#HERstory
Text
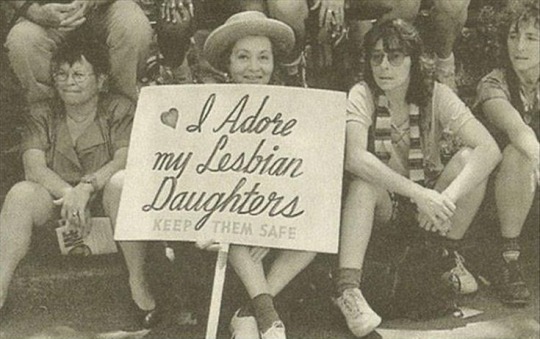
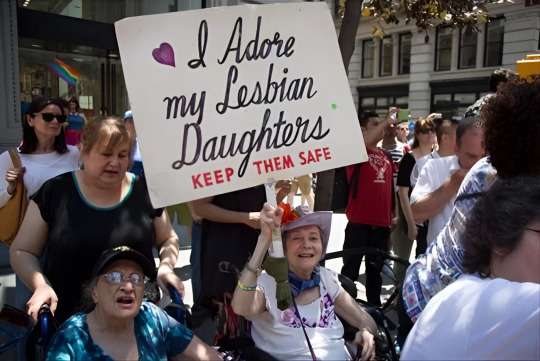
(x)
#lesbian visibility week#lesbian#lesbian history#wlw#wlw history#sapphic#sapphic history#sapphics#lgbt#lgbt history#lgbtq#lgbtqia#lgbtqia+#queer history#history#herstory#women#b&w#b&w photography#bw#bwphotography#aesthetic#a e s t h e t i c#source: pinterest
187 notes
·
View notes
Text

Mathematician, physician and philosopher (1776-1831), Sophie Germain was a genius who fought hard to be heard a recognized.
A self-taught prodigy
The daughter of a silk merchant, Sophie was born in Paris to a relatively wealthy family. When the French Revolution broke out in 1789, her father became a member of the Constituent Assembly. Amidst the chaos, Sophie found solace in her father's library and discovered mathematics.
Fascinated by the subject, she learned everything she could, studying at night. Her parents disapproved. Mathematics was thought to be too complex for women who had to focus first and foremost on their home.
Sophie's parents tried to stop her by putting out the fire in her room at night and confiscating her clothes and candles after nightfall. Sophie's thirst for knowledge was stronger. According to her obituary, she studied “at night in a room so cold that the ink often froze in its well, working enveloped with covers by the light of a lamp”. She even taught herself Latin to read the essential works.
Sophie impresses
The École Polytechnique was founded in 1974 with to train a new elite of engineers, mathematicians and scientists. Being a woman, Sophie couldn’t attend. She learned that a student named Leblanc wasn’t able to go to class. She wrote to the school, pretending to be him, and managed to obtain lecture notes. She was also able to complete and submit assignments.
This promising student impressed mathematician Joseph-Louis Lagrange who found her answers brilliant. The self-taught Sophie had gained the admiration of one of the most renowned mathematicians of her time.
Lagrange's desire to meet her forced Sophie to reveal her real identity. Lagrange was at first surprised to learn that his correspondent was a woman. He nonetheless became Sophie’s mentor, introducing her to a new world and opportunities.
Sophie made major contributions to number theory. She worked on Fermat's last theorem, making major observations and creating her own theorem. This would be one of her major contributions to mathematics.
In 1804, she began a correspondence with another mathematician, Carl Friedrich Gauss, whose work she admired. He was similarly impressed by her intelligence:
“But how to describe to you my admiration and astonishment at seeing my esteemed correspondent Monsieur Leblanc metamorphose himself into this illustrious personage who gives such a brilliant example of what I would find it difficult to believe. A taste for the abstract sciences in general and above all the mysteries of numbers is excessively rare: one is not astonished at it: the enchanting charms of this sublime science reveal only to those who have the courage to go deeply into it. But when a person of the sex which, according to our customs and prejudices, must encounter infinitely more difficulties than men to familiarize herself with these thorny researches, succeeds nevertheless in surmounting these obstacles and penetrating the most obscure parts of them, then without doubt she must have the noblest courage, quite extraordinary talents and superior genius.”
An incomplete recognition
Sophie was also interested in physics. In 1811, she entered a contest held by the French Academy of Sciences, but her lack of formal education turned against her. She didn't give up and won the contest in 1816 with her Memoir on the vibrations of Elastic Plates. She kept working on the theory of elasticity and published several more memoirs. Her work would prove pivotal in the field.
This prize also meant official recognition for Sophie. In 1823, she became the first woman to be allowed at the Academy of Sciences' sessions. Though respected as an equal collaborator by some, she still felt like a “foreigner” in the scientific community.
Sophie Germain died at the age of 55, on June 27, 1831, after a battle with breast cancer. Carl Friedrich Gauss had convinced the university of the University of Gottingen to give her an honorary degree but Sophie was dead before she could receive it.
Her death certificate designated her as a "rentière-annuitant" (a single woman with no profession) instead of a mathematician.
Today, a street in Paris, schools in France and a crater on Venus are named in her honor. She appeared on a French postal stamp released in 2016.
Feel free to check out my Ko-Fi if you like what I do! Your support would be greatly appreciated.

