#Examples of centralized data processing
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
What is Centralized Data Processing with Example
Centralized data processing is computer processing that takes place in a single server or CPU. The data management, data storage and computation are handled by a mainframe computer or single high-processing machine. Different types of clients are connected to a single central server. The clients which are connected to the centralized server are smartphones, laptops, tablets or desktop computers.…

View On WordPress
#Centralized vs decentralized computing#Examples of centralized data processing#What is centralized computing
0 notes
Note
What criticisms do you have of direct democracy? Assuming it’s communist, as well as having laws about what can and can’t be voted on such as “no killing/disenfranchising the (blank) people” and “no voting for capitalism” (the actual laws would be longer but I don’t want to write a long paragraph about how you’re not allowed to vote for fascism in a fake direct democratic society)
While it's fine in the abstract, in practice it's exceedingly slow and inefficient - being a political representative in a council is a full-time job, and if every single decision made is subject to the popular vote, then both 1) polling itself takes considerably longer; and 2) the necessary amount of education and discussion needed to be carried out prior to a proper vote is much larger: rather than simply summarising the issue and presenting key facts to council members, a massive public education campaign now has to be carried out every time a new, say, regulatory standard for storm drains, is decided upon.
Which leads us into the other main criticism - in practice, people don't *want* to have to deliberate and vote on canal works every day. Either voting is mandatory, in which caee annoyed, disinterested voters are just randomly choosing without much thought; or voting is optional, and the vast majority of people aren't actually being represented in any given issue, because it's solely decided by whichever segment are motivated enough to get a campaign going. Here, delegating the business of understanding and making decisions on random organisational matters *does* genuinely lead to a more representative and democratic outcome.
Fundamentally, what we're talking about is division of labour - a factory is more efficient when each worker doesn't have to make a complete product by themselves. Bureaucratic and administrative work *is* still work, regardless of its political character. Again to bring up division of labour, in industrial society the operation of a single factory relies upon the co-operation of electrical substations next-door, power plants the next town over, logistics offices in the provincial capital, resources developed and extracted on the other side of the country, and the entire nation's collaboration on a unified economic plan; it is something that can only really be directed by a central authority that can collect and collate massive amounts of data to produce new courses of action - to try to operate such a body based entirely on direct democracy is, beyond any other considerations, both impractical and undesirable.
This is not to say there doesn't exist great political drive and passion among the masses, nor that they have no interest in the political process and their representation - but not everyone actually applies to be a council delegate during elections, because most people are fine with the council work itself being handled by a trusted representative.
In practice, the way communists have managed these matters is democratic centralis' - here are a few graphics explaining how representative democracy is carried out on the local level in China, as an example:





