#global climate action summit
Text
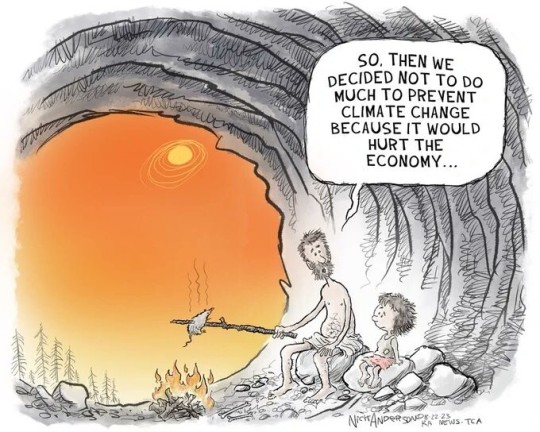

#comics#comic#cartoons#cartoon#global warming#climate change#climate crisis#humza yousaf branded hypocrite for jetting to cop28 in dubai while his government misses emissions targets#cop28 climate summit#cop28climateconference#cop28 president#cop28#climate action#climate emergency#climate catastrophe#ecology#environmentalism#environmental activism#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#environmental#environment
84 notes
·
View notes
Text
COP28 countries reach landmark deal to “transition” away from fossil fuels
The COP28 climate talks in Dubai have culminated in a historic agreement that will see the world phase out all fossil fuels for the first time.
The president of this year’s UN-organised summit, Sultan Al Jaber of the UAE, brokered an agreement that was strong enough for the US and the EU on the need to sharply curb the use of fossil fuels while keeping Saudi Arabia and other oil producers on board.
The final agreement calls for countries to phase out fossil fuels from their energy systems in a swift and orderly fashion, which helped convince sceptics. The agreement also calls for countries to contribute to the global transition effort – rather than explicitly forcing the transition on their own.
The so-called “UAE Consensus” ends the hottest year on record, which led to droughts and devastating wildfires. Al Jaber, who’s also chief executive officer of Abu Dhabi National Oil Co, noted:
“Together we have confronted the realities and sent the world in the right direction.”
Read more HERE

#world news#world politics#news#current events#cop28#cop28 climate summit#cop28climateconference#climate catastrophe#climate emergency#fossil fuels#global warming#climate change#cop 28#net zero#climate crisis#climate action#climate emissions#emissions reduction#carbon emissions#co2 emissions#greenhouse gas emissions#fossil fighters#oil and gas#crude oil#natural gas
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
#COP28#Indian Minister#Climate Talks#Equity#UN Negotiations#Global Climate Action#Developing Country#Energy-related Emissions#World's Third-biggest Emitting Country#China#US#COP28 Summit#Dubai#Fossil Fuel Use#Fossil Fuels#Wealthy Countries#Climate-warming Emissions#Industrial Revolution#Climate Justice#Bhupender Yadav#Narendra Modi#COP33 Talks#2028#Pramod Thomas#December 10#2023#India#Environment Minister#Impasse#Climate Summit
0 notes
Text
#Hussein Arnous#Syria#Anwar Mohammed Gargash#United Arab Emirates#UAE#Global Action Climate Summit#COP28#COP28 Climate Summit#climate change#climate
1 note
·
View note
Text
Formula 1, Sportswashing and Greenwashing a Genocide ... in other words, just an ordinary day in baku

As the final Formula 1 Grand Prix is set to take place tomorrow in baku, azerbaijan, I find it impossible to remain silent. The world is gearing up for what’s supposed to be an exciting event but behind the gleaming lights of the racetrack, there’s a much darker story that demands attention: the ethnic cleansing of Artsakh and azerbaijan’s ongoing brutal actions against Armenians.
azerbaijan’s history of oppression toward the Armenian people is not a secret. The forced displacement of Armenians from their ancestral lands, the violent campaign of ethnic cleansing in Artsakh, and the inhumane imprisonment and torture of Armenian captives in baku are undeniable facts. The world has remained shockingly quiet as over 200 Armenians languish in azerbaijani prisons, subjected to treatment that violates every principle of human rights.
One of the most glaring symbols of azerbaijan’s hatred toward Armenians is the Genocide Theme Park in baku, a chilling place that mocks the pain and suffering of an entire people. This is not just an internal issue; it’s an attack on humanity. But instead of confronting azerbaijan’s actions, the world is endorsing them.
These atrocities are certainly not limited to the government and the officials; the indescribable hatred has extended over to the people as well - take a glimpse into the azeri society
Now, let's imagine that you were fortunate enough to watch the F1 Grand Prix live in baku. How would you feel knowing that the azerbaijani person sitting next to you might be one of the many who were selling beheaded bodies of Armenian children on Facebook? Or perhaps they took their children to the Genocide Park and photographed them pretending to choke the statues of Armenian soldiers?
azerbaijan is not only hosting the Formula 1 Grand Prix but is also set to host COP29, a global climate summit. These events are being used to greenwash and sportwash the regime’s crimes.
How can we watch Formula 1 without acknowledging that the very ground this race is held on is soaked in the suffering of Armenians? How can we cheer for a spectacle when the cries of the oppressed go unheard?
This is not a political issue; it’s a matter of basic human decency. While the world enjoys the race, we must not forget the injustices happening in the shadows. Formula 1 should be about fairness and excellence. But in azerbaijan, it’s about something far more sinister—using sport to hide atrocities.
So, as you watch the Grand Prix in baku, remember the Armenian lives shattered by violence, hatred and silence. Let’s refuse to let sports and international events become tools for erasing history and ignoring the suffering of innocent people.