Further reading
Alkalay-Houlihan Coleen, “Sophie Germain and special cases of Fermat’s last theorem”
Boyé Anne,, “Sophie Germain, une mathématicienne face aux préjugés de son temps”
“Biographies of women mathematicians : Sophie Germain”
Lamboley Gilbert, “Math’s hidden woman”
Koppe Martin, “Sophie Germain, une pionnière enfin reconnue”
#sophie germain#history#historyedit#women in history#19th century#france#french history#upthebaguette#herstory#mathematics#mathematicians#historical#historical figures#women in stem#european history#historyblr
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
Women's Not So Distant History
This #WomensHistoryMonth, let's not forget how many of our rights were only won in recent decades, and weren’t acquired by asking nicely and waiting. We need to fight for our rights. Here's are a few examples:

📍 Before 1974's Fair Credit Opportunity Act made it illegal for financial institutions to discriminate against applicants' gender, banks could refuse women a credit card. Women won the right to open a bank account in the 1960s, but many banks still refused without a husband’s signature. This allowed men to continue to have control over women’s bank accounts. Unmarried women were often refused service by financial institutions entirely.

📍 Before 1977, sexual harassment was not considered a legal offense. That changed when a woman brought her boss to court after she refused his sexual advances and was fired. The court stated that her termination violated the 1974 Civil Rights Act, which made employment discrimination illegal.⚖️

📍 In 1969, California became the first state to pass legislation to allow no-fault divorce. Before then, divorce could only be obtained if a woman could prove that her husband had committed serious faults such as adultery. 💍By 1977, nine states had adopted no-fault divorce laws, and by late 1983, every state had but two. The last, New York, adopted a law in 2010.

📍In 1967, Kathrine Switzer, entered the Boston Marathon under the name "K.V. Switzer." At the time, the Amateur Athletics Union didn't allow women. Once discovered, staff tried to remove Switzer from the race, but she finished. AAU did not formally accept women until fall 1971.

📍 In 1972, Lillian Garland, a receptionist at a California bank, went on unpaid leave to have a baby and when she returned, her position was filled. Her lawsuit led to 1978's Pregnancy Discrimination Act, which found that discriminating against pregnant people is unlawful

📍 It wasn’t until 2016 that gay marriage was legal in all 50 states. Previously, laws varied by state, and while many states allowed for civil unions for same-sex couples, it created a separate but equal standard. In 2008, California was the first state to achieve marriage equality, only to reverse that right following a ballot initiative later that year.