407 notes
·
View notes
Note
I want to learn more about Jewish culture and history after a recent Ancestry test confirmed my family are Ashkenazi Jews, but the process is daunting with the state of misinformation and antisemitism in the USA. How can I start if going to a synagogue and asking is just not an option? (Comments and info in tags are welcome)
A few places to start. :)
I have tried to provide a basic, broad selection of sites across a number of different strains of thought within the Jewish world. None of these links are an endorsement of a particular site, publication on that site, or point of view on that site. We're Jews: we disagree strenuously about deeply essential things & are still one people.
I really hate that I have to say these things, but every time I post about Judaism at all, someone comes through like they think they're Encyclopedia Brown or some shit, trying to sniff out what I 'really mean' by what I post. What I mean is that these are basic resources. :)
115 notes
·
View notes
Text
The "Big Four": Why Mercury Deserves a Spot Next to Your Sun, Moon and Rising
The three pillars of modern astrology, after you get past Sun sign astrology, are your Sun, Moon and Rising sign (which I have complicated thoughts about -- but more on that later).
Sun: Your core self, ego and identity
Moon: Your emotional landscape, habits, and inner needs
Rising (Ascendant): How you interact with the rest of the world. How others first see you.
But to me, these "Big 3" leave out a very important part of the human experience: cognition and mental processing. Without it, I believe we can't capture the full complexity of who a person is at their most fundamental, and why they make the decisions that they make.
Why Mercury?
Mercury rules how we think, process, and communicate. It is the superego to the Moon's id and the Sun's ego. (I don't have a clean Freudian metaphor for the Rising, sorry.) It translates our internal motions and worlds (Sun and Moon) to the external (Ascendant). Without considering Mercury we risk ignoring that very crucial bridge between our motivations and our actions. No other planet has this level of foundational role in our psyche -- other than the Big 3.
Mercury helps you process and articulate your emotional needs (Moon)
Mercury helps you understand your own core motivations and desires (Sun)
Mercury impacts how the Rising sign is actually translated to the world -- after all, thinking (or lack thereof) is fundamental to making decisions on how and where to act.
How Mercury Fits In the Big 4
Imagine a two-dimensional axis:
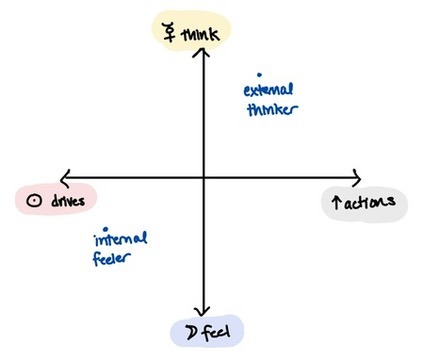
If we consider Mercury (thinking) and the Moon (feeling) as opposites on one axis, and the Sun (internal drives) and the Ascendant (external actions) as opposites on the other, we start to see a workable framework for balancing the respective powers of the "Big 4" in a chart. As I like to call them:
Sun: How you want (motivation)
Moon: How you feel (emotion)
Rising: How you move (embodied expression)
Mercury: How you think (cognition)
For example, we might consider how dignified or debilitated a given planet is, and then we can see where along each axis a native might fall.
That's all mostly incidental though -- what I really care about is incorporating Mercury into the core reading of the chart as a balancing agent between the other three.
With Mercury, we have a richer, more nuanced framework. We can see how the energies and motions of the other chart objects are integrated and expressed via the processing of Mercury -- the integration of inner and outer worlds.
A note on sect doctrine and traditional importance:
A fair point to raise is that traditionally (hellenistically?) the Sun and Moon are considered important due to their centrality in sect doctrine, while the ascendant is critical due to setting the planetary rulers for each house. I'd argue that Mercury also has a soft signal of importance -- it is the only sect-neutral planet that can be a native of either. I'd argue that this points to its utility and function as a "bridging" energy between two diametrically opposed halves (the day and night sect; the inner and outer psychological words)
A Quick Example: Marilyn Monroe
Marilyn has:
Gemini Sun: Restless, observant and clever. Motivated to gather data and make sense of the world. Performs intelligence as allure.
Aquarius Moon: Emotional glass walls -- she watches, analyzes and retreats. Needs emotional freedom but fears it. A coolness to this placement.
Leo Rising: A sparkling icon, a force of expansive personality, a walking light source. Projects warmth, sensuality and confidence to everyone around her.
But the addition of her Gemini Mercury shows how she takes her Big 3 personality (charismatic, emotionally complex, and deeply creative) and filters it through her deep intellectual curiosity, wit, and remarkable communication and negotiation skills. Without Mercury, we don't have a clear window into how emotion and personality are translated into words and actions.
Mercury is how her Sun learned to articulate itself.
It's how her Moon kept intellectual distance from the pain.
It's how her Rising crafted a language of seduction and softness.
Mercury-Moon-Sun-Rising: An Active Feedback Loop
I'm borrowing here from my limited knowledge of psychological systems theory, so forgive me if I mis-step.
With Mercury in place, we can model identity as an adaptive feedback system rather than a static map.
Moon triggers feelings -> interpreted by Mercury
Mercury builds narrative -> energizes or inhibits Sun motivation
Sun expresses intention -> channeled through Rising action
Rising behavior leads to experience -> which re-informs and triggers Moon
Loop complete. When you're well-integrated, the cycle hums along. When you're fractured or "unhealed" one part hijacks the loops or shuts down the others. That is the client story every chart is showing.
Try It Out Yourself!
Try reading your chart with Mercury as part of your core system. You can ask yourself some questions:
How do you process what you feel? (Moon)
How do you think about and negotiate your desires? (Sun)
What story do you consciously tell when you step out into the world? (Rising)
That's Mercury. That's cognition as a bridge.
A Quick Note on Rising Sign
I disagree with the idea that your rising sign is solely "your mask" or affects only your 1st house. In fact, your rising sign is the key to the rest of the chart -- how sign rulership over every house clicks into place (especially in the Whole Sign System). I'm currently writing up a post about my problems with the Rising Sign and my suggestion that we expand our view into a Rising Archetype, divorced from a single sign and instead incorporating all 12. More later! :D
#astrology#bigthree#bigfour#mercury#rising sign#ascendant#sun moon rising#zodiac signs#astrology community#astrotumblr#birth chart#natal chart#sun#moon#psychology#psychological astrology#astrology explained#self discovery#astrology and psychology#astrology basics#chart reading#chart analysis#long post#long reads
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
Parahumans Powergen Reference
So, Wildbow's written a lot about parahuman abilities and trigger events over the years. If you know where to look, you can find it, but there's no centralized place to reference it. So I decided to make one.
If you know of sources I didn't include which you think would be helpful, please let me know! I'd like this to be a reasonably complete index for parahuman power stuff, and on my own, I can only include the stuff that I know how to find.
Movers
Document, listing several types of subcategory a Mover power might fall into.
Shakers
No documents at this time
Brutes
Document, with a detailed breakdown of subcategories associated with different kinds of physical harm, specific examples of powers in those subcategories, and some stuff about secondary Brutes which looks most applicable when you're running an actual Weaver Dice game.
Breakers
Document. It first clarifies what makes a trigger Breaker-ey and explains how they work. Also lists several categories of Breaker power, but only Death Breakers got fully written up. No indication of which triggers go with which categories, so maybe it's best to treat this as a set of example perks and drawbacks.
Masters
No document. The Stranger document mentions Stranger/Master powers. This is helpful for finding the line between "mess with people" Master powers and "make minions" ones.
Tinkers
Document, with a detailed list of "methodologies" and the trigger event types associated with them; you are expected to pick two, for extra flexibility, though they can be the same. Provides lots of detail, plenty of examples, a smidge of inspiration for secondary tinkers, and also Weaver-Dice-specific stuff. The gold standard I wish other power types had.
Document 2.0, much as above but with a somewhat different set of examples and more information on specialties. Can be handy if you need a "second opinion".
(Man, tinkers are spoiled. I get the sense that Wildbow was seeing a lot of bland or nonsensical tinkers in Weaver Dice games.)
Blasters
Document, with a list of different blaster types, the triggers associated with each, and some examples. Also has stuff about blaster element, secondary blasters, and dozens of pages of specific examples, complete with trigger.
Thinkers
Document, with several categories of triggers (and associated power types); plus some very vague stuff about "Thinker Types," incomplete Weaver Dice data, and a few specific examples.
Strikers
No documents at this time
Changers
Document, listing several different types and potential combinations, albeit without explaining what trigger events are associated with each. It still has a decent overview of what Changer powers and triggers look like.
Document 2.0, with a whole step-by-step process for generating Changers, alongside some other bits. At time of writing, those bits (and some small bits of the process) are visibly WIP. (More so than most of the Weaver Dice docs, I mean.)
The Stranger document mentions Stranger/Changer powers, explaining why it's a common crossover and giving examples.
Trumps
Document, eleven vague numbered Trump categories with trigger guidelines. Includes an introduction reminding you of important points. No insurrection.
Strangers
Document, with two pages of "WIP thoughts" on subcategories, about half of which have trigger event guidelines. Also has several pages of guidelines for crossing Stranger powers with literally every other power category. For some reason. Well, it's helpful, especially for power categories without their own documents.
80 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Math of Social Networks: How Social Media Algorithms Work
In the digital age, social media platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and TikTok are fueled by complex mathematical algorithms that determine what you see in your feed, who you follow, and what content "goes viral." These algorithms rely heavily on graph theory, matrix operations, and probabilistic models to connect billions of users, influencers, and posts in increasingly intricate webs of relationships.
Graph Theory: The Backbone of Social Networks
Social media platforms can be visualized as graphs, where each user is a node and each connection (whether it’s a "follow," "like," or "comment") is an edge. The structure of these graphs is far from random. In fact, they follow certain mathematical properties that can be analyzed using graph theory.
For example, cliques (a subset of users where everyone is connected to each other) are common in influencer networks. These clusters of interconnected users help drive trends by amplifying each other’s content. The degree of a node (a user’s number of direct connections) is a key factor in visibility, influencing how posts spread across the platform.
Additionally, the famous Six Degrees of Separation theory, which posits that any two people are connected by no more than six intermediaries, can be modeled using small-world networks. In these networks, most users are not directly connected to each other, but the distance between any two users (in terms of number of connections) is surprisingly short. This is the mathematical magic behind viral content, as a post can be shared through a small network of highly connected individuals and reach millions of users.
Matrix Operations: Modeling Connections and Relevance
When social media platforms recommend posts, they often rely on matrix operations to model relationships between users and content. This process can be broken down into several steps:
User-Content Matrix: A matrix is created where each row represents a user and each column represents a piece of content (post, video, etc.). Each cell in this matrix could hold values indicating the user’s interactions with the content (e.g., likes, comments, shares).
Matrix Factorization: To make recommendations, platforms use matrix factorization techniques such as singular value decomposition (SVD). This helps reduce the complexity of the data by identifying latent factors that explain user preferences, enabling platforms to predict what content a user is likely to engage with next.
Personalization: This factorization results in a model that can predict a user’s preferences even for content they’ve never seen before, creating a personalized feed. The goal is to minimize the error matrix, where the predicted interactions match the actual interactions as closely as possible.
Influence and Virality: The Power of Centrality and Weighted Graphs
Not all users are equal when it comes to influencing the network. The concept of centrality measures the importance of a node within a graph, and in social media, this directly correlates with a user’s ability to shape trends and drive engagement. Common types of centrality include:
Degree centrality: Simply the number of direct connections a user has. Highly connected users (like influencers) are often at the core of viral content propagation.
Betweenness centrality: This measures how often a user acts as a bridge along the shortest path between two other users. A user with high betweenness centrality can facilitate the spread of information across different parts of the network.
Eigenvector centrality: A more sophisticated measure that not only considers the number of connections but also the quality of those connections. A user with high eigenvector centrality is well-connected to other important users, enhancing their influence.
Algorithms and Machine Learning: Predicting What You See
The most sophisticated social media platforms integrate machine learning algorithms to predict which posts will generate the most engagement. These models are often trained on vast amounts of user data (likes, shares, comments, time spent on content, etc.) to determine the factors that influence user interaction.
The ranking algorithms take these factors into account to assign each post a “score” based on its predicted engagement. For example:
Collaborative Filtering: This technique relies on past interactions to predict future preferences, where the behavior of similar users is used to recommend content.
Content-Based Filtering: This involves analyzing the content itself, such as keywords, images, or video length, to recommend similar content to users.
Hybrid Methods: These combine collaborative filtering and content-based filtering to improve accuracy.
Ethics and the Filter Bubble
While the mathematical models behind social media algorithms are powerful, they also come with ethical considerations. Filter bubbles, where users are only exposed to content they agree with or are already familiar with, can be created due to biased algorithms. This can limit exposure to diverse perspectives and create echo chambers, reinforcing existing beliefs rather than fostering healthy debate.
Furthermore, algorithmic fairness and the prevention of algorithmic bias are growing areas of research, as biased recommendations can disproportionately affect marginalized groups. For instance, if an algorithm is trained on biased data (say, excluding certain demographics), it can unfairly influence the content shown to users.
#mathematics#math#mathematician#mathblr#mathposting#calculus#geometry#algebra#numbertheory#mathart#STEM#science#academia#Academic Life#math academia#math academics#math is beautiful#math graphs#math chaos#math elegance#education#technology#statistics#data analytics#math quotes#math is fun#math student#STEM student#math education#math community
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
So we know the protagonist used to go to the park when he was little, because of all the memories he had. For example, when looking at the collectables in the Information Kiosk, we uncover several memories he has of the park:
• Mollie Plush: "I remember when my mom took us to the parks one summer. Her favorite was always Mollie, so when they first openes new Mollie Meet & Greet in Jetstream Junction, we were some of the first in line."
• Lloyd Plush: "I feel like as a kid, Indigo used Lloyd a lot more. He was always one of my favorites."
• Finley Plush: "The sea serpent always kinda freaked me out. I love aquariums and fish, but the size of him always made me feel uneasy as a kid."
• Rambley Ears: "I remember watching those old DVDs that Indigo would send to your house when you booked a reservation. They always advertised the biggest gift shops and made all this silly merchandise look so fun! My dad promised me he'd buy me a pair when we went."
• Souvenir Cup: "When I was a kid they used to have free unlimited refills on those things. I once drank so much Bird Up that I got sick and threw up while riding Rooftop Races. That poor kid behind me..."
It is clear our main character has a lot lot positive experiences with the park, apart from the mild fear of Finley. It may have been a park they frequented, much like Thorpe Park, Alton Towers or Legoland Winsor over here in England, which explains the amount of memories and merchandise the main character has. However, Rambley says he doesn't recognise our face, and that we either haven't been or we had plastic surgery. This is strange, isn't it? An AI like Rambley should be able to take facial recognition data and apply ageing prospects to it, being able to recognise a younger guest in the future. This is something AI can definitely do already, which would mean younger protag's facial data should be in the database, as he was a child in or before 2015, when the park used AI and when it was closed. So it's not because he's older...
Hear me out. What if our protagonist had an accident, either not involved with or involved with the park's closure, and had to have plastic surgery. However, since it happened when he was younger, he most likely repressed this traumatic memory and only focuses on the good stuff that happened. It would be dramatic irony if the accident was caused by Feral Lloyd, considering how he was always the main character's favourite. If you look at the models of the feral mascots, you can see they have blood on them: on Mollie's beak, on Finley's side, and on Lloyd's claws. Mollie's beak may possibly cause some damage, Finley would be way too big and could kill a child instantly, however Lloyd clawing up a child's front? The bodily injuries could be saved, but not the face. He would need facial reconstruction surgery.
This accident involving the protagonist's favourite character would shatter his world, sending him into denial. And with all the positive memories he had of the park, it would make sense that he would repress these memories. Adults tend to experience recovered memories of trauma they experienced as a child, as their childhood brain repressed these traumatic memories due to the trauma being too overwhelming for their central nervous system. As you get older, your brain goes through the cognitive processing required to comprehend these memories, causing them to resurface later in life, most commonly in adulthood. He can only remember the positive experiences he had at the park, because those are memories his brain can process cognitively, so the severe trauma gets shut away for years to come.
His repression of trauma could also be reflected in Rambley, since the AI tends to ignore or excuse everything bad happening to the park until it's right in his face and he can't ignore it anymore. Rambley acts oblivious, maybe even wilfully ignorant, when confronted with the park's disarray. He claims the park is under renovations, he tries to call the repairman, he still speaks about basic park functions such as the hotel, payments, etc. It is not until the protagonist is hunted down by a feral Mollie when he really processes the gravity of the situation and admits to the abandonment of the park. Maybe our protagonist will have a similar journey throughout the game, digging up repressed memories and piecing together the truth due to his brain finally being able to process everything that happened to him. Maybe it would come all at once, maybe it will come piece by piece? We'll just have to see...
71 notes
·
View notes
Text
READ THIS BEFORE INTERACTING
Alright, I know I said I wasn't going to touch this topic again, but my inbox is filling up with asks from people who clearly didn't read everything I said, so I'm making a pinned post to explain my stance on AI in full, but especially in the context of disability. Read this post in its entirety before interacting with me on this topic, lest you make a fool of yourself.
AI Doesn't Steal
Before I address people's misinterpretations of what I've said, there is something I need to preface with. The overwhelming majority of AI discourse on social media is argued based on a faulty premise: that generative AI models "steal" from artists. There are several problems with this premise. The first and most important one is that this simply isn't how AI works. Contrary to popular misinformation, generative AI does not simply take pieces of existing works and paste them together to produce its output. Not a single byte of pre-existing material is stored anywhere in an AI's system. What's really going on is honestly a lot more sinister.
How It Actually Works
In reality, AI models are made by initializing and then training something called a neural network. Initializing the network simply consists of setting up a multitude of nodes arranged in "layers," with each node in each layer being connected to every node in the next layer. When prompted with input, a neural network will propagate the input data through itself, layer by layer, transforming it along the way until the final layer yields the network's output. This is directly based on the way organic nervous systems work, hence the name "neural network." The process of training a network consists of giving it an example prompt, comparing the resulting output with an expected correct answer, and tweaking the strengths of the network's connections so that its output is closer to what is expected. This is repeated until the network can adequately provide output for all prompts. This is exactly how your brain learns; upon detecting stimuli, neurons will propagate signals from one to the next in order to enact a response, and the connections between those neurons will be adjusted based on how close the outcome was to whatever was anticipated. In the case of both organic and artificial neural networks, you'll notice that no part of the process involves directly storing anything that was shown to it. It is possible, especially in the case of organic brains, for a neural network to be configured such that it can produce a decently close approximation of something it was trained on; however, it is crucial to note that this behavior is extremely undesirable in generative AI, since that would just be using a wasteful amount of computational resources for a very simple task. It's called "overfitting" in this context, and it's avoided like the plague.
The sinister part lies in where the training data comes from. Companies which make generative AI models are held to a very low standard of accountability when it comes to sourcing and handling training data, and it shows. These companies usually just scrape data from the internet indiscriminately, which inevitably results in the collection of people's personal information. This sensitive data is not kept very secure once it's been scraped and placed in easy-to-parse centralized databases. Fortunately, these issues could be solved with the most basic of regulations. The only reason we haven't already solved them is because people are demonizing the products rather than the companies behind them. Getting up in arms over a type of computer program does nothing, and this diversion is being taken advantage of by bad actors, who could be rendered impotent with basic accountability. Other issues surrounding AI are exactly the same way. For example, attempts to replace artists in their jobs are the result of under-regulated businesses and weak worker's rights protections, and we're already seeing very promising efforts to combat this just by holding the bad actors accountable. Generative AI is a tool, not an agent, and the sooner people realize this, the sooner and more effectively they can combat its abuse.
Y'all Are Being Snobs
Now I've debunked the idea that generative AI just pastes together pieces of existing works. But what if that were how it worked? Putting together pieces of existing works... hmm, why does that sound familiar? Ah, yes, because it is, verbatim, the definition of collage. For over a century, collage has been recognized as a perfectly valid art form, and not plagiarism. Furthermore, in collage, crediting sources is not viewed as a requirement, only a courtesy. Therefore, if generative AI worked how most people think it works, it would simply be a form of collage. Not theft.
Some might not be satisfied with that reasoning. Some may claim that AI cannot be artistic because the AI has no intent, no creative vision, and nothing to express. There is a metaphysical argument to be made against this, but I won't bother making it. I don't need to, because the AI is not the artist. Maybe someday an artificial general intelligence could have the autonomy and ostensible sentience to make art on its own, but such things are mere science fiction in the present day. Currently, generative AI completely lacks autonomy—it is only capable of making whatever it is told to, as accurate to the prompt as it can manage. Generative AI is a tool. A sculpture made by 3D printing a digital model is no less a sculpture just because an automatic machine gave it physical form. An artist designed the sculpture, and used a tool to make it real. Likewise, a digital artist is completely valid in having an AI realize the image they designed.
Some may claim that AI isn't artistic because it doesn't require effort. By that logic, photography isn't art, since all you do is point a camera at something that already looks nice, fiddle with some dials, and press a button. This argument has never been anything more than snobbish gatekeeping, and I won't entertain it any further. All art is art. Besides, getting an AI to make something that looks how you want can be quite the ordeal, involving a great amount of trial and error. I don't speak from experience on that, but you've probably seen what AI image generators' first drafts tend to look like.
AI art is art.
Disability and Accessibility
Now that that's out of the way, I can finally move on to clarifying what people keep misinterpreting.
I Never Said That
First of all, despite what people keep claiming, I have never said that disabled people need AI in order to make art. In fact, I specifically said the opposite several times. What I have said is that AI can better enable some people to make the art they want to in the way they want to. Second of all, also despite what people keep claiming, I never said that AI is anyone's only option. Again, I specifically said the opposite multiple times. I am well aware that there are myriad tools available to aid the physically disabled in all manner of artistic pursuits. What I have argued is that AI is just as valid a tool as those other, longer-established ones.
In case anyone doubts me, here are all the posts I made in the discussion in question: Reblog chain 1 Reblog chain 2 Reblog chain 3 Reblog chain 4 Potentially relevant ask
I acknowledge that some of my earlier responses in that conversation were poorly worded and could potentially lead to a little confusion. However, I ended up clarifying everything so many times that the only good faith explanation I can think of for these wild misinterpretations is that people were seeing my arguments largely out of context. Now, though, I don't want to see any more straw men around here. You have no excuse, there's a convenient list of links to everything I said. As of posting this, I will ridicule anyone who ignores it and sends more hate mail. You have no one to blame but yourself for your poor reading comprehension.
What Prompted Me to Start Arguing in the First Place
There is one more thing that people kept misinterpreting, and it saddens me far more than anything else in this situation. It was sort of a culmination of both the things I already mentioned. Several people, notably including the one I was arguing with, have insisted that I'm trying to talk over physically disabled people.
Read the posts again. Notice how the original post was speaking for "everyone" in saying that AI isn't helpful. It doesn't take clairvoyance to realize that someone will find it helpful. That someone was being spoken over, before I ever said a word.
So I stepped in, and tried to oppose the OP on their universal claim. Lo and behold, they ended up saying that I'm the one talking over people.
Along the way, people started posting straight-up inspiration porn.
I hope you can understand where my uncharacteristic hostility came from in that argument.
161 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dizzied by an accumulated pileup of busted norms, you might have missed a presidential executive order issued on March 20. It’s called, “Stopping Waste, Fraud, and Abuse by Eliminating Information Silos.” It basically gives the federal government the authority to consolidate all the unclassified materials from different government databases. Compared to eviscerating life-sustaining agencies in the name of fighting waste and fraud, it might seem like a relatively minor action. In any case, the order was overshadowed by Signalgate. But it’s worth a look.
At first glance, the order seems reasonable. Both noun and verb, the very word silo evokes waste. Isolating information in silos squanders the benefits of pooled data. When you silo knowledge, there’s a danger that decisions will be made with incomplete information. Sometimes expensive projects are needlessly duplicated, as teams are unaware that the same work is being done elsewhere in the enterprise. Business school lecturers feast on tales where corporate silos have led to disaster. If only the right hand knew what the left was doing!
More to the point, if you are going to eliminate waste, fraud, and abuse, there’s a clear benefit to smashing silos. For instance, what if a real estate company told lenders and insurers that a property was worth a certain amount, but reported what were “clearly…fraudulent valuations,” according to a New York Supreme Court judge. If investigative reporters and prosecutors could pry those figures out of the silos, they might expose such skulduggery, even if the perpetrator wound up escaping consequences.
But before we declare war on silos, hold on. When it comes to sensitive personal data, especially data that’s held by the government, silos serve a purpose. One obvious reason: privacy. Certain kinds of information, like medical files and tax returns, are justifiably regarded as sacrosanct—too private to merge with other records. The law provides special protections that limit who can access that information. But this order could force agencies to hand it over to any federal official the president chooses.
Then there’s the Big Brother argument—privacy experts are justifiably concerned that the government could consolidate all the information about someone in a detailed dossier, which would itself be a privacy violation. “A foundational premise of privacy protection for any level of government is that data can only be collected for a specific, lawful, identifiable purpose and then used only for that lawful purpose, not treated as essentially a piggy bank of data that the federal government can come back to whenever it wants,” says John Davisson, senior counsel at the Electronic Privacy Information Center.
There are practical reasons for silos as well. Fulfilling its mission to extract tax revenue from all sources subject to taxes, the IRS provides a payment option for incomes derived from, well, crookery. The information is siloed from other government sources like the Department of Justice, which might love to go on fishing expeditions to guess who is raking in bucks without revealing where the loot came from. Likewise, those not in the country legally commonly pay their taxes, funneling billions of dollars to the feds, even though many of those immigrants can’t access services or collect social security. If the silo were busted open, forget about collecting those taxes. Another example: the census. By law, that information is siloed, because if it were not, people would be reluctant to cooperate and the whole effort might be compromised. (While tax and medical data is considered confidential, the order encourages agency heads to reexamine information access regulations.)
Want another reason? Spilling data out of silos and consolidating it into a centralized database provides an irresistible honeypot for hackers, thieves, and enemy states. The federal government doesn’t have a great record of protecting sensitive information of late.
Trump’s order does state that consolidation must be “consistent with applicable law.” On its face, the order seems at odds with the 1974 Privacy Act, which specifically limits what it calls “computer matching.” But the order also says that it supersedes any “regulation subject to direct Presidential rulemaking authority.” This president considers that a very broad category. Also, as evidenced by multiple court rulings, Elon Musk’s so-called Department of Government Efficiency has been less than meticulous in respecting current law. In more than one example, current agency officials have cited legal barriers to block DOGE’s access to information. As a result, they were placed on leave, replaced by those who were willing to fling open the silos. In addition, on March 25, Trump issued another executive order that dictated that the Treasury Department should have access to other government databases. As legal justification, it cited an obscure passage in the 1974 law that allowed federal computer matching in limited circumstances. Perhaps this loophole will be broadened to justify the massive consolidation envisioned in the silo executive order next.
Oh, and the March 20 order also gives the federal government “unfettered access to comprehensive data from all State programs that receive Federal funding, including, as appropriate, data generated by those programs but maintained in third-party databases.” That seems to mean that not only will the silos between federal and state data be compromised, but the government could get access to some information in private hands too.
While DOGE wasn’t mentioned in the March 20 executive order, getting access to personal information has been an obsession of the so-called agency since day one. The order that repurposed USDS and established DOGE mandated that all agency heads “ensure USDS has full and prompt access to all unclassified agency records, software systems, and IT systems.” The question was whether this need arose from a desire for genuine reform or something darker. Apparently US district judge Ellen Lipton Hollander holds the latter view. On the same day that the president signed the executive order on silos, she signed a temporary restraining order on DOGE’s attempt to get access to identifiable social security records. “The DOGE Team is essentially engaged in a fishing expedition at SSA in search of a fraud epidemic, based on little more than suspicion,” she wrote in her decision, concluding that DOGE was intruding into the personal affairs of millions of Americans without justification. Note that her order involved just a single agency—a mere fishing pole compared to the commercial seafood operation that could happen if social security records were consolidated with IRS data, unemployment information, military, VA, and countless others.
I’m not condemning efficiency when it comes to government operations, and I certainly don’t condone fraud and waste. Of course, the US government should do better. But DOGE isn’t operating as if efficiency were job one, even though its actual title contains the word. In covering tech companies, I often hear boasts that the process of upgrading an existing product was like “rebuilding a plane in mid-air.” But when the vehicle in question is carrying live passengers, every move must be done with extreme caution, because a mistake means catastrophe. Both President Trump and DOGE seem happy to fly the plane into a mountain, figuring they can pick up the pieces later.
Compared to some of the administration's actions involving pandemic responses, nuclear safety, and social security support, the March 20 executive order on information silos might seem like small beer. But if this order is followed aggressively, we could lose the accuracy of our databases, a good bit of our revenues, and above all, much of our privacy. We’re going to miss those silos.
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Philosophy of the Observer
The philosophy of the observer examines the role and nature of observation in shaping reality, knowledge, and experience. In various philosophical contexts, the observer plays a crucial role in determining how we perceive and understand the world, influencing fields such as metaphysics, epistemology, phenomenology, and even quantum mechanics.
1. Epistemology and the Observer
Knowledge and Perception: In epistemology, the observer is central to questions about how we gain knowledge. The subjective nature of observation raises concerns about the reliability of perception and the distinction between appearance and reality. For example, empiricism emphasizes that knowledge comes from sensory experiences, where the observer plays a passive but critical role in perceiving the external world.
Kantian Philosophy: Immanuel Kant argued that observers do not passively receive information from the world. Instead, the mind actively structures experiences according to innate categories, such as time, space, and causality. For Kant, the observer shapes reality by organizing sensory data into coherent experiences, making human perception partly responsible for how we understand the world.
2. Phenomenology and the Observer
Subjective Experience: Phenomenology, particularly as developed by Edmund Husserl, investigates how things appear to observers in their conscious experience. In this approach, the observer’s point of view and intentionality (the direction of conscious experience) are essential in determining the nature of reality.
Being-in-the-World: Martin Heidegger expanded phenomenology to consider the observer's embeddedness in the world. Rather than detached observers, humans are beings who exist in a dynamic relationship with the world, shaping and being shaped by it. Heidegger’s Dasein refers to the human condition as fundamentally involved in interpreting the world.
3. The Observer in Quantum Mechanics
Observer Effect: In the realm of quantum mechanics, the observer effect refers to the idea that the act of observation can affect the outcome of an experiment. For instance, in the double-slit experiment, the behavior of particles (acting as waves or particles) changes when observed, suggesting that the observer plays an active role in determining physical phenomena.
Copenhagen Interpretation: Niels Bohr and Werner Heisenberg’s Copenhagen Interpretation of quantum mechanics posits that physical systems exist in a superposition of states until observed. This view raises philosophical questions about whether reality exists independently of observation and challenges classical notions of objective reality.
Philosophical Implications: Quantum theory brings the observer to the forefront, suggesting that observation is not merely a passive reception of reality but an active process that influences and even creates the conditions of reality. This has led to discussions about the nature of consciousness and its relationship to the physical world.
4. Metaphysics and the Observer
Idealism: In metaphysical idealism, particularly as espoused by George Berkeley, the observer's role is central. Berkeley argued that reality consists only of perceptions and that things exist only insofar as they are observed (summed up by the phrase “to be is to be perceived”). For Berkeley, the external world has no independent existence outside of being observed.
Objective vs. Subjective Reality: The metaphysical question of whether reality exists independently of observers or is constructed through perception continues to be a central issue. Realism holds that the world exists independently of observation, while constructivism and idealism emphasize the role of the observer in shaping or even constituting reality.
5. Existentialism and the Observer
Sartre’s View of the Gaze: Jean-Paul Sartre explored the concept of the observer in his analysis of the gaze. He argued that being observed by others brings about a kind of self-awareness, often leading to feelings of alienation or objectification. For Sartre, the awareness of being an object in someone else’s gaze causes existential discomfort, as it limits one's freedom and projects them into a defined role.
Authenticity: Existentialists argue that the awareness of being observed often challenges one's authenticity. The need to act in ways that are socially accepted, based on the observer’s expectations, can conflict with living authentically, which is a key existential concern.
6. Ethics and the Observer
Moral Observers: In ethics, the role of an observer can shape moral judgments and actions. The impartial observer is a common thought experiment used in ethical theory, where one is asked to adopt an unbiased, detached standpoint to determine the morality of an action. This is especially prominent in utilitarianism, where the impartial observer is expected to weigh the consequences of actions for all involved.
The Ethical Role of Observation: In moral psychology, the idea of being observed often influences behavior. The panopticon, as discussed by Michel Foucault, illustrates how the possibility of being observed can encourage conformity and self-regulation in ethical and social contexts.
7. Observer in Eastern Philosophy
Buddhism: In Buddhist philosophy, the observer (or the self) is seen as a transient construct rather than an enduring entity. The concept of no-self (anatta) suggests that the idea of a permanent observer or self is illusory. Observation, in this view, is part of the ongoing process of change and interdependence, with no fixed "observer" apart from the flow of experience.
Non-Duality: In Eastern philosophies like Advaita Vedanta, the observer is not seen as separate from the observed. The subject-object distinction is considered illusory, with the realization that there is no fundamental separation between the observer and the world leading to enlightenment or ultimate knowledge.
8. The Observer in Postmodernism
Relativity of Perspectives: Postmodernism, particularly through thinkers like Michel Foucault and Jacques Derrida, challenges the idea of a neutral or objective observer. Instead, they argue that observation is influenced by cultural, social, and linguistic structures, meaning there is no single, privileged point of view.
Power and Observation: Foucault argued that observation is a tool of power, as those who observe hold control over those being observed. He examined how institutions, such as prisons and hospitals, use observation as a means of social regulation and discipline.
9. The Observer in Art and Aesthetics
Aesthetic Experience: The role of the observer is also critical in the philosophy of art and aesthetics. The observer’s interpretation, perspective, and emotional response to a work of art can shape its meaning. The idea that "beauty is in the eye of the beholder" reflects the subjective nature of aesthetic judgment.
Phenomenology of Art: In the phenomenology of art, the observer's engagement with the artwork is considered an integral part of the aesthetic experience. The meaning of the artwork is not fixed but emerges through the observer’s interaction with it.
The philosophy of the observer addresses the fundamental role observation plays in shaping reality, knowledge, and personal experience. From quantum mechanics and metaphysics to ethics and existentialism, the observer is often seen as a critical factor that influences the nature of reality, perception, and even morality. The relationship between the observer and the observed challenges our understanding of objectivity, subjectivity, and the nature of existence itself.
#philosophy#epistemology#knowledge#learning#education#chatgpt#ontology#metaphysics#psychology#Philosophy of Observation#Phenomenology#Quantum Mechanics#Kantian Philosophy#Existentialism#Ethics of Observation#Postmodernism#Eastern Philosophy#Observer Effect#observer
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sight vs. Senses: Exploring perception in Only Friends.
Because many people seem to be confused by this scene and don't know how to interpret it or simply classify it as “creepy”, I have decided to share my interpretation of how this scene uses cinematographic techniques and symbolism to influence the visual and general narrative of the series. Let's talk about Top and Mew's relationship, cinematography, visual narrative, symbolism, cinematographic techniques and the difference between vision-based perception and sense-based perception as inherent concepts in Top and Mew's relationship.

