#the sasanian empire
Photo

Ancient Iranian Carving Seized at a London Airport
An ancient sculpture illicitly carved from a rock relief in Iran will soon go on display at the British Museum before being repatriated to the National Museum in Tehran.
Carved in calcareous limestone, the sculpture depicts a standing male figure with an ornamental headdress. The piece likely hails from the 3rd century C.E. when the Sasanian Empire ruled greater Iran, according to the Guardian.
“It belongs to a period when Iran was the center of a powerful empire stretching from Syria to the Caucasus and Central Asia, and with its capital at Ctesiphon, south of present-day Baghdad,” St. John Simpson, an archaeologist and senior curator the British Museum’s department of the Middle East, told the paper. “The Sasanians were powerful rivals of Rome, and famous today for their fine silverwares and cut glass.”
The relief was seized at the Stansted airport outside of London, where border officers pulled the item aside because of its suspicious packaging—an unpadded, slapdash crate held together by nails. Inside was the carving, which had recently been excised with an angle grinder.
“We almost never come across a case of something being cut out of the ‘living rock,’” Simpson said. “That’s a level of brutalism that surpasses anything.”
Exactly where the carving came from remains a mystery, though context clues may help to narrow the list of potential locations. Roughly only 30 Sasanian rock reliefs are known to exist today, and almost all them came from the small Fars Province in southwest Iran.
Simpson suspects it “comes from somewhere in the Shiraz area” of the province. “Stylistically, it is similar to one known in the region,” he explained. “I think it probably is part of a big sequence. There might be more bits out there.”
The subject of the piece is similarly difficult to determine. “The lack of an inscription makes it impossible to identify the person depicted, but his dress and diademed headdress signifies him as a person of high rank,” the curator said. “His gesture of greeting and submission, with a raised bent forefinger, is a feature of Sasanian art when figures are in the presence of royalty, which suggests that this was part of a larger composition, with the king to the right and perhaps other figures behind.”
Interpol and the National Crime Agency have both investigated the object, but no arrests have yet been made. An internet auction site in the U.K. was listed as the package’s destination address, but the company claimed not to be expecting it.
Because of its poor padding, the relief broke in two pieces during transport. Conservators have since put it back together.
“The British Museum is committed to contributing to the preservation of cultural heritage in the U.K. and globally, partnering with law enforcement agencies to identify illicitly trafficked antiquities,” read a statement from the museum. “Objects seized in this way are brought to the British Museum for identification and cataloguing.”
The London institution obtained permission from the Iranian government to display the carving for three months. After that time, it will be repatriated to the National Museum in Tehran.
Simpson called the newly repaired piece “stunningly attractive,” before weighing in on its potential worth.
“The valuation could be anything, really. We’re talking £20 million to £30 million-plus,” ($25 million to $37 million) he said. “There’s never been anything like it on the market.”
By Taylor Dafoe.
#Ancient Iranian Carving Seized at a London Airport#the sasanian empire#rock releif#rock sculpture#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#stolen#looted
48 notes
·
View notes
Text

Stucco panel depicting a winged horse, Sasanian period
From the Jahangir archaeological site in Ilam province, Iran
Photo by Leila Khosravi, Pourdavoud Institute, UCLA
108 notes
·
View notes
Text

Ancient Iran, Achaemenid, Parthian and Sasanian empires based aromantic moodboard~ ^^
For an anon!! Hope you like~
Want one? Send an ask! -mod Jay
#ancient#ancient iran#iran#iranian#ancient iran aesthetic#achaemenid#achaemenid empire#parthian#parthian empire#sasanian#sasanian empire#empires#aro#aromantic#aro pride#arospec#arospec pride#pride#edits#lgbt#lgbtqia#lgbtqa#flag edit#flag edits#pride flag edit#pride flag edits#edit#moodboard#moodboards#mood board
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
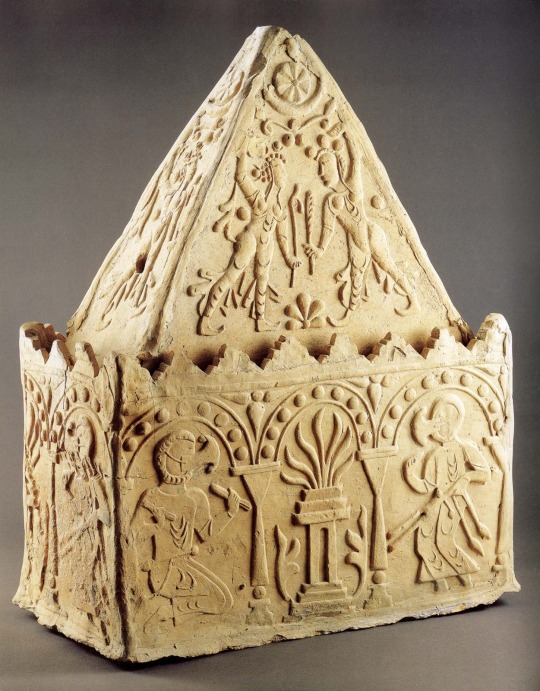

