#pp maria
Text
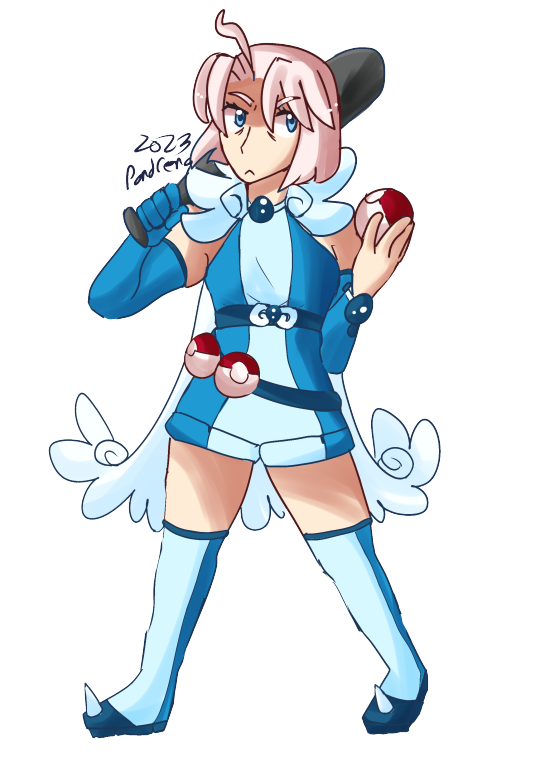








Happy October! Here's some Pokemon AU stuff. Thank you to Servantparent as always for the help with Allen's outfit.
Allen is fire, Nori is fighting, Maria is ghost, and Emi is dragon! Hopefully more will come, but I figured I'd pop these into a post.
Icons are from here.
28 notes
·
View notes
Text

6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pentiment's Complete Bibliography, with links to some hard-to-find items:
I've seen some people post screenshots of the game's bibliography, but I hadn't found a plain text version (which would be much easier to work from), so I put together a complete typed version - citation style irregularities included lol. I checked through the full list and found that only four of the forty sources can't be found easily through a search engine. One has no English translation and I'm not even close to fluent enough in German to be able to actually translate an academic article, so I can't help there. For the other three (a museum exhibit book, a master's thesis, and portions of a primary source that has not been entirely translated into English), I tracked down links to them, which are included with their entries on the list.
If you want to read one of the journal articles but can't access it due to paywalls, try out 12ft.io or the unpaywall browser extension (works on Firefox and most chromium browsers). If there's something you have interest in reading but can't track down, let me know, and I can try to help! I'm pretty good at finding things lmao
Okay, happy reading, love you bye
Beach, Alison I. Women as Scribes: Book Production and Monastic Reform in Twelfth-Century Bavaria. Cambridge Univeristy Press, 2004.
Berger, Jutta Maria. Die Geschichterder Gastfreundschaft im hochmittel alterlichen Monchtum: die Cistercienser. Akademie Verlag GmbH, 1999. [No translation found.]
Blickle, Peter. The Revolution of 1525. Translated by Thomas A. Brady, Jr. and H.C. Erik Midelfort. The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1985.
Brady, Thomas A., Jr. “Imperial Destinies: A New Biography of the Emperor Maximilian I.” The Journal of Modern History, vol 62, no. 2., 1990. pp.298-314.
Brandl, Rainer. “Art or Craft: Art and the Artist in Medieval Nuremberg.” Gothic and Renaissance Art in Nuremberg 1300-1550. The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 1986. [LINK]
Byars, Jana L., “Prostitutes and Prostitution in Late Medieval Bercelona.” Masters Theses. Western Michigan University, 1997. [LINK]
Cashion, Debra Taylor. “The Art of Nikolaus Glockendon: Imitation and Originality in the Art of Renaissance Germany.” Journal of Historians of Netherlandish Art, vol 2, no. 1-2, 2010.
de Hamel, Christopher. A History of Illuminated Manuscripts. Phaidon Press Limited, 1986.
Eco, Umberto. The Name of the Rose. Translated by William Weaver. Mariner Books, 2014.
Eco, Umberto. Baudolino. Translated by William Weaver. Mariner Books, 2003.
Fournier, Jacques. “The Inquisition Records of Jacques Fournier.” Translated by Nancy P. Stork. Jan Jose Univeristy, 2020. [LINK]
Geary, Patrick. “Humiliation of Saints.” In Saints and their cults: studies in religious sociology, folklore, and history. Edited by Stephen Wilson. Cambridge University Press, 1985. pp. 123-140
Harrington, Joel F. The Faithrul Executioner: Life and Death, Honor and Shame in the Turbulent Sixteenth Century. Farrar, Straus and Giroux, 2013.
Hertzka, Gottfired and Wighard Strehlow. Grosse Hildegard-Apotheke. Christiana-Verlag, 2017.
Hildegard von Bingen. Physica. Edited by Reiner Hildebrandt and Thomas Gloning. De Gruyter, 2010.
Julian of Norwich. Revelations of Divine Love. Translated by Barry Windeatt. Oxford Univeristy Press, 2015.
Karras, Ruth Mazo. Sexuality in Medieval Europe: Doing Unto Others. Routledge, 2017.
Kerr, Julie. Monastic Hospitality: The Benedictines in England, c.1070-c.1250. Boudell Press, 2007.
Kieckhefer, Richard. Forbidden rites: a necromancer’s manual of the fifteenth century. Sutton, 1997.
Kuemin, Beat and B. Ann Tlusty, The World of the Tavern: Public Houses in Early Modern Europe. Routledge, 2017.
Ilner, Thomas, et al. The Economy of Duerrnberg-Bei-Hallein: An Iron Age Salt-mining Center in the Austrian Alps. The Antiquaries Journal, vol 83, 2003. pp. 123-194
Lang, Benedek. Unlocked Books: Manuscripts of Learned Magic in the Medieval Libraries of Central Europe. The Pennsylvania State University Press, 2008
Lindeman, Mary. Medicine and Society in Early Modern Europe. Cambridge University Press, 2019.
Lowe, Kate. “’Representing’ Africa: Ambassadors and Princes from Christian Africa to Renaissance Italy and Portugal, 1402-1608.” Transactions of the Royal Historical Society Sixth Series, vol 17, 2007. pp. 101-128
Meyers, David. “Ritual, Confession, and Religion in Sixteenth-Century Germany.” Archiv fuer Reformationsgenshichte, vol. 89, 1998. pp. 125-143.
Murat, Zuleika. “Wall paintings through the ages: the medieval period (Italy, twelfth to fifteenth century).” Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, vol 23, no. 191. Springer, October 2021. pp. 1-27.
Overty, Joanne Filippone. “The Cost of Doing Scribal Business: Prices of Manuscript Books in England, 1300-1483.” Book History 11, 2008. pp. 1-32.
Page, Sophie. Magic in the Cloister: Pious Motives, Illicit Interests, and Occullt Approaches to the Medieval Universe. The Pennsylvania State University Press, 2013.
Park, Katharine. “The Criminal and the Saintly Body: Autopsy and Dissectionin Renaissance Italy.” Renaissance Quarterly, vol 47, no. 1, Spring 1994. pp. 1-33.
Rebel, Hermann. Peasant Classes: The Bureaucratization of Property and Family Relations under Early Habsburg Absolutism, 1511-1636. Princeton University Press, 1983.
Rublack, Ulinka. “Pregnancy, Childbirth, and the Female Body in Early Modern Germany.” Past & Present,vol. 150, no. 1, February 1996.
Salvador, Matteo. “The Ethiopian Age of Exploration: Prester John’s Discovery of Europe, 1306-1458.” Journal of World History, vol. 21, no. 4, 2011. pp.593-627.
Sangster, Alan. “The Earliest Known Treatise on Double Entry Bookkeeping by Marino de Raphaeli.” The Accounting Historians Journal, vol. 42, no. 2, 2015. pp. 1-33.
Throop, Priscilla. Hildegarde von Bingen’s Physica: The Complete English Translation of Her Classic Work on Health and Healing. Healing Arts Press, 1998.
Usher, Abbott Payson. “The Origins of Banking: The Brimitive Bank of Deposit, 1200-1600.” The Economic History Review, vol. 4, no. 4. 1934. pp.399-428.
Waldman, Louis A. “Commissioning Art in Florence for Matthias Corvinus: The Painter and Agent Alexander Formoser and his Sons, Jacopo and Raffaello del Tedesco.” Italy and Hungary: Humanism and Art in the Early Renaissance. Edited by Peter Farbaky and Louis A. Waldman, Villa I Tatti, 2011. pp.427-501.
Wendt, Ulrich. Kultur and Jagd: ein Birschgang durch die Geschichte. G. Reimer, 1907.
Whelan, Mark. “Taxes, Wagenburgs and a Nightingale: The Imperial Abbey of Ellwangen and the Hussite Wars, 1427-1435.” The Journal of Ecclesiastical History, vol. 72, no. 4, 2021, pp.751-777.
