#Language and Meaning
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Philosophy of Imagism
The philosophy of Imagism is grounded in clarity, precision, and directness in both thought and expression. Originating in early 20th-century poetry, Imagism was a literary movement that rejected the ornate and sentimental style of Victorian poetry in favor of clear, sharp imagery and economy of language. Philosophically, Imagism can be understood as a response to the changing perceptions of truth, language, and beauty in modernity.
Core Philosophical Principles of Imagism:
1. Direct Treatment of the “Thing”
Imagists believed that a poem should present an object, emotion, or scene without unnecessary abstraction or embellishment. This reflects a philosophical commitment to phenomenological clarity—capturing experience as it is perceived, not mediated by convention or vague generalities.
2. Precision and Economy of Language
Imagists strove for linguistic minimalism, where every word earned its place. This economy reflects an anti-rhetorical stance, opposing the idea that more words equal more meaning. In this way, it shares ground with analytic philosophy and logical positivism, which also value precision and clarity in language.
3. Image as Epiphany
The image in Imagism is not merely descriptive—it is revelatory. A single image, rendered cleanly and truthfully, can convey complex emotions and insights. This approach resonates with Zen philosophy, where truth is often transmitted through the immediate and the concrete.
4. Rejection of Traditional Forms
Imagists often broke away from strict meter and rhyme, favoring free verse that matched the natural rhythm of thought and speech. This rebellion mirrors a broader modernist critique of tradition, questioning inherited structures in both art and life.
5. Sensory Experience as Truth
Imagism’s reliance on visual and sensory imagery places it close to empiricism, the philosophical view that knowledge arises from sensory experience. The image becomes a primary unit of meaning, conveying truth without requiring conceptual explanation.
Philosophical Influences and Parallels:
Ezra Pound (a key Imagist) was influenced by Chinese and Japanese poetry, especially haiku, which share a focus on simplicity and immediacy.
T.E. Hulme, another foundational figure, drew on Bergson’s philosophy of intuition, arguing that art should convey the essence of experience, not abstract ideas.
Symbolist poetry and phenomenology are also close cousins to Imagism in their emphasis on perception and inner experience.
Summary:
Imagism, philosophically, is a poetic discipline rooted in clarity, perception, and minimalism. It values truth that arises from direct experience and believes that a well-rendered image can carry the weight of philosophical insight. Imagism is not just a style of poetry—it is a way of seeing, one that honors the concrete over the abstract, the specific over the general, and the immediate over the idealized.
#philosophy#epistemology#knowledge#learning#education#chatgpt#Imagism#Modernism#Poetry#Literary Philosophy#Aesthetic Theory#Minimalism#Symbolism#Language and Meaning#Visual Imagery#Artistic Expression#Ezra Pound#H.D. (Hilda Doolittle)#Creative Philosophy#Form and Content#Literary Movements
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
we love the whimsy of the english language
tonight in particular we love how light can cast itself ("the traffic lights cast a red glow over her face"), but a shadow is always cast - as though the shadow is thrown by whatever object it's the shadow of
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
bro i LOVE indigenous fusion music i love it when indigenous people take traditional practices and language and apply them in new cool ways i love the slow decay and decolonisation of the modern music industry
#but also !!!!!!! indigenous people who make traditional music and release it !!!!! just as cool !!! equally as valid !!!!!!!!!!! indigenous#people who just release in english/the main language of their country are also very cool !!!!!! more love and focus on the art of#indigenous ppl !!!!!!!!#anyway i have been on a big Inuit pop/indie fusion kick lately#i've also been meaning to do a deep dive into the Blak (indigenous australian) music scene#anyway ! :3#music#words of wyrm
56K notes
·
View notes
Text
There's this sort of anthropomorphizing that inherently happens in language that really gets me sometimes. I'm still not over the terminology of "gravity assist," the technique where we launch satellites into the orbit of other planets so that we can build momentum via the astounding and literally astronomical strength of their gravitational forces, to "slingshot" them into the direction we need with a speed that we could never, ever, ever create ourselves. I mean, some of these slingshots easily get probes hurtling through space at tens of thousands of miles per hour. Wikipedia has a handy diagram of the Voyager 1 satellite doing such a thing.