BREAK THE CHAIN OF IGNORANCE:
Share Information: use social media platforms like Tumblr, Instagram, X, Facebook and others to share articles, videos, and testimonies about the atrocities being committed by azerbaijan. The more people know, the harder it becomes to ignore.
Engage in Dialogue: talk to friends, family, and colleagues about the situation in azerbaijan and encourage others to take action too.
Support Armenian Communities: donate to/support organizations helping displaced Armenians and those impacted by the conflict in Artsakh. Even small contributions can go a long way in providing humanitarian aid.
Artsakh Relocation Project
All For Armenia
TAKE ACTION by adding your name to THE LIST of supporters.
Remember that this is not a political issue; it’s a matter of basic human decency.
#break the chain of ignorance#azeri crimes#baku#f1#f1 grand prix#f1 grand prix baku#genocide#armenia#turkish crimes#armenian genocide#artsakh is armenia#f1 x reader#formula 1#nobel prize#nobel peace prize#oscar piastri#max verstappen#lewis hamilton#franco colapinto#azerbaijan gp 2024#baku gp 2024#carlos sainz
310 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here’s Where Kamala Harris Stands on Climate
She pursued polluters as attorney general in California and later staked out bold positions as a senator, including sponsorship of the Green New Deal.
By Lisa Friedman
The New York Times
July 22, 2024
Vice President Kamala Harris has for years made the environment a top concern, from prosecuting polluters as California’s attorney general to sponsoring the Green New Deal as a senator to casting the tiebreaking vote as vice president for the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act, the largest climate investment in United States history.
As she runs for the White House, Ms. Harris is widely expected to try to protect the climate achievements of the Biden administration, a position that could resonate with voters during a summer of record heat. A clear majority of Americans, 65 percent, wants the country to focus on increasing solar, wind and other renewable energy and not fossil fuels, according to a May survey by the Pew Research Center.
Last year, Ms. Harris flew to the United Nations global climate summit in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, where she told world leaders that “the urgency of this moment is clear. The clock is no longer just ticking, it is banging. And we must make up for lost time.”
That was a subtle reference to former President Donald J. Trump, who made the United States the first and only country to withdraw from the global Paris Agreement to limit greenhouse gas emissions. (The United States subsequently rejoined under President Biden.) The Republican nominee in the current race for the White House, Mr. Trump has indicated that he would again pull back from the global fight against climate change if he is elected in November.
“Around the world, there are those who seek to slow or stop our progress, leaders who deny climate science, delay climate action, and spread misinformation,” Ms. Harris said at the summit. “In the face of their resistance and in the context of this moment, we must do more.”
Republicans have targeted the Inflation Reduction Act, promising to overturn it if they win control of Congress and the White House. That law pumps more than $370 billion over 10 years into wind, solar, batteries and electric vehicles. It is designed to help the country move away from fossil fuels, the burning of which is driving up global temperatures. At their convention last week, Republicans promised to halt any transition away from oil, gas and coal, and to promote more fossil fuel development.
Asked if Ms. Harris would pursue the policies she supported as a senator, like the Green New Deal, her climate adviser, Ike Irby, said she would focus on implementing the Inflation Reduction Act, which she helped to pass.
“She will fight every day for all Americans to have access to clean air, clean water, and a healthy environment,” Gina McCarthy, who served as national climate adviser under Mr. Biden, said in a statement Sunday. “Vice President Harris would kick ass against Trump.”
The vice president incorporated climate change into foreign relations, holding a round table in Bangkok to connect environmental activists with clean energy experts and starting a partnership with Caribbean countries to address climate change.
As a senator from California, the state that is at the forefront of climate policy, Ms. Harris promoted electrifying school buses to reduce greenhouse gases and to cut children's exposure to diesel engine pollution. She also supported efforts to replace lead water pipes and promoted measures to help agriculture become more resilient to drought.
But she also took positions far to the left of Mr. Biden on climate change.
She was an original co-sponsor of the Green New Deal, a nonbinding resolution supported by liberal Democrats that called for the United States to transition to 100 percent clean energy within a decade while providing people with job guarantees and “high-quality health care.” The measure never got out of committee.
When Ms. Harris ran for president in 2020, her climate plan called for a $10 trillion increase in spending over a decade as well as a price on carbon, with a dividend that would have been returned directly to households. Economists have said that a carbon tax would be the most effective way to get industries to reduce their pollution.
She also favored a ban on hydraulic fracturing, known as fracking, which Mr. Biden said he opposed. Fracking is a technique that injects water and chemicals underground at high pressure to extract oil or gas that is otherwise difficult to access. Environmentalists say it pollutes the air and groundwater. California regulators have taken steps to ban fracking.
As California’s attorney general, Ms. Harris challenged federal approvals of offshore fracking along the California coast. She investigated whether Exxon Mobil lied to the public and its shareholders about the risks to its business from climate change, and whether such actions could amount to securities fraud and violations of environmental laws, but the case did not result in a prosecution.
She would later claim during a Democratic forum on climate change in 2019 that she had sued Exxon Mobil, which fact checkers reported as untrue. She did obtain settlements from other oil and gas companies, including Chevron and BP, over allegations that they violated pollution laws.
In 2019, Ms. Harris joined Representative Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez, Democrat of New York, to introduce legislation that would require the government to consider the impact of environmental regulations or laws on low-income communities, which tend to be disproportionately vulnerable to climate disruption because they are often located in flood zones, near highways, power plants and polluted land.
