#building a character
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
CREATING AUTHENTIC DEAF AND HARD OF HEARING CHARACTERS: A WRITER'S JOURNAL
Introduction
Creating authentic characters in your writing is essential for engaging storytelling, and this includes characters who are deaf or hard of hearing. To craft a character that accurately represents this community, it's crucial to do your research, gain a deep understanding of their experiences, and portray them with sensitivity and respect. In this journal, we'll explore how to write a deaf or hard-of-hearing character, including key information and preparation steps.
Understanding Deaf and Hard-of-Hearing Characters
Research: Start by researching deaf and hard-of-hearing individuals' experiences, challenges, and culture. Read books, articles, and personal stories, and watch documentaries or