#Automated Library System
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
oh my god i don't speak to my dad anymore cuz hes nutty but i know what he does for a living
and musk is currently pulling a "the software govs use is 50 years old which means there can be no advances"
and that's..... that's what my dad does for a living, he gets paid 500-1k an hour to make software that specifically communicates with old legacy software cause he's a 90s dev who knows the old languages still and it's more efficient to hire a freak who knows how to make something to bridge between the old and new programs than to fully trash the old system
like there's literally consultants that get hired for that specific purpose and as a software guy musk KNOWS this
#personal#im losing a LOT of money and decent work connections cause its less stressful than dealing with the crazy man#who literally called my professors at their personal art studios =_=#but ummm???? um??? hes like a low level linkedin influencer lmfao ._.#for software and THIS specific subject matter#the thing ive been getting raises on at work is making scripts to communicate between adobe software with the spreadsheets our#PLM system at work spits out....to automate a bunch of artwork thru libraries.........????#the way my boss gets me to not leave is by giving me /coolmathgames.com/ as a treat basically#and more money for being able to solve /coolmathgames.com/#i work in corporate and one of our order management systems specifically gets routed thru a windows vista virtual machine#cause they dont feel the need to fix....cuz if its not broke#just make the new things that bridge between the two systems?????#instead of having to transfer over decades of a database it makes 0 sense#idk man im rlly frustrated online cuz one of my dads patents is for a legacy speech to text software#(and the other is for a logistics/shipment thing)#like he wasnt the lead on either project but the speech to text specifically is irritating cuz theres#things ppl call 'AI' and im like....thats a buzzword this is litcherally 90s/00s tech and ive been in the office it was made lol
1 note
·
View note
Text

Level Up Your Library with a Modern Library Management System
Organise books, streamline workflows, and empower users—all in one go! Discover an innovative approach to library organisation and patron satisfaction with our advanced library management system. Partner with us to unlock the full potential of your library!
0 notes
Text
How can libraries ensure the security of their data and protect patron privacy when using a library management system?
In today's digital age, libraries rely heavily on technology to manage their collections, provide access to resources, and serve their patrons. However, with the use of technology comes the risk of data breaches and privacy violations. As libraries increasingly adopt library management systems, it is important to consider how these systems can be secured to protect patron privacy and ensure the integrity of library data.
At Metaguard, we understand the importance of data security and privacy in the library setting. Our team of experts works with libraries to implement security measures and provide training and support to ensure that library management systems are secure and compliant with privacy regulations.
One of the first steps libraries can take to ensure data security and privacy is to implement access controls. Access controls limit who has access to sensitive data and ensure that only authorized personnel can view and modify data. Libraries can also implement multi-factor authentication to further enhance security and prevent unauthorized access.
Another important step is to ensure that all data is encrypted when it is transmitted or stored. Encryption ensures that data is protected from hackers and other unauthorized users. Libraries should also regularly update their software and systems to ensure that they are protected from known security vulnerabilities.
In addition to securing the library management system, libraries must also protect patron privacy. This includes implementing policies and procedures for handling and storing patron data, as well as obtaining consent before collecting any personal information. Libraries should also provide clear and transparent privacy policies to patrons and ensure that they are informed about how their data is being used and protected.
At Metaguard, we work with libraries to implement privacy and security best practices, including regular audits and assessments to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. We also provide training and support to library staff to ensure that they have the knowledge and skills to maintain a secure and privacy-compliant library management system.
In conclusion, library management systems are an essential tool for modern libraries, but they also come with security and privacy risks. By implementing access controls, encryption, and other security measures, libraries can protect their data and ensure the integrity of their systems. At Metaguard, we are committed to helping libraries achieve these goals and providing the necessary support and training to ensure that data security and privacy remain a top priority.
0 notes
Text
How I ditched streaming services and learned to love Linux: A step-by-step guide to building your very own personal media streaming server (V2.0: REVISED AND EXPANDED EDITION)
This is a revised, corrected and expanded version of my tutorial on setting up a personal media server that previously appeared on my old blog (donjuan-auxenfers). I expect that that post is still making the rounds (hopefully with my addendum on modifying group share permissions in Ubuntu to circumvent 0x8007003B "Unexpected Network Error" messages in Windows 10/11 when transferring files) but I have no way of checking. Anyway this new revised version of the tutorial corrects one or two small errors I discovered when rereading what I wrote, adds links to all products mentioned and is just more polished generally. I also expanded it a bit, pointing more adventurous users toward programs such as Sonarr/Radarr/Lidarr and Overseerr which can be used for automating user requests and media collection.
So then, what is this tutorial? This is a tutorial on how to build and set up your own personal media server using Ubuntu as an operating system and Plex (or Jellyfin) to not only manage your media, but to also stream that media to your devices both at home and abroad anywhere in the world where you have an internet connection. Its intent is to show you how building a personal media server and stuffing it full of films, TV, and music that you acquired through indiscriminate and voracious media piracy various legal methods will free you to completely ditch paid streaming services. No more will you have to pay for Disney+, Netflix, HBOMAX, Hulu, Amazon Prime, Peacock, CBS All Access, Paramount+, Crave or any other streaming service that is not named Criterion Channel. Instead whenever you want to watch your favourite films and television shows, you’ll have your own personal service that only features things that you want to see, with files that you have control over. And for music fans out there, both Jellyfin and Plex support music streaming, meaning you can even ditch music streaming services. Goodbye Spotify, Youtube Music, Tidal and Apple Music, welcome back unreasonably large MP3 (or FLAC) collections.
On the hardware front, I’m going to offer a few options catered towards different budgets and media library sizes. The cost of getting a media server up and running using this guide will cost you anywhere from $450 CAD/$325 USD at the low end to $1500 CAD/$1100 USD at the high end (it could go higher). My server was priced closer to the higher figure, but I went and got a lot more storage than most people need. If that seems like a little much, consider for a moment, do you have a roommate, a close friend, or a family member who would be willing to chip in a few bucks towards your little project provided they get access? Well that's how I funded my server. It might also be worth thinking about the cost over time, i.e. how much you spend yearly on subscriptions vs. a one time cost of setting up a server. Additionally there's just the joy of being able to scream "fuck you" at all those show cancelling, library deleting, hedge fund vampire CEOs who run the studios through denying them your money. Drive a stake through David Zaslav's heart.
On the software side I will walk you step-by-step through installing Ubuntu as your server's operating system, configuring your storage as a RAIDz array with ZFS, sharing your zpool to Windows with Samba, running a remote connection between your server and your Windows PC, and then a little about started with Plex/Jellyfin. Every terminal command you will need to input will be provided, and I even share a custom #bash script that will make used vs. available drive space on your server display correctly in Windows.
If you have a different preferred flavour of Linux (Arch, Manjaro, Redhat, Fedora, Mint, OpenSUSE, CentOS, Slackware etc. et. al.) and are aching to tell me off for being basic and using Ubuntu, this tutorial is not for you. The sort of person with a preferred Linux distro is the sort of person who can do this sort of thing in their sleep. Also I don't care. This tutorial is intended for the average home computer user. This is also why we’re not using a more exotic home server solution like running everything through Docker Containers and managing it through a dashboard like Homarr or Heimdall. While such solutions are fantastic and can be very easy to maintain once you have it all set up, wrapping your brain around Docker is a whole thing in and of itself. If you do follow this tutorial and had fun putting everything together, then I would encourage you to return in a year’s time, do your research and set up everything with Docker Containers.
Lastly, this is a tutorial aimed at Windows users. Although I was a daily user of OS X for many years (roughly 2008-2023) and I've dabbled quite a bit with various Linux distributions (mostly Ubuntu and Manjaro), my primary OS these days is Windows 11. Many things in this tutorial will still be applicable to Mac users, but others (e.g. setting up shares) you will have to look up for yourself. I doubt it would be difficult to do so.
Nothing in this tutorial will require feats of computing expertise. All you will need is a basic computer literacy (i.e. an understanding of what a filesystem and directory are, and a degree of comfort in the settings menu) and a willingness to learn a thing or two. While this guide may look overwhelming at first glance, it is only because I want to be as thorough as possible. I want you to understand exactly what it is you're doing, I don't want you to just blindly follow steps. If you half-way know what you’re doing, you will be much better prepared if you ever need to troubleshoot.
Honestly, once you have all the hardware ready it shouldn't take more than an afternoon or two to get everything up and running.
(This tutorial is just shy of seven thousand words long so the rest is under the cut.)
Step One: Choosing Your Hardware
Linux is a light weight operating system, depending on the distribution there's close to no bloat. There are recent distributions available at this very moment that will run perfectly fine on a fourteen year old i3 with 4GB of RAM. Moreover, running Plex or Jellyfin isn’t resource intensive in 90% of use cases. All this is to say, we don’t require an expensive or powerful computer. This means that there are several options available: 1) use an old computer you already have sitting around but aren't using 2) buy a used workstation from eBay, or what I believe to be the best option, 3) order an N100 Mini-PC from AliExpress or Amazon.
Note: If you already have an old PC sitting around that you’ve decided to use, fantastic, move on to the next step.
When weighing your options, keep a few things in mind: the number of people you expect to be streaming simultaneously at any one time, the resolution and bitrate of your media library (4k video takes a lot more processing power than 1080p) and most importantly, how many of those clients are going to be transcoding at any one time. Transcoding is what happens when the playback device does not natively support direct playback of the source file. This can happen for a number of reasons, such as the playback device's native resolution being lower than the file's internal resolution, or because the source file was encoded in a video codec unsupported by the playback device.
Ideally we want any transcoding to be performed by hardware. This means we should be looking for a computer with an Intel processor with Quick Sync. Quick Sync is a dedicated core on the CPU die designed specifically for video encoding and decoding. This specialized hardware makes for highly efficient transcoding both in terms of processing overhead and power draw. Without these Quick Sync cores, transcoding must be brute forced through software. This takes up much more of a CPU’s processing power and requires much more energy. But not all Quick Sync cores are created equal and you need to keep this in mind if you've decided either to use an old computer or to shop for a used workstation on eBay
Any Intel processor from second generation Core (Sandy Bridge circa 2011) onward has Quick Sync cores. It's not until 6th gen (Skylake), however, that the cores support the H.265 HEVC codec. Intel’s 10th gen (Comet Lake) processors introduce support for 10bit HEVC and HDR tone mapping. And the recent 12th gen (Alder Lake) processors brought with them hardware AV1 decoding. As an example, while an 8th gen (Kaby Lake) i5-8500 will be able to hardware transcode a H.265 encoded file, it will fall back to software transcoding if given a 10bit H.265 file. If you’ve decided to use that old PC or to look on eBay for an old Dell Optiplex keep this in mind.
Note 1: The price of old workstations varies wildly and fluctuates frequently. If you get lucky and go shopping shortly after a workplace has liquidated a large number of their workstations you can find deals for as low as $100 on a barebones system, but generally an i5-8500 workstation with 16gb RAM will cost you somewhere in the area of $260 CAD/$200 USD.
Note 2: The AMD equivalent to Quick Sync is called Video Core Next, and while it's fine, it's not as efficient and not as mature a technology. It was only introduced with the first generation Ryzen CPUs and it only got decent with their newest CPUs, we want something cheap.
Alternatively you could forgo having to keep track of what generation of CPU is equipped with Quick Sync cores that feature support for which codecs, and just buy an N100 mini-PC. For around the same price or less of a used workstation you can pick up a mini-PC with an Intel N100 processor. The N100 is a four-core processor based on the 12th gen Alder Lake architecture and comes equipped with the latest revision of the Quick Sync cores. These little processors offer astounding hardware transcoding capabilities for their size and power draw. Otherwise they perform equivalent to an i5-6500, which isn't a terrible CPU. A friend of mine uses an N100 machine as a dedicated retro emulation gaming system and it does everything up to 6th generation consoles just fine. The N100 is also a remarkably efficient chip, it sips power. In fact, the difference between running one of these and an old workstation could work out to hundreds of dollars a year in energy bills depending on where you live.
You can find these Mini-PCs all over Amazon or for a little cheaper on AliExpress. They range in price from $170 CAD/$125 USD for a no name N100 with 8GB RAM to $280 CAD/$200 USD for a Beelink S12 Pro with 16GB RAM. The brand doesn't really matter, they're all coming from the same three factories in Shenzen, go for whichever one fits your budget or has features you want. 8GB RAM should be enough, Linux is lightweight and Plex only calls for 2GB RAM. 16GB RAM might result in a slightly snappier experience, especially with ZFS. A 256GB SSD is more than enough for what we need as a boot drive, but going for a bigger drive might allow you to get away with things like creating preview thumbnails for Plex, but it’s up to you and your budget.
The Mini-PC I wound up buying was a Firebat AK2 Plus with 8GB RAM and a 256GB SSD. It looks like this:

Note: Be forewarned that if you decide to order a Mini-PC from AliExpress, note the type of power adapter it ships with. The mini-PC I bought came with an EU power adapter and I had to supply my own North American power supply. Thankfully this is a minor issue as barrel plug 30W/12V/2.5A power adapters are easy to find and can be had for $10.
Step Two: Choosing Your Storage
Storage is the most important part of our build. It is also the most expensive. Thankfully it’s also the most easily upgrade-able down the line.
For people with a smaller media collection (4TB to 8TB), a more limited budget, or who will only ever have two simultaneous streams running, I would say that the most economical course of action would be to buy a USB 3.0 8TB external HDD. Something like this one from Western Digital or this one from Seagate. One of these external drives will cost you in the area of $200 CAD/$140 USD. Down the line you could add a second external drive or replace it with a multi-drive RAIDz set up such as detailed below.
If a single external drive the path for you, move on to step three.
For people with larger media libraries (12TB+), who prefer media in 4k, or care who about data redundancy, the answer is a RAID array featuring multiple HDDs in an enclosure.
Note: If you are using an old PC or used workstatiom as your server and have the room for at least three 3.5" drives, and as many open SATA ports on your mother board you won't need an enclosure, just install the drives into the case. If your old computer is a laptop or doesn’t have room for more internal drives, then I would suggest an enclosure.
The minimum number of drives needed to run a RAIDz array is three, and seeing as RAIDz is what we will be using, you should be looking for an enclosure with three to five bays. I think that four disks makes for a good compromise for a home server. Regardless of whether you go for a three, four, or five bay enclosure, do be aware that in a RAIDz array the space equivalent of one of the drives will be dedicated to parity at a ratio expressed by the equation 1 − 1/n i.e. in a four bay enclosure equipped with four 12TB drives, if we configured our drives in a RAIDz1 array we would be left with a total of 36TB of usable space (48TB raw size). The reason for why we might sacrifice storage space in such a manner will be explained in the next section.
A four bay enclosure will cost somewhere in the area of $200 CDN/$140 USD. You don't need anything fancy, we don't need anything with hardware RAID controls (RAIDz is done entirely in software) or even USB-C. An enclosure with USB 3.0 will perform perfectly fine. Don’t worry too much about USB speed bottlenecks. A mechanical HDD will be limited by the speed of its mechanism long before before it will be limited by the speed of a USB connection. I've seen decent looking enclosures from TerraMaster, Yottamaster, Mediasonic and Sabrent.
When it comes to selecting the drives, as of this writing, the best value (dollar per gigabyte) are those in the range of 12TB to 20TB. I settled on 12TB drives myself. If 12TB to 20TB drives are out of your budget, go with what you can afford, or look into refurbished drives. I'm not sold on the idea of refurbished drives but many people swear by them.
When shopping for harddrives, search for drives designed specifically for NAS use. Drives designed for NAS use typically have better vibration dampening and are designed to be active 24/7. They will also often make use of CMR (conventional magnetic recording) as opposed to SMR (shingled magnetic recording). This nets them a sizable read/write performance bump over typical desktop drives. Seagate Ironwolf and Toshiba NAS are both well regarded brands when it comes to NAS drives. I would avoid Western Digital Red drives at this time. WD Reds were a go to recommendation up until earlier this year when it was revealed that they feature firmware that will throw up false SMART warnings telling you to replace the drive at the three year mark quite often when there is nothing at all wrong with that drive. It will likely even be good for another six, seven, or more years.

