#translation blog
Text




"I love you", Husik Ara (translated by Tathev Simonyan)
#he's come here to stay#both in my heart and on this blog#armenian literature#love poems#husik ara#quotes#literature#poetry#romantic academia#translated literature#poems#armenian poetry#my translations
3K notes
·
View notes
Text





hadn't seen anyone post the full comic about laios + falin's family on tumblr yet so. here you go
source is from the reddit
#in general i haven't seen as many translations of the new content get posted here which is like fine#but it was annoying me that the pages shared here and on twitter were missing sections. lore is serious business#the less lore the average tumblr user knows about the more nonsensical takes i'm forced to read. so im taking direct action#this is the last time im posting manga pages here i don't want to become a manga pages blog#beepbeep.txt#dungeon meshi#dungeon meshi spoilers
5K notes
·
View notes
Text

happy year of the dragon from this guy…
#something deeply wrong with him (affectionate)#also#eyeing the third panel like: hm. this too is yuri.#this is art ryoko kui posted to her official blog by the way#i just translated it from japanese#dungeon meshi#lunar new year#year of the dragon#manga#falin#laois#marcille#art
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Apparently much-needed reminder that reposting artists' art (by saving the images or screenshotting them and reuploading them yourself) on other platforms without the artists' expressed permission and without credit is theft and an insult to their passion and craft. You are profiting (in views, in attention, in feedback) from someone else's work and ideas, who do not get that feedback for sharing their creation.
If you are an art reposter, you are a thief and I have no respect for you.

#learn basic internet etiquette i am begging but also holding a knife. yes i'm mad. more about others than myself.#do you know how many artists i have seen leave social media because their art started being reposted all over?#tip: way too fucking many#i've had many people tell me about people reposting my art on tiktok#no one ever asked to repost my art on tiktok. ever. they just save super fried bad crunchy jpegs of my art and repost them#they get 20k likes and don't even bother naming me#also a reason i started signing my name more legibly and why my blog web address is always there but apparently no one can even read that#a few people got an ok for translations on other platforms though#i'm going to be annoying with this post and reblog it a few times to try to catch the people who apparently need to be told#tiny skk adventures#nawy's comics#nawy's doodles#apparently those are reposters' favourites so here look at this
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
Gendered pronouns in Japanese vs English
In Revolutionary Girl Utena, the main character Utena is a girl (it says so in the title), but very conspicuously uses the masculine first person pronoun 僕 (boku) and dresses in (a variation of) the boys school uniform. Utena's gender, and gender in general, is a core theme of the work. And yet, I haven’t seen a single translation or analysis post where anyone considers using anything other than she/her for Utena when speaking of her in English. This made me wonder: how does one’s choice of pronouns in Japanese correspond to what one’s preferred pronouns would be in English?

There are 3 main differences between gendered pronouns in Japanese vs English
Japanese pronouns are used to refer to yourself (first-person), while English pronouns are used to refer to others (third-person)
The Japanese pronoun you use will differ based on context
Japanese pronouns signify more than just gender
Let’s look at each of these differences in turn and how these differences might lead to a seeming incongruity between one’s Japanese pronoun choice and one’s English pronoun choice (such as the 僕 (boku) vs she/her discrepancy with Utena).
Part 1: First-person vs third-person
While Japanese does technically have gendered third person pronouns (彼、彼女) they are used infrequently¹ and have much less cultural importance placed on them than English third person pronouns. Therefore, I would argue that the cultural equivalent of the gender-signifying third-person pronoun in English is the Japanese first-person pronoun. Much like English “pronouns in bio”, Japanese first-person pronoun choice is considered an expression of identity.
Japanese pronouns are used exclusively to refer to yourself, and therefore a speaker can change the pronoun they’re using for themself on a whim, sometimes mid-conversation, without it being much of an incident. Meanwhile in English, Marquis Bey argues that “Pronouns are like tiny vessels of verification that others are picking up what you are putting down” (2021). By having others use them and externally verify the internal truth of one’s gender, English pronouns, I believe, are seen as more truthful, less frivolous, than Japanese pronouns. They are seen as signifying an objective truth of the referent’s gender; if not objective then at least socially agreed-upon, while Japanese pronouns only signify how the subject feels at this particular moment — purely subjective.
Part 2: Context dependent pronoun use
Japanese speakers often don’t use just one pronoun. As you can see in the below chart, a young man using 俺 (ore) among friends might use 私 (watashi) or 自分 (jibun) when speaking to a teacher. This complicates the idea that these pronouns are gendered, because their gendering depends heavily on context. A man using 私 (watashi) to a teacher is gender-conforming, a man using 私 (watashi) while drinking with friends is gender-non-conforming. Again, this reinforces the relative instability of Japanese pronoun choice, and distances it from gender.