📍In 2018, Utah and Idaho were the last two states that lacked clear legislation protecting chest or breast feeding parents from obscenity laws. At the time, an Idaho congressman complained women would, "whip it out and do it anywhere,"

📍 In 1973, the Supreme Court affirmed the right to safe legal abortion in Roe v. Wade. At the time of the decision, nearly all states outlawed abortion with few exceptions. In 1965, illegal abortions made up one-sixth of all pregnancy- and childbirth-related deaths. Unfortunately after years of abortion restrictions and bans, the Supreme Court overturned Roe in 2022. Since then, 14 states have fully banned care, and another 7 severely restrict it – leaving most of the south and midwest without access.

📍 Before 1973, women were not able to serve on a jury in all 50 states. However, this varied by state: Utah was the first state to allow women to serve jury duty in 1898. Though, by 1927, only 19 states allowed women to serve jury duty. The Civil Rights Act of 1957 gave women the right to serve on federal juries, though it wasn't until 1973 that all 50 states passed similar legislation

📍 Before 1988, women were unable to get a business loan on their own. The Women's Business Ownership Act of 1988 allowed women to get loans without a male co-signer and removed other barriers to women in business. The number of women-owned businesses increased by 31 times in the last four decades.
Free download

📍 Before 1965, married women had no right to birth control. In Griswold v. Connecticut (1965), the Supreme Court ruled that banning the use of contraceptives violated the right to marital privacy.

📍 Before 1967, interracial couples didn’t have the right to marry. In Loving v. Virginia, the Supreme Court found that anti-miscegenation laws were unconstitutional. In 2000, Alabama was the last State to remove its anti-miscegenation laws from the books.

📍 Before 1972, unmarried women didn’t have the right to birth control. While married couples gained the right in 1967, it wasn’t until Eisenstadt v. Baird seven years later, that the Supreme Court affirmed the right to contraception for unmarried people.

📍 In 1974, the last “Ugly Laws” were repealed in Chicago. “Ugly Laws” allowed the police to arrest and jail people with visible disabilities for being seen in public. People charged with ugly laws were either charged a fine or held in jail. ‘Ugly Laws’ were a part of the late 19th century Victorian Era poor laws.

📍 In 1976, Hawaii was the last state to lift requirements that a woman take her husband’s last name. If a woman didn’t take her husband’s last name, employers could refuse to issue her payroll and she could be barred from voting.

📍 It wasn’t until 1993 that marital assault became a crime in all 50 states. Historically, intercourse within marriage was regarded as a “right” of spouses. Before 1974, in all fifty U.S. states, men had legal immunity for assaults their wives. Oklahoma and North Carolina were the last to change the law in 1993.

📍 In 1990, the Americans with Disability Act (ADA) – most comprehensive disability rights legislation in U.S. history – was passed. The ADA protected disabled people from employment discrimination. Previously, an employer could refuse to hire someone just because of their disability.

📍 Before 1993, women weren’t allowed to wear pants on the Senate floor. That changed when Sen. Moseley Braun (D-IL), & Sen. Barbara Mikulski (D-MD) wore trousers - shocking the male-dominated Senate. Their fashion statement ultimately led to the dress code being clarified to allow women to wear pants.

📍 Emergency contraception (Plan B) wasn't approved by the FDA until 1998. While many can get emergency contraception at their local drugstore, back then it required a prescription. In 2013, the FDA removed age limits & allowed retailers to stock it directly on the shelf (although many don’t).

📍 In Lawrence v. Texas (2003), the Supreme Court ruled that anti-cohabitation laws were unconstitutional. Sometimes referred to as the ‘'Living in Sin' statute, anti-cohabitation laws criminalize living with a partner if the couple is unmarried. Today, Mississippi still has laws on its books against cohabitation.
#art#feminism#women's history#women's history month#iwd2024#international women's day#herstory#educational#graphics#history#70s#80s#rights#women's rights#human rights
14K notes
·
View notes
Text

Shel Silverstein for Playboy, 1965
13K notes
·
View notes
Text

All of this PLUS many women stayed in abusive horrible relationships because the Church is a patriarchal cheerleader for abusive men.
15K notes
·
View notes
Text
Katherine Johnson: The Mathematician Who Launched Astronauts into Space and Women into STEM 🚀👩🚀

In the vast expanse of the cosmos, where men first dreamed of reaching the stars, Katherine Johnson calculated the path that would get them there. This story isn't just about trajectories and orbits; it's about a woman whose brilliance in mathematics helped break the barriers of space and gender.