As vice president, Ms. Harris does not use the phrase “Green New Deal,” which has been relentlessly mocked by conservatives, who use it as shorthand for all climate and clean energy policies.
Her Republican opponents are not likely to let her forget it, though.
“During her ill-fated and short-lived 2020 presidential campaign, Harris was an early and enthusiastic supporter of the Green New Deal and called for so-called ‘carbon neutrality’ by 2030, all of it with a $10 trillion price tag,” Daniel Turner, executive director of Power The Future, a group that advocates for fossil fuels, said in a statement.
He called Ms. Harris part of the “climate cult that calls the shots in today’s Democratic Party.”
Evergreen Action, an environmental group, endorsed Ms. Harris on Sunday. The youth-led Sunrise Movement, which last week called on Mr. Biden to end his bid for re-election, praised his decision to step away. The group did not directly endorse Ms. Harris but said any replacement must “put forth a bold vision to tackle the climate crisis and fight for our generation.”
Other organizations said they were holding back an endorsement until the Democratic nomination process is completed.
Article share from The New York Times.
#kamala harris#2024 presidential race#environment#green new deal#net zero#sunrise movement#fossil fuels#big oil#climate change#climate crisis
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
The accomplishments of Joe Biden during his presidency
Joe Biden, the 46th President of the United States, assumed office at a pivotal moment in history, facing a myriad of challenges ranging from a global pandemic to economic uncertainty and social unrest.
Throughout his presidency, President Biden has pursued an ambitious agenda aimed at addressing these pressing issues and advancing key policy priorities. In this essay, we will examine some of the notable accomplishments of Joe Biden during his time in office and the impact of his leadership on the nation.
One of the most significant accomplishments of President Biden during his presidency has been his administration's response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Upon taking office, President Biden made the pandemic a top priority and swiftly implemented a national strategy to combat the spread of the virus and accelerate the vaccination campaign.
Under his leadership, the administration successfully exceeded its initial goal of administering 100 million vaccine doses within the first 100 days, ultimately surpassing 200 million doses. This aggressive vaccination effort has been instrumental in curbing the spread of the virus and has contributed to a significant reduction in COVID-19 cases and deaths across the country.
In addition to his focus on public health, President Biden has made substantial strides in revitalizing the American economy in the wake of the pandemic. The administration's American Rescue Plan, a comprehensive COVID-19 relief package, provided much-needed financial assistance to individuals, families, and businesses impacted by the economic downturn. The plan included direct stimulus payments to Americans, extended unemployment benefits, support for small businesses, and funding for vaccine distribution and testing.
President Biden's economic agenda has also centered on job creation and infrastructure investment, culminating in the passage of the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, a historic legislation that allocates substantial funding for modernizing the nation's infrastructure, creating millions of jobs, and bolstering economic growth. Furthermore, President Biden has been a vocal advocate for advancing racial equity and social justice in the United States. His administration has taken concrete steps to address systemic inequalities and promote inclusivity, including the signing of executive orders to combat discrimination, promote fair housing, and strengthen tribal sovereignty.
Additionally, President Biden signed into law the Juneteenth National Independence Day Act, establishing Juneteenth as a federal holiday to commemorate the end of slavery in the United States. These actions underscore the administration's commitment to confronting the legacy of racism and fostering a more equitable society for all Americans.
Moreover, President Biden has demonstrated a strong commitment to combating climate change and advancing environmental sustainability.
His administration rejoined the Paris Agreement on climate change, signaling a renewed dedication to global cooperation in addressing the climate crisis. In November 2021, President Biden convened a virtual Leaders Summit on Climate, bringing together world leaders to discuss ambitious measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and accelerate the transition to clean energy.
Additionally, the administration has unveiled a comprehensive plan to invest in clean energy infrastructure, promote energy efficiency, and prioritize environmental justice, aiming to position the United States as a global leader in the fight against climate change.
In the realm of foreign policy, President Biden has sought to reassert American leadership on the world stage and rebuild alliances with international partners. His administration has prioritized diplomacy and multilateral engagement, working to address global challenges such as nuclear proliferation, cybersecurity threats, and human rights abuses.
President Biden has reaffirmed the United States' commitment to NATO and other key alliances, signaling a departure from the isolationist policies of the previous administration. His approach to foreign affairs has emphasized the importance of collaboration and collective action in tackling shared global concerns, fostering a more cohesive and cooperative international order. Furthermore,
President Biden has been a steadfast proponent of expanding access to affordable healthcare and strengthening the Affordable Care Act. His administration has taken steps to bolster the ACA, including increasing enrollment outreach, expanding coverage options, and lowering healthcare costs for millions of Americans.
President Biden has also championed efforts to address mental health challenges and substance abuse disorders, recognizing the critical importance of mental and behavioral health in overall well-being.
In conclusion, President Joe Biden has achieved a range of significant accomplishments during his tenure in office, from his swift and effective response to the COVID-19 pandemic to his ambitious efforts to revitalize the economy, promote racial equity, combat climate change, and reinvigorate America's role in global affairs.
His leadership has been marked by a steadfast commitment to addressing pressing domestic and international challenges and advancing a progressive policy agenda aimed at fostering a more equitable, resilient, and prosperous future for the nation. As his presidency continues to unfold, the enduring impact of his accomplishments is likely to shape the trajectory of the United States for years to come, leaving a lasting imprint on the fabric of American society and the global community.
