#utahraptor ostrommaysi
Text
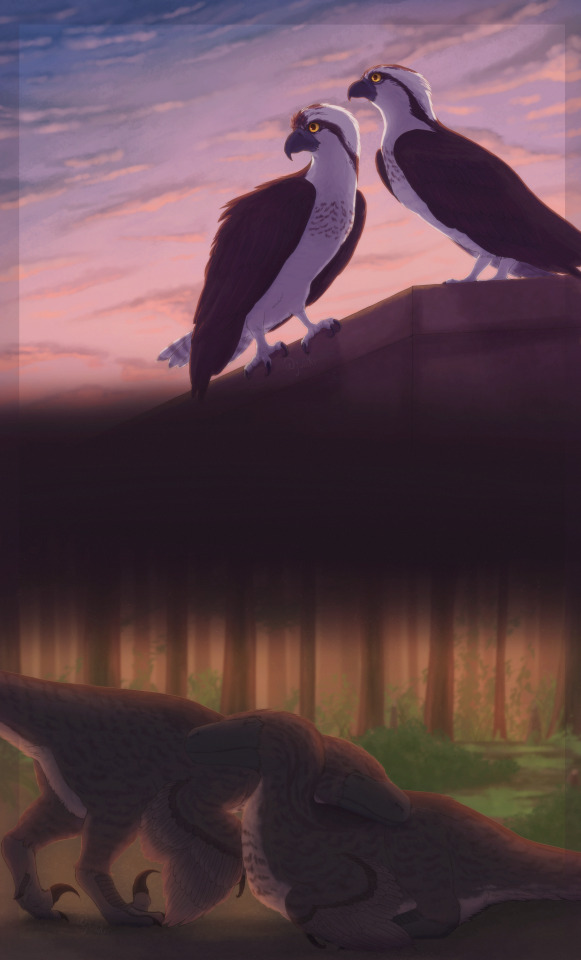

we'll meet again
#psst#theyre lesbians (:#osprey#osprey bird#ospreys#bird#birds#raptors#pandion haliaetus#bird of prey#utahraptor#utahraptor ostrommaysi#dromaeosaur#dromaeosaurid#dromaeosaurids#dromaeosauridae#dinosaur#dinosaurs#theropod#theropoda#theropod dinosaur#feathered dinosaur#bird art#dinosaur art#paleontology#paleoart#been pretty sick sorry#my kidneys are a skill issue#my art#lesbian coded
387 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dinofact #15
Originally, the species Utahraptor ostrommaysi was originally intended to be named U. speilbergi after movie director Steven Spielberg, in exchange for financial contributions to paleontology. However, no agreement could be made on how much he should contribute, so Utahraptor was named after John Ostrom and Chris Mays for their contributions in paleontology.
Source: wikipedia
#dinosaurs#dinosaur#paleontology#utahraptor#utahraptor ostrommaysi#steven spielberg#john ostrom#chris mays#fun facts#trivia#dinosaur trivia#dinosaur fun facts#30th#august#2022#august 30th#august 2022#august 30th 2022
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

Utahraptor ostrommaysi, by me
280 notes
·
View notes
Text
So giving them robo arms to hold their shit has been the best decision ever (info after imgs)




So im going absolutely feral about this AU, so in order to make sure they can still fight their war with guns i gave them robotic arms attached to the thingys on their armour.
Sim Troopers and regular soldiers have about what Church/Sarge wear, while Freelancers and special ops like Locus and Felix are closer to Tex. Hiding specific markings + making them more resilient.
Also please enjoy this height reference I've made (Locus gets honorary Red bc he deserves it). Some heights have been changed to be larger, in Lopez and Tex's case have been drastically changed as they are robots. Nerd stuff about who is what below.

Caboose [Ankylosaurus magniventris]
Church, Carolina, Tex [Utahraptor ostrommaysi]
Washington [Megalosaurus bucklandii]
Tucker [Allosaurus fragilis]
Doc [Kentrosaurus aethiopicus]
Donut [Deinonychus antirrhopus]
Grif, Kaikaina [Pachyrhinosaurus lakustai]
Simmons [Maiasaura peeblesorum]
Sarge [Daspletosaurus torosus]
Lopez [Nasutoceratops titusi]
Locus [Lythronax argestes]
Edit: I forgot Donut and Doc my sons I'm so sorry the bit has breached containment
#RvB Dino AU#dinosaurs#rvb art#rvb church#rvb tex#rvb sarge#red vs blue art#rvb tucker#red vs. blue#dinosaurification ray#the tism
54 notes
·
View notes
Text

you know it, you love it, utahraptor ostrommaysi!
I was particularly impressed by this statue bc it balances on one hind foot. a very active and exciting pose
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
I love this raptor base, so I think I'm gonna use it for every and each of my raptors
This design was a lot of fun especially on the pattern and colors !
Crimson is a Utahraptor Ostrommaysi
Crimson © Me
Adopted from stephweredragon
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Utahraptor ostrommaysi, which was the first thing I posted onto this account.
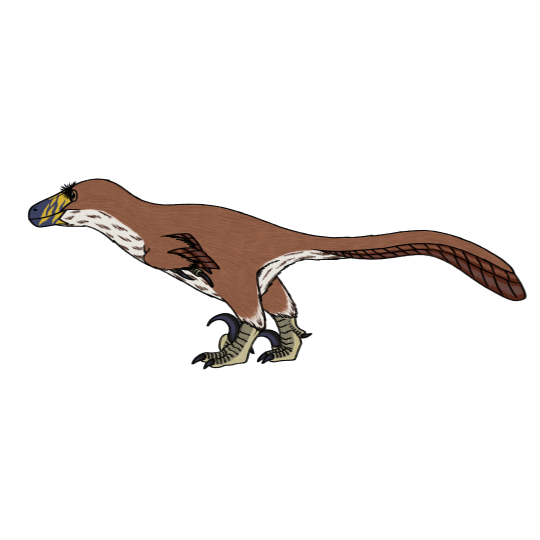