Wiesner-Hanks, Merry E. Women and Gender in Early Modern Europe. Cambridge University Press, 2008.
Yardeni, Ada. The Book of Hebrew Script: History, Palaeography, Script Styles, Calligraphy & Design. Tyndale House Publishers, 2010.
417 notes
·
View notes
Text

I typed up the Pentiment bibliography for my own use and thought I’d share it here too. In case anyone else is fixated enough on this game to embark on some light extra-curricular reading
I haven’t searched for every one of these books but a fair few can be found via one of the following: JSTOR / archive.org / pdfdrive.com / libgen + libgen.rocks; or respective websites for the journal articles.
List below the cut!
Beach, Alison I, Women as Scribes: Book Production and Monastic Reform in Twelfth-Century Bavaria. Cambridge University Press, 2004
Berger, Jutta Maria. Die Geschichte der Gastfreundschaft im hochmittelalterlichen Mönchtum die Cistercienser. Akademie Verlag GmbH, 1999
Blickle, Peter. The Revolution of 1525. Translated by Thomas A. Brady, Jr. and H.C. Erik Midelfort. The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1985
Brady, Thomas A., Jr. “Imperial Destinies: A New Biography of the Emperor Maximilian I.” The Journal of Modern History, vol.62, no.2, 1990. pp. 298-314
Brandl, Rainer. “Art or Craft? Art and the Artist in Medieval Nuremberg.” Gothic and Renaissance Art in Nuremberg 1300-2550. The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 1986
Byars, Jana L., “Prostitutes and Prostitution in Late Medieval Barcelona.” Masters Theses. Western Michigan University, 1997
Cashion, Debra Taylor. “The Art of Nikolaus Glockendon: Imitation and Originality in the Art of Renaissance Germany.” Journal of Historians of Netherlandish Art, vol.2, no.1-2, 2010
de Hamel, Christopher. A History of Illuminated Manuscripts. Phaidon Press Limited, 1986
Eco, Umberto. The Name of the Rose. Translated by William Weaver. Mariner Books, 2014
Eco, Umberto. Baudolino. Translated by William Weave. Boston, Mariner Books, 2003
Fournier, Jacques. “The Inquisition Records of Jacques Fournier.” Translated by Nancy P. Stork, San Jose University, 2020
Geary, Patrick. “Humiliation of Saints.” In Saints and their cults: studies in religious sociology, folklore, and history. Edited by Stephen Wilson. Cambridge University Press, 1985. pp. 123-140
Harrington, Joel F. The Faithful Executioner: Life and Death, Honor and Shame in the Turbulent Sixteenth Century. Farrar, Straus and Giroux, 2013
Hertzka, Gottfied and Wighard Strehlow. Große Hildegard-Apotheke. Christiana-Verlag, 2017
Hildegard von Bingen. Physica. Edited by Reiner Hildebrandt and Thomas Gloning. De Gruyter, 2010
Julian of Norwich. Revelations of Divine Love. Translated by Barry Windeatt. Oxford University Press, 2015
Karras, Ruth Mazo. Sexuality in Medieval Europe: Doing Unto Others. Routledge, 2017
Kerr, Julie. Monastic Hospitality: The Benedictines in England, c.1070-c.1250. Boydell Press, 2007
Kieckhefer, Richard. Forbidden rites: a necromancer's manual of the fifteenth century. Sutton, 1997
Kümin, Beat and B. Ann Tlusty. The World of the Tavern: Public Houses in Early Modern Europe. Routledge, 2017
Ilner, Thomas, et al. The Economy of Dürnberg-Bei-Hallein: an Iron Age Salt-mining Centre in the Austrian Alps. The Antiquaries Journal, vol. 83, 2003. pp. 123-194
Làng, Benedek. Unlocked Books: Manuscripts of Learned Magic in the Medieval Libraries of Central Europe. The Pennsylvania State University Press, 2008
Lindeman, Mary. Medicine and Society in Early Modern Europe. Cambridge University Press, 2010
Lowe, Kate. “'Representing' Africa: Ambassadors and Princes from Christian Africa to Renaissance Italy and Portugal, 1402-1608.” Transactions of the Royal Historical Society Sixth Series, vol. 17, pp. 101-128
Meyers, David. “Ritual, Confession, and Religion in Sixteenth-Century Germany.” Archiv für Reformationsgeschichte, vol. 89, 1998. pp. 125-143
Murat, Zuleika. “Wall paintings through the ages: the medieval period (Italy, twelfth to fifteenth century).” Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, vol. 12, no. 191. Springer, October 2021. pp. 1-27
Overty, Joanne Filippone. “The Cost of Doing Scribal Business: Prices of Manuscript Books in England, 1300-1483.” Book History 11, 2008. pp. 1-32
Page, Sophie. Magic in the Cloister: Pious Motives, Illicit Interests and Occult Approaches to the Medieval Universe. The Pennsylvania State University Press, 2013
Park, Katharine. “The Criminal and the Saintly Body: Autopsy and Dissection in Renaissance Italy.” Renaissance Quarterly, vol. 47, no. 1, Spring 1994. pp. 1-33
Rebel, Hermann. Peasant Classes: The Bureaucratization of Property and Family Relations under Early Habsburg Absolutism, 1511-1636. Princeton University Press, 1983
Rublack, Ulinka. “Pregnancy, Childbirth, and the Female Body in Early Modern Germany.” Past & Present, vol. 150, no. 1, February 1996. pp. 84-110
Salvadore, Matteo. “The Ethiopian Age of Exploration: Prester John's Discovery of Europe, 1306-1458.” Journal of World History, vol. 21, no. 4, 2011. pp. 593 - 627
Sangster, Alan. “The Earliest Known Treatise on Double Entry Bookkeeping by Marino de Raphaeli”. The Accounting Historians Journal, vol. 42, no. 2, 2015. pp. 1-33.
Throop, Priscilla. Hildegard von Bingen's Physica: The Complete English Translation of Her Classic Work on Health and Healing. Healing Arts Press, 1998
Usher, Abbott Payson. “The Origins of Banking: The Primitive Bank of Deposit, 1200-1600.” The Economic History Review, vol. 4, no. 4, 1934. pp. 399-428
Waldman, Louis A. “Commissioning Art in Florence for Matthias Corvinus: The Painter and Agent Alexander Formoser and his Sons, Jacopo and Raffaello del Tedesco.” Italy and Hungary: Humanism and Art in the Early Renaissance. Edited by Péter Farbaky and Louis A. Waldman, Villa I Tatti, 2011. pp. 427-501
Wendt, Ulrich. Kultur und Jagd: ein Birschgang durch die Geschichte. G. Reimer, 1907
Whelan, Mark. “Taxes, Wagenburgs and a Nightingale: The Imperial Abbey of Ellwangen and the Hussite Wars, 1427-1435.” The Journal of Ecclesiastical History, vol. 72, no. 4, 2021, pp. 751-777.e
Wiesner-Hanks, Merry E. Women and Gender in Early Modern Europe. Cambridge University Press, 2008
Yardeni, Ada. The Book of Hebrew Script: History, Paleography, Script Styles, Calligraphy & Design. Tyndale House Publishers, 2010
#pentiment#Pentiment bibliography#some of these books give me strong first-year undergrad vibes#even just seeing ulinka rublack’s name gives me semi-traumatic flashbacks to cultural history seminars#would I cope better with it now that I don’t have to write essays each week on the topic?#¯\_ (ツ)_/¯#probs not tbh#also it probably would have been a lot faster if I could have pulled this list from game files somehow#but I do not know how to do that :)))#Anyway I hope this is of use to somebody at some point#I wish you all a very happy reading about the primitive deposit banking system everybody 😌
778 notes
·
View notes
Text
ALL of La Fayette’s Grandchildren
(This post discusses the death and loss of children)
While four children are still pretty easy to keep track of, La Fayette’s abundance of grandchildren can be quite confusing. You often see the following graphic, published in Jules Germain Cloquet’s book:

Jules Germain Cloquet, Recollections of the Private Life of General Lafayette, Baldwin and Cradock, London, 1835, p. 227.