#politics#donald trump#joe biden#potus#scotus#heritage foundation#trump#democracy#democrats#republicans#maga morons#maga cult#maga#usa#us news#white house#biden#the united states#usa politics
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
The FAO roadmap was published at the Cop28 climate summit in December and accepts that diets “absolutely must [change] for human and planetary health”. But its 120 actions do not include reducing meat and dairy consumption in nations where most people already eat unhealthy amounts. Instead, many of the FAO’s recommendations are to intensify the efficiency of animal farming techniques.
“It’s very striking: the FAO doesn’t include one of the clearest interventions that would help meet both environmental and health targets,” said Cleo Verkuijl, of the Stockholm Environment Institute US and one of the eight authors of the commentary from academic institutions in the US, the Netherlands and Brazil.
“Also really surprising is the fact that the FAO completely dismisses alternative proteins,” she said. These had been shown to have far smaller environmental impacts than conventional meat but the FAO claimed, without providing evidence, that plant-based meats had “nutritional deficiencies”, the experts said.
A report from the UN Environment Programme (Unep), published in December, said “alternatives to animal products such as meat and dairy may contribute to significantly reducing the environmental footprint of the current global food system”.
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
In January 2020, Mexico made history as the first Latin American country to adopt a feminist foreign policy. Pioneered by Sweden six years earlier in 2014, feminist foreign policy (FFP) initially began as a niche effort in the Nordic region. For many years, Sweden stood alone on the global stage, emphasizing that its FFP focused on enhancing women’s “rights, resources, and representation” in the country’s diplomatic and development efforts worldwide. That effort was the result of the vision and leadership of Sweden’s foreign minister at the time, Margot Wallström, although there was widespread support for the policy across the government and it was continued by subsequent ministers.
It would be another three years before other nations followed suit: In 2017, Canada announced a Feminist International Assistance Policy. At the end of 2018, Luxembourg’s new coalition government committed to developing a FFP in their coalition agreement. And in 2019, Mexico and France pledged to co-host a major women’s rights anniversary conference in 2021 while beginning to explore the development of feminist foreign policies simultaneously.
I had an inside view on that process having convened the existing FFP governments and numerous international experts just before Mexico’s announcement. Together, we developed a global definition and framework for FFP. As I wrote for this magazine in January 2020, this approach was largely followed by the Mexican policy. The goals for Mexico in adopting an FFP were to increase the rights of women and LGBTQ+ individuals on the world stage, diversify their diplomatic corps, boost resourcing for gender equality issues, and ensure that internal policies within the foreign ministry aligned with this approach, including a zero-tolerance policy toward gender-based harassment.
Now, under the leadership of a new female foreign minister, Alicia Bárcena, and following the election of Mexico’s first woman president, Claudia Sheinbaum, I was excited to travel to Mexico City in July as it hit another milestone: becoming the first country outside Europe to host the annual ministerial-level conference on FFP. It was an opportunity for me to take stock of what Mexico has achieved since it adopted an FFP, and to see what progress it has made toward its goals.
Initially convened by Germany’s Annalena Baerbock in 2022 and then by the Dutch last year, Mexico took a unique approach to the conference by focusing it on a specific policy issue—in this case, the forthcoming Summit of the Future. This conference, taking place at the U.N. General Assembly in September, aims to begin laying the groundwork for the successor goals to the Sustainable Development Goals framework. It is already a fraught and polarized process, and progressive leadership is sorely needed.
Last week provided clear evidence that Mexico is making progress in modeling that leadership—including in consistently advocating for progressive language in often contentious international multilateral negotiations, such as the United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP). For example, in its interventions at the latest COP, Mexico placed human rights, intersectionality and gender equity at the heart of climate action and recognized the role of women environmental defenders and Indigenous women in a just transition.
“Mexico is often a lone voice in holding the line on critical human rights, Indigenous rights and gender equality language at the climate talks, even among the FFP countries,” said Bridget Burns, the executive director of the Women’s Environment and Development Organization who has spent the last 15 years organizing women’s rights activists in climate negotiations and attended the July conference to speak on the sustainable development panel.
Mexico’s decision to link their hosting of the FFP Conference to the Summit of the Future—as evidenced in an outcome document they published and are circulating for signature ahead of the General Assembly’s high-level week in September—challenged FFP governments to engage a feminist approach in mainstream foreign policy dialogue, not just in gender-related discussions like the U.N. Commission on the Status of Women. “The Summit of the Future aspires to a better tomorrow, but lofty goals won’t translate to real systemic change without feminist civil society,” said Sehnaz Kiymaz, senior coordinator of the Women’s Major Group.
On the multilateral front, Mexico has shown leadership by co-chairing the Feminist Foreign Policy Plus Group (FFP+) at the UN, alongside Spain. This body held the first ministerial-level meeting on FFP at the General Assembly last year and adopted the world’s first political declaration on FFP. Signed by 18 countries, governments pledged “to take feminist, intersectional and gender-transformative approaches to our foreign policies,” and outlined six areas for action in this regard. This was the first time FFP countries publicly pledged to work together as a group to address pressing global challenges through a feminist approach. While smaller subsets of this cohort have worked together multilaterally to condemn women’s rights rollbacks in Afghanistan or in support of an international legal framework on the right to care and be cared for, the first big test of this more systematic approach will be the forthcoming Summit of the Future, where feminists have been advocating for gender to be referenced as a cross-cutting priority.
Mexico has also recently ratified two international instruments to directly benefit women: Convention 189 of the International Labor Organization (ILO) on domestic workers and Convention 190 of the ILO on violence and harassment in the workplace. Under the mantle of its FFP, Mexico has championed the importance of care work in the advancement of women’s rights and countries’ development at the U.N. Human Rights Council and at the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean through the Global Alliance for Care Work.
