Text
Life on Earth
Life on Earth
A unique combination of an oxygen-rich atmosphere and plentiful water is the key to life on Earth. Apart from the polar ice caps, there are few areas which have not been colonized by animals or plants over the course of the Earth's history. Plants process sunlight to provide them with their energy, and ultimately all the Earth's animals rely on plants for survival. Because of this reliance, plants are known as primary producers, and the availability of nutrients and temperature of an area is defined as its primary productivity, which affects the quantity and type of animals which are able to live there. This index is affected by climatic factors - cold and aridity restrict the quantity of life, whereas warmth and regular rainfall allow a greater diversity of species.
Biogeographical regions
The Earth can be divided into a series of biogeographical regions, or biomes, ecological communities where certain species of plant and
animal co-exist within particular climatic conditions. Within these broad classifications, other factors including soil richness, altitude and human activities such as urbanization, intensive agriculture and deforestation, affect the local distribution of living species within each biome.
#world #earth #plantas #nature #follower #forest #plantlife #science #everyoneシ゚ #academy #education #knowledge #geography #physics #geology #naturephotography #naturelovers #natural #TravelPhotography #travel #travelgram #travelblogger #scenic #worldwide #worldnaturebeauty #sea #ocean #seaview #flowers #rain #summer #natureza #NaturalBeauty #view #viewers #educational #earthcapture #geologist #fb #insta










#world#earthquake#earth science#biology#biodiversity#ecology#ecofriendly#ecological#green day ecosystem#science#botani#botanical garden#forest#trees and forests#trees#life#plants#food forest#food#university#knowledge#quotes#books#writing#positivity#information#info#ecosystem#flowers#rainforest
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Life on Earth
Life on Earth
A unique combination of an oxygen-rich atmosphere and plentiful water is the key to life on Earth. Apart from the polar ice caps, there are few areas which have not been colonized by animals or plants over the course of the Earth's history. Plants process sunlight to provide them with their energy, and ultimately all the Earth's animals rely on plants for survival. Because of this reliance, plants are known as primary producers, and the availability of nutrients and temperature of an area is defined as its primary productivity, which affects the quantity and type of animals which are able to live there. This index is affected by climatic factors - cold and aridity restrict the quantity of life, whereas warmth and regular rainfall allow a greater diversity of species.
Biogeographical regions
The Earth can be divided into a series of biogeographical regions, or biomes, ecological communities where certain species of plant and
animal co-exist within particular climatic conditions. Within these broad classifications, other factors including soil richness, altitude and human activities such as urbanization, intensive agriculture and deforestation, affect the local distribution of living species within each biome.
#world #earth #plantas #nature #follower #forest #plantlife #science #everyoneシ゚ #academy #education #knowledge #geography #physics #geology #naturephotography #naturelovers #natural #TravelPhotography #travel #travelgram #travelblogger #scenic #worldwide #worldnaturebeauty #sea #ocean #seaview #flowers #rain #summer #natureza #NaturalBeauty #view #viewers #educational #earthcapture #geologist #fb #insta






#world#earth#nature#natural#biodiversity#biology#ecology#ecological#botani#ecofriendly#positivity#forest#rainforest#trees#trees and forests#education#earth science#science#knowledge#university#writing#books#collage#information#ecoliving#plants#info#quotes#technology#environment
0 notes
Text
Oceanic water circulation
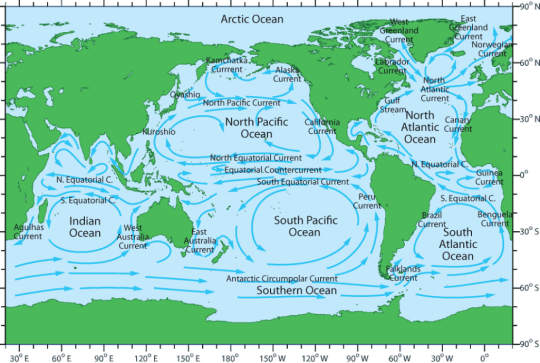
In general, ocean currents parallel the movement of winds across the Earth's surface. Incoming solar energy is greatest at the Equator and least at the poles. So, water in the oceans heats up most at the Equator and flows polewards, cooling as it moves north or south towards the Arctic or Antarctic. The flow is eventually reversed and cold water currents move back towards the Equator. These ocean currents act as a vast system for moving heat from the Equator towards the poles and are a major influence on the distribution of the Earth's climates.
#world #earth #ocean #science #Current #sea #water #education #everyoneシ゚ #academy #knowledge #information #physics #geography #geology #oceanography #marinescience #geologist #Info #insta #university #waves #nature #natural #photography #photo #UN #unique #fb #news #bestphotochallenge #weather #pacific #welcome #books