All fine and dandy, but I was looking for more detailed information and I wanted to include the children that had already died by the time Cloquet publishes his book – I therefor made a graphic of my own. :-)
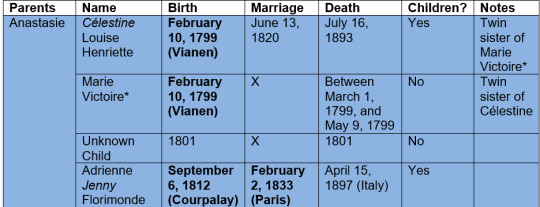
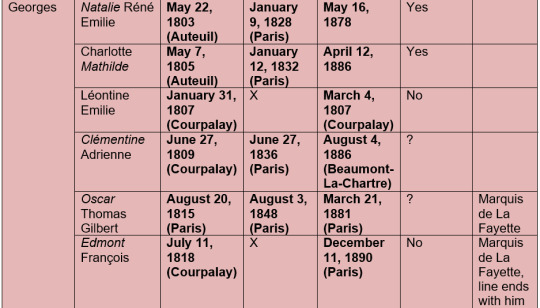
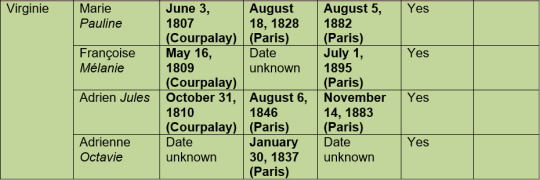
I am tempted to make one for the great-grandchildren as well, since La Fayette was very exited to become a Great-Grandfather – but this one was already a wild ride and La Fayette had more great-grandchildren then grand-children, let me tell you.
Anyway, some names are written in italics, these are the names the individuals commonly went by. I find it funny to see that all of Virginie’s children went by their second name, just like Virginie herself mostly just used her second name. Anastasie’s second child has an Asterix to her name. I have only once seen the name spelled out, on the certificate of baptism. The twins were baptized in Vianen (modern day Netherlands) and the name on the document was the Germanic spelling “Maria Victorina” – I used what I assumed is the best French spelling of the name.
The dates in bold indicate that the corresponding documentation of the birth/marriage/death can be found in the archives.
Anastasie and Charles: Finding Célestine’s dead twin sister was actually a surprise for me since I have never before seen her being mentioned. Anastasie gave birth for the first time in a town near Utrecht in what today are the Netherlands. The achieves there still have the certificate of baptism (on February 30, was the clerk sloppy or did the region in 1799 adhere to a different calendar style where February could have more then 29 days?) and we can very clearly see that there were too children. By May 9, 1799, La Fayette wrote to George Washington and referred to only one grand-child:
My wife, my daughters, and Son in law, join in presenting their affectionate respects to Mrs Washington & to you my dear g[ener]al the former is recovered & sets out for france on monday next with Virginia—our little grand Daughter [Célestine] is well, will your charming one accept our tender regard?
“To George Washington from Lafayette, 9 May 1799,” Founders Online, National Archives, https://founders.archives.gov/documents/Washington/06-04-02-0041. [Original source: The Papers of George Washington, Retirement Series, vol. 4, 20 April 1799 – 13 December 1799, ed. W. W. Abbot. Charlottesville: University Press of Virginia, 1999, pp. 54–59.] (02/12/2024)
I suspect that Anastasie had a stillbirth around August/September of 1801. La Fayette mentioned in a letter to Thomas Jefferson on June 21, 1801:
Anastasia Will Before long Make me Once More a Grand Father
“To Thomas Jefferson from Lafayette, 21 June 1801,” Founders Online, National Archives, https://founders.archives.gov/documents/Jefferson/01-34-02-0318. [Original source: The Papers of Thomas Jefferson, vol. 34, 1 May–31 July 1801, ed. Barbara B. Oberg. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2007, pp. 403–404.] (02/12/2024)
There is no mention of this child being born and both the achieves in Paris and Courpalay yield no information so that it is unlikely that the child was born and then died young. Georges’ daughter died very young and she still is in the archives. Given La Fayette’s wording we can assume that Anastasie’s pregnancy was already somewhat advanced and the term miscarriage is only used up until the 20th week of a pregnancy, after that it is considered a stillbirth.
Georges and Emilie: The couple lost at least one daughter, Léontine Emilie, young, aged just four weeks. La Fayette wrote in a letter to Thomas Jefferson on February 20, 1807:
My family are pretty well and beg to be most affectionately respectfully and gratefully presented to you—We expected a Boy to be called after your name—But little Tommy has again proved to be a Girl [Léontine Emilie].
“To Thomas Jefferson from Marie-Joseph-Paul-Yves-Roch-Gilbert du Motier, marquis de Lafayette, 20 February 1807,” Founders Online, National Archives, https://founders.archives.gov/documents/Jefferson/99-01-02-5122. [This is an Early Access document from The Papers of Thomas Jefferson. It is not an authoritative final version.] (02/12/2024)
La Fayette later wrote to James Madison on June 10, 1807:
We Have Had the Misfortune to Loose a female Child of His, four Weeks old [Léontine Emilie]. My Younger daughter Virginia Has Lately presented us With an other infant of the Same Sex [Marie Pauline]. My Wife’s Health is Not Worse at this Moment, But Ever too Bad.
To James Madison from Marie-Adrienne-Françoise de Noailles, marquise de Lafayette, 10 June 1807,” Founders Online, National Archives, https://founders.archives.gov/documents/Madison/99-01-02-1768. [This is an Early Access document from The Papers of James Madison. It is not an authoritative final version.] (02/12/2024)
As a sidenote because it confused me while searching for the letter; the archives list Adrienne as the author. I am certain that is wrong because a) Adrienne was not corresponding with James Madison, b) this is not her writing style but La Fayette’s, c) the letter does not have her typical signature and d) there is the passage about the authors wife’s health – this one at the least gives it away.
Identifying Léontine Emilie was actually quite a bit of luck as well. I found the letter to Madison by accident and that letter is the only source that mentions her that I know of. I have never seen her in any other letters, documentation, contemporary or secondary books. The letter helped to narrow her birthday and her date of death down and with that information I searches the archives in Paris and Courpalay in the hopes of finding the child – and I was lucky. While I of course understand the order of things, it still saddens me to see that you can be born into such a prominent family – your father was a Marquis, your grand-father was the Marquis, and still, not even your families biographers care to even mention you.
Virginie und Louis: For all I know, and I again have to say that I have not nearly as much data/correspondence as I would like with regard to these topics, Virginie never lost a child. There is always the question what La Fayette would feel comfortable telling and to whom. There is also the question if La Fayette himself was always aware of everything. For example, in the case of a miscarriage very early on in the pregnancy he might have not included it in his correspondence or in fact maybe not even known himself.
As much as would wish a happy family life for Virginie, stillbirths, infant deaths and especially miscarriages were and still are not uncommon.
I have put excerpts from a few more letters by La Fayette to his American friends under the cut that help identify his grandchildren.
La Fayette to Thomas Jefferson, June 4, 1803:
I am Here, with my Wife, Son, daughter in law, and New Born little grand daughter [Natalie Renée Émilie] taking Care of my Wounds, and Stretching My Rusted Articulations untill I can Return to my Beloved Rural Abode at La Grange.
“To Thomas Jefferson from Lafayette, 4 June 1803,” Founders Online, National Archives, https://founders.archives.gov/documents/Jefferson/01-40-02-0361. [Original source: The Papers of Thomas Jefferson, vol. 40, 4 March–10 July 1803, ed. Barbara B. Oberg. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2013, pp. 485–486.] (02/12/2024)
La Fayette to Thomas Jefferson, April 20, 1805:
Here I am with my son and daughter in law who is going to increase our family [Charlotte Mathilde]. Her father is to stand god father to the child and if He is a Boy we intend taking the liberty to give Him Your Name.
“To Thomas Jefferson from Marie-Joseph-Paul-Yves-Roch-Gilbert du Motier, marquis de Lafayette, 20 April 1805,” Founders Online, National Archives, https://founders.archives.gov/documents/Jefferson/99-01-02-1556. [This is an Early Access document from The Papers of Thomas Jefferson. It is not an authoritative final version.] (02/12/2024)
La Fayette to Thomas Jefferson, April 8, 1809:
(…) My Children are in Good Health. Two of them, My daughter in Law [Clémentine Adrienne], and Virginia [Françoise Mélanie] are Going to increase the family.
“To Thomas Jefferson from Marie-Joseph-Paul-Yves-Roch-Gilbert du Motier, marquis de Lafayette, 14 December 1822,” Founders Online, National Archives, https://founders.archives.gov/documents/Jefferson/98-01-02-3215. [This is an Early Access document from The Papers of Thomas Jefferson: Retirement Series. It is not an authoritative final version.] (02/12/2024)
#marquis de lafayette#la fayette#french history#history#letters#founders online#george washington#thomas jefferson#james madison#archieve#resources#1799#1801#1812#1803#1805#1807#1809#1815#1818#1810#georges de la fayette#anastasie de la fayette#virginie de la fayette
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
" Educare all'ozio significa insegnare a scegliere un film, uno spettacolo teatrale, un libro. Insegnare a sbrigare le attività domestiche e a far da sé molte cose che fin qui abbiamo comprato. Insegnare la convivialità, l'introspezione, il gioco. Anche la pedagogia dell'ozio ha una sua etica, una sua estetica, una sua dinamica, delle sue tecniche. E tutto questo va insegnato.
