#STEM (Science
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
IF NOT FOR EAT WHY CAKE?

IF NOT FOR MOUTH WHY HONEYCOMB?

IF NOT FOOD WHY LOOK LIKE FORBIDDEN SNACK?

#science#chemistry#physics#nuclear#uranium#nuclear physics#stem#stemblr#science side of tumblr#forbidden snack
18K notes
·
View notes
Text
Scientists at UC Riverside have demonstrated a new, RNA-based vaccine strategy that is effective against any strain of a virus and can be used safely even by babies or the immunocompromised. Every year, researchers try to predict the four influenza strains that are most likely to be prevalent during the upcoming flu season. And every year, people line up to get their updated vaccine, hoping the researchers formulated the shot correctly. The same is true of COVID vaccines, which have been reformulated to target sub-variants of the most prevalent strains circulating in the U.S. This new strategy would eliminate the need to create all these different shots, because it targets a part of the viral genome that is common to all strains of a virus. The vaccine, how it works, and a demonstration of its efficacy in mice is described in a paper published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. “What I want to emphasize about this vaccine strategy is that it is broad,” said UCR virologist and paper author Rong Hai. “It is broadly applicable to any number of viruses, broadly effective against any variant of a virus, and safe for a broad spectrum of people. This could be the universal vaccine that we have been looking for.”
Continue Reading.
22K notes
·
View notes
Text
I FUCKING LOVE INFORMATION!!! I WANT TO LEARN EVERY THING AND KNOW EVERYTHING!!!!! I WANT TO UNDERSTAND EVERYTHING ABOUT LIFE, THE UNIVERSE, AND EVERYTHING!!!!!! I AM UTTERLY CONSUMED BY MY THIRST FOR KNOWLEDGE!!!!!!!!!!!!
#nessie on drugs#autism#r/196#196#r/196archive#/r/196#rule#meme#memes#shitpost#shitposting#actually autistic#neurodivergence#academic#learning#knowledge#information#biology#science#universe#space#planets#chemistry#astronomy#physics#stem#earth#everything#general#gen
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Seeing the Invisible Universe
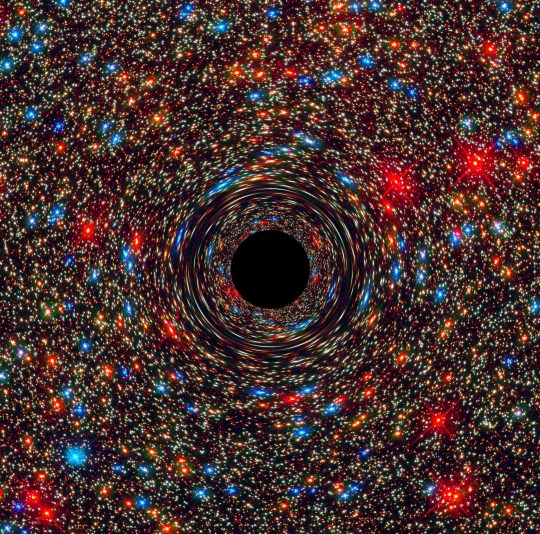

This computer-simulated image shows a supermassive black hole at the core of a galaxy. The black region in the center represents the black hole’s event horizon, beyond which no light can escape the massive object’s gravitational grip. The black hole’s powerful gravity distorts space around it like a funhouse mirror. Light from background stars is stretched and smeared as it skims by the black hole. You might wonder — if this Tumblr post is about invisible things, what’s with all the pictures? Even though we can’t see these things with our eyes or even our telescopes, we can still learn about them by studying how they affect their surroundings. Then, we can use what we know to make visualizations that represent our understanding.
When you think of the invisible, you might first picture something fantastical like a magic Ring or Wonder Woman’s airplane, but invisible things surround us every day. Read on to learn about seven of our favorite invisible things in the universe!
1. Black Holes

