#Network distribution analysis
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Good News for New Writers & Bad News for Established Ones
But Both Can Be Winners with a Strategic Approach I am pleased that my new account, with 100 followers, now gets more visibility than my old account, with 101835 followers. Here is what new and established writers could do to adapt. Today, I experienced a mix of emotions when I discovered that my new Medium account, created out of necessity after being targeted by scammers, organically gained…
#Boost program on Medium#Building your own platform for grwoth#business#Freelance writing strategy#Growing audience on Medium#How to build an audience without Medium#How to integrate Substack and Patreon#Medium#Medium publication growth#Medium vs. Substack#Network distribution analysis#No network distribution on mediim#Organic growth on Medium#Paid subscribers on Substack#stories#Substack success tips#Why not to trust Medium#Writer community insights#writers#writing#Writing strategy for established writers on Medum#Writing strategy for new writers on medium#writingcommunity
0 notes
Text
Don't Miss Out: Why AMC Networks Inc. Stock is Set to Soar
Discover AMC Networks Inc.'s stock price trends, and investment potential. Learn why this undervalued stock might be a great addition. #StockPriceForecast #AMCNetworks #AMCX #InvestmentInsights #UndervaluedStocks #StreamingServices #MarketAnalysis #invest
AMC Networks Inc. is an American entertainment company headquartered in New York City. The company owns and operates several cable channels, including AMC, IFC, We TV, and Sundance TV. It also provides subscription streaming services like Acorn TV, Shudder, Sundance Now, and AMC+. Additionally, AMC Networks is involved in film distribution through IFC Films and RLJE Films, and it owns the anime…
#AMC Networks Inc#Entertainment industry#Film distribution#Financial performance#Investment#Investment Insights#Investment Opportunities#Stock Forecast#Stock Insights#Stock market analysis#Stock Price Forecast#Streaming services#Undervalued stocks
0 notes
Link
Class C IP Checker - Analyze Your IP Network Segmentation
#Class C IP Checker#Free Micro Tools#IP analysis#network segmentation#IP management#SEO tools#IP class distribution#network management
0 notes
Text
To accomplish its mission of increasing the health security of the U.S., the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that it "conducts critical science and provides health information" to protect the nation. But since President Trump's administration assumed power in January, many of the platforms the CDC used to communicate with the public have gone silent, an NPR analysis found.
Many of the CDC's newsletters have stopped being distributed, workers at the CDC say. Health alerts about disease outbreaks, previously sent to health professionals subscribed to the CDC's Health Alert Network, haven't been dispatched since March. The agency's main social media channels have come under new ownership of the Department of Health and Human Services, emails reviewed by NPR show, and most have gone more than a month without posting their own new content.
268 notes
·
View notes
Text
Judd Legum and Rebecca Crosby at Popular Information:
Today, the National Security Agency (NSA) is planning a "Big Delete" of websites and internal network content that contain any of 27 banned words, including "privilege," "bias," and "inclusion." The "Big Delete," according to an NSA source and internal correspondence reviewed by Popular Information, is creating unintended consequences. Although the websites and other content are purportedly being deleted to comply with President Trump's executive orders targeting diversity, equity, and inclusion, or "DEI," the dragnet is taking down "mission-related" work. According to the NSA source, who spoke on the condition of anonymity because they are not authorized to speak to the media, the process is "very chaotic," but is plowing ahead anyway. A memo distributed by NSA leadership to its staff says that on February 10, all NSA websites and internal network pages that contain banned words will be deleted. This is the list of 27 banned words distributed to NSA staff:
Anti-Racism Racism Allyship Bias DEI Diversity Diverse Confirmation Bias Equity Equitableness Feminism Gender Gender Identity Inclusion Inclusive All-Inclusive Inclusivity Injustice Intersectionality Prejudice Privilege Racial Identity Sexuality Stereotypes Pronouns Transgender Equality
The memo acknowledges that the list includes many terms that are used by the NSA in contexts that have nothing to do with DEI. For example, the term "privilege" is used by the NSA in the context of "privilege escalation." In the intelligence world, privilege escalation refers to "techniques that adversaries use to gain higher-level permissions on a system or network." The purge extends beyond public-facing websites to pages on the NSA's internal network, including project management software like Jira and Confluence.
[...]
The government memory hole
Since Trump took office, thousands of web pages across various federal agencies have been altered or removed entirely. Federal agencies have taken down or edited resources about HIV, contraceptives, LGBTQ+ health, abortion, and climate change. Some web pages have later come back online “without clarity on what had been changed or removed.” An analysis by the Washington Post of 8,000 federal web pages “found 662 examples of deletions and additions” since Trump took office. The analysis found that words like diversity, equity, and inclusion were removed at least 231 times from the websites of federal agencies, including the Department of Labor, the Department of Education, the Department of Health and Human Services, and the Department of Transportation.
The NSA’s “Big Delete” is a form of authoritarian censorship under the MAGA regime led by the Trump-Musk-Vance axis of evil.
See Also:
NCRM: The 27 Words the NSA Is Scrubbing From Its Websites: Report
60 notes
·
View notes
Text

DEEP-SEA DOMINANCE: THE SUPERGIANT AMPHIPOD ACROSS THE ABYSS
The deep-sea amphipod Alicella gigantea, described in 1899, currently known as the world’s largest amphipod, inhabits depths of the lower abyssal and upper hadal zones. Historically, it has been sampled or observed in situ infrequently relative to other deep-sea amphipods, suggesting low population densities and providing a sense of rarity. Consequently, little is known about the demography, genetic variation and population dynamics of A. gigantea.