Step Three: Installing Linux
For this step you will need a USB thumbdrive of at least 6GB in capacity, an .ISO of Ubuntu, and a way to make that thumbdrive bootable media.
First download a copy of Ubuntu desktop (for best performance we could download the Server release, but for new Linux users I would recommend against the server release. The server release is strictly command line interface only, and having a GUI is very helpful for most people. Not many people are wholly comfortable doing everything through the command line, I'm certainly not one of them, and I grew up with DOS 6.0. 22.04.3 Jammy Jellyfish is the current Long Term Service release, this is the one to get.
Download the .ISO and then download and install balenaEtcher on your Windows PC. BalenaEtcher is an easy to use program for creating bootable media, you simply insert your thumbdrive, select the .ISO you just downloaded, and it will create a bootable installation media for you.
Once you've made a bootable media and you've got your Mini-PC (or you old PC/used workstation) in front of you, hook it directly into your router with an ethernet cable, and then plug in the HDD enclosure, a monitor, a mouse and a keyboard. Now turn that sucker on and hit whatever key gets you into the BIOS (typically ESC, DEL or F2). If you’re using a Mini-PC check to make sure that the P1 and P2 power limits are set correctly, my N100's P1 limit was set at 10W, a full 20W under the chip's power limit. Also make sure that the RAM is running at the advertised speed. My Mini-PC’s RAM was set at 2333Mhz out of the box when it should have been 3200Mhz. Once you’ve done that, key over to the boot order and place the USB drive first in the boot order. Then save the BIOS settings and restart.
After you restart you’ll be greeted by Ubuntu's installation screen. Installing Ubuntu is really straight forward, select the "minimal" installation option, as we won't need anything on this computer except for a browser (Ubuntu comes preinstalled with Firefox) and Plex Media Server/Jellyfin Media Server. Also remember to delete and reformat that Windows partition! We don't need it.
Step Four: Installing ZFS and Setting Up the RAIDz Array
Note: If you opted for just a single external HDD skip this step and move onto setting up a Samba share.
Once Ubuntu is installed it's time to configure our storage by installing ZFS to build our RAIDz array. ZFS is a "next-gen" file system that is both massively flexible and massively complex. It's capable of snapshot backup, self healing error correction, ZFS pools can be configured with drives operating in a supplemental manner alongside the storage vdev (e.g. fast cache, dedicated secondary intent log, hot swap spares etc.). It's also a file system very amenable to fine tuning. Block and sector size are adjustable to use case and you're afforded the option of different methods of inline compression. If you'd like a very detailed overview and explanation of its various features and tips on tuning a ZFS array check out these articles from Ars Technica. For now we're going to ignore all these features and keep it simple, we're going to pull our drives together into a single vdev running in RAIDz which will be the entirety of our zpool, no fancy cache drive or SLOG.
Open up the terminal and type the following commands:
sudo apt update
then
sudo apt install zfsutils-linux
This will install the ZFS utility. Verify that it's installed with the following command:
zfs --version
Now, it's time to check that the HDDs we have in the enclosure are healthy, running, and recognized. We also want to find out their device IDs and take note of them:
sudo fdisk -1
Note: You might be wondering why some of these commands require "sudo" in front of them while others don't. "Sudo" is short for "super user do”. When and where "sudo" is used has to do with the way permissions are set up in Linux. Only the "root" user has the access level to perform certain tasks in Linux. As a matter of security and safety regular user accounts are kept separate from the "root" user. It's not advised (or even possible) to boot into Linux as "root" with most modern distributions. Instead by using "sudo" our regular user account is temporarily given the power to do otherwise forbidden things. Don't worry about it too much at this stage, but if you want to know more check out this introduction.
If everything is working you should get a list of the various drives detected along with their device IDs which will look like this: /dev/sdc. You can also check the device IDs of the drives by opening the disk utility app. Jot these IDs down as we'll need them for our next step, creating our RAIDz array.
RAIDz is similar to RAID-5 in that instead of striping your data over multiple disks, exchanging redundancy for speed and available space (RAID-0), or mirroring your data writing by two copies of every piece (RAID-1), it instead writes parity blocks across the disks in addition to striping, this provides a balance of speed, redundancy and available space. If a single drive fails, the parity blocks on the working drives can be used to reconstruct the entire array as soon as a replacement drive is added.
Additionally, RAIDz improves over some of the common RAID-5 flaws. It's more resilient and capable of self healing, as it is capable of automatically checking for errors against a checksum. It's more forgiving in this way, and it's likely that you'll be able to detect when a drive is dying well before it fails. A RAIDz array can survive the loss of any one drive.
Note: While RAIDz is indeed resilient, if a second drive fails during the rebuild, you're fucked. Always keep backups of things you can't afford to lose. This tutorial, however, is not about proper data safety.
To create the pool, use the following command:
sudo zpool create "zpoolnamehere" raidz "device IDs of drives we're putting in the pool"
For example, let's creatively name our zpool "mypool". This poil will consist of four drives which have the device IDs: sdb, sdc, sdd, and sde. The resulting command will look like this:
sudo zpool create mypool raidz /dev/sdb /dev/sdc /dev/sdd /dev/sde
If as an example you bought five HDDs and decided you wanted more redundancy dedicating two drive to this purpose, we would modify the command to "raidz2" and the command would look something like the following:
sudo zpool create mypool raidz2 /dev/sdb /dev/sdc /dev/sdd /dev/sde /dev/sdf
An array configured like this is known as RAIDz2 and is able to survive two disk failures.
Once the zpool has been created, we can check its status with the command:
zpool status
Or more concisely with:
zpool list
The nice thing about ZFS as a file system is that a pool is ready to go immediately after creation. If we were to set up a traditional RAID-5 array using mbam, we'd have to sit through a potentially hours long process of reformatting and partitioning the drives. Instead we're ready to go right out the gates.
The zpool should be automatically mounted to the filesystem after creation, check on that with the following:
df -hT | grep zfs
Note: If your computer ever loses power suddenly, say in event of a power outage, you may have to re-import your pool. In most cases, ZFS will automatically import and mount your pool, but if it doesn’t and you can't see your array, simply open the terminal and type sudo zpool import -a.
By default a zpool is mounted at /"zpoolname". The pool should be under our ownership but let's make sure with the following command:
sudo chown -R "yourlinuxusername" /"zpoolname"
Note: Changing file and folder ownership with "chown" and file and folder permissions with "chmod" are essential commands for much of the admin work in Linux, but we won't be dealing with them extensively in this guide. If you'd like a deeper tutorial and explanation you can check out these two guides: chown and chmod.
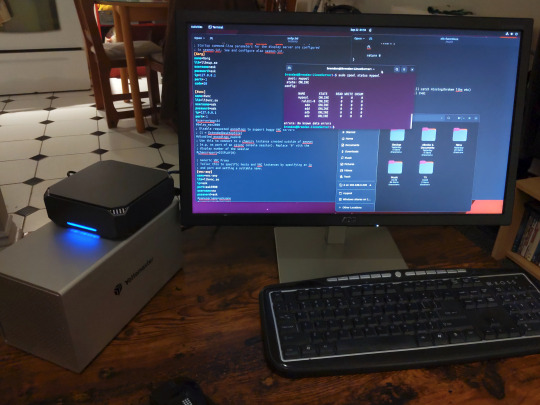
You can access the zpool file system through the GUI by opening the file manager (the Ubuntu default file manager is called Nautilus) and clicking on "Other Locations" on the sidebar, then entering the Ubuntu file system and looking for a folder with your pool's name. Bookmark the folder on the sidebar for easy access.
Your storage pool is now ready to go. Assuming that we already have some files on our Windows PC we want to copy to over, we're going to need to install and configure Samba to make the pool accessible in Windows.
Step Five: Setting Up Samba/Sharing
Samba is what's going to let us share the zpool with Windows and allow us to write to it from our Windows machine. First let's install Samba with the following commands:
sudo apt-get update
then
sudo apt-get install samba
Next create a password for Samba.
sudo smbpswd -a "yourlinuxusername"
It will then prompt you to create a password. Just reuse your Ubuntu user password for simplicity's sake.
Note: if you're using just a single external drive replace the zpool location in the following commands with wherever it is your external drive is mounted, for more information see this guide on mounting an external drive in Ubuntu.
After you've created a password we're going to create a shareable folder in our pool with this command
mkdir /"zpoolname"/"foldername"
Now we're going to open the smb.conf file and make that folder shareable. Enter the following command.
sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.conf
This will open the .conf file in nano, the terminal text editor program. Now at the end of smb.conf add the following entry:
["foldername"]
path = /"zpoolname"/"foldername"
available = yes
valid users = "yourlinuxusername"
read only = no
writable = yes
browseable = yes
guest ok = no
Ensure that there are no line breaks between the lines and that there's a space on both sides of the equals sign. Our next step is to allow Samba traffic through the firewall:
sudo ufw allow samba
Finally restart the Samba service:
sudo systemctl restart smbd
At this point we'll be able to access to the pool, browse its contents, and read and write to it from Windows. But there's one more thing left to do, Windows doesn't natively support the ZFS file systems and will read the used/available/total space in the pool incorrectly. Windows will read available space as total drive space, and all used space as null. This leads to Windows only displaying a dwindling amount of "available" space as the drives are filled. We can fix this! Functionally this doesn't actually matter, we can still write and read to and from the disk, it just makes it difficult to tell at a glance the proportion of used/available space, so this is an optional step but one I recommend (this step is also unnecessary if you're just using a single external drive). What we're going to do is write a little shell script in #bash. Open nano with the terminal with the command:
nano
Now insert the following code:
#!/bin/bash CUR_PATH=`pwd` ZFS_CHECK_OUTPUT=$(zfs get type $CUR_PATH 2>&1 > /dev/null) > /dev/null if [[ $ZFS_CHECK_OUTPUT == *not\ a\ ZFS* ]] then IS_ZFS=false else IS_ZFS=true fi if [[ $IS_ZFS = false ]] then df $CUR_PATH | tail -1 | awk '{print $2" "$4}' else USED=$((`zfs get -o value -Hp used $CUR_PATH` / 1024)) > /dev/null AVAIL=$((`zfs get -o value -Hp available $CUR_PATH` / 1024)) > /dev/null TOTAL=$(($USED+$AVAIL)) > /dev/null echo $TOTAL $AVAIL fi
Save the script as "dfree.sh" to /home/"yourlinuxusername" then change the ownership of the file to make it executable with this command:
sudo chmod 774 dfree.sh
Now open smb.conf with sudo again:
sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.conf
Now add this entry to the top of the configuration file to direct Samba to use the results of our script when Windows asks for a reading on the pool's used/available/total drive space:
[global]
dfree command = /home/"yourlinuxusername"/dfree.sh
Save the changes to smb.conf and then restart Samba again with the terminal:
sudo systemctl restart smbd
Now there’s one more thing we need to do to fully set up the Samba share, and that’s to modify a hidden group permission. In the terminal window type the following command:
usermod -a -G sambashare “yourlinuxusername”
Then restart samba again:
sudo systemctl restart smbd
If we don’t do this last step, everything will appear to work fine, and you will even be able to see and map the drive from Windows and even begin transferring files, but you'd soon run into a lot of frustration. As every ten minutes or so a file would fail to transfer and you would get a window announcing “0x8007003B Unexpected Network Error”. This window would require your manual input to continue the transfer with the file next in the queue. And at the end it would reattempt to transfer whichever files failed the first time around. 99% of the time they’ll go through that second try, but this is still all a major pain in the ass. Especially if you’ve got a lot of data to transfer or you want to step away from the computer for a while.
It turns out samba can act a little weirdly with the higher read/write speeds of RAIDz arrays and transfers from Windows, and will intermittently crash and restart itself if this group option isn’t changed. Inputting the above command will prevent you from ever seeing that window.
The last thing we're going to do before switching over to our Windows PC is grab the IP address of our Linux machine. Enter the following command:
hostname -I
This will spit out this computer's IP address on the local network (it will look something like 192.168.0.x), write it down. It might be a good idea once you're done here to go into your router settings and reserving that IP for your Linux system in the DHCP settings. Check the manual for your specific model router on how to access its settings, typically it can be accessed by opening a browser and typing http:\\192.168.0.1 in the address bar, but your router may be different.
Okay we’re done with our Linux computer for now. Get on over to your Windows PC, open File Explorer, right click on Network and click "Map network drive". Select Z: as the drive letter (you don't want to map the network drive to a letter you could conceivably be using for other purposes) and enter the IP of your Linux machine and location of the share like so: \\"LINUXCOMPUTERLOCALIPADDRESSGOESHERE"\"zpoolnamegoeshere"\. Windows will then ask you for your username and password, enter the ones you set earlier in Samba and you're good. If you've done everything right it should look something like this:

You can now start moving media over from Windows to the share folder. It's a good idea to have a hard line running to all machines. Moving files over Wi-Fi is going to be tortuously slow, the only thing that’s going to make the transfer time tolerable (hours instead of days) is a solid wired connection between both machines and your router.
Step Six: Setting Up Remote Desktop Access to Your Server
After the server is up and going, you’ll want to be able to access it remotely from Windows. Barring serious maintenance/updates, this is how you'll access it most of the time. On your Linux system open the terminal and enter:
sudo apt install xrdp
Then:
sudo systemctl enable xrdp
Once it's finished installing, open “Settings” on the sidebar and turn off "automatic login" in the User category. Then log out of your account. Attempting to remotely connect to your Linux computer while you’re logged in will result in a black screen!
Now get back on your Windows PC, open search and look for "RDP". A program called "Remote Desktop Connection" should pop up, open this program as an administrator by right-clicking and selecting “run as an administrator”. You’ll be greeted with a window. In the field marked “Computer” type in the IP address of your Linux computer. Press connect and you'll be greeted with a new window and prompt asking for your username and password. Enter your Ubuntu username and password here.
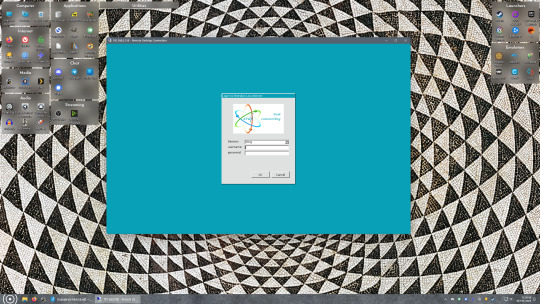
If everything went right, you’ll be logged into your Linux computer. If the performance is sluggish, adjust the display options. Lowering the resolution and colour depth do a lot to make the interface feel snappier.
Remote access is how we're going to be using our Linux system from now, barring edge cases like needing to get into the BIOS or upgrading to a new version of Ubuntu. Everything else from performing maintenance like a monthly zpool scrub to checking zpool status and updating software can all be done remotely.