Part 3: Signifying more than gender
English pronouns signify little besides the gender of the antecedent. Because of this, pronouns in English have come to be a shorthand for expressing one’s own gender experience - they reflect an internal gendered truth. However, Japanese pronoun choice doesn’t reflect an “internal truth” of gender. It can signify multiple aspects of your self - gender, sexuality, personality.
For example, 僕 (boku) is used by gay men to communicate that they are bottoms, contrasted with the use of 俺 (ore) by tops. 僕 (boku) may also be used by softer, academic men and boys (in casual contexts - note that many men use 僕 (boku) in more formal contexts) as a personality signifier - maybe to communicate something as simplistic as “I’m not the kind of guy who’s into sports.” 俺 (ore) could be used by a butch lesbian who still strongly identifies as a woman, in order to signify sexuality and an assertive personality. 私 (watashi) may be used by people of all genders to convey professionalism. The list goes on.
I believe this is what’s happening with Utena - she is signifying her rebellion against traditional feminine gender roles with her use of 僕 (boku), but as part of this rebellion, she necessarily must still be a girl. Rather than saying “girls don’t use boku, so I’m not a girl”, her pronoun choice is saying “your conception of femininity is bullshit, girls can use boku too”.

Through translation, gendered assumptions need to be made, sometimes about real people. Remember that he/they, she/her, they/them are purely English linguistic constructs, and don’t correspond directly to one’s gender, just as they don’t correspond directly to the Japanese pronouns one might use. Imagine a scenario where you are translating a news story about a Japanese genderqueer person. The most ethical way to determine what pronouns they would prefer would be to get in contact with them and ask them, right? But what if they don’t speak English? Are you going to have to teach them English, and the nuances of English pronoun choice, before you can translate the piece? That would be ridiculous! It’s simply not a viable option². So you must make a gendered assumption based on all the factors - their Japanese pronoun use (context dependent!), their clothing, the way they present their body, their speech patterns, etc.
If translation is about rewriting the text as if it were originally in the target language, you must also rewrite the gender of those people and characters in the translation. The question you must ask yourself is: How does their gender presentation, which has been tailored to a Japanese-language understanding of gender, correspond to an equivalent English-language understanding of gender? This is an incredibly fraught decision, but nonetheless a necessary one. It’s an unsatisfying dilemma, and one that poignantly exposes the fickle, unstable, culture-dependent nature of gender.

Notes and References
¹ Usually in Japanese, speakers use the person’s name directly to address someone in second or third person
² And has colonialist undertones as a solution if you ask me - “You need to pick English pronouns! You ought to understand your gender through our language!”
Bey, Marquis— 2021 Re: [No Subject]—On Nonbinary Gender
Rose divider taken from this post
#langblr#japanese#japanese language#language#language learning#linguistics#learning japanese#utena#revolutionary girl utena#shojo kakumei utena#rgu#sku#gender#transgender#nonbinary#trans#official blog post#translation#media analysis
1K notes
·
View notes
Text





