#novel writing
Text
#911 lone star#pierce the veil#pop#lance reddick#橋本梨菜#tartaglia#novel writing#aemond targaryen x reader#amy adams#elizabeth taylor#furry art
130 notes
·
View notes
Text
#novel writing#aemond targaryen x reader#amy adams#photojournalism#elizabeth taylor#borzoi#adult adhd#furry art#black hair#funny tweets#saki yanase#aesthetic#digital art#Joseph Gordon-Levitt
61 notes
·
View notes
Text
Writers tip: pretend you don't care about the wip and engage in a rigorous who cares less contest with said wip. Eventually you'll lose and finish it.
#.ranting like a madwoman#thank me later#writeblr#creative writing#my writing#writers#writers on tumblr#shitpost#writers life#writers block#novel writing#writing stuff#fiction writing#writing blog#writing community#writing ideas#writing advice#writing inspiration#writing is hard#writing tips#writerscommunity#writer things#writers of tumblr#writerslife#writers and poets#writer#writing
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
#fanfiction#writeblr#writer#writers#writing#writerscommunity#writblr#writer problems#writings#my writing#wip#write#being a writer#creative writing#female writers#fiction writing#just writer things#novel writing#writer life#writer meme#writer memes#writer struggles#writer stuff#writer things#writerblr#writers block#writers community#writers life#writers of tumblr#writers on tumblr
21K notes
·
View notes
Text
Things That May Be Causing Your Writer's Block- and How to Beat Them
I don't like the term 'Writer's Block' - not because it isn't real, but because the term is so vague that it's useless. Hundreds of issues all get lumped together under this one umbrella, making writer's block seem like this all-powerful boogeyman that's impossible to beat. Worse yet, it leaves people giving and receiving advice that is completely ineffective because people often don't realize they're talking about entirely different issues.
In my experience, the key to beating writer's block is figuring out what the block even is, so I put together a list of Actual Reasons why you may be struggling to write:
(note that any case of writer's block is usually a mix of two or more)
Perfectionism (most common)
What it looks like:
You write one sentence and spend the next hour googling "synonyms for ___"
Write. Erase. Write. Rewrite. Erase.
Should I even start writing this scene when I haven't figured out this one specific detail yet?
I hate everything I write
Cringing while writing
My first draft must be perfect, or else I'm a terrible writer
Things that can help:
Give yourself permission to suck
Keep in mind that nothing you write is going to be perfect, especially your first draft
Think of writing your first/early drafts not as writing, but sketching out a loose foundation to build upon later
People write multiple drafts for a reason: write now, edit later
Stop googling synonyms and save that for editing
Write with a pen to reduce temptation to erase
Embrace leaving blank spaces in your writing when you can't think of the right word, name, or detail
It's okay if your writing sucks. We all suck at some point. Embrace the growth mindset, and focus on getting words on a page
Lack of inspiration (easiest to fix)
What it looks like:
Head empty, no ideas
What do I even write about???
I don't have a plot, I just have an image
Want to write but no story to write
Things that can help:
Google writing prompts
If writing prompts aren't your thing, instead try thinking about what kind of tropes/genres/story elements you would like to try out
Instead of thinking about the story you would like to write, think about the story you would like to read, and write that
It's okay if you don't have a fully fleshed out story idea. Even if it's just an image or a line of dialogue, it's okay to write that. A story may or may not come out of it, but at least you got the creative juices flowing
Stop writing. Step away from your desk and let yourself naturally get inspired. Go for a walk, read a book, travel, play video games, research history, etc. Don't force ideas, but do open up your mind to them
If you're like me, world-building may come more naturally than plotting. Design the world first and let the story come later
Boredom/Understimulation (lost the flow)
What it looks like:
I know I should be writing but uugggghhhh I just can'tttttt
Writing words feels like pulling teeth
I started writing, but then I got bored/distracted
I enjoy the idea of writing, but the actual process makes me want to throw my laptop out the window
Things that can help:
Introduce stimulation: snacks, beverages, gum, music such as lo-fi, blankets, decorate your writing space, get a clickity-clackity keyboard, etc.