While international women’s rights activists at the conference largely gave positive feedback on Mexico’s track record, the response from Mexican civil society was more critical. Activists organized a side event to present their more skeptical view of Mexican FFP. María Paulina Rivera Chávez, a member of the Mexican coalition and an organizer of the event, argued a conference could only go so far. “It is fundamental to decenter the state, understanding that feminist foreign policies must be horizontal,” she said.
A major theme of that side event and of Mexican activists’ interventions in the official ministerial conference was the incongruence of the Mexican government’s leadership on feminist approaches internationally while women’s human rights at home have suffered. Such criticisms of the Andrés Manuel López Obrador government are not unfounded. In one particularly troubling interview a few years ago, he suggested that Mexico’s high rate of femicide—11 women are murdered daily, with rates on the rise compared to other crimes—was merely a false provocation by his political opponents. Negative biases against women are pervasive in Mexico, with 90 percent of the population holding such biases.
Mexico has made strides in improving gender equality in other areas, however. Women now make up half of the Mexican legislature and have been appointed to lead high-level institutions, such as the Supreme Court, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, and the Central Bank, with cascading positive effects on gender equality. Bárcena, for instance, clearly asserted from her first speech on the job that Mexico’s FFP would remain a top priority. This is no accident. At the federal level, significant efforts have been made to enforce gender parity laws and implement more than 80 percent of the legal frameworks promoting, enforcing and monitoring gender equality as stipulated by international benchmarks. Mexican women have also seen some improvements in maternal mortality rates, access to internet services, and protections to the right to abortion, with numerous national commitments to improve gender equality, such as measures to alleviate the burden of care on women.
But while there has been an increase in the number of women in the legislature and government positions, women from Indigenous, Afro-descendent, and working-class backgrounds continue to be underrepresented in political roles. And there has been a steady increase over the last decade in femicides, disappearances and sexual violence which Mexican feminist organizations and international actors have found are directly linked to the militarization of law enforcement under the guise of Mexico’s war on drugs and organized crime.
Additional criticisms of the Mexican FFP itself include the foreign ministry’s insularity and reluctance to engage with Mexican feminist activists in the development and implementation of its FFP. There was also a hesitation by the previous foreign ministry leadership to collaborate with Inmujeres, Mexico’s gender ministry, preferring to keep control of the FFP within the foreign ministry alone. It is not uncommon for gender ministries to be excluded in foreign policymaking as they are often perceived as lacking the necessary expertise or authority on foreign policy. However, Inmujeres is an exception in this regard and the criticism was valid. This was on my mind as I participated in the conference last month, and straight out of the gate I could observe a clear departure from the past approach under Bárcena’s leadership: The foreign ministry officially partnered with Inmujeres to co-host the conference, and the heads of both agencies were equally prominent voices throughout the three-day event. Similarly, the foreign ministry also made efforts to engage Mexican feminist civil society in conference planning, inviting civil society to a consultation day in the weeks leading up to the conference.
Following the right-wing electoral successes and likely abandonment of FFP in countries like Sweden, Argentina, and potentially the Netherlands, the success of a Mexican model of FFP is all the more important. Mexican activists I spoke with expressed optimism about Bárcena’s leadership, which they had not extended to her predecessor. Certainly, there is some cynicism about whether Mexico’s next president, a woman, will be any better on the issue of femicide than her mentor and predecessor, López Obrador, but there is some room for hope. If the leadership of a female foreign minister like Bárcena has been more effective in mobilizing political and convening power behind FFP, there’s potential that Sheinbaum will also show more interest than her predecessor.
While Mexican civil society has critiqued that Sheinbaum did not present a plan on how she would continue and improve the country’s FFP and repair the government’s relationship with feminist civil society, Sheinbaum’s plan—entitled 100 Pasos Para La Transformación—takes a human rights-based approach to gender equality. This is promising, because political approaches, which are more common, tend to reduce the human rights of women, girls, and gender-diverse persons as a means to an end, such as better economic, education, or health outcomes. The plan proposes measures to alleviate the care burden on women, safeguard sexual and reproductive health and rights, protect LGBTQ+ communities, promote gender parity in cabinets, improve land rights for rural women, reduce femicides, and more.
That Sheinbaum has not explicitly addressed the importance of Mexico’s FFP is not necessarily surprising. Most feminist and women’s rights organizations are understandably more focused on issues within their own borders, and foreign policy rarely drives political power and the focus of the electorate. Discussion of feminist foreign policy is thus typically the domain of the foreign minister and in some cases other relevant ministers—such as international development in Germany, or the trade ministry in Sweden under its previous government. (Canada’s Justin Trudeau stands out as a rare exception, having championed feminism and Canada’s feminist approach to policymaking at the Group of Seven and international gender equality forums throughout his tenure as prime minister.)
But even without top-down leadership from a president, savvy officials within the Mexican foreign and gender ministries are using FFP to make progress. While there has not yet been a public accounting of the progress made in implementing FFP, the clear leadership Mexico is demonstrating on the world stage in key negotiations, its successful conference, and the anticipated new government set the stage for Mexico to boldly advance its FFP. It will serve as a valuable example to the world.
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Climate anxiety means different things to different income groups. At the bottom, it means fear of heat and floods. At the top, it means fear of increasingly desperate people. Billionaires often live in protective bubbles maintained at a considerable cost in dollars and emissions. Some are preparing for “the event”, with plans for doomsday bunkers in New Zealand, Nevada and other remote areas. Others blast off the planet in private rockets and talk of colonising space. Instead of making every effort to reduce emissions, the rich increase their carbon footprint by putting more distance between themselves and the masses.