Johnson's journey began in White Sulphur Springs, West Virginia, where her curiosity and intelligence shone from an early age. Despite encountering segregation and sexism, she charted a course that would lead her to NASA, where her skills became indispensable to the success of the U.S. space program. Her calculations were critical to the success of the Mercury missions, including John Glenn's pioneering orbital flight, for which he specifically requested Johnson verify the computer's numbers. "If she says they're good," Glenn said, "then I'm ready to go."

But Johnson's contributions went beyond Mercury. She also played a role in the Apollo missions, including the first lunar landing, and her work on orbital mechanics laid the groundwork for the Space Shuttle program and plans for a Mars mission.

Her legacy is a beacon for women and people of color in STEM, symbolizing the power of intelligence and perseverance to overcome societal constraints. Johnson's story teaches us that the path to the stars is paved with determination, hard work, and an unwavering belief in one's own abilities.

Katherine Johnson's calculations helped lead humanity to the moon, but her impact extends far beyond the numbers. She charted a course for future generations of women in STEM, proving that the sky is not the limit—it's just the beginning. As we look up at the stars, we remember her legacy, not just as a mathematician, but as a trailblazer who launched us into a new era of exploration and equality.
#PiDay#KatherineJohnson#Katherine Johnson#NASA#Mathematics#National Archives#Women's History Month#HERstory#Archives#Apollo13#Mercury#STEM#Women in STEM#Science
503 notes
·
View notes
Text
A video of "human calculator" Shakuntala Devi solving complex mathematical equations within seconds.
In 1982, she was awarded the Guinness World Record for fastest human computation. She was assigned a multiplication problem with two random numbers of 13 digits each (7,686,369,774,870 × 2,465,099,745,779) and gave the correct answer (18,947,668,177,995,426,462,773,730) in 28 seconds.
She travelled to several countries for the purpose of having her talents studied. In 1988, her abilities were tested by Arthur Jenson, a professor at the University of California, Berkeley. Problems given to her included calculating the cube root of 61,629,875 and the seventh root of 170,859,375. Jensen reported that Devi came up with the solutions (395 and 15) before he could write them down in his notebook.
Before all that, in 1977, at Southern Methodist University, she gave the 23rd root of a 201-digit number in 50 seconds. Her answer (546,372,891) was confirmed by calculations done by the UNIVAC 1101 computer, for which a special program had to be written to perform such a large calculation. The computer took longer to solve the problem than Devi did.
Oh, also, in 1979, she wrote the earliest book about homosexuality in India.
(info stolen from Wikipedia)
#women and girls in STEM#incredible women and girls#women in history#herstory#neat stuff#LGB history#feminist history
762 notes
·
View notes
Text