Add variety: write in a new location, try a new idea/different story for a day or so, switch up how you write (pen and paper vs. computer) or try voice recording or speech-to-text
Gamify writing: create an arbitrary challenge, such as trying to see how many words you can write in a set time and try to beat your high score
Find a writing buddy or join a writer's group
Give yourself a reward for every writing milestone, even if it's just writing a paragraph
Ask yourself whether this project you're working on is something you really want to be doing, and be honest with your answer
Intimidation/Procrastination (often related to perfectionism, but not always)
What it looks like:
I was feeling really motivated to write, but then I opened my laptop
I don't even know where to start
I love writing, but I can never seem to get started
I'll write tomorrow. I mean next week. Next month? Next month, I swear (doesn't write next month)
Can't find the time or energy
Unreasonable expectations (I should be able to write 10,000 words a day, right????)
Feeling discouraged and wondering why I'm even trying
Things that can help:
Follow the 2 min rule (or the 1 paragraph rule, which works better for me): whenever you sit down to write, tell yourself that you are only going to write for 2 minutes. If you feel like continuing once the 2 mins are up, go for it! Otherwise, stop. Force yourself to start but DO NOT force yourself to continue unless you feel like it. The more often you do this, the easier it will be to get started
Make getting started as easy as possible (i.e. minimize barriers: if getting up to get a notebook is stopping you from getting started, then write in the notes app of your phone)
Commit to a routine that will work for you. Baby steps are important here. Go with something that feels reasonable: every day, every other day, once a week, twice a week, and use cues to help you remember to start. If you chose a set time to write, just make sure that it's a time that feels natural to you- i.e. don't force yourself to writing at 9am every morning if you're not a morning person
Find a friend or a writing buddy you can trust and talk it out or share a piece of work you're proud of. Sometimes we just get a bit bogged down by criticism- either internal or external- and need a few words of encouragement
The Problem's Not You, It's Your Story (or Outline (or Process))
What it looks like:
I have no problems writing other scenes, it's just this scene
I started writing, but now I have no idea where I'm going
I don't think I'm doing this right
What's an outline?
Drowning in documents
This. Doesn't. Make. Sense. How do I get from this plot point to this one?!?!?! (this ColeyDoesThings quote lives in my head rent free cause BOY have I been there)
Things That Can Help:
Go back to the drawing board. Really try to get at the root of why a scene or story isn't working
A part of growing as a writer is learning when to kill your darlings. Sometimes you're trying to force an idea or scene that just doesn't work and you need to let it go
If you don't have an outline, write one
If you have an outline and it isn't working, rewrite it, or look up different ways to structure it
You may be trying to write as a pantser when you're really a plotter or vice versa. Experiment with different writing processes and see what feels most natural
Study story structures, starting with the three act structure. Even if you don't use them, you should know them
Check out Ellen Brock on YouTube. She's a professional novel editor who has a lot of advice on writing strategies for different types of writers
Also check out Savage Books on YouTube (another professional story editor) for advice on story structure and dialogue. Seriously, I cannot recommend this guy enough
Executive Dysfunction, Usually From ADHD/Autism
What it looks like:
Everything in boredom/understimulation
Everything in intimidation/procrastination
You have been diagnosed with and/or have symptoms of ADHD/Autism
Things that can help:
If you haven't already, seek a diagnosis or professional treatment
Hire an ADHD coach or other specialist that can help you work with your brain (I use Shimmer; feel free to DM me for a referral)
Seek out neurodiverse communities for advice and support
Try body doubling! There's lot's of free online body doubling websites out there for you to try. If social anxiety is a barrier, start out with writing streams such as katecavanaughwrites on Twitch
Be aware of any sensory barriers that may be getting in the way of you writing (such as an uncomfortable desk chair, harsh lighting, bad sounds)
And Lastly, Burnout, Depression, or Other Mental Illness
What it looks like:
You have symptoms of burnout or depression
Struggling with all things, not just writing
It's more than a lack of inspiration- the spark is just dead
Things that can help:
Forget writing for now. Focus on healing first.
