continue using Unity for up to 3 days while offline. More details to come, when this change takes effect.
It's unclear whether this requirement will be attached to any and all Unity games, though it would explain how they're theoretically able to track "the number of installs", and why the methodology for tracking these installs is so shit, as we'll discuss later.
Unity claims that it will only leverage this fee to games which surpass a certain threshold of downloads and yearly revenue.
Only games that meet the following thresholds qualify for the Unity Runtime Fee: Unity Personal and Unity Plus: Those that have made $200,000 USD or more in the last 12 months AND have at least 200,000 lifetime game installs. Unity Pro and Unity Enterprise: Those that have made $1,000,000 USD or more in the last 12 months AND have at least 1,000,000 lifetime game installs.
They don't say how they're going to collect information on a game's revenue, likely this is just to say that they're only interested in squeezing larger products (games like Genshin Impact and Honkai: Star Rail, Fate Grand Order, Among Us, and Fall Guys) and not every 2 dollar puzzle platformer that drops on Steam. But also, these larger products have the easiest time porting off of Unity and the most incentives to, meaning realistically those heaviest impacted are going to be the ones who just barely meet this threshold, most of them indie developers.
Aggro Crab Games, one of the first to properly break this story, points out that systems like the Xbox Game Pass, which is already pretty predatory towards smaller developers, will quickly inflate their "lifetime game installs" meaning even skimming the threshold of that 200k revenue, will be asked to pay a fee per install, not a percentage on said revenue.

[IMAGE DESCRIPTION: Hey Gamers!
Today, Unity (the engine we use to make our games) announced that they'll soon be taking a fee from developers for every copy of the game installed over a certain threshold - regardless of how that copy was obtained.
Guess who has a somewhat highly anticipated game coming to Xbox Game Pass in 2024? That's right, it's us and a lot of other developers.
That means Another Crab's Treasure will be free to install for the 25 million Game Pass subscribers. If a fraction of those users download our game, Unity could take a fee that puts an enormous dent in our income and threatens the sustainability of our business.
And that's before we even think about sales on other platforms, or pirated installs of our game, or even multiple installs by the same user!!!
This decision puts us and countless other studios in a position where we might not be able to justify using Unity for our future titles. If these changes aren't rolled back, we'll be heavily considering abandoning our wealth of Unity expertise we've accumulated over the years and starting from scratch in a new engine. Which is really something we'd rather not do.
On behalf of the dev community, we're calling on Unity to reverse the latest in a string of shortsighted decisions that seem to prioritize shareholders over their product's actual users.
I fucking hate it here.
-Aggro Crab - END DESCRIPTION]
That fee, by the way, is a flat fee. Not a percentage, not a royalty. This means that any games made in Unity expecting any kind of success are heavily incentivized to cost as much as possible.

[IMAGE DESCRIPTION: A table listing the various fees by number of Installs over the Install Threshold vs. version of Unity used, ranging from $0.01 to $0.20 per install. END DESCRIPTION]
Basic elementary school math tells us that if a game comes out for $1.99, they will be paying, at maximum, 10% of their revenue to Unity, whereas jacking the price up to $59.99 lowers that percentage to something closer to 0.3%. Obviously any company, especially any company in financial desperation, which a sudden anchor on all your revenue is going to create, is going to choose the latter.
Furthermore, and following the trend of "fuck anyone who doesn't ask for money", Unity helpfully defines what an install is on their main site.
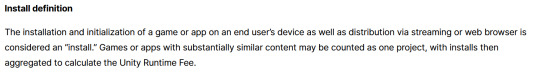
While I'm looking at this page as it exists now, it currently says
The installation and initialization of a game or app on an end user’s device as well as distribution via streaming is considered an “install.” Games or apps with substantially similar content may be counted as one project, with installs then aggregated to calculate the Unity Runtime Fee.