#world#earth#ocean#waves#sea#oceanography#oceancurrent#high tide#flow#deep sea#education#knowledge#learning#university#science#earth science#marine science#ecology#writing#oceanografi#information#travel#weather#info#physics#marine biology#positivity#books#collage#quotes
0 notes
Text
The global climate
The Earth's climatic types consist of stable patterns of weather conditions averaged out over a long period of time. Different climates are categorized according to particular combinations of temperature and humidity. By contrast, weather consists of short-term fluctuations in wind, temperature and humidity conditions. Different climates are determined by latitude, altitude, the prevailing wind and circulation of ocean currents. Longer-term changes in climate, such as global warming or the onset of ice ages, are punctuated by shorter-term events which comprise the day-to-day weather of a region, such as frontal depressions, hurricanes and blizzards.






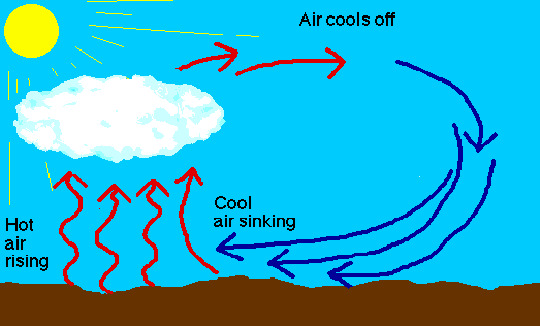

Global air circulation
Air does not simply flow from the Equator to the poles, it circulates in giant cells known as Hadley and Ferrel cells. As air warms it expands, becoming less dense and rising; this creates areas of low pressure. As the air rises it cools and condenses, causing heavy rainfall over the tropics and slight snowfall over the poles. This cool air then sinks, forming high pressure belts. At surface level in the tropics these sinking currents are deflected polewards as the westerlies and towards the equator as the trade winds. At the poles they become the polar easterlies.
#everyoneシ゚ #follower #world #earth #ocean #sea #air #waves #Global #climate #climatechange #ClimateAction #science #education #knowledge #academy #physics #Geography #geography #weather #polution #aircirculation #strom #rain #hotweather #information #geoscience #marinescience #biochemistry #seawaves #fb #insta #books #news #BreakingNews
#world#earth#global#climate change#climate crisis#ocean#sea#earth science#geology#geography#physics#education#positivity#writing#knowledge#university#nature#nature photography#natural history#air pollution#glacier#hotair#weather#collage#books#quotes#history#highlights#climate action
0 notes
Text
Tides and Waves are both forms of water movement in the ocean, but they are distinct phenomena. Tides are the regular, long-period rise and fall of sea levels, primarily caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun. Waves, on the other hand, are the shorter-period, rhythmic disturbances of the water surface, often caused by wind.


Here's a more detailed breakdown:
Tides:
Definition:
The periodic rise and fall of sea levels due to the gravitational forces of the Moon and Sun.
Period:
Tides occur in a cyclical pattern, typically twice a day (semi-diurnal) or once a day (diurnal).
Causes:
Primarily the gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun, as well as the Earth's rotation and the shape of ocean basins.
Effects:
Tides affect coastal areas, impacting water levels, shoreline erosion, and marine ecosystems.