This is how my server lives its life now, happily humming and chirping away on the floor next to the couch in a corner of the living room.
Step Seven: Plex Media Server/Jellyfin
Okay we’ve got all the ground work finished and our server is almost up and running. We’ve got Ubuntu up and running, our storage array is primed, we’ve set up remote connections and sharing, and maybe we’ve moved over some of favourite movies and TV shows.
Now we need to decide on the media server software to use which will stream our media to us and organize our library. For most people I’d recommend Plex. It just works 99% of the time. That said, Jellyfin has a lot to recommend it by too, even if it is rougher around the edges. Some people run both simultaneously, it’s not that big of an extra strain. I do recommend doing a little bit of your own research into the features each platform offers, but as a quick run down, consider some of the following points:
Plex is closed source and is funded through PlexPass purchases while Jellyfin is open source and entirely user driven. This means a number of things: for one, Plex requires you to purchase a “PlexPass” (purchased as a one time lifetime fee $159.99 CDN/$120 USD or paid for on a monthly or yearly subscription basis) in order to access to certain features, like hardware transcoding (and we want hardware transcoding) or automated intro/credits detection and skipping, Jellyfin offers some of these features for free through plugins. Plex supports a lot more devices than Jellyfin and updates more frequently. That said, Jellyfin's Android and iOS apps are completely free, while the Plex Android and iOS apps must be activated for a one time cost of $6 CDN/$5 USD. But that $6 fee gets you a mobile app that is much more functional and features a unified UI across platforms, the Plex mobile apps are simply a more polished experience. The Jellyfin apps are a bit of a mess and the iOS and Android versions are very different from each other.
Jellyfin’s actual media player is more fully featured than Plex's, but on the other hand Jellyfin's UI, library customization and automatic media tagging really pale in comparison to Plex. Streaming your music library is free through both Jellyfin and Plex, but Plex offers the PlexAmp app for dedicated music streaming which boasts a number of fantastic features, unfortunately some of those fantastic features require a PlexPass. If your internet is down, Jellyfin can still do local streaming, while Plex can fail to play files unless you've got it set up a certain way. Jellyfin has a slew of neat niche features like support for Comic Book libraries with the .cbz/.cbt file types, but then Plex offers some free ad-supported TV and films, they even have a free channel that plays nothing but Classic Doctor Who.
Ultimately it's up to you, I settled on Plex because although some features are pay-walled, it just works. It's more reliable and easier to use, and a one-time fee is much easier to swallow than a subscription. I had a pretty easy time getting my boomer parents and tech illiterate brother introduced to and using Plex and I don't know if I would've had as easy a time doing that with Jellyfin. I do also need to mention that Jellyfin does take a little extra bit of tinkering to get going in Ubuntu, you’ll have to set up process permissions, so if you're more tolerant to tinkering, Jellyfin might be up your alley and I’ll trust that you can follow their installation and configuration guide. For everyone else, I recommend Plex.
So pick your poison: Plex or Jellyfin.
Note: The easiest way to download and install either of these packages in Ubuntu is through Snap Store.
After you've installed one (or both), opening either app will launch a browser window into the browser version of the app allowing you to set all the options server side.
The process of adding creating media libraries is essentially the same in both Plex and Jellyfin. You create a separate libraries for Television, Movies, and Music and add the folders which contain the respective types of media to their respective libraries. The only difficult or time consuming aspect is ensuring that your files and folders follow the appropriate naming conventions:
Plex naming guide for Movies
Plex naming guide for Television
Jellyfin follows the same naming rules but I find their media scanner to be a lot less accurate and forgiving than Plex. Once you've selected the folders to be scanned the service will scan your files, tagging everything and adding metadata. Although I find do find Plex more accurate, it can still erroneously tag some things and you might have to manually clean up some tags in a large library. (When I initially created my library it tagged the 1963-1989 Doctor Who as some Korean soap opera and I needed to manually select the correct match after which everything was tagged normally.) It can also be a bit testy with anime (especially OVAs) be sure to check TVDB to ensure that you have your files and folders structured and named correctly. If something is not showing up at all, double check the name.
Once that's done, organizing and customizing your library is easy. You can set up collections, grouping items together to fit a theme or collect together all the entries in a franchise. You can make playlists, and add custom artwork to entries. It's fun setting up collections with posters to match, there are even several websites dedicated to help you do this like PosterDB. As an example, below are two collections in my library, one collecting all the entries in a franchise, the other follows a theme.

My Star Trek collection, featuring all eleven television series, and thirteen films.
My Best of the Worst collection, featuring sixty-nine films previously showcased on RedLetterMedia’s Best of the Worst. They’re all absolutely terrible and I love them.
As for settings, ensure you've got Remote Access going, it should work automatically and be sure to set your upload speed after running a speed test. In the library settings set the database cache to 2000MB to ensure a snappier and more responsive browsing experience, and then check that playback quality is set to original/maximum. If you’re severely bandwidth limited on your upload and have remote users, you might want to limit the remote stream bitrate to something more reasonable, just as a note of comparison Netflix’s 1080p bitrate is approximately 5Mbps, although almost anyone watching through a chromium based browser is streaming at 720p and 3mbps. Other than that you should be good to go. For actually playing your files, there's a Plex app for just about every platform imaginable. I mostly watch television and films on my laptop using the Windows Plex app, but I also use the Android app which can broadcast to the chromecast connected to the TV in the office and the Android TV app for our smart TV. Both are fully functional and easy to navigate, and I can also attest to the OS X version being equally functional.
Part Eight: Finding Media
Now, this is not really a piracy tutorial, there are plenty of those out there. But if you’re unaware, BitTorrent is free and pretty easy to use, just pick a client (qBittorrent is the best) and go find some public trackers to peruse. Just know now that all the best trackers are private and invite only, and that they can be exceptionally difficult to get into. I’m already on a few, and even then, some of the best ones are wholly out of my reach.
If you decide to take the left hand path and turn to Usenet you’ll have to pay. First you’ll need to sign up with a provider like Newshosting or EasyNews for access to Usenet itself, and then to actually find anything you’re going to need to sign up with an indexer like NZBGeek or NZBFinder. There are dozens of indexers, and many people cross post between them, but for more obscure media it’s worth checking multiple. You’ll also need a binary downloader like SABnzbd. That caveat aside, Usenet is faster, bigger, older, less traceable than BitTorrent, and altogether slicker. I honestly prefer it, and I'm kicking myself for taking this long to start using it because I was scared off by the price. I’ve found so many things on Usenet that I had sought in vain elsewhere for years, like a 2010 Italian film about a massacre perpetrated by the SS that played the festival circuit but never received a home media release; some absolute hero uploaded a rip of a festival screener DVD to Usenet. Anyway, figure out the rest of this shit on your own and remember to use protection, get yourself behind a VPN, use a SOCKS5 proxy with your BitTorrent client, etc.
On the legal side of things, if you’re around my age, you (or your family) probably have a big pile of DVDs and Blu-Rays sitting around unwatched and half forgotten. Why not do a bit of amateur media preservation, rip them and upload them to your server for easier access? (Your tools for this are going to be Handbrake to do the ripping and AnyDVD to break any encryption.) I went to the trouble of ripping all my SCTV DVDs (five box sets worth) because none of it is on streaming nor could it be found on any pirate source I tried. I’m glad I did, forty years on it’s still one of the funniest shows to ever be on TV.
Part Nine/Epilogue: Sonarr/Radarr/Lidarr and Overseerr
There are a lot of ways to automate your server for better functionality or to add features you and other users might find useful. Sonarr, Radarr, and Lidarr are a part of a suite of “Servarr” services (there’s also Readarr for books and Whisparr for adult content) that allow you to automate the collection of new episodes of TV shows (Sonarr), new movie releases (Radarr) and music releases (Lidarr). They hook in to your BitTorrent client or Usenet binary newsgroup downloader and crawl your preferred Torrent trackers and Usenet indexers, alerting you to new releases and automatically grabbing them. You can also use these services to manually search for new media, and even replace/upgrade your existing media with better quality uploads. They’re really a little tricky to set up on a bare metal Ubuntu install (ideally you should be running them in Docker Containers), and I won’t be providing a step by step on installing and running them, I’m simply making you aware of their existence.
The other bit of kit I want to make you aware of is Overseerr which is a program that scans your Plex media library and will serve recommendations based on what you like. It also allows you and your users to request specific media. It can even be integrated with Sonarr/Radarr/Lidarr so that fulfilling those requests is fully automated.
And you're done. It really wasn't all that hard. Enjoy your media. Enjoy the control you have over that media. And be safe in the knowledge that no hedgefund CEO motherfucker who hates the movies but who is somehow in control of a major studio will be able to disappear anything in your library as a tax write-off.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Humans are not perfectly vigilant

I'm on tour with my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me in BOSTON with Randall "XKCD" Munroe (Apr 11), then PROVIDENCE (Apr 12), and beyond!