The Oxfam report reveals that the decision-making classes who will dominate at Cop28 – senior politicians including US senators, British ministers and European commissioners – are also in the top 1% of income earners. Corporate CEOs, whose lobbyists also flock to Cop summits, are often wealthier and more heavily invested in carbon assets. Boardroom share options and bonus structures have created an incentive for oil company executives to resist climate action. Instead, they have successfully pushed for expansion of fossil fuel production. Dario Kenner, the author of Carbon Inequality, has identified what he calls a “polluter elite”: anyone with a net worth over $1m who reinforces the use of fossil fuel technologies through their high carbon consumption, investments in polluting companies and, most importantly, political influence. “The polluter elite have blocked an alternative history where the destruction of extreme weather events and air pollution could have been reduced,” he told the Guardian.
The international climate negotiating process has failed to keep pace with the growing power of the super-rich. Thirty-one years ago, when the world first came together to tackle climate and biodiversity problems at the Rio de Janeiro Earth summit, there was optimism for a solution on behalf of billions of humans and the countless other forms of life on Earth. Since then, the opposite has happened. Governments remain deeply divided, 60% more emissions are being pumped into the atmosphere and more money, carbon and power is being concentrated in ever fewer hands.
The solution to all this is complex but also very simple. Many believe that the key lies in politicians wresting back control of the climate issue with strong legislation and policy. Oxfam is calling for a wealth tax, and a windfall tax on corporations based on the “polluter pays” principle, placing the highest burden on those most responsible and most able to pay.
“We need a political discourse that is class conscious, that recognises that the rich and capitalism are the major drivers of the climate crisis,” said Jason Hickel, an economic anthropologist at the London School of Economics and the author of The Divide: A Brief Guide to Global Inequality and its Solutions. “This is about bringing production – and provisioning systems and energy systems – under democratic control.”
72 notes
·
View notes
Text

""This is directed at world leaders," said Mitzi Jonelle Tan, a climate activist with youth movement Fridays for Future in Manila, the Philippines.
"The fossil fuel industry's time is up. We need a just transition, and we need to phase out the fossil fuels causing the destruction of our environment," she told Reuters.
"We're taking to the streets to demand that African leaders phase out on fossil fuels and focus on investing in community-led renewable energy, to meet the energy demand for the 600 million Africans who do not have access to electricity," said Eric Njuguna, a climate activist based in Nairobi, Kenya.
Organisers said they would call on governments to immediately end subsidies for oil and gas and to cancel any plans for expanding production.
Governments spent a record-high $7 trillion in subsidies to oil, gas and coal last year, according to an IMF analysis
The demonstrations take place two months before this year's U.N. COP28 climate summit, where more than 80 countries plan to push for a global agreement to gradually phase out coal, oil and gas.
[...]A U.N. report last week warned that the world was on a dangerous track toward severe global warming, and said more action was needed on all fronts, including a drastic drop in coal-fuelled power use by 2030.
The report also urged a massive boost in financial investment to developing countries for both clean energy and measures to adapt to rising heat, worsening storms and other consequences of the warming climate, the U.N. said.
Use the link to find a protest near you

#climate change#current events#global warming#lgbt#direct action#leftist#capitalism#ndn#indigenous#biden#trump#important#boost#things you can do#how to help#how to get involved#global action#global protests#climate strike#liberals#democrats#leftists#anarchists#socialism#greta thunberg#fridays for future#activists#nature#witchcraft#seattle
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
COP28 draft agreement omits plan to phase out fossil fuels | ABC News
youtube
https://climate.nasa.gov/


#humza yousaf branded hypocrite for jetting to cop28 in dubai while his government misses emissions targets#cop28 climate summit#taoiseach leo varadkar reveals at cop28#cop28climateconference#cop28#ecology#earth#global warming#climate change#climate crisis#climate action#climate emergency#climate catastrophe#environmentalism#environmental activism#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#environmental#environment#capitalism#fascism#pollution
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
UAE president to establish $30bn fund to bridge climate finance gap
Sheikh Mohammed Bin Zayed Al Nahyan, President of the United Arab Emirates, which is hosting the COP28 climate summit, announced the establishment of a $30 billion fund for global climate solutions on Friday.
The fund, dubbed ALTÉRRA, will allocate $25 billion for climate strategies and $5 billion to attract $250 billion in investments by the end of the decade, according to the COP28 chairman’s statement.
In a statement, ALTÉRRA, in collaboration with global asset managers BlackRock, Brookfield and TPG, announced that it has committed $6.5 billion in climate change funds for global investments, including the Global South.
The programme “aims to steer private markets towards climate investment and focus on transforming emerging markets and developing economies, where traditional investment has been lacking due to the higher perceived risks across those geographies.”
Learn more HERE

#world news#world politics#news#uae#united arab emirates#ALTERRA#cop28#cop28 climate summit#cop28climateconference#cop28uae#fossil fuels#climate change#climate crisis#global warming#climate and environment#cop 28#climate action#climate summit#climate emergency#greenhouse gas emissions#greenhouse
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from this story from Mongabay Environmental News:
A NASA study analyzed the future action of six climate variables in all the world’s regions — air temperature, precipitation, relative humidity, short- and long wave solar radiation and wind speed — if Earth’s average temperature reaches 2° Celsius (3.6° Fahrenheit) above preindustrial levels, which could occur by 2040 if emissions keep rising at current rates.