With Hatsune Miku for scale:

9 notes
·
View notes
Note
I'm currently rewatching all the Jurassic Park movies w my husband, the OGs, of course. I'm trying to remember the exact "discovery" or whatever that was presented by the movies before the dinosaur fact/ species/ behavior was actually discovered by paleontologists and scientists. I feel like you'd know?
Oh yeah, that’d be the discovery of the holotype of Utahraptor ostrommaysi during production in 1991 and the subsequent publishing of the findings the same month the movie was originally released in 1993, specifically for being the first large dromaeosaur in the average human height range (while the raptors in JP are actually both in Crichton’s original novel and at one point in the movie itself intended to be Deinonychus, it wasn’t actually quite that large whereas Utahraptor was much closer).
That, or just the general fact that JP is what brought the general public up to date on the concept of agile active dinosaurs that had become more and more accepted by actual paleontologists in the preceding decade.
#ask#jurassic park#I very easily could have picked paleontology instead of archaeology is was equally obsessed with both as a kid
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

At 7.0 meters (23 feet) long, about as tall as a horse and as heavy as a polar bear, Utahraptor ostrommaysi is the largest known dromaeosaur. It was heavily built with sharper than average foreclaws and strong legs, and likely the apex predator of early Cretaceous Utah. Due to its size and heft, it was probably an ambush predator: it would not have been as fast as its smaller relatives; but just fast enough to keep pace with iguanodonts Hippodraco and Cedrorestes.
In early 2000, a 9-ton block of sandstone was uncovered in eastern Utah. This block was determined to contain at least seven individual Utahraptors: an adult, four juveniles, and a hatchling, as well as at least one possible unidentified iguanodont. It’s speculated that the iguanodont had become mired in quicksand, and when the Utahraptors arrived to scavenge its remains (or finish it off) they became trapped as well. It’s unclear whether these raptors approached as a pack/family group or rather arrived one by one to investigate. Excavation of this fossil is apparently ongoing, but it is potentially a goldmine of information on Utahraptor behavior.
#my art#SaritaDrawsPalaeo#Utahraptor#Utahraptor ostrommaysi#dromeosaur#raptor#theropods#dinosaurs#archosaurs
200 notes
·
View notes
Text
Utahraptor ostrommaysi

By Nix, CC BY-NC 4.0
Etymology: Thief from Utah
First Described By: Kirkland et al., 1993
Classification: Dinosauromorpha, Dinosauriformes, Dracohors, Dinosauria, Saurischia, Eusaurischia, Theropoda, Neotheropoda, Averostra, Tetanurae, Orionides, Avetheropoda, Coelurosauria, Tyrannoraptora, Maniraptoromorpha, Maniraptoriformes, Maniraptora, Pennaraptora, Paraves, Eumaniraptora, Dromaeosauridae, Eudromaeosauria, Dromaeosaurinae
Status: Extinct
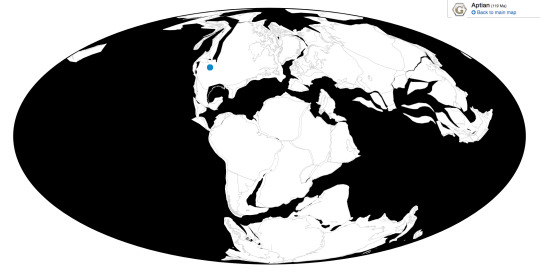
Time and Place: Between 129 and 120 million years go, from the Barremian to the Aptian ages of the Early Cretaceous
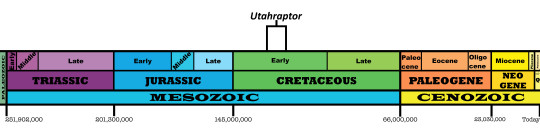

Utahraptor is known from the Yellow Cat and Poison Strip members of the Cedar Mountain Formation
Physical Description: Utahraptor was a very large raptor dinosaur, and had the associated bodily characteristics - a bulky trunk, shorter legs, long arms, large head, and long, stiffened tail. It was really and truly huge, about 7 meters long and 500 kilograms in weight - about the size of a modern Grizzley or Polar Bear, though they might have been heavier than previously thought. Like other raptors, it had huge sickle claws on its feet, and the claws were probably around 24 centimeters long - or even longer, if they had been covered in a keratin sheath as potentially thought. The skull of Utahraptor has not yet been described, so for now we can only say that it had a long, triangular head like other raptors, with sharp serrated teeth. As with other raptors, it would have been feathered - with very large wings for flapping, and a distinctively huge tail fan. The legs of Utahraptor would have been slightly less feathered, but still distinctive. In short, it was a big and fluffy bird-bear, and the largest predator in its environment.

By Matt Martyniuk, CC BY-SA 3.0
Diet: Utahraptor was a large predator and, accordingly, ate large sources of food such as ornithopods and younger sauropods.

By PaleoNeolitic, in the Public Domain
Behavior: As a raptor, Utahraptor would have been most analogous to a cat - probably stalking alone rather than in packs, and utilizing ambush behavior to trap its prey. Since it had somewhat stubby legs and wasn’t very fast at all, it couldn’t have relied on pursuit to attack its food, even if its food was just as slow as it was. Instead, these powerful legs helped Utahraptor to jump onto its food and surprise it, even from the ground where it spent its time. It then could use raptor prey restraint (RPR) to stay balanced on the prey, flapping its wings rapidly as the prey moved around and tried to escape. Those impossibly large sickle claws then were used to strategically stab at places where the prey would bleed out - important veins and arteries - rather than slash. In addition to this, Utahraptor would have been able to flap its wings rapidly and run up steep surfaces - a technique called Wing-Assisted Inclined Running (WAIR) - even vertical ones, like cliff faces and trees. This allowed Utahraptor to reach strategic vantage points and search for prey - and even jump down onto it from high heights. These techniques allowed Utahraptor to not only hunt the similarly-sized Ornithopods of the time, but also potentially attack the even larger Sauropods with which it shared its home. When it needed a smaller snack, that large claw could be used to pin down struggling furry mammals and lizards, in order for Utahraptor to then take a bite.