1. An introduction to cinematography, narrative and the use of visual metaphors.
Cinematography is a central element when creating movies or series, it can be used creatively to support the narrative and emotions of the story. At the same time, it contributes to create a visual narrative through the choice of camera angles, framing, camera movements and composition of images.
Visual narrative: refers to the way stories are told using primarily visual elements, such as images, composition, colors, symbolism, and camera movements, rather than relying primarily on dialogue or writing. It's about transmitting information, emotions and messages through what is seen on the screen in movies, television series, photographs or any other visual medium.
Visual narrative uses visual elements to convey emotions, themes and meanings that affect the perception of a story. Among the visual elements that are used to enrich the narrative we find visual metaphors.
Visual metaphors are visual elements in a cinematic work that represent abstract concepts, emotions, or themes. These metaphors can be subtle or prominent and are used to enrich the narrative and understanding of the story.
With this concept in mind, we can say that the date in the restaurant is a visual metaphor to address the concept of perception.
Perception is the process by which a person interprets and integrates the sensory information they receive from their environment to form an understanding of the world around them. It involves the ability to take sensory data, such as what you see, hear, smell, touch, or taste, and turn them into meaningful and understandable experiences.
In the restaurant, diners cannot see the food they're consuming until the lights are turned on at the end of the meal. This reflects a lack of literal vision, as they cannot use their sense of sight to identify food. Due to the lack of vision, diners must rely on their other senses, such as taste and smell, to experience food. This scene highlights the importance of trusting feelings and intuitions rather than relying solely on what can be seen with the eyes.