Here's a fun AI story: a security researcher noticed that large companies' AI-authored source-code repeatedly referenced a nonexistent library (an AI "hallucination"), so he created a (defanged) malicious library with that name and uploaded it, and thousands of developers automatically downloaded and incorporated it as they compiled the code:
https://www.theregister.com/2024/03/28/ai_bots_hallucinate_software_packages/
These "hallucinations" are a stubbornly persistent feature of large language models, because these models only give the illusion of understanding; in reality, they are just sophisticated forms of autocomplete, drawing on huge databases to make shrewd (but reliably fallible) guesses about which word comes next:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3442188.3445922
Guessing the next word without understanding the meaning of the resulting sentence makes unsupervised LLMs unsuitable for high-stakes tasks. The whole AI bubble is based on convincing investors that one or more of the following is true:
There are low-stakes, high-value tasks that will recoup the massive costs of AI training and operation;
There are high-stakes, high-value tasks that can be made cheaper by adding an AI to a human operator;
Adding more training data to an AI will make it stop hallucinating, so that it can take over high-stakes, high-value tasks without a "human in the loop."
These are dubious propositions. There's a universe of low-stakes, low-value tasks – political disinformation, spam, fraud, academic cheating, nonconsensual porn, dialog for video-game NPCs – but none of them seem likely to generate enough revenue for AI companies to justify the billions spent on models, nor the trillions in valuation attributed to AI companies:
https://locusmag.com/2023/12/commentary-cory-doctorow-what-kind-of-bubble-is-ai/
The proposition that increasing training data will decrease hallucinations is hotly contested among AI practitioners. I confess that I don't know enough about AI to evaluate opposing sides' claims, but even if you stipulate that adding lots of human-generated training data will make the software a better guesser, there's a serious problem. All those low-value, low-stakes applications are flooding the internet with botshit. After all, the one thing AI is unarguably very good at is producing bullshit at scale. As the web becomes an anaerobic lagoon for botshit, the quantum of human-generated "content" in any internet core sample is dwindling to homeopathic levels:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/03/14/inhuman-centipede/#enshittibottification
This means that adding another order of magnitude more training data to AI won't just add massive computational expense – the data will be many orders of magnitude more expensive to acquire, even without factoring in the additional liability arising from new legal theories about scraping:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/17/how-to-think-about-scraping/
That leaves us with "humans in the loop" – the idea that an AI's business model is selling software to businesses that will pair it with human operators who will closely scrutinize the code's guesses. There's a version of this that sounds plausible – the one in which the human operator is in charge, and the AI acts as an eternally vigilant "sanity check" on the human's activities.
For example, my car has a system that notices when I activate my blinker while there's another car in my blind-spot. I'm pretty consistent about checking my blind spot, but I'm also a fallible human and there've been a couple times where the alert saved me from making a potentially dangerous maneuver. As disciplined as I am, I'm also sometimes forgetful about turning off lights, or waking up in time for work, or remembering someone's phone number (or birthday). I like having an automated system that does the robotically perfect trick of never forgetting something important.
There's a name for this in automation circles: a "centaur." I'm the human head, and I've fused with a powerful robot body that supports me, doing things that humans are innately bad at.
That's the good kind of automation, and we all benefit from it. But it only takes a small twist to turn this good automation into a nightmare. I'm speaking here of the reverse-centaur: automation in which the computer is in charge, bossing a human around so it can get its job done. Think of Amazon warehouse workers, who wear haptic bracelets and are continuously observed by AI cameras as autonomous shelves shuttle in front of them and demand that they pick and pack items at a pace that destroys their bodies and drives them mad:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/04/17/revenge-of-the-chickenized-reverse-centaurs/
Automation centaurs are great: they relieve humans of drudgework and let them focus on the creative and satisfying parts of their jobs. That's how AI-assisted coding is pitched: rather than looking up tricky syntax and other tedious programming tasks, an AI "co-pilot" is billed as freeing up its human "pilot" to focus on the creative puzzle-solving that makes coding so satisfying.
But an hallucinating AI is a terrible co-pilot. It's just good enough to get the job done much of the time, but it also sneakily inserts booby-traps that are statistically guaranteed to look as plausible as the good code (that's what a next-word-guessing program does: guesses the statistically most likely word).
This turns AI-"assisted" coders into reverse centaurs. The AI can churn out code at superhuman speed, and you, the human in the loop, must maintain perfect vigilance and attention as you review that code, spotting the cleverly disguised hooks for malicious code that the AI can't be prevented from inserting into its code. As "Lena" writes, "code review [is] difficult relative to writing new code":
https://twitter.com/qntm/status/1773779967521780169
Why is that? "Passively reading someone else's code just doesn't engage my brain in the same way. It's harder to do properly":
https://twitter.com/qntm/status/1773780355708764665
There's a name for this phenomenon: "automation blindness." Humans are just not equipped for eternal vigilance. We get good at spotting patterns that occur frequently – so good that we miss the anomalies. That's why TSA agents are so good at spotting harmless shampoo bottles on X-rays, even as they miss nearly every gun and bomb that a red team smuggles through their checkpoints:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/23/automation-blindness/#humans-in-the-loop
"Lena"'s thread points out that this is as true for AI-assisted driving as it is for AI-assisted coding: "self-driving cars replace the experience of driving with the experience of being a driving instructor":
https://twitter.com/qntm/status/1773841546753831283
In other words, they turn you into a reverse-centaur. Whereas my blind-spot double-checking robot allows me to make maneuvers at human speed and points out the things I've missed, a "supervised" self-driving car makes maneuvers at a computer's frantic pace, and demands that its human supervisor tirelessly and perfectly assesses each of those maneuvers. No wonder Cruise's murderous "self-driving" taxis replaced each low-waged driver with 1.5 high-waged technical robot supervisors:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/01/11/robots-stole-my-jerb/#computer-says-no
AI radiology programs are said to be able to spot cancerous masses that human radiologists miss. A centaur-based AI-assisted radiology program would keep the same number of radiologists in the field, but they would get less done: every time they assessed an X-ray, the AI would give them a second opinion. If the human and the AI disagreed, the human would go back and re-assess the X-ray. We'd get better radiology, at a higher price (the price of the AI software, plus the additional hours the radiologist would work).
But back to making the AI bubble pay off: for AI to pay off, the human in the loop has to reduce the costs of the business buying an AI. No one who invests in an AI company believes that their returns will come from business customers to agree to increase their costs. The AI can't do your job, but the AI salesman can convince your boss to fire you and replace you with an AI anyway – that pitch is the most successful form of AI disinformation in the world.
An AI that "hallucinates" bad advice to fliers can't replace human customer service reps, but airlines are firing reps and replacing them with chatbots:
https://www.bbc.com/travel/article/20240222-air-canada-chatbot-misinformation-what-travellers-should-know
An AI that "hallucinates" bad legal advice to New Yorkers can't replace city services, but Mayor Adams still tells New Yorkers to get their legal advice from his chatbots:
https://arstechnica.com/ai/2024/03/nycs-government-chatbot-is-lying-about-city-laws-and-regulations/
The only reason bosses want to buy robots is to fire humans and lower their costs. That's why "AI art" is such a pisser. There are plenty of harmless ways to automate art production with software – everything from a "healing brush" in Photoshop to deepfake tools that let a video-editor alter the eye-lines of all the extras in a scene to shift the focus. A graphic novelist who models a room in The Sims and then moves the camera around to get traceable geometry for different angles is a centaur – they are genuinely offloading some finicky drudgework onto a robot that is perfectly attentive and vigilant.
But the pitch from "AI art" companies is "fire your graphic artists and replace them with botshit." They're pitching a world where the robots get to do all the creative stuff (badly) and humans have to work at robotic pace, with robotic vigilance, in order to catch the mistakes that the robots make at superhuman speed.
Reverse centaurism is brutal. That's not news: Charlie Chaplin documented the problems of reverse centaurs nearly 100 years ago:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Modern_Times_(film)
As ever, the problem with a gadget isn't what it does: it's who it does it for and who it does it to. There are plenty of benefits from being a centaur – lots of ways that automation can help workers. But the only path to AI profitability lies in reverse centaurs, automation that turns the human in the loop into the crumple-zone for a robot:
https://estsjournal.org/index.php/ests/article/view/260

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/01/human-in-the-loop/#monkey-in-the-middle

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
--
Jorge Royan (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Munich_-_Two_boys_playing_in_a_park_-_7328.jpg
CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en
--
Noah Wulf (modified) https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Thunderbirds_at_Attention_Next_to_Thunderbird_1_-_Aviation_Nation_2019.jpg
CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#ai#supervised ai#humans in the loop#coding assistance#ai art#fully automated luxury communism#labor
379 notes
·
View notes
Text
Limbus company sinner's favourite games
(source: vibes)
Yi sang - Scribblenauts unlimited, creative and puzzling which seems right for him, maybe escape room puzzle games too
Faust - rhythm games, the one thing that faustcord cant spoil her on, also maybe games that take forever to learn and need 2 wikis open to understand like dwarf fortress.
I feel like her and yi sang would also play uber modded Minecraft together, she has all the knowledge about every mod and he likes tinkering with them to combine the systems into new ways of automation
Don Quixote - Baldur's gate 3, skyrim, anything with a lot of exploration and adventure, alternatively maybe she'd be into doom
Gregor - Fruit ninja... (in reality probably something like stardew valley or another calming survival game)
Rodion - those slot machine simulators, online poker, extremely degenerate gambling
Sinclair - dance dance revolution baby wooo (they have a really old and terrible Xbox 360 hooked up in the back of the bus) ((he always gets obliterated by faust))
Ishmael - sea of thieves (in reality probably The Sims)
Heathcliff - in public he plays competitive first person shooters and fighting games, flames people in chat when they mess up, the secret he plays wholesome romantic visual novels
hong lu - plays fighting games with heathcliff, wins 80% of the time, never gets angry when he loses which makes heathcliff even angrier, sometimes lets him win (it makes him even more angry),
I also imagine him going along with what the other sinners want to play and doesn't really suggest anything of his own
Meursault - New York times style newspaper games 100%, sudoku, crossword, etc,
alternatively stuff like factorio
Outis - 1000% she plays real-time strategy games like Hearts of iron 4 and stellaris, maybe even Warhammer total war, the more simulated war crimes the better
possibly a League of legends ranked player (in which case she's 1,000% diamond 2 and banned from chat)
Ryoshu - cyberpunk, GTA, any game which lets her cause general mayhem upon the populace, possibly also metal gear revengeance due to the cutting action
Dante - library of ruina
vergilius - he does NOT game
charon - forza
55 notes
·
View notes
Text
Russian State Library
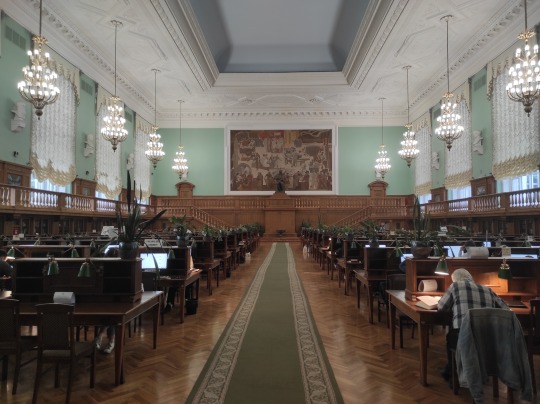

The biggest library in Russia and one of the biggest in the world. It was designed in late 1920s, soon after the birth of the new Soviet state, and fully finished in the 1950s. In includes 4 buildings and one 19-floor book repository. There are several reading halls, a cafe, and a whole bunch of book-filled nooks and crannies.
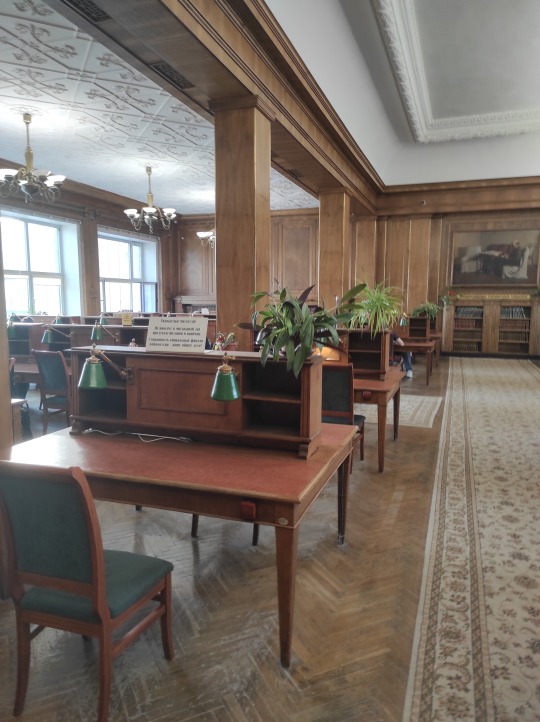
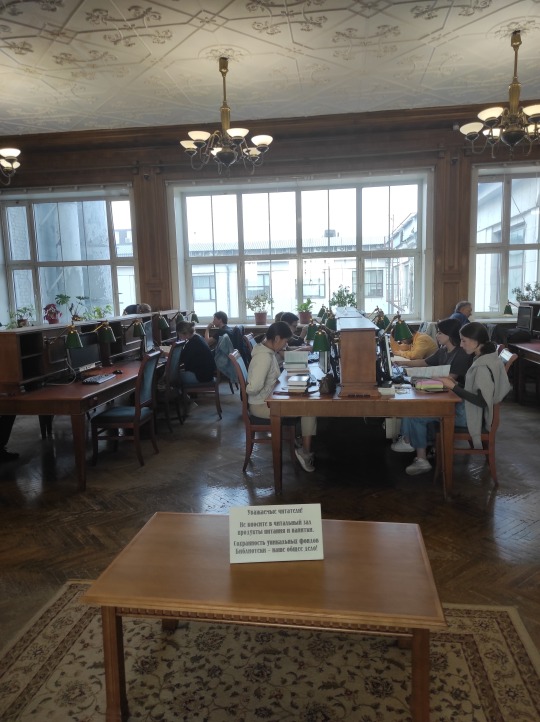
I'm writing this post sitting in the library's biggest reading hall - Reading Hall No. 3. It was opened in 1957 and still retains most of the original furniture and design (only there are now individual power sockets in every desk). Most of the tables are occupied by people with books and laptops. It's very quiet.

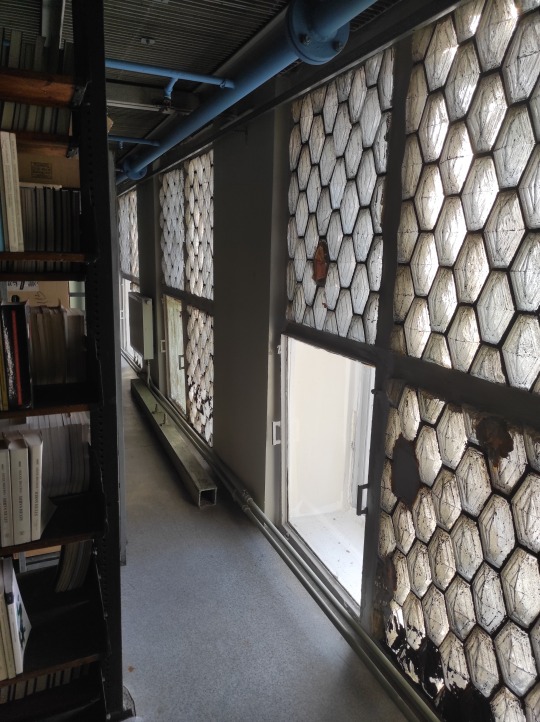
The book depository is a huge building that rises high above everything else in this historical area. It had 10 floors originally, each 5m high, but later it was divided into 19 smaller floors. We visited one of the floors. I was impressed to see that the windows are made out of Falconnier glass blocks (made specially for the library in Gus Khrustalny).
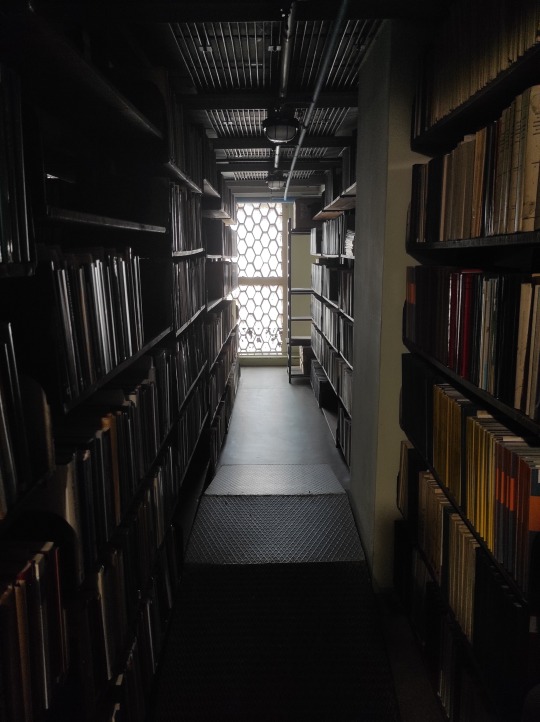



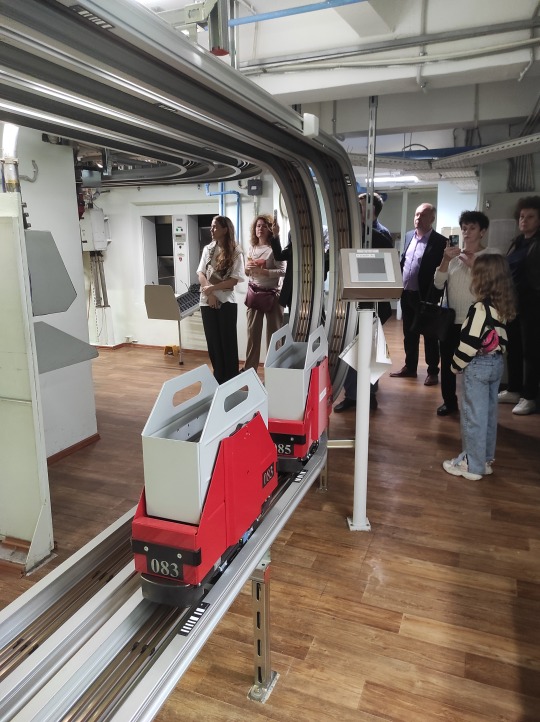
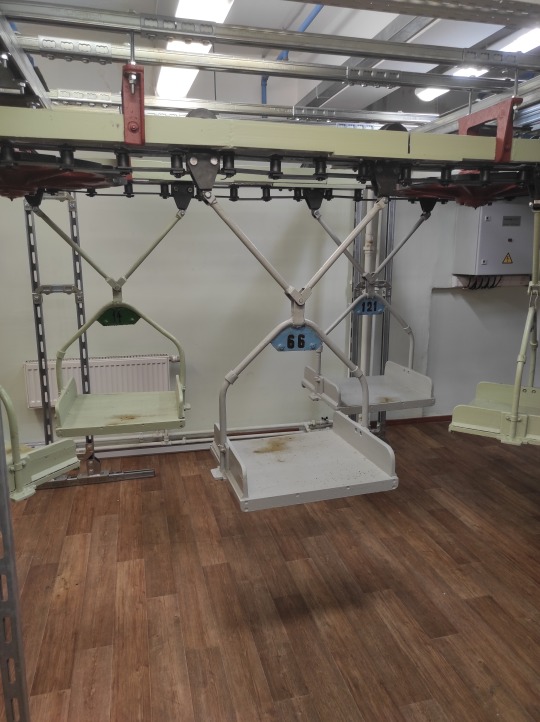
There are two automated delivery systems in the library: one delivers readers' orders into the depository (pneumatic tubes) and the other delivers books back to the reader (monorail). We had a chance to see both of them in action, very impressive! They also kept a bit of the old book delivery system that worked from 1953 until 2015. I saw it on pictures before, and it was great to see the granny in real life. :) There are a lot of "grannies" in the library, from the green lamps to rotary phones to wall clocks. The pneumatic tube system has been in place since 1975. People whose job is to preserve books are very likely to preserve everything else.