By Fred Wierum, CC By-SA 4.0
Though Utahraptor did not hunt in packs, that doesn’t mean it wasn’t social - and, indeed, there is considerable evidence not yet described that it lived in dense family groups. This would probably mean that adult Utahraptor would go out hunting on their own, while the little ones would gather their own food, before coming together in the same space for safety from other Utahraptor and just to spend the night. It is very likely that Utahraptor took care of its own young based on its relatives - and there’s hopefully more evidence on the way to corroborate this. This was a very complex social animal, using those fancy wings and tail fan to display to other Utahraptor - by holding up the wings and lifting the tail fan to display, it could communicate with others that it was a threat, that it wanted to mate, or to stay away from its nest. In general, it would have behaved very bird-like - walking around, bobbing its head, and moving its head to look for food and for each other rather than moving the eyes. And, like birds, it would have been very active, and warm-blooded.
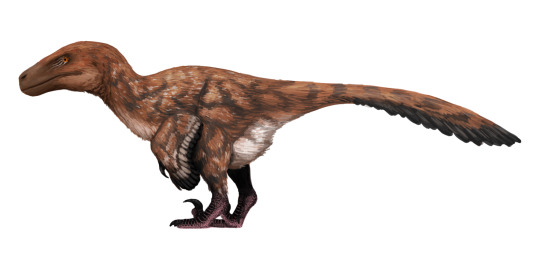
By Ashley Patch
Ecosystem: When the Cedar Mountain Formation supported Utahraptor, it was a very large floodplain environment, that periodically flash flooded and filled the valley with mud. This was a seasonally wet environment with a variety of rivers, forests, prairies, and open woodlands. The ecosystem had a short wet system and a very long, tedious dry season. Utahraptor shared this environment with countless creatures - the tuataran Toxolophosaurus, the turtle Glyptops, a variety of fish, the mammaliaform Cifelliodon, and - of course - other dinosaurs. There was the ankylosaur Gastonia, the large Iguanodon-like Ornithopods Cedrorestes, Hippodraco, and Iguanacolossus; the Sauropods Cedarosaurus and Mierasaurus; the Therizinosaurs Martharaptor and Falcarius; the Troodontid Geminiraptor; the Ornithomimosaur Nedcolbertia; and another raptor - Yurgovuchia! This gave Utahraptor a wide variety of things to hunt in its environment.

By Emily Willoughby, CC By-SA 3.0
By the time of the later Poison Strip environment, things were changing rapidly in Cedar Mountain. Dry seasons were longer now, and a significant amount of sand was washing through the ecosystem. This made life higher in the floodplain, and probably eliminated many of the forests and river-woods that had been present prior to, leaving only a somewhat scrubland-esque plain. Accordingly, creature diversity actually went down - it was something of an ecosystem collapse. There was still food for Utahraptor to eat - the Ornithopod Planicoxa, and the sauropods Moabosaurus and Venenosaurus; but that was it. Utahraptor, thus, was living in a miniature extinction event - and disappears from the environment by the time the mud and rainy seasons returned in the Ruby Ranch Environment, and the large predator niche was replaced by the carnosaur Acrocanthosaurus.