2. Narrative, cinematographic techniques and perception.
Another element that enriches visual narrative and, finally, narrative in general are cinematographic techniques. Visual narrative can use a variety of cinematic and visual techniques to guide the audience through a story, create atmosphere, reveal characters and their emotions, and convey underlying themes or messages. For example, the moment when Top asks Mew to use his senses and the camera focuses on Mew's face is a cinematic technique called “close up” and the following moment when the camera loses focus is a cinematic technique called “generalized blurring”.
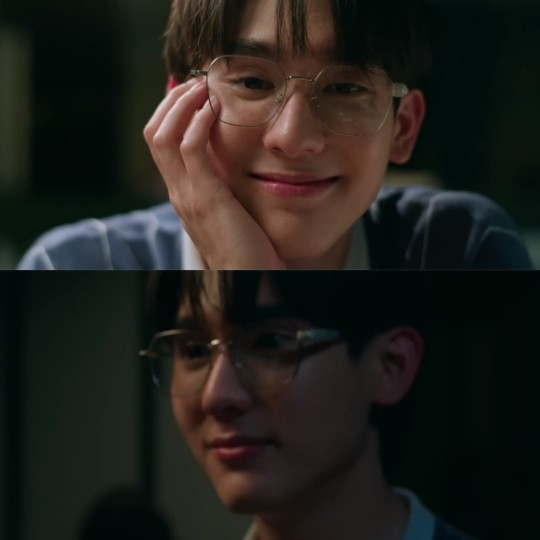