L'ozio richiede luoghi adatti per riposarsi, per distrarsi, per divertirsi. Ai giovani perciò bisogna insegnare a districarsi non solo nei meandri del lavoro, ma anche nei meandri delle varie offerte di loisirs. Significa educare a fare il genitore e a fare il coniuge, ai rapporti con l'altro sesso, al volontariato, cioè ad attività socialmente utili da svolgere nel tempo libero che avremo in abbondanza. Ce n'è da insegnare! La massa della gente non sa scegliere neppure un luogo di vacanze: va in un'agenzia e si fa rifilare quello che capita. La massa della gente non sa come distrarsi e come riposarsi. Bisogna educare alla notte: la nostra cultura è tutta diurna, vede la notte come uno spazio privatissimo, peccaminoso. E poi bisogna educare alla cultura post-moderna: molte espressioni della nostra cultura non sono godibili immediatamente com'era per la pittura classica o per la musica tradizionale. Siano architettura, scultura o design, spesso possiamo apprezzarle solo se ne conosciamo storia, senso e scopo. Posso rimanere istantaneamente colpito di fronte alla Gioconda o a una statua di Canova, ma per capire Mondrian devo sapere cos'è stato il movimento De Stijl, e per ammirare davvero Van Gogh devo sapere cos'è stato l'Impressionismo.
Educare significa insegnare ad arricchire le cose di significato, come diceva Dewey. Più educato sei, più significati cogli nelle cose e conferisci alle cose. "
Domenico De Masi, Ozio creativo. Conversazione con Maria Serena Palieri, Ediesse (collana Interventi), Roma, 1997¹; pp. 141-142.
#Ozio creativo#letture#leggere#citazioni#saggi#saggistica#Domenico De Masi#sociologia#scienze umane#lavoro#libri#Maria Serena Palieri#convivialità#mass media#futuro#vita#introspezione#gioco#etica#estetica#tecnica#intellettuali italiani#informatica#cultura#giovani#scegliere#società della conoscenza#Piet Mondrian#Vincent van Gogh#John Dewey
26 notes
·
View notes
Text

A.3.5 What is Anarcha-Feminism?
Although opposition to the state and all forms of authority had a strong voice among the early feminists of the 19th century, the more recent feminist movement which began in the 1960’s was founded upon anarchist practice. This is where the term anarcha-feminism came from, referring to women anarchists who act within the larger feminist and anarchist movements to remind them of their principles.
The modern anarcha-feminists built upon the feminist ideas of previous anarchists, both male and female. Indeed, anarchism and feminism have always been closely linked. Many outstanding feminists have also been anarchists, including the pioneering Mary Wollstonecraft (author of A Vindication of the Rights of Woman), the Communard Louise Michel, and the American anarchists (and tireless champions of women’s freedom) Voltairine de Cleyre and Emma Goldman (for the former, see her essays “Sex Slavery”, “Gates of Freedom”, “The Case of Woman vs. Orthodoxy”, “Those Who Marry Do Ill”; for the latter see “The Traffic in Women”, “Woman Suffrage”, “The Tragedy of Woman’s Emancipation”, “Marriage and Love” and “Victims of Morality”, for example). Freedom, the world’s oldest anarchist newspaper, was founded by Charlotte Wilson in 1886. Anarchist women like Virgilia D’Andrea and Rose Pesota played important roles in both the libertarian and labour movements. The “Mujeres Libres” (“Free Women”) movement in Spain during the Spanish revolution is a classic example of women anarchists organising themselves to defend their basic freedoms and create a society based on women’s freedom and equality (see Free Women of Spain by Martha Ackelsberg for more details on this important organisation). In addition, all the male major anarchist thinkers (bar Proudhon) were firm supporters of women’s equality. For example, Bakunin opposed patriarchy and how the law “subjects [women] to the absolute domination of the man.” He argued that ”[e]qual rights must belong to men and women” so that women can “become independent and be free to forge their own way of life.” He looked forward to the end of “the authoritarian juridical family” and “the full sexual freedom of women.” [Bakunin on Anarchism, p. 396 and p. 397]
Thus anarchism has since the 1860s combined a radical critique of capitalism and the state with an equally powerful critique of patriarchy (rule by men). Anarchists, particularly female ones, recognised that modern society was dominated by men. As Ana Maria Mozzoni (an Italian anarchist immigrant in Buenos Aires) put it, women “will find that the priest who damns you is a man; that the legislator who oppresses you is a man, that the husband who reduces you to an object is a man; that the libertine who harasses you is a man; that the capitalist who enriches himself with your ill-paid work and the speculator who calmly pockets the price of your body, are men.” Little has changed since then. Patriarchy still exists and, to quote the anarchist paper La Questione Sociale, it is still usually the case that women “are slaves both in social and private life. If you are a proletarian, you have two tyrants: the man and the boss. If bourgeois, the only sovereignty left to you is that of frivolity and coquetry.” [quoted by Jose Moya, Italians in Buenos Aires’s Anarchist Movement, pp. 197–8 and p. 200]
Anarchism, therefore, is based on an awareness that fighting patriarchy is as important as fighting against the state or capitalism. For ”[y]ou can have no free, or just, or equal society, nor anything approaching it, so long as womanhood is bought, sold, housed, clothed, fed, and protected, as a chattel.” [Voltairine de Cleyre, “The Gates of Freedom”, pp. 235–250, Eugenia C. Delamotte, Gates of Freedom, p. 242] To quote Louise Michel:
“The first thing that must change is the relationship between the sexes. Humanity has two parts, men and women, and we ought to be walking hand in hand; instead there is antagonism, and it will last as long as the ‘stronger’ half controls, or think its controls, the ‘weaker’ half.” [The Red Virgin: Memoirs of Louise Michel, p. 139]
Thus anarchism, like feminism, fights patriarchy and for women’s equality. Both share much common history and a concern about individual freedom, equality and dignity for members of the female sex (although, as we will explain in more depth below, anarchists have always been very critical of mainstream/liberal feminism as not going far enough). Therefore, it is unsurprising that the new wave of feminism of the sixties expressed itself in an anarchistic manner and drew much inspiration from anarchist figures such as Emma Goldman. Cathy Levine points out that, during this time, “independent groups of women began functioning without the structure, leaders, and other factotums of the male left, creating, independently and simultaneously, organisations similar to those of anarchists of many decades and regions. No accident, either.” [“The Tyranny of Tyranny,” Quiet Rumours: An Anarcha-Feminist Reader, p. 66] It is no accident because, as feminist scholars have noted, women were among the first victims of hierarchical society, which is thought to have begun with the rise of patriarchy and ideologies of domination during the late Neolithic era. Marilyn French argues (in Beyond Power) that the first major social stratification of the human race occurred when men began dominating women, with women becoming in effect a “lower” and “inferior” social class.
The links between anarchism and modern feminism exist in both ideas and action. Leading feminist thinker Carole Pateman notes that her “discussion [on contract theory and its authoritarian and patriarchal basis] owes something to” libertarian ideas, that is the “anarchist wing of the socialist movement.” [The Sexual Contract, p. 14] Moreover, she noted in the 1980s how the “major locus of criticism of authoritarian, hierarchical, undemocratic forms of organisation for the last twenty years has been the women’s movement … After Marx defeated Bakunin in the First International, the prevailing form of organisation in the labour movement, the nationalised industries and in the left sects has mimicked the hierarchy of the state … The women’s movement has rescued and put into practice the long-submerged idea [of anarchists like Bakunin] that movements for, and experiments in, social change must ‘prefigure’ the future form of social organisation.” [The Disorder of Women, p. 201]
Peggy Kornegger has drawn attention to these strong connections between feminism and anarchism, both in theory and practice. “The radical feminist perspective is almost pure anarchism,” she writes. “The basic theory postulates the nuclear family as the basis of all authoritarian systems. The lesson the child learns, from father to teacher to boss to god, is to obey the great anonymous voice of Authority. To graduate from childhood to adulthood is to become a full-fledged automaton, incapable of questioning or even of thinking clearly.” [“Anarchism: The Feminist Connection,” Quiet Rumours: An Anarcha-Feminist Reader, p. 26] Similarly, the Zero Collective argues that Anarcha-feminism “consists in recognising the anarchism of feminism and consciously developing it.” [“Anarchism/Feminism,” pp. 3–7, The Raven, no. 21, p. 6]
Anarcha-feminists point out that authoritarian traits and values, for example, domination, exploitation, aggressiveness, competitiveness, desensitisation etc., are highly valued in hierarchical civilisations and are traditionally referred to as “masculine.” In contrast, non-authoritarian traits and values such as co-operation, sharing, compassion, sensitivity, warmth, etc., are traditionally regarded as “feminine” and are devalued. Feminist scholars have traced this phenomenon back to the growth of patriarchal societies during the early Bronze Age and their conquest of co-operatively based “organic” societies in which “feminine” traits and values were prevalent and respected. Following these conquests, however, such values came to be regarded as “inferior,” especially for a man, since men were in charge of domination and exploitation under patriarchy. (See e.g. Riane Eisler, The Chalice and the Blade; Elise Boulding, The Underside of History). Hence anarcha-feminists have referred to the creation of a non-authoritarian, anarchist society based on co-operation, sharing, mutual aid, etc. as the “feminisation of society.”