Seek professional help
If you feel like it, use writing as a way to explore your feelings. It can take the form of journaling, poetry, an abstract reflection of your thoughts, narrative essays, or exploring what you're feeling through your fictional characters. The last two helped me rediscover my love of writing after I thought years of depression had killed it for good. Just don't force yourself to do so, and stop if it takes you to a darker place instead of feeling cathartic
#writing#creative writing#writer problems#writing advice#writing community#writing a book#writing problems#novel writing#on writing#writing tips#writing help#writers on tumblr#writers block#female writers#writers of tumblr#writers blog#adhd writer
17K notes
·
View notes
Text

#it me#hmmm daydreaming go brrr#writing#fiction#creative writing#author#writerblr#writing community#my writing#writer#writers of tumblr#indie author#writing memes#novel writing#am writing#fantasy writing#book writing#fiction writing#story writing#writing blog#writing fiction#writing inspiration#writing meme
10K notes
·
View notes
Text
Some of my writer’s block cures:
Handwrite. (If you already are, write in a different coloured pen.)
Write outside or at a different location.
Read.
Look up some writing prompts.
Take a break. Do something different. Comeback to it later.
Write something else. (A different WIP, a poem, a quick short story, etc.)
Find inspiring writing music playlists on YouTube. (Themed music, POV playlists, ambient music, etc.)
Do some character or story prompts/questions to get a better idea of who or what you’re writing.
Word sprints. Set a timer and write as much as you can. Not a lot of time to overthink things.
Set your own goals and deadlines.
Write another scene from your WIP. (You don’t have to write in order.) Write a scene you want to write, or the ending. (You can change it or scrap it if it doesn’t fit into your story later.)
Write a scene for your WIP that you will never post/add to your story. A prologue, a different P.O.V., how your characters would react in a situation that’s not in your story, a flashback, etc.
Write down a bunch of ideas. Things that could happen, thing that will never happen, good things, bad things.
Change the weather (in the story of course.)
Feel free to add your own.
#writeblr#writing help#writing tips#writing advice#books#writing#wattpad#stories#author#writing community#creative writing#writers on tumblr#writers block#writers blog#writblr#female writers#writerscorner#writing motivation#writers block cures#novel writing#writer things#writing encouragement#authors supporting authors#author blog
13K notes
·
View notes
Text

#writing#writers#writers on tumblr#writing community#writer things#writerslife#writerscommunity#novel writing#writers and readers#writing tips#writing memes#writing problems#writer problems#writing humor#writer stuff#writer memes
9K notes
·
View notes
Text
traits turned sour
honest - insensitive
persuasive - manipulative
caring - overprotective
confidence - arrogance
fearless - cocky
loyalty - an excuse
devotion - obsession
agreeable - lazy
perfectionism - insatisfaction
reserved - aloof
cautious - skeptical
self loved - selfish
available - distractible
emotional - dramatic
humble - attention-seeking
diligent - imposing
dutiful - submissive
assertive - bossy
strategic - calculated
truthful - cruel
#this isn't meant to be taken the wrong way#but#I wanted to show how good traits#can so easily been seen as bad#writerblr#lyralit#creative writing#writing prompts#novel writing#writers#writing tips
26K notes
·
View notes
Text
Why Writers Don't Finish Writing Their Stories, and How to Fix It
Hello fellow writers and storytellers,
The journey of writing a story is an exhilarating adventure, but it's not without its share of obstacles. Many of us have embarked on a creative endeavor, only to find ourselves mired in the struggle to finish what we started. In this blog post, I'll unravel the common reasons why writers don't finish their stories and explore practical strategies to overcome these hurdles and reignite the flame of creativity.