This animation illustrates what happens when an unlucky star strays too close to a monster black hole. Gravitational forces create intense tides that break the star apart into a stream of gas. The trailing part of the stream escapes the system, while the leading part swings back around, surrounding the black hole with a disk of debris. A powerful jet can also form. This cataclysmic phenomenon is called a tidal disruption event.
You know ‘em, and we love ‘em. Black holes are balls of matter packed so tight that their gravity allows nothing — not even light — to escape. Most black holes form when heavy stars collapse under their own weight, crushing their mass to a theoretical singular point of infinite density.
Although they don’t reflect or emit light, we know black holes exist because they influence the environment around them — like tugging on star orbits. Black holes distort space-time, warping the path light travels through, so scientists can also identify black holes by noticing tiny changes in star brightness or position.
2. Dark Matter

A simulation of dark matter forming large-scale structure due to gravity.
What do you call something that doesn’t interact with light, has a gravitational pull, and outnumbers all the visible stuff in the universe by five times? Scientists went with “dark matter,” and they think it's the backbone of our universe’s large-scale structure. We don’t know what dark matter is — we just know it's nothing we already understand.
We know about dark matter because of its gravitational effects on galaxies and galaxy clusters — observations of how they move tell us there must be something there that we can’t see. Like black holes, we can also see light bend as dark matter’s mass warps space-time.
3. Dark Energy

Animation showing a graph of the universe’s expansion over time. While cosmic expansion slowed following the end of inflation, it began picking up the pace around 5 billion years ago. Scientists still aren’t sure why.
No one knows what dark energy is either — just that it’s pushing our universe to expand faster and faster. Some potential theories include an ever-present energy, a defect in the universe’s fabric, or a flaw in our understanding of gravity.
Scientists previously thought that all the universe’s mass would gravitationally attract, slowing its expansion over time. But when they noticed distant galaxies moving away from us faster than expected, researchers knew something was beating gravity on cosmic scales. After further investigation, scientists found traces of dark energy’s influence everywhere — from large-scale structure to the background radiation that permeates the universe.
4. Gravitational Waves

Two black holes orbit each other and generate space-time ripples called gravitational waves in this animation.
Like the ripples in a pond, the most extreme events in the universe — such as black hole mergers — send waves through the fabric of space-time. All moving masses can create gravitational waves, but they are usually so small and weak that we can only detect those caused by massive collisions. Even then they only cause infinitesimal changes in space-time by the time they reach us. Scientists use lasers, like the ground-based LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory) to detect this precise change. They also watch pulsar timing, like cosmic clocks, to catch tiny timing differences caused by gravitational waves.
This animation shows gamma rays (magenta), the most energetic form of light, and elusive particles called neutrinos (gray) formed in the jet of an active galaxy far, far away. The emission traveled for about 4 billion years before reaching Earth. On Sept. 22, 2017, the IceCube Neutrino Observatory at the South Pole detected the arrival of a single high-energy neutrino. NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope showed that the source was a black-hole-powered galaxy named TXS 0506+056, which at the time of the detection was producing the strongest gamma-ray activity Fermi had seen from it in a decade of observations.
5. Neutrinos

This animation shows gamma rays (magenta), the most energetic form of light, and elusive particles called neutrinos (gray) formed in the jet of an active galaxy far, far away. The emission traveled for about 4 billion years before reaching Earth. On Sept. 22, 2017, the IceCube Neutrino Observatory at the South Pole detected the arrival of a single high-energy neutrino. NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope showed that the source was a black-hole-powered galaxy named TXS 0506+056, which at the time of the detection was producing the strongest gamma-ray activity Fermi had seen from it in a decade of observations.
Because only gravity and the weak force affect neutrinos, they don’t easily interact with other matter — hundreds of trillions of these tiny, uncharged particles pass through you every second! Neutrinos come from unstable atom decay all around us, from nuclear reactions in the Sun to exploding stars, black holes, and even bananas.
Scientists theoretically predicted neutrinos, but we know they actually exist because, like black holes, they sometimes influence their surroundings. The National Science Foundation’s IceCube Neutrino Observatory detects when neutrinos interact with other subatomic particles in ice via the weak force.
6. Cosmic Rays