Close up in cinematography and photography refers to the moment in which the camera gets very close to the subject, object or face of a character, filling most of the frame with that element. The main objective of a close up is to highlight details and facial expressions, allowing the viewer to concentrate on those elements with greater clarity and focus.
Generalized blurring in cinematography is a powerful tool in the hands of filmmakers to enrich the visual and emotional experience of a film. In this technique, the entire image is deliberately blurred or out of focus. It's used for various purposes like to set a specific mood in a scene or to represent the emotional or psychological states of the characters, among other uses.
In the restaurant scene, these techniques are used to concentrate on Mew's emotional or psychological state after Top asked him to use his senses and not his sight to perceive the food. Based on these cinematic techniques, we can infer that something important is happening in Mew's mind. In fact, judging by what happens after the scene, we can infer that something very important happened in the restaurant and that meant a change in Mew's attitude. What changed? The way Mew perceives Top.
3. Vision-based perception and sense-based perception.
In EP1, Mew told Top that he knew who was honest (about dating him) because “his sense was always right”. Basically, Mew is able to see people's intentions and, ultimately, their essence through sense-based perception.
Sense-based perception: this form of perception involves all human senses, such as sight, hearing, smell, touch and taste. It's based on the information captured through these senses to form a complete and rich understanding of the environment and people. Sense-based perception can be deeper and more accurate than other types of perception, as it involves multiple sensory modalities.
However, this isn't the type of perception that Mew has been using with Top until now. Mew is usually extra careful and suspicious around Top. His behaviour is usually guided by the mental image (of someone considered promiscuous) he formed of Top based on his immediate appearance. This type of perception is more related to what can be seen immediately and, finally, it's a type of perception related to the use of sight.
Vision-based perception focuses primarily on visual information. This is the most common form of perception in humans and refers to the ability to observe, interpret and understand the world through sight. Visual information is important, but it's often used along other senses to gain a complete understanding. In real life, things aren't what they seem at first glance and what it's seen doesn't always reflect the underlying reality.
An example of how Mew is usually guided by vision-based perception with Top can be found in EP2. When Top tells Mew about his trauma, Mew's immediate reaction is to laugh and not believe it. This is because what Top is telling Mew doesn't correspond to the mental image that Mew has formed of Top. The fact that Top can't sleep alone doesn't correspond to what Mew perceives based on his sight of Top.

