#Tooling Blocks
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
10 Non-Lethal Injuries to Add Pain to Your Writing
New Part: 10 Lethal Injury Ideas
If you need a simple way to make your characters feel pain, here are some ideas:
1. Sprained Ankle
A common injury that can severely limit mobility. This is useful because your characters will have to experience a mild struggle and adapt their plans to their new lack of mobiliy. Perfect to add tension to a chase scene.
2. Rib Contusion
A painful bruise on the ribs can make breathing difficult, helping you sneak in those ragged wheezes during a fight scene. Could also be used for something sport-related! It's impactful enough to leave a lingering pain but not enough to hinder their overall movement.
3. Concussions
This common brain injury can lead to confusion, dizziness, and mood swings, affecting a character’s judgment heavily. It can also cause mild amnesia.
I enjoy using concussions when you need another character to subtly take over the fight/scene, it's an easy way to switch POVs. You could also use it if you need a 'cute' recovery moment with A and B.
4. Fractured Finger
A broken finger can complicate tasks that require fine motor skills. This would be perfect for characters like artists, writers, etc. Or, a fighter who brushes it off as nothing till they try to throw a punch and are hit with pain.
5. Road Rash
Road rash is an abrasion caused by friction. Aka scraping skin. The raw, painful sting resulting from a fall can be a quick but effective way to add pain to your writing. Tip: it's great if you need a mild injury for a child.
6. Shoulder Dislocation
This injury can be excruciating and often leads to an inability to use one arm, forcing characters to confront their limitations while adding urgency to their situation. Good for torture scenes.
7. Deep Laceration
A deep laceration is a cut that requires stitches. As someone who got stitches as a kid, they really aren't that bad! A 2-3 inch wound (in length) provides just enough pain and blood to add that dramatic flair to your writing while not severely deterring your character.
This is also a great wound to look back on since it often scars. Note: the deeper and wider the cut the worse your character's condition. Don't give them a 5 inch deep gash and call that mild.
8. Burns
Whether from fire, chemicals, or hot surfaces, burns can cause intense suffering and lingering trauma. Like the previous injury, the lasting physical and emotional trauma of a burn is a great wound for characters to look back on.
If you want to explore writing burns, read here.
9. Pulled Muscle
This can create ongoing pain and restrict movement, offering a window to force your character to lean on another. Note: I personally use muscle related injuries when I want to focus more on the pain and sprains to focus on a lack of mobility.
10. Tendonitis
Inflammation of a tendon can cause chronic pain and limit a character's ability to perform tasks they usually take for granted. When exploring tendonitis make sure you research well as this can easily turn into a more severe injury.
This is a quick, brief list of ideas to provide writers inspiration. Since it is a shorter blog, I have not covered the injuries in detail. This is inspiration, not a thorough guide. Happy writing! :)
Looking For More Writing Tips And Tricks?
Check out the rest of Quillology with Haya; a blog dedicated to writing and publishing tips for authors!
Instagram Tiktok
#hayatheauthor#haya's book blog#haya blogs#writing community#quillology with haya#writing tools#writer things#writing advice#writer community#writing techniques#writing prompt#writing stuff#creative writing#ya writing advice#writing tips and tricks#writer tools#writers of tumblr#writer blog#writers block#quillology with haya sameer#writers on tumblr#writerscommunity#writer stuff#author help#author advice#author#writing inspiration#writeblr#novel writing#on writing
63K notes
·
View notes
Text
Other Words for "Look" + With meanings | List for writers
Many people create lists of synonyms for the word 'said,' but what about the word 'look'? Here are some synonyms that I enjoy using in my writing, along with their meanings for your reference. While all these words relate to 'look,' they each carry distinct meanings and nuances, so I thought it would be helpful to provide meanings for each one.
Gaze - To look steadily and intently, especially in admiration or thought.
Glance - A brief or hurried look.
Peek - A quick and typically secretive look.
Peer - To look with difficulty or concentration.
Scan - To look over quickly but thoroughly.
Observe - To watch carefully and attentively.
Inspect - To look at closely in order to assess condition or quality.
Stare - To look fixedly or vacantly at someone or something.
Glimpse - To see or perceive briefly or partially.
Eye - To look or stare at intently.
Peruse - To read or examine something with great care.
Scrutinize - To examine or inspect closely and thoroughly.
Behold - To see or observe a thing or person, especially a remarkable one.
Witness - To see something happen, typically a significant event.
Spot - To see, notice, or recognize someone or something.
Contemplate - To look thoughtfully for a long time at.
Sight - To suddenly or unexpectedly see something or someone.
Ogle - To stare at in a lecherous manner.
Leer - To look or gaze in an unpleasant, malicious way.
Gawk - To stare openly and stupidly.
Gape - To stare with one's mouth open wide, in amazement.
Squint - To look with eyes partially closed.
Regard - To consider or think of in a specified way.
Admire - To regard with pleasure, wonder, and approval.
Skim - To look through quickly to gain superficial knowledge.
Reconnoiter - To make a military observation of a region.
Flick - To look or move the eyes quickly.
Rake - To look through something rapidly and unsystematically.
Glare - To look angrily or fiercely.
Peep - To look quickly and secretly through an opening.
Focus - To concentrate one's visual effort on.
Discover - To find or realize something not clear before.
Spot-check - To examine something briefly or at random.
Devour - To look over with eager enthusiasm.
Examine - To inspect in detail to determine condition.
Feast one's eyes - To look at something with great enjoyment.
Catch sight of - To suddenly or unexpectedly see.
Clap eyes on - To suddenly see someone or something.
Set eyes on - To look at, especially for the first time.
Take a dekko - Colloquial for taking a look.
Leer at - To look or gaze in a suggestive manner.
Rubberneck - To stare at something in a foolish way.
Make out - To manage to see or read with difficulty.
Lay eyes on - To see or look at.
Pore over - To look at or read something intently.
Ogle at - To look at in a lecherous or predatory way.
Pry - To look or inquire into something in a determined manner.
Dart - To look quickly or furtively.
Drink in - To look at with great enjoyment or fascination.
Bask in - To look at or enjoy something for a period of time.
#on writing#creative writing#writing#writing tips#writers block#how to write#thewriteadviceforwriters#writeblr#writers and poets#writers on tumblr#novel writing#fiction writing#romance writing#writing advice#writing blog#writing characters#writing community#writing help#writing ideas#writing inspiration#writing guide#writing prompts#writing a book#writing resources#writing reference#writing tips and tricks#writers#writing tools#writing life#writing software
20K notes
·
View notes
Text
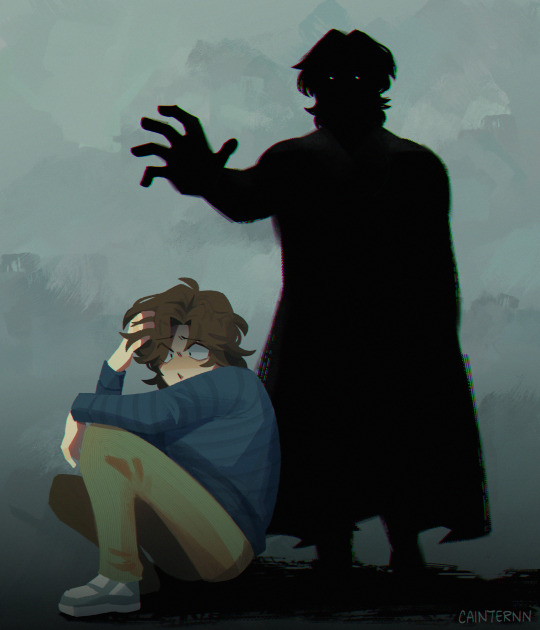