I loved this anecdote. In one of the reading halls, there's a big painting of Lenin (pictured below). Apparently it was put in place in mid-1950s to cover the bas-relief that was there originally. On the bas-relief there are Karl Marx, Friedrich Engels, Vladimir Lenin and Joseph Stalin. After Stalin's death in 1953 and debunking the cult of personality, images of him were quickly removed from everywhere. The library, being true preservers of history, kept theirs but covered it up. It just shows what kind of people librarians are. :)


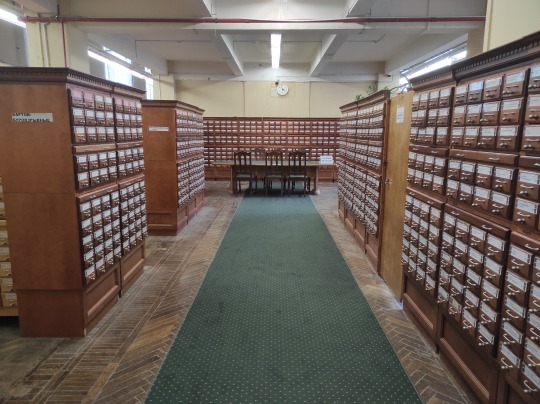
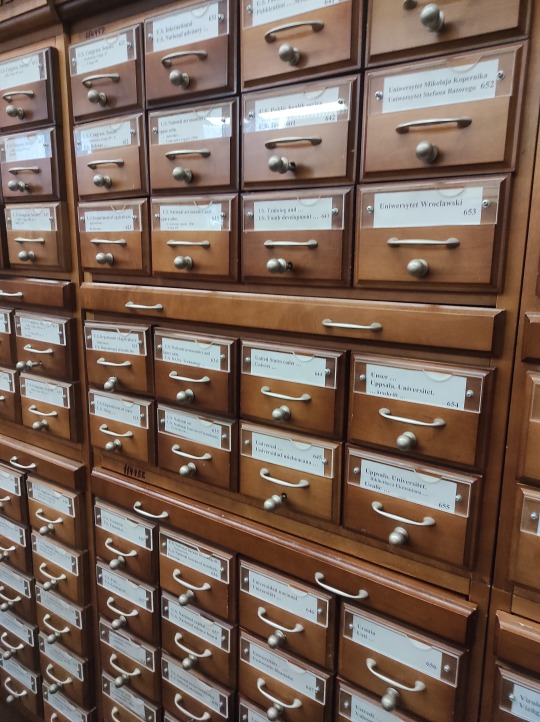
Although the library is working on running a full digital catalogue of all their 48 million items, if you want access to older editions you'll probably need to use the old paper card catalogue. The room gave me major nostalgy - I remember using this kind of catalogue in my local library when I was a kid. The sound of pulling out a narrow box, then the little built-in table, going through the cards one by one, writing down what you need on library cards. It was a whole process! Of course, the local library's catalogue was WAY smaller.
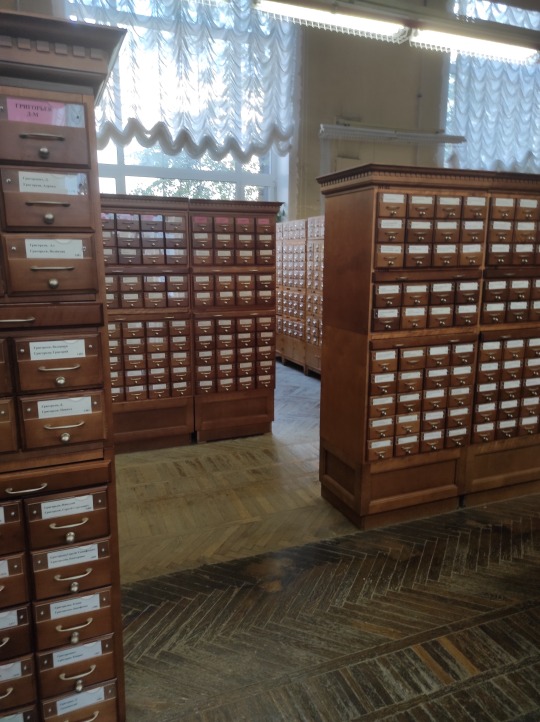
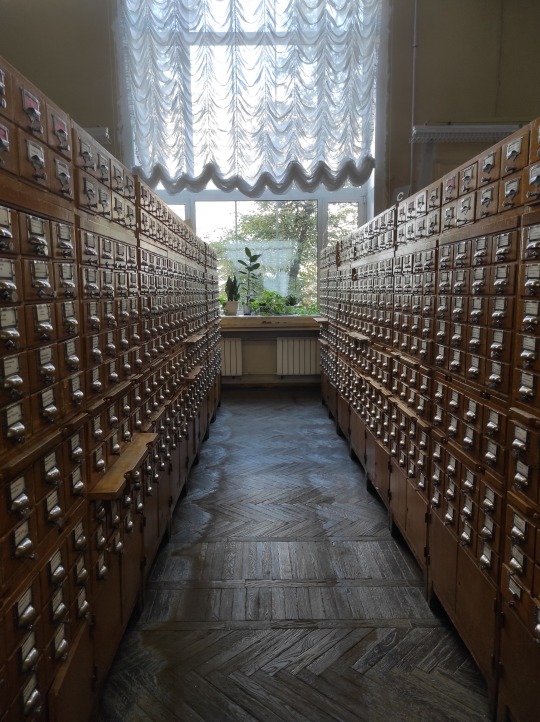




A few more shots of interiors. Although the building itself was designed in 1920s (during the era of avantgarde and art deco), the interiors were mostly done in 1950s when the main design style was neo classicism.
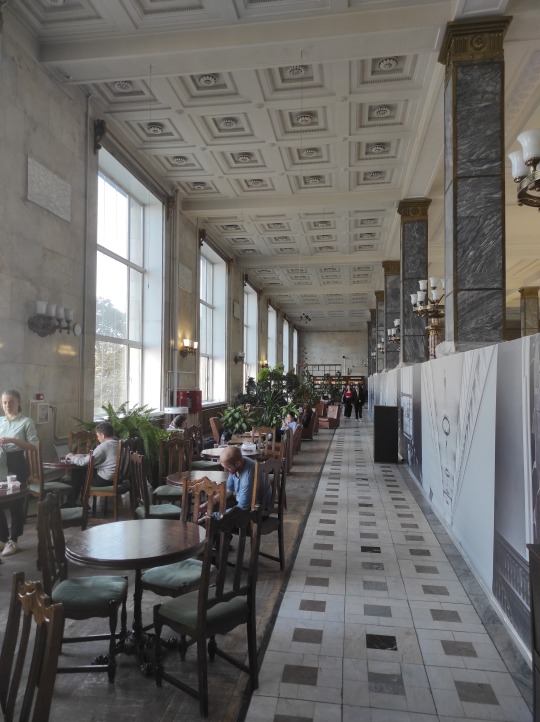




I enjoyed this tour immensely, so much so that I had to go back and get a library card so I can see more of it, sit in every reading hall and drink a cup of tea in the marble hall cafeteria. Also, the idea of 48 million books at the tip of my fingers makes me giddy. Thank you to my followers for the monetary support and making this real for me: K. T., H. W., T. B., m., @depetium, @transarkadydzyubin, S. R.
774 notes
·
View notes
Note
hi :) i’m usamerican and also a librarian, and I really want to offer up my library system as a way for people to get free cards and hella (!!!) online library access — I’m sending it here on anon because I don’t want to doxx myself and I also think it might have a better chance of reaching the people it’d benefit via your account. I realize that’s kind of presumptuous so i understand if you ignore this!
all that said — How To Get A Free Library Card With Libby Access To 8 Different MA Library Systems
(note that that is SYSTEMS and some systems have multiple libraries within them!)
CLAMS (cape libraries automated materials sharing) libraries will register you for a card, totally free —you do need to call but the process is super easy, and if you call Snow Library of Orleans or Wellfleet Public I can vouch that everyone there should be friendly :)
once you have your card you can download the Libby app and sign in, and it gives you super easy access to audiobooks and ebooks from 8 different ma library systems
this also isn’t your only option, there are many libraries that will do the same or similar across the us. and even if internet access is an issue, if you are usamerican and have a local library there’s a decent chance it has public computers and maybe even a phone you can use (so even if its collection isn’t very good you might be able to use it to get library access elsewhere too)
ALSO literally just ask your local librarians for help accessing knowledge & resources we are there to help and there’s so many more ways we can do that than just checking out books we already have on the shelves
you are an angel sent from heavens !! ALSO MA libraries are super super great!!!!
also if anyone, anyone at all, wants to drop an NYPL and/or LAPL card into my anon as a birthday gift or a Christmas gift or a new years gift I will love you forever and ever I will even write you omegaverse porn if you so wish
#asks#anonymous#Libby tag#I am tagging everything with that#like UGH I want an NYPL card so baaaadly but they require in person verification#so if anyone has. a spare. please.
69 notes
·
View notes
Note
hey..
at what point do collectors opt to turn things from puppets to scrolls? I feel like turning an entire living creature into [a piece of paper] is very complicated, while turning them into simple puppets is easier because they keep all the same parts, just simplified and wood?
It is! It depends on the person's proficiency and understanding of the mechanism regarding when and how they change the creature. Once someone gets good at it, the creature can be transformed into a lifeless object without it dying in the process, and they will move on to more complex and efficient ways.
The way I see it, archiving is a form of information compression and storage—and there is A LOT of information. When looking at Earth creatures we have everything from single-cell bacteria to whales that range up to 100 quadrillion cells, all with different sizes. The smallest single-cell critter is 0.3 μm, while the largest single cell is an ostrich egg that can get to 18 cm. So it's not just noting "a cell"—there's also a lot of information about the cell content, size, the DNA, current water, and oxygen levels, what protein it contains and how much. Then there are spatial dimensions. (While we can consider there being more, especially in fiction, I’m sticking to three; trying to visualize four fills me with frustration and existential dread xD) Every cell has its place in space in relation to the others, and all the contents' relations are also important. If, suddenly, all histones materialize inside a mitochondria instead of the nucleus, we can have a problem. Additionally, physical and chemical processes gotta be considered. There's electricity powering our brains, hearts, running nerves, air in airways traveling to lungs, chemical signals traveling between synapses that also need to be accounted for. So, you have all the contents in space, their vectors, and building blocks. Thats a ton to save. This information has to be compressed to be preserved in an organized manner while also remaining lossless so that when returned to its original shape, it's as it was. Not even mentioning that in intelligent beings, there are also minds to take care of. Jellyfish might be fine after 100 years in a static void, but a human? Yhhhhh.
I think the mechanism would work by saving information in intangible magic and assigning it to a physical medium—be it a statue, doll, book, or scroll. If it is physical and can carry information, it can be used. We can argue the mind is part of the soul, or it is a biochemical process, but the fact is nobody really knows for sure what it is and Im not a theolog, so for the sake of this universe, I'll say it's something that occupies the same space magic does and is influenced by chemical processes, meeeeaning it can also be tricked by them. And the magic.
The first degree of preservation would be spells that only change the material but keep all shapes and info in place. This wouldn't require much thought while executing and could be "automated" or worse, taught to mortals (if they have enough magic to power the spell), like petrification or changing someone into wood, metal, or any other solid material. It's not perfect, if the structure is damaged, the spatial information is damaged too. Breaking is one thing, but imagine if the statue melts.
The next step would be assigning objects with some compression and change, like toys and dolls. I feel like there would need to be a system like a content library, so not every single atom is saved each time, but chemical structures like nucleotides in DNA (the ATGC thingies) would just have a shortcut. Larger repeating patterns could also be assigned their own id to save data, and it would slowly stack up. While things are written in intangible magic form and anchored to the medium, the medium can be somewhat customized, like the decorations the Collector added to the dolls. The mind, running in controlled magic, can also be affected, as we saw with Collie trying to scare them and Luz’s dream. On the spell keeping the preserved critter stable has a link to what shortcut it uses so with countless diffrent worlds and structres it wouldnt mix up.
Then we go further into compression, reducing size and dimensions until we reach a point where one axis is almost entirely removed, and we end up with a scroll. Then there are other things—creatures saved as amber miniatures, snow globes, scrolls, or drawings, sometimes purely to annoy the sibling that has to deal with the creature in unhandy form. A more permanent binding would be in a book that can contain a bunch of different animals. Rebinding for long-term preservation is the Curator’s job.
Looking at Earth creatures, eucariotic life shares ancestry with some ancient bacteria that decided to rebel and started to cooperate, so we share similarities even with distant organisms in some strutures since they come from each other. So when it comes to preserving whole populations with relations, the library of compression doesn’t have to be separate for every single animal or plant. For each section of the archive, there would be a common library of building blocks, and scrolls being somewhat separate carrying the exact instructions for body arrangement and the soul/mind/the part that makes them alive attached.
Next is unpacking the information. I think this requires the ability to interpret and recreate what was saved that mortals lack. While they couldn't really unpetrify others, a collector could (assuming the mind hadn’t deteriorated into a husk). In the case of an automated spell, I think it would result in a very lossy transmutation—like a jpg losing pixels, the creature might lose like heart funtion. The Collector's spell also looked temporary or incomplete since an influx of other types of magic (like in Amity or Raine’s case) was able to push back on it. That might also be why they were conscious in the form they were in. Not meant for long just enough to take them to archive in normal conditions. When a creature is heavily compressed, it needs external force to rebuild, as it's essentially written fully in magic. That’s what I think happened to the Owl Beast. Lilith released it from the medium, but since it wasn’t fully rebuilt, it being a magic form attached itself to a magic source.
SO YEAH, its a process that takes quite a while for them to master and it comes with experience. But when experience is based on life it often makes it hard to practice so those with less empathetic approach master it faster. Thanks for the ask! I was dying to talk about that for such a long time and that was a perfect thing to organise thoughts
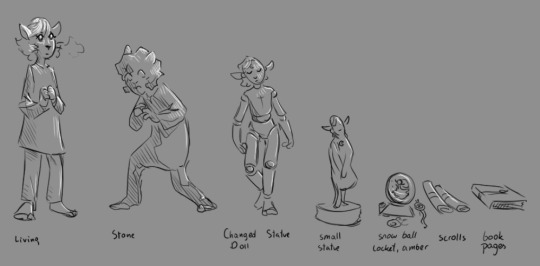
#and consider the absolute body horror that is transmutation#imagine how it has to feel on the border of skin that is being turned to stone when nerve endings cant send what is happening#but can send the numbness of “there is something super wrong” like in severe frostbite#both must feel like tissue dying#tw body horror#i did not use that one in a moment#In the begining i had a concept that it all saves the same way like a doll so diffrent archivists would have diffrent methods#like Anatomist using scrolls Wayfarer drawings and so on but then realised that would be super unhandy when a book carries more info#and its easier to fix a doll than a scroll so settled on this#thats also why in the comic where Way damaged creature they were turned into a doll Way was just very unexperienced with archiving spells#Collection Incomplete au#the owl house#owl house#toh#the collector#toh collector#toh archivists#the archivists#toh collectors#ask#i took sleeping meds before writing this safe to say they didnt work
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
Terry Pratchett, "Going Postal"
Sir Terry wrote many a great series, continuing many great characters. And yet, had I to name the Discworld novel I enjoy the most, "Going Postal" would probably be it. It isn't the start of a great series, even though it features a fantastic protagonist. But if it had never had a sequel it would have been a towering achievement all by itself.
Yes, it's that good.
Paced well, threaded thoroughly
"Going Postal" is, at its heart, the story of a con. Kind of, sort of. It's the story of a scoundrel using his talent for escalation and his way with people to a purpose we can empathize with. It's the story of somebody cheating themselves into becoming a better person.
As such, it's incredibly well-paced.
Another thread in the story is an unraveling mystery about how the post office, the center piece of the story, got into its current state. This would normally require a lot of exposition but is woven gradually into the first half of the book, presented without tiring the reader.