Look at this beautiful ossuary.
#history#ancient history#zoroastrianism#ancient iran#ancient persia#sasanian empire#sassanian empire#zoroastrian priests#sogdian#fire temple
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

Persian manuscript describing how an ambassador from India, probably sent by the Maukhari King Śarvavarman of Kannauj, brought chess to the Persian court of Khosrow I.
The same scene from another manuscript.An illustration from a Persian manuscript "A treatise on chess". The Ambassadors from India present the Chatrang to Khosrow I Anushirwan, "Immortal Soul", King of Persia
From Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_Iran#/media/File:A_treatise_on_chess_2.jpg
#iran#india#iranian#persia#persian#chess history#chess#Maukhari#sasanian empire#sasanian dynasty#pre-islam persia#medieval#6th c. persia#6th century
6 notes
·
View notes
Photo
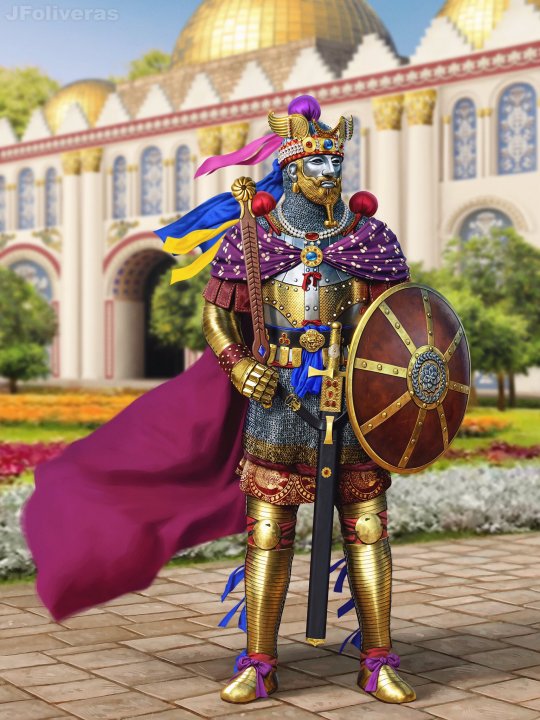
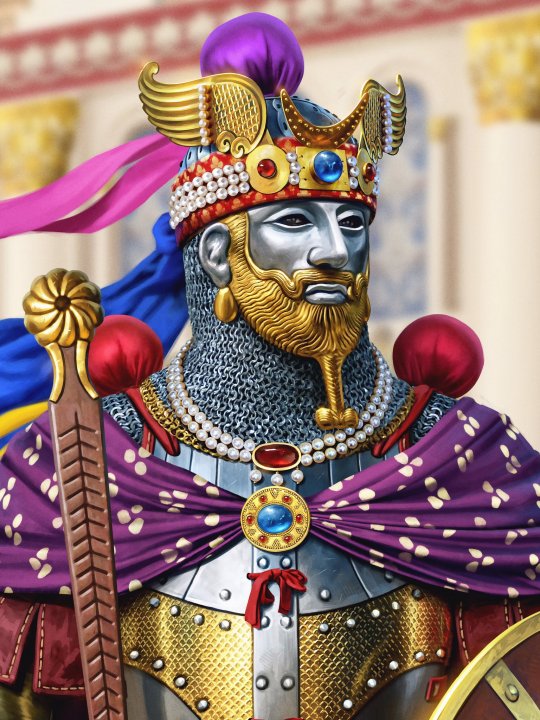



art by Joan Francesc Oliveras
“Pushtigban-salar (royal bodyguard commander) of the Sasanian Empire of Persia. The armor is an interpretation of the plate armor worn by some god in a Sasanian column capital.”
8 notes
·
View notes
Text




Gaul
New Kingdom
Persia
Qin Empire
#Hetalia#Hetalia ancient#gaul#Hetalia gaul#Mama gaul#Hetalia mama gaul#Hetalia oc#Hetalia ancient egypt#Hetalia New kingdom#Hetalia mama egypt#Mama egypt#Hetalia persia#Persia#Sasanian Empire#Hetalia Sasanian Empire#Hetalia china#Hetalia qin empire#qin empire#Immedorica Bonnefoy#Merit Iset Hassan#Wang Yao#Nabuhaithu Bel-Anzu
0 notes
Note

true?
TRUE ✅
[THIS POST HAS BEEN FACT CHECKED BY PATRIOTS OF THE SASANIAN EMPIRE]
613 notes
·
View notes
Photo
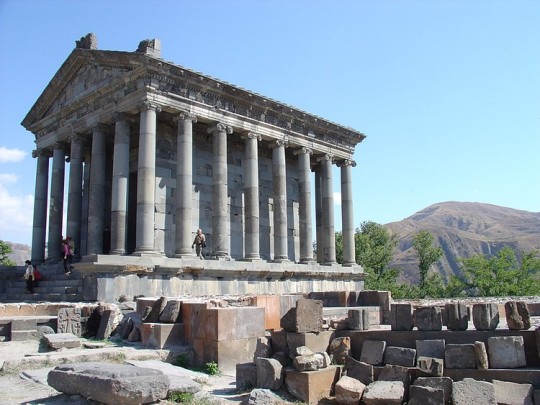