By Calum O’Halloran
Other: Utahraptor was the largest raptor known, and we actually have many fossils of it - but they’re trapped in a block! Well, there isn’t funding to remove them from the block, anyway. So much more could be (and will be, dammit!) written about this excellent dinosaur if it was adequately funded to be researched properly. Check out the Utahraptor Project if you want to learn more about Utahraptor - and consider donating! Literally every penny helps. Utahraptor is also one of the inspirations for the raptors of Jurassic Park, along with Deinonychus - though, obviously, those creatures do not resemble their real counterparts in the slightest.
~ By Meig Dickson
Sources under the Cut
Apesteguía, S., S. de Valais, G. R. Cordero and O. M. Ramírez. 2011. New ichnological record from the late Campanian Toro Toro Formation at Toro Toro, Potosí (Bolivia): first probably dromaeosaurid tracks from South America. Ameghiniana 48(4):662-667
Aubrey, W.M. 1998. A newly discovered, widespread fluvial facies and unconformity marking the Upper Jurassic/Lower Cretaceous boundary, Colorado Plateau. Modern Geology, v. 22, p. 209-233.
Barco, J. L., and J. I. Ruiz-Omeñaca. 2001. Primeros dientes de terópodo (Dinosauria, Saurischia) en la Formación Villar del Arzobispo (Tithónico-Berriasiense): yacimientos Cuesta Lonsal y Las Cerradicas 2 (Galve, Teruel) [First teeth of a theropod (Dinosauria, Saurischia) in the Villar del Arzobispo Formation (Tithonian–Berriasian): Cuesta Lonsal and Las Cerradicas 2 localities (Galve, Teruel)]. In G. Meléndez, Z. Herrera, G. Delvene & B. Azanza (eds.), XVII Jornadas de la Sociedad Española de Paleontología. Los Fósiles y la Paleogeografía. Ayuntamiento de Albarracín y Fundación Conjunto Paleontólogico de Teruel, Albarracin, Spain 5.1:239-246
Campione, N. E., D. C. Evans, C. M. Brown, M. T. Carrano. 2014. Body mass estimation in non-avian bipeds using a theoretical conversion to quadruped stylopodial proportions. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 5 (9): 913 - 923.
Carpenter, K. 1998. Evidence of predatory behavior by carnivorous dinosaurs. Gaia 15: 135 - 144.
Carpenter, K. 2002. Forelimb biomechanics of nonavian theropod dinosaurs in predation. Senckenbergiana Lethaea 82: 59 - 76.
Carpenter, K., 2006, Assessing dinosaur faunal turnover in the Cedar Mountain Formation (Lower Cretaceous) of eastern Utah, USA. Ninth International Symposium on Mesozoic Terrestrial Ecosystems and Biota, Abstract and Proceedings Volume, p. 21-25.
Carpenter, Kenneth; Bartlett, Jeff; Bird, John; Barrick, Reese (2008). "Ankylosaurs from the Price River Quarries, Cedar Mountain Formation (Lower Cretaceous), east-central Utah". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 28 (4): 1089–1101.
Chure, Daniel; Britt, Brooks; Whitlock, John A.; Wilson, Jeffrey A. (2010). "First complete sauropod dinosaur skull from the Cretaceous of the Americas and the evolution of sauropod dentition". Naturwissenschaften. 97 (4): 379–91.
Cifelli, R. L., Nydam, R. L., Gardner, J. D., Weil, A., Eaton, J. G., Kirkland, J. I., and Madsen, S., 1999, Medial Cretaceous vertebrates from the Cedar Mountain Formation, Emery County, Utah: the Mussentuchit Local Fauna, in, Gillette, D., Vertebrate Paleontology in Utah. Utah Geological Survey Miscellaneous Publication 99-1, p. 219-242.
Britt, B. B., K. L. Stadtman, and R. D. Scheetz. 1996. The Early Cretaceous Dalton Wells dinosaur fauna and the earliest North American titanosaurid sauropod. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 16(3, suppl.):24A
Britt, B. B., and K. L. Stadtman. 1997. Dalton Wells Quarry. In P. J. Currie & K. Padian (ed.), Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs 165-166
Britt, B. B., D. A. Eberth, R. D. Scheetz, B. W. Greenhalgh, and K. L. Stadtman. 2009. Taphonomy of debris-flow hosted dinosaur bonebeds at Dalton Wells, Utah (Lower Cretaceous, Cedar Mountain Formation, USA). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 280:1-22
Burnham, D. A., P. Senter, R. Barsbold and B. B. Britt. 2004. Phylogeny of the Dromaeosauridae. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 24(3, suppl.):42A
Currie, P. J. 1995. New information on the anatomy and relationships of Dromaeosaurus albertensis (Dinosauria: Theropoda). Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 15(3):576-591
Currie, P. J. 1997. Dromaeosauridae. In P. J. Currie & K. Padian (ed.), Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs 194-195
Currie, P. J. 2000. Theropods from the Cretaceous of Mongolia. In M. J. Benton, M. A. Shishkin, D. M. Unwin, & E N. Kurichkin (eds.), The Age of Dinosaurs in Russia and Mongolia 434-455
DePalma, R. A., D. A. Burnham, L. D. Martin, P. L. Larson, R. T. Bakker. 2015. The first Giant Raptor (Theropoda: Dromaeosauridae) from the Hell Creek Formation. Paleontological Contributions 14: 1-16.
Dinets, V. 2014. Apparent coordination and collaboration in cooperatively hunting crocodilians. Ethology Ecology & Evolution 27 (2): 244 - 250.
Erickson, G. M., K. Curry Rogers, D. J. Varricchio, M. A. Norell, X. Xu. 2007. Growth patterns in brooding dinosaurs reveals the timing of sexual maturity in non-avian dinosaurs and genesis of the avian condition. Biology Letters 3 (5): 558 - 61.
Fowler, D. W., E. A. Freedman, J. B. Scannella, R. E. Kambic. 2011. The Predatory Ecology of Deinonychus and the Origin of Flapping in Birds. PLoS ONE 6 (12): e28964.
Frederickson, J. A., M. H. Engel, R. L. Cifelli. 2018. Niche Partitioning in Theropod Dinosaurs: Diet and Habitat Preference in Predators from the Uppermost Cedar Mountain Formation (Utah, U.S.A.). Scientific Reports 8: 17872.
Galton, P. M., and J. A. Jensen. 1975. Hypsilophodon and Iguanodon from the Lower Cretaceous of North America. Nature 257:668-669
Gauthier, J., K. Padian. 1985. Phylogenetic, Functional, and Aerodynamic Analyses of the Origin of Birds and their Flight. Hecht, M. K., J. H. Ostrom, G. Viohl, P. Wellnhofer (ed.). The Beginnings of Birds. Proceedings of the International Archaeopteryx Conference, Eichstätt: Freunde des Jura-Museums Eichstätt: 185 - 197.
Gishlick, A. D. 2001. The function of the manus and forelimb of Deinonychus antirrhopus and its importance for the origin of avian flight. In Gauthier, J., L. F. Gall. New Perspectives on the Origin and Early Evolution of Birds. New Haven: Yale Peabody Museum: 301 - 318.
Godefroit, P., P. J. Currie, H. Li, C. Y. Shang, and Z.-M. Dong. 2008. A new species of Velociraptor (Dinosauria: Dromaeosauridae) from the Upper Cretaceous of northern China. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 28(2):432-438
Kiernan, K., and D. R. Schwimmer. 2004. First record of a celociraptorine theropod (Tetanurae, Dromaeosauridae) from the eastern Gulf Coastal United States. The Mosasaur 7:89-93
Kirkland, J. I., D. Burge, and R. Gaston. 1993. A large dromaeosaur (Theropoda) from the Lower Cretaceous of eastern Utah. Hunteria 2(10):1-16