Although elusive, Alicella gigantea is one of the most widely distributed amphipods known, thriving across more than half of the world’s oceans, according to a recent study by researchers at the University of Western Australia. Amphipods like A. gigantea are shrimp-like crustaceans with narrow bodies and a distinctive hunched posture. They inhabit nearly every aquatic habitat on Earth, from shallow coasts to the hadal trenches, though their numbers dwindle with increasing depth.
In the most comprehensive assessment to date, scientists compiled 195 records from 75 locations across the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, including both published data and new expeditions. Genetic analysis of mitochondrial and nuclear genes revealed extremely low divergence among global populations, supporting the existence of a single, globally distributed species. The haplotype network showed minimal regional differentiation, with shared haplotypes across vast distances and the Pacific identified as the species’ main stronghold. Far from being rare, A. gigantea occupies nearly 60% of the global ocean, a silent giant spanning the deep.
Main photograph: The supergiant amphipods. Oceanlab, University of Aberdeen, UK.
Reference (Open Access): Paige et al., 2025. The supergiant amphipod Alicella gigantea may inhabit over half of the world’s oceansR. Soc. Open Sci.
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Locally adapted, decentralised innovation is reshaping what environmental monitoring in Africa

Projects like AirQo in Uganda and Clarity Nodes in Nairobi are deploying low-cost particulate matter sensors to create real-time urban air quality maps.
These portable devices, calibrated against reference stations, are not housed in government ministries—they’re installed in schools, markets, and transit corridors.
This hyperlocal, community-focused deployment marks a decisive shift toward monitoring as a distributed public good.
In the water space, compact mobile testing kits—some linked to smartphones—are enabling NGOs and universities to test for E. coli, nitrates, and fluoride in boreholes and streams. These kits don’t require lab infrastructure or formal training, making them ideal for community-led sampling in rural areas.
Remote sensing is also playing a vital role. Satellite data from programs like Sentinel and MODIS is being used to track vegetation loss, algal blooms, and surface water dynamics.
In Lake Victoria, a hybrid approach pairs satellite analysis with on-the-ground sensors—offering a model for blended, multilayered monitoring frameworks that don’t depend on centralised equipment alone.
Perhaps the most transformative development is the rise of citizen science networks.
In Ghana, Nigeria, and Uganda, residents are using hand-held air monitors to document conditions in their own neighbourhoods.
These datasets are often shared via open-access platforms, where they inform city planning and regulatory debates. They also demonstrate a growing confidence in decentralised data ownership and interpretation.
Universities across the continent are enabling much of this innovation. Institutions like the University of Cape Town and Makerere University are not only building and testing sensors but also training local technicians and hosting data platforms. Their work has become a central node in an emerging, distributed monitoring ecosystem.
Source
#solarpunk#solar punk#community#africa#environmental monitoring#citizen science#distributed public goods
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Separately, the DOJ accused two Russian employees of RT, the Russian state-owned media outlet, of a nearly $10 million scheme to create and distribute content to U.S. audiences while keeping the connection to Russia hidden.
RT worked with an online content creation company in Tennessee, which was directed to contract with U.S. social media influencers to distribute its content on social media platforms including, TikTok, X, Instagram and YouTube. Since November, the company posted more than 2,000 videos that received more than 16 million views on YouTube, according to the indictment.
United States intelligence and security officials have been warning for months about Russia’s efforts to interfere in the 2024 election, specifically to undermine the Democratic presidential nominee, exploit social divisions, sow distrust in democratic institutions and to erode support for Ukraine.
The U.S. has provided arms to Ukraine to support its war following Russia's invasion in 2022.
“Russia remains the most active foreign threat to our elections,” Director of National Intelligence Avril Haines told senators in May at a briefing about election risks.
This is not the first time the U.S. has taken action against those behind the Doppelganger influence campaign.
In March, the U.S. Treasury sanctioned Social Design Agency and Structura, as well as their founders, for a network of fake accounts and phony news websites, saying they carried out the campaign "at the direction of the Russian Presidential Administration."
A report released on Tuesday by social network analysis company Graphika documents a cross-platform influence operation linked to the Chinese government with the aim of influencing online discourse ahead of the November 5 elections.
The operation has relied on "spamouflage" to spread misleading or false information, adopting faux American accounts to sow division through anti-government narratives and posts on divisive topics such as the Israel-Hamas conflict, gun control, and racial inequality.
Using ATLAS, its proprietary platform for real-time intelligence and data analysis, Graphika identified 15 such accounts on X (formerly Twitter) and one on TikTok. Mimicking both U.S. nationals and advocacy groups, these accounts have taken aim at both major political parties and called into question the legitimacy of the U.S. electoral process.
They exhibited certain patterns, including the use of U.S.-related hashtags like #American, and presented themselves as U.S. voters who "love America" but feel alienated by issues ranging from abortion to U.S. support for the war in Ukraine.
One X post from June 2023 stated: "Although I am an American, I am extremely opposed to NATO and the behavior of the U.S. government in war. I think soldiers should protect their own country's people and territory from being violated, and should not initiate wars on their own initiative." The post was accompanied by an image depicting NATO's expansion in Europe.
Not to say "I told you so" but I've been saying this for months. Social engineers are hard at work trying to influence the outcome of the election in November. It is very likely happening on a larger scale than we know of. Take everything you read online with a grain of salt between now and November.
#politics#us politics#it's the 'internet research agency' all over again#news#us news#2024 election#op
38 notes
·
View notes
Text

Tools of the Trade for Learning Cybersecurity
I created this post for the Studyblr Masterpost Jam, check out the tag for more cool masterposts from folks in the studyblr community!
Cybersecurity professionals use a lot of different tools to get the job done. There are plenty of fancy and expensive tools that enterprise security teams use, but luckily there are also lots of brilliant people writing free and open-source software. In this post, I'm going to list some popular free tools that you can download right now to practice and learn with.