Ancient Armenia
Ancient Armenia, located in the south Caucasus area of Eurasia, was settled in the Neolithic era but its first recorded state proper was the kingdom of Urartu from the 9th century BCE. Incorporated into the Persian Empire of Cyrus the Great in the 6th century BCE, the Orontid dynasty ruled as Persian satraps, a function they performed for their next overlords the Macedonians and Seleucid Empire into the 3rd century BCE. Under the Artaxiad and Arsacid dynasties the country flourished but was often caught between the ambitions of Parthia and Rome, and then the Sasanian and Byzantine Empires. The boundaries of the state varied considerably over the centuries but such common factors as religion and language were united by long-lasting dynastic clans, which gave Armenia its own unique identity throughout antiquity.
Hayasa-Azzi (1500-1200 BCE)
The first identifiable culture in the region is the Hayasa-Azzi, an indigenous tribal confederation which flourished on the fertile plateau of ancient Armenia around Mount Ararat and parts of modern-day eastern Turkey between c. 1500 and c. 1200 BCE. The Hayasa-Azzi are the eponym of the Hay people, the term Armenians use to describe themselves and their state, Hayastan. Over time, the Hayasa-Azzi mixed with other ethnic groups and local tribes such as the Hurrians, Arme-Shupria, and Nairi, probably motivated by the need for defence against more aggressive and powerful neighbours like the Hittites and the Assyrians. They were probably infiltrated by the Thraco-Phrygians following the collapse of the Hittite Empire c. 1200 BCE. Eventually, these various peoples and kingdoms would be fused into the region's first recognisable and recorded state, the kingdom of Urartu from the 9th century BCE.
Continue reading...
105 notes
·
View notes
Text
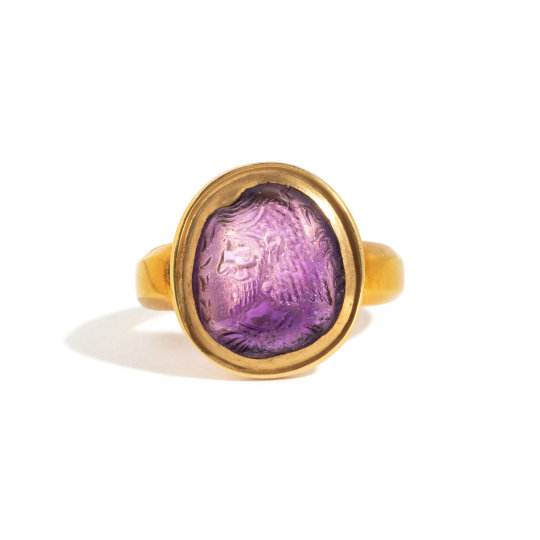
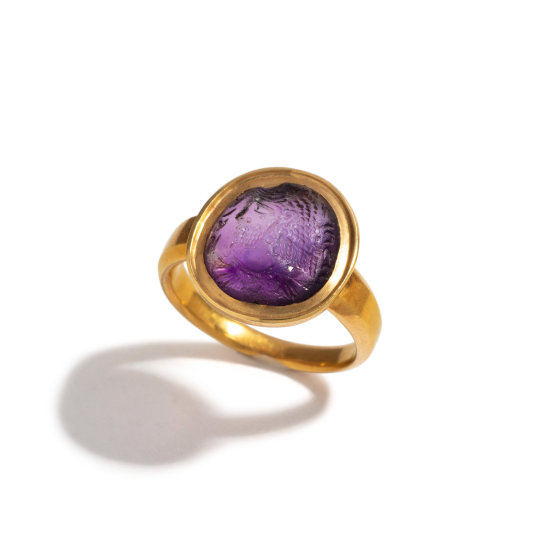
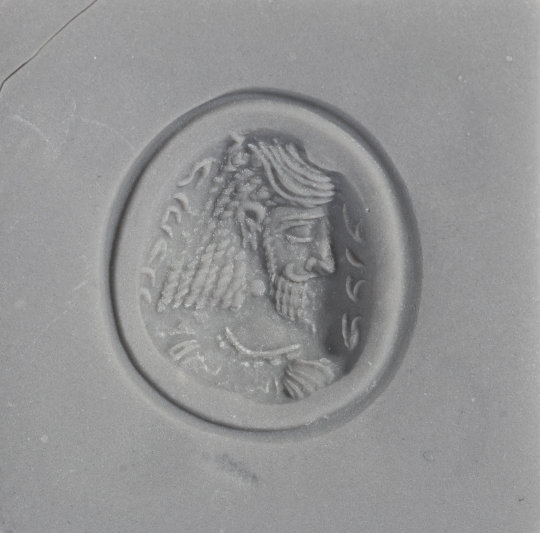