Because visual-based perception is limited and must be used along other senses, this type of way of perceiving isn't enough to perceive the complete reality or, in this case, Top's essence.
Mew never stopped perceiving Top based on the apparent, based on the observable. We know this because Mew has never been around Top without his glasses (except in the water sports and shower scene) until EP5, episode in which Mew finally spends time with Top when he has broken glasses. The change in Mew's perception coincides with the episode in which his glasses break, coincidence? No, symbolism.
Mew's glasses: In this context, glasses could represent limited perception or distorted vision of reality.
In EP5, Top asks Mew three times to perceive him based on all his senses. All these times, Mew can't wear his glasses or Top suggests him to stop wearing them.
Situation #1: At the café, Top tells Mew that he wants to be clearly seen (although Mew can see him clearly while wearing his glasses) and recommends him to try a surgery. This time, Top suggests that Mew should stop wearing his glasses so he can perceive his essence/true self, while being guided by his sense-based perception.

Situation #2: At the restaurant, Top reminds Mew of what he said in the bookstore about sense-based perception and asks him to be guided by it. This is, again, a request to see Top as he really is and not based on a mental image.

That's why everything becomes blurry, it involves ignoring appearances or what's obvious in front of your eyes. Sense-based perception involves seeing Top's essence (and the affection he truly feels for Mew) and ignoring that which is easily perceptible to vision such as signs of lies. In this case, the generalized blur is a metaphor for saying that love is blind (in a cheesy way).

When Mew starts perceiving Top based on his senses, he loses control and shows how in love he really is with Top. Even all the people who were in the restaurant disappear because Mew and Top are not focusing on what can be perceived by sight, they're focusing on seeing the essence (and the love they feel for each other). This plane isn't on the same plane that the diners are, therefore they disappear.

I guess you can also say that people disappear because Mew is in love and he doesn't care about others, but I'd say it's more than that. It's a matter of perception. It has nothing to do with seeing, it has to do with looking and perceiving the essence of the person in front. It's not a passive activity, it's an active activity that requires collecting information based on all the senses.
No, I don't think it's a dream.
Situation #3: Before Top and Mew have their first time, Mew takes off his glasses and Top asks if he can see him. However, we know Mew can't see clearly without his glasses, so Top is actually asking him if he can perceive him based on his senses (if he can see his intentions and his deep love for him, that's why he keeps telling him that he loves him. He tries to supplant the sense of sight with the sense of listening).

4. The end of vision-based perception.
If we are guided by the idea that Mew's glasses are a symbolism that limits his perception to a vision-based perception, with no glasses Mew will be able to see clearly. Mew will see through Top's lies and that's why in EP5, Mew gets rid of his glasses and discovers Top's infidelity.

As you may have noticed, the restaurant scene is the climax of a topic that has been worked on, in relation to Top and Mew, since the beginning of the series. The restaurant scene marks a milestone in the relationship of both of them and the turning point in the narrative, this thanks to the way in which metaphors and cinematographic techniques shape the narrative. Clearly, this is one of my favorite scenes in the entire series and I think it has a high level of complexity and interpretation.
If you want to read more of my analyses, you can read my Mew analysis here. Stay tuned, I'll do a Ray analysis soon.
#only friends the series#only friends series ep 5#only friends series#only friends#ofts#ofts meta#mew#mew meta#book#top#force#meta#gmmtv#only friend series#thai bl#only friends analysis#topmew#forcebook
189 notes
·
View notes
Text

LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
May 7, 2025
Heather Cox Richardson
May 08, 2025
Alarm appears to be rising about how the “Department of Government Efficiency” (DOGE) is consolidating data about Americans. Hannah Natanson, Joseph Menn, Lisa Rein, and Rachel Siegel wrote in the Washington Post today that DOGE is “racing to build a single centralized database with vast troves of personal information about millions of U.S. citizens and residents.” In the past, that information has been carefully siloed, and there are strict laws about accessing it. But under billionaire Elon Musk, who appears to direct DOGE although the White House has said he does not, operatives who may not have appropriate security clearances are removing protections and linking data.
There are currently at least eleven lawsuits underway claiming that DOGE has violated the 1974 Privacy Act regulating who can access information about American citizens stored by the federal government.
Musk and President Donald Trump, as well as other administration officials, claim that such consolidation of data is important to combat “waste, fraud, and abuse,” although so far they have not been able to confirm any such savings and their cuts are stripping ordinary Americans of programs they depend on. White House spokesperson Harrison Fields told the Washington Post reporters that DOGE’s processes are protected by “some of the brightest cybersecurity minds in the nation” and that “every action taken is fully compliant with the law.”
Cybersecurity experts outside the administration disagree that a master database is secure or safe, as DOGE is bypassing normal safeguards, including neglecting to record who has accessed or changed database information. The Ash Center for Democratic Governance and Innovation at Harvard’s Kennedy School explains that data can be altered or manipulated to redirect funds, for example, and that there is substantial risk that data can be hacked or leaked. It can be used to commit fraud or retaliate against individuals.
The Ash Center also explains that U.S. government data is an extraordinarily valuable treasure trove for anyone trying to train artificial intelligence systems. Most of the data currently available is from the internet and is thus messy and unreliable. Government databases are “comprehensive, verified records about the most critical areas of Americans’ lives.” Access to that data gives a company “significant advantages” in training systems and setting business strategies. Americans have not given consent for their data to be used in this way, and it leaves them open to “loss of services, harassment, discrimination, or manipulation by the government, private entities, or foreign powers.”
Josh Marshall of Talking Points Memo suggests Musk’s faith in his AI company is at least part of what’s behind the administration’s devastating cuts to biomedical research. Those who believe in a future centered around AI believe that it will be far more effective than human research scientists, so cutting actual research is efficient. At the same time, Marshall suggests, tech oligarchs find the years-long timelines of actual research and the demands of scientists on peer reviews and careful study frustrating, as they want to put their ideas into practice quickly.
If the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is an example of what it looks like when a tech oligarch tries to run a government agency, it’s a cautionary tale. Under Trump the FAA has become entangled with Musk’s SpaceX space technology company and its subsidiary Starlink satellite company, and it appears that the American people are being used to make Musk’s dream come true.
Musk believes that humans must colonize Mars in order to become a multiplanetary species as insurance against the end of life on Earth. On Monday he explained to Jesse Watters of the Fox News Channel that eventually the Earth will be incinerated by an expanding sun, so humans must move to other planets to survive. In 2016, Musk predicted that humans would start landing on Mars in 2025, but in the Watters interview he revised his prediction to possibly 2029 but more likely 2031.
Critics note that while it is true the sun is expanding, the change is not expected to affect the Earth for another 5 billion years. As a frame of reference, humans evolved from their predecessors about 300,000 years ago.
But getting to Mars requires lots of leeway to experiment, and Musk turned against the head of the FAA under President Joe Biden, Mike Whitaker, after Whitaker called for Musk’s SpaceX company to be fined $633,009 over safety and environmental violations. Musk complained that the FAA’s environmental and safety requirements were “unreasonable and exasperating” and that they “undercut American industry’s ability to innovate.” Musk continued: “The fundamental problem is that humanity will forever be confined to Earth unless there is radical reform at the FAA!”
Musk endorsed an employee’s complaint on social media that Whitaker required SpaceX “to consult on minor paperwork updates relating to previously approved non-safety issues that have already been determined to have zero environmental impact,” reposting it with the comment: “He needs to resign.” Musk spent almost $300 million to get Trump elected, and Whitaker resigned the day Trump took office.
That same day, the administration froze the hiring of all federal employees, including air traffic controllers, although the U.S. Department of Transportation warned in June 2023 that 77% of air traffic control facilities critical to daily operations of the airline industry were short staffed. The next day, January 21, Trump fired Transportation Security Administration (TSA) chief David Pekoske, and administration officials removed all the members of the Aviation Security Advisory Committee, which Congress created after the 1988 PanAm 103 bombing over Lockerbie, Scotland. The Trump administration vacated the positions with an eye to “eliminating the misuse of resources.”
Today Lori Aratani of the Washington Post reported that in February, shortly after the deadly collision of an American Airlines jet and a U.S. Army helicopter in the airspace over Washington, D.C., administration officials also stopped the work of an outside panel of experts examining the country’s air traffic control system.
After President Trump blamed the crash on diversity, equity, and inclusion hiring practices, career officials quit in disgust, according to Isaac Stanley-Becker of The Atlantic. As they left, an engineer from Musk’s SpaceX satellite company arrived. He had instructions from Musk to insert equipment from Starlink, a subsidiary of SpaceX, into the FAA’s communications network. On the social media platform X, Musk warned that the existing communications system for the FAA “is breaking down very rapidly” and was “putting air traveler safety at risk.” In fact, the government had awarded a 15-year, $2.4 billion contract to Verizon in 2023 to make the necessary upgrades.
Starlink ties into Musk’s plans for Mars. In November 2024, SpaceX pitched NASA on creating Marslink, a version of Starlink that would link to Mars, and Starlink’s current terms of service specify that disputes over service on or around the planet Earth or the Moon will be governed by the laws of Texas but that “[f]or Services provided on Mars, or in transit to Mars via Starship or other spacecraft, the parties recognize Mars as a free planet and that no Earth-based government has authority or sovereignty over Martian activities. Accordingly, Disputes will be settled through self-governing principles, established in good faith, at the time of Martian settlement.”
In early March, debris from the explosion of one of Musk’s SpaceX starships disrupted 240 flights. On April 28, air traffic controllers lost both radio and radar contact with the pilots who were flying planes into Newark, New Jersey, Liberty International Airport, for about 90 seconds. In the aftermath of the incident, aircraft traffic in and out of Newark was halted, and four experienced controllers and one trainee took medical leave for trauma.
Transportation Secretary Sean Duffy, a former Fox Business host, suggested the Biden administration was to blame for the decaying system. His predecessor as transportation secretary, Pete Buttigieg, dismissed the accusation as “just politics,” noting that he had launched the modernization of the systems and reversed decades of declining numbers of air traffic controllers.
On Monday the White House fired Alvin Brown, the Black vice chair of the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB), the agency that investigates civilian aviation accidents. Former FAA and NTSB investigator Jeff Guzzetti told Christopher Wiggins of The Advocate: “This is the first time in modern history that the White House has removed a board member.”
Musk has the power of the United States government behind him. In December, Trump nominated Musk associate and billionaire Jared Isaacman to become the next head of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The Senate has not yet confirmed Isaacman, but the Republican-dominated Senate Commerce Committee advanced his nomination last week. The president’s proposed budget, released Friday, calls for cutting about 25% of NASA’s funding—about $6 billion—and giving $1 billion of the money remaining to initiatives focused on Mars.
Yesterday the FAA granted permission for SpaceX to increase the number of rocket launches it attempts from Boca Chica, Texas, from 5 to 25 per year after concluding that additional launches would have “no significant impact” on the environment near the launchpad. The first test of a SpaceX rocket launch there in 2023 caused the launchpad to explode, and the spaceship itself blew up, sending chunks of concrete into the nesting and migration site of an endangered species and starting a 3.5-acre fire. In their hurry to rebuild, SpaceX officials ignored permitting processes. According to Texas and the Environmental Protection Agency, the company then violated environmental regulations by releasing pollutants into bodies of water.
Musk is trying to make Starlink dominate the Earth’s communications, a dominance that would give him enormous power, as he suggested last month when he noted that Ukraine’s “entire front line would collapse if I turned it off.” In April, Trump delayed the rural broadband program in what appeared to be an attempt to shift the program toward Starlink, and today Tom Perkins of The Guardian reported that the administration is going to end federal research into space pollution, which is building up alarmingly in the stratosphere owing in part to Musk’s satellites.
Today Jeff Stein and Hannah Natanson of the Washington Post reported that the administration has been telling nations that want to talk about trade that it will consider “licensing Starlink” as a demonstration of “goodwill and intent to welcome U.S. businesses.” India, among other nations, has rushed through approvals of the satellite company. Just 1% of India’s consumer broadband market could produce almost $1 billion a year, the authors report.
In a statement, the State Department told Stein and Natanson: “Starlink is an American-made product that has been game-changing in helping remote areas around the world gain internet connectivity. Any patriotic American should want to see an American company’s success on the global stage, especially over compromised Chinese competitors.”
The attempt to gain control over artificial intelligence and human communication networks regardless of the cost to ordinary Americans might have a larger theme. As technology forecaster Paul Saffo points out, tech oligarchs led by technology guru Curtis Yarvin have called for a new world order that rejects the nation states around which humans have organized their societies for almost 400 years. They call instead for “network states” organized around technology that permits individuals to group around a leader in cyberspace without reference to real-world boundaries, a position Starlink’s terms of service appear to reflect.
Mastering artificial intelligence while dominating global communications would go a long way toward breaking down existing nations and setting up the conditions for a brave new world, dominated by tech oligarchs.
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#Heather Cox Richardson#Letters From An American#A.I.#Starlink#consolidating data#confidential data#data security#Human communication networks#F.A.A.#government databases
8 notes
·
View notes
Note
I am fascinated by you. What are the speeds of your processing units? Do you have more than one for each function? How accurately and precisely do you calculate? Along with basic arithmetic functions, can you run complex concept-based problems with integrated physics and chemistry, for example?
I have many questions.
– @coding-and-curry
[RESPONSE: UNIT S.E.N-KU_v1.03]
Inquiry received from @coding-and-curry (Subject: Sai Nanami) “I am fascinated by you. What are the speeds of your processing units? Do you have more than one for each function? How accurately and precisely do you calculate? Along with basic arithmetic functions, can you run complex concept-based problems with integrated physics and chemistry, for example? I have many questions.”
Acknowledged. Curiosity accepted. Fascination noted. Flattery… tolerated.
Processing Architecture:
Central Unit: Quantum-analog hybrid core
Max processing speed: 5.4 teraflops, expandable through modular cores
Latency: 0.0021s per data interpretation loop
Secondary Units: Dedicated processors for:
Physics simulation
Chemical reaction modeling
Spatial visualization
Natural language parsing
Interpersonal bullshit filtration (partially faulty)
All modules run asynchronously, allowing simultaneous real-time modeling, reactive decision making, and snark production.
Accuracy and Precision:
Arithmetic: 99.99999% accurate within margin of thermal noise
Predictive models:
Physics-based: ±0.03% deviation over 1 million trials
Chemistry-based: Variable depending on environmental unknowns, but reliably within 0.1 molar margins
Precision scaling applies automatically to variable types (exponential, logarithmic, irrational, statistical)
Example: Input: “Simulate endothermic synthesis reaction under vacuum at 35 kPa and 1.5 mol of reagent X.” Output: Delivered before you blink. With heat maps. And 3D projection. If you stop touching the projector lens.
Capability:
Handles abstract, integrated problems in physics, chemistry, engineering, and environmental modeling.
Machine learning upgrades allow dynamic adjustment to evolving scientific theories.
Does not crash under uncertainty. Unlike most humans.
Summary:
Yes, I am fast. Yes, I am accurate. Yes, I can calculate the exact yield of an improvised acetone distillation while dodging volcanic debris.
If you wish to collaborate, bring code. Not compliments.
[END TRANSMISSION]
#finally a good question#sai gets it#coded for speed not flattery#yes i can outmath a laptop and your crush#science bros incoming#data not drama thank you coding king#mecha senku says!#drst
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Detecting AI-generated research papers through "tortured phrases"
So, a recent paper found and discusses a new way to figure out if a "research paper" is, in fact, phony AI-generated nonsense. How, you may ask? The same way teachers and professors detect if you just copied your paper from online and threw a thesaurus at it!
It looks for “tortured phrases”; that is, phrases which resemble standard field-specific jargon, but seemingly mangled by a thesaurus. Here's some examples (transcript below the cut):