In my opinion, one of the most important tools you can learn how to use is a virtual machine. If you're not already familiar with Linux, this is a great way to learn. VMs are helpful for separating all your security tools from your everyday OS, isolating potentially malicious files, and just generally experimenting. You'll need to use something like VirtualBox or VMWare Workstation (Workstation Pro is now free for personal use, but they make you jump through hoops to download it).
Below is a list of some popular cybersecurity-focused Linux distributions that come with lots of tools pre-installed:
Kali is a popular distro that comes loaded with tools for penetration testing
REMnux is a distro built for malware analysis
honorable mention for FLARE-VM, which is not a VM on its own, but a set of scripts for setting up a malware analysis workstation & installing tools on a Windows VM.
SANS maintains several different distros that are used in their courses. You'll need to create an account to download them, but they're all free:
Slingshot is built for penetration testing
SIFT Workstation is a distro that comes with lots of tools for digital forensics
These distros can be kind of overwhelming if you don't know how to use most of the pre-installed software yet, so just starting with a regular Linux distribution and installing tools as you want to learn them is another good choice for learning.
Free Software
Wireshark: sniff packets and explore network protocols
Ghidra and the free version of IDA Pro are the top picks for reverse engineering
for digital forensics, check out Eric Zimmerman's tools - there are many different ones for exploring & analyzing different forensic artifacts
pwntools is a super useful Python library for solving binary exploitation CTF challenges
CyberChef is a tool that makes it easy to manipulate data - encryption & decryption, encoding & decoding, formatting, conversions… CyberChef gives you a lot to work with (and there's a web version - no installation required!).
Burp Suite is a handy tool for web security testing that has a free community edition
Metasploit is a popular penetration testing framework, check out Metasploitable if you want a target to practice with
SANS also has a list of free tools that's worth checking out.
Programming Languages
Knowing how to write code isn't a hard requirement for learning cybersecurity, but it's incredibly useful. Any programming language will do, especially since learning one will make it easy to pick up others, but these are some common ones that security folks use:
Python is quick to write, easy to learn, and since it's so popular, there are lots of helpful libraries out there.
PowerShell is useful for automating things in the Windows world. It's built on .NET, so you can practically dip into writing C# if you need a bit more power.
Go is a relatively new language, but it's popular and there are some security tools written in it.
Rust is another new-ish language that's designed for memory safety and it has a wonderful community. There's a bit of a steep learning curve, but learning Rust makes you understand how memory bugs work and I think that's neat.
If you want to get into reverse engineering or malware analysis, you'll want to have a good grasp of C and C++.
Other Tools for Cybersecurity
There are lots of things you'll need that aren't specific to cybersecurity, like:
a good system for taking notes, whether that's pen & paper or software-based. I recommend using something that lets you work in plain text or close to it.
general command line familiarity + basic knowledge of CLI text editors (nano is great, but what if you have to work with a system that only has vi?)
familiarity with git and docker will be helpful
There are countless scripts and programs out there, but the most important thing is understanding what your tools do and how they work. There is no magic "hack this system" or "solve this forensics case" button. Tools are great for speeding up the process, but you have to know what the process is. Definitely take some time to learn how to use them, but don't base your entire understanding of security on code that someone else wrote. That's how you end up as a "script kiddie", and your skills and knowledge will be limited.
Feel free to send me an ask if you have questions about any specific tool or something you found that I haven't listed. I have approximate knowledge of many things, and if I don't have an answer I can at least help point you in the right direction.
#studyblrmasterpostjam#studyblr#masterpost#cybersecurity#late post bc I was busy yesterday oops lol#also this post is nearly a thousand words#apparently I am incapable of being succinct lmao
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Mycelial Networking Project - A New Kind of Employment Structure for Neurodivergent Talent
Hey y'all--some of you might remember I used to be fairly active on here during my final few years of grad school, and then I nearly burned out of my PhD, found out I was autistic, and subsequently drastically reduced the time I spent on tumblr. Well, good news: I'm ok, I recovered from burnout, graduated, and discovered something surprising both in my PhD research and during my burnout recovery--cooperating with other people who are on the same wavelength as you is both more efficient for knowledge transfer in a variety of expert fields, and also socially healthier than struggling alone! Whoda thunk!
With that in mind, myself and Mykola Bilokonsky (creator of r/AutismTranslated, software developer, and Autistic coach) have been working for the past few months on the Mycelial Institute (at mycelial.institute in your address bar--I haven't linked it because tumblr search suppresses outside links, oops)
The Mycelial Institute is attempting to create a new kind of workplace that’s optimized for neurodivergent people. If you follow me on here or found this post from the tags, chances are you already know there are so many autistic, ADHD and other neurodivergent folks who have so much to give but who struggle to do so in a traditional employment context. We can be some of the most passionate experts you know and we'll still be languishing in unemployment because we're not able to do things the way everyone else does - and as a result everyone is worse off.
What if there was a different kind of employment available? One that:
Was completely worker owned, without any kind of profit-taking or power hierarchy orthogonal to the specific goals of the organization?
Understood that there are many different ways to contribute, and that some people can be profoundly valuable in some of those ways while struggling with others - and so decoupled them!
Accepted the fact that disability isn’t a fringe experience to marginalize but a core component of most peoples’ lives - especially during the age of Covid - and so prioritized accommodation?
Embraced non-punitive accountability - we have goals, we have challenges. Sometimes we can’t meet a goal because of a challenge. Instead of that being a source of shame, how can we make that an accepted learning experience and build in additional supports?
If this sounds like something you'd be interested in, please visit mycelial.institute. We are currently very early in this process, and are actively seeking collaborators. Currently we’re trying to build a diverse leadership team, meaning we want to find folks across as many marginalized identities as we can to help us make foundational decisions. This includes disability - we want non-speakers and intellectually disabled leadership as well. (You don’t need to be interested in a leadership role to fill out our submission form, we’re gathering a pool of folks in general.)