Gold and amethyst intaglio ring with royal portrait and Pahlavi inscription, Sasanian Empire, 5th century AD
from Hindman Auctions
212 notes
·
View notes
Text
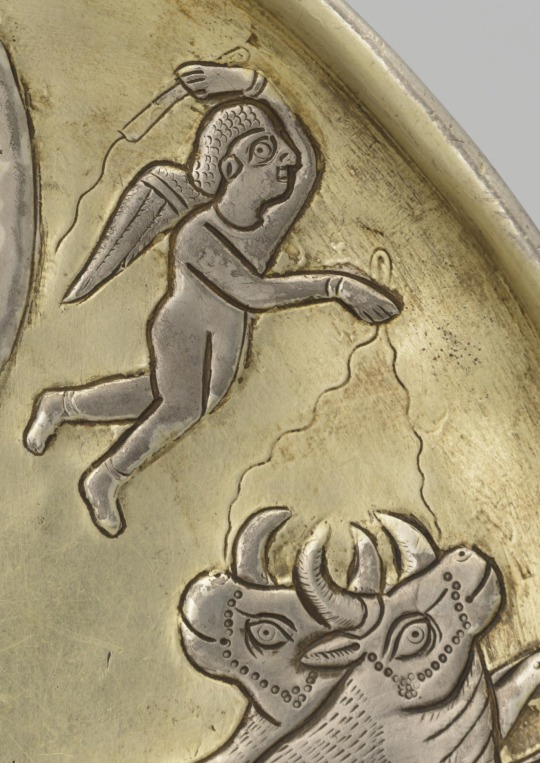