This animation illustrates cosmic ray particles striking Earth's atmosphere and creating showers of particles.
Every day, trillions of cosmic rays pelt Earth’s atmosphere, careening in at nearly light-speed — mostly from outside our solar system. Magnetic fields knock these tiny charged particles around space until we can hardly tell where they came from, but we think high energy events like supernovae can accelerate them. Earth’s atmosphere and magnetic field protect us from cosmic rays, meaning few actually make it to the ground.
Though we don’t see the cosmic rays that make it to the ground, they tamper with equipment, showing up as radiation or as “bright” dots that come and go between pictures on some digital cameras. Cosmic rays can harm astronauts in space, so there are plenty of precautions to protect and monitor them.
7. (Most) Electromagnetic Radiation

The electromagnetic spectrum is the name we use when we talk about different types of light as a group. The parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, arranged from highest to lowest energy are: gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet light, visible light, infrared light, microwaves, and radio waves. All the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum are the same thing — radiation. Radiation is made up of a stream of photons — particles without mass that move in a wave pattern all at the same speed, the speed of light. Each photon contains a certain amount of energy.
The light that we see is a small slice of the electromagnetic spectrum, which spans many wavelengths. We frequently use different wavelengths of light — from radios to airport security scanners and telescopes.
Visible light makes it possible for many of us to perceive the universe every day, but this range of light is just 0.0035 percent of the entire spectrum. With this in mind, it seems that we live in a universe that’s more invisible than not! NASA missions like NASA's Fermi, James Webb, and Nancy Grace Roman space telescopes will continue to uncloak the cosmos and answer some of science’s most mysterious questions.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Join us in celebrating Women's History Month with Ellen, our senior aquarist who does incredible work with sunflower stars at the Aquarium! 🌟
These once-abundant predators played a key role in keeping Monterey Bay kelp forests healthy, but Sea Star Wasting Disease brought them to the brink of extinction.
We're partnering with amazing organizations like the California Academy of Sciences, Aquarium of the Pacific, Birch Aquarium at Scripps, San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance, and the Sunflower Sea Star Lab to bring them back.
Learn more about our efforts and how we're growing sunflower stars from tiny babies to giant sea stars!
#kelp us save stars#women in science#women's history month#here comes the sun for the stars#stellar women in STEM
4K notes
·
View notes
Text










Find out more:
https://womeninstem.org/ and
https://womenrefusingtobeerased.org/
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
Here's the link to the video
👏 SAY 👏 IT 👏 LOUDER 👏
#history#science#scienceblr#stem#stemblr#mathematics#mathblr#ancient persia#ancient india#ancient egypt#babylon#pythagorean theorem#snell's law#quadratic formula#fibonacci's sequence#pascal's triangle
11K notes
·
View notes
Text



You guys wanna see a science Lego set? Well, here's Lego DNA!
With a scientifically accurate DNA model, and a historically accurate lab + 5 scientists!
Aims: to promote science to kids and honor Rosalind Franklin.
Less than 600 votes needed to reach 10K when it will be considered as a real official Lego set to be sold worldwide!
If you like it, please support here and share with your friends: https://ideas.lego.com/projects/c92cd95b-49e7-46ec-b844-ac6482c51139
More details below!