Waves:
Definition:
Rhythmic disturbances of the water surface, caused by various forces like wind, earthquakes, or landslides.
Period:
Waves have shorter periods than tides, ranging from a few seconds to several minutes.
Causes:
Primarily wind, but can also be caused by other factors like earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or landslides.
Effects:
Waves play a crucial role in coastal erosion, sediment transport, and wave-related phenomena like surfing and coastal hazards.



Key Differences:
Periodicity:
Tides are long-period, with a typical cycle of about 12 hours, while waves are short-period, with cycles ranging from a few seconds to several minutes.
Cause:
Tides are primarily caused by gravitational forces, while waves are primarily caused by wind.
Water Movement:
Tides involve the vertical rise and fall of water levels, while waves involve the oscillating movement of water particles.
In essence, tides are a global, large-scale phenomenon, while waves are more localized, smaller-scale disturbances.
#world #Earth #ocean #water #sea #science #academy #everyoneシ゚ #education #follower #knowledge #geography #physics #geology #geography #oceanography #oceanscience #waves #seawaves #current #sealife #information #university #Un #worldwide #oceanlife #marinescience #fb #insta #geologist #news #marinelife #college #photography #photochallenge #
#world#earth#water#ocean#sea#Tide#waves#ocean view#sea life#deep sea#oceanography#geography#geology#marine science#weather#ocean waves#knowledge#information#writing#physics#positivity#collage#university#books#quotes#science#wave power#marine biology#navy#navigation
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The World Ocean Currents
Ocean currents are driven by wind, water density differences, and tides. Oceanic currents describe the movement of water from one location to another. Currents are generally measured in meters per second or in knots (1 knot = 1.85 kilometers per hour or 1.15 miles per hour).








#follower #world #earth #ocean #science #Current #sea #water #education #everyoneシ゚ #academy #knowledge #information #physics #geography #geology #oceanography #marinescience #geologist #Info #insta #university #waves #nature #natural #photography #photo #UN #unique #fb #news #bestphotochallenge #weather #pacific #welcome #books
0 notes
Text
Surface Water
The water surface is the top layer of any body of water, like a lake, river, or ocean. It's the visible boundary between the water and the air above it, where you can see the water and objects can float.


Here's a more detailed explanation:
Definition: Surface water refers to water that is on top of land, forming bodies like rivers, lakes, and streams.


Boundary: It's the interface between the water and the atmosphere.


Visibility: You can see the surface of water, and it's where things float.
Importance: Surface water is a vital part of the hydrologic cycle and provides various services, including drinking water, irrigation, and habitat.
#Earth #world #water #sea #ocean #ice #coolwater #naturalwater #surface #mountains #river #science #everyoneシ゚ #follower #friends #education #academy #knowledge #geography #physics #educational #geologist #Info #riverwater #Geoscience #photochallenge #insta #instagram #sciencefacts #marinebiology #oceanography #Sciencefiction #watercolor #waterfall
#world#earth#watercolor#earth science#ocean#sea#minaral Water#physics#knowledge#collage#university#books#writing#helthylife#life#mental health awareness#helth care#school#waterscience#positivity#drinking water#information#nature#nature photography#natural food#photography#info#ocean view#weather#rain world
0 notes
Text
Ocean Structure
The ocean is structured into layers based on depth and the amount of sunlight that penetrates. These layers include the surface layer (mixed layer), the thermocline, and the deep ocean. The surface layer is warmed by sunlight and mixed by wind and wave action, while the thermocline is a transition zone where temperature changes significantly with depth. The deep ocean is a colder, more dense, and less mixed zone below the thermocline.


Here's a more detailed breakdown:
1. Surface Layer (Mixed Layer):
This is the uppermost layer, where sunlight penetrates and warms the water.
It's characterized by mixing due to wind and wave action, creating a relatively homogeneous water mass.
This layer accounts for about 2% of the total ocean volume.


2. Thermocline:
A transition zone between the warm surface layer and the colder, deeper ocean.
It's marked by a rapid decrease in temperature with depth, inhibiting mixing between surface and deep waters.
The depth and strength of the thermocline can vary seasonally and geographically.