The Perils of Unfinished Stories
As writers, we often find ourselves in the throes of unfinished tales, grappling with the intricate web of characters, plots, and themes. There are several reasons why the ink dries up and the story remains untold. Let's shine a light on the familiar adversaries that stand between us and the triumphant completion of our narratives:
1. Lack of Planning:
Some of us brazenly dive into our stories without a clear roadmap, resulting in uncertainty about the direction of the plot and the fate of our characters. The lack of a solid plan can lead us astray, leaving our stories wandering in the wilderness of aimlessness.
2. Self-Doubt and Perfectionism:
Ah, the relentless whispers of self-doubt and the siren call of perfectionism! These twin adversaries can cast a shadow over our creative vision, compelling us to endlessly revise and perfect the early chapters, trapping us in a whirlpool of perpetual edits.
3. Time Management:
Balancing the demands of daily life with the ardor of writing can be akin to walking a tightrope. The struggle to find consistent time for our craft often leaves our stories languishing in prolonged periods of inactivity, longing for the touch of our pen.
4. Writer's Block:
The mighty barrier that even the most intrepid writers encounter. Writer's block can be an insurmountable mountain, leaving us stranded in the valleys of creative drought, unable to breathe life into new ideas and narratives.
5. Lack of Motivation:
The flame that once burned brightly can flicker and wane over time, leaving us adrift in the murky waters of disillusionment. The initial excitement for our stories diminishes, making it arduous to stay committed to the crafting process.
6. Fear of Failure or Success:
The twin specters that haunt many writers' dreams. The apprehension of rejection and the unsettling prospect of life-altering success can tether us to the shores of hesitation, preventing us from reaching the shores of completion.
7. Criticism and Feedback Anxiety:
The looming dread of judgment casts a long shadow over our creative endeavors. The mere thought of receiving criticism or feedback, whether from peers or potential readers, can cast a cloud over our storytelling pursuits.
8. Plotting Challenges:
Crafting a cohesive and engaging plot is akin to navigating a labyrinth without a map. Faced with hurdles in connecting story elements, we may find ourselves lost in a maze of plot holes and unresolved threads.
9. Character Development Struggles:
Breathing life into multi-dimensional, relatable characters is a complex art. The intricate process of character development can become a quagmire, ensnaring us in the challenge of creating personas that drive the story forward. (Part one of Character Development Series)
10. Life Events and Distractions:
Unexpected events in our personal lives can cast ripples on our writing routines, interrupting the flow of our creativity and causing a loss of momentum.
Rallying Against the Odds: Strategies for Success
Now that we've confronted the adversaries that threaten to stall our storytelling odysseys, let's arm ourselves with strategies to conquer these barriers and reignite the flames of our creativity.
Embrace the Power of Planning:
A clear roadmap illuminates the path ahead. Arm yourself with outlines, character sketches, and plot maps to pave the way for your story's journey.
Vanquish Self-Doubt with Action:
Silence the voices of doubt with the power of progress. Embrace the imperfect beauty of your early drafts, knowing that every word brings you closer to the finish line.
Mastering the Art of Time:
Carve out sacred writing time in your schedule. Whether it’s ten minutes or two hours, every moment dedicated to your craft is a step forward.
Conquering Writer's Block:
Embrace the freedom of imperfection. Write, even if the words feel like scattered puzzle pieces. The act of writing can unravel the most stubborn knots of writer's block.
Reigniting the Flame of Motivation:
Seek inspiration in the wonders of the world. Reconnect with the heart of your story, rediscovering the passion that set your creative spirit ablaze.
Reshaping Fear into Fuel:
Embrace the uncertainty as an integral part of the creative journey. Embrace the lessons within rejection and prepare for the winds of change that success may bring.
Navigating the Realm of Criticism:
Embrace feedback as a catalyst for growth. Constructive criticism is a powerful ally, shaping your story into a work of art that resonates with readers.