In a completely bizarre fashion, another thread is the evolution of telecommunications, wrapped into clockwork, no less. It's a side aspect, but deep and well explored.
They come together as a heady and entertaining mix, never letting the more cerebral aspects spoil the sheer fun of empathizing with a character who is impostor syndrome personified due to his history of being an impostor. It's a story built around "fake it until you make it" beginning to end. And it works!
Detail under the hood
I said bizarre, and I mean it. Pterry delved into how telecommunications works once you automate it, and fascinatingly so. I'm a telecoms engineer by profession, and this aspect of the book shines.
In order to communicate reliably you need an established protocol, what can be said and in what fashion, to minimize the overhead of understanding the message and correcting errors. Terry went as far as including the idea of a message or protocol header, additional or "meta" information that travels with the message. Just like the sender and return address of a letter are not part of the letter itself but meant for the postal system transporting it, every message sent over Terry's fictional "clacks" or every packet sent over the internet carries additional information telling the system how to handle it - how to route it to its destination, what to do in case of problems, how to prioritize it.
The explanations in the book nail it, they are simple enough to be understood, they make sense, and they fit into the story. That's a masterful feat!
The whole thing is then contrasted with the charms and ills of the precursor, the postal system, for which the author also shows quite some affection. If this was the history of the US, this would be the contrast between post office and mail coach on one side and the "singing wire," the telegraph, on the other side. Again, putting them side to side and in competition, the elements of the story mesh incredibly well.
A rounded novel
Now add a sub-story about golems in it, an idea begun in "Feet of Clay" and you get surprisingly deep world-building elements meshing together and serving a story that is both simple and complex and has all the properties of a great Discworld story.
It also expands on ideas posed in earlier books. The Watch novels introduced the idea of communicating with semaphores, and eventually the idea of clacks - but only "Going Postal" puts it together for good. As mentioned, the idea of golem emancipation started much earlier, but we catch it now as it reaches a stage where the honeymoon is over and the long slog through the institutions, or rather into the heart of the populace, is well underway.
Beyond that, the book is full of Ankh Morpork staples... the Watch, the priesthood, the Wizards and the Library, the newspaper, a rent-a-horse stable, Lord Vetinary's ways of ruling an unrulable city... The book oozes charm and completeness all around. Ankh-Morpork feel alive.

Which makes for two sad facts.
First, its sequels can never recapture the charm. "Making Money" tries to capture the madness of the world of banks and the ideas behind money but never quite manages to leave the world of satire and become real. Maybe the ideas behind it were too... unreal... if you think about it. And "Raising Steam" is an epilogue, a book about one of Terry's passions, less a dramatic novel and more like a love letter. And yet... seeing the characters again makes you read them, and there's still good in these books.
Second, there's a live action adaptation. Mine came on two discs. The first disc made me super happy. Great actors, great delivery. The second disc disappointed me thoroughly. The producers figured nobody would understand the actual story of the books and began simplifying things. They did not, in my opinion, do that well. In this way they marred an adaptation that had probably the most potential of all live action versions of Discworld books. Sir Terry always found a good middle ground of reaching his readers. The movie serves as testament that trying to make everything easily consumable can create an unappetizing mess. But that's just me, maybe.
Still, just like the dead linesmen may travel on the clacks, this book is for the ages. I will probably reread it for a long time until it falls apart and beyond.
24 notes
·
View notes
Text





🎄💾🗓️ Day 11: Retrocomputing Advent Calendar - The SEL 840A🎄💾🗓️
Systems Engineering Laboratories (SEL) introduced the SEL 840A in 1965. This is a deep cut folks, buckle in. It was designed as a high-performance, 24-bit general-purpose digital computer, particularly well-suited for scientific and industrial real-time applications.
Notable for using silicon monolithic integrated circuits and a modular architecture. Supported advanced computation with features like concurrent floating-point arithmetic via an optional Extended Arithmetic Unit (EAU), which allowed independent arithmetic processing in single or double precision. With a core memory cycle time of 1.75 microseconds and a capacity of up to 32,768 directly addressable words, the SEL 840A had impressive computational speed and versatility for its time.
Its instruction set covered arithmetic operations, branching, and program control. The computer had fairly robust I/O capabilities, supporting up to 128 input/output units and optional block transfer control for high-speed data movement. SEL 840A had real-time applications, such as data acquisition, industrial automation, and control systems, with features like multi-level priority interrupts and a real-time clock with millisecond resolution.
Software support included a FORTRAN IV compiler, mnemonic assembler, and a library of scientific subroutines, making it accessible for scientific and engineering use. The operator’s console provided immediate access to registers, control functions, and user interaction! Designed to be maintained, its modular design had serviceability you do often not see today, with swing-out circuit pages and accessible test points.
And here's a personal… personal computer history from Adafruit team member, Dan…
== The first computer I used was an SEL-840A, PDF:
I learned Fortran on it in eight grade, in 1970. It was at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, where my parents worked, and was used to take data from cyclotron experiments and perform calculations. I later patched the Fortran compiler on it to take single-quoted strings, like 'HELLO', in Fortran FORMAT statements, instead of having to use Hollerith counts, like 5HHELLO.
In 1971-1972, in high school, I used a PDP-10 (model KA10) timesharing system, run by BOCES LIRICS on Long Island, NY, while we were there for one year on an exchange.
This is the front panel of the actual computer I used. I worked at the computer center in the summer. I know the fellow in the picture: he was an older high school student at the time.
The first "personal" computers I used were Xerox Alto, Xerox Dorado, Xerox Dandelion (Xerox Star 8010), Apple Lisa, and Apple Mac, and an original IBM PC. Later I used DEC VAXstations.
Dan kinda wins the first computer contest if there was one… Have first computer memories? Post’em up in the comments, or post yours on socialz’ and tag them #firstcomputer #retrocomputing – See you back here tomorrow!
#retrocomputing#firstcomputer#electronics#sel840a#1960scomputers#fortran#computinghistory#vintagecomputing#realtimecomputing#industrialautomation#siliconcircuits#modulararchitecture#floatingpointarithmetic#computerscience#fortrancode#corememory#oakridgenationallab#cyclotron#pdp10#xeroxalto#computermuseum#historyofcomputing#classiccomputing#nostalgictech#selcomputers#scientificcomputing#digitalhistory#engineeringmarvel#techthroughdecades#console
31 notes
·
View notes
Text



Kia ora! Just a wee re-introduction
I'm just another solarpunk in Aotearoa looking for other like-minded friends, inspiration, and advice on other ways I can green up my life. I love sewing, baking, making, gardening, and animals.
I live in an off-grid tiny home I built with my partner in 2016 out of wood and second-hand windows/doors/appliances. We run off solar power, rain water, a composting toilet, and try to repair, mend, make, borrow, and buy 2nd hand or local. Our meat is all hunted, which here in Aotearoa is a huge help for our environment as our only native mammals are seals and bats. Everything else is a pest. We also grow a lot of our own fruit and veggies, but the garden is still a work in progress. This year, i have a new wing of the veggie garden built, but I still have so much work to do around the herb and fairy garden.
I'm looking at irrigating the garden and automating the process. I saw something about https://www.home-assistant.io/ online but would love any advice you might have. I'd like to automate and chart my watering as well as integrate moisture monitors and a weather monitoring system.
I have an electric bike and an old 1996 honda crv. I'd like to switch to an electric vehicle, something like a Pickman 4x4 or another small farm vehicle, as I only need to get to the village bus stop, neighbouring farms, and the occasional trip into town via back roads.
Clothes are me-made with 2nd hand materials, mostly from the dump shop. I've helped start a collection point for alternative recycling like bottle lids and tetrapaks, a library of things, and a community workshop. We are working towards a bike repair hub and time bank but it might be a couple years before they are operational.
Please share all your inspiration, book recommendations, and thoughts around other ways I can make an impact in my community 😊
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
All-in-One Software for Managing Your Library