"Gravity assist." "Slingshot." Of course, on a very basic and objective level, yes, we are taking advantage of forces generated by outside objects to specifically help in our goals. We're getting help from objects in the same way a river can power a mill. And of course we call it a "slingshot," because the motion is very similar (mentally at least; I can't be sure about the exact physics).
Plus, especially compared to the other sciences, the terminology for astrophysics is like, really straightforward. "Black hole?" Damn yeah it sure is. "Big bang?" It sure was. "Galactic cluster?" Buddy you're never gonna guess what this is. I think it's an effect of the fact that language is generally developed for life on earth and all the strange variances that happen on its surface, that applying it to something as alien and vast as space, general terms tend to suffice very well in a lot more places than, like... idk, botany.
But, like. "Gravity assist." I still can't get the notion out of my head that such language implies us receiving active help from our celestial neighbors. They come to our aid. We are working together. We are assisted. Jupiter and the other planets saw our little messengers coming from its pale blue molecular cousin, and we set up the physics just right, so that they could help us send them out to far stranger places than this, to tell us all about what they find out there.
We are assisted.
And there is no better way to illustrate my feelings on the matter than to just show you guys one of my favorite paintings, this 1973 NASA art by Rick Guidice to show the Pioneer probe doing this exact thing:

"... You, sent out beyond your recall, go to the limits of your longing. Embody me. ..."
Gravity assist.
#space#astronomy#astrophysics#language#paintings#the antidote to despair is awe#the quote is from the poem ''go to the limits of your longing'' by rainer maria rilke and translated by joanna macy#druid speaks#the thing that got me thinking about this was watching Animation VS Physics tbh#because the whole gravity assist section is so epic in scale and the music swells and its so. Romantic in the art movement sense#i mean the whole thing is epic like that. but seeing the term ‘’gravity assist’’ pop up did something to my brain specifically
17K notes
·
View notes
Text












"You just have to look closely."
#anyway how we're feeling with this last episode folks#my art#tadc#fanart#the amazing digital circus#art#i had been meaning to draw this comic for a while but never had the energy for it#i got a burst of inspiration from the episode#tadc fanart#tadc kinger#tadc queenie#kinger x queenie#tadc episode 3#tadc spoilers#kinger tadc#kinger#btw sorry for any gramatical mistakes english aint my first language my bad#comic#tadc comic#i don't know if kinger and his wife knew each other before the circus but going with the yes option just because
29K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Logic of Saying “Tadaima” and “Okaeri”: How Everyday Greetings Reflect Belonging in Japan
In Japanese homes, when someone returns, they say tadaima—”I’m home.” The response is okaeri—”Welcome back.” These greetings happen countless times a day across the country. They’re brief, familiar, almost automatic. But behind these simple words lies a powerful logic of belonging, routine, and emotional anchoring. This article explores how these habitual phrases help maintain social connection…
#Beginner Friendly#Belonging#Cultural Intelligence#Emotional Connection#Home Life#Japanese Logic#Language and Meaning#Okaeri#Social Rituals#Tadaima
0 notes
Text








(open pages for better image quality)
the moment I heard elphaba's delivery of "there's a girl i know..." in i'm not that girl i knew i had to draw this comic, i strongly recommend listening to it while you read for the full experience!
this comic is a companion to this piece (which was inspired by glinda's delivery of the same line in the i'm not that girl reprise).
pages 1-4 are from elphie's pov, pages 5-8 are from glinda's.
prints of individual pages: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
flower meanings in order of appearance:


#wicked#gelphie#(girl who has so many thoughts about i'm not that girl)#even jonathan bailey said i'm not that girl is a queer anthem. if nobody gets me i know he does#had to hold myself back from doing an animatic to the entire song (i don't have time)#i don't usually work in b&w so i was a little nervous but i'm really proud of how this comic turned out :')#it was a labor of love of many many weeks drawing this in between work#updated with prints for all 8 individual pages since a few people asked♡#might compile it as a little pdf zine when i have time for anyone who wants to keep it in higher resolution to re-read it#elphaba#glinda#gelphie fanart#wicked fanart#wlw#sapphic#lesbian#wlw art#sapphic art#lesbian art#comic#artists on tumblr#glinda x elphaba#elphaba thropp#glinda upland#galinda upland#i'm not that girl#flower meanings#language of flowers
21K notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding the Gospel: Can Something Be Translated Without Fully Grasping Its Meaning?
A timeless message, transcending language and culture—capturing the essence of the gospel’s profound wisdom through history, context, and interpretation. In the quest to understand sacred texts like the gospel, we are often confronted with one fundamental question: Can something truly be translated if its meaning is not fully understood? This question touches on the core of language,…