null and void
#thunderbolts#bob reynolds#sentry#void#marvel#the avengers#mcu#my art#finally drew something for sentry bc the vfx were so cool in the movie#like having the voided people turn into those nuclear shadows?? cinema#just blocked this in with the lasso tool and didnt do lineart#i think it turned out ok
640 notes
·
View notes
Text

good grief.
#roblox#block tales#block tales fanart#block tales griefer#brad thaniyel#block tales mayor thaniyel#mayor thaniyel#venomshank#myart#eye strain#eyestrain#delete tool delete tool collide.wav delete tool
483 notes
·
View notes
Text



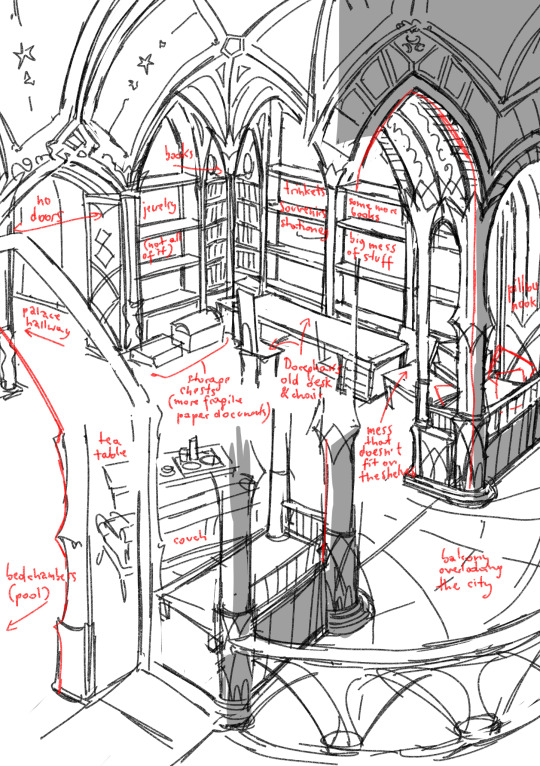
I wanted to draw teen Sidon and Bazz hanging out in Sidon's room, so it was a good moment to finally plan out said room study (that is just a part of his quarters).
It's actually Dorephan’s old quarters, repurposed after he outgrew them. He's responsible for like, half of the clutter, the rest is all Sidon.
#botw#sidon#bazz#zora#loz#zora architecture#Sidon having that much -stuff- is doubly impressive seeing how average zora has like#maybe three personal items that are not weapons#jewelry or tools#bazz looks at all this and all he can think of is three centuries of nonstop fight with mold#the desk is swithed for a bigger one every 20 years or so#luckily they have a bunch of progressively larger desks and chairs from Dorephan’s growing times#there's no doors or windows since zoras arent too worried about privacy#if sidon really wants there are folding screens and seaweed tarps that can be set up for some extra coverage#they're also used during strong storms to block out the rain from damaging the study#also!#bazz compares the study to his (and Seggin’s) house and i wouldn’t have included it if i didnt have it at least roughly sketched out#its much more normal for a zora living space#just a bit bigger#but before i post about it i have to make up my mind about the general housing policies in the domain#caring about fictional politics makes my life so hard
188 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi! Could I ask for some body language for general love? Like fluffy kind of love? Shy but like.. I don’t know, flustered? A little hard to describe what I mean haha
Hi Anon! I had a lot of fun with this one
Writing Fluffy/Shy Love