Revolutionise your library operations with seamless book management, real-time updates, and automated reminders. LDT Technology provides a bespoke Library Management System to streamline your library's efficiency. Book your demo now and empower your firm with the latest technology!
0 notes
Text
update
im hi guys i’m sorry i haven’t been writing or talking to you that much. i miss you guys so much but ive grown so depressed lately. i lost all my friends at school and pushed my friends from home away but thankfully they forgave me. things are getting better with my boyfriend too but things in my country are going so horribly. i’m not out of the closet and now i don’t think i ever will be until people stop harassing trans kids at their sports games and doxxing them on the internet. you wake up and look at the news and see that a highschool kid who’s doing to a volleyball game gets detained because ICE was looking for his father. they’re setting off smoke bombs and they’re dressed in military uniform in the streets with LRAD while they’re pushing us and arresting us and beating us. and if they’re not dressed in military uniforms, they’re wearing plainclothes and refusing to identify themselves. they’re raiding homes and businesses and farms and sending people to a death camp before shaving their heads and parading them to humiliate them entire the whole world. or they send them to country that they didn’t come from. they’re banning students from overseas to come to our colleges. they’re firing thousands of federal workers. they’re trying to shut down libraries. they’ve shut down Job Corps.
i’m safe now, but nobody stays that way. if they’re targeting one group of people, then they’ll target you. they say they’re arresting “aliens” and some of them did come here illegally, but they’re not trying to give them a chance to gain citizenship. they’ve shut down the app that helps immigrants with gaining citizenship. there’s a woman who tried to gain her citizenship but they deported her at the meeting. she could hardly speak english. they’re arresting judges and staffers.
over half of us live paycheck to paycheck. but they say that immigrants are the enemy because they want us divided while they buy politicians so they can get each other rich. they blame queer people for being predators while they worship a rapist. they hate black people because we’ve always been the easy target, so they blame us for the crime while they worship a felon. they call us “welfare queens” because they created a system that’s made to keep the rich richer and the poor making money for them. they deny you healthcare coverage and they make you pay a gross amount of money just live. they fearmonger about arabic people and muslims say they’re “invading” our country and say they’ll impose sharia law, when they support tyrannical terrorist who are essentially Jihadists. they hate the homeless because they can’t make money for them.
they automate their labor because a machine doesn’t need sick time. then they say that “they’re stealing your jobs” one minute and say they’re “freeloaders” the second. they make money off of weapons to send our troops overseas to fight in endless and meaningless wars for legacy politicians and the CEOs that donate thousands and millions of dollars to support wars that will make them more money.
i don’t even recognize the country that i had six months ago. five years ago i read ann franks diary and i hoped that it would never happen here. but deep down i knew that plenty of people would be completely fine if it did.
#black metal#bandom#extreme metal#mayhem#mayhem band#burzum#øystein aarseth#dsbm#niklas kvarforth#metal music
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
ESSAY: My Hearthome in ABZÛ
by Ocean Watcher from House of Chimeras (He/they) I was inspired to write this essay after attending the panel, "No Place Like Home: On Hearthomes" at Othercon 2024 Note: This won't be the official home of this essay. I'm planning on adding it to our system's website, The Chimeras Library sometime in the future either as a standalone essay or part of something bigger.
My Hearthome in ABZU
by Ocean Watcher from House of Chimeras Date Written: 15 August 2024 Approx. Word Count: ~2,180
Approx. Reading Time: ~17 minutes
“They say home is where the heart is, and for most people it consists of four walls and a welcome mat. For me, it’s the ocean.” ~ Bethany Hamilton, Soul Surfer. Directed by Sean McNamara. California: Sony Pictures Releasing, 2011.
Defining Hearthome
A hearthome is a location, whether real or otherwise, that an individual has a strong emotional connection toward to the point it feels like a “home,” typically despite never having lived or spent a significant amount of time there. The specifics on what qualifies as a hearthome within this general definition is largely up for personal interpretation.
The location in question can be as all-encompassing as a whole planet all the way down to something much, much smaller. The location could be a real place (whether that be one that still currently exists or a location that once existed but doesn’t anymore), a setting depicted in fictional media, or something else entirely. It can also be a specific easily named location or merely a general description of a place. Finally, the exact kind of emotional connection and feeling like “home” a location can elicit can range from a feeling of familiarity, of comfort and relaxation, safety, nostalgia, homesickness, and/or more. In short, within the definition of hearthome there are many possibilities on how the experience can exist.
The term used to describe someone who has a hearthome or the state of having a hearthome is sometimes called hearthic, though not everyone uses it. (So, for example someone might say “I have a hearthome in [insert place here]” rather than saying “I am [insert place here]hearthic.” Whether hearthic is used or not alongside the term hearthome is largely personal preference.
Describing ABZÛ
ABZÛ (also written as Abzû) is a video game initially released in 2016. The game fits within several genres including adventure, simulation, and art video game. It has no dialogue and so the story is told solely through visuals. The main draw of the game is the graphics put into the diverse ocean environments and the wide range of marine life that inhabits each area. Most of ABZÛ is home to animal species that can be found in today’s oceans; however, there are over a dozen or so species that appear in the game that went extinct a long time ago.
The gameplay itself consists of the player controlling an android diver exploring a large variety of ocean environments in a vast ocean and getting to see a myriad of marine life at every turn.
Knowing the backstory of what occurs isn’t needed, but for some context: Deep at the bottom of this ocean was a primordial source of infinite energy. Where the energy permeated from the ground life spontaneously came into being. An ancient civilization discovered they could collect and use it to create (marine) life whenever and wherever they wished. However, at some point, they created machines to automate the process. The creation of these machines caused a disruption of the natural flow of life as they took up so much energy they drained the vitality of the ocean away. The civilization disappeared, leaving their machines to continue to operate. The objective of the player-controlled robot diver, another creation of the ancient civilization, is to return the energy back to the ocean and put an end to the machines causing the destruction.
ABZÛ is overall a short game, with most players seeming to complete it within an hour and thirty minutes to two hours, on average.
Home is Where the Heart Is Indeed
So, my hearthome is ABZÛ.
To start, I want to put some context between the game ABZÛ and my hearthome ABZÛ. The environments in the game are striking and hold an emotional importance to an extent that I have labeled it as a hearthome; however, the ABZÛ that I think of in my mind’s eye and thoughts is not just an exact mirror of the game. That is because the ABZÛ I have conceptualized in my own mind is laid out like a normal(ish) ocean thanks to some noemata I have.
The noemata I have reads that all the “game-y” elements necessary for it to function as, well, a game, aren’t present in the idea of ABZÛ that makes up my hearthome. So, all the things necessary to keep a player in a defined area and on a specific path are absent. Further, all the different locations shown in the game would exist in a much more natural way. Plus, even more biodiversity would exist than shown in the game itself (as it is only populated with a little more than a few hundred different species whereas a more realistic ocean would have tens of thousands). Basically, the concept of ABZÛ in my mind looks and functions a lot more like a natural ocean (if a much, much more vibrant and filled with even more aquatic life, one).
I also have noemata that reads that while the old structures of the civilization still exist in a way like how they appear in the game, the inverted pyramid machines have long broken down and been reclaimed by the ocean and there are no unnatural dead zones. (So, I guess, one could say my hearthome is based off how things look at the end of the game.)
So, there is all that.
That is all well and good, but now I want to cover why exactly I distinguish ABZÛ as a hearthome; why I feel it warrants a special label of significance to me at all.
Not to state the obvious, but games are meant to be emotionally and/or mentally moving. They are meant to make a player feel something. ABZÛ is no different. It is meant to be a “pretty ocean” game, if you will. The environments in ABZÛ certainly reflect a more idealized and concentrated concept of ocean life (the magnitude of marine life at any particular point in the game itself being far more than an ecosystem could sustain). So, of course, the game is meant to be visually stunning and calming (save for a section in the game roughly 3/5ths in) in relation to the ocean, but my feelings for the game go deeper than what would be normally expected.
It is true that much of the allure I have toward ABZÛ could be dismissed as merely as a natural consequence of my alterhumanity being so immersed in the ocean if not for the fact there are aspects of ABZÛ that draw out emotions and noemata that can’t be easily waved off in that manner. There are plenty of ocean-themed games and whatnot, yet it’s this specific one I have this connection toward. I have no idea why exactly I have a hearthome in this game specifically. I couldn’t tell you why. For whatever reason, its ABZÛ that resonates with me so strongly.
The biggest thing that stands out for me is the fact the area in the game that holds the most profound feelings of familiarity and belonging is the underwater city. At one point in the game, some underwater caves open into a vast underground space where a half-submerged city exists. (My view of things through some more noemata looks a lot more like an ancient city proper because, again, ABZÛ is a game so what exists is a lot more simplified and limited.) It is a city abandoned and in ruins and yet every surface is still covered in tile and brick of beautiful blue hues. Plants like trees, flowers, and vines populate the space above the water, lily pads and other floating plants pepper the water’s surface, and below sea plants like kelp, sea grass, and so much more cover much of the floor. Sunlight shines down from high above; my noemata filling in with the idea the city resides within a long extinct volcano rising above the ocean’s surface. Animals are everywhere both above and below the water. It’s this place I gravitate towards the most.

But what exactly do I feel?
Something about it resonates with me. It is a place that feels like home to a part of me. Something about it feels deeply right and missed despite never having lived there nor do I feel like it is a place I am “from,” in any specific way. The feelings my hearthome draw out of me can mostly be best described as comfort, relief, safety, and rightness. There is something familiar about it, even upon my first playthrough. There is maybe even a tinge of nostalgia even though I strongly feel like there isn’t anything past-life-like at play as to why I have this hearthome. It just feels so familiar and comforting to me.
Starting out, my feelings also included what I can best describe as a yearning or longing to want to be there, even if only to visit. There was a desire to know a place like it with my own eyes as much as I knew it already in my heart somehow. So, there was a bit of almost homesickness there too. All these feelings are described in the past tense because of something that happened a bit after first playing the game.
Sometime after first playing ABZÛ, a sunken city with strong similarities to the one in the game was discovered in the ocean in our system’s innerworld. It is not a perfect exact copy, but it has all the same elements and looks how my hearthome appears through the lens of the noemata I have. I know I didn’t consciously will the location in our innerworld to come into existence, no one here can make such blatant conscious changes to our innerworld; however, I’m far less certain if my discovery of the game and the emotions it elicited didn’t cause the sunken city to appear in our innerworld as an involuntary reaction. (Not long after its appearance, several other areas in the game also found their way into the ocean of our system’s innerworld.) Since its appearance and discovery, I spend much of my time in these impacted areas, especially the sunken abandoned city. Since its appearance, the location has become a much beloved place to be, not just for me but also for many other aquatics in the system. The area is aesthetically pleasing and interesting to move around in. There is a lot of wildlife so hunting instincts can be indulged and so on. When not focused on fronting it is a nice place to exist in.

I’ve been aware of my emotional connection to the setting depicted in ABZÛ since July 2018 after playing it for the first time. Since buying it on Steam, I’ve logged many hours on it and have played through its entirety several times. However, I had not labeled my feelings towards this game as a hearthome until recently. Back then, I never questioned or analyzed my feelings surrounding the environments in the game. I knew it soothed something in me to play the game, going out to the sunken city in the innerworld for a while, or even just imagine myself swimming in one of my favorite areas, but I didn’t think about why exactly that was the case.
I didn’t make the connection between my experiences with ABZÛ to the term, hearthome until August of 2024. The moment of realization came while listening to the panel, “No Place Like Home: On Hearthomes” at Othercon 2024. Upon Rani, the panel’s host, describing the meaning of the term, I realized my feelings towards ABZÛ fit perfectly within the word. It wasn’t even a particularly jarring realization, and I am not sure how I had never made the connection before. Since that realization, I’ve come to label my feelings around the game, ABZÛ as my hearthome.
On the topic of alterhuman terms, I don’t use the term hearthic to refer to my state of having a hearthome at this time, solely because the word just doesn’t feel right when I try to use it in context. That could change, but for now, that is that.
I do consider my hearthome to be a part of my alterhumanity. My hearthome certainly fits neatly into my wider alterhumanity; ocean life and all that. That being said, I don’t think my hearthome has as strong of an impact on my daily experiences as other aspects do. My feelings around my hearthome are most often closer to something in the background more than anything. It is still there, and it is still important, it is just not as blatant and impactful in my daily life compared to something like my phantom body from my theriotypes. The fact parts of the game now exist in the innerworld and are prime locations for me to go after fronting to alleviate species dysphoria is perhaps the most blatant way my hearthome impacts my greater alterhumanity.
Bibliography
505 Games, ABZÛ. 505 Games, 2015, Microsoft Windows.
“Glossary,” Alt+H, https://alt-h.net/educate/glossary.php . Archived on 19 Apr 2020: https://web.archive.org/web/20200419100422/https://alt-h.net/educate/glossary.php
Lepidoptera Choir. “Hearthic” astrophellian on Tumblr. 9 April 2022. https://astrophellian.tumblr.com/post/681107250894503936/hearthic . Archived on 30 September 2022: https://web.archive.org/web/20220930143533/https://astrophellian.tumblr.com/post/681107250894503936/hearthic
Rani. “No Place Like Home: On Hearthomes,” Othercon 2024, 11 August 2024, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lYVF_R6v50Q
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
The enshittification of garage-door openers reveals a vast and deadly rot

I'll be at the Studio City branch of the LA Public Library on Monday, November 13 at 1830hPT to launch my new novel, The Lost Cause. There'll be a reading, a talk, a surprise guest (!!) and a signing, with books on sale. Tell your friends! Come on down!