Kirkland, J.I., Britt, B., Burge, D., Carpenter, K., Cifelli, R., DeCourten, F., Eaton, J., Hasiotis, S., and Lawton, T., 1997b, Lower to Middle Cretaceous dinosaur faunas of the Central Colorado Plateau: a key to understanding 35 million years of tectonics, sedimentology, evolution, and biogeography. Brigham Young University Geology Studies, v. 42, p. 69-103.
Kirkland, J.I. and Madsen, S.K. (2007). "The Lower Cretaceous Cedar Mountain Formation, eastern Utah: the view up an always interesting learning curve." Fieldtrip Guidebook, Geological Society of America, Rocky Mountain Section. 1-108 p.
Kirkland, J. I., Edward L. Simpson, Donald D. DeBlieux, Scott K. Madsen, Emily Bogner & Neil E. Tibert (2016). Depositional constraints on the Lower Cretaceous Stikes Quarry dinosaur site: Upper Yellow Cat Member, Cedar Mountain Formation, Utah. Palaios 31(9): 421-439; doi: 10.2110/palo.2016.041
Kowallis, B. J., Christiansen, E. H., Deino, A. L., Peterson, F., Turner, C.E., Kunk, M. J., and Obradovich, J. D., 1998, The age of the Morrison Formation. Modern Geology, v. 22, p. 235-260.
Le Loeuff, J., and E. Buffetaut. 1998. A new dromaeosaurid theropod from the Upper Cretaceous of southern France. Oryctos 1:105-112
Longrich, N. R., and P. J. Currie. 2009. A microraptorine (Dinosauria–Dromaeosauridae) from the Late Cretaceous of North America. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Martyniuk, M. 2016. You’re Doing It Wrong: Microraptor Tails and Mini-Wings. DinoGoss Blog.
McDonald, AT, Kirkland JI, DeBlieux DD, Madsen SK, Cavin J, et al. (2010). Farke AA (ed.). "New Basal Iguanodonts from the Cedar Mountain Formation of Utah and the Evolution of Thumb-Spiked Dinosaurs". PLoS ONE. 5 (11): e14075.
Norell, M. A., and P. J. Makovicky. 2004. Dromaeosauridae. In D. B. Weishampel, P. Dodson, and H. Osmolska (eds.), The Dinosauria (second edition). University of California Press, Berkeley 196-209
Paul, Gregory S. (2016). The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs (2nd Edition). Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. pp. 151, 163, 229, 252, 314, 319, 326, 327.
Pei, R., Q. Li, Q. Meng, K.-Q. Gao, and M. A. Norell. 2014. A New Specimen of Microraptor (Theropoda: Dromaeosauridae) from the Lower Cretaceous of Western Liaoning, China. American Museum Novitates 3821:1-28
Prum, R.; Brush, A.H. (2002). "The evolutionary origin and diversification of feathers". The Quarterly Review of Biology. 77 (3): 261–295.
Rauhut, O. W. M. 2003. The interrelationships and evolution of basal theropod dinosaurs. Special Papers in Palaeontology 69:1-213
Roca-Argemi, X. and Nadon, G. C. 2003. The Buckhorn Conglomerate as the upper member of the Morrison Formation: new evidence from the type section, Cedar Mountain, Utah. Geological Society of America, Rocky Mountain Section, 55th Annual Meeting, Paper 14-1.
Rothschild, B., Tanke, D. H., and Ford, T. L., 2001, Theropod stress fractures and tendon avulsions as a clue to activity: In: Mesozoic Vertebrate Life, edited by Tanke, D. H., and Carpenter, K., Indiana University Press, p. 331-336.
Ruiz-Omeñaca, J. I., and J. I. Canudo. 2003. Dinosaurios (Saurischia, Ornithischia) en el Barremiense (Cretácico Inferior) de la península Ibérica [Dinosaurs (Saurischia, Ornithischia) in the Barremian (Lower Cretaceous) of the Iberian peninsula]. In F. Pérez Lorente (ed.), Dinosaurios y Otros Reptiles Mesozóicos de España 269-312
Sanders, F.; Manley, K.; Carpenter, K. (2001). "Gastroliths from the Lower Cretaceous sauropod Cedarosaurus weiskopfae". In Tanke, Darren; Carpenter, Ken (eds.). Mesozoic Vertebrate Life: New Research Inspired by the Paleontology of Philip J. Currie. Indiana University Press. pp. 166–180.
Senter, P., R. Barsbold, B. B. Britt and D. A. Burnham. 2004. Systematics and evolution of Dromaeosauridae (Dinosauria, Theropoda). Bulletin of the Gunma Museum of Natural History 8:1-20
Senter, P., J. I. Kirkland, and D. D. DeBlieux. 2012. Martharaptor greenriverensis, a new theropod dinosaur from the Lower Cretaceous of Utah. PLoS ONE 7(8):e43911:1-12
Senter, P.; Kirkland, J.I.; Deblieux, D. D.; Madsen, S.; Toth, N. (2012). Dodson, Peter (ed.). "New Dromaeosaurids (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Lower Cretaceous of Utah, and the Evolution of the Dromaeosaurid Tail". PLoS ONE. 7 (5): e36790.
Shapiro, R.S., Fricke, H.C., and Fox, K. 2009. Dinosaur-bearing oncoids from ephemeral lakes of the Lower Cretaceous Cedar Mountain Formation, Utah. Palaios 2(4):51-58.
Smith, D. K. 1997. Museum of Earth Science, Brigham Young University. In P. J. Currie & K. Padian (ed.), Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs 457-458
Stokes, W. L. 1944, Morrison and related deposits in the Colorado Plateau. Geological Society of America Bulletin v. 55, p. 951-992.
Stokes, W.L. 1952. Lower Cretaceous in the Colorado Plateau. American Association of Petroleum Geologists v. 36: 1766-1776.
Sues, H.-D., and A. Averianov. 2014. Dromaeosauridae (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Bissekty Formation (Upper Cretaceous: Turonian) of Uzbekistan and the phylogenetic position of Itemirus medullaris Kurzanov, 1976. Cretaceous Research 51:225-240
Switek, Brian (January 7, 2015). "Utah's Dinosaur 'Death Trap' Reveals Trove of Giant Predators". National Geographic. Retrieved April 15, 2017.
Turner, A. H., S. H. Hwang, and M. A. Norell. 2007. A small derived theropod from Öösh, Early Cretaceous, Baykhangor Mongolia. American Museum Novitates 3557:1-27
Turner, Alan H.; Pol, D.; Clarke, J.A.; Erickson, G.M.; Norell, M. (2007). "A basal dromaeosaurid and size evolution preceding avian flight". Science. 317 (5843): 1378–1381.
Turner, AH; Makovicky, PJ; Norell, MA (2007). "Feather quill knobs in the dinosaur Velociraptor". Science. 317 (5845): 1721.
Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. 861 pp.
Williamson, T. E., and S. L. Brusatte. 2014. Small theropod teeth from the Late Cretaceous of the San Juan Basin, northwestern New Mexico and their implications for understanding latest Cretaceous dinosaur evolution. PLoS ONE 9(4):e93190:1-23
Xu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X.; Kuang, X.; Zhang, F.; Du, X. (2003). "Four-winged dinosaurs from China". Nature. 421 (6921): 335–340.
#Utahraptor ostrommaysi#Utahraptor#Dinosaur#Utahraptor ostrommaysorum#Raptor#Bird#Dromaeosaur#Birds#Feathered Dinosaurs#Dinosaurs#Birblr#Palaeoblr#Factfile#Cretaceous#Carnivore#Theropod Thursday#North America#paleontology#prehistory#prehistoric life#biology#a dinosaur a day#a-dinosaur-a-day#dinosaur of the day#dinosaur-of-the-day#science#nature
710 notes
·
View notes
Text
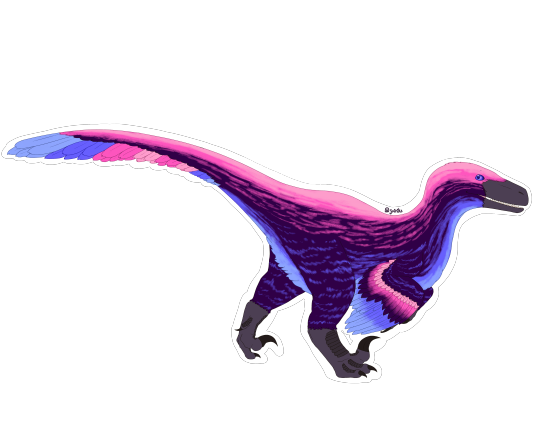
adding omnisexual utahraptor to the bunch! <3
#utahraptor#utahraptor ostrommaysi#dromaeosaur#dromaeosaurid#dromaeosaurids#feathered dinosaur#feathered dinosaurs#dinosaur#dinosaurs#theropod#theropods#theropoda#theropod dinosaur#maniraptora#pride#lgbt#lgbtq#lgbtq pride#omnisexual#omnisexual pride#paleontology#paleoart#mesozoic#my art
190 notes
·
View notes
Photo