3. Deep Ocean:
Water below the thermocline, characterized by low temperatures and high pressure.
It's relatively well-mixed, but the temperature and density differences with the surface layer limit vertical mixing.
This layer accounts for a large portion of the ocean's volume.

#world #earth #ocean #science #everyoneシ゚ #knowledge #academy #education #geography #physics #geologist #Info #information #structure #wave #sea #university #geology #UN #environment #environmental #ecology #nature #natural #water #watercolor #waterfall #deepsea #oceanview #educational #insta #instagram #naturelovers #naturephotography #book #image
#world#earth#ocean#sea#waves#deep sea#sea life#ocean view#physics#pacific ocean#atlantic ocean#indian ocean#artic ocean#southern ocean#positivity#knowledge#university#writing#books#collage#information#books and reading#photography#earth science#geology#geography#oceanography#marine science#marine biology#learning
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
The World's Oceans
The two-thirds of the Earth's surface is covered by the oceans. The landscape of the ocean floor, like the surface of the land,has been shaped by the movements of the Earth's crust for over a million years to form volcanic mountain ranges, deep trenches,basins and plateaux. Ocean currents constantly redistribute warm and cold water around the world. Major warm current,such as El Niño in the Pacific ocean,can increase surface temperature by up to 46°F ( 8°C ) ,causing change in weather patterns which can lead to both droughts and flooding .The world has five major oceans: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic, and Southern (Antarctic) Oceans. These oceans are interconnected, forming a single, vast body of water that covers about 71% of the Earth's surface.

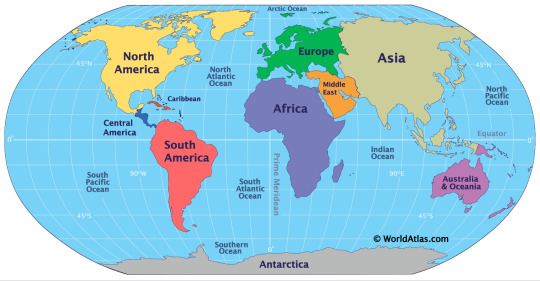





Detailed Information:
Pacific Ocean: The largest and deepest, containing more than half of the world's free-flowing water, according to H M Y Yachts. It's bordered by North and South America on the east, and Asia and Australia on the west.
Atlantic Ocean: Located between the Americas and Europe/Africa.
Indian Ocean: Situated between Asia, Africa, and Australia.
Arctic Ocean: The smallest and shallowest of the five, often covered in ice, especially during the winter months. It's located in the Arctic region.
Southern (Antarctic) Ocean: A relatively new designation, it's the body of water around Antarctica, sometimes considered an extension of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans.
Key Features:
Interconnectedness:
The oceans are interconnected, and the term "world ocean" refers to this single, continuous body of water.
Climate:
The oceans play a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate by absorbing heat and influencing weather patterns.
Biodiversity:
The oceans are home to a vast array of marine life, and their health is essential for global ecosystems.
Human Impact:
Human activities, such as pollution and overfishing, can have significant impacts on the health of the oceans.
#Earth #world #everyoneシ゚ #science #academy #education #knowledge #geography #physics #Info #sea #geology #weather #time #ocean #surface #wind #air #water #seaworld #continent #asia #africa #europe #america #oceania #geologist #university #UN #sealife #books #information #fb
#positivity#writing#books#collage#knowledge#quotes#university#physics#world#earth#earth science#sea#ocean#pacific ocean#atlantic ocean#indian ocean#artic ocean#southern ocean#education#geology#geolocation#geography#ice#information#info#oceanography#marine science#marine biology#mountains#ecology
1 note
·
View note
Text
Ice
During its long history, the Earth has experienced a number of glacial episodes when temperatures were considerably lower than today. During the last Ice Age, 18,000 years ago, ice covered an area three times larger than it does today. Over these periods, the ice has left a remarkable legacy of transformed landscapes.