Anarcha-feminists have noted that “feminising” society cannot be achieved without both self-management and decentralisation. This is because the patriarchal-authoritarian values and traditions they wish to overthrow are embodied and reproduced in hierarchies. Thus feminism implies decentralisation, which in turn implies self-management. Many feminists have recognised this, as reflected in their experiments with collective forms of feminist organisations that eliminate hierarchical structure and competitive forms of decision making. Some feminists have even argued that directly democratic organisations are specifically female political forms. [see e.g. Nancy Hartsock “Feminist Theory and the Development of Revolutionary Strategy,” in Zeila Eisenstein, ed., Capitalist Patriarchy and the Case for Socialist Feminism, pp. 56–77] Like all anarchists, anarcha-feminists recognise that self-liberation is the key to women’s equality and thus, freedom. Thus Emma Goldman:
“Her development, her freedom, her independence, must come from and through herself. First, by asserting herself as a personality, and not as a sex commodity. Second, by refusing the right of anyone over her body; by refusing to bear children, unless she wants them, by refusing to be a servant to God, the State, society, the husband, the family, etc., by making her life simpler, but deeper and richer. That is, by trying to learn the meaning and substance of life in all its complexities; by freeing herself from the fear of public opinion and public condemnation.” [Anarchism and Other Essays, p. 211]
Anarcha-feminism tries to keep feminism from becoming influenced and dominated by authoritarian ideologies of either the right or left. It proposes direct action and self-help instead of the mass reformist campaigns favoured by the “official” feminist movement, with its creation of hierarchical and centralist organisations and its illusion that having more women bosses, politicians, and soldiers is a move towards “equality.” Anarcha-feminists would point out that the so-called “management science” which women have to learn in order to become mangers in capitalist companies is essentially a set of techniques for controlling and exploiting wage workers in corporate hierarchies, whereas “feminising” society requires the elimination of capitalist wage-slavery and managerial domination altogether. Anarcha-feminists realise that learning how to become an effective exploiter or oppressor is not the path to equality (as one member of the Mujeres Libres put it, ”[w]e did not want to substitute a feminist hierarchy for a masculine one” [quoted by Martha A. Ackelsberg, Free Women of Spain, pp. 22–3] — also see section B.1.4 for a further discussion on patriarchy and hierarchy).
Hence anarchism’s traditional hostility to liberal (or mainstream) feminism, while supporting women’s liberation and equality. Federica Montseny (a leading figure in the Spanish Anarchist movement) argued that such feminism advocated equality for women, but did not challenge existing institutions. She argued that (mainstream) feminism’s only ambition is to give to women of a particular class the opportunity to participate more fully in the existing system of privilege and if these institutions “are unjust when men take advantage of them, they will still be unjust if women take advantage of them.” [quoted by Martha A. Ackelsberg, Op. Cit., p. 119] Thus, for anarchists, women’s freedom did not mean an equal chance to become a boss or a wage slave, a voter or a politician, but rather to be a free and equal individual co-operating as equals in free associations. “Feminism,” stressed Peggy Kornegger, “doesn’t mean female corporate power or a woman President; it means no corporate power and no Presidents. The Equal Rights Amendment will not transform society; it only gives women the ‘right’ to plug into a hierarchical economy. Challenging sexism means challenging all hierarchy — economic, political, and personal. And that means an anarcha-feminist revolution.” [Op. Cit., p. 27]
Anarchism, as can be seen, included a class and economic analysis which is missing from mainstream feminism while, at the same time, showing an awareness to domestic and sex-based power relations which eluded the mainstream socialist movement. This flows from our hatred of hierarchy. As Mozzoni put it, “Anarchy defends the cause of all the oppressed, and because of this, and in a special way, it defends your [women’s] cause, oh! women, doubly oppressed by present society in both the social and private spheres.” [quoted by Moya, Op. Cit., p. 203] This means that, to quote a Chinese anarchist, what anarchists “mean by equality between the sexes is not just that the men will no longer oppress women. We also want men to no longer to be oppressed by other men, and women no longer to be oppressed by other women.” Thus women should “completely overthrow rulership, force men to abandon all their special privileges and become equal to women, and make a world with neither the oppression of women nor the oppression of men.” [He Zhen, quoted by Peter Zarrow, Anarchism and Chinese Political Culture, p. 147]
So, in the historic anarchist movement, as Martha Ackelsberg notes, liberal/mainstream feminism was considered as being “too narrowly focused as a strategy for women’s emancipation; sexual struggle could not be separated from class struggle or from the anarchist project as a whole.” [Op. Cit., p. 119] Anarcha-feminism continues this tradition by arguing that all forms of hierarchy are wrong, not just patriarchy, and that feminism is in conflict with its own ideals if it desires simply to allow women to have the same chance of being a boss as a man does. They simply state the obvious, namely that they “do not believe that power in the hands of women could possibly lead to a non-coercive society” nor do they “believe that anything good can come out of a mass movement with a leadership elite.” The “central issues are always power and social hierarchy” and so people “are free only when they have power over their own lives.” [Carole Ehrlich, “Socialism, Anarchism and Feminism”, Quiet Rumours: An Anarcha-Feminist Reader, p. 44] For if, as Louise Michel put it, “a proletarian is a slave; the wife of a proletarian is even more a slave” ensuring that the wife experiences an equal level of oppression as the husband misses the point. [Op. Cit., p. 141]
Anarcha-feminists, therefore, like all anarchists oppose capitalism as a denial of liberty. Their critique of hierarchy in the society does not start and end with patriarchy. It is a case of wanting freedom everywhere, of wanting to ”[b]reak up … every home that rests in slavery! Every marriage that represents the sale and transfer of the individuality of one of its parties to the other! Every institution, social or civil, that stands between man and his right; every tie that renders one a master, another a serf.” [Voltairine de Cleyre, “The Economic Tendency of Freethought”, The Voltairine de Cleyre Reader, p. 72] The ideal that an “equal opportunity” capitalism would free women ignores the fact that any such system would still see working class women oppressed by bosses (be they male or female). For anarcha-feminists, the struggle for women’s liberation cannot be separated from the struggle against hierarchy as such. As L. Susan Brown puts it:
“Anarchist-feminism, as an expression of the anarchist sensibility applied to feminist concerns, takes the individual as its starting point and, in opposition to relations of domination and subordination, argues for non-instrumental economic forms that preserve individual existential freedom, for both men and women.” [The Politics of Individualism, p. 144]
Anarcha-feminists have much to contribute to our understanding of the origins of the ecological crisis in the authoritarian values of hierarchical civilisation. For example, a number of feminist scholars have argued that the domination of nature has paralleled the domination of women, who have been identified with nature throughout history (See, for example, Caroline Merchant, The Death of Nature, 1980). Both women and nature are victims of the obsession with control that characterises the authoritarian personality. For this reason, a growing number of both radical ecologists and feminists are recognising that hierarchies must be dismantled in order to achieve their respective goals.
In addition, anarcha-feminism reminds us of the importance of treating women equally with men while, at the same time, respecting women’s differences from men. In other words, that recognising and respecting diversity includes women as well as men. Too often many male anarchists assume that, because they are (in theory) opposed to sexism, they are not sexist in practice. Such an assumption is false. Anarcha-feminism brings the question of consistency between theory and practice to the front of social activism and reminds us all that we must fight not only external constraints but also internal ones.
This means that anarcha-feminism urges us to practice what we preach. As Voltairine de Cleyre argued, “I never expect men to give us liberty. No, Women, we are not worth it, until we take it.” This involves “insisting on a new code of ethics founded on the law of equal freedom: a code recognising the complete individuality of woman. By making rebels wherever we can. By ourselves living our beliefs . … We are revolutionists. And we shall use propaganda by speech, deed, and most of all life — being what we teach.” Thus anarcha-feminists, like all anarchists, see the struggle against patriarchy as being a struggle of the oppressed for their own self-liberation, for ”as a class I have nothing to hope from men . .. No tyrant ever renounced his tyranny until he had to. If history ever teaches us anything it teaches this. Therefore my hope lies in creating rebellion in the breasts of women.” [“The Gates of Freedom”, pp. 235–250, Eugenia C. Delamotte, Gates of Freedom, p. 249 and p. 239] This was sadly as applicable within the anarchist movement as it was outside it in patriarchal society.