View On WordPress
#biblical history#biblical interpretation#cultural context in the bible#gospel symbolism#gospel understanding#interpreting parables#language and meaning#metaphor in scripture#religious philosophy#sacred texts#spiritual lessons#spiritual truths#translation challenges#understanding the gospel message
0 notes
Text
Terms to Not Live By
It’s Friday the 13! Yay! This is a quick one, I have lots to say, but I’m pacing myself. Frequent short posts instead of infrequent long ones. That’s my mantra. And I’m getting used to the scheduling process – hopefully, you haven’t seen this already because I made a stupid mistake; cause I don’t know how to unschedule a post. Duh! Question of the Day: How long is a split second, exactly? Am I…
#Cultural Critique#journaling#Language and Meaning#Problematic Phrases#relationships#social commentary#Word Play
0 notes
Text
Key Differences Between AI and Human Communication: Mechanisms, Intent, and Understanding
The differences between the way an AI communicates and the way a human does are significant, encompassing various aspects such as the underlying mechanisms, intent, adaptability, and the nature of understanding. Here’s a breakdown of key differences:
1. Mechanism of Communication:
AI: AI communication is based on algorithms, data processing, and pattern recognition. AI generates responses by analyzing input data, applying pre-programmed rules, and utilizing machine learning models that have been trained on large datasets. The AI does not understand language in a human sense; instead, it predicts likely responses based on patterns in the data.
Humans: Human communication is deeply rooted in biological, cognitive, and social processes. Humans use language as a tool for expressing thoughts, emotions, intentions, and experiences. Human communication is inherently tied to understanding and meaning-making, involving both conscious and unconscious processes.
2. Intent and Purpose:
AI: AI lacks true intent or purpose. It responds to input based on programming and training data, without any underlying motivation or goal beyond fulfilling the tasks it has been designed for. AI does not have desires, beliefs, or personal experiences that inform its communication.
Humans: Human communication is driven by intent and purpose. People communicate to share ideas, express emotions, seek information, build relationships, and achieve specific goals. Human communication is often nuanced, influenced by context, and shaped by personal experiences and social dynamics.
3. Understanding and Meaning:
AI: AI processes language at a syntactic and statistical level. It can identify patterns, generate coherent responses, and even mimic certain aspects of human communication, but it does not truly understand the meaning of the words it uses. AI lacks consciousness, self-awareness, and the ability to grasp abstract concepts in the way humans do.
Humans: Humans understand language semantically and contextually. They interpret meaning based on personal experience, cultural background, emotional state, and the context of the conversation. Human communication involves deep understanding, empathy, and the ability to infer meaning beyond the literal words spoken.
4. Adaptability and Learning:
AI: AI can adapt its communication style based on data and feedback, but this adaptability is limited to the parameters set by its algorithms and the data it has been trained on. AI can learn from new data, but it does so without understanding the implications of that data in a broader context.
Humans: Humans are highly adaptable communicators. They can adjust their language, tone, and approach based on the situation, the audience, and the emotional dynamics of the interaction. Humans learn not just from direct feedback but also from social and cultural experiences, emotional cues, and abstract reasoning.
5. Creativity and Innovation:
AI: AI can generate creative outputs, such as writing poems or composing music, by recombining existing patterns in novel ways. However, this creativity is constrained by the data it has been trained on and lacks the originality that comes from human creativity, which is often driven by personal experience, intuition, and a desire for expression.
Humans: Human creativity in communication is driven by a complex interplay of emotions, experiences, imagination, and intent. Humans can innovate in language, create new metaphors, and use language to express unique personal and cultural identities. Human creativity is often spontaneous and deeply tied to individual and collective experiences.
6. Emotional Engagement:
AI: AI can simulate emotional engagement by recognizing and responding to emotional cues in language, but it does not experience emotions. Its responses are based on patterns learned from data, without any true emotional understanding or empathy.
Humans: Human communication is inherently emotional. People express and respond to emotions in nuanced ways, using tone, body language, and context to convey feelings. Empathy, sympathy, and emotional intelligence play a crucial role in human communication, allowing for deep connections and understanding between individuals.
7. Contextual Sensitivity:
AI: AI's sensitivity to context is limited by its training data and algorithms. While it can take some context into account (like the previous messages in a conversation), it may struggle with complex or ambiguous situations, especially if they require a deep understanding of cultural, social, or personal nuances.
Humans: Humans are highly sensitive to context, using it to interpret meaning and guide their communication. They can understand subtext, read between the lines, and adjust their communication based on subtle cues like tone, body language, and shared history with the other person.
8. Ethical and Moral Considerations:
AI: AI lacks an inherent sense of ethics or morality. Its communication is governed by the data it has been trained on and the parameters set by its developers. Any ethical considerations in AI communication come from human-designed rules or guidelines, not from an intrinsic understanding of right or wrong.
Humans: Human communication is deeply influenced by ethical and moral considerations. People often weigh the potential impact of their words on others, considering issues like honesty, fairness, and respect. These considerations are shaped by individual values, cultural norms, and societal expectations.
The key differences between AI and human communication lie in the underlying mechanisms, the presence or absence of intent and understanding, and the role of emotions, creativity, and ethics. While AI can simulate certain aspects of human communication, it fundamentally operates in a different way, lacking the consciousness, experience, and meaning-making processes that characterize human interaction.
#philosophy#epistemology#knowledge#learning#education#chatgpt#metaphysics#ontology#AI Communication#Human Communication#Language Understanding#Natural Language Processing#Machine Learning#Cognitive Science#Artificial Intelligence#Emotional Intelligence#Ethics in AI#Language and Meaning#Human-AI Interaction#Contextual Sensitivity#Creativity in Communication#Intent in Communication#Pattern Recognition
5 notes
·
View notes
Text