#chemistry #science #biology #design #diy #education #nature #environmental science #molecular biology #stem #women in stem #research #laboratory #women scientists #school #university #college #students #learning #lego art #lego photography #afol #lego sets #lego ideas #lego builds #lego moc #rosalind franklin #james watson #francis crick #university student
#biology#chemistry#college#afol#science#design#diy#education#nature#environmental science#environment#stem#women in stem#stemblr#stem student#stem academia#biochemistry#phd#university#universidad#lego art#lego moc#moc#lego photography#lego minifigures#molecular biology#molecules#research#knowledge#intelligence
2K notes
·
View notes
Text


























My favourite space images from Hubble space telescope. Thank you so much for giving us the stunning visuals of galaxies, stars and nebula. Happy 35th anniversary to the Hubble space telescope 🔭
#hubble space telescope#astrophotography#photographers on tumblr#photography#universe#galaxy#nebula#space#science side of tumblr#women in stem#stem academia#cosmology
3K notes
·
View notes
Text










What is the difference between a cathedral and a physics lab? Are they not both saying: Hello?
Paolo Giordano, “The Solitude of Prime Numbers” / Antonio Tonelli / Laura Giplin, “A Toast to the Alchemists” / Dennis Overbye, “Music of the Heavens Turns Out to Sound a Lot Like a B Flat” / Carina Nebula / Marie Howe, “Singularity” / Alan Bean, “Is Anyone Out There?” / Bill Bryson, “A Short History of Nearly Everything” / Garrett Lee, “Canyon” / Whit Bronaugh, “The Trees That Miss The Mammoths”
#this is one of my favourite things in the world#mine#compilations#parallels#web weaving#web weave#words#poetry#comparatives#stem#science#scienceblr#space#on nature
23K notes
·
View notes
Text
What can we learn from a dinosaur feather preserved in amber? Let’s go behind the scenes of the Museum’s collection of amber fossils to find out!
#science#amnh#museum#fossil#natural history#nature#animals#dinosaur#fact of the day#paleontology#did you know#natural history museum#museum of natural history#amber#cool animals#evolution#stem#insects#entomology#museum collections#ancient animals#prehistoric animals#dinosaurs
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
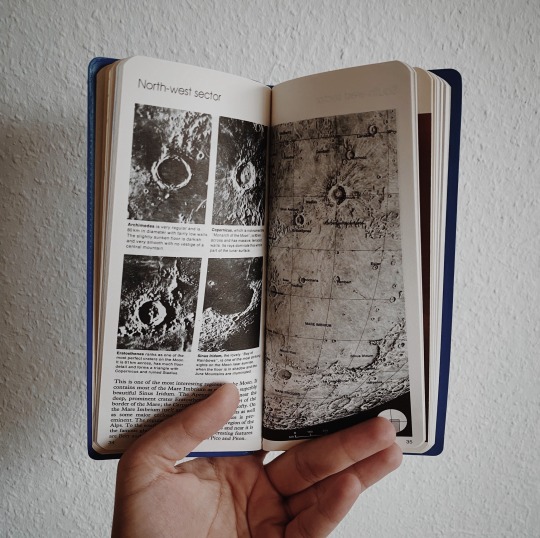
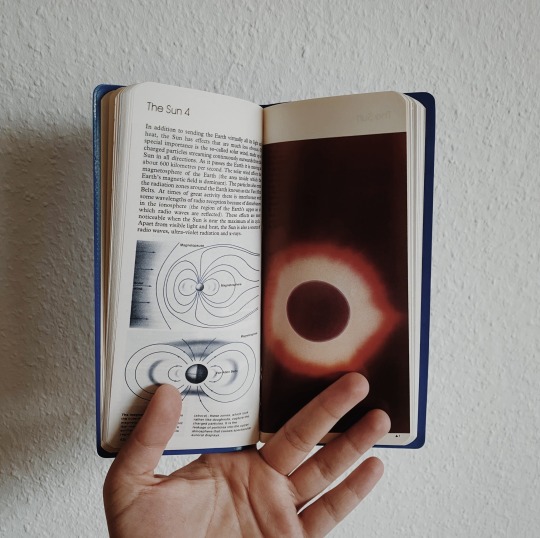
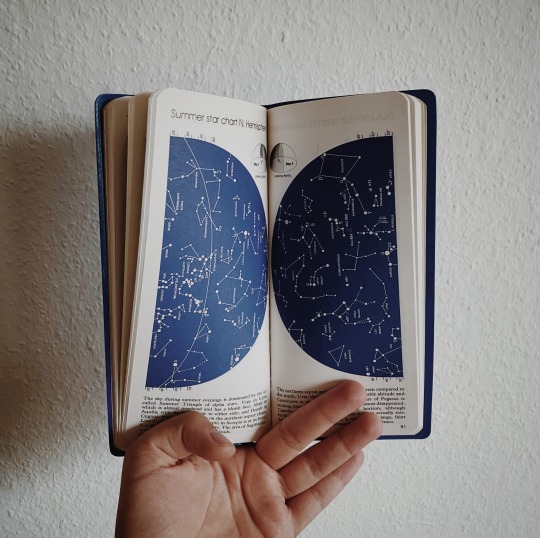