Body language:
Prolonged or fleeting eye contact, dilated pupils, lingering gazes at the person your character(s) interested in. As if they’re fixated on something about this person, or looking for something new about them to fixate on. (If flustered, then darting their eyes away or quickly averting their gaze if caught staring)
Fidgeting, sweaty palms, leaning in
Closeness: your characters will find any excuse to touch. Holding hands, sitting close to one another, touching knees when seated, draping arms around shoulders or legs across laps, gentle touches, playful nudges, etc. This type of physical contact is gonna be a slow burn with flustered/shy characters. For example, if they're holding hands, don't just say they are, describe them inching closer, brushing one of their fingers against the other’s palm, making eye contact. Find nonverbal cues/body language that initiates closeness.
Soft smiles, relaxed brows, attentive looks (watching the other’s hands, eyes, lips, etc)
Frequent laughter, open posture
Subconsciously mirroring the other’s body language/picking up some of each other’s mannerisms or habits without realizing it
Inner thoughts or Dialogue:
Overthinking/over-analyzing interactions between them and the one they love
Deeper concern and empathy for the person they love
More genuine interest in what the other says/does, deeper understanding/knowledge of their habits and behavior. Maybe a character loads more attention on their partner’s words/wants above their own.
Dialogue/dynamics in a couple depends on their personalities. Can be more playful/teasing with banter, passionate, casual, quiet, etc. All relationships are different from more passionate ones to companionate ones, and more.
Are both character’s flustered? Explore what it looks like when they're both hesitant or shy around each other.
If it's one flustered character, what happens when the other notices how shy they are?
General tips:
Linger more on the simplicity/normalcy of the moment. Fluff isn't dramatic twists or arguments. Cuddling while watching a movie, character A playing with character B’s hair while they do the dishes, one doting on the other when they're sick.
The tone here is going to be more cute, domestic, and comfortable.
Remember that in fluffy/shy love it's a great start to have a friendship between the characters as a foundation rather than a romance standing on its own. Why do your characters love each other? What little things do they love about each other?
should i do dialogue prompts with this or try a post diving deeper on relationship dynamics?
#writersbloxx#writers on tumblr#creative writing#writers community#writing#writers and poets#my writing#writeblr#writers block#writers blog#writers#writing tool#writing tips#aspiring author
198 notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Theory: Dialogue

One question, I often get asked on this blog concerns dialogue and how to write it. Dialogue is the characters speaking to one another or even to themselves and while it sounds easy, it can be difficult to chose what your character might say or how they might say it or even how it might present on the page/word doc/napkin you're writing it on.
Content: The What and Why

What is your character actually saying? Your character is in a situation (which hopefully you put them in or at least know what is going on, if you do not, it is OK). But in most situations, most characters interact in some way, whether it is verbal or not. What your character says has to link to the situation in some way. Picture yourself on a bus sitting next to a friend and you have just seen a dog out of the window. What would be the response or the natural line of conversation here? Probably 'Oh, that dog is cute.' or 'This journey is taking forever.' etc. It unlikely would be a long monologue about a character's deepest darkest secrets or an admission of murder. It is unlikely, but of course not impossible. But generally, one usually tries to keep the conversation to the present and the now. Allow your character to get their point, or even part of it, across to who they talking about clearly. Remember not only does their companion need to know what is being said, but as do your readers.
Why is this person saying this? There is a deeper level to what anybody says and we all know this. A person will generally keep to neutral phrases or topics in order to keep the peace, distance themselves from whoever they are having the conversation with or a person will be curt and short with somebody they are not getting along with or a person will be polite and formal to somebody who demands the respect. There is a reason behind word choice, a reason behind tone and even topic. You won't have to delve into the intricacies of the 'hello' or 'hey' types of dialogue but say if a character was in a situation they must or do chose their words carefully, then you have to consider the why of it as you write the conversation.
Characteristics of Speech

Characters don't talk like they are reading from an instruction manual. Personality, experience and other factors effect how your character might speak. Next time you are in a group setting, focus on how the people around you speak, whether its the sentence structure, the tone, the volume or the flow of their words. No character speaks the same as another, and nor should they. I go further into this in this post here. Now you have established your character's voice as it pertains to personality, now consider the actual voice of your character. How would you describe your character's voice? Even if you don't include a description of it in your narrative, you should have some idea of how your character speaks. Some people have gravelly voices, high pitched voices, clear, garbled, etc. You can of course, fan cast a voice if you wish. The way your character speak can give away things about them as people. Contractions, slang and colloquial phrases are often used to denote those of working class or poorer factions whether the lack of them, including a larger vocabulary, are often attributed to a wealthier, more educated class. You can say a lot about somebody by the way they speak and is an important tool in the entire show don't tell deal. Speaking of...
Showing, Not Telling when Your Character is Yapping