Weaving the Threads of Plot:
Connect the dots with fresh eyes. Step back and survey the tapestry of your plot, seeking innovative solutions to bridge the gaps and untangle the knots.
Breathing Life into Characters:
Engage with your characters as if they were old friends. Dive into their depths, unraveling their quirks, fears, and dreams, and watch as they breathe life into your story.
Navigating Life's Tempests:
Embrace the ebb and flow of life. Every pause in your writing journey is a chance to gather new experiences and perspectives, enriching your storytelling tapestry.
The Ever-Resting Pen: Harnessing the Power Within
Fellow writers, the journey of completing a story is filled with peaks and valleys, each offering us the opportunity to sharpen our resolve and unleash our creative potential. As we stand at the crossroads, staring at the canvas of unfinished tales, let's rally against the odds, armed with the power of purpose, passion, and perseverance.
Let the ink flow once more, breathing life into tales left untold, and watch as your stories triumphantly reach their long-awaited conclusion. You possess the power to conquer the adversaries that stand in your way, and within you lies the essence of untold narratives waiting to unfurl onto the page.
Here's to the journey that lies ahead, the stories waiting to be written, and the unyielding spirit of creativity that thrives within each of us.
Warm regards and unwavering encouragement,
Ren T.
#creative writing#thewriteadviceforwriters#writing#writeblr#on writing#writing tips#writers block#how to write#writers and poets#novelist#novel writing#november#novel
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Words to use instead of ‘said’
**Using the word ‘said’ is absolutely not a bad choice, and in fact, you will want to use it for at least 40% of all your dialogue tags. Using other words can be great, especially for description and showing emotion, but used in excess can take away or distract from the story.
Neutral: acknowledged, added, affirmed, agreed, announced, answered, appealed, articulated, attested, began, bemused, boasted, called, chimed in, claimed, clarified, commented, conceded, confided, confirmed, contended, continued, corrected, decided, declared, deflected, demurred, disclosed, disputed, emphasized, explained, expressed, finished, gloated, greeted, hinted, imitated, imparted, implied, informed, interjected, insinuated, insisted, instructed, lectured, maintained, mouthed, mused, noted, observed, offered, put forth, reassured, recited, remarked, repeated, requested, replied, revealed, shared, spoke up, stated, suggested, uttered, voiced, volunteered, vowed, went on
Persuasive: advised, appealed, asserted, assured, begged, cajoled, claimed, convinced, directed, encouraged, implored, insisted, pleaded, pressed, probed, prodded, prompted, stressed, suggested, urged
Continuously: babbled, chattered, jabbered, rambled, rattled on
Quietly: admitted, breathed, confessed, croaked, crooned, grumbled, hissed, mumbled, murmured, muttered, purred, sighed, whispered
Loudly: bellowed, blurted, boomed, cried, hollered, howled, piped, roared, screamed, screeched, shouted, shrieked, squawked, thundered, wailed, yelled, yelped
Happily/Lovingly: admired, beamed, cackled, cheered, chirped, comforted, consoled, cooed, empathized, flirted, gushed, hummed, invited, praised, proclaimed, professed, reassured, soothed, squealed, whooped
Humour: bantered, chuckled, giggled, guffawed, jested, joked, joshed
Sad: bawled, begged, bemoaned, blubbered, grieved, lamented, mewled, mourned, pleaded, sniffled, sniveled, sobbed, wailed, wept, whimpered
Frustrated: argued, bickered, chastised, complained, exasperated, groaned, huffed, protested, whinged
Anger: accused, bristled, criticized, condemned, cursed, demanded, denounced, erupted, fumed, growled, lied, nagged, ordered, provoked, raged, ranted remonstrated, retorted, scoffed, scolded, scowled, seethed, shot, snapped, snarled, sneered, spat, stormed, swore, taunted, threatened, warned
Disgust: cringed, gagged, groused, griped, grunted, mocked, rasped, sniffed, snorted
Fear: cautioned, faltered, fretted, gasped, quaked, quavered, shuddered, stammered, stuttered, trembled, warned, whimpered, whined
Excited: beamed, cheered, cried out, crowed, exclaimed, gushed, rejoiced, sang, trumpeted
Surprised: blurted, exclaimed, gasped, marveled, sputtered, yelped
Provoked: bragged, dared, gibed, goaded, insulted, jeered, lied, mimicked, nagged, pestered, provoked, quipped, ribbed, ridiculed, sassed, teased
Uncertainty/Questionned: asked, challenged, coaxed, concluded, countered, debated, doubted, entreated, guessed, hesitated, hinted, implored, inquired, objected, persuaded, petitioned, pleaded, pondered, pressed, probed, proposed, queried, questioned, quizzed, reasoned, reiterated, reported, requested, speculated, supposed, surmised, testified, theorized, verified, wondered
This is by no means a full list, but should be more than enough to get you started!