Sassanid silver plate 7th C. CE. Decorated with a figure seated on a couch in a crescent moon and a figure standing in an archway. Found in Klimova, Russia in 1907. The base of the vessel appears to have runic script scratched into it. This item is sometimes referred to as The ‘Clock of Khosrow’ or The ‘Throne of Khosrow’ Plate. Diameter: 21.6cm.
I'm just going to do a brief summary of what caused Persia to fall to Islam.
The Islamic invasion of Persia began sometime between 628-632 CE. From 541 CE to this time Persia had been exhausted by an almost constant state of war. Most of the fighting was with the Byzantine Empire in the west: The Lazic War (541-562), Byzantine–Sasanian War of 572–591, Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628.
However, there were also wars with the Turks to the north and the east: Perso-Turkic war of 588–589, Perso-Turkic war of 606–608, Perso-Turkic war of 627–629. In this final war the Byzantines and Turks were allies. This alliance took time to come into being but had been sought out by the Turks almost immediately after they destroyed the Hephthalites, indicating they planned to do to the Persians what they had done to the Huns. The medieval historian Movses Kaghankatvatsi described the war of 627-629:
"At the arrival of the all-powerful scourge (universal wrath) confronting us, the invaders [Turks], like billowing waves of the sea, crashed against the walls and demolished them to their foundations. [In Partaw], seeing the terrible danger from the multitude of hideously ugly, vile, broad-faced, without eyelashes, and with long flowing hair like women, which descended upon them, a great terror (trembling) seized the inhabitants. They were even more horrified when they saw the accurate and strong [Khazar] archers, whose arrows rained down upon them like heavy hailstones, and how they [Khazars], like ravenous wolves that had lost all shame, fell upon them and mercilessly slaughtered them on the streets and squares of the city. Their eyes had no mercy for neither the beautiful, nor handsome, nor the young men or women; they did not spare even the unfit, harmless, lame, nor old; they had no pity (compassion, regrets), and their hearts did not shrink at the sight of the babies embracing their murdered mothers; to the contrary, they suckled blood from their breasts like milk."
Ironically, the Sassanid ruler Khosrow I had married a Turkic princess to win an alliance with them so the two could destroy the Huns together in 560 CE at the Battle of Gol-Zarriun. Khosrow I chose his Turkic progeny, Hormizd IV, as ruler over his Persian children. From Iranica Online:
"Hormozd’s character displeased everyone. He antagonized the Zoroastrian clergy, allegedly killing many of them, even the chief mowbed, and alienated the nobility by killing thousands of them (Ṭabari, I, p. 991; tr., V, pp. 297-98; Balʿami, ed. Bahār, pp. 1072-73; Masʿudi, Moruj, ed. Pellat, sec. 632; Šāh-nāma, Moscow, VIII, pp. 319 ff.). In diplomacy he showed inflexibility, even poor judgement. He disrupted the peace negotiations with the Byzantines and made demands (payment of “tribute”) that the Romans could not accept (Menander, frag., 23.9-24-12529). His contemporary, Menander Protector, lamented that “the Romans and the Persians would have made peace, had not Ḵosrow left this life and his son, Hormisdas [Hormizd IV], a truly wicked man, assumed the crown” (tr., pp. 207-9)."
Finally the Sassanid Empire went into a civil war from 628-632 CE where it had become politically decentralized. The Plague of Sheroe also occurred in 627-628 CE, most heavily devastating the populations in the western provinces with some areas experiencing a 50% mortality rate. Afterward, the Arab Muslims flooded into an already ravaged Persia like bacteria infesting an open wound.
96 notes
·
View notes
Text
Shoemaker on literacy, memory, oral tradition, and the Quran:
Studies of literacy in pre-Islamic Arabia have been severely overlooked in recent Quran scholarship; in fact, literacy in the 7th century Hijaz was "almost completely unknown" and "writing was hardly practiced at all in the time of Muhammad." "[T]here seems to be a widespread agreement among experts on the early history of the Arabic language 'that, before and immediately after the rise of Islam, Arab culture was in all important respects fundamentally oral.'" Ancient graffiti in the region seems to have been a bit like early runic writing in Scandinavia--not central to the culture, mostly decorative and incidental, and certainly not used for long, important texts. "There is, in effect, a lot of 'Kilroy was here' scattered across the Arabian desert." Indeed, most of these graffiti are personal names or private in nature--we're not talking monumental inscriptions here, we're talking bored herders scratching stuff onto rocks to pass the time.
Southern Arabia and the larger oases to the north had more in the way of literate elites (and thus things like monumental inscriptions), but these places were far from the central inland Hijaz. If someone in this region did want to become literate, they would probably have learned to read and write in Greek or Aramaic, which were useful and important linguae francae.
As in very early Christianity, writing occupied a controversial position vis a vis orality--oral tradition was primary for the production and transmission of culturally important things like religious texts, poetry, literary prose, genealogy, and history. The shift to a literate culture came only with the expansion of Muhammad's polity into a wealthy, multicultural empire rather than a tribal state. Indeed, much of the early Caliphate's administration used Greek and other languages--Arabic entered administration only slowly, since a lot of early bureaucrats were drawn from the Roman and Sasanian bureaucracy.
And like early Christianity, another reason not to feel any urgency to write down Muhammad's teachings was that early Muslims expected the end of the world to come very soon, maybe initially even before Muhammad's own death.
The dialect of the Quran is distinctive and unusual; it is very difficult to locate where this dialect might have originated. Ahmad Al-Jallad tentatively identifies an Old Hijazi dialect, but the evidence for this dialect (besides the Quran itself) is limited and mostly much more recent, and he assumes the Quran was produced in the Hijaz.
The Arabic of the Quran can probably be identified with the prestige dialect of Levantine Arabic in the Ummayad period, but the origin of that dialect, and what Arabic dialects were brought together there in that time, is hard to ascertain with certainty.