utahraptor ! or jurassic park 3 velociraptor
art assignment ! gotta show off our most recent pieces related to what kinda art were looking at and i refuse to show any ygo (i also work a lot and have nothing to show except shit from like 2016)
heres the ref i used

#my art#dinos#utahraptor#blood 0#idk what im gonna do next.... maybe a full body indricothere..#Utahraptor ostrommaysi#therapod#dromaeosaur
71 notes
·
View notes
Photo
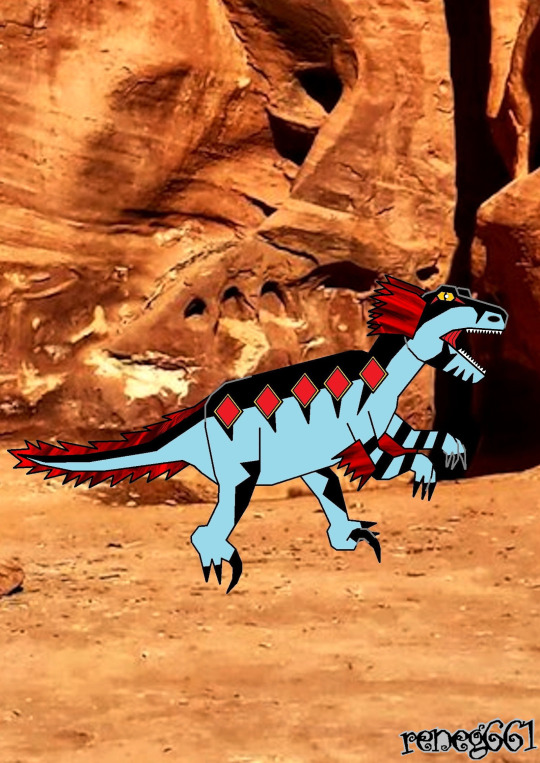