More info below the readmore:
We are the 🍄Mycelial Institute because we are inspired by the decompositional half of ecologies that often goes overlooked. Rather than competing for winner-take-all dominance, mushrooms accept that everything dies eventually and simply wait their turn to build large distributed networks that break down the waste of the broader system, giving rise to new forms of life. No ecosystem is complete without this component, and our economics generally fail to acknowledge this meaningfully.
A “Mycelial Network” here is a new kind of collective workplace. The corporate structure is such that there’s a board that steers the organization, made up of members. The organization seeks paying work from large clients who have needs that can be served by our diverse and specialized membership - but it’s not really important what kind of work that is, as long as it’s ethical. So we may do R&D for one client, engineering for another client, data analysis for another client, whatever - as long as we have folks in our membership who have things to contribute, we can match member to tasks.
The way this is structured is something we’re still working on, but we are thinking it’s likely going to be something like a Social Purpose Corporation or an L3C. The point is, we seek high paying work and exceed the expectations of our clients with specialist output, but those specialists are supported by other members as they carry out their tasks.
So there’s room in this organization for folks with e.g. a deep special interest in esoteric engineering practices, but there’s also room for those folks who derive deep satisfaction from filling out paperwork, or doing compliance or QA oversight, etc. We are a collective, and that means that everyone’s time is valuable and we sink or swim collectively.
Members are paid based on the decisions made by the board, but we’re leaning towards a flatter pay scale where folks are paid for contributing period, rather than treating some peoples’ time as more valuable than others, because we recognize that it requires a collective effort to get the work done and keep the client happy.
The organization itself may choose to keep a portion of proceeds to pay into a “Subsidy Pool”, which can be used to pay members to provide services to other members who couldn’t otherwise afford them. But nobody is getting a cut just for investing or anything like that, this institution doesn’t exist to enrich founders, it exists to cast a wide net of support for members of the served community.
(So far everyone involved is US-based and this will likely be a US-based organization, at least to start. That said, we don’t yet know what we don’t know, and welcome collaborators from other parts of the world at least for early days when we’re not making money etc yet anyway.
Just, we’re going to be figuring it out as we go along.)
-> mycelial.institute <-
#autism#autistic#actually autistic#adhd#audhd#neurodivergent#neurodiversity#neurospicy#disability#text
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
by Melanie Phillips
But on June 4, the Famine Review Committee published a report in which it rejected the FEWS NET analysis as not “plausible” and said it could not endorse its famine projection.
The committee said there was a lack of reliable evidence about the number of trucks entering Gaza and the level of humanitarian assistance that was arriving and being distributed around its various areas.
In order to compensate for these gaps in the data, it said, FEWS NET had relied on “multiple layers of assumptions and inference” about food availability and access as well as nutritional status and mortality, and had made “deliberate choices over assumptions, without the necessary supporting evidence”.
Such assumptions, said the committee, had ignored or underestimated the value of both commercial sources of food and certain forms of humanitarian aid.
Although this didn’t alter the fact that Gaza was experiencing “extreme human suffering” and that urgent measures were needed to boost humanitarian supplies, the committee concluded that flows of aid and the availability of food had increased significantly in March and April and “that nearly 100 percent of daily kilocalorie requirements were available for the estimated population of 300,000 people in April, even using conservative calculations”.
In other words, the committee reversed its own dire predictions and damned the famine early warning network for excluding evidence that gave the lie to its anti-Israel narrative. The categorical declarations of imminent famine being caused by wicked, heartless, war-criminal Israel just weren’t true.
It’s worth remembering that USAID, the parent body of FEWS NET, is run by Samantha Power, who served as US ambassador to the United Nations during the Obama administration.
In 2002, Power suggested in a “thought experiment” that America might have to invade Israel to prevent an Israeli genocide against the Palestinians. She also suggested that the only people who might be alienated by this would be American Jews, who she said exercised tremendous political and financial power over America.
Other research has also exploded the “Gaza famine” claims. At Columbia University, two professors have said the evidence shows that sufficient amounts of food are being supplied to Gaza.
They told The Jerusalem Post that it was “a myth that Israel is responsible for famine in Gaza” and suggested that the International Criminal Court and UN had joined Hamas in blaming Israel for a “famine that never was, hoping to stop the war”.
Yet there are no signs that these rebuttals of the “Gaza famine” claim are having any effect on the Israel-bashing crowd. A few days ago, The New York Times was still referring to “starving civilians” and blaming deaths from malnutrition on “restrictions on aid and commercial goods entering Gaza”.
BBC News reported this week that “warnings of famine are looming once again in northern Gaza,” broadcasting distressing footage of infants said to be suffering from dehydration and malnutrition caused by restrictions on aid at the Rafah and Kerem Shalom border crossings.
Other than Fox News, it seems that no mainstream media outlet has reported the Famine Review Committee’s findings that the claim of famine in Gaza cannot be justified. Nor have the anti-Israel humanitarian organisations, although the World Health Organisation’s Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus has now subtly adjusted his rhetoric by talking about “famine-like conditions”.
Famine is not the only anti-Israel falsehood whose debunking has been ignored. The mainstream media and humanitarian crowd are still using the Hamas figure of 37,000-plus civilians killed in Gaza, despite the fact that the UN itself revised its own casualty totals sharply downwards after it emerged that some of the claimed deaths had been drawn from media sources and were fabricated.
Some outlets such as The New York Times, the Australian Broadcasting Corporation and Time magazine are still claiming that the International Court of Justice said the Palestinians in Gaza faced a “plausible risk of genocide” even though the court said no such thing. As the ICJ President Joan Donoghue herself said, the court decided “that the Palestinians had a plausible right to be protected from genocide. … It didn’t decide that the claim of genocide was plausible”.