People don't often come out with what they really want to say. Thankfully or else I would be unemployed and in jail.
Concealment: Like I said before, characters will sometimes chose words or specific tones when speaking or breaking off at certain points to conceal what they are thinking. The dialogue might look something similar to using different approaches either with a character trailing off before the offending phrase (...) or catching themselves (-) or hesitating/considering their words/pausing before speaking. It doesn't often mean a character is being evasive, they may be avoiding harming somebody's feelings.
Class/Social rank: Like I said above, the way somebody speaks can be an indication of their status in society. This is not a bad thing, we have different ways of speaking because we come from different walks of life, we have totally different experiences. Writing the character's voice with this in mind can indicate your character's background.
Nationality/Culture: As in the real world, we don't all speak the same language, it makes us who we are and marks out our culture and place in the world. Phrases, sayings and specific words or even pauses to consider the wording or sentence structure can denote a character from having a different mother tongue or culture than those around them. Your character may sometimes have to tailor what they say to somebody of a different culture or nationality even if they speak the same language. For example, if I'm writing a post here or in my WIP, I often have to steer clear of slang, sentence structure. grammar structure and phrases that non-Irish people are not familiar with.
Emotion: Emotion and dialogue walk hand in hand, a character will not speak without some emotion behind it and most emotions make us want to say something. Anger will make our words sharper, harsher, more abrupt. Happiness will make words flow faster, more positive and sometimes even jumbled. Grief will make one sound disconnected, numb and unable to think straight. The way your characters speak can tell your reader and the rest of the cast able to read their emotional state even if they cannot see their face or your helpful dialogue tags.
Sensibilities and Personality: Word choice and avoidance of certain words can tell somebody a lot about the person speaking. Somebody who avoids cursing or using 'vulgar' language might be considered proper, mannerly and formal. Somebody who does might be judged. Somebody who avoids topics that are considered taboo is somebody who aligns to social norms and expectations while somebody who tends to venture into incendiary topics is likely not and more free willed. These are not bad things but it can tell you a lot about the person speaking or in the way that person responds to somebody's words.
On Dialogue Tags and the Controversy of 'Said'