The authors used advanced statistical techniques to downscale climate models at a resolution eight times greater than most previous models. This allows for identification of climate variations on a daily basis across the world, something essential since climate impacts unfold gradually, rather than as upheavals.
The study found that the Amazon will be the area with the greatest reduction in relative humidity. An analysis by the Brazilian space agency INPE showed that some parts of this rainforest biome have already reached maximum temperatures of more than 3°C (5.4°F) over 1960 levels.
Regardless of warnings from science and Indigenous peoples of the existential threat posed by climate change, the world’s largest fossil fuel producers, largely with government consent, plan to further expand fossil fuel exploration, says a U.N. report. That’s despite a COP28 climate summit deal “transitioning away from fossil fuels.”
In view of the current nonstop rise in greenhouse gas emissions responsible for intensifying climate change, NASA researchers this year posed two key questions: When will the planet’s temperature likely reach an annual average of 2° Celsius (3.6° Fahrenheit) above preindustrial levels? And what will the global climate look like in great detail all over the world at that temperature?
Disturbingly, their findings indicate that a 2°C increase could be reached between 2041 and 2044 (under higher and lower emission scenarios, respectively) in comparison with the preindustrial period (1850-1900). The planet is currently at 1.15°C (2.07°F) above 19th century levels, with most of this warming occurring since 1975.
A rise above 2°C could put Earth on track for catastrophic climate change impacts, according to the 2023 report by the U.N. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
To investigate the potential multiple effects of a 2°C planet, scientists at the NASA Earth eXchange analyzed the projections of 35 of the world’s leading climate models with a very high resolution that gives results for areas of just 25 square kilometers (9.6 square miles). Many climate models currently use a far coarser resolution of 200 km2 (77 mi2). NEX fine-scaling allowed for estimated climate impact projections on both a local and regional scale, and even on a daily basis.
“If merged into a monthly average, a few days projected to be dangerously hot and humid could get lost in the numbers, concealing the risk for human lives,” explained study lead author Taejin Park, a researcher at NASA’s Ames Research Center. “Finer-scale information can help identify variations in projected climate change that may be overlooked, so leading to significant impacts on planning and decision-making.”

In the 2040s, global mean near-surface air temperature over land is projected to increase 2.33-2.79°C (4.2-5°F), compared with the baseline period 1950–79. Greenland, Alaska, Canada, Northern Europe and Asia are projected to reach above a 3°C (5.4°F) increase in annual temperature. Image courtesy of NASA/Taejin Park.

If NASA’s projections are correct, a precipitation increase will occur over much of the northern hemisphere, especially in southeastern Greenland, but also in western and eastern Africa and South Asia, among other places. The Amazon Basin, on the other hand, will see a major decrease in precipitation. Dry regions such as Southern Africa, the North American Southwest and the Mediterranean also could see a precipitation decline. Image courtesy of NASA/Taejin Park.

After 2040, most regions of the world are expected to have more days with extreme heat stress, with heat especially pronounced in the Amazon, Central and Eastern North America, the Mediterranean and Eastern and Northern Asia. Heat stress can be devastating to wildlife, plants and of course, people. Image courtesy of NASA/Taejin Park.

Under a moderate emission scenario, Western and Central North America, the Amazon, the Mediterranean and South Africa will be at higher risk of fires in the 2040s, compared with 1950-79. Image courtesy of NASA/Taejin Park.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
WASHINGTON ― President Joe Biden is hiking tariffs on electric vehicles, semiconductors and several other goods imported from China, escalating a trade war between the two world's largest economies as the U.S. accuses Chinese competitors of unfair practices in industries the U.S. is trying to grow.
The moves, which come amid rising tensions between the U.S. and China, are designed to protect American industries in clean energy that the administration has targeted with major investments to try to catch up with China.
Other goods from China slapped with higher tariffs include solar cells, batteries, battery materials, cranes used at ports, and certain medical supplies, as well as steel and aluminum imported from China.
The Biden administration has for months accused China of unfair trade practices by flooding the global markets with goods at artificially low prices, putting U.S. manufacturing of electric vehicles, microchips and other goods at a steep disadvantage.
Lael Brainard, director of the National Economic Council in the White House, said the objective of the higher tariffs is to "make sure that historic investments in jobs spurred by President Biden's actions are not undercut by a flood of unfairly underpriced exports from China."
Biden, whose administration reviewed the tariff rates over the past year, is keeping intact more than $300 billion in tariffs imposed by former President Donald Trump. Biden will announce the new increases during a White House speech Tuesday.
Some of the tariff hikes include:
Electric vehicles from China: from 25% to 100% beginning this year.
Semiconductors from China: from 25% to 50% by 2025.
Lithium-ion batteries from China used in electric vehicles: from 7.5% to 25% this year.
Solar cells imported from China: from 25% to 50% this year.
Steel and aluminum products: form 0%-7.5% to 25% this year.
Ship-to-shore container cranes imported from China: from zero to 25% this year
Hospital syringes and needles made in China: from zero to 50% this year.
China pushed back strongly against the higher tariffs.
Wang Wenbin, a spokesman for the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs, called the moves "self-defeating" and against the consensus reached last November by Biden and Chinese President Jinping Xi during a summit in San Francisco.
"More importantly, it will harm the world’s green economic transition and climate action," Wenbin said. "We urge the U.S. to stop repairing and digging up the road at the same time, so to speak, and create enabling conditions for China-U.S. climate cooperation and global green transition."
Another ministry spokesman last Friday said, "China will take all necessary measures to defend its rights and interests."
The moves come as Biden is courting the support of working-class voters in Midwest battleground states including Michigan, the center of the U.S. auto industry, for the November election.