Any more words you favor? Add them in the comments!
Happy Writing :)
#writing resources#writing advice#creative writing#writers on tumblr#tumblr writers#dialogue#writing dialogue#dialogue tags#instead of said#writing community#writer#writeblr#writerscommunity#novel writing#writing#fiction
13K notes
·
View notes
Text
"Oh being a writer must be so cool and artistic"
No being a writer is frantically googling shit like this at 1 am on a work night
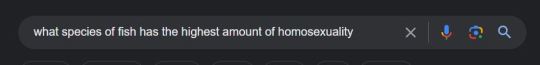
#yes that is a real and important search I made for my current WIP#sigh#writers on tumblr#writing#writers#novel writing
4K notes
·
View notes
Text

the elusive 7 act Structure
#writing tips#novel writing#writerscommunity#writersociety#writing advice#writer problems#writer things#writers block#writers of tumblr#storytelling#storytellers#writers#storyteller#writing#writerideas#writersoftwitter#stories#storyideas#writersoftumblr#writingideas#writingtips#writinghelp#badwriter
52K notes
·
View notes
Text
the toughest part about writing isn't getting words on the page. the toughest part about writing is ignoring the voice in my head that says,
"hey man— sorry to interrupt, but that last sentence? it could use a few more emdashes. maybe just— and i know this seems nuts— ten or fifteen?? thanks— great stuff btw."
#writeblr#writers#creative writing#original writing#writeblr community#jgmartin#writing#writers of tumblr#writerscommunity#tumblr writers#writer problems#am writing#fiction writing#novel writing#writblr#writer community#writer things#writers and poets#writers on tumblr#writerslife#writing advice#text post#writing blog
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Weird Brain Hacks That Help Me Write
I'm a consistently inconsistent writer/aspiring novelist, member of the burnt-out-gifted-kid-to-adult-ADHD-diagnosis-pipeline, recently unemployed overachiever, and person who's sick of hearing the conventional neurotypical advice to dealing with writer's block (i.e. "write every single day," or "there's no such thing as writer's block- if you're struggling to write, just write" Like F*CK THAT. Thank you, Brenda, why don't you go and tell someone with diabetes to just start producing more insulin?)
I've yet to get to a point in my life where I'm able to consistently write at the pace I want to, but I've come a long way from where I was a few years ago. In the past five years I've written two drafts of a 130,000 word fantasy novel (currently working on the third) and I'm about 50,000 words in on the sequel. I've hit a bit of a snag recently, but now that I've suddenly got a lot of time on my hands, I'm hoping to revamp things and return to the basics that have gotten me to this point and I thought I might share.
1) My first draft stays between me and God
I find that I and a lot of other writers unfortunately have gotten it into our heads that first drafts are supposed to resemble the finished product and that revisions are only for fixing minor mistakes. Therefore, if our first draft sucks that must mean we suck as writers and having to rewrite things from scratch means that means our first draft is a failure.
I'm here to say that is one of the most detrimental mentalities you can have as a writer.