bought this gem secondhand and can’t get over how stunning it is 🪐 reblog is okay, don’t repost/use
#my photos#space science#study space#space#outer space#astronomy#science#stem#stemblr#astrophysics#books#book cover#bookworm#booklover#bookaddict#bookaholic#book aesthetic#bookblr#book blog#studyblr#academia#stem academia#stem aesthetic#light academia#light academia aesthetic
8K notes
·
View notes
Text
Playing through the greenery and litter of a mini forest's undergrowth for just one month may be enough to change a child's immune system, according to an experiment in Finland. When daycare workers rolled out a lawn, planted forest undergrowth (such as dwarf heather and blueberries), and allowed children to care for crops in planter boxes, the diversity of microbes in the guts and on the skin of the young kids appeared healthier in a very short space of time. Compared to other city kids who play in standard urban daycares with yards of pavement, tile, and gravel, 3-, 4-, and 5-year-olds at these greened-up daycare centers in Finland showed increased T-cells and other important immune markers in their blood within 28 days.
Continue Reading.
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
Video by me and Ainsley Seago trying to explain the important work insect taxonomists do
#insects#bugs#beetles#moths#caterpillar#entomology#invertebrates#bugblr#agriculture#farming#farmers#usda#government#biosecurity#humor#new music#music video#songs#insectblr#herpblr#science#biology#environment#research#stem#stemblr
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Love Letters from Space
Love is in the air, and it’s out in space too! The universe is full of amazing chemistry, cosmic couples held together by gravitational attraction, and stars pulsing like beating hearts.
Celestial objects send out messages we can detect if we know how to listen for them. Our upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will help us scour the skies for all kinds of star-crossed signals.
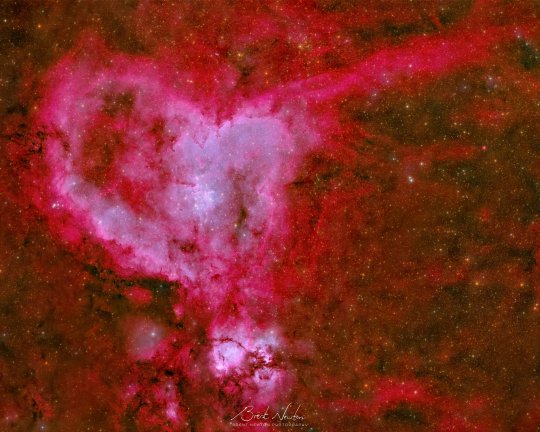