How could this happen? Owners of Chamberlain MyQ automatic garage door openers just woke up to discover that the company had confiscated valuable features overnight, and that there was nothing they could do about it.
Oh, we know what happened, technically speaking. Chamberlain shut off the API for its garage-door openers, which breaks their integration with home automation systems like Home Assistant. The company even announced that it was doing this, calling the integration an "unauthorized usage" of its products, though the "unauthorized" parties in this case are the people who own Chamberlain products:
https://chamberlaingroup.com/press/a-message-about-our-decision-to-prevent-unauthorized-usage-of-myq
We even know why Chamberlain did this. As Ars Technica's Ron Amadeo points out, shutting off the API is a way for Chamberlain to force its customers to use its ad-beshitted, worst-of-breed app, so that it can make a few pennies by nonconsensually monetizing its customers' eyeballs:
https://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2023/11/chamberlain-blocks-smart-garage-door-opener-from-working-with-smart-homes/
But how did this happen? How did a giant company like Chamberlain come to this enshittening juncture, in which it felt empowered to sabotage the products it had already sold to its customers? How can this be legal? How can it be good for business? How can the people who made this decision even look themselves in the mirror?
To answer these questions, we must first consider the forces that discipline companies, acting against the impulse to enshittify their products and services. There are four constraints on corporate conduct:
I. Competition. The fear of losing your business to a rival can stay even the most sociopathic corporate executive's hand.
II. Regulation. The fear of being fined, criminally sanctioned, or banned from doing business can check the greediest of leaders.
III. Capability. Corporate executives can dream up all kinds of awful ways to shift value from your side of the ledger to their own, but they can only do the things that are technically feasible.
IV. Self-help. The possibility of customers modifying, reconfiguring or altering their products to restore lost functionality or neutralize antifeatures carries an implied threat to vendors. If a printer company's anti-generic-ink measures drives a customer to jailbreak their printers, the original manufacturer's connection to that customer is permanently severed, as the customer creates a durable digital connection to a rival.
When companies act in obnoxious, dishonest, shitty ways, they aren't merely yielding to temptation – they are evading these disciplining forces. Thus, the Great Enshittening we are living through doesn't reflect an increase in the wickedness of corporate leadership. Rather, it represents a moment in which each of these disciplining factors have been gutted by specific policies.
This is good news, actually. We used to put down rat poison and we didn't have a rat problem. Then we stopped putting down rat poison and rats are eating us alive. That's not a nice feeling, but at least we know at least one way of addressing it – we can start putting down poison again. That is, we can start enforcing the rules that we stopped enforcing, in living memory. Having a terrible problem is no fun, but the best kind of terrible problem to have is one that you know a solution to.
As it happens, Chamberlain is a neat microcosm for all the bad policy choices that created the Era of Enshittification. Let's go through them:
Competition: Chamberlain doesn't have to worry about competition, because it is owned by a private equity fund that "rolled up" all of Chamberlain's major competitors into a single, giant firm. Most garage-door opener brands are actually Chamberlain, including "LiftMaster, Chamberlain, Merlin, and Grifco":
https://www.lakewoodgaragedoor.biz/blog/the-history-of-garage-door-openers
This is a pretty typical PE rollup, and it exploits a bug in US competition law called "Antitrust's Twilight Zone":
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/16/schumpeterian-terrorism/#deliberately-broken
When companies buy each other, they are subject to "merger scrutiny," a set of guidelines that the FTC and DoJ Antitrust Division use to determine whether the outcome is likely to be bad for competition. These rules have been pretty lax since the Reagan administration, but they've currently being revised to make them substantially more strict:
https://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/justice-department-and-ftc-seek-comment-draft-merger-guidelines
One of the blind spots in these merger guidelines is an exemption for mergers valued at less than $101m. Under the Hart-Scott-Rodino Act, these fly under the radar, evading merger scrutiny. That means that canny PE companies can roll up dozens and dozens of standalone businesses, like funeral homes, hospital beds, magic mushrooms, youth addiction treatment centers, mobile home parks, nursing homes, physicians’ practices, local newspapers, or e-commerce sellers:
http://www.economicliberties.us/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/Serial-Acquisitions-Working-Paper-R4-2.pdf
By titrating the purchase prices, PE companies – like Blackstone, owners of Chamberlain and all the other garage-door makers – can acquire a monopoly without ever raising a regulatory red flag.
But antitrust enforcers aren't helpless. Under (the long dormant) Section 7 of the Clayton Act, competition regulators can block mergers that lead to "incipient monopolization." The incipiency standard prevented monopolies from forming from 1914, when the Clayton Act passed, until the Reagan administration. We used to put down rat poison, and we didn't have rats. We stopped, and rats are gnawing our faces off. We still know where the rat poison is – maybe we should start putting it down again.
On to regulation. How is it possible for Chamberlain to sell you a garage-door opener that has an API and works with your chosen home automation system, and then unilaterally confiscate that valuable feature? Shouldn't regulation protect you from this kind of ripoff?
It should, but it doesn't. Instead, we have a bunch of regulations that protect Chamberlain from you. Think of binding arbitration, which allows Chamberlain to force you to click through an "agreement" that takes away your right to sue them or join a class-action suit:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/10/20/benevolent-dictators/#felony-contempt-of-business-model
But regulation could protect you from Chamberlain. Section 5 of the Federal Trade Commission Act allows the FTC to ban any "unfair and deceptive" conduct. This law has been on the books since 1914, but Section 5 has been dormant, forgotten and unused, for decades. The FTC's new dynamo chair, Lina Khan, has revived it, and is use it like a can-opener to free Americans who've been trapped by abusive conduct:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/10/the-courage-to-govern/#whos-in-charge
Khan's used Section 5 powers to challenge privacy invasions, noncompete clauses, and other corporate abuses – the bait-and-switch tactics of Chamberlain are ripe for a Section 5 case. If you buy a gadget because it has five features and then the vendor takes two of them away, they are clearly engaged in "unfair and deceptive" conduct.
On to capability. Since time immemorial, corporate leaders have fetishized "flexibility" in their business arrangements – like the ability to do "dynamic pricing" that changes how much you pay for something based on their guess about how much you are willing to pay. But this impulse to play shell games runs up against the hard limits of physical reality: grocers just can't send an army of rollerskated teenagers around the store to reprice everything as soon as a wealthy or desperate-looking customer comes through the door. They're stuck with crude tactics like doubling the price of a flight that doesn't include a Saturday stay as a way of gouging business travelers on an expense account.
With any shell-game, the quickness of the hand deceives the eye. Corporate crooks armed with computers aren't smarter or more wicked than their analog forebears, but they are faster. Digital tools allow companies to alter the "business logic" of their services from instant to instant, in highly automated ways:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/19/twiddler/
The monopoly coalition has successfully argued that this endless "twiddling" should not be constrained by privacy, labor or consumer protection law. Without these constraints, corporate twiddlers can engage in all kinds of ripoffs, like wage theft and algorithmic wage discrimination:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/12/algorithmic-wage-discrimination/#fishers-of-men
Twiddling is key to the Darth Vader MBA ("I am altering the deal. Pray I don't alter it further"), in which features are confiscated from moment to moment, without warning or recourse:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/26/hit-with-a-brick/#graceful-failure
There's no reason to accept the premise that violating your privacy, labor rights or consumer rights with a computer is so different from analog ripoffs that existing laws don't apply. The unconstrained twiddling of digital ripoff artists is a plague on billions of peoples' lives, and any enforcer who sticks up for our rights will have an army of supporters behind them.
Finally, there's the fear of self-help measures. All the digital flexibility that tech companies use to take value away can be used to take it back, too. The whole modern history of digital computers is the history of "adversarial interoperability," in which the sleazy antifeatures of established companies are banished through reverse-engineering, scraping, bots and other forms of technological guerrilla warfare:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2019/10/adversarial-interoperability
Adversarial interoperability represents a serious threat to established business. If you're a printer company gouging on toner, your customers might defect to a rival that jailbreaks your security measures. That's what happened to Lexmark, who lost a case against the toner-refilling company Static Controls, which went on to buy Lexmark:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2019/06/felony-contempt-business-model-lexmarks-anti-competitive-legacy
Sure, your customers are busy and inattentive and you can degrade the quality of your product a lot before they start looking for ways out. But once they cross that threshold, you can lose them forever. That's what happened to Microsoft: the company made the tactical decision to produce a substandard version of Office for the Mac in a drive to get Mac users to switch to Windows. Instead, Apple made Iwork (Pages, Numbers and Keynote), which could read and write every Office file, and Mac users threw away Office, the only Microsoft product they owned, permanently severing their relationship to the company:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2019/06/adversarial-interoperability-reviving-elegant-weapon-more-civilized-age-slay
Today, companies can operate without worrying about this kind of self-help measure. There' a whole slew of IP rights that Chamberlain can enforce against you if you try to fix your garage-door opener yourself, or look to a competitor to sell you a product that restores the feature they took away:
https://locusmag.com/2020/09/cory-doctorow-ip/
Jailbreaking your Chamberlain gadget in order to make it answer to a rival's app involves bypassing a digital lock. Trafficking in a tool to break a digital lock is a felony under Section 1201 of the Digital Millennium Copyright, carrying a five-year prison sentence and a $500,000 fine.
In other words, it's not just that tech isn't regulated, allowing for endless twiddling against your privacy, consumer rights and labor rights. It's that tech is badly regulated, to permit unlimited twiddling by tech companies to take away your rightsand to prohibit any twiddling by you to take them back. The US government thumbs the scales against you, creating a regime that Jay Freeman aptly dubbed "felony contempt of business model":
https://pluralistic.net/2022/10/23/how-to-fix-cars-by-breaking-felony-contempt-of-business-model/
All kinds of companies have availed themselves of this government-backed superpower. There's DRM – digital locks, covered by DMCA 1201 – in powered wheelchairs:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2022/06/when-drm-comes-your-wheelchair
In dishwashers:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/05/03/cassette-rewinder/#disher-bob
In treadmills:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/06/22/vapescreen/#jane-get-me-off-this-crazy-thing
In tractors:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/05/08/about-those-kill-switched-ukrainian-tractors/
It should come as no surprise to learn that Chamberlain has used DMCA 1201 to block interoperable garage door opener components:
https://scholarship.law.marquette.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1233&context=iplr
That's how we arrived at this juncture, where a company like Chamberlain can break functionality its customers value highly, solely to eke out a minuscule new line of revenue by selling ads on their own app.
Chamberlain bought all its competitors.
Chamberlain operates in a regulatory environment that is extremely tolerant of unfair and deceptive practices. Worse: they can unilaterally take away your right to sue them, which means that if regulators don't bestir themselves to police Chamberlain, you are shit out of luck.
Chamberlain has endless flexibility to unilaterally alter its products' functionality, in fine-grained ways, even after you've purchased them.
Chamberlain can sue you if you try to exercise some of that same flexibility to protect yourself from their bad practices.
Combine all four of those factors, and of course Chamberlain is going to enshittify its products. Every company has had that one weaselly asshole at the product-planning table who suggests a petty grift like breaking every one of the company's customers' property to sell a few ads. But historically, the weasel lost the argument to others, who argued that making every existing customer furious would affect the company's bottom line, costing it sales and/or fines, and prompting customers to permanently sever their relationship with the company by seeking out and installing alternative software. Take away all the constraints on a corporation's worst impulses, and this kind of conduct is inevitable:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/28/microincentives-and-enshittification/
This isn't limited to Chamberlain. Without the discipline of competition, regulation, self-help measures or technological limitations, every industry in undergoing wholesale enshittification. It's not a coincidence that Chamberlain's grift involves a push to move users into its app. Because apps can't be reverse-engineered and modified without risking DMCA 1201 prosecution, forcing a user into an app is a tidy and reliable way to take away that user's rights.
Think about ad-blocking. One in four web users has installed an ad-blockers ("the biggest boycott in world history" -Doc Searls). Zero app users have installed app-blockers, because they don't exist, because making one is a felony. An app is just a web-page wrapped in enough IP to make it a crime to defend yourself against corporate predation:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/27/an-audacious-plan-to-halt-the-internets-enshittification-and-throw-it-into-reverse/
The temptation to enshitiffy isn't new, but the ability to do so without consequence is a modern phenomenon, the intersection of weak policy enforcement and powerful technology. Your car is autoenshittified, a rolling rent-seeking platform that spies on you and price-gouges you:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/24/rent-to-pwn/#kitt-is-a-demon
Cars are in an uncontrolled skid over Enshittification Cliff. Honda, Toyota, VW and GM all sell cars with infotainment systems that harvest your connected phone's text-messages and send them to the corporation for data-mining. What's more, a judge in Washington state just ruled that this is legal:
https://therecord.media/class-action-lawsuit-cars-text-messages-privacy
While there's no excuse for this kind of sleazy conduct, we can reasonably anticipate that if our courts would punish companies for engaging in it, they might be able to resist the temptation. No wonder Mozilla's latest Privacy Not Included research report called cars "the worst product category we have ever reviewed":
https://foundation.mozilla.org/en/privacynotincluded/articles/its-official-cars-are-the-worst-product-category-we-have-ever-reviewed-for-privacy/
I mean, Nissan tries to infer facts about your sex life and sells those inferences to marketing companies:
https://foundation.mozilla.org/en/privacynotincluded/nissan/
But the OG digital companies are the masters of enshittification. Microsoft has been at this game for longer than anyone, and every day brings a fresh way that Microsoft has worsened its products without fear of consequence. The latest? You can't delete your OneDrive account until you provide an acceptable explanation for your disloyalty:
https://www.theverge.com/2023/11/8/23952878/microsoft-onedrive-windows-close-app-notification
It's tempting to think that the cruelty is the point, but it isn't. It's almost never the point. The point is power and money. Unscrupulous businesses have found ways to make money by making their products worse since the industrial revolution. Here's Jules Dupuis, writing about 19th century French railroads:
It is not because of the few thousand francs which would have to be spent to put a roof over the third-class carriages or to upholster the third-class seats that some company or other has open carriages with wooden benches. What the company is trying to do is to prevent the passengers who can pay the second class fare from traveling third class; it hits the poor, not because it wants to hurt them, but to frighten the rich. And it is again for the same reason that the companies, having proved almost cruel to the third-class passengers and mean to the second-class ones, become lavish in dealing with first-class passengers. Having refused the poor what is necessary, they give the rich what is superfluous.
https://www.tumblr.com/mostlysignssomeportents/731357317521719296/having-refused-the-poor-what-is-necessary-they
But as bad as all this is, let me remind you about the good part: we know how to stop companies from enshittifying their products. We know what disciplines their conduct: competition, regulation, capability and self-help measures. Yes, rats are gnawing our eyeballs, but we know which rat-poison to use, and where to put it to control those rats.
Competition, regulation, constraint and self-help measures all backstop one another, and while one or a few can make a difference, they are most powerful when they're all mobilized in concert. Think of the failure of the EU's landmark privacy law, the GDPR. While the GDPR proved very effective against bottom-feeding smaller ad-tech companies, the worse offenders, Meta and Google, have thumbed their noses at it.
This was enabled in part by the companies' flying an Irish flag of convenience, maintaining the pretense that they have to be regulated in a notorious corporate crime-haven:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/05/15/finnegans-snooze/#dirty-old-town
That let them get away with all kinds of shenanigans, like ignoring the GDPR's requirement that you should be able to easily opt out of data-collection without having to go through cumbersome "cookie consent" dialogs or losing access to the service as punishment for declining to be tracked.
As the noose has tightened around these surveillance giants, they're continuing to play games. Meta now says that the only way to opt out of data-collection in the EU is to pay for the service:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/30/markets-remaining-irrational/#steins-law
This is facially illegal under the GDPR. Not only are they prohibited from punishing you for opting out of collection, but the whole scheme ignores the nature of private data collection. If Facebook collects the fact that you and I are friends, but I never opted into data-collection, they have violated the GDPR, even if you were coerced into granting consent:
https://www.nakedcapitalism.com/2023/11/the-pay-or-consent-challenge-for-platform-regulators.html
The GDPR has been around since 2016 and Google and Meta are still invading 500 million Europeans' privacy. This latest delaying tactic could add years to their crime-spree before they are brought to justice.
But most of this surveillance is only possible because so much of how you interact with Google and Meta is via an app, and an app is just a web-page that's a felony to make an ad-blocker for. If the EU were to legalize breaking DRM – repealing Article 6 of the 2001 Copyright Directive – then we wouldn't have to wait for the European Commission to finally wrestle these two giant companies to the ground. Instead, EU companies could make alternative clients for all of Google and Meta's services that don't spy on you, without suffering the fate of OG App, which tried this last winter and was shut down by "felony contempt of business model":
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/05/battery-vampire/#drained
Enshittification is demoralizing. To quote @wilwheaton, every update to the services we use inspires "dread of 'How will this complicate things as I try to maintain privacy and sanity in a world that demands I have this thing to operate?'"
https://wilwheaton.tumblr.com/post/698603648058556416/cory-doctorow-if-you-see-this-and-have-thoughts
But there are huge natural constituencies for the four disciplining forces that keep enshittification at bay.
Remember, Antitrust's Twilight Zone doesn't just allow rollups of garage-door opener companies – it's also poison for funeral homes, hospital beds, magic mushrooms, youth addiction treatment centers, mobile home parks, nursing homes, physicians’ practices, local newspapers, or e-commerce sellers.
The Binding Arbitration scam that stops Chamberlain customers from suing the company also stops Uber drivers from suing over stolen wages, Turbotax customers from suing over fraud, and many other victims of corporate crime from getting a day in court.
The failure to constrain twiddling to protect privacy, labor rights and consumer rights enables a host of abuses, from stalking, doxing and SWATting to wage theft and price gouging:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/11/06/attention-rents/#consumer-welfare-queens
And Felony Contempt of Business Model is used to screw you over every time you refill your printer, run your dishwasher, or get your Iphone's screen replaced.
The actions needed to halt and reverse this enshittification are well understood, and the partisans for taking those actions are too numerous to count. It's taken a long time for all those individuals suffering under corporate abuses to crystallize into a movement, but at long last, it's happening.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/11/09/lead-me-not-into-temptation/#chamberlain

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#monopolists#anticircumvention#myq#home assistant#pay or consent#enshittification#surveillance#autoenshittification#privacy#self-help measures#microsoft#onedrive#twiddling#comcom#competitive compatibility#interop#interoperability#adversarial interoperability#felony contempt of business model#darth vader mba
376 notes
·
View notes