Is a genus of large dromaeosaurid dinosaur that lived in North America during the Early Cretaceous period. It was a heavy-built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore. It contains a single species, Utahraptor ostrommaysi, which is the largest-known member of the family Dromaeosauridae. The holotype of Utahraptor, CEU 184v.86 consists of a second pedal ungual, with potentially assigned elements from other specimens: pedal ungual CEU 184v.294, tibia CEU 184v.260 and premaxilla CEU 184v.400. These elements have huge proportions compared to other dromaeosaurids, suggesting an animal about twice the length of Deinonychus or, surpassing it in a 100%.[1] Like other dromaeosaurids, Utahraptor had large curved claws on their second toes. The second pedal ungual is preserved at 22 cm (8.7 in) in length and is estimated to reach 24 cm (9.4 in) restored. The largest described U. ostrommaysi specimen (BYUVP 15465, referred by Erickson et al. 2009) is estimated to have reached up to 7 m (23 ft) long and somewhat less than 500 kg (1,100 lb) in weight, comparable to a polar bear in weight.[1] In 2012, the paleontologist Thomas R. Holtz Jr. estimated its weight around 230 to 450 kg (500 to 1,000 lb), comparable to a grizzly bear. However, the 2001 Kirkland discovery indicates the species may be far heavier than previously estimated. In 2016 Rubén Molina-Pérez and Asier Larramendi estimated the largest specimen (BYU 15465) at 4.65 m (15.3 ft) long, 1.5 m (4.9 ft) tall at the hips and 280 kg (620 lb) in weight; they claim the larger estimates are due to nine specimens of various ages being mixed. For instance, some elements were wrongly referred to the genus; the lacrimal bone of the specimen CEU 184v.83 turned out to be a postorbital from the ankylosaur Gastonia. Britt et al. also suggested that the previously identified manual unguals of the specimens CEU 184v.294, BYU 9438 and BYU 13068 are indeed pedal unguals. This suggestion was confirmed by Senter in 2007. According to Kirkland et al. in 1993, Utahraptor can be recognised by the following autapomorphies: claws on the hand that are more specialized as cutting blades than in other dromaeosaurids; a lacrimal bone with distinctly parallel mesial and outer sides, giving it an elongate subrectangular appearance in top view; and a base of nasal opening on the premaxilla parallel to the premaxillary tooth row. In the revised diagnosis conducted by Turner et al. in 2012, Utahraptor differs from other dromaeosaurids in: an elongate nasal process of the premaxilla; a distal end of metatarsal III that is smooth, not ginglymoid; an L-shaped quadratojugal without a posterior process; the presence of a well developed notch between the lesser trochanter and greater trochanter; and dorsal vertebrae that lack pleurocoels. Although feathers have never been found in association with Utahraptor specimens, there is strong phylogenetic evidence suggesting that all dromaeosaurids possessed them. The genus Microraptor is one of the oldest-known dromaeosaurids, and is phylogenetically more primitive than Utahraptor. Since Microraptor and other dromaeosaurids possessed feathers, it is reasonable to assume that this trait was present in all of Dromaeosauridae. Feathers were very unlikely to have evolved more than once, so assuming that any given dromaeosaurid, such as Utahraptor, lacked feathers would require positive evidence that they did not have them. So far, there is nothing to suggest that feathers were lost in larger, more derived species of dromaeosaurs. The presence of quill knobs in Dakotaraptor evidenced that even larger dromaeosaurids had feathers.
Carnivore
Utahraptor (c) Primal Prey
Art (c) reneg661
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Utahraptor
Utahraptor ostrommaysi
Source: Here
263 notes
·
View notes
Text
An Analysis of the Creature Designs in Jurassic Fight Club
The 2008 History Channel miniseries Jurassic Fight Club was not a good show. Almost objectively, it was a badly-done series. The effects were of generally high quality, but those decent effects were in service of a poorly-scripted, gratuitously-violent, scientifically-inaccurate gorefest masquerading as a documentary.
It’s not worth your time.
That said, one bit of unambiguous praise I can give it lies in the designs for the dinosaurs. While they are frequently very inaccurate, they are completely unlike any dinosaur designs in any other media. The showrunners very easily could have just appropriated stock footage from older programs to pad their runtime, but they created unique clips featuring their own designs, which is commendable.
In this post, I’m going to be going through all of the creature designs that appear in Jurassic Fight Club and give my honest thoughts on them. I will factor in both accuracy to the real animal and my own personal tastes, and ultimately assign each one a score out of 10.
So, without further ado, let’s begin:

Majungasaurus crenatissimus (male)
Let’s cover these in order of appearance, which means that the male Majungasaurus is first on the plate. (I am choosing to ignore that they call it Majungatholus in the narration; that is not what this creature’s name is.)
This is a pretty interesting portrayal of this animal. They very easily could have just thrown some skin over the bones and called it a day. But, they stretched their creativity a bit and gave it some speculative soft tissue, and I like that.
That said, the anatomy is completely wrong for a Majungasaurus. The skull is correct, but the arms are too well-developed, and the legs are way too long and lean. Those proportions would work pretty well if this were a Carnotaurus, but it’s a bit too athletic for a majungasaur.
7/10.

Majungasaurus crenatissimus (female)
This is much more in line with what I was expecting from their Majungasaurus. It has the exact same problems as the male, and is missing the speculative soft tissue that I liked so much. Still okay, but not as interesting as the male.
6/10.

Tyrannosaurus rex
No, I don’t know why it’s squatting like that in this promotional image.
Ignoring the weird pose, this isn’t too bad, actually. Sure, it still has broken wrists, and the skull is a bit off, but it otherwise looks about right. For a depiction of T. rex from 2008, this is pretty decent stuff. I like the muted purple color, and I am immensely appreciative of the fact that they didn’t just copy-paste a Jurassic Park rex into their show. They could have very easily done that, but they chose to make something more representative of the actual animal.
8/10.

Nanotyrannus lancensis
This one’s a bit tough to judge. You see, Nanotyrannus doesn’t actually exist. In 2008, it was considered its own genus. But, in the decade since this series aired, it has been all but confirmed that Nanotyrannus is just a juvenile Tyrannosaurus.
That said, as a juvenile Tyrannosaurus, this is pretty good. It’s slim and fierce, with a good color scheme and decent accuracy to the fossils. Aside from the fact that this animal never existed, this is decent. Not bad at all.
7/10.

Deinonychus antirrhopus
I am of completely mixed opinions about this one. On the one hand, aside from the broken wrists, the anatomy is pretty much spot-on. You can tell that the designers actually looked at real Deinonychus skeletons to model this. Also, the blue body with the striping on the tail is a very striking color pallete. As a design, this is actually pretty good.
But, then we get to the elephant in the room. Not a single feather to be found anywhere on its body. Even in 2008, no feathers at all was barely acceptable, and it is completely unforgiveable today.
I have heard that they didn’t do feathers because of budgetary restrictions, which is understandable, but it does drag this design down quite a bit.
I’m going to have to give it a neutral score. It’s a great monster design, but it’s a terrible raptor.
5/10.
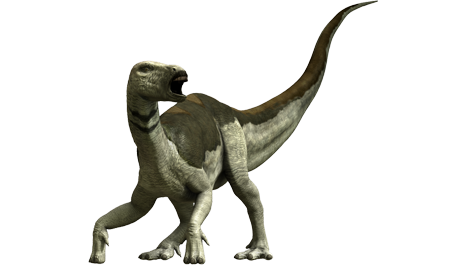
Tenontosaurus tilletti
Poor Tenontosaurus. It pretty much only ever gets media representation so that it can be killed by either Deinonychus or Acrocanthosaurus, and nobody ever seems to give it the time of day.
Fortunate, then, that this is a fantastic design.
Anatomically, it’s spot-on. The colors are dull, but not boring. It has a good amount of soft tissue, and carries a real sense of weight. Out of all the dinosaurs in the show, this one looks the most like a real animal. I have absolutely no complaints.
10/10.