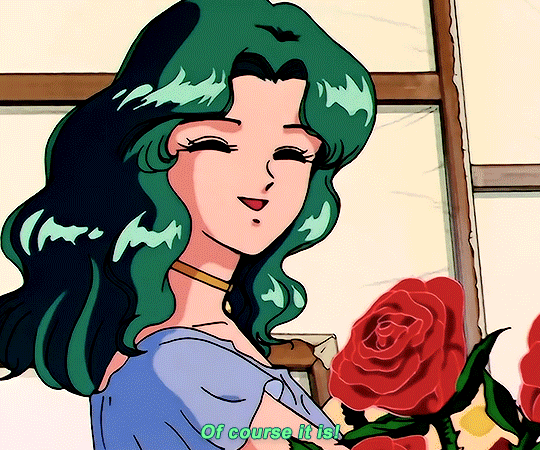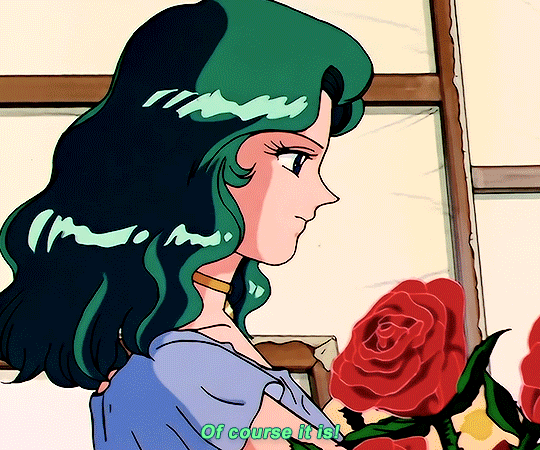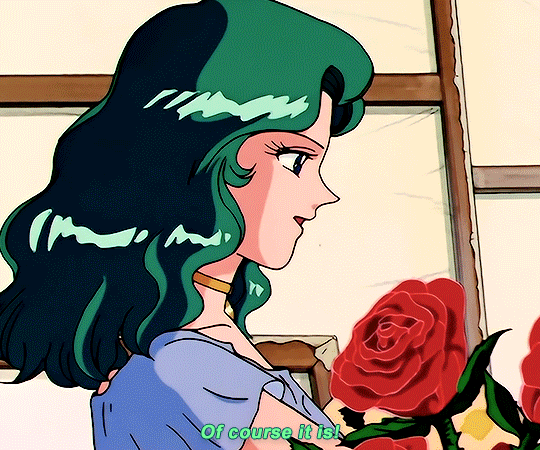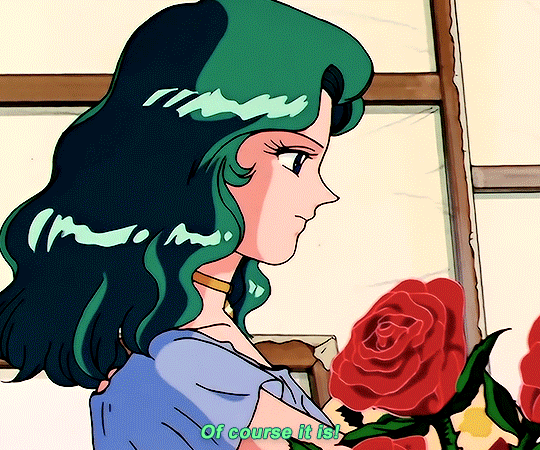
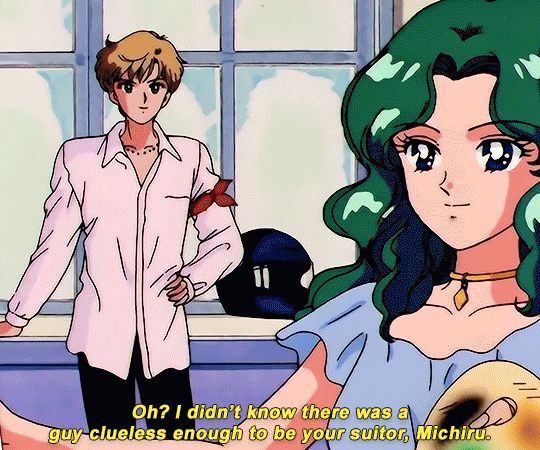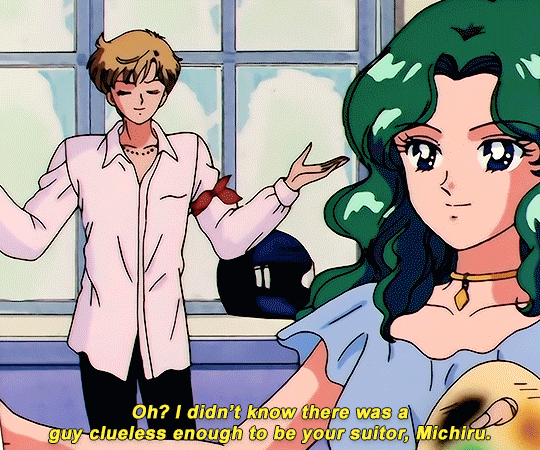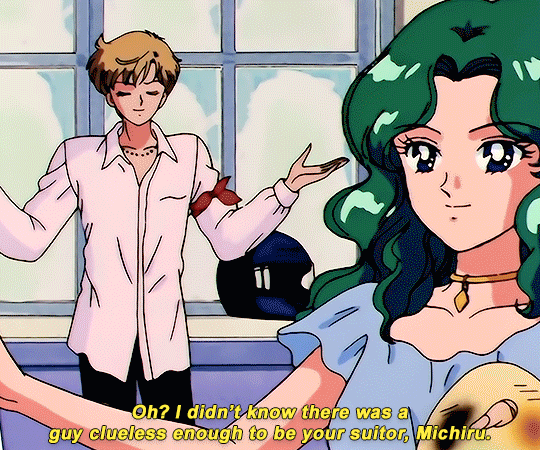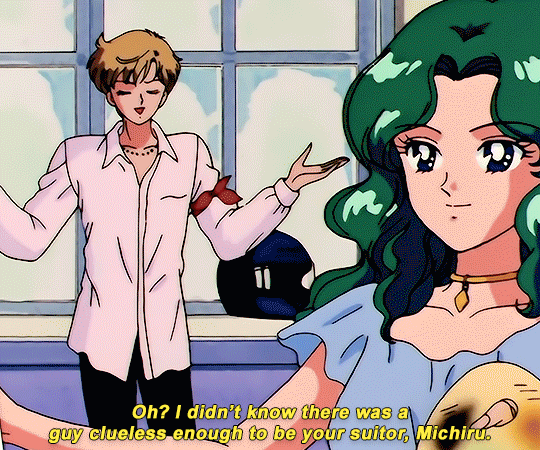
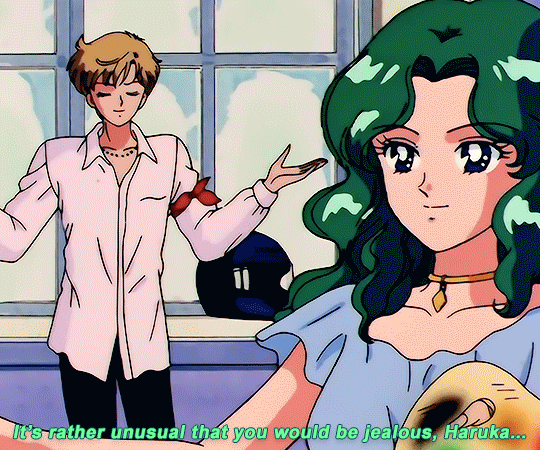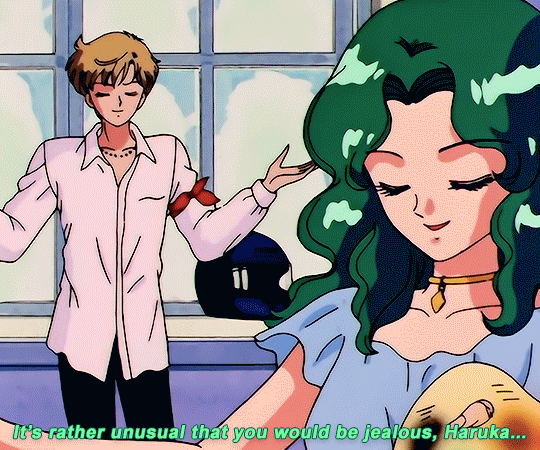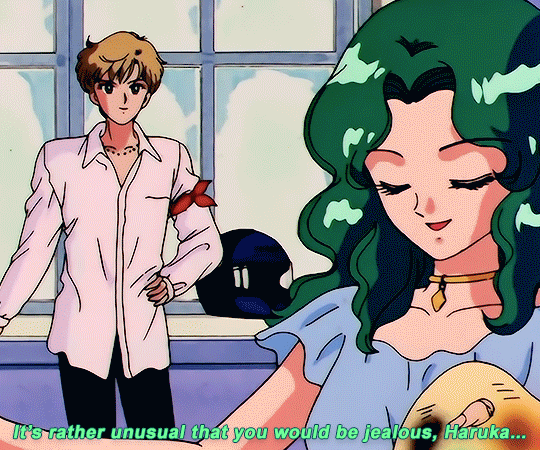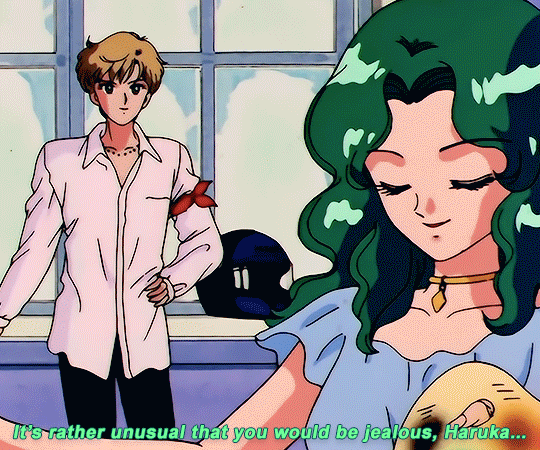
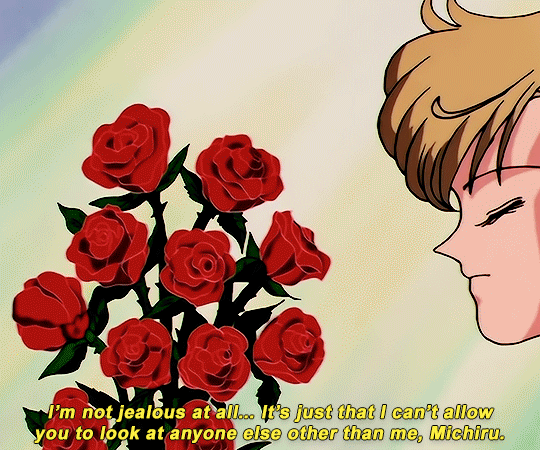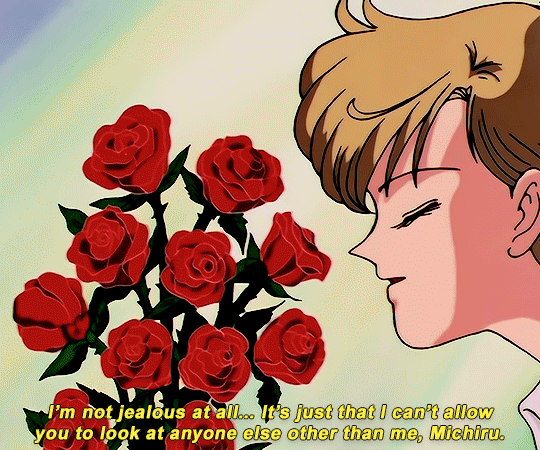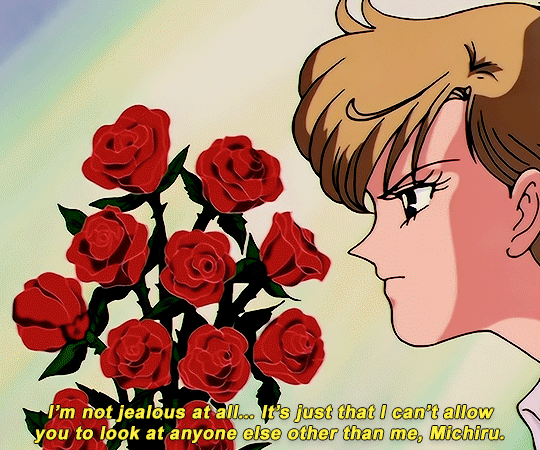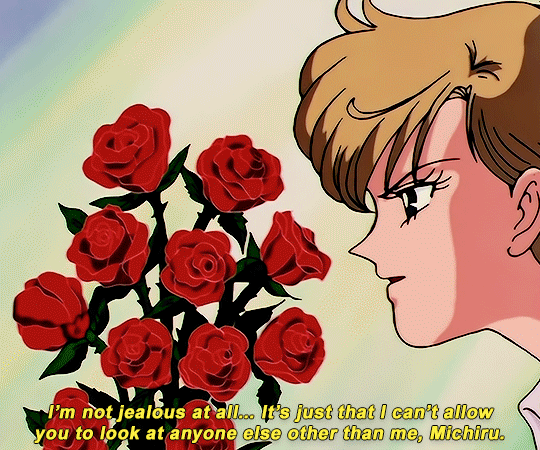
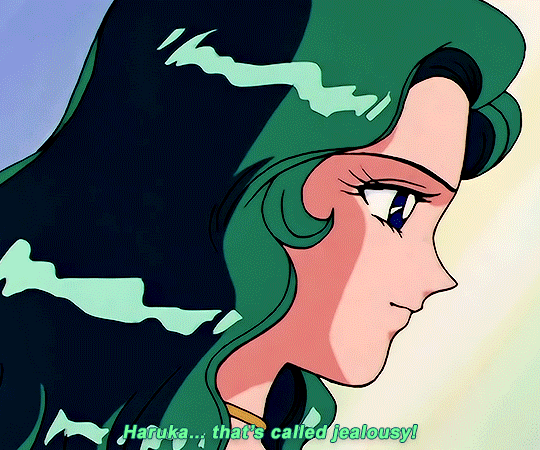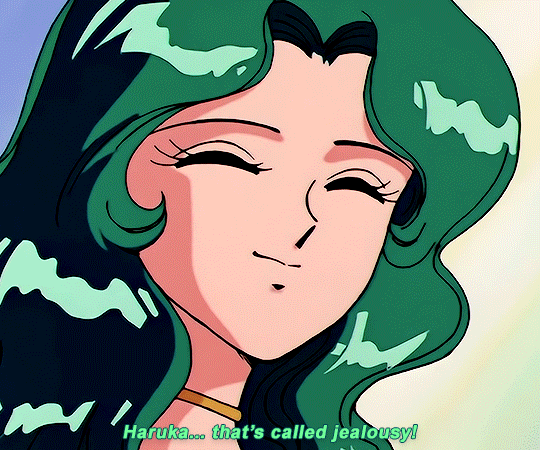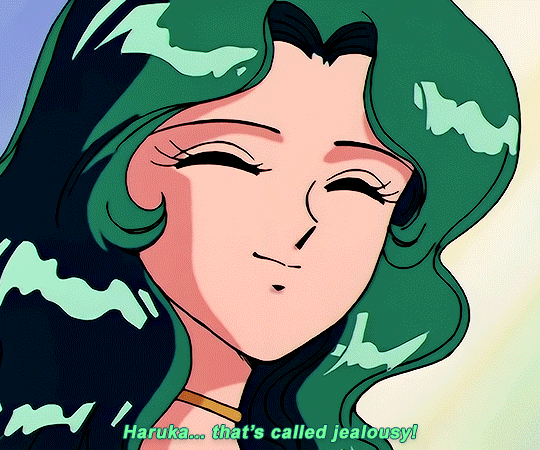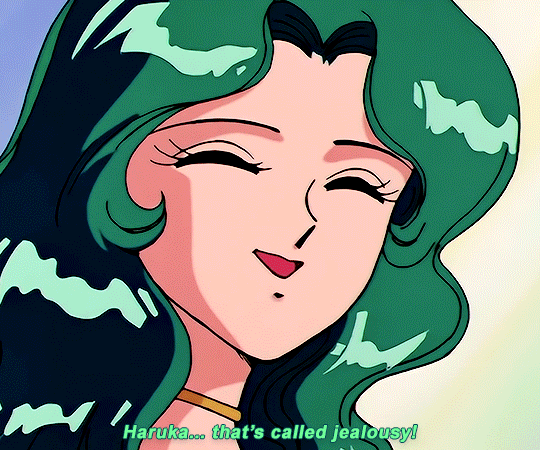
SAILOR MOON S: Episode 18 - 「芸術は愛の爆発!ちびうさの初恋」