#famine#famine myth#famine in gaza#gaza famine#melanie phillips#media bias#samantha powers#united nations#save the children
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
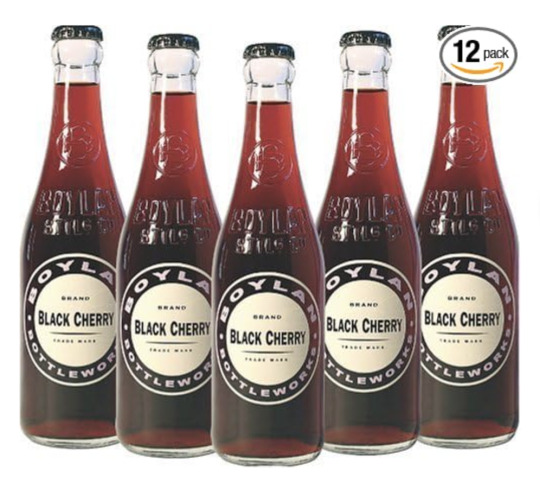

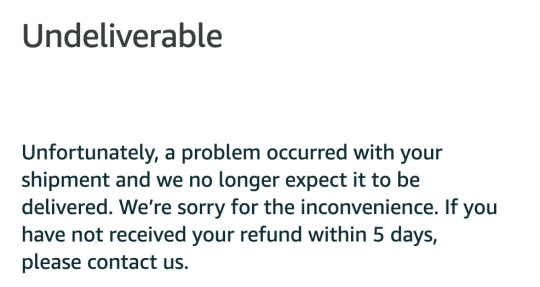
Some of you may remember me mentioning my quest to get black cherry soda and several shipments ending in tragic bottle breakage. I have been seriously craving this soda for nearly a month now.
I contacted Boylan and accused them of shoddy shipping.

They very politely informed me it was not their shoddy shipping store on Amazon.
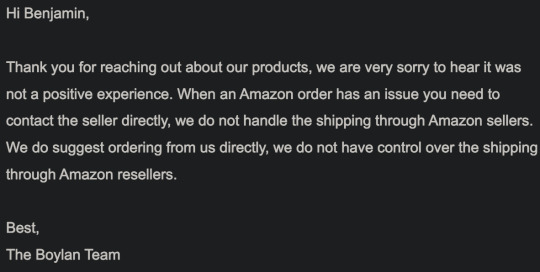
After some additional Amazon analysis, I felt foolish about my inaccurate accusations.
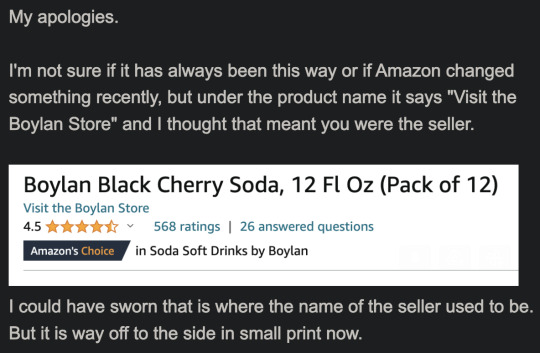

They informed me there were no local distributors of Boylan brand bottled black cherry beverages. They said they had no control over Amazon shipments and recommended I order directly from them. That would make this already pretty pricey pop about $15 more expensive after shipping and tax.
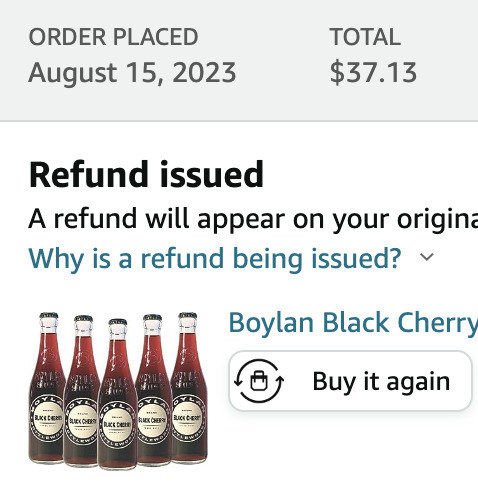
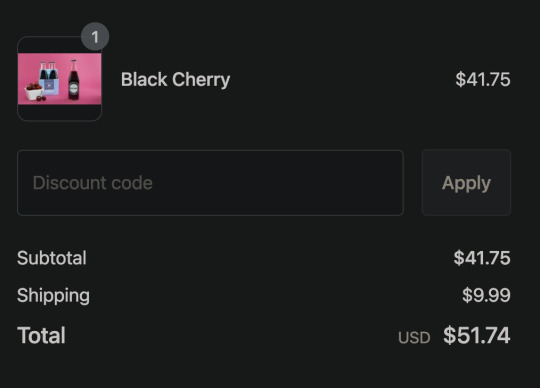
I had nearly given up.
After the $220 pizza and the $250 battery replacement and an almost assured account overdraw in my future, I'd have to wait at least until next month to satisfy my soda craving.
But when I went to my local Schnucks grocery store last night I decided to check the soda aisle to see if there were any alternatives.
My first find was Schnucks' own generic brand black cherry soda.

I have to say, that is a cute label for a generic store brand product.
After some research, I discovered this is a rebrand of a classic Vess soda. I like Vess soda! They make a wonderful cream soda concoction that my grandma used to buy whenever I would visit on the weekends. And I specifically told my mom never to buy cream soda for home because then it wouldn't be special when I had it at my grandma's house.