I had this dumb idea going ‘round in my head so I let it out as a quick comic.
NEXT
#Hazbin hotel#radioapple#hazbin alastor#hazbin lucifer#hazbin hotel comic#hazbin hotel fanart#lucifer morningstar#hazbin hotel alastor#flower meanings from my copy of The language of Flowers by Mandy Kirkby#except the lily. I already knew that one#felt like something Alastor would do while ‘playing nice’#I’m not a flower expert so the comparative sizing might be off#so if they are let’s just say they can grow like that in hell…#click for better quality
15K notes
·
View notes
Text
Theres moreeee, this is so so good.. it makes me emotional realizing that these kids are on the path to being fluent cherokee speakers and will be able to keep the language going.
This family is a part of the little cherokee seeds program, creating new first language Cherokee speakers by paying mothers to just bring their babies and craft and cook and speak cherokee with cherokee elders all day. There are only 1500 first language Cherokee speakers, most of them over 65. They also take donations if you want to help keep them going and doing the extremely important work they do!!

#this was posted half an hour ago. i go on tiktok solely to check out her stuff now#cherokee#ndn#language#linguistics#native american#the first one is blowing up and this one might not but im still putting the info actually in the post this time#the baby going 'ni! ni!' 😭😭😭#[ni means 'look!']
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
The word tuxedo for the men's outfit only cropped up in the late 1880s, were tuxedo cats just called irish marked before then?
#did you know the word tuxedo is likely derived from a corruption of an indigenous word#iirc the exact language and meaning are contested but it became a NY park called tuxedo#then some bitch wore a suit nearby and the rest is history
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
recent realization has been just how much of rgu is based on soviet art. we all know by now how ohtori's warping architecture is inspired by constructivism


but apart from that, the thing that makes rgu's cinematography special—it's usage of esoteric images to create visual new meanings + it's repeated shots of lined up objects—is so clearly Eisenstein






rgu directly utilizes Eisenstein's theory of montage—and it's my favorite usage of it too. it feels like the technique was created ex professo for rgu's cinematography. i could think of no better use for it. that girl sure is revolutionary.
#rgu#revolutionary girl utena#it's hard to understand the montage thing through screenshots cause#you need to be familiarized w eisensteins work ig#and his usage of montage#but I promise once you watch battleship potemkin or october it's just. so clear#that this is where rgu gets it's visual language#and it gives the Revolutionary a new meaning
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Logic of Saying “Itadakimasu”: Gratitude Before—and After—a Meal in Japanese Culture
Before eating a meal in Japan, it’s common to say “Itadakimasu.” After eating, people say “Gochisousama deshita.” These short phrases bookend daily meals across the country. To outsiders, they might seem like simple equivalents of “bon appétit” or “thanks for the food.” But both carry deeper meaning—expressing humility, appreciation, and awareness of unseen efforts. This article explores how…
#Beginner Friendly#Cultural Intelligence#Daily Habits#Gochisousama#Gratitude#Itadakimasu#Japanese Logic#Language and Meaning#Mealtime#Respect#Social Rituals
1 note
·
View note
Text
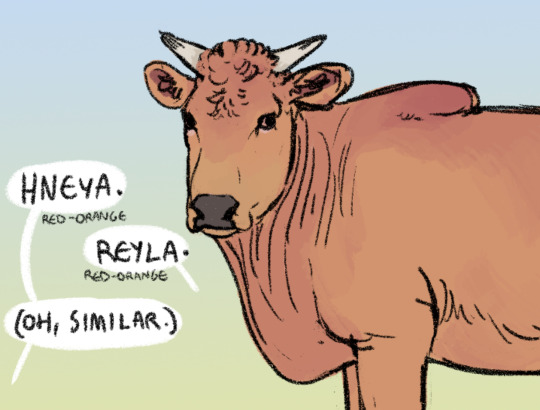