Shoemaker thinks the Quran started as short collections drawn from individual memories following the conquest and encounters with widespread literacy; these collections would have been considered open, and subject to influence from oral tradition. They were combined into increasingly larger collections, with additional traditions and revisions, emergin as something like divergent versions of the Quran (though still not fully static and closed). Finally, the traditions of these regional versions, with other written and oral traditions, were fashioned into their canonical form under Abd al-Malik, and this version was progressively enforced across the empire.
Shoemaker brings in memory science and the anthropology of oral cultures: memory is highly frangible and fallible. Even though it functions well for day to day tasks, it's important not to overlook how common misremembering and re-remembering alters information in both personal and collective memory when talking about a text that even Islamic tradition agrees was not written down within Muhammad's lifetime.
Most forgetting occurs shortly after an event in question; a small core of memories we develop about an event will persist for a significant time after. These findings have been corroborated both in the lab and in the circumstances of everyday life.
Memory is not primarily reproductive; literal recall is, in evolutionary terms, pretty unimportant, and brains omit needless detail. Remembering thus involves a lot of reconstruction more than it does reproduction; memories are storied piecewise in different parts of the brain, and are assembled on recall, with the gaps being filled in using similar memory fragments drawn from comparable experiences.
Note Bartlett's experiments using a short Native American folktale; when asked to recall this story, even after only fifteen minutes participants introduced major and minor changes. Subsequent recall didn't improve accuracy, though the basic structure of the memory developed pretty quickly in each individual. But this structure was not especially accurate, and significant details vanished or were replaced with new information. Most often this information was drawn from the subject's culture (in this case, Edwardian England), forming a memory that made more sense to them and had more relevance in their context. The overall style was quickly lost, and replaced by new formations, and there was a persistent tendency to abbreviate. After a few months, narrative recall consisted mostly of false memory reports, a finding verified by subsequent replications of his experiments.
Experiential and textual memory in particular degrades very rapidly; this degredation is much faster when information is transmitted from one person to another. Epithets change into their opposites, incidents and events are transposed, names and numbers rarely survive intact more than a few reproductions, opinions and conclusions are reversed, etc. Figures like Jesus or Muhammad will hardly be remembered accurately even by people who knew them.
The style of the Quran (e.g., prose, and often terse, elliptic, and occasionally downright nonsensical prose at that) does not lend itself to memorization; Shoemaker argues it is only possible for people to memorize the Quran now because it has become a written document they can consult in the process.
Eyewitness testimony is of course also notoriously unreliable, despite what apologists (in particular Christian apologists) have argued. Cf. Franz von Liszt's experiment in 1902, where a staged argument in a lecture escalates to one student pulling a gun on another--after revealing this event was scripted and staged, and asking different students to recall the details of the event at different intervals afterward, literally none of them got it right--the best reports, taken immediately, got things about one quarter correct. Even repeatedly imagining a scenario vividly enough can eventually lead to a false memory of it occurring (a phenomenon which may explain some alien abduction reports). People mistake post-even hearsay or visualization for firsthand knowledge, especially in the case of dramatic events.
What memory excels at is remembering broad strokes--we are adapted to retain the information which is most likely to be needed, i.e., the gist (or, more likely, the broad themes) of events and information, and not its exact form.
There's a long digression here about John Dean's testimony on the Watergate conspiracy--this may be the first book in early Islamic studies to have Richard Nixon in the index.
Even competitive memory champions train for short-term recall of large amounts of information; they, and other people with preternaturally good memories, are of course exceedingly rare. It's very unlikely that someone could remember, several decades after the fact, precisely (or even mostly) what was told to them by their friend whose brother's wife's cousin was really there. So even within the traditional account of the Quran's composition, it makes no sense to claim it is in fact the verbatim word of Muhammad.
As in the case of Solomon Shereshevski, when you do have preternaturally good recall even for (say) lists of nonsense syllables, the result is actually kind of debilitating--you have so many useless details to sort through, it makes it quite hard to function at an abstract level. And hyperthymesiacs, though they exhibit a high level of recall about their past, still often remember things incorrectly, at about the same rate as people with normal memories--they are no less susceptible to false or distorted memories.
Nevertheless most modern scholars treat the Quran as a verbatim transcript of Muhammad's words. This is exceedingly unlikely! Especially given that "group" or "collaborative" memory--memories as reconstructed by individuals working together--appears to be even less accurate than individual memory. You get better results having people try to recall events by themselves.
Since during the age of conquests the majority of converts were not closely preoccurpied with the interpretation of the Quran, it would have had to have been rediscovered and hermeneutically reinvented later; the memory of Muhammad's words were being shaped by the nature of the community he founded, as its members collective and individual needs continued to evolve along with the context of transmission.
Many people, both scholars and the general public, seem to believe that people in oral cultures have remarkable capacities for memory not possessed by those of written cultures. Study of oral cultures has shown this is demonstrably false; literacy in fact strengthens verbal and visual memory, while illiteracy impairs these abilities. People in literate cultures have better memories!