Ever try drawing a circle? You know how when you try to free-hand draw a perfect circle in one go, it never turns out right? Whereas if you scribble, say, ten circles on top of one another really quickly and then erase the messy lines until it looks like you drew a circle with a singular line, it ends up looking pretty decent?
Yeah. That's what the drafting process is.
Your first draft is supposed to suck. I don't care who you are, but you're never going to write a perfect first draft, especially if you're inexperienced. The purpose of the first draft is to lay down a semi-workable foundation. A really loose, messy sketch if you will. Get it all down on paper, even if it turns out to be the most cliche, cringe-inducing writing you've ever done. You can work out those kinks in the later drafts. The hardest part of the first draft is the most crucial part: getting started. Don't stress yourself out and make it even harder than it already is.
If that means making a promise to yourself that no one other than you will ever read your first draft unless it's over your cold, dead body, so be it.
2) Tell perfectionism to screw off by writing with a pen
I used to exclusively write with pencil until I realized I was spending more time erasing instead of writing.
Writing with a pen keeps me from editing while I right. Like, sometimes I'll have to cross something out or make notes in the margins, but unlike erasing and rewriting, this leaves the page looking like a disaster zone and that's a good thing.
If my writing looks like a complete mess on paper, that helps me move past the perfectionist paralysis and just focus on getting words down on the page. Somehow seeing a page full of chicken scratch makes me less worried about making my writing all perfect and pretty- and that helps me get on with my main goal of fleshing out ideas and getting words on a page.
3) It's okay to leave things blank when you can't think of the right word
My writing, especially my first draft, is often filled with ___ and .... and (insert name here) and red text that reads like stage directions because I can't think of what is supposed to go there or the correct way to write it.
I found it helps to treat my writing like I do multiple choice tests. Can't think of the right answer? Just skip it. Circle it, come back to it later, but don't let one tricky question stall you to the point where you run out of brain power or run out of time to answer the other questions.
If I'm on a role, I'm not gonna waste it by trying to remember that exact word that I need or figure out the right transition into the next scene or paragraph. I'm just going to leave it blank, mark to myself that I'll need to fix the problem later, and move on.
Trust me. This helps me sooooo much with staying on a roll.
4) Write Out of Order
This may not be for everyone, but it works wonders for me.
Sure, the story your writing may need to progress chronologically, but does that mean you need to write it chronologically? No. It just needs to be written.
I generally don't do this as much for editing, but for writing, so long as you're making progress, it doesn't matter if it's in the right order. Can't think of how to structure Chapter 2, but you have a pretty good idea of how your story's going to end? Write the ending then. You'll have to go back and write Chapter 2 eventually, but if you're feeling more motivated to write a completely different part of the book, who's to say you can't do that?
When I'm working on a project, I start off with a single document that I title "Scrap for (Project Title)" and then just write whatever comes to mind, in whatever order. Once I've gotten enough to work with, then I start outlining my plot and predicting how many chapters I'm going to need. Then, I create separate google docs for each individual chapter and work on them in whatever order I feel like, often leaving several partially complete as I jump from one to the other. Then, as each one gets finished, I copy and paste the chapter into the full manuscript document. This means that the official "draft" could have Chapters 1 and 9, but completely be missing Chapters 2-8, and that's fine. It's not like anyone will ever know once I finish it.
Sorry for the absurdly long post. Hopes this helps someone. Maybe I'll share more tricks in the future.
#writing#creative writing#writerscommunity#writers on tumblr#writing tips#writing advice#writers block#novel writing#fiction writing#writer#writers of tumblr
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

#just in case y'all needed a reminder <3#fiction#this is a reminder for myself too#take breaks and drink some water too#writing#creative writing#author#writerblr#writing community#my writing#writer#writers of tumblr#indie author#writing memes#novel writing#am writing#book writing#fantasy writing#fiction writing#story writing#writing advice#writing blog#writing fiction#writing inspiration#writing meme#writing mood#writing on tumblr#writing problems#writing progress#writing stuff
5K notes
·
View notes