If Not, Winter: Fragments of Sappho
translated by Anne Carson
#sappho#if not winter#anne carson#lesbian visibility week#wlw#wlw romance#wlw love#wlw poem#wlw poetry#wlw history#sapphic#sapphic romance#sapphic love#sapphic poem#sapphic poetry#sapphic history#sapphics#lgbt#lgbt poem#lgbt poetry#lgbtq#lgbtqia#lgbtqia+#poem#poetry#history#herstory#womens history#aesthetic#a e s t h e t i c
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Burginda’s letter is instructing the young man in his spiritual endeavours, and the contents of the (albeit short) letter reveal that she was highly educated and well-read. Written in a period that many still refer to erroneously as an intellectual ‘Dark Ages’, Burginda’s letter uses Greek words, utilises biblical exegesis, imitates Christian poetry like the fifth-century Psychomachia of Prudentius, and references both the sixth-century Italian poet Arator and the classical Roman poet Virgil. It also contains a reworking of a description of heaven found in a Latin poem from Africa that dates to c. 500. Burginda was clearly a very well-read intellectual.
This letter can be used as an example to refute many popular misconceptions about the early middle ages. The first misconception is that antique texts were neglected or unknown in this period. The second misconception is that medieval women were uneducated and unintellectual. The third misconception is that there was little or no intellectual transmission between Africa and Europe in this period. Burginda’s letter proves all these assumptions false. Not bad for two paragraphs of Latin."
#burginda#history#women in history#women's history#8th century#england#english history#female writers#herstory#middle ages#medieval#medieval women
448 notes
·
View notes
Text
They've found another prehistoric cave in France, with engravings, silex and jewellery made of seashells. One of the major engravings is of a vulva and it's said to be 16 000 years old.
It's not the first time they find female engravings in french caves so I'll leave you with some more:
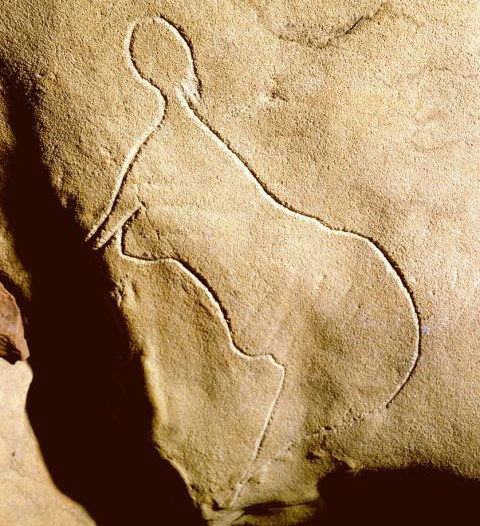










2K notes
·
View notes
Text
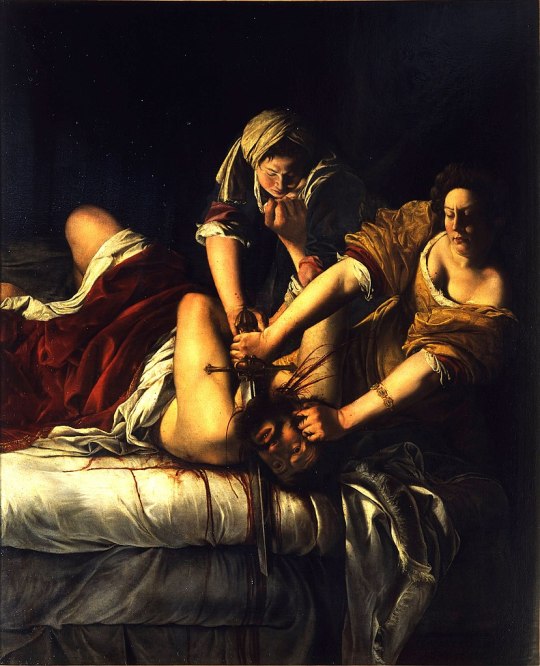

Judith Slaying Holofernes (c. 1612)
Artemisia Gentileschi
#international women's rights day#international women's day#judith slaying holofernes#artemisia gentileschi#feminism#misandry#art#herstory#fuck the patriarchy#femminismo#8th march
384 notes
·
View notes
Text
TLT fans: did you guys know about the real Wake? I hadn't heard about her until we covered World War II in my world civ class this semester
Nancy Grace Augusta Wake (1912-2011) was a covert operative who was at the top of the Nazi's most wanted list in WW2, nicknamed "The White Mouse" for her ability to repeatedly evade capture. She was born in New Zealand with Māori heritage, grew up in Australia, and joined the Resistance after traveling to Europe and witnessing the harsh treatment of Jews in Vienna by the Nazis