Oral transmission is not rote replication; it is a process of recomposition as the tradition is recreated very time it is transmitted. Oral cultures can effectively preserve the gist of events over time, but each time the details are reconstituted, and the tradition can radically diverge from its first repetition, with the stories of the past being reshaped to make them relevant to the present and present concerns.
The collective memory of Muhammad and the origins of Islam as preserved in the Sunni tradition would have forgotten many details as a matter of course, many others because they were no longer relevant to the later Sunni community, and they would have been reshaped in ways that made them particularly suited to the life and community of their contemporary circumstances, exemplifying and validating their religious beliefs--ones very different from those of Muhammad's earliest followers.
The early Muslim conquests put a comparatively small number of soldiers, scattered across a huge territory, in a wildly different cultural and social context, especially in close contact with different Christian and Jewish communities, esp. in the Levant, which rapidly became the cultural center of the new empire. Jews and Christians may have joined the new religious community in large numbers in this time also; their faith and identity would have continued to evolve in this period, as we would expect from comparative episodes in the history of other religions. By the time that Muhammad's teachings were formally inscribed, the memories of his few hundred initial companions would have been transmitted and dispersed to a large number of people in a totally different set of circumstances, with consequences for how those memories exactly were recalled.
Jack Goody, researcher on oral traditions: "It is rather in literate societies that verbatim memory flourishes. Partly because the
existence of a fixed original makes it much easier; partly because of the elaboration of spatially oriented memory techniques; partly because of the school situation which has to encourage "decontextualized" memory tasks since it has removed learning from doing and has redefined the corpus of knowledge. Verbatim memorizing is the equivalent of exact copying, which is intrinsic to the transmission of scribal culture, indeed manuscript cultures generally."
Techniques like the ars memoriae belong to literate cultures and were invented by literate people; they are unknown in oral cultures. Oral and literate cultures in fact have a radically different idea of what it means for a text to be "the same"--in the former, word-for-word reproduction is not necessary. A poem can be "the same poem" even if every time it is performed it is largely unique.
Case of the Bagre, the sacred text of the LoDagaa people of Ghana, an extended religious poem used in a liturgical context. Variations in its recitation aren't just variations in wording; changes in recitation can be radical, and the last version is always the starting point. Nevertheless (as in other oral cultures) it is considered "the same," functionally identical with each recitation. These differences appeared even among different performances by the same reciter, or multiple times in the same ceremony. Even the most formulaic parts have great variability. Similar variability in oral texts in other oral cultures has been documented by other anthropologists, including for historical events.
Shoemaker notes that the tradition that the Vedas were transmitted without variation from the time of their composition remains an article of faith in some quarters of South Asian studies; this flies in the face of all available evidence. In fact we have no idea what the state of the Vedic texts was prior to the earliest manuscripts; they may have been written all along.
Collective memory is shaped by contemporary cultural imperatives--examples of Abe Lincoln, a white supremacist considered nothing special by his peers; Christopher Columbus, once revered; the last stand at Masada, considered a minor event of little importance to broader Jewish history until the founding of Israel.
There doesn't have to be any conspiracy or coordinated effort for false narratives about the past to take root.
The hard horizon of communicative memory is around eighty years; so historical consciousness basically only has two modes: the mythic past of collective memory, and the recent past less than eighty or so years ago.
Lack of a clear "generic" monotheism in the Hijaz around the time of Muhammad's birth means the expectations and memory of Muhammad would have been profoundly shaped by Christian and Jewish beliefs.
Early Islam, like early Christianity, wasn't old enough to have a clear distinction between historical/origins memory and recent/communicative memory.
"For most of the seventh century, then, Muhammad’s followers had a memory that was still immersed in the social and cultural milieux of the late ancient Near East, from which they had yet to clearly differentiate themselves. They eventually would do this in large part by developing a distinctive collective memory for their group, different from those inherited from Judaism and Christianity, a process that was no doubt delayed by their fervent belief that the world would soon come to an end, making such an endeavor rather pointless for a time. Only as the end continued to remain in abeyance, and the community’s living memory grew ever distant from the time of origins did they develop a collective memory of their own. Yet, as Islamic collective memory began to evolve, one imagines that it initially took different shapes within the various pockets of Believers that were scattered across their empire. The basic elements of this nascent collective memory were, as Halbwachs says of the early Christians, “still dispersed among a multitude of spatially separated small communities. These communities were neither astonished, anxious, nor scandalized that the beliefs of one community differed from those of another and that the community of today was not exactly the same as that of yesterday.” Thus, we should expect to find a significant degree of diversity in religious faith and memory among the different early communities of the Believers, scattered and outnumbered as they were among the Jews and Christians of their burgeoning empire. Only with ʿAbd al-Malik’s program of Arabization and Islamicization was a new, distinctively Islamic collective memory and identity concretized and established for this new religious community. It was a collective identity that was formed from the top down and imposed, at the expense of any other alternative collective memories, with the full power and backing of the imperial state."
The limits of oral tradition apply even more strongly to the hadith and biographies.
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
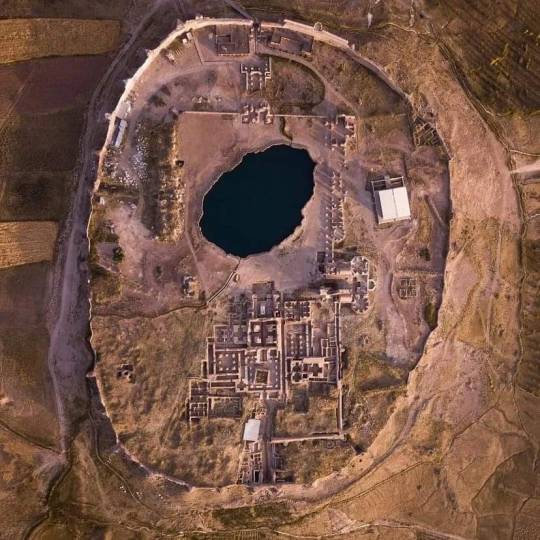