Celestial Conversation Hearts
Communication is key for any relationship – including our relationship with space. Different telescopes are tuned to pick up different messages from across the universe, and combining them helps us learn even more. Roman is designed to see some visible light – the type of light our eyes can see, featured in the photo above from a ground-based telescope – in addition to longer wavelengths, called infrared. That will help us peer through clouds of dust and across immense stretches of space.
Other telescopes can see different types of light, and some detectors can even help us study cosmic rays, ghostly neutrinos, and ripples in space called gravitational waves.
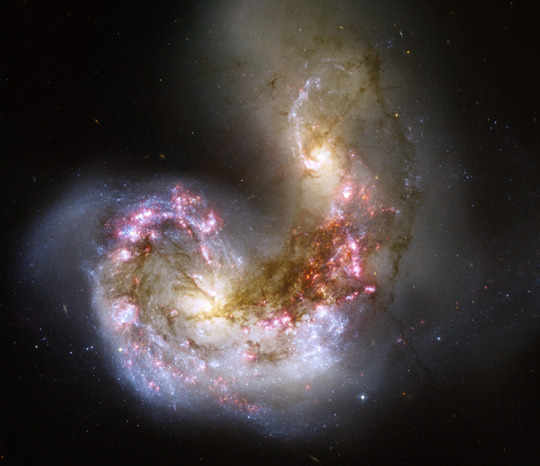

Intergalactic Hugs
This visible and near-infrared image from the Hubble Space Telescope captures two hearts locked in a cosmic embrace. Known as the Antennae Galaxies, this pair’s love burns bright. The two spiral galaxies are merging together, igniting the birth of brand new baby stars.
Stellar nurseries are often very dusty places, which can make it hard to tell what’s going on. But since Roman can peer through dust, it will help us see stars in their infancy. And Roman’s large view of space coupled with its sharp, deep imaging will help us study how galaxy mergers have evolved since the early universe.
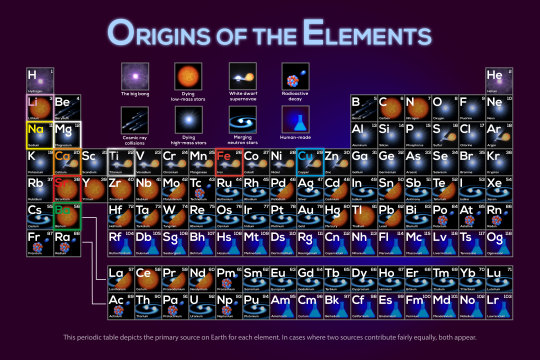
Cosmic Chemistry
Those stars are destined to create new chemistry, forging elements and scattering them into space as they live, die, and merge together. Roman will help us understand the cosmic era when stars first began forming. The mission will help scientists learn more about how elements were created and distributed throughout galaxies.
Did you know that U and I (uranium and iodine) were both made from merging neutron stars? Speaking of which…

Fatal Attraction
When two neutron stars come together in a marriage of sorts, it creates some spectacular fireworks! While they start out as stellar sweethearts, these and some other types of cosmic couples are fated for devastating breakups.
When a white dwarf – the leftover core from a Sun-like star that ran out of fuel – steals material from its companion, it can throw everything off balance and lead to a cataclysmic explosion. Studying these outbursts, called type Ia supernovae, led to the discovery that the expansion of the universe is speeding up. Roman will scan the skies for these exploding stars to help us figure out what’s causing the expansion to accelerate – a mystery known as dark energy.

Going Solo
Plenty of things in our galaxy are single, including hundreds of millions of stellar-mass black holes and trillions of “rogue” planets. These objects are effectively invisible – dark objects lost in the inky void of space – but Roman will see them thanks to wrinkles in space-time.
Anything with mass warps the fabric of space-time. So when an intervening object nearly aligns with a background star from our vantage point, light from the star curves as it travels through the warped space-time around the nearer object. The object acts like a natural lens, focusing and amplifying the background star’s light.
Thanks to this observational effect, which makes stars appear to temporarily pulse brighter, Roman will reveal all kinds of things we’d never be able to see otherwise.

Roman is nearly ready to set its sights on so many celestial spectacles. Follow along with the mission’s build progress in this interactive virtual tour of the observatory, and check out these space-themed Valentine’s Day cards.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
#NASA#astronomy#telescope#Roman Space Telescope#Valentine’s Day#space#science#STEM#nebula#chemistry#galaxies#black holes#rogue planets#exoplanets#Hubble Space Telescope#tech
3K notes
·
View notes