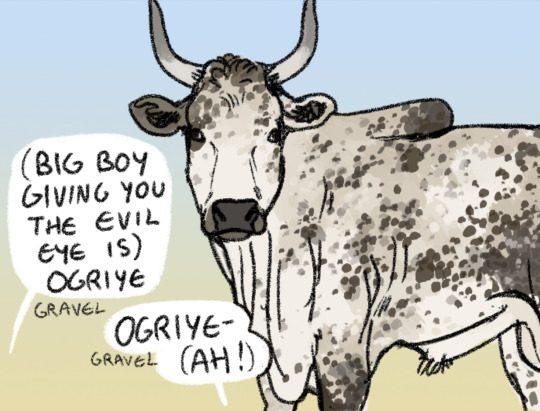

Comparing livestock color-words.
Both the Chenahyeigi and Wardi languages are derived from peoples who have been pastoralists for millennia, and both have an absolute ton of words for livestock coloration.
Both languages have had at least some mutual influence for about a thousand years (to varying extents by dialect, depending on geography/trade connection) so you'll see similar or identical words crop up here and there.
THE WORDS:
Hneya - [hne:ʝɑ] or [hne:jɑ] (whether the ʝ sound is retained in speech and to what extent varies by dialect)
Straightforwardly refers to bright reddish-orange color, but is mostly used for animals rather than other orangeish things. The word Was probably influenced by an older form of the Wardi 'reyla', and absorbed with the introduction of orange colored cattle. It may have been merged with the Chenahyeigi '(h)ne', which is the root of several red color-related terms.
Reyla - [rejlɑ]
This is a Wardi word for most reddish-orange hues in general. When applied to livestock, it refers to solid orange coats without spotting/masks/notable countershading.
Fels akhri - [fels] [ɑ:khɾi]
Translates readily as 'storm cloud' (the 'storm' here specifies thunderstorms). When applied to livestock, it describes fur that is rich dark blue-gray with white guard hairs.
Aganne - [ɑgɑ:ne]
This doesn't actually translate to 'night sea' in a straightforward manner, but as a color word it's poetically associated with dark seas, at night or in storms. When used for livestock, it describes this coloration exclusively.
Woud et lleng - [woʊd] [ɛt] [ɬeŋk]
Woud is the word for rich moist soil specifically, lleng refers to laterite and its association with iron deposits. This phrase is used to describe livestock with dark brown heads and and orange-brown bodies.
Tsipanibe - [t͡sipɑnibe]
This would be more literally translated as 'ochred'. Many Wardi words with the -ibe stem from verbs or nouns modified to indicate that the subject matter has 'received' an action or concept. (Examples of such words are long-established linguistically, you can't just add '-ibe' to any noun or verb). This one takes the root 'tsipan' (ochre) and applies it to the subject matter (cattle coloration).
Livestock with a dark brown or black head and orange-brown body are given this description, the idea being that their bodies look like they've been painted in ochre. This word is extremely rare outside of this context (you would usually just say the full 'ochre-painted' to convey this idea for other things)
Drengh yipeg - [dɾeŋg(h) yɪpɛ:g]
This is pretty straightforwardly 'little moon'. Yipeg comes from the same root as the Wardi 'hippe' for 'small', while drengh refers to the appearance of the moons in the sky (rather than the gods they embody). It's used to describe small round white blaze marks.
Ipalen hamita - [ipɑlɛn (h)ɑmitə]
Straightforwardly 'star marked', used for small round white blaze marks. Wardi actually does have a 'moon marked' (ipalen amit) to describe round white blazes that entirely cover the animal's forehead.
Brinyavir - [bɾi:nʝɑvir] (ʝ is retained for this word in most dialects)
This one is not directly translatable, 'celestial' or 'heavenly' just function closely enough. The word conceptually relates to stars but most specifically describes a layer of sky in which the afterlife rests (brinyavir is part of the phrase I translate as 'celestial fields'). The cattle there are said to have these markings. The stars in the night sky are sometimes playfully described as the spots of these cattle (though not literally, in Chenahyeigi cosmology stars are spirit-inhabited bonfires lit along pathways through the heavens).
As a color word for livestock, brinyavir refers to this rare (I Think nonexistent irl) white-spotted black coloration, due to both resembling the stars and the cattle that are moved among them.
Asi inwetadi - [ɑsi in:wetɑ:di]