(nobody would ever fucking say that)
I don't buy into this drama over dialogue tags. Some writers will denounce them, some swear by them and they have been arguing over this as often as we do about the Oxford Comma. The real truth is that it is up to you. It is not a cardinal sin to use them and there is nothing - NOTHING - wrong with using the word said. There are of course some dialogue tags I personally hate and some I love but there is nothing wrong with the word 'said' or 'says'. Here are a few commonly used tags.
A
Accused: Used to pin the blame on somebody.
Added: Usually used when the character is adding to something they or somebody else has said.
Agonized: When a character is distressed over something.
Agreed: Used when a character allows something or agrees with something that is said.
Acknowledged: Used when giving voice to a fact.
Announced: Used for a statement.
Asked: Posing a question
Answered: To address a question.
Addressed: When a character draws attention to something or draws the attention of somebody.
Affirmed: Used when a character is stating an opinion or fact.
Apologized: When a character is saying sorry for something.
Approved: When a character is giving their support to a fact or something somebody has said.
Articulated: When a character expresses a thought/idea.
Asserted: When a character affirms an opinion firmly.
Advertised: Used when a character is drawing attention to something.
B
Babbled: Used when a character is talking excitedly, often nonsensically.
Backtracked: Used when a character is going back on something they have said.
Badgered: Used when a character is nagging another.
Bawled: Used when a character is crying out, usually wildly and very loudly.
Bellowed: When a character is shouting.
Began: When a character begins a sentence or thought.
Bemoaned: When a character complains of something.
Bit: Used when a character is being sharp with something that is irritating them or angering them.
Blamed: Used when a character is assigning blame for something.
Bleated: When a character is complaining or moaning, usually used in a derogatory way.
Blurted: When a character says something without pause or thought.
Boasted: When a character displays self-pride.
Boomed: When a character speaks loudly.
Broadcasted: Used when a character is announcing something, usually loudly.
C
Called: When a character cries out for somebody.
Chanted: When a character speaks in a monotone or often repeating words over and over.
Chattered: When a character speaks rapidly, usually out of nerves or excitement.
Chastised: When a character rebukes another character.
Cheered: Used when a character is excited or pleased about something.
Chimed: When a character adds something to something already said.
Choked: Used when a character is having a difficult time getting the words out.
Chuckled: When a character laughs slightly.
Chortled: When a character laughs slightly and breathlessly.
Coughed: When a character’s breath catches.
Croaked: Used when a character’s voice is strained or dry.
Crowed: When a character boasts loudly about something.
Cried: When a character exclaims or weeps.
Cursed: When a character use swear words or denounces another character.
Cautioned: Used when a character warns somebody.
Complimented: Used when a character is lavishing praise on somebody.
Condemned: When a character denounces something.
Considered: Used when a character is thinking aloud.
Conferred: When a character discusses something with another, usually quiet.
Commented: Used when a character is expressing a thought or opinion.
Complained: Used when a character is annoyed over something.
Criticized: When a character comments negatively on something.
D
Declared: When a character announces something.
Denoted: When a character is indicating something.
Dictated: When a character is insisting on something, usually forcefully.
Drawled: When a character is talking in a low, slow voice.
Droned: When a character is talking on and on, usually derogatory.
E
Elaborated: When a character goes into detail explaining something.
Emitted: Used when a character makes a sound.
Enunciated: Used when a character makes their words clear, often to add emphasis.
Expressed: When a character conveys their thoughts and opinions on something.
F
Fumed: Usually when a character is angry over something.
Fretted: When a character is anxious, usually a reputation of intrusive thoughts.
G
Gasped: When a character inhales suddenly, usually in shock or pain.
Giggled: Used when a character laughing.
Gloated: When a character is boasting over besting another character.
Grinned: When a character is smiling widely when speaking.
Groaned: When a character makes a low sound, usually in pain or discomfort.
Growled: Used when conveying anger.
Grumbled: Used when a character is complaining but in a quiet, low way.
Gulped: When a character swallows.
Gushed: Used when a character is talking excitedly about something they care about.
H
Hissed: Used when a character is angry or irritated.
Howled: Used when a character is making a loud, drawn-out sound noise out of pain and grief.
I
Insisted: When a character speaks or lends their support persistently.
Interjected: When a character adds something into somebody else’s discussion.
Insulted: To speak negatively about another character.
J
Jabbered: Used when a character isn’t making sense but talking rapidly.
Joked: Used when a character is making a jest or fun of something.
L
Lamented: When a character expresses a deep thought or grief over something.
Laughed: Used when a character is laughing.
M
Mewled: When a character’s voice is talking in a feeble voice.
Mentioned: When a character interjects something but doesn’t explain it.
Mocked: Used when a character is teasing, either in humour or spite.
Moaned: Used when a character is complaining, in pain or discomfort.
Mumbled: When a character is speaking in a low, almost unintelligible voice.
Muttered: When a character speaks quietly, usually in an effort to not be overheard.
Murmured: When a character talks quietly, usually not to be overheard or to not gain attention.
N
Noted: When a character brings attention to something.
Nattered: When a character goes on about something almost absent-mindedly, usually when nervous or preoccupied.
O
Observed: When a character is offering their view on something.
Ordered: When a character is giving instruction to another, usually forcefully.
P
Panted: Used when a character is out of breath or panicked.
Praised: When a character is showing positive attention to something or somebody.
Prattled: When a character is talking about something without a line of thought or sometimes reason or attention.
Persisted: When a character keeps at a thought or opinion.
Q
Quavered: When a character’s voice warbles usually out of fear or anxiety or sadness.
Quipped: When a character makes a witty remark.
R
Raged: Used when a character is angry.
Ranted: When a character goes on about something, usually in a monologue expressing their emotion about the subject.
Rambled: Used when a character is talking about something that doesn’t matter or warrant attention.
Relayed: Used when a character is telling another character about something that happened previously.
Remarked: Used when a character speaks about something.
Replied: When a character answers back.
Reprimanded: Used when a character is rebuking another for an action or word.
Responded: When a character replies to something said.
Recited: When a character repeats something from memory.
Repeated: When a character says something again, usually right after they have said it.
Retorted: When a character replies tartly or sharply.
S
Sang: Used when a character is happy or light about something.
Scolded: When somebody is reprimanding a character.
Screamed: Used when a character is scared or angry.
Squalled: When a character is crying out loudly.
Smiled: When somebody speaks when they are smiling, usually positively but can be negative.
Smirked: Used when a character is being smug.
Sneered: When a character is speaking in a derogatory way.
Snarled: Used when a character is being aggressive or angry.
Snivelled: When a character is speaking through a runny nose or tears. It is usually used to denote a character as weak or vulnerable.
Sniffled: When a character is speaking with a runny nose and tears.
Shouted: When a character is saying something loudly or with extreme emotional.
Shrieked: When a character makes a sharp sound, usually from extreme emotion.
Stammered: When a character’s voice becomes halted with pauses, usually an indicator of a speech impediment or nerves or anxiety or fear.
Stated: When a character makes a statement.
Stuttered: When a character speaks with difficulty, often repeating the beginning of words, usually out of fear, anxiety or nerves. But it can also be attributed to a speech impediment.
Swore: When a character curses or uses vulgar words to express their anger.
Scoffed: Used when a character is being derisive about something.
Sighed: When a character exhales out of annoyance, anger, tiredness or boredom.
Screeched: When a character’s voice becomes high-pitched and erratic.
Spat: When a character speaks so forcefully that they almost spit saliva in their effort to get their often emotion driven words out.
Sputtered: Used when a character is unable to get the words out, usually out of disbelief.
Sobbed: When a character is crying so hard that their voice is garbled by their tears and gasps for breath.
Suggested: When a character proposes an idea.
T
Thundered: When a character is talking about something in an angry way, usually loudly.
Told: When your character is relaying something to another.
Tittered: Used when a character is half-laughing, half-trying to stifle it.
Thanked: When a character expresses thanks.
Trumpeted: Used when a character is excitedly announcing something.
U
Uttered: When a character speaks.
Urged: Used when a character is prompting another to take an action.
V
Voiced: When a character expresses their opinion verbally.
Vociferated: When a character argues vehemently.
W
Wailed: When a character makes a sound of grief, pain or discomfort.
Warbled: used when a character’s voice quavers.
Wept: When a character cries when speaking.
Whispered: Used when a character speaks quietly, so not to be overheard.
Whimpered: Used when a character’s voice is feeble and weak, usually in pain or fear
Wheezed: When a character’s voice is strained from lack of breath, such as after a coughing fit.
Whined: When a character complains usually in an irritating way.
Y
Yammered: When a character is talking about something with no line of thought.
Yelped: When a character cries out in shock, pain or discomfort.
Yawned: Used when a character is tired or bored.
Yelled: When a character speaks loudly out of anger or panic.
Yowled: When a character cries out, usually high-pitchedly.
Overusing dialogue tags can sometimes take a reader out of the narrative and make your scenes read more like plays. I generally follow the rule of 'if it not essential' it is out the window. You can simply write dialogue in speech quotes and nobody will stop you.
What's in a Voice?