Stegosaurus ungulatus
This is top-quality stuff right here. The proportions are good, even if the tail is a bit on the short side. The hands have the correct number of digits, and all of the plates and spikes seem to be in order. Again, the colors are a bit drab, but it feels appropriate for an animal of this size.
Also, how strange is it that, of all shows, Jurassic Fight Club is the only one I’ve seen that gets Stegosaurus’s weirdly long neck right?
Another triumph.
10/10.

Ceratosaurus nasicornis
Wow.
This is almost entirely perfect.
It has the right skull, it has the long teeth, it has the osteoderms on the back, the proportions are correct. Literally the only inaccuracy I can find is the pronated wrists, but that’s hardly enough to tarnish this thing’s otherwise perfect score.
This may be the best depiction of Ceratosaurus I’ve ever seen, and it is unquestionably the best design in the show.
10/10.

Camarasaurus supremus
Eh.
It looks about right, but it just feels...plain. This is the first one where the dull color scheme is a downside. It’s just flat grey with a yellow head. I do like that detail, but that’s pretty much all it has going for it.
Also, it has elephant feet, which is just wrong.
4/10.

Allosaurus fragilis
Alright, buckle down, because this one’s really bad.
Whereas everything up to this point at least feels like they looked at the actual animal as they were rendering, I’m not certain anyone involved in this thing’s design process had ever seen an Allosaurus skeleton. Let me count the issues:
The skull is so utterly wrong I’m unconvinced they didn’t just completely make it up.
The horns are the wrong size, the wrong shape, and in the wrong spot.
The wrists are broken and stuck on the end of way-too-long human arms.
The torso is too shallow, and has this weird hunchback thing going on.
The legs are too short, and those dainty little feet are bordering on comical. It doesn’t look like it should be able to stand up.
Literally no component of this thing’s anatomy resembles the animal it is supposed to be. It’s a trainwreck.
1/10.

Carcharocles megalodon
To begin with, yes, I am all aboard Team Carcharocles.
With that out of the way, this is a very “meh” design. It’s literally just a big great white shark. No real creativity or imagination at play here. Normally, that would be fine, but C. megalodon isn’t particularly closely related to the great white, so I can’t rate this too highly.
4/10.

Brygmophyseter shigensis
Conversely, I think that making Brygmophyseter a modified sperm whale is completely appropriate. This animal was a close cousin of the modern sperm whale, and thus would probably look fairly similar.
Decent colors, realistic anatomy, appropriate role within the episode’s story. Pretty decent stuff.
7/10.

Gastonia burgei
The show’s designers keep doing a really good job with their armored dinosaurs. The Stegosaurus above was one of their best, and Gastonia here is no different.
It certainly helps that Gastonia is known from pretty solid remains, so they had a lot of material to work with. It looks pretty much as it should, and the color scheme is vibrant, but not overdone. Pretty stellar work overall.
9/10.

Utahraptor ostrommaysi
Okay, I was willing to be forgiving of the Deinonychus because of the colors, plus the fact that they nailed its skeletal anatomy. This thing doesn’t have either of those advantages.
I can forgive the incorrect skull, Utahraptor‘s skull wasn’t known until nearly a decade after the show came out. What I cannot forgive is the drab, boring color scheme and those AWFUL feathers. If this is all they were going to do to add feathers to their raptors, I’m almost glad they left Deinonychus scaly.
Just awful.
2/10.

Arctodus simus
Wait. They didn’t have the budget to render raptors with proper feathers, but they did have the budget to do an episode all about furry Pleistocene mammals?
Anyways, this is alright. The skull looks a bit off to me, and the legs are too short, but it’s not awful. Y’know, aside from the fact that they gave this bear human eyes for some reason.
6/10.

Panthera leo atrox
That sure is a lion.
5/10.

Pachyrhinosaurus canadensis
That is not Pachyrhinosaurus. Even ignoring the erroneous horn, -- which is addressed as speculative within the show -- that is straight-up not the skull of a Pachyrhinosaurus. They just modelled an (admittedly okay-looking) Achelousaurus, and then had the narrator call it Pachyrhinosaurus.
3/10.

Albertosaurus sarcophagus
I don’t even know what to say here. All of the show’s other theropods had something interesting or noteworthy about them, either good or bad. But, this is just every pop-culture Albertosaurus I’ve ever seen.
It certainly is there.
4/10.

Edmontosaurus annectens
This is one of the most completely unremarkable creature designs I’ve ever seen in my life. It’s a single dull color, it has no speculative soft tissue, and its only role in the episode is to be killed and eaten by predators.
This is the closest thing I’ve ever seen to a representation of a Perfectly Normal Beast. There is not a single remarkable thing here.
And it’s a shame, because Edmontosaurus is a very interesting and underrated animal, but here it gets saddled with this halfhearted shrug of a design.
4/10.

Dromaeosaurus albertensis
Yeesh.
This has the advantage of being more anatomically accurate than the Utahraptor and the colors are okay, but those feathers are, again, absolutely appalling.
Topping that off, the narration talks about them communicating with each other via sign language, which is just...dumb. Even as a kid, I thought that was dumb.
2/10.
7 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Didn't work on my huge bunch of adopts, so I finally worked on the next one, and this is definitely a great way to train !
My younger self from when I was 6 or 7 would be so proud to see that one day I could at least draw dinosaurs !
Pearl is a Utahraptor Ostrommaysi
Adopted from Unknown (Can't find their page anymore)
Pearl © Me
10 notes
·
View notes