Glaciers
Glaciers are formed by the compaction of snow into 'rivers' of ice. As they move over the landscape, glaciers pick up and carry a load of rocks and boulders which erode the landscape they pass over, and are eventually deposited at the end of the glacier.

Glacial valleys
Glaciers can erode much more powerfully than rivers. They form steep-sided, flat- bottomed valleys with a typical U-shaped profile. Valleys created by tributary glaciers, whose floors have not been eroded to the same depth as the main glacial valley floor, are called hanging valleys.

Post-glacial features
When a glacial episode ends, the retreating ice leaves many features. These include depositional ridges called moraines, which may be eroded into low hills known as drumlins; sinuous ridges called eskers; kames, which are rounded hummocks, depressions known as kettle holes, and windblown loess deposits.


#follower #everyone
#Earth #world #physics #geography #geology #water #ocean #ice #glacier #glacialwater #valley #mountains #science #everyoneシ゚ #academy #education #knowledge #sea #fb #Info #university #icewater #life #instagram #information #college #school #books #UN #BD #photography #Youtube #health #luxury
#world#waterfall#weather#watercolor#rain world#ocean#physics#nature#university#knowledge#collage#books#school#positivity#writing#information#glacier#mountains#mount everest#sea#geology#geography#geoscience#education#ice#info#picture#polls#marine science#marine biology
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
THE WORLD Shaping the Landscape
Shaping the landscape
The basic material of the Earth's surface is solid rock: valleys, deserts, soil, and sand are all evidence of the powerful agents of weathering, erosion, and deposition which constantly shape and transform the Earth's landscapes. Water, either flowing continually in rivers or seas, or frozen and compacted into solid sheets of ice, has the most clearly visible impact on the Earth's surface. But wind can transport fragments of rock over huge distances and strip away protective layers of vegetation, exposing rock surfaces to the impact of extreme heat and cold.

Coastal water
The world's coastlines are constantly changing; every day, tides deposit, sift and sort sand,and gravel on the shoreline. Over longer periods, powerful wave action erodes cliffs and headlands and carves out bays.

Water
Less than 2% of the world's water is on the land, but it is the most powerful agent of landscape change. Water, as rainfall, groundwater and rivers. can transform landscapes through both erosion and deposition. Eroded material carried by rivers forms the world's most fertile soils.

Groundwater
In regions where there are porous rocks such as chalk, water is stored underground in large quantities, these reservoirs of water are known as aquifers. Rain percolates through topsoil into the underlying bedrock, creating an underground store of water. The limit of the saturated zone is called the water table.


#World #water #groundwater #coastal #sea #ocean #science #everyoneシ゚ #physics #geography #geology #Earth #landscape #education #knowledge #Academy #Info #fb #worldwide #university #college #school #watercolor #mountains #deepsea #information #weather #scenery #surface #instagram #oceanography #photography #MarineScience
#writing#knowledge#positivity#quotes#books#collage#university#world#ocean#landscape#shape#geology#geography#waterfall#physics#information#info#weather#mountains#writers on tumblr#earth science#sea#photography#nature#nostalgia#nature photography#rain world#earth#reading#books and reading
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Thank you to everyone who got me to 100 likes!
Thank you all . Who gave me a like share . Support.
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Earth's Geology.
Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its physical structure, processes, and history. It encompasses a wide range of topics, from understanding the formation of rocks and minerals to examining plate tectonics, earthquakes, and the history of the Earth's surface. The National Park Service notes that geology is a discipline that aims to understand the Earth's features, processes, and history.