Faced with the sexism of male anarchists who spoke of sexual equality, women anarchists in Spain organised themselves into the Mujeres Libres organisation to combat it. They did not believe in leaving their liberation to some day after the revolution. Their liberation was a integral part of that revolution and had to be started today. In this they repeated the conclusions of anarchist women in Illinois Coal towns who grew tried of hearing their male comrades “shout in favour” of sexual equality “in the future society” while doing nothing about it in the here and now. They used a particularly insulting analogy, comparing their male comrades to priests who “make false promises to the starving masses … [that] there will be rewards in paradise.” The argued that mothers should make their daughters “understand that the difference in sex does not imply inequality in rights” and that as well as being “rebels against the social system of today,” they “should fight especially against the oppression of men who would like to retain women as their moral and material inferior.” [Ersilia Grandi, quoted by Caroline Waldron Merithew, Anarchist Motherhood, p. 227] They formed the “Luisa Michel” group to fight against capitalism and patriarchy in the upper Illinois valley coal towns over three decades before their Spanish comrades organised themselves.
For anarcha-feminists, combating sexism is a key aspect of the struggle for freedom. It is not, as many Marxist socialists argued before the rise of feminism, a diversion from the “real” struggle against capitalism which would somehow be automatically solved after the revolution. It is an essential part of the struggle:
“We do not need any of your titles … We want none of them. What we do want is knowledge and education and liberty. We know what our rights are and we demand them. Are we not standing next to you fighting the supreme fight? Are you not strong enough, men, to make part of that supreme fight a struggle for the rights of women? And then men and women together will gain the rights of all humanity.” [Louise Michel, Op. Cit., p. 142]
A key part of this revolutionising modern society is the transformation of the current relationship between the sexes. Marriage is a particular evil for “the old form of marriage, based on the Bible, ‘till death doth part,’ … [is] an institution that stands for the sovereignty of the man over the women, of her complete submission to his whims and commands.” Women are reduced “to the function of man’s servant and bearer of his children.” [Goldman, Op. Cit., pp. 220–1] Instead of this, anarchists proposed “free love,” that is couples and families based on free agreement between equals than one partner being in authority and the other simply obeying. Such unions would be without sanction of church or state for “two beings who love each other do not need permission from a third to go to bed.” [Mozzoni, quoted by Moya, Op. Cit., p. 200]
Equality and freedom apply to more than just relationships. For “if social progress consists in a constant tendency towards the equalisation of the liberties of social units, then the demands of progress are not satisfied so long as half society, Women, is in subjection… . Woman … is beginning to feel her servitude; that there is a requisite acknowledgement to be won from her master before he is put down and she exalted to — Equality. This acknowledgement is, the freedom to control her own person. “ [Voltairine de Cleyre, “The Gates of Freedom”, Op. Cit., p. 242] Neither men nor state nor church should say what a woman does with her body. A logical extension of this is that women must have control over their own reproductive organs. Thus anarcha-feminists, like anarchists in general, are pro-choice and pro-reproductive rights (i.e. the right of a woman to control her own reproductive decisions). This is a long standing position. Emma Goldman was persecuted and incarcerated because of her public advocacy of birth control methods and the extremist notion that women should decide when they become pregnant (as feminist writer Margaret Anderson put it, “In 1916, Emma Goldman was sent to prison for advocating that ‘women need not always keep their mouth shut and their wombs open.’”).
Anarcha-feminism does not stop there. Like anarchism in general, it aims at changing all aspects of society not just what happens in the home. For, as Goldman asked, “how much independence is gained if the narrowness and lack of freedom of the home is exchanged for the narrowness and lack of freedom of the factory, sweat-shop, department store, or office?” Thus women’s equality and freedom had to be fought everywhere and defended against all forms of hierarchy. Nor can they be achieved by voting. Real liberation, argue anarcha-feminists, is only possible by direct action and anarcha-feminism is based on women’s self-activity and self-liberation for while the “right to vote, or equal civil rights, may be good demands … true emancipation begins neither at the polls nor in the courts. It begins in woman’s soul … her freedom will reach as far as her power to achieve freedom reaches.” [Goldman, Op. Cit., p. 216 and p. 224]
The history of the women’s movement proves this. Every gain has come from below, by the action of women themselves. As Louise Michel put it, ”[w]e women are not bad revolutionaries. Without begging anyone, we are taking our place in the struggles; otherwise, we could go ahead and pass motions until the world ends and gain nothing.” [Op. Cit., p. 139] If women waited for others to act for them their social position would never have changed. This includes getting the vote in the first place. Faced with the militant suffrage movement for women’s votes, British anarchist Rose Witcop recognised that it was “true that this movement shows us that women who so far have been so submissive to their masters, the men, are beginning to wake up at last to the fact they are not inferior to those masters.” Yet she argued that women would not be freed by votes but “by their own strength.” [quoted by Sheila Rowbotham, Hidden from History, pp. 100–1 and p. 101] The women’s movement of the 1960s and 1970s showed the truth of that analysis. In spite of equal voting rights, women’s social place had remained unchanged since the 1920s.
Ultimately, as Anarchist Lily Gair Wilkinson stressed, the “call for ‘votes’ can never be a call to freedom. For what is it to vote? To vote is to register assent to being ruled by one legislator or another?” [quoted by Sheila Rowbotham, Op. Cit., p. 102] It does not get to the heart of the problem, namely hierarchy and the authoritarian social relationships it creates of which patriarchy is only a subset of. Only by getting rid of all bosses, political, economic, social and sexual can genuine freedom for women be achieved and “make it possible for women to be human in the truest sense. Everything within her that craves assertion and activity should reach its fullest expression; all artificial barriers should be broken, and the road towards greater freedom cleared of every trace of centuries of submission and slavery.” [Emma Goldman, Op. Cit., p. 214]
#feminism#anarchy faq#revolution#anarchism#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#climate change#climate crisis#climate#ecology#anarchy works#environmentalism#environment#solarpunk#anti colonialism#mutual aid#cops#police
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
I made an art piece
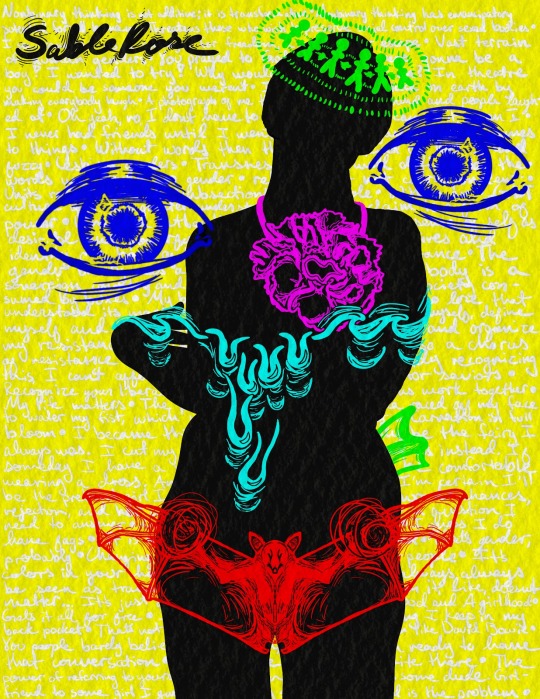

It's about trans people and the nebulous of womanhood and my gender and :)


The silhouette is mine. I love it :)
Works Cited:
Benaway, Gwen. “A transgender poet reflects on her first year of experiencing womanhood.” CBC Arts, 2 March 2017, www.cbc.ca/amp/1.4006567
Gibson, Andrea. “My Gender is the Undoing of Gender” YouTube, uploaded by Button Poetry, 26 May 2022, www.youtube.com/watch?v=s8NvkY15yGs.
Levitt, Heidi M., and Maria R. Ippolito. “Being Transgender: The Experience of Transgender Identity Development.” Journal of Homosexuality, vol. 61, no. 12, 2014, pp. 1727–58, doi.org/10.1080/00918369.2014.951262.
Personal interview. 26 February 2024.
Rees, Yves. “Feminism beyond the Binary.” Lilith: A Feminist History Journal, vol. 28, no. 28, 2022, pp. 123–27, doi.org/10.22459/lfhj.28.10.
Stewart, D-L. “Scenes from a Black trans life” YouTube, uploaded by TED, 11 August 2020, www.youtube.com/watch?v=epUmQP6VuDs.
Wright, Mars. “Trans Joy is Resistance.” ProjectQ Community Center, Los Angeles, March 2022.
@toddhowardschildhoodbully
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
Waterloo Letters #4 (4/4): Hometown stuff
Re: Hometown stuff
A [email protected] 9/4/20 8:31 PM to Henry
H,
Fuck.
I’m so sorry. I don’t know what else to say. I’m so sorry. June and Nora send their love. Not as much love as me. Obviously.
Please don’t worry about me. We’ll figure it out. It just might take time. I’ve been working on patience. I’ve picked up all kinds of things from you.
God, what can I possibly write to make this better?