#animeedit#sailor moon#sailormoonedit#oldanimeedit#harumichi#haruka x michiru#smedit#wlwedit#haruka tenoh#kaioh michiru#ep 107#bssm#bssmedit#pretty guardian sailor moon#bishojo senshi sailor moon#sailor neptune#sailor uranus#michiru kaioh#tenoh haruka#HI YES THIS BLOG IS ALIVE im trying to juggle trying to make gifs for this sideblog and the other fandom one lol#i had to change some of the translation bc the context was slightly wrong...#japanese is such a hard language to translate into english sometimes#also coloring anime is so difficult sometimes im really not used to it#especially old anime haha
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
I love you messy artstyle i love you visible brush strokes I love you textures and rough edges I love you imperfections I love you roughness and colour blobs I love you scratchy sketches and bold stylisation and dirt and imperfections I love you ugly and raw emotion!!!!! ❤️
#i talk sometimes#art talk#i made a tweet like this on twatter ages ago but i've been feeling this a lot lately#also this is the start of me writing more on this blog and not only using it as art because who cares!! i don't!!#I wanna translate raw emotion into colors and shapes. I wanna know where to ignore all details and where to go ham you feel me?#i used to dream about developing a style like for MtG where it looked like a masterful oil painting that oozes realism and details#and i've realised the last two years or so that I would actually hate that for me. I know I wouldn't enjoy doing it. For myself.#it's that pipeline from wanting to be the perfect realistic wotc artist to accepting that I will never be that#instead i wanna learn how to stylise better and get a good brush economy going yknow. I wanna be bolder.#i doubt i'll ever be as incredible as all these MtG artists no matter what anyone says. but it's ok!! i don't have to be!!!#i just luv art man!!
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