While we have already gone through the personal sound of your character's voice, what does it actually sound like when they are speaking? When describing the voice of your character while they speak, allows the reader to hear what they can only read and offer a clue how the character is feeling in the moment.
Absent-mindedly: When a voice betrays one’s distraction
Booming: When a voice is loud and carrying.
Breathy: When a voice is peppered with breathes.
Brittle: When a voice betrays a strained mind or fragile sense of mind.
Clear: When a voice is devoid of anything to obstruct or conceal it.
Deep: When a voice is low pitched.
Flat: When a voice is devoid of pitch or emotion.
Gravelly: When a voice is rough, croaking like when one just wakes up.
Guttural: When a voice is rough, coming from the back of the throat.
Harsh: When a voice is unkind and hard.
Husky: When a voice is rough.
Monotonous: When a voice is unvaried in pitch, all in one tone of voice.
Muffled: When a voice is obstructed, such as when the mouth is covered.
Nasally: When a voice sounds like it is coming from the nose, often sharp.
Piping: When a voice is high-pitched, almost sing-song.
Raspy: When a voice is dry and rough sounding.
Rich: When a voice is pleasant sounding to the ear.
Shrill: When a voice is high-pitched.
Silvery: When a voice is clear, soft, and musical.
Soft: When a voice is quiet.
Sonorous: When a voice is deep in sound.
Thin: When a voice is strained, with uneven pitch and tone.
Throaty: When a voice comes from the throat, often rough and croaky.
Tremulous: When a voice is shaking.
Velvety: When a voice is smooth.
Warm: When a voice is comforting, gentle.
Weak: When a voice lacks any strength.
Whispery: When a voice is low, hushed.
Wobbly: When a voice is unsteady.
Avoid the monologues if you can

Nobody can really have a conversation with somebody when that person is rattling off about themselves or their dastardly plans etc. It's not really realistic but in fiction, we kind of want to allow characters to do on a little, to let loose and bare their soul in a speech worthy of Peter Dinklage's best work (Laws of Gods and Men, GoT Season 4). Personally I only give somebody monologuing a few minutes before I interrupt with the good old "that's crazy" or multiple "yeah"s. A character has to be captivated - or captive - to listen to somebody keep talking, talking, talking.
Interaction

Again, your characters are meant to be real people, they are not robots on stage. When people are talking, it isn't perfect. When emotions are high, people will often cut across one another or interrupt one another. When characters are excited or in agreement, they might finish one another's sentences. The dialogue in The Bear, is fantastic for this as the interactions feel real. The characters interrupt one another, talk over one another and finish each other's thoughts. People follow a pattern of talking with people they know, they are less guarded and more prone to speaking their mind if they are comfortable with them or know what to avoid saying. People are more formal when speaking to strangers. People will speak differently to different people, there are things you can only say to your sibling and you wouldn't talk to a classmate you barely know the same way you will speak with a dear friend. The way character's interact can tell the reader a lot about the relationship between the characters.
#writing theory: dialogue#writing dialogue#writing guide#writing resources#writing reference#writeblr#writing advice#writing#writer's problems#spilled words#writer's life#writer#writers on tumblr#wtwcommunity#writeblr community#writing community#writers community#writers#creative writing#writers block#writing help#writing tools#writing tips
383 notes
·
View notes
Text

spent a little time trying out Tahoma2D the other night, and animated a messy lil Vivian to test it out!
might try polishing this more later, it was just a quick thing to learn the tools. rest assured, if i do improve/extend this, there WILL probably be a big stupid explosion involved
#taffy art#animation#tahoma2D#paper mario#paper mario ttyd#vivian#vivian ttyd#been hunting for animation software with an intuitive timeline for a while now#cuz most of them just copy the clunky photoshop setup and i HATE it#the tricky thing is that the few apps i've tried with good timelines often lack some key QoL features/shortcuts#which are standard in other art software and REALLY throw off my rhythm and momentum when they're absent#like being able to hold a key to temporarily switch to a tool and then release to switch back (especially the eraser)#tahoma2D also has this problem but at least the rest of it seems solid enough that i could definitely see it working for rough animation#just a matter of getting past my huge mental block that makes me never wanna animate unless it's on a whim (before i can think about it)#so a lower barrier-to-entry is always gonna be better just sorta in general
108 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blocktales. Again.