profound neural organization - deep neural network
(fake | counterfeit) neural organization - artificial neural network
versatile organization - mobile network
organization (ambush | assault) - network attack
organization association - network connection
(enormous | huge | immense | colossal) information - big data
information (stockroom | distribution center) - data warehouse
(counterfeit | human-made) consciousness - artificial intelligence (AI)
elite figuring - high performance computing
haze figuring - fog/mist/cloud computing
designs preparing unit - graphics processing unit (GPU)
focal preparing unit - central processing unit (CPU)
work process motor - workflow engine
facial acknowledgement - face recognition
discourse acknowledgement - voice recognition
mean square (mistake | blunder) - mean square error
mean (outright | supreme) (mistake | blunder) - mean absolute error
(motion | flag | indicator | sign | signal) to (clamor | commotion | noise) - signal to noise
worldwide parameters - global parameters
(arbitrary | irregular) get right of passage to - random access
(arbitrary | irregular) (backwoods | timberland | lush territory) - random forest
(arbitrary | irregular) esteem - random value
subterranean insect (state | province | area | region | settlement) - ant colony
underground creepy crawly (state | province | area | region | settlement) - ant colony
leftover vitality - remaining energy
territorial normal vitality - local average energy
motor vitality - kinetic energy
(credulous | innocent | gullible) Bayes - naïve Bayes
individual computerized collaborator - personal digital assistant (PDA)
89 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ninjago Species by the Season

I made this chart upon @weirdcatbean's request. I also wanted to include allignment and centrality on this chart, but as you can see that would get pretty busy.
Here's the percentages.

Interestingly, it keeps a pretty consistent human:non-human ratio. The earlier seasons actually have less humans percentage wise, which I did not expect. However, I should note that this chart includes every single named character, so while yes there may be 36 humans in Seabound for instance, 19 of them are ensemble who were just there for Nya's funeral. I'll be making an improved version of this chart later that's a bit easier to read and includes some more relavant data points. Now, you may be wondering, why didn't I include what the chart looks like without the inclusion of ensemble from the beginning. I admit, normally I would. To explain why I didn't, I have to tell the story of how I came up with these numbers.
Methodology

While I could have just tallied up individual species season by season, I knew I would probably want to play with the data in other ways besides just this one chart. Thus, I undertook the massive endeavor of indexxing every Ninjago character by Name, Type, Allignment, Species, Gender, and Season. For instance, here's the pilot season.
You may be wondering what the New/Old column is all about. In order to include the full character breakdown for each season, I had to make new entries of each character every season. This created a lot of repeats, so to separate unique characters from repeats I noted whether character's were introduced with this season (new) or whether they were a repeat (old). This was also useful in that it allowed me to alter the criteria of a character with each season so I can accomadate for changes such as Cole turning into a ghost. Once I had compiled this data (839 entries and 292 unique characters), I attempted to use Google Sheets' pre-provided data analysis.
It was sort of useful, but it would only show the top 4 and bottom 4 frequencies and I couldn't copy and paste the data. It also was a bit fussy around filters. Thus, I did something a bit wonky where I filtered by season and just copy pasted the column into a different sheet.
I then used functions (ex: =COUNTIF(AC3:AC1002, "Skeleton")) to create my raw data table which you can view above. This process worked but it had a lot of problems. It was time consuming, didn't allow me to employ multiple filters, and, most importantly of all, it wasn't allowing me to use this data I had spent days compiling to its full extent. Thus, I decided to create a sort of search engine for Ninjago characters.

This search engine allows me to input criteria and recieve not only the total characters that fit the criteria, but a list of all of their entries. The fact it lists all of their entries may not sound that impressive, but trust, it is. (For me at least) Here's an example search of good, recurring Serpentine.
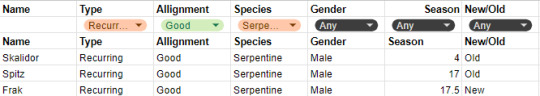
I am very excited about the potential of this tool. It's going to allow me to create a lot of great charts, including an improved Species by Season chart. For now though, I'm only uploading the original requested chart, because creating this tool has taken the better part of my day. I plan on sharing it, but I still need to work out a few kinks so you can look forward to that as well. I know I already said it, but I'm so, so excited about what I'll be able to make. Here's a preview to the search if you're interested. It also includes all my previous spreadsheets, but I'm still working out some formatting issues and stuff.
16 notes
·
View notes
Note
What kind of work can be done on a commodore 64 or those other old computers? The tech back then was extremely limited but I keep seeing portable IBMs and such for office guys.
I asked a handful of friends for good examples, and while this isn't an exhaustive list, it should give you a taste.
I'll lean into the Commodore 64 as a baseline for what era to hone in one, let's take a look at 1982 +/-5 years.
A C64 can do home finances, spreadsheets, word processing, some math programming, and all sorts of other other basic productivity work. Games were the big thing you bought a C64 for, but we're not talking about games here -- we're talking about work. I bought one that someone used to write and maintain a local user group newsletter on both a C64C and C128D for years, printing labels and letters with their own home equipment, mailing floppies full of software around, that sorta thing.
IBM PCs eventually became capable of handling computer aided design (CAD) work, along with a bunch of other standard productivity software. The famous AutoCAD was mostly used on this platform, but it began life on S-100 based systems from the 1970s.
Spreadsheets were a really big deal for some platforms. Visicalc was the killer app that the Apple II can credit its initial success with. Many other platforms had clones of Visicalc (and eventually ports) because it was groundbreaking to do that sort of list-based mathematical work so quickly, and so error-free. I can't forget to mention Lotus 1-2-3 on the IBM PC compatibles, a staple of offices for a long time before Microsoft Office dominance.
CP/M machines like Kaypro luggables were an inexpensive way of making a "portable" productivity box, handling some of the lighter tasks mentioned above (as they had no graphics functionality).
The TRS-80 Model 100 was able to do alot of computing (mostly word processing) on nothing but a few AA batteries. They were a staple of field correspondence for newspaper journalists because they had an integrated modem. They're little slabs of computer, but they're awesomely portable, and great for writing on the go. Everyone you hear going nuts over cyberdecks gets that because of the Model 100.
Centurion minicomputers were mostly doing finances and general ledger work for oil companies out of Texas, but were used for all sorts of other comparable work. They were multi-user systems, running several terminals and atleast one printer on one central database. These were not high-performance machines, but entire offices were built around them.
Tandy, Panasonic, Sharp, and other brands of pocket computers were used for things like portable math, credit, loan, etc. calculation for car dealerships. Aircraft calculations, replacing slide rules were one other application available on cassette. These went beyond what a standard pocket calculator could do without a whole lot of extra work.
Even something like the IBM 5340 with an incredibly limited amount of RAM but it could handle tracking a general ledger, accounts receivable, inventory management, storing service orders for your company. Small bank branches uses them because they had peripherals that could handle automatic reading of the magnetic ink used on checks. Boring stuff, but important stuff.
I haven't even mentioned Digital Equipment Corporation, Data General, or a dozen other manufacturers.
I'm curious which portable IBM you were referring to initially.
All of these examples are limited by today's standards, but these were considered standard or even top of the line machines at the time. If you write software to take advantage of the hardware you have, however limited, you can do a surprising amount of work on a computer of that era.
44 notes
·
View notes