This directly means 'like night sky', and is applied to this coat pattern with a similar underlying logic- it looks like a starry night sky. You will often see asi (like/akin to) retained in place or animal names like this, and it is sometimes part of names for people (the name Asinya is derived from a contracted 'like the sun').
Ogriye - Chenahyeigi: [oʊ:gɾije] Wardi: [oʊgɾi:je]
This word is (or was) a way to say 'gravel' or 'gravelly' in both Chenahyeigi and Wardi, and is pronounced very similarly in both (with the only significant difference being emphasis)
In Chenahyeigi it is a loanword from the Wardi language family, most likely received in the exchange of cattle of this coloration. It is retained in general speech as a word for gravel, more specifically the adjective 'gravelly'.
The word is mostly obsolete in contemporary Wardi, speakers do not know it used to mean 'gravel' (though it sounds close enough to assume a connection, the word is 'ogri') and exclusively use it to describe this livestock coloration (one of the more common among Wardi native cattle).
---
Also here's some cow lore.
There's some fairly tremendous diversity in Wardi cattle herds, given they have genetic influence from at least two separate aurochs domestication events (also distant and negligibly minor influence from one instance of bison domestication) and from multiple relatively isolated domestic cattle populations. Present day herds within Wardi provincial territory near-ubiquitously have at least some ancestry from the kulustaig and the Burri tepang cattle.
The ancestors of the Wardi native cow have been in the region for at Least 5,000 years. Burri cattle Possibly could have had tiny, isolated introductions between 2500-3000 years ago (this is extremely unlikely, but maize Was probably introduced by seafaring proto-Burri peoples at this time) or at more recent points since, and the tepang was certainly introduced during Imperial Burri occupation. High quality cattle are also occasionally received in diplomacy with the present-day Different Entity that is the Burri Republic. The kulustaig cattle arrived with proto-Finnic migrants starting 1500 years ago, and is the biggest external genetic influence on Wardi herds. Small populations of Yuroma native cattle arrived with migrants 540 years ago, though these have been wholly absorbed into Wardi herds, with their biggest trace being genes for naturally polled horns. Some Finn cattle were extracted in the recent two decades of Wardi occupation, though not enough to have a noteworthy genetic impact on any herds.
Most of the cattle in this post show predominantly Wardi native cattle + kulustaig ancestry (this takes place in the Ephenni riverlands, where the ancestry of herds tends to be around 2:1). The one with the blaze has a delicate sloping muzzle that suggests Burri tepang ancestry, and also likely has a wild aurochs grandparent (the white ring around the nose is a telltale sign, as it usually vanishes within a few generations of introgression).
Diversity in color and coat pattern is culturally favored for Wardi cattle herds, and selective breeding for aesthetics is usually limited to the purpose of preserving unique coats. The average herd tends to be very colorful, though the one shown here is a bit of an outlier, the universe having mysteriously put in place perfect conditions to compare the words for a variety of coat patterns.
#My marginal comprehension of the IPA has advanced somewhat. For those who don't know : indicates the vowel/consonant beforehand#is long and () means a sound is marginal/optional/not articulated#The 'h's you see at the end of a lot of Chenahyeigi words are usually soft unvoiced exhalations and very subtle#It's part of the accent but not doing it doesn't change the meaning of the word in most cases#The Wardi language has a tendency of dropping H sounds at the beginnings of words over time/in certain dialects#(especially when followed by the [i] vowel. A lot of people pronounce hippegalga as just ippegalga) and in a lot of words#pronunciation of leading H's is essentially optional#One aspect of Wardi formal register is always enunciating these droppable H's
3K notes
·
View notes