Key aspects of geology include:
Understanding Earth's Structure:
Geology explores the Earth's layered structure, from the crust and mantle to the core.
Studying Earth's Processes:
Geologists investigate how forces like plate tectonics, weathering, erosion, and volcanism shape the Earth's surface.
Analyzing Earth's History:
Geology helps decipher the Earth's past, including the evolution of life, climate change, and past geological events.
Examining Rocks and Minerals:
Geologists study the composition, formation, and properties of rocks and minerals.
Understanding Earth's Resources:
Geology plays a crucial role in understanding the location and distribution of natural resources like minerals, fossil fuels, and groundwater.
Assessing Natural Hazards:
Geologists help assess and predict natural hazards like earthquakes, landslides, and volcanic eruptions.
In essence, geology provides a comprehensive understanding of the Earth, its history, and the processes that have shaped it into the planet we know today.
#earth #science #everyoneシ゚ #knowledge #academy #geography #education #physics #Info #learning #books #geography #rock #university #follower #friends #viralvideochallenge #un #world #information #fb #instagram #wonderful #ocean #beautiful #beauty #life #earthscience #travel #earrings #wonderful_places #astro #Astrology #planet #lifeisbeautiful #luxury #Youtube #insta #socialmedia #fy
#quotes#writing#astro community#books#collage#knowledge#university#astrology#positivity#earth science#earth#earthbound#school#marine science#science#geology#geography#architecture#marine biology#history#information#info#instagram#weather#geoscience#climate change#clouds#climate crisis#soil science#agriculture
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
1.The Hawaiian island chain
A hot spot lying deep beneath the Pacific Ocean pushes a plume of magma from the Earth's mantle up through the Pacific Plate to form volcanic islands. While the hot spot remains stationary, the plate on which the island sits is moving slowly. A long chain of islands has been created as the plate passes over the hot spot.


2.Creation of the Himalayas
Between 10 and 20 million years ago, the Indian
The subcontinent, part of the ancient continent of Gondwanaland, collided with the continent of Asia. The Indo-Australian Plate continued to move northwards, displacing continental crust and uplifting the Himalayas, the world's highest mountain chain.




#world #hawaii #hawaiian #honolulu #usa #Pacific #ocean #himalayas #mounteverest #Napel #mountains #kathmandu #everyoneシ゚ #science #academy #education #knowledge #geography #physics #Info #learning #geography #university #instagram #India #BD #weather #cold #hawaiian #hawaiilife #photography #sea #travel #travelling #travelblogger #top #bottom
#hawaii#honolulu#USA#pacific ocean#sea#himalayas#nepal#kathmandu#travel#mountains#earthquake#earth science#earth#knowledge#mount everest#hiking#exercise#positivity#quotes#writing#university#education#engineering#luxury#books#ocean#hawaiilife#travel and tourism#rich life#collage
0 notes
Text
Continental Shields
A continental shield is a stable, ancient, and large area of the Earth's crust made up of Precambrian crystalline rocks. These shields are found in the cores of continents and are part of the stable portions of continents called cratons. They are known for their low relief and extensive exposure of basement rocks at the surface.





Key characteristics of continental shields:
Age:
Continental shields are among the oldest rocks preserved in the Earth's crust, dating back to the Precambrian Era (540 million years ago or older). Some shields are as old as 2 to 3 billion years.
Stability:
They are very stable areas, meaning they have experienced little tectonic deformation.
Location:
They are found in the cores of continents and are often covered by younger sedimentary rocks.
Composition:
They are typically composed of crystalline rocks, including granite, gneiss, and other metamorphic and igneous rocks.
Surface:
The surface of continental shields is generally low-lying and relatively flat, with erosion having shaped the landforms.
Examples of Continental Shields:
Canadian Shield: Extends from Lake Superior to the Arctic Islands and across much of eastern Canada.
Amazonian Shield: Found in the eastern bulge of South America.
Indian Shield: Located in the Indian subcontinent.
West African Shield: Found in West Africa.
Formation:
Shields are formed through processes associated with the accretion of continental crust, which involved the merging of smaller crustal blocks (tectonic plates) over geological time. Plate tectonics, erosion, and glaciations also play a role in shaping the shields over time.
#Earth #science #physics #geography #geology #everyoneシ゚ #spacescience #academy #education #knowledge #learning #sea #university #college #school #information #ocean #mountains #earth #earthquake #Info #Informative #books #knowledgeispower #like #news #BreakingNews #earthscience #un #world #usa #uk #russia #canada #wildlife #wild #astrology
#positivity#quotes#writing#astro community#books#collage#knowledge#university#astrology#home & lifestyle#school#earth#earth science#earthquake#science#space#teacher x student#learning#info#information#instagram#books and reading#ocean#geography#geology#sea#physics#volcano#news#breaking news
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Continental drift is the scientific theory explaining the horizontal movement and rotation of continents over geological time, essentially describing how Earth's continents have shifted and changed position over millions of years. This theory, initially proposed by Alfred Wegener, posits that the continents were once united in a single supercontinent called Pangaea, which then broke apart and drifted to their current locations.