Biden is borrowing from the trade playbook of Trump, the Republican presumptive nominee, who routinely raised tariffs on Chinese goods during his four years in office.
"Where have you been for the last three and a half years? They should have done it a long time ago," Trump said Biden's tariffs, speaking outside a New York courtroom, where is attending day 17 of his hush-money trial. "But they've also got to do it on other vehicles, and they have to do it on a lot of other products. Because China's eating our lunch right now."
Biden has sought to differentiate his tariff approach with his predecessor's plan for new tariffs. Biden last month slammed Trump's campaign proposals as "across-the-board tariffs on all imports from all countries that could badly hurt American consumers." Trump has proposed a 60% or more tariff on all Chinese imports and warned the U.S. auto industry will face a "bloodbath" if he loses his election in November.
Biden has staked his economic agenda on reigniting a U.S. manufacturing boom centered on electric vehicles and clean energy.
The Biden administration says it has helped spur more than $860 billion in private investment through legislation passed during Biden's first two years in office that incentivized the manufacturing of electric vehicles, clean-energy products, microchips and other investments.
Brainard said the tariff hikes will "ensure that American businesses and workers have the opportunity to compete on a level playing field in industries that are vital to our future such as clean energy and semiconductors."
Biden called for the tripling of tariffs on steel and aluminum imports from China during a campaign speech last month before the United Steelworkers union in Pittsburgh.
Each of the tariff increases reflect the recommendations of Biden's United States Trade Representative, Katherine Tai, who evaluated the rates as part of a mandatory four-year review.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
By Olivia Rosane
Common Dreams
Dec. 19, 2023
"This COP has once again proven that the COP processes are not working in our favor," the climate activist said.
Swedish climate activist Greta Thunberg called the outcome of the 28th United Change Climate Conference—which agreed to "transitioning away from fossil fuels" but stopped short of the phaseout demanded by civil society and climate-vulnerable nations—a "betrayal and a stab in the back."
COP28 concluded in the United Arab Emirates on December 13. The outcome, also called the "UAE Consensus," marks the first time that fossil fuels have made it into the final text to emerge from a U.N. climate summit. While some are celebrating this milestone, Thunberg was not impressed.
"The final outcome of COP28 is not a 'historic win,'" she wrote on social media Friday. "It is yet another example of extremely vague and watered down texts full of loopholes that in no way is even close to being sufficient for staying within the 1.5°C limit and ensur[ing] climate justice."

Speaking to Reuters at a protest outside the Swedish parliament on Friday, Thunberg said the agreement was the "bare minimum" and rejected the idea that it was a "first step."
"We've already had first steps and they haven't led us anywhere," Thunberg said. "The emissions are still increasing. We are experiencing record highs."
She also questioned the validity of U.N. climate negotiations.
"This COP has once again proven that the COP processes are not working in our favor," she told Reuters. "They are not designed to solve the climate crisis. They are more working as an alibi for world leaders" to hide behind their signature on a document while continuing to do nothing.
"We need drastic immediate emission cuts and binding commitments from the largest contributors of the climate crisis to finance loss and damages, adaptation, and a just transition in the most affected areas."
Thunberg's remarks build on her criticism of COPs in recent years. She stopped attending the gatherings beginning with last year's COP27 in Sharm El Sheikh, Egypt, which she called an opportunity for "greenwashing, lying, and cheating," according to Euronews Green.
This year, she particularly criticized the fact that members of small island states were not in the room when the final deal was adopted.
Thunberg said this was "undemocratic" and "completely unacceptable."
"We cannot talk about climate justice when without having the most affected in the room," she told Reuters.
On her Friday social media thread, Thunberg outlined what she thought successful climate action would look like.
"We need drastic immediate emission cuts and binding commitments from the largest contributors of the climate crisis to finance loss and damages, adaptation, and a just transition in the most affected areas," she said.
Thunberg's remarks add to those of many other climate activists and scientists who have criticized the deal for falling short of ensuring the 1.5°C target, inadequately funding the renewable energy transition in the Global South, and allowing dangerous loopholes such as carbon capture and storage technology promoted by the fossil fuel industry as a way to keep pumping while promising to "abate" their emissions.
"Although the text mentions a transition away from fossil fuel energy systems in a just and equitable manner, the text is full of loopholes and false solutions on unproven and expensive technology like nuclear, abatement, carbon capture and storage, transitional fuels, etc.," Philippines climate activist Mitzi Jonelle Tan said, as Euronews Green reported.
The group Scientist Rebellion put out a statement Friday calling for a global movement to keep fossil fuels in the ground.

"The United Nations climate summit, hijacked by the fossil fuel cartel, has gifted a blank check to rich countries and Big Oil to kill one billion people and force billions more to flee their homes by 2100," the group wrote. "The so-called 'historic' outcome of COP28 fails to deliver the most basic and necessary measures which would have prevented societal and 'Earth systems' collapse, as outlined by the IPCC: eliminate fossil fuel subsidies and halt all new gas and oil projects."
Their statement concluded: "It is time to listen to the scientists, hundreds of whom have been driven out of their labs and into the streets to engage in civil disobedience: If we want to avoid condemning both this generation and all that follow to the worst outcomes of the climate crisis, we must all rise together in order to keep fossil fuels in the ground. The time is now."
Our work is licensed under Creative Commons (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0). Feel free to republish and share widely.
#cop28#fossil fuels#carbon capture and storage#greta thunberg#climate crisis#climate emergency#climate finance#climate justice#scientist rebellion
28 notes
·
View notes