#block tales#blocktales#blocktales hatred#block tales hatred#block tales player#player#blocktales player#player blocktales#player block tales#hatredxplayer#playerxhatred#greed#greed blocktales#greed block tales#block tales greed#blocktales greed#kleki#kleki paint tool#whiteboardfox#riptides art
88 notes
·
View notes
Text
100 Dialogue Tags You Can Use Instead of “Said”
For the writers struggling to rid themselves of the classic ‘said’. Some are repeated in different categories since they fit multiple ones (but those are counted once so it adds up to 100 new words).
1. Neutral Tags
Straightforward and unobtrusive dialogue tags:
Added, Replied, Stated, Remarked, Responded, Observed, Acknowledged, Commented, Noted, Voiced, Expressed, Shared, Answered, Mentioned, Declared.
2. Questioning Tags
Curious, interrogative dialogue tags:
Asked, Queried, Wondered, Probed, Inquired, Requested, Pondered, Demanded, Challenged, Interjected, Investigated, Countered, Snapped, Pleaded, Insisted.
3. Emotive Tags
Emotional dialogue tags:
Exclaimed, Shouted, Sobbed, Whispered, Cried, Hissed, Gasped, Laughed, Screamed, Stammered, Wailed, Murmured, Snarled, Choked, Barked.
4. Descriptive Tags
Insightful, tonal dialogue tags:
Muttered, Mumbled, Yelled, Uttered, Roared, Bellowed, Drawled, Spoke, Shrieked, Boomed, Snapped, Groaned, Rasped, Purred, Croaked.
5. Action-Oriented Tags
Movement-based dialogue tags:
Announced, Admitted, Interrupted, Joked, Suggested, Offered, Explained, Repeated, Advised, Warned, Agreed, Confirmed, Ordered, Reassured, Stated.
6. Conflict Tags
Argumentative, defiant dialogue tags:
Argued, Snapped, Retorted, Rebuked, Disputed, Objected, Contested, Barked, Protested, Countered, Growled, Scoffed, Sneered, Challenged, Huffed.
7. Agreement Tags
Understanding, compliant dialogue tags:
Agreed, Assented, Nodded, Confirmed, Replied, Conceded, Acknowledged, Accepted, Affirmed, Yielded, Supported, Echoed, Consented, Promised, Concurred.
8. Disagreement Tags
Resistant, defiant dialogue tags:
Denied, Disagreed, Refused, Argued, Contradicted, Insisted, Protested, Objected, Rejected, Declined, Countered, Challenged, Snubbed, Dismissed, Rebuked.
9. Confused Tags
Hesitant, uncertain dialogue tags:
Stammered, Hesitated, Fumbled, Babbled, Mumbled, Faltered, Stumbled, Wondered, Pondered, Stuttered, Blurted, Doubted, Confessed, Vacillated.
10. Surprise Tags
Shock-inducing dialogue tags:
Gasped, Stunned, Exclaimed, Blurted, Wondered, Staggered, Marvelled, Breathed, Recoiled, Jumped, Yelped, Shrieked, Stammered.
Note: everyone is entitled to their own opinion. No I am NOT telling people to abandon said and use these. Yes I understand that said is often good enough, but sometimes you WANT to draw attention to how the character is speaking. If you think adding an action/movement to your dialogue is 'good enough' hate to break it to you but that ruins immersion much more than a casual 'mumbled'. And for the last time: this is just a resource list, CALM DOWN. Hope that covers all the annoyingly redundant replies :)
Looking For More Writing Tips And Tricks?
Check out the rest of Quillology with Haya; a blog dedicated to writing and publishing tips for authors!
Instagram Tiktok
#hayatheauthor#haya's book blog#haya blogs#writing community#quillology with haya#writing tools#writer things#writing advice#writer community#writing techniques#writing prompt#writing stuff#creative writing#ya writing advice#writing tips and tricks#writer tools#writers of tumblr#writer blog#writers block#quillology with haya sameer#writers on tumblr#writerscommunity#writer stuff#author help#author advice#author#writing inspiration#writeblr#novel writing#on writing
33K notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Start Writing Again When the Spark Fades
Sometimes the well of creativity runs dry, leaving you staring at a blank page with nothing but frustration. But trust that the art of writing is as much about the journey as it is about the destination. Here are some ideas to help you reconnect with your writing practice when you feel like your passion has dimmed.
Redefine Your Environment Consider taking a deliberate step outside your usual writing space. The environment in which you work can drastically affect your mindset and creative flow. Even if it’s setting up in a different corner of your home, finding refuge in a local café, or enjoying the subtle distractions of a park bench, a change in scenery often signals a mental reset. This isn’t about permanent relocation, just a simple shift can break the monotony and stir new ideas that have been hiding in plain sight.
Embrace Imperfection The pressure to produce perfect prose can be paralyzing. Give yourself permission to create something imperfect yet honest. Think of every sentence you write as a rough sketch, a necessary experiment in understanding your own voice. When you allow yourself the space to write without the weight of perfection, you invite experimentation and genuine self-expression. That freedom lies at the heart of rediscovering why you fell in love with writing in the first place.
Set Incremental Goals for Continuous Momentum When the idea of diving into a full chapter feels overwhelming, scale back to manageable, bite-sized projects that feel achievable. Instead of demanding a polished page, challenge yourself to write a paragraph or even a single sentence each day. These micro-goals build a foundation of small successes, gradually restoring confidence and momentum. Over time, these consistent efforts enrich your creative reservoir, proving that every little step is indeed a victory.
Engage Deeply in the Process of Freewriting Allow yourself to spill thoughts onto the page without judgment or expectation. Freewriting is an exercise in vulnerability and self-exploration, offering you a space to unburden tangled ideas and unexpected insights. In these unfiltered moments, you might stumble upon a germ of an idea or a rediscovered passion that rekindles your creative fire. Embracing this unstructured approach can transform an intimidating blank page into an open canvas of potential you haven't tapped back into.
Rekindle Old Inspirations There is power in revisiting the work and moments that first ignited your creative spirit. Even if it’s rereading an old journal entry, rediscovering a favorite piece of literature, or reflecting on the stories that once moved you, reconnecting with your past inspirations can shed new light on your present creative journey. This reflective practice not only reminds you of your original passion but may also reveal new directions for your current writing endeavors.
Create a Consistent, Loving Writing Routine Creating a structured yet gentle routine can help reestablish your relationship with writing. Treat your writing time as a vital appointment, a moment carved out just for you. Even if inspiration seems scarce, the simple act of sitting down, opening your notebook, and letting words flow without self-censorship can be incredibly healing. Over time, this practice transforms writing from an obligation into a ritual of self-discovery and mindfulness.
Connect with a Community That Understands Engaging with fellow writers can remind you that you’re not alone in this struggle. The shared experience of creative highs and lows can be profoundly comforting. Join writing groups, participate in online forums, or simply reach out to someone whose work inspires you. These interactions foster a sense of belonging and accountability, encouraging you to keep writing even when the path isn’t clear. In the gentle exchange of ideas and feedback, there is often a spark that reignites your dedication.
Every writer’s journey is unique, filled with ebbs and flows. If you’re feeling disconnected, know that these moments are integral to growth. Embrace each phase as an opportunity to rediscover writing on its own terms, and allow your passion to guide you back into the words you love. If you need any advice from me, never be afraid to send me an ask.
Until next time, Rin T.
#on writing#creative writing#writing#writing tips#writers block#how to write#thewriteadviceforwriters#writeblr#writers and poets#writers on tumblr#novel writing#fiction writing#romance writing#writing advice#writing blog#writing characters#writing community#writing help#writing ideas#writing inspiration#writing guide#writing prompts#writing a book#writing resources#writing reference#writing tips and tricks#writers#writing tools#writing life#writing software
4K notes
·
View notes
Text