Key aspects of continental drift:
Movement of continents:
The theory states that continents are not stationary but move across the Earth's surface.
Pangaea:
Wegener proposed that all continents were once joined together in a supercontinent called Pangaea, which then fragmented and drifted apart over millions of years.
Evidence:
Evidence supporting continental drift includes the fit of continents along coastlines, similar rock formations and fossils found on different continents, and evidence from Earth's magnetic field.
Plate tectonics:
Continental drift is now part of the broader theory of plate tectonics, which explains the movement of Earth's lithosphere, including the continents, on plates.
Mechanism:
While Wegener initially proposed mechanisms like centrifugal force and tidal forces, the modern understanding relies on the movement of tectonic plates driven by convection currents in the Earth's mantle.
Geological time:
Continental drift is a slow, ongoing process occurring over geological time scales, meaning millions of years.
#earth #EarthDay #earthfocus #earthmoving #geography #geology #nature #science #education #knowledge #physics #spacescience #earthscience #movement #ocean #sea #History #university #UN #earthquake #planet #school #collage #learning #reading #power #information #academy #Academic #everyoneシ゚ #follower #friends #books #instagram #GoogleMaps #fb #news #BreakingNews #life #journey #journal #travel #photochallenge #photographychallenge
#positivity#quotes#writing#astro community#books#collage#knowledge#university#astrology#physics#nasa#geography#geology#ocean#marine science#sea#information#info#books and reading#education#united states#school#college#travel#sea life#oxford#climate change#climate crisis#weather#earth science
1 note
·
View note
Text
Inside the Earth
The Earth's hot inner core ismade up of solid iron, while the outer core is composed of liquid iron and nickel. The mantle nearest the core is viscous, whereas the rocky upper mantle is fairly rigid. The crust is the rocky outer shell of the Earth. Together, the upper mantle and the crust form the lithosphere.





Convection currents
Deep within the Earth, at its inner core, temperatures may exceed 8100°F (4500°C). This heat warms rocks in the mesosphere which rise through the partially molten mantle, displacing cooler rocks just below the solid crust, which sink, and are warmed again by the heat of the mantle. This process is continually repeated, creating convection currents which form the moving force beneath the Earth's crust.


Ocean plates meeting
AA Oceanic crust is denser and thinner than continental crust; on average it is 3 miles (5 km) thick, while continental crust averages 18-24 miles (30-40 km). When oceanic plates of similar density meet, the crust is contorted as one plate overrides the other, forming deep sea trenches and volcanic island arcs above sea level.



▲ Mount Pinatubo is an active volcano, lying on the Pacific 'Ring of Fire'.
#earth #mountains #instagram #Youtube #marine #world #un #book #information #knowledge #learning #reading #geology #ocean
#photochallenge #everyoneシ゚ #science #knowledge #spacescience #astronomy #education #physics #Educational #sun #earth #astrology #astronaut #astrophysics #NASA #uk #spaceexploration #university #college #school #spaceshuttle #astrophotography
#solarpower #solarenergy #energy #spacewalk
#positivity#quotes#writing#astro community#books#collage#knowledge#university#astrology#education#school#united states#earth science#engineering#reading#books & libraries#books and reading#learning#information#info#nasa#geography#geology#life#physics#earth#earthquake#news#writers and poets#soundwave
0 notes