#bpd#borderline personality disorder#bpd girl#manic pixie dream girl#lana del rey#female rage#coquette#femcel#girl interrupted#female manipulator#divine feminine#feminine urge#girl interrupted syndrome#girl boss gaslight gatekeep#girlblogging#girl blogging#girl blogger#lost in translation#girl in pieces#this is depressing#gloomy coquette
1K notes
·
View notes
Text


04.04.24 next step will be translating texts which means I’ll stay at the library until 8 pm. Then I’ll go eat sushi and contemplate the meaning of life 🍵
#chaotic academia#chaotic academic aesthetic#my post#study blog#studyblr#books#bookblr#study aesthetic#university#studying#study notes#latin language#translation#uniblr
651 notes
·
View notes
Text


recent purchase 💸 i've been trying to slow down with my book buying this year (it's not going well), but ever since i saw 'the house on via gemito' on the international booker longlist, i knew i wanted to read it. especially because italy is one of the countries i'm focusing on this year for my "read around the world" challenge!!
#haul#book haul#photo diaries#photo diary#literature aesthetics#books#book#bookish#bookblr#bookworm#bookstagram#dark academia#booklover#books and libraries#italy#italian literature#the house on via gemito#domenico starnone#translated#studyblr#study space#study hard#read around the world#study tips#studying#study motivation#study blog#student#city#london
285 notes
·
View notes
Text