Sadly, I was unaware it was Vess-in-disguise and I was not trusting of a generic store-branded soda. Sometimes these low-cost rebranded items can be good, but it is always a crapshoot. I mean, their generic peas are 70 cents cheaper than Green Giant, but they are also mushy as heck. So based on my previous peas experience, there was a good chance it would taste more like black cherry cough syrup than soda.
I didn't know it was Vess, okay?
REMEMBER THE PEAS, PLEASE!
I fell into a soda research rabbit hole. Vess was acquired by a company called Cott Beverages in 1994. And Cott was then acquired by a company called Refresco in 2018. And Refresco partnered with Coca-Cola and is now their main manufacturer in the United States.
So I guess it is actually a Refresco Cott Vess Schnucks brand black cherry soda in partnership with Coca-Cola.
Capitalism is fucking weird, dude.
So the possible cough syrup RefresCoVesScnhucks was in my cart. I was considering taking the risk.
But then I noticed... the Fitz's section.

A locally owned and operated boutique soda bottler.
*heavenly music*
And do you know who owns Fitz's?
Mr. Alfred J. Fitz! (I don't actually know his first name or middle initial.)
Who founded Fitz's in 1947 as a drive-in restaurant based around his popular secret root beer recipe.
That's right. Fitz's was not enveloped by an incestuous line of conglomerates successively eating each other.
And because of that, they went out of business in 1976. The soda biz is rough if you don't have a multinational manufacturing and distribution network.
But then Fitz's was revived in 1993 by two plucky entrepreneurs who were determined to rebuild the brand using the original secret root beer recipe from Mr. Alfred J. Fitz.
Small business wins the day!
And then they sold out to The Westgate Group in late 1999.
Which then sold it again to Clayton Capital Partners in 2003.
Will capitalism please stop fucking with soda?
But then one of those plucky entrepreneurs thought the brand was being damaged by soulless investment firms and bought back Fitz's. He restored it to glory and I'm sure he will never sell it again*. He is intent on maintaining the Fitz's tradition and image as a beloved St. Louis small business that culturally enriches our famed Delmar Loop with vintage soda bottling techniques customers can watch when they visit the Fitz's restaurant. Neat!

*Unless RefresCoVesScnhucks offers him a bunch of money.
I can't believe I forgot about Fitz's. I used their root beer as a subject for one of my favorite product photos.

To make a long story as long as humanly possible my god why are you even still reading this...
...wouldn't you know it, Fitz's makes black cherry soda!
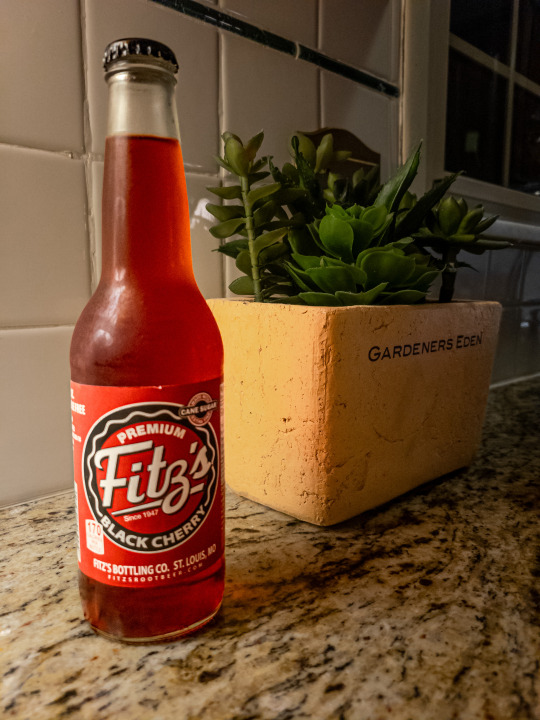

It is delicious.
Craving accomplished.
108 notes
·
View notes
Text
i've said it before and i'll say it again but there were two perspectives in the ai art discussion that were handed down to you by industry professionals so we could all argue over two outcomes that are beneficial for them. these are not the only possible outcomes, but nobody has contributed any lasting or pervasively distributed analysis to the discussion since then. this is another example of the thing i'm always talking about where distribution networks are invisible, and i'm concerned that none of the people repeating the point have really considered the implications of strengthening copyright law
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bloomberg: The Second Trump Presidency, Brought to You by Right-Leaning Male YouTubers
Davey Alba, Leon Yin, Julia Love, Ashley Carman, Priyanjana Bengani, Rachael Dottle, and Elena Mejía at Bloomberg:
As Donald Trump was sworn in as the 47th US President on Monday, he was surrounded by his family, donors and wealthy tech executives. Just a few feet farther away stood a political newcomer who’s been credited with encouraging lots of votes: Joe Rogan. The fact that Rogan, the host of the world’s most popular podcast, watched from the Capitol Rotunda as Republican luminaries like Florida Governor Ron DeSantis were confined to overflow speaks volumes about the new dynamics at play in Washington and the media writ large. Over the past two years, a set of massively popular podcasters and streamers cemented themselves as the new mainstream source of information for millions of young men, and, according to a new Bloomberg analysis, used their perch to rally these constituents in support of Trump and the political right.
In an effort to understand the media diet of a generation, Bloomberg watched and analyzed over 2,000 videos from nine prominent YouTubers. Reporters reviewed nearly 1,300 hours of footage from their channels, mapped out the podcasters’ guest networks and quantified the frequency of key political messages that they distributed to tens of millions of subscribers each day. To hear them tell it, America is in a desperate place, destabilized by soaring inflation, migrants streaming across the border and the beginnings of a third world war. Gender politics have gotten out of hand while schools and the medical establishment duped the public. The same messages were communicated in Trump’s inaugural address on Monday. Now that Trump is back in power, the broadcasters are well-positioned to help build support for his political agenda, transforming grievances into policy that could have lasting effects even beyond Trump’s term in office.