Here: I can’t decide if your emails make me miss you more or less. Sometimes I feel like a funny-looking rock in the middle of the most beautiful clear ocean when I read the kinds of things you write to me. You love so much bigger than yourself, bigger than everything. I can’t believe how lucky I am to even witness it—to be the one who gets to have it, and so much of it, is beyond luck and feels like fate. Catholic God made me to be the person you write those things about. I’ll say five Hail Marys. Muchas gracias, Santa Maria.
I can’t match you for prose, but what I can do is write you a list.
AN INCOMPLETE LIST: THINGS I LOVE ABOUT HRH PRINCE HENRY OF WALES
1. The sound of your laugh when I piss you off.
2. The way you smell underneath your fancy cologne, like clean linens but somehow also fresh grass (what kind of magic is this?).
3. That thing you do where you stick out your chin to try to look tough.
4. How your hands look when you play piano.
5. All the things I understand about myself now because of you.
6. How you think Return of the Jedi is the best Star Wars (wrong) because deep down you’re a gigantic, sappy, embarrassing romantic who just wants the happily ever after.
7. Your ability to recite Keats.
8. Your ability to recite Bernadette’s “Don’t let it drag you down” monologue from Priscilla, Queen of the Desert.
9. How hard you try.
10. How hard you’ve always tried.
11. How determined you are to keep trying.
12. That when your shoulders cover mine, nothing else in the entire stupid world matters.
13. The goddamn issue of Le Monde you brought back to London with you and kept and have on your nightstand (yes, I saw it).
14. The way you look when you first wake up.
15. Your shoulder-to-waist ratio.
16. Your huge, generous, ridiculous, indestructible heart.
17. Your equally huge dick.
18. The face you just made when you read that last one.
19. The way you look when you first wake up (I know I already said this, but I really, really love it).
20. The fact that you loved me all along.
I keep thinking about that last one ever since you told me, and what an idiot I was. It’s so hard for me to get out of my own head sometimes, but now I’m coming back to what I said to you the night in my room when it all started, and how I brushed you off when you offered to let me go after the DNC, how I used to try to act like it was nothing sometimes. I didn’t even know what you were offering to do to yourself. God, I want to fight everyone who’s ever hurt you, but it was me too, wasn’t it? All that time. I’m so sorry.
Please stay gorgeous and strong and unbelievable. I miss you I miss you I miss you I love you. I’m calling you as soon as I send this, but I know you like to have these things written down.
A
P.S. Richard Wagner to Eliza Wille, re: Ludwig II–1864 (Remember when you played Wagner for me? He’s an asshole, but this is something.)
It is true that I have my young king who genuinely adores me. You cannot form an idea of our relations. I recall one of the dreams of my youth. I once dreamed that Shakespeare was alive: that I really saw and spoke to him: I can never forget the impression that dream made on me. Then I would have wished to see Beethoven, though he was already dead. Something of the same kind must pass in the mind of this lovable man when with me. He says he can hardly believe that he really possesses me. None can read without astonishment, without enchantment, the letters he writes to me.
McQuiston, Casey. Red, White & Royal Blue: A Novel (pp. 301-304). St. Martin's Publishing Group. Kindle Edition.
1 | 2 | 3
#waterloo letters#hometown stuff#firstprince#alex claremont diaz#henry fox mountchristen windsor#red white and royal blue#casey mcquiston#out of credits
59 notes
·
View notes
Text

Leanne Betasamosake Simpson, Naawakwe, from Poetry From Isolation: Leanne Betasamosake Simpson, Karen Solie, Adèle Barclay, Ken Babstock, Maria Borio, Illustrations by Makoto Chi, «NUVO», Issue 86, (pp. 66-73), 2020, p. 68
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Animation Night 179: Unicorn Wars
Hey everyone! Real brief blurb tonight because I talked about Alberto Vázquez last week - tonight I'm going to be re-running Unicorn Wars since last week it was way too late for people to attend!

Unicorn Wars could be roughly described as Apocalypse Now with teddy bears. We encounter a world in which a militaristic country of teddies is locked in a revanchist forever-war against the unicorns who now occupy the Magic Forest. It is a conflict in part religious in nature: the bears are convinced that whoever drinks the blood of the last unicorn will enter into a transcendant state of being.
Our story concerns a fresh batch of recruits, sent on a mission that none of them know is sacrificial. Led by a sergeant who has no idea what he's in for and a reserved priest, they set out with grenades and bows and arrows to find out what became of a lost unit.
Our main characters are a pair of brothers, Azulín and Gordi, or Bluey and Tubby as the English sub renders it. Both of them are deeply screwed up by their parents separation and their mothers' death; Azulín in particular, who took more after their father, has a determination to prove himself at whatever cost, and a contemptuous, bullying relationship to his brother.

But we also encountere the rest of the doomed bears and there are some real characters. The bear culture is a fascinating blend of cute fluffy signifiers and militaristic ones, joined into one nihilistically eugenic competition for status. There's a real fascination in the animation with the physicality of the bears' bodies, the way they squish around, messy scenes of eating, and of course a great deal of gore. You see quite a bit of teddybear pp.
Naturally the mission goes south fast. A lurid trip on colourful bugs brings the first casualties - a fantastic blast of psychedelia - but the teddies are also completely unprepared for fighting the unicorns. Or their willingness to murder each other. In the end, Azulín and Gordi are the only survivors, surviving off the land - and then things really take a turn.
Of the unicorns, we learn much less. One unicorn, María, is something of a deuteragonist - desperately searching for her missing sibling, she finds an old church, where the apes of the forest worship a strange, morphing fleshy entity. We do not immediately see what becomes of this - but María ends up falling afoul of the two surviving bears. Azulín attacks Maria while Gordi can only watch; Azulín hits María multiple times but is ultimately pierced by a young unicorn and cast into the river, leaving María alone with Gordi. (In contrast, in the original short, the Gordi analogue kills the Azulín analogue after they kill a unicorn.)
Azulín, horribly injured, washes up back at the main teddybear base, where the military higherups attempt to make a figurehead of him - completely failing to anticipate his capacity to turn their own forces against them and stage a coup. Where the previous command was simply using the war as a way to stay in power, vengeful Azulín is a true zealot and mobilises the full teddybear army against the unicorns. Meanwhile, Gordi has managed to forge an unlikely friendship with the unicorn María who he has nursed back to health after Bluey's attack.

Vázquez is no stranger to blending cute imagery and extremely dark themes. In contrast to Psiconautas, which felt like a story of the forlorn hope of escape against the bleakness of the world, Unicorn Wars seems more bleak and nihilistic. You know none of this is going to end well; the ending pushes it into a direction of alchemical synthesis, and we'll talk about it when we get there in the film.
Unicorn Wars generally looks amazing, vividly coloured and elegantly blending 2D and 3D animation. And well, there's a reason for that: like I Lost My Body, which shared many of the same animators, this is an all-Blender production, using Grease Pencil for 2D animation, and a very inventive process for the unicorns where the 3D render is converted to a 2D grease pencil drawing which can be further edited by the anmiators. The result is that the unicorns get the sense of life that comes from the slightly imperfections 2D animation, and yet the precise perspective of 3D animation. It's a fantastic showcase of what Blender's 2D-in-3D can enable, and it honestly just makes me really happy to see from a tech-art perspective.
In short, Unicorn Wars is an intense, bleak and also very funny film, I loved it. If you have a reasonable threshold for gore, I hope you'll come to see it with me!
Also check out this cool pixel art of Azulín I found in the gif picker, by @none-dc. (He's such a little shit and this captures it so well.)

Animation Night 179 will be going live now at twitch.tv/canmom, going live now with the film to start in about half an hour (21:50 UK time) - hope to see you there!
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
Surprise!
Two: Him
Letter one of the Surprise! writing Challenge
Warnings: unplanned pregnancy, cursing, Frankie being a cute idiot, references to sex.
Word count: 350 words
Banner made by @toomanystoriessolittletime

Him
Dear
Hi
Y/N,
Fuck! Shit sorry, I’m really bad at this. I can’t even remember when the last time I wrote a letter was. I don’t think I’ve ever written one. Maybe to my mom. I don’t know. Sorry, I’m rambling.
I don’t have access to a computer or phone right now - we’re on a mission off base for another three weeks - which is shit because I want to talk face to face (or at least hear your voice).
I’m sorry I got you pregnant.
Shit. That’s not what I wanted to say. I’m sorry I got you pregnant and now you’re all alone with this. I wish I was there for you.
Mierda. You’re having a baby. My baby. I can’t believe it. I never thought I would ever have a kid but now, it’s all I want.
I know we don’t know each other - well, not really anyway - but you don’t have to question my involvement, I’ll be there for you and her. 100%. I had a hand in creating her, I’m gonna have a hand in raising her. However I can. However you’ll let me. I’m gonna send you some money, it won’t be much but I want to help in any way I can until I’m home.