#sofia coppola#the virgin suicides#lost in translation#priscilla movie#palo alto#girl interrupted#black swan#girl blog#im just a girl#girlhood#hell is a teenage girl#girl blogger#delusional#female rage#girlcore#lana del rey#lana del ray aka lizzy grant#lux lisbon#let me live in my delusions#this is what makes us girls#manic pixie dream girl#buffalo 66#coquette dollete#dollette#coquette angel#coquette#cinnamon girl#esoteric#this is me if you even care#put me in a movie
269 notes
·
View notes
Text


POV ur my lamp 🦋
#I got complimented a lot on the glasses today#but I swear it doesn’t translate to selfies#anyway#giving the people what they want#me#selfie#hi face#girl#australia#pop punk#pop punk blog#band blog#alt girl#pop punk girl#music blog#gpoy
179 notes
·
View notes
Text

“Poorly-Drawn” Poorly-Drawn-MDZS by my friend who has no context for what MDZS is, but has read every comic of mine in support.
#poorly drawn mdzs#mdzs#fan art#[text translation]: ‘Are you sure? I haven't done art in my life and I dont even own any coloured pens or have funny things to say-#or know what mdzs is? I have never seen the show I mean are you sure you want this? Your loss dude.’#The context for this was my curiosity about their impressions of what was going on after a whole year of second hand exposure.#Honestly I think you (I know you'll see this) knocked it out of the park with this comic - despite protesting about a ‘lack of art skills’.#The punchlines absolutely incapacitated me. So glad this is my highly specific legacy.#Round of applause for Larry; the guy who's literally been here from the start. The ultimate cheerleader.#Makes me drink water when I’m nearly incapacitated from dehydration.#And lets me talk about this blog without judgment.#Merci de m'avoir soutenu mon pote
408 notes
·
View notes
Text