In the months leading up to election, hosts had more politicians and pundits on their shows and discussed the issues more frequently. Of the broadcasters’ videos that reached over 1 million views on YouTube during the time span Bloomberg reviewed, more than a third of videos mentioned voting or the US elections — often with the host explicitly calling on listeners to vote. None of the broadcasters style themselves as political pundits, and their conservative talking points were sandwiched between free-wheeling discussions of sports, masculinity, internet culture, gambling and pranks — making the rhetoric more palatable to an apolitical audience. Still, their popularity is sparking a “very big sea change in terms of who are the voices that matter,” Mark Zuckerberg, Meta Platforms Inc. chief executive officer, said in a conversation with Rogan published Jan. 10. “There’s this wholesale generational shift in who are the people who are being listened to.”
According to Edison Research, close to 50% of people over the age of 12 listen to a podcast monthly. Rogan’s three-hour interview with Trump in late October drew about 50 million views on YouTube. Zuckerberg, for his part, recently loosened Meta’s policies on Facebook and Instagram to allow more of the type of rhetoric that’s common among the podcasters, such as disparagement of transgender people. He added Ultimate Fighting Championship CEO Dana White, who encouraged Trump to join as a guest on such podcasts, to Meta’s board. Elon Musk, the owner of X, has made product changes to allow longer video streaming, in support of podcasters — and joined several as a guest himself. Google, meanwhile, wants to work through some Republican perceptions of its liberal bias and show that YouTube has already long been popular with conservatives, according to a person familiar with the company’s thinking. Over the weekend before the inauguration, many of the podcasters were coveted guests at parties hosted by YouTube, Spotify and other organizations. YouTube declined to comment. Spotify said “podcasts offer candidates a direct and influential way to engage with their audiences,” noting that both Trump and Democratic rival Kamala Harris took advantage of the medium. With the podcasters’ audiences skewing about 80% male on average, according to people familiar with the shows’ listener demographics, the hosts connected directly to a voting bloc that helped propel Trump back to the White House. Of the 903 podcast guests tracked by Bloomberg in the past two years, only 106 people, or 12 percent, were women. Men, and particularly white men, have long made up Trump’s core support base. But in November’s election, young men swung especially hard to the right. More than half of men under 30 supported Trump, according to the AP VoteCast survey of more than 120,000 voters, though outgoing President Joe Biden won the group in 2020. Exit polls have shown that Trump received more support from young men than any Republican candidate in more than two decades.
“We definitely helped with the young male vote,” Kyle Forgeard, a member of the Nelk Boys, said in an interview. “On the podcast, we just speak our mind, try to be true to ourselves and say what we think.” Above all, the broadcasters described American men as victims of a Democratic campaign to strip them of their power — a comforting message to a disspirited audience. These days, young men are lonelier than ever, with those aged 18 to 23 the least optimistic about their futures, and having the lowest levels of social support, according to Equimundo’s 2023 State of American Men report. Trump and his allies showed up for young men in the places where they were already spending their time — and supplied them with answers.
[...] The male-oriented podcasts tracked by Bloomberg each have their own style of show. Theo Von often discusses substance abuse issues and childhood experiences with his interviewees, while Lex Fridman focuses on expert opinions and tech topics. Shawn Ryan chats with people associated with military and law enforcement, saying he exposes the inner workings of the US government. Logan Paul, the Nelk Boys and Adin Ross tend to focus on humor, sports, pranks and creator drama. Of the programs reviewed, The Joe Rogan Experience, Flagrant by Andrew Schulz and The PBD Podcast by Patrick Bet-David follow the most typical host-and-interview talk show format, discussing news and popular culture, all while challenging political correctness. The hosts largely do not push back against their guests’ ideas. Von, Rogan and Schulz are also comedians, and they often recast controversial content as edgy humor. Yet even as the podcasts have tried to brand themselves uniquely, similar themes and characters appear across the network. Bloomberg’s analysis of 2,002 episodes across the shows reveals how closely interconnected the podcasters’ relationships are, and how much the shows’ talking points overlap. Over the past two years, 152 guests made an appearance on at least two of the shows. Recurring characters are common, not just as guests, but as “friends of the shows,” including the UFC CEO White and comedian Shane Gillis. The effect gives viewers a sense of being inducted into a virtual, close-knit friend group from home.

Read the full story at Bloomberg.
Bloomberg reports on how 9 male YouTubers that have a mostly right-leaning audience, such as Joe Rogan, Logan Paul, Patrick Bet-David, and Nelk Boys, helped push young male voters toward Donald Trump this recent election.
#YouTube#Podcasts#Joe Rogan#Shawn Ryan#Lex Fridman#Patrick Bet David#Theo Von#Logan Paul#Nelk Boys#Adin Ross#Andrew Schulz#The Joe Rogan Experience#PBD Podcast#This Past Weekend#Impaulsive#Full Send Podcast#Flagrant#Donald Trump#2024 Presidential Election
46 notes
·
View notes
Text
About one sixth of global cropland is contaminated by toxic heavy metals, researchers have estimated, with as many as 1.4 billion people living in high-risk areas worldwide.
Approximately 14 to 17% of cropland globally – roughly 242m hectares – is contaminated by at least one toxic metal such as arsenic, cadmium, cobalt, chromium, copper, nickel or lead, at levels that exceed agricultural and human health safety thresholds.
The analysis, which was conducted by the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and published in the journal Science, collected data from more than 1,000 regional studies across the globe, as well as using machine learning technology.
Dr Liz Rylott, a senior lecturer in the department of biology at the University of York, who was not involved in the research, said: “These findings reveal the deeply worrying extent to which these natural poisons are polluting our soils, entering our food and water, and affecting our health and our environment.
“Often collectively called heavy metals, these elements cause a range of devastating health problems, including skin lesions, reduced nerve and organ functions, and cancers.”
Toxic metal pollution in soil originates from both natural and human activity. Contaminated soil causes significant risks to ecosystems and human health as well as reducing crop yields, jeopardising water quality and food safety owing to bioaccumulation in farm animals. Toxic metal contamination can persist for decades once pollution has been introduced into soil.
As demand for critical metals increases, scientists have warned that the heavy metal pollution of soils is likely to worsen. “Our drive for technology-critical metals to build the green infrastructure required to tackle climate change (wind turbines, electric vehicle batteries and photovoltaic panels) will exacerbate this pollution,” said Rylott.
By combining the data in the study with the global population distribution, researchers estimate that between 900 million and 1.4 billion people live in high-risk areas across the world.
Cadmium was found to be the most widespread toxic metal and was particularly prevalent in south and east Asia, parts of the Middle East and Africa.
“This map illustrates how metal pollution is independent of human borders; to tackle this problem, countries will have to work together,” said Rylott. “Much of the pollution is in low- and middle-income countries, where communities are directly affected, exacerbating poverty. The effect of these contaminated crops entering global food networks is not as clear.”
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

How NASA science data defends Earth from asteroids
The asteroid 2024 YR4 made headlines in February with the news that it had a chance of hitting Earth on Dec. 22, 2032, as determined by an analysis from NASA's Center for Near Earth Object Studies (CNEOS) at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. The probability of collision peaked at over 3% on Feb. 18—the highest ever recorded for an object of its size. This sparked concerns about the damage the asteroid might do should it hit Earth.
New data collected in the following days lowered the probability to well under 1%, and 2024 YR4 is no longer considered a potential Earth impactor. However, the event underscored the importance of surveying asteroid populations to reveal possible threats to Earth. Sharing scientific data widely allows scientists to determine the risk posed by the near-Earth asteroid population and increases the chances of identifying future asteroid impact hazards in NASA science data.
"The planetary defense community realizes the value of making data products available to everyone," said James "Gerbs" Bauer, the principal investigator for NASA's Planetary Data System Small Bodies Node at the University of Maryland in College Park, Maryland.
How scientists spot asteroids that could hit Earth
Professional scientists and citizen scientists worldwide play a role in tracking asteroids. The Minor Planet Center, which is housed at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory in Cambridge, Massachusetts, collects and verifies vast numbers of asteroid and comet position observations submitted from around the globe. NASA's Small Bodies Node distributes the data from the Minor Planet Center for anyone who wants to access and use it.
A near-Earth object (NEO) is an asteroid or comet whose orbit brings it within 120 million miles of the sun, which means it can circulate through Earth's orbital neighborhood. If a newly discovered object looks like it might be an NEO, information about the object appears on the Minor Planet Center's NEO Confirmation Page. Members of the planetary science community, whether or not they are professional scientists, are encouraged to follow up on these objects to discover where they're heading.
When an asteroid's trajectory looks concerning, CNEOS alerts NASA's Planetary Defense Coordination Office at NASA Headquarters in Washington, which manages NASA's ongoing effort to protect Earth from dangerous asteroids. NASA's Planetary Defense Coordination Office also coordinates the International Asteroid Warning Network (IAWN), which is the worldwide collaboration of asteroid observers and modelers.
Orbit analysis centers such as CNEOS perform finer calculations to nail down the probability of an asteroid colliding with Earth. The open nature of the data allows the community to collaborate and compare, ensuring the most accurate determinations possible.
How NASA discovered risks of asteroid 2024 YR4
The asteroid 2024 YR4 was initially discovered by the NASA-funded ATLAS (Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System) survey, which aims to discover potentially hazardous asteroids. Scientists studied additional data about the asteroid from different observatories funded by NASA and from other telescopes across the IAWN.
At first, 2024 YR4 had a broad uncertainty in its future trajectory that would pass over Earth. As the planetary defense community collected more observations, the range of possibilities for the asteroid's future position on Dec. 22, 2032, clustered over Earth, raising the apparent chances of collision. However, with the addition of even more data points, the cluster of possibilities eventually moved off Earth.
Having multiple streams of data available for analysis helps scientists quickly learn more about NEOs. This sometimes involves using data from observatories that are mainly used for astrophysics or heliophysics surveys, rather than for tracking asteroids.
"The planetary defense community both benefits from and is beneficial to the larger planetary and astronomy-related ecosystem," said Bauer, who is also a research professor in the Department of Astronomy at the University of Maryland. "Much of the NEO survey data can also be used for searching astrophysical transients like supernova events. Likewise, astrophysical sky surveys produce data of interest to the planetary defense community."
How does NASA stop asteroids from hitting Earth?
In 2022, NASA's DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) mission successfully impacted with the asteroid Dimorphos, shortening the time it takes to orbit around its companion asteroid Didymos by 33 minutes. Didymos had no chance of hitting Earth, but the DART mission's success means that NASA has a tested technique to consider when addressing a future asteroid potential impact threat.
To increase the chances of discovering asteroid threats to Earth well in advance, NASA is working on a new space-based observatory, NEO Surveyor, which will be the first spacecraft specifically designed to look for asteroids and comets that pose a hazard to Earth. The mission is expected to launch in the fall of 2027, and the data it collects will be available to everyone through NASA archives.
"Many of the NEOs that pose a risk to Earth remain to be found," Bauer said. "An asteroid impact has a very low likelihood at any given time, but consequences could be high, and open science is an important component to being vigilant."
IMAGE: Artist’s impression of NASA’s upcoming NEO Surveyor mission, which will search for potentially hazardous near-Earth objects. The mission will follow open data practices to improve the chances of identifying dangerous asteroids. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
3 notes
·
View notes