Aerial shot of Takht-e Soleymān (Throne of Solomon), an archaeological site in West Azerbaijan province, Iran, dating back to Sasanian Empire (224-651 CE).
208 notes
·
View notes
Text
Incantation bowl
These wonderful bowls are beautiful and while not used anymore provide a snapshot into history and Babylonian Spiritual Beliefs
Originating from Ancient Mesopotamia, now the Middle East, they were popular in antiquity with the Jewish, Christians, and Ancient Babylonians in the Area. Over 2000 have been found in Archeological digs, bringing to light a popular folk practice of the time.

They work as protective charms which were thought to trap demons, the bowls were usually inscribed in a spiral, beginning from the rim and moving toward the center. They were buried face down, commonly placed under the threshold, in courtyards, the corner of the homes of the recently deceased, and the entrance to graveyards.

Important Wikipedia Excerpt
A subcategory of incantation bowls is those used in Jewish and Christian practices. Aramaic incantation bowls are an important source of knowledge about Jewish occult practices, mainly the nearly eighty surviving Jewish incantation bowls from Babylon during the rule by the Sasanian Empire, primarily from the Jewish diaspora settlement in Nippur. These bowls were used in magic to protect against evil influences such as the evil eye, Lilith, and Bagdana. These bowls could be used by any community member, and almost every house excavated in the Jewish settlement in Nippur had such bowls buried in them. The inscriptions often include scriptural quotes and quotes from rabbinic texts. The text on incantation bowls is the only written material documenting the Jewish language and religion recovered from the period around the writing of the Babylonian Talmud. Scholars say that the use of rabbinic texts demonstrates that they were considered to have supernatural power comparable to that of biblical quotes. The bowls often refer to themselves as "amulets" and the Talmud discusses the use of amulets and magic to drive away demons.
The majority of recovered incantation bowls were written in Jewish Aramaic and while not commonly used anymore it is a cool folk practice that can be found branching across cultures.
Thank you for being here with me and having tea with me on the other side of the Great Divide :)
#occult#occultism#occultist#demons#ars goetia#solomonic magick#magick#witchcraft#folklore#folklorist#magi#magus#grimoire#grimoires#witch#witchblr#witches#witchythings#witchlife#pagan witch#Avatar#WanderingSorcerer
109 notes
·
View notes
Text
more about blood of eden naming because i have sunk my teeth into it, especially on how they use the names of destroyed and mythical places.
the wings/cells
merv: also alexandria, antiókheia in margiana, marw al-shāhijān. located in iran. inhabited from c. 2000BCE, a holy site to zoroastrians, one-time capital of the islamic caliphate, razed to the ground in 1788/9.
ctesiphon: also tyspwn, ktesiphōn. located in iran iraq (sorry, my geography of this area begins with sumerian cities and ends with aššur). founded c.120BCE, capital of the parthian, sasanian empires. besieged in the battle of al-qādisiyyah in 637CE, became a ghost town afterward.
troia: troy, illios, wiluša. the one heinrich schliemann “““excavated”““. located in turkey. inhabited from c. 3600BCE, the troy, the one we all know, hektor, akhilleus, kassandra. the milawata letter. destroyed multiple times over the millennia, the last being in thee roman era.
lemuria: mythical lost continent beneath the indian ocean, proposed by philip sclater, later appropriated by occultists. identified with the lost continent of kumari kandam by some tamils, which is believed to be their ‘cradle of civilization’ where the population was solely tamils.
mu: also a mythical lost continent, name also used interchangeably for lemuria and atlantis, the product of the mind of augustis le plongeon.
further, we see we suffer use the following names for other military cells in chapter 27:
saaftinge, zoar, birmingham, maputo, taree, memphis, taksa, calakmul, valencia, opava, dundee
normal cities, to us. however, to the people of blood of eden, these are all mythical, lost places regardless of the reality of merv, tyspwn, and wiluša. they are at a remove of ten thousand years. they are in the space between the fall of roman troy and the re-discovery of it, though there can be no rediscovery, only stories. much like australian aboriginal stories stretch back before certain parts of australia were underwater, blood of eden preserves the names of places that have been obliterated by the nuclear bombs, by whatever john continued to do to earth to have it so completely covered by water except for canaan house.
‘the flood, you know? You can wash things clean. that’s all the end of earth was … making things clean’, says john, and that’s what he did. he re-enacted the story of atra-hasis, of utnapištim, but there was no one to speak through the reed wall to save humanity even though, through the ages, it is very likely that the story of john destroying the earth became their new flood myth, their ‘god decided the world was too populous and was going to destroy it, and we are the chosen people who managed to survive.’ the whole of earth is mu, is lemuria.
#nona the ninth spoilers#ntn spoilers#blood of eden#LOOK I HAVE A LOT OF THOUGHTS ABOUT WHAT BOE'S MYTHOLOGY MUST BE LIKE#also about how the greek flood myth might tie in because one of the survivors is named PYRRHA
419 notes
·
View notes
Photo

This lovely dark blue Roman glass plate was found in a 5th century tomb at Niizawa Senzuka-kofun Tumulus Cluster, Nara, Japan. The dish was possibly produced in a workshop on the western side of the Euphrates & before the plate reached Japan, the inner surface became decorated with a bird, horse, person, and plants. These figures were drawn in a Central Asian style and were likely the product of the Sasanian Empire. From there it was imported to Japan.
Photo credit Tokyo National Museum.
9 notes
·
View notes