.
#utmv#sanscest#reaper sans#error sans#DestructiveDeath#undertale au#this was a request but tumblr ate the thing i'm sorry dragon anon#there was supposed to be like an afterdeath implication but it does not translate at all#this ship has only brought me despair and i think it's fitting tbh#i had to redraw this thing because halfway the lights went out and half of it was gone#i have like a thousand takes on how reaper would react to geno being error#the only thing i'm sure is that reaper would stick around error#like a friendly shadow#his very own angel of death kind of thing#like did he learn something from losing tori and geno? was it for the better?#does he give up on everything and is on board with error's whole destruction thing?#does he only put up with it because he doesn't want to lose him and death is the only connection he has with him?#does he have problems letting go of geno and starting over with error?#is this like angsty or is it more silly???#why did i make an awful playlist for all this???#anyways if anyone ever requests destructivedeath to me ever again i'm deleting my blog i swear/j#maybee i'll post the other doodles i made for this thing but that's it
244 notes
·
View notes
Text


Summer Clothes
TL: I always laugh at these kinda jokes XD
( Original Source )

#Ik I have other translations planned#but Im caught up with work so I thought I'd do another smaller translation just to update the blog#submas#ingo#emmet#kudari#nobori#subway bosses#translations#okepoketranslates#pokemon black and white#pokemon
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
I’ve been having trouble putting this idea into words so you’ll have to bear with me, but I was struck when I saw a Japanese news program interviewing foreign tourists in Japan, and some australian women were dubbed over with a stereotypically feminine speech register (lots of のs and わs), and my first thought was “they weren’t speaking that femininely in english”.
A friend of mine from the UK recently mentioned that he noticed that australia has a generally more masculine culture than england - he felt that everyone is a bit more masculine here, including women. This kind of confirmed to me that my impressions of the dubbing were right - the tourists were speaking in a relatively (internationally) more masculine way. Yet their dub made them sound so much more feminine.
It made me wonder. When translating something, do you translate the manner of speaking “directly”, or “relatively” in terms of cultural norms? Maybe this graph will help me explain the question.
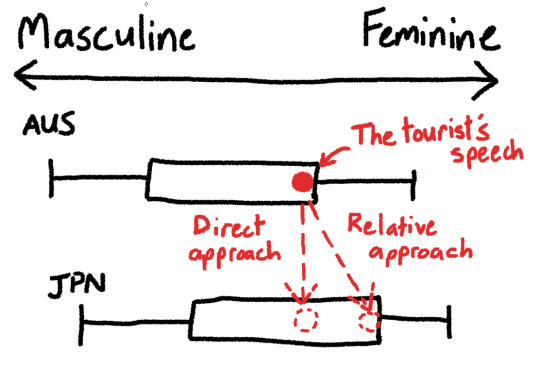
A direct appoach in this case might appear to a Japanese person to result in an unexpectedly masculine register, but preserves how the speaker's cultural upbringing has influenced their speech.
The news program translators chose the relative approach - I think I would prefer the direct approach. I think I prefer it because I believe translation should be a rewriting of the original utterance as if the speaker was originally speaking the target language, and the direct approach compliments that way of thinking the best.
Actually now that I type that, I’m second guessing myself. Does it? It does, if for the purposes of the “rewrite it as if they spoke japanese” thought experiment, we suppose the speaker magically learned japanese seconds before making the utterance, but what if we suppose the speaker magically grew up learning japanese - then maybe they would conform to the relative cultural values. But also, maybe they would never have said such a thing in the first place - their original utterance was informed by their upbringing and cultural values, so how could you possibly know what they would have said if they had known japanese from birth? Maybe my initial instinct was right after all?
If you work in translation, I’m very interested to hear if you have come across this problem and how you deal with it 🙏
Further reading: I think this question also ties into this problem I’ve been struggling to answer for a while.
#linguistics#language#langblr#japanese#japanese language#translation#jimmy blogthong#official blog post
1K notes
·
View notes