I’ve applied for leave so I can come home - just for a few days - and we can talk things through. I don’t know if I’ll get it though, it’s usually only given in extreme circumstances. I’ll write again to let you know.
I hope you don’t mind but I’ve also told mi mama. She is gonna be so excited. Anyways, I’ll write to you again soon and if you need anything at all please let me know. I’ve included my mom's number too just in case.
Maria Morales: 555-2424
Yours,
Frankie
Ps: Of course I remember you. How could I not. I can’t get that night out of my head. It’s all I can think about some nights. Most nights.
Pps: I’m sorry that was inappropriate.
————————————————————————
Tagging @prolix-yuy for the next part 💕
————————————————————————
Writing challenge tag list: @toomanystoriessolittletime @misspearly1 @scorpio-marionette @boliv-jenta @kybitchcrystal
————————————————————————-
Frankie Morales: @paulalikestuff @vanemando15 @hb8301 @djarinslove @agingerindenial @afootnoteinyourhappiness @almaeunice @readsalot73 @xxlaynaxx
@marielovesstuff @a3trogirl @loonymagizoologist @kirsteng42
@amb11 @absolutegeek
#pedro pascal#frankie morales x female reader#pedro pascal x reader#frankie x reader#frankie morales x f!reader#pedro pascal x female reader#surprise! writing game
193 notes
·
View notes
Text
Over the past ten years, these types of attacks have grown increasingly aggressive. Not since the movement for women's suffrage have women's rights activists in the west been subjected to such massive hate campaigns. Several feminists who have spoken out about women's rights in relation to gender identity theory have been physically assaulted. In September 2017, a women's meeting titled “We Need to Talk About Gender” was held in Hyde Park in London; the location – Speakers' Corner – was decided on following the organisers receiving threats and pressure to cancel including cancellations of offers to host them from several venues. At this historics meeting place where the suffragettes had met to demand the vote for women, a group of counter protesters arrived with signs that read “No Debate” and “Terfs not Welcome.” They violently attacked the meeting attendees and a 25-year-old man named Wolf was later sentenced for assault of a 60-year-old woman. Wolf identifies as female and had previously tweeted that he planned to attend the meeting to “fuck some terfs up” and “if you are a terf and/or dont [sic] think transwomen are women, you can suck my cock you cuntface.” An observer at the trial writes:
“Two dozen individuals-mostly men with masks on some in some in full combat gear -accompanied Wolf to court. […] Three of Wolf's supporters brought fighting dogs (Dobermans and Mastiffs), as well as a huge sound system blaring death metal. Half stayed outside the court, half came in. The machismo of it all was palpable. […] By day two, Wolf's supporters had dwindled to around a dozen. All but one were men. [Maria] McLachlan's supporters were all women.”
An odd scene indeed: a group of young, masked men gather in support of a man who has struck down a 60-year-woman, all convinced that they are women. The women's movement has gone through many ideological conflicts over the years but these have rarely been solved by assaulting one another.
– Kajsa Ekis Ekman (2023) On the Meaning of Sex: Thoughts on the New Definition of Woman, pp. 289-90.
#kajsa ekis ekman#on the meaning of sex#feminism#radical feminism#maria mclachlan#let women speak#male violence#misogyny#lilac posts
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Johannes Brassart (c. 1400 - c. 1455)
– Regina coeli
[(no. 87-179. pp.197r-198r) MS 1374 [87] (Trent 87). Museo Provinciale d'Arte, Castello del Buonconsiglio, Trento, Italy]
Regina coeli, laetare, alleluia. / Quia quem meruisti portare, alleluia. / Resurrexit sicut dixit, alleluia. / Ora pro nobis Deum. // Alle Domine, nate matris Deus alme / nobis confer praestaque vivere. / Quoniam te decet laus honor Domine, / qui de morte surrexisti rex pie. / Fac nos post te surgere, alleluia.
– Ave Maria
[(no. 87-036. p.51r) MS 1374 [87] (Trent 87). Museo Provinciale d'Arte, Castello del Buonconsiglio, Trento, Italy]
SUPERIUS I
Ave Maria gratia plena Dominus tecum / Et tua gratia sit mecum / gloria mulierum, gemma virginum / stella sacerdotum, rosa martyrum / domina apostolorum, regina angelorum / Iocunditas celorum, Iesu dei mater. / Amen.
SUPERIUS II
Ave Maria gratia plena / ego peccator suspiro ad te / inclinans ad te intercede pro me / ad dilectissimum filium tuum / ut mundet me a peccatis, liberet me a poenis / ut salvet me in cælis, ut vivam cum beatis. / Benedicta tu in mulieribus / et benedictus Iesus / dulcissimus fructus ventris tui. / Amen
_
Arnold de Lantins: Missa Verbum Incarnatum
Capilla Flamenca. Dirk Snellings
Psallentes. Hendrik Vanden Abeele
Clari Cantuli. Ria Vanwing
(2002, Ricercar RIC207)
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mi ricordo
“ Mi ricordo che una volta la Valle d'Aosta aveva il mare.
Era abitata dai Salassi (che in greco vuol dire «popolo del mare») che per le navi di passaggio avevano costruito sul Cervino un faro alto almeno come Mike Bongiorno.
Adesso, con gli anni, il mare si è ritirato ed è rimasta soltanto la Dora Baltea, ma prima, al posto delle trote c'erano i delfini salmonati. I delfini più belli venivano catturati e portati a Cogne dove, invece delle acciaierie, c'era un acquario e se si girava cadeva la neve finta. Bisognava stare attenti, però, perché usciva tutta l'acqua e i delfini senza acqua muoiono, quasi come gli uomini.
Mi ricordo che al porto di Courmayeur si arrivava in skilift. Dalla banchina partiva il motoscafo più alto del mondo; si saliva e poi via, ottocento chilometri di piste. Sci d'acqua, naturalmente. Mi ricordo che il Piccolo San Bernardo era un'isola e il Gran San Bernardo era un'altra isola, ma più grande ed era piena di cani da valanga che passavano le giornate a guardarsi in faccia e a dirsi: «Boh?» Per quello gli è venuta la bocca all'ingiù. Oggi risulta chiaro che i cani da valanga erano fuori luogo, ma oggi, col progresso, si sanno tante cose che una volta non si potevano capire.
Per esempio allora ci si chiedeva perché tutti i rifugi del Cai si chiamavano «Miramare» e perché un antico proverbio pugliese diceva più o meno: «Se Aosta avesse i monti sarebbe una piccola Sestrière». «Che cosa c'entrano i monti», pensava il guardapesca ributtando in mare un camoscio che gli era rimasto impigliato nella rete. Già allora i camosci erano una razza protetta. Li tenevano al Gran Paradiso assieme alle foche, due panda e qualche Duna giardinetta.
Mi ricordo che i valdostani cantavano in coro un'antica canzone di montagna. «Giù pei ponti/ giù pei ponti che noi andremo/ coglieremo/ coglieremo le stelle marine/ per donarle/ per donarle alle bambine…» Mi ricordo che l'aquila faceva – abbastanza bene – il verso del gabbiano e tutt'intorno c'era un delizioso profumo di spaghetti alle vongole e di fontina. Erano i marinai che tornavano con le loro greggi di tonni. Passavano sotto l'Arco di Augusto (che allora era un ponte), baciavano le loro mogli e andavano a rifocillarsi al bar «Caa custa quel caa custa viva el battagliùn d'Aùsta». Era un nome un po' lungo per un semplice bar dove si beveva soltanto genepì e si mangiava soltanto genepesca. Per questo i marinai familiarmente lo chiamavano «Caa custa».
Mi ricordo che fu quando il «Caa custa» venne venduto a Maria Josè (una nobildonna che aveva curiosamente il nome di Altafini ma lanciava i piatti come Suarez) che incominciarono a cambiare le cose. Al «Caa custa» prese piede irreversibilmente la Nouvelle Cuisine e nella zuppa di pesce comparvero i primi savoiardi. Era troppo. I valdostani chiesero aiuto a una città amica, Bergùm de Hura e al suo re, Mais, che a tappe forzate occupò Aosta e impose su tutta la Valle la polenta. I savoiardi vennero mandati in esilio e il mare si ritirò a Cascais. “
Gino & Michele, Saigon era Disneyland (in confronto), Milano, Baldini & Castoldi, 1991¹; pp. 107-108.
#Gino & Michele#satira#leggere#Valle d'Aosta#montagna#Saigon era Disneyland (in confronto)#anni '90#Alpi#Cogne#riscaldamento globale#Gran Paradiso#natura#Courmayeur#Piccolo San Bernardo#Sestrière#Dora Baltea#mari e monti#Gran San Bernardo#ambiente#Cascais#Nouvelle Cuisine#geografia italiana#Arco di Augusto#Cervino#Mike Bongiorno#rovesciamento#paradossi#Italia Settentrionale#Italia del Nord#Bergamo
12 notes
·
View notes