Wake worked in the Pat O'Leary Line escape network until her Resistance organization was compromised by the Germans in 1942. After that she fled on foot across the Pyrenees—with several close calls that she escaped by flirting with German soldiers—and made her way to England to join the Special Operations Executive. She was part of a three person team codenamed "Freelance" which parachuted into occupied France. During this operation she got stuck in a tree after her parachute became tangled in its branches. The local Resistance leader who found her reportedly said “I hope that all the trees in France bear such beautiful fruit this year" to which she replied "Cut out that French bullshit and get me out of this tree"
While working in the Freelance operation Wake once biked 500 km (310 mi) without stopping in the span of 72 hours across Nazi territory to retrieve a new radio and codes after her team's were destroyed in a Gestapo raid. Without this feat, Freelance would not have been able to communicate with London and there would have been no more supply drops to support their Resistance organization. During the war she was also part of a raid which destroyed the Gestapo headquarters in Montluçon, in which she reportedly killed a Nazi sentry with her bare hands to prevent him from raising an alarm
Wake's fellow operatives described her as "a real Australian bombshell. Tremendous vitality, flashing eyes. Everything she did, she did well. She was an excellent shot, excelled at fieldcraft and put the men to shame by her cheerful spirit and strength of character." "She is the most feminine woman I know until the fighting starts. Then she is like five men." "We both came to the conclusion that she was 10 times the man I would ever be"
By the time of her death in 2011, Wake had been awarded the George Medal by Britain; the Medal of Freedom by the United States; the Médaille de la Résistance, the Croix de Guerre (x3), and the Légion d’Honneur by France; and the Badge in Gold by New Zealand. Due to a complicated relationship with Australia, she originally refused to accept any awards from the Australian government, saying that they could "stick their medals where the monkey stuck his nuts." In 2004, however, she accepted the honor of Companion of the Order of Australia as well
#the locked tomb#commander wake#awake remembrance of these valiant dead kia hua ko te pai snap back to reality oops there goes gravity#harrow the ninth#tamsyn muir#world war ii#world war 2#nancy wake#nancy grace augusta wake#rambling#idk what exactly to do with this information but i thought it was really cool#and let me tell you. the fact that commander wake seems to be based on a key resistance op in WW2 at the top of the nazis most wanted list#does NOT make john and his empire look good. in case we needed anymore hints#ww2 tw#nazis tw#herstory#nona the ninth#greatest hits
895 notes
·
View notes
Text
Instead of twisty trapdoor vaginas, we now have the Pill and the diaphragm. Instead of the Bruce effect, we have methotrexate and misoprostol. Instead of waiting for a less dangerous birth canal to evolve, we have midwives who help our newborns squeeze through the gauntlet and the miracle of modern C-sections. When, in other species, physiological evolution would have created a newly evolved feature to enable female reproductive choice, hominins used behavioural innovations instead—some of them social and others involving new tools and pharmaceuticals. That control we have over the most powerful levers of our evolutionary fitness got us to where we are today. It allowed the early human population to finally explode, expanding into nearly every ecological niche our ancestors stumbled upon. It also improved the survival rates of every pregnant female with a too-narrow pelvis and a greedy placenta.
What got us here is not tool triumphalism but womb triumphalism. Out species' success was, and still is, borne on the laboring bellies and backs of women who made difficult choices throughout their reproductive lives. The deep history of gynecology isn't just the story of how we found ways for women to suffer less; it's the story of why we are alive today at all.
So maybe we need a better narrative to describe humanity's "triumph." Our story doesn't begin with a weapon. It doesn't begin with a man. The symbols of our ultimate technological achievements shouldn't be the atom bomb, the internet, the Hoover Dam. Instead, they should be the Pill, the speculum, the diaphragm.
– Cat Bohannon (2023) Eve: How the Female Body Drove 200 Million Years of Human Evolution, pp. 236-7.
247 notes
·
View notes
Photo


the world needs more proud butch women.
#my drawings#butch#lesbian#gay#body positive#gnc#gender nonconforming#herstory#radfem friendly#sketch#looking at photos of lesbians from the 80s and 90s#got me wishing i could have been born earlier to be part of that culture#rather than dealing with the clusterfuck that is the contemporary lgbt community
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

hey
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

evil dead rise enthusiasts may I interest you in the original maggot mommy
#mimimakes#tma#the magnus archives#tma memes#jane prentiss#jon sims#tma the corruption#the corruption#tma entities#evil dead rise#ellie bixler#horror memes#horror#herstory
569 notes
·
View notes