i’ve learned so much from you, i just hope there’s still time to prove it. i promise we’ll see each other again.
#my art#block tales#kyoko block tales#eyestrain#< i think????#my internal monologue drawing this: this is just like noelle and dess (repeated over and over and over)#this was drawn entirely with the lasso + fill tool besides some minor details like the freckles or some halftone brushes btw#kyoko tag
144 notes
·
View notes
Text
x
#Fandom#Baldur's Gate 3#Dragon Age#Cyberpunk 2077#< putting it in the tag since whole fandom war started cause people couldn't block OR handle a block like adults so y'know fuck it#There's nothing shameful about using the block button to curate your space#taking care of your online space is taking care of your mental health#realizing someone's content - regardless of what it is - isn't good for you and dealing with it with the available tools IS mature#if you mock someone for doing so you're a piece of shit at best and lowkey ableist at worst#special Fuck You to people who start wholass witch hunt over it - it's fucking pathetic and says more about you than whoever blocked you
291 notes
·
View notes
Text

panda panda circus circus
#Panda Circus#Daniel Mullins Games#Pony Island#<- Does that tag apply??? No idea.#Found a slightly quicker way to do this. Emphasis on slightly though it... doesn't work 100% of the way </3#The process was blocking out the sections with the lasso tool and then using the dithering brushes I have instead of just.#Doing it pixel-by-pixel. Then I added random black and white pixels everywhere for weirdness because it looked too uniform otherwise.#Anyway pro tip don't do this when you have a migraine. You will regret it. Quickly.#Hrokkall Art
611 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you have a friend that is struggling to write:
Put that motherfucker in their most comfortable clothes, stick them in the car with their laptop, and go for a mini road trip together somewhere in the country.
Get coffee. Stop at a middle-of-nowhere diner for food. Visit a used book store. Open Spotify and play instrumental music like popular low-fi cover songs (perfect for writing to). Make a day of driving and going nowhere somewhere far away.
Are you both writers? Take turns. Create your own writers’ retreat. Fill your day talking about story ideas or simply spend quality time in the silence filled with the clacking of keys from the passenger seat.
#writing#reading and writing#creative writing#writing community#writing tool#writing stories#writing fiction#fiction writing#creative fiction#creativity#writers community#writing and writers#writers on tumblr#writerscommunity#writer thoughts#writer stuff#writers and poets#writer problems#writer things#writers block#writerblr#writeblr#writing stuff#cozycore#writing motivation#writing inspiration#cashmere ink
69 notes
·
View notes
Note
Could we get some body language tips on disgust and/or sickness?
Body Language
When someone is...
Disgusted/Sick

Disgust:
Face/Body:
If a character's disgust is visible, the face will be more wrinkly/scrunched up.
Furrowed or lowered brow, wrinkled nose, raised upper lip, grimacing
Hunched over, turning away, and/or covering sensory areas like nose, eyes, mouth. Just trying to block out whatever is triggering their disgust
Voice:
Inflections that give away disapproval/revulsion. Maybe short or clipped speech patterns
Sharp tone/raised pitch. Maybe gagging or choking sounds
Sickness:
This will depend on what illness your character has. Research symptoms/side effects and build off of those.
For example, if the character is experiencing congestion, their voice will be nasally/heavy. If they're coughing or have a sore throat, their voice will be hoarse, or they'll speak quieter to keep from straining.
Look at how their mood/behavior changes if they are feverish, delirious, etc. Some people can go about their everyday lives with a common cold, but many people aren't themselves when bedridden or in pain.
If you are writing a character with a chronic illness, put a lot of research into the symptoms, any medicines and their side effects, how a person's mind is affected, and even look at how it can affect your character's relationship with others.
happy writing!
#writersbloxx#creative writing#writers on tumblr#writers community#writing#writeblr#writers and poets#writers blog#writersblr#writers block#writers#writing community#writing tool#writing tips#aspiring author
99 notes
·
View notes