However, I saw a screenshot saying something different, and utilizing the Wayback Machine we can see that this phrasing was changed at some point in the few hours since this announcement went up. Instead, it reads:
The installation and initialization of a game or app on an end user’s device as well as distribution via streaming or web browser is considered an “install.” Games or apps with substantially similar content may be counted as one project, with installs then aggregated to calculate the Unity Runtime Fee.
Screenshot for posterity:
That would mean web browser games made in Unity would count towards this install threshold. You could legitimately drive the count up simply by continuously refreshing the page. The FAQ, again, doubles down.
Q: Does this affect WebGL and streamed games? A: Games on all platforms are eligible for the fee but will only incur costs if both the install and revenue thresholds are crossed. Installs - which involves initialization of the runtime on a client device - are counted on all platforms the same way (WebGL and streaming included).
And, what I personally consider to be the most suspect claim in this entire debacle, they claim that "lifetime installs" includes installs prior to this change going into effect.
Will this fee apply to games using Unity Runtime that are already on the market on January 1, 2024? Yes, the fee applies to eligible games currently in market that continue to distribute the runtime. We look at a game's lifetime installs to determine eligibility for the runtime fee. Then we bill the runtime fee based on all new installs that occur after January 1, 2024.
Again, again, doubled down in the FAQ.
Q: Are these fees going to apply to games which have been out for years already? If you met the threshold 2 years ago, you'll start owing for any installs monthly from January, no? (in theory). It says they'll use previous installs to determine threshold eligibility & then you'll start owing them for the new ones. A: Yes, assuming the game is eligible and distributing the Unity Runtime then runtime fees will apply. We look at a game's lifetime installs to determine eligibility for the runtime fee. Then we bill the runtime fee based on all new installs that occur after January 1, 2024.
That would involve billing companies for using their software before telling them of the existence of a bill. Holding their actions to a contract that they performed before the contract existed!
Okay. I think that's everything. So far.
There is one thing that I want to mention before ending this post, unfortunately it's a little conspiratorial, but it's so hard to believe that anyone genuinely thought this was a good idea that it's stuck in my brain as a significant possibility.
A few days ago it was reported that Unity's CEO sold 2,000 shares of his own company.
On September 6, 2023, John Riccitiello, President and CEO of Unity Software Inc (NYSE:U), sold 2,000 shares of the company. This move is part of a larger trend for the insider, who over the past year has sold a total of 50,610 shares and purchased none.
I would not be surprised if this decision gets reversed tomorrow, that it was literally only made for the CEO to short his own goddamn company, because I would sooner believe that this whole thing is some idiotic attempt at committing fraud than a real monetization strategy, even knowing how unfathomably greedy these people can be.
So, with all that said, what do we do now?
Well, in all likelihood you won't need to do anything. As I said, some of the biggest names in the industry would be directly affected by this change, and you can bet your bottom dollar that they're not just going to take it lying down. After all, the only way to stop a greedy CEO is with a greedier CEO, right?
(I fucking hate it here.)
And that's not mentioning the indie devs who are already talking about abandoning the engine.
[Links display tweets from the lead developer of Among Us saying it'd be less costly to hire people to move the game off of Unity and Cult of the Lamb's official twitter saying the game won't be available after January 1st in response to the news.]
That being said, I'm still shaken by all this. The fact that Unity is openly willing to go back and punish its developers for ever having used the engine in the past makes me question my relationship to it.
The news has given rise to the visibility of free, open source alternative Godot, which, if you're interested, is likely a better option than Unity at this point. Mostly, though, I just hope we can get out of this whole, fucking, environment where creatives are treated as an endless mill of free profits that's going to be continuously ratcheted up and up to drive unsustainable infinite corporate growth that our entire economy is based on for some fuckin reason.
Anyways, that's that, I find having these big posts that break everything down to be helpful.
#Unity#Unity3D#Video Games#Game Development#Game Developers#fuckshit#I don't know what to tag news like this
6K notes
·
View notes