#Poverty in Africa
Text
Africa is NOT Poor Because of Colonialism: Here’s Why. - Magatte Wade
youtube
#politics#africa#colonialism#poverty#poverty in africa#Magatte Wade#Triggernometry#contradicting beliefs#Francophone Africa#the wrong conversation#corruption#too much regulation#over regulation#business#laws in African countries#Youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text
TheUgliNessInThisBeautifulWorld
I see children deprived of basic rights. I see children wanting to die, take their life. I see children desperately hoping to get their old life back. once. when they're parents were alive.
Their cries bleed my ears, bleed my ears. What did the innocent children ever do to you? What did they spoil of yours? What did they steal of yours? What did they deprive you of?
I see it everywhere, every nook and corner of the world. Ugliness. Ugliness. In this supposedly beautiful world. I don't see it beautiful. The beauty has been lost. The humanity has been lost. Hearts merely pump blood. Emotions exiting our bodies.
Whether it be Denys, whether it be Liza, whether it be Jawad Mizar , whether it be Fiajo, whether it be Arjun, whether it be Anne, whether it be Fatima, whether it be Chandana. It doesn't matter. Their identity doesn't matter. All of them. Killed.
Do not ask which religion did the murdered belong to. Remember. Do not ask. They have no religion. The have no heart. They have no remorse. They have no humanity.
My sisters. Listen. I say. Listen. No matter the distance join hands - the milk spilt by men can must be cleaned. Oh those with hearts. Oh those with/without kids. Listen to the muffled voiced of these children. Listen to their tortured voice. Listen to the their cries of help.
Look at their hearts, minds, soul forever changes, forever traumatised. Maybe we couldn't save them from losing their mind but we can from losing their bodies.
This is a small writing on wars around the world and how severely it affects children in different places- ukraine, palestine, africa, pakistan, india
i really, really hope this post finds many
#palestine#freepalastine🇵🇸#free ukraine#africa#poverty in africa#help africa#free manipur#free ladakh#eyes everywhere
1 note
·
View note
Text
Things Biden and the Democrats did, this week #19
May 17-24 2024
President Biden wiped out the student loan debt of 160,000 more Americans. This debt cancellation of 7.7 billion dollars brings the total student loan debt relieved by the Biden Administration to $167 billion. The Administration has canceled student loan debt for 4.75 million Americans so far. The 160,000 borrowers forgiven this week owned an average of $35,000 each and are now debt free. The Administration announced plans last month to bring debt forgiveness to 30 million Americans with student loans coming this fall.
The Department of Justice announced it is suing Ticketmaster for being a monopoly. DoJ is suing Ticketmaster and its parent company Live Nation for monopolistic practices. Ticketmaster controls 70% of the live show ticket market leading to skyrocketing prices, hidden fees and last minute cancellation. The Justice Department is seeking to break up Live Nation and help bring competition back into the market. This is one of a number of monopoly law suits brought by the Biden administration against Apple in March and Amazon in September 2023.
The EPA announced $225 million in new funding to improve drinking and wastewater for tribal communities. The money will go to tribes in the mainland US as well as Alaska Native Villages. It'll help with testing for forever chemicals, and replacing of lead pipes as well as sustainability projects.
The EPA announced $300 million in grants to clean up former industrial sites. Known as "Brownfield" sites these former industrial sites are to be cleaned and redeveloped into community assets. The money will fund 200 projects across 178 communities. One such project will transform a former oil station in Philadelphia’s Kingsessing neighborhood, currently polluted with lead and other toxins into a waterfront bike trail.
The Department of Agriculture announced a historic expansion of its program to feed low income kids over the summer holidays. Since the 1960s the SUN Meals have served in person meals at schools and community centers during the summer holidays to low income children. This Year the Biden administration is rolling out SUN Bucks, a $120 per child grocery benefit. This benefit has been rejected by many Republican governors but in the states that will take part 21 million kids will benefit. Last year the Biden administration introduced SUN Meals To-Go, offering pick-up and delivery options expanding SUN's reach into rural communities. These expansions are part of the Biden administration's plan to end hunger and reduce diet-related disease by 2030.
Vice-President Harris builds on her work in Africa to announce a plan to give 80% of Africa internet access by 2030, up from just 40% today. This push builds off efforts Harris has spearheaded since her trip to Africa in 2023, including $7 billion in climate adaptation, resilience, and mitigation, and $1 billion to empower women. The public-private partnership between the African Development Bank Group and Mastercard plans to bring internet access to 3 million farmers in Kenya, Tanzania, and Nigeria, before expanding to Uganda, Ethiopia, and Ghana, and then the rest of the continent, bring internet to 100 million people and businesses over the next 10 years. This is together with the work of Partnership for Digital Access in Africa which is hoping to bring internet access to 80% of Africans by 2030, up from 40% now, and just 30% of women on the continent. The Vice-President also announced $1 billion for the Women in the Digital Economy Fund to assure women in Africa have meaningful access to the internet and its economic opportunities.
The Senate approved Seth Aframe to be a Judge on the US Court of Appeals for the First Circuit, it also approved Krissa Lanham, and Angela Martinez to district Judgeships in Arizona, as well as Dena Coggins to a district court seat in California. Bring the total number of judges appointed by President Biden to 201. Biden's Judges have been historically diverse. 64% of them are women and 62% of them are people of color. President Biden has appointed more black women to federal judgeships, more Hispanic judges and more Asian American judges and more LGBT judges than any other President, including Obama's full 8 years in office. President Biden has also focused on backgrounds appointing a record breaking number of former public defenders to judgeships, as well as labor and civil rights lawyers.
#Thanks Biden#Joe Biden#kamala harris#student loans#student loan forgiveness#ticketmaster#Africa#free lunch#hunger#poverty#internet#judges#politics#us politics#american politics
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
African poverty is partly a consequence of energy poverty. In every other continent the vast majority of people have access to electricity. In Africa 600m people, 43% of the total, cannot readily light their homes or charge their phones. And those who nominally have grid electricity find it as reliable as a Scottish summer. More than three-quarters of African firms experience outages; two-fifths say electricity is the main constraint on their business.
If other sub-Saharan African countries had enjoyed power as reliable as South Africa’s from 1995 to 2007, then the continent’s rate of real GDP growth per person would have been two percentage points higher, more than doubling the actual rate, according to one academic paper. Since then South Africa has also had erratic electricity. So-called “load-shedding” is probably the main reason why the economy has shrunk in four of the past eight quarters.
Solar power is increasingly seen as the solution. Last year Africa installed a record amount of photovoltaic (PV) capacity (though this still made up just 1% of the total added worldwide), notes the African Solar Industry Association (AFSIA), a trade group. Globally most solar PV is built by utilities, but in Africa 65% of new capacity over the past two years has come from large firms contracting directly with developers. These deals are part of a decentralised revolution that could be of huge benefit to African economies.
Ground zero for the revolution is South Africa. Last year saw a record number of blackouts imposed by Eskom, the state-run utility, whose dysfunctional coal-fired power stations regularly break down or operate at far below capacity. Fortunately, as load-shedding was peaking, the costs of solar systems were plummeting.
Between 2019 and 2023 the cost of panels fell by 15%, having already declined by almost 90% in the 2010s. Meanwhile battery storage systems now cost about half as much as five years ago. Industrial users pay 20-40% less per unit when buying electricity from private project developers than on the cheapest Eskom tariff.
In the past two calendar years the amount of solar capacity in South Africa rose from 2.8GW to 7.8GW, notes AFSIA, excluding that installed on the roofs of suburban homes. All together South Africa’s solar capacity could now be almost a fifth of that of Eskom’s coal-fired power stations (albeit those still have a higher “capacity factor”, or ability to produce electricity around the clock). The growth of solar is a key reason why there has been less load-shedding in 2024...
Over the past decade the number of startups providing “distributed renewable energy” (DRE) has grown at a clip. Industry estimates suggest that more than 400m Africans get electricity from solar home systems and that more than ten times as many “mini-grids”, most of which use solar, were built in 2016-20 than in the preceding five years. In Kenya DRE firms employ more than six times as many people as the largest utility. In Nigeria they have created almost as many jobs as the oil and gas industry.
“The future is an extremely distributed system to an extent that people haven’t fully grasped,” argues Matthew Tilleard of CrossBoundary Group, a firm whose customers range from large businesses to hitherto unconnected consumers. “It’s going to happen here in Africa first and most consequentially.”
Ignite, which operates in nine African countries, has products that include a basic panel that powers three light bulbs and a phone charger, as well as solar-powered irrigation pumps, stoves and internet routers, and industrial systems. Customers use mobile money to “unlock” a pay-as-you-go meter.
Yariv Cohen, Ignite’s CEO, reckons that the typical $3 per month spent by consumers is less than what they previously paid for kerosene and at phone-charging kiosks. He describes how farmers are more productive because they do not have to get home before dark and children are getting better test scores because they study under bulbs. One family in Rwanda used to keep their two cows in their house because they feared rustlers might come in the dark; now the cattle snooze al fresco under an outside lamp and the family gets more sleep.
...That is one eye-catching aspect of Africa’s solar revolution. But most of the continent is undergoing a more subtle—and significant—experiment in decentralised, commercially driven solar power. It is a trend that could both transform African economies and offer lessons to the rest of the world."
-via The Economist, June 18, 2024. Paragraph breaks added.
#one of the biggest stories of this century is going to be the story of the African Renaissance#I promise you#well preferably they'll come up with a non-European term for it lol#but trust me it WILL happen and it will be SO good to see#africa#south africa#nigeria#kenya#solar#solar power#solar panels#solar pv#energy#clean energy#poverty#electrification#distributed energy#electricity#infrastructure#hope#solarpunk#good news#solar age#<- making that a tag now
410 notes
·
View notes
Text
African countries are being forced to spend billions of dollars a year coping with the effects of the climate crisis, which is diverting potential investment from schools and hospitals and threatens to drive countries into ever deeper poverty.
Dealing with extreme weather is costing close to 6% of GDP in Ethiopia alone, equating to a spend of more than $1 repairing climate damage for every $20 of national income, according to research by the thinktank Power Shift Africa.
The warning comes just before the major new scientific report from the global authority on climate science, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. This report, the second part of the IPCC’s comprehensive summary of global climate science, will set out the consequences of climate breakdown across the world, looking at the floods, droughts, heatwaves and storms that are affecting food systems, water supplies and infrastructure. As global temperatures have risen in recent decades, and as the impact of extreme weather has become more apparent around the world, efforts to make infrastructure and communities more resilient have largely stalled.
Africa will be one of the worst-hit regions, despite having done least to cause the climate crisis. According to the Power Shift Africa study, titled Adapt or Die: An analysis of African climate adaptation strategies, African countries will spend an average of 4% of GDP on adapting to climate breakdown.
These countries include some of the world’s poorest people, whose responsibility for greenhouse gas emissions is many times less than those of people in developed countries, or in large emerging economies such as China. Sierra Leone will have to spend $90m a year on adapting to the climate crisis, though its citizens are responsible for about 0.2 tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions a year each, while US citizens generate about 80 times more.
Mohamed Adow, director of Power Shift Africa, said: “This report shows the deep injustice of the climate emergency. Some of the poorest countries in the world are having to use scarce resources to adapt to a crisis not of their making. Despite only having tiny carbon footprints compared with those of the rich world, these African countries are suffering from droughts, storms and floods which are putting already stretched public finances under strain and limiting their ability to tackle other problems.”
He called for more funding from developed countries, which promised at the Cop26 UN climate summit to double the money available to help poor countries adapt to the climate crisis. Rich countries promised in 2009 to provide $100bn a year to help poor countries cut their greenhouse gas emissions and cope with the effects of climate breakdown. But so far they have fallen short of that target, and most of the funds that have been provided have gone to projects to cut emissions, such as windfarms and solar panels, rather than efforts to help countries adapt.
The study examined national adaptation plans submitted to the UN by seven African countries: Ethiopia, Kenya, Liberia, Sierra Leone, South Africa, South Sudan and Togo. South Sudan, which is the world’s second poorest country, was hit by floods last year that displaced 850,000 people, and led to outbreaks of water-borne diseases. The country is to spend $376m a year on adaptation, about 3.1% of its GDP.
Chukwumerije Okereke, director of the centre for climate change and development at the Alex Ekwueme Federal University in Nigeria, said rich countries must respond to the findings, and to the IPCC report.
“It is both irresponsible and immoral for those that are the chief cause of climate change to look on while Africa, which has contributed next to nothing to climate change, continues to bear a disproportionate share of the impact,” he said. “The time for warm words is long gone. We need urgent, scaled-up, long-term support from the world-leading climate polluters.”
— African countries spending billions to cope with climate crisis
#fiona harvey#current events#climate change#global warming#climate justice#economics#international relations#poverty#ethiopia#sierra leone#kenya#liberia#south africa#south sudan#togo#mohammed adow#chukwumerije okereke
962 notes
·
View notes
Text
Show Up, Take Photos
The Meghans are global frauds. Every "good" deed, Every word & Every dollar is a GRIFT. "Nigerian girls & women" my arse.💔
Do they really expect us to believe that a global games event could ever be hosted by a country that repeatedly loses track of women & children? Harry and Meghan have the lowest of low in IQs but the rest of the world can see that THIS poverty tourism trip is yet another SUSSEX SCAM.
No country will send disabled athletes or veterans to compete in a country that cannot keep track of school kids. Shame on Nigeria's Defense Minister and all at Invictus who are involved in this fraudulent visit.
"Bring Back our Girls 2.0
"The abduction of the 287 children in Kaduna state on March 7, 2024 near the West African nation’s capital, is one of the largest school kidnappings in the decade since the kidnapping of schoolgirls in Borno state’s Chibok village in 2014 stunned the world. Analysts and activists say the security lapses that allowed that mass abduction remain..."
"One man was shot dead as he tried to save the students, school authorities said"
"The parallels between the two kidnappings have created more worry for parents, as even to this day nearly 100 of the Chibok girls remain missing."


BY CHINEDU ASADU
March 8, 2024
ABUJA, Nigeria (AP) — "Security forces swept through large forests in Nigeria’s northwest region on Friday in search of nearly 300 children abducted from their school by motorcycle-riding gunmen in the latest mass kidnapping, which analysts and activists blamed on the failure of intelligence and a slow security response.
The abduction of the 287 children in Kaduna state, near the West African nation’s capital, is one of the largest school kidnappings in the decade since the kidnapping of schoolgirls in Borno state’s Chibok village in 2014 stunned the world. Analysts and activists say the security lapses that allowed that mass abduction remain.
The victims of the latest attack — among them at least 100 children aged 12 or under — were surrounded and marched into a forest just as they were starting the school day, said locals in Kuriga town, located 55 miles (89 kilometers) from the city of Kaduna. One man was shot dead as he tried to save the students, school authorities said."
J-P Mauro - published on 03/14/24
"With no word from the abductors, the bishops are calling on the state to identify the kidnappers and save the hostages.
The remote town of Kuriga, in Nigeria’s Kaduna state, is still reeling after dozens of armed extremists kidnapped hundreds of students out of their classes in broad daylight on the morning of March 7. Worried parents are now calling for government intervention, after days without any word from the abductors. As of March 13, the children have yet to be found.
The AP reports that at least 287 students were abducted – with about 100 of them aged 12 or under – making it one of the largest kidnappings since the 2014 abduction of the Chibok girls, when 275 girls were taken from their school by Boko Haram.
The parallels between the two kidnappings have created more worry for parents, as even to this day nearly 100 of the Chibok girls remain missing.
The March 7 kidnapping saw children taken from the school just as the day was starting, at around 8 a.m.. They were herded into the forest. It took authorities several hours to respond to the scene and begin a search operation, but it is unclear how deep into the forest the kidnappers went.
Locals have suggested that the abductors belong to a group of bandits who have been terrorizing remote villages in Nigeria’s northwest and central regions.
14-year-old Nigerian girl could declared a martyr. Nigeria is one of the places of most intense suffering for Christians in our day.
Bishop Wilfred Anagbe of Makurdi has called on the government to intercede on behalf of the Christian population, which he said is being targeted by these attacks. Bishop Anagbe told OSV:
“The kidnappings, killings and destroying churches we are experiencing every day are aimed at finishing Christians. We are worried that despite such killings and kidnappings, the government has never arrested anyone. As a church, we now demand that the government act quickly to stop these vices that continue to dishearten people.”
I try hard not to hate anyone, but The Meghans sure know how to push the right buttons. 🤐🤬
Safety 1st: The UK is unsafe but African countries where Nigerian schoolgirls are kidnapped & Zika Zones for childbearing royals are no problem.

Team Sussex: Global Court Jesters

#royal grifters#sussex scam#megxit#africa#african parks#scammers#nigeria#religious martyrs#christian persecution#kidnapping#nigerian girls#Nigerian Schoolchildren Kidnapped#Meghan & Harry are Frauds#Nigerian kidnappers#IPP Status#InGRIFTus#InFLICTus#racists#profit off poverty#poverty vultures#archewell is a fraud#show up do nothing#waaagh#spare us#worldwide privacy tour#misan harriman is a fraud#Sussex Global Court Jesters#poverty tourism#Bring Back Our Girls 2.0#meghan harry & misan are nigerian scammers
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
POVERTY PORN…..Wyt ppl love this…it plays on their Superiority complex …The Jesus complex…..SMFH
66 notes
·
View notes
Text
South Africa is deeply divided along socio-economic lines. According to the World Bank, it is the most unequal society on earth. Broadly, whites who were rich under apartheid - which was scrapped in 1994 - remain rich. The black middle class is growing, but blacks who were poor under apartheid remain so. While racism is no longer the law of the land, its tenets remain, in too many ways, the way South Africa functions. Or doesn't. Rampant government corruption, widespread white resistance to change, and the tendency of the moneyed - old and new, white and black - to insulate themselves from their country's many challenges stymies attempts to build a fairer, better society. Cricket is part of the flotsam and jetsam of all that. The better facilities are in largely white areas. To make their way in the game, black and brown players are all but forced to subject themselves to the comparative outlandishness of what not long ago were all-white elite schools. Affluent families have the means to indulge a younger member's ambition of a career in professional cricket. Poorer families need them to get a proper job in an economy where the unemployment rate rose to 32.1% in the last quarter of 2023, and that's the untrusted government figure.
Telford Vice, ‘How does South Africa fix its broken selection system?’, Cricbuzz
#Cricbuzz#Telford Vice#cricket#South Africa#World Bank#socioeconomic inequality#poverty#unemployment
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
#corporations#leftism#anti capitalism#socialism#communism#anarchy#fuck corporations#corporation blog#capitalism#eat the rich#late stage capitalism#poverty#economics#african culture#south africa#africa#tanzania#west africa#zambia#uganda#nigeria#ghana#senegal#cameroon#lagos
10 notes
·
View notes
Text

"The entire West is untethered from reality. Everyone likes to believe they would’ve been anti-apartheid back in the day, but in actual fact they would have wept tears for white settlers in South Africa. And in fact, that is exactly what happened for most of the Apartheid era."
#south africa#africa#class war#apartheid#anc#african national congress#jerktrillionaires#jerkbillionaires#jerkmillionaires#poverty#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#capitalism#anti capitalist#capitalist hell#capitalist dystopia#capitalist bullshit#eat the rich#eat the fucking rich#fuck the gop#fuck the police#fuck the patriarchy
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
Taps a sign that reads if you believe that africa is a continent where everyone is living in poverty, violence runs wild and nobody can get access to things like electricity and internet, that is just you buying into propaganda and being convinced africa and its people is lesser and more dangerous than white ppl, its just disguised and you need to think abt and change how you see non white places
This post also applies to the middle east
#smth smth everywhere on earth has ppl in poverty and being subjected to violence#if someone misinterprets this post as me saying there are no struggling ppl in africa and the middle east i will walk of a bridge#idk i am incredibly tired and dissociated lol#tw racism#garlic breath
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

#meme#memes#shitposting#shitpost#humor#dark humor#facts#funny#funny humor#funny memes#africa#poverty#challenge idea#How would you solve poverty in Africa?#satire#irony#joke
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Odd jobs are few and far between in Nearobo. Peter knows because every day he walks the streets of his village in south-east Liberia looking for one. In a good month, he might make $20 (£16.70). That’s hardly enough to feed himself, let alone his children.
But today things are looking up. As part of an innovative new donation scheme, Peter receives $40 (£33.40) per month for a minimum of three years. No paperwork. No requests for receipts. No catch of any kind, in fact. Just hard cash transferred straight to his mobile phone.
The 59-year-old casual labourer plans to use the money to buy materials for a new home for himself and his family, he says. “Although it is going to take long, I will continue until my house is completed.”
The scheme is part of a new-look approach to development assistance that, if taken to scale, could potentially turn the £156bn international aid industry on its head.
At least, so says Rory Stewart, the former UK foreign secretary turned podcaster-in-chief (he co-hosts ‘The Rest is Politics’ with Alastair Campbell, a surprise hit which has topped the Apple podcast charts virtually every week since it launched a year ago). From his new base in Amman, Jordan, Stewart heads up GiveDirectly – the world’s fastest growing nonproft – who are behind the initiative.
“It’s a rather radical, simple idea to help people out of extreme poverty. We deliver the cash directly … there’s no middleman and no government getting in the way.”
It feels like an odd statement from someone who has spent much of his life in government service: first as a junior diplomat for eight years (during which he penned a bestselling book about dodging Taliban bullets and hungry wolves whilst walking across Afghanistan), followed by almost a decade as a politician at Westminster.
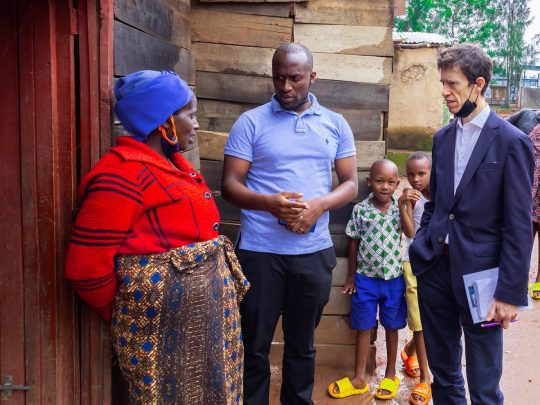

Pictured: Rory Stewart and GiveDirectly’s Ivan Ntwali talk with a refugee household in Rwanda. Image: GiveDirectly
His enthusiasm is even more surprising given his initial caution. During his various ministerial stints at the UK’s department for international development (including three months as secretary of state), he was an out-and-out “cash sceptic.”
Giving away money with no strings attached was, he felt at the time, an impossible sell to tax-paying voters. What’s stopping recipients spending it down the pub? Or investing in a hair-brained business venture?
Quite a lot it turns out. No one knows the value of money more than those who don’t have any, he argues. Give an impoverished mother-of-four $40 (£33.40) cash and, 99 times out of 100, she’ll spend it on something useful: repairs to the house, say, or school fees for her kids...
By virtue of GiveDirectly’s model, participants can spend their money on whatever they choose, but the charity’s research indicates that most goes towards food, medical and education expenses, durables, home improvement and social events.
On the flipside, Stewart also has numerous examples of well-funded aid projects that deliver next to nothing. A decade ago, the then United Nations general secretary Ban Ki-moon estimated that 30 per cent of aid money disappears in corruption. There is little to suggest much has changed.
The aid industry doesn’t need corrupt officials to see its funds evaporate, however; it has its own voluminous bureaucracy. Stewart recalls once visiting a $40,000 (£33,560) water and sanitation project in a school in an unnamed African country. The ‘deliverables’ were two brick latrines and five red buckets for storing water...
The beauty of direct giving, he stresses, is not just that it annuls opportunities for thievery and red tape; it also frees the world’s poorest individuals from the well-meaning but, very often, misplaced guidance of donors. An aid expert in Brussels or Washington DC may well have a PhD in development economics, but who is best to judge what a single mother in a Kinshasa slum needs most and how to obtain it most cheaply: the expert with her degree, or the mother with her hungry children?
Empowering recipients to decide for themselves helps end the kind of “mad world” where aid agencies pay to ship wheat from Idaho, US, to Antananarivo, Madagascar, only for local people to sell it in order to buy what they really want, Stewart reasons.
“So often, these communities are having to turn the goods we send them into cash anyway, but just in a very inefficient and wasteful fashion … instead [with direct cash transfers] they are given the choice and freedom in how to spend it.”

Pictured: Villagers in Kilif, Kenya, at a public meeting about the GiveDirectly programme. Image: GiveDirectly
Is the system perfect? No, clearly not. Stewart concedes that opportunities for fraud and coercion exist. To minimise these risks, GiveDirectly employs field officers to meet face-to-face with recipients, as well as a team of telephone handlers and internal auditors to follow up on reports of irregularity.
By his reckoning, however, the biggest impediment to direct giving really taking off is donor reticence. At present, only 2 per cent of official aid is given direct in cash. Stewart thinks it should be closer to 60 or 70 per cent...
‘My children will not have to beg anymore’

Happiness Kadzmila from Malawi enrolled on GiveDirectly’s Basic Income project last summer. She will now receive $50 (£41) a month for a year ($600/£496 in total).
What are the biggest hardships you’ve faced in life?
I am a divorced mother of four children. I got divorced in 2020 while I was eight months pregnant with my last-born child. Since then, I have been depending on working on other people’s farms. I get paid $0.49 (£0.43), or a plate of maize flour per day. As a result, it has been a challenge to feed my children, buy clothes for them, and to pay their school fees My firstborn child is in year 4, the school charges $0.69 (£0.61) per day for her. My second is in year 3, I pay $0.49 (£0.43) for him. There were days when I would have no food in my home, and my children would go to my neighbours’ homes to beg for food. This made me feel sorry for my children as a mother.
What does receiving this money mean for you?
I was so happy the day I received cash amounting to $51.75 (£43.56) from GiveDirectly. I used the money to buy maize at $9.88 (£8.32). My children will not have to go to our neighbours to beg for food anymore. I also bought a sheep at $34.58 (£29.10). I will be selling sheep in future when they multiply. I also bought lotion and soap at $1.88 (£1.58).
How will you spend your future payments?
I plan to renovate my house. I have always admired those who sleep in houses made of a roof with iron sheets because they do not have to think of fetching grass every year for a new roof. I will also start a business selling doughnuts to sustain my income after I receive my last transfer. I did not know that an organisation like GiveDirectly would come to help me this way All I can say to those who are giving us this money is ‘thank you’."
-via Positive News, 3/3/23
More and More People to Help
In addition to their universal basic income programs, GiveDirectly also has dedicated programs where you can donate to emergency disaster relief, people living under the protracted civil war and human rights disaster in Yemen, refugees, and survivors of the Syria-Turkey earthquake.
They have also commissioned a number of large-scale, third-party studies on the effectiveness of their numerous universal basic income models. Find these and other projects here.
#charity#donations#foreign aid#extreme poverty#poverty#economic inequality#africa#yemen#syria#turkey#malawi#kenya#rwanda#refugees#refugee crisis#givedirectly#universal basic income#good news#hope
198 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ignorant rant
As much as I love complaining (joking and otherwise), sometimes it truly does hit me how fortunate I am to be in the position I am and how purely random it is. And ofc that covers the basic necessities like always having food, clean water, clothes, shelter, medicine, etc, but just like other aspects. I think so often about how thankful I am that I have access to good therapy and have the ability to have been in it long term. Just some of the trauma you see people go through for just being born in a certain place at a certain time and knowing even if they survive, you still have to deal with that. I study history, I could rip on america, from its creation to present day, for days. The flaws are many and problems are plentiful, but I also am so grateful to live here as well. Like this is just so fucking random and out of touch but it’s just like one of those things that you know but don’t know until you see it. I also think social media desensitizes a lot of it as well but another conversation. Just in a head.
#this comes off as ignorant I am aware#not to be random but this was inspired by watching a BBC Africa documentary about sex workers and it’s just#I’m thankful for so many aspects of my life#even though there were fucked up stuff#I’m still able to advance#if that makes sense#idk#just feeling really grateful and I love all my mutuals in developing countries or politically unstable situations or poverty or just a bad#situation I love you so much#rae’s rambles
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
Just saw the video and commentary you posted around the poverty cosplaying and I just want to add that there used to be a different place in Arkansas that did a similar thing, sorta. It was through a charity organization that shifted focus so they no longer run the program, but they used to have a "global village" where people would get assigned different regions of the world to live in by lottery with a couple key differences. First, they used actual names of actual countries and provided actual information about the country/culture. Secondly, it wasn't for mission training but instead was meant to be an educational tool to help middle school and high school students to consider how existing in different global and socio-economic circumstances change your decision making etc. and in depth discussion and educational activities were facilitated frequently. I went there as part of an overnight high school trip and while in retrospect the "poverty cosplaying" does give me the ick I still feel like that particular program was informative. Mostly I'm shook that two distinct programs like this exist in AR? I've literally never heard of the Harding one from the video until now and went on a Google deep dive to see if they were connected in some way, but not that I can tell. Anyway, no deep thoughts really, just thought it was super interesting/weird.
There is something in the water over there in Arkansas man lol. I can never learn just some normal fact about AR, it's always something weird.
I totally understand wanting to create more empathy for those who live in poverty, especially in teenagers who are in a really formative years of their lives. And it's one thing to replicate conditions in your immediate area which you are intimately familiar with, but I just can't get on board with play-acting poverty in different areas of the world. I just think about how I'd feel if some religious group in another country tried to replicate my life experience for shock value.
Even replicating the conditions semi-well can't replicate the actual stakes faced by the people they're cosplaying. You can't replicate the stress of a single mother working 2 jobs and supporting 3 kids in a one-room house, you can't replicate the stress of food insecurity and legitimately being worried about when your next meal will be, etc etc. And something about pretending to do them when you can just go back to normal life at any time just feels disrespectful in a way I can't really articulate.
Idk if people get something from it that's great and I do get the thinking behind the one you described at least, I'm mostly still ranting about the first camp lol. I don't have any doubt that some of the people running the camp you went to had good intentions (the other one though I'm really not sure based on the town names) I just have a lot of mixed experience in Christian missionary culture where poverty is treated voyeuristically which is just definitely the vibe I got from the first camp.
#idk my dad grew up really really poor and i live in an area with a lot of poverty and so maybe i'm just overly touchy about it#but so much of the “philanthropic” culture i experienced in Christianity was making an other out of poor people#it's hard for me to really articulate well i feel but it was just this disconnect like we are different. we are the saviors.#we're on a different level. when in reality i mean everyone is an arm's length away from being in a bad situation in the right circumstance#i think the fact that a lot of the missionary work we did too was just classic surface level stuff like putting a bandaid on a gaping wound#kind of stuff that never addresses the root issues of poverty left a bad taste in my mouth for the community too#my church in particular has had this fundraising event every year for 80 years for the same area in africa building infrastructure and its#like....it's been damn near a century. how has this goal not been accomplished yet like where is this money going too??#why have the missionaries in question seemed to make so little progress#idk ok im done lol i havent ranted in the tags in so long
7 notes
·
View notes
Photo




The Country That Drowned,
The climate crisis is no longer just the future It takes place now and here. It demands human life and it destroys the future of children. South Sudan is experiencing severe floods in its fourth year, which is a direct consequence of climate change. 800,000 people have lost their homes to the water masses, and every day that number is getting bigger.
The roads are washed away along with crops, cattle, clean water and toilets. Emergency aid in the form of food and medicine cannot emerge and people are fighting across the dry land against poisonous snakes and crocodiles.
In 1991, the year he graduated, Grarup won the Danish Press Photographer of the Year award, a prize he would receive on several further occasions. In 1993, he moved to Berlin for a year, working as a freelance photographer for Danish newspapers and magazines.
During his career, Grarup has covered many wars and conflicts around the world including the Gulf War, the Rwandan genocide, the Siege of Sarajevo and the Palestinian uprising against Israel in 2000 and latest Ukraine and the climate changes have had his focus.
Jan Grarup / StudioMadebygrarup
#art#photography#soudan#africa#climate change#climate crisis#human rights#humanity#flood#underwater#sea level rise#jan grarup#Black and White#poverty#migration#climate migration#BIFA#BIFA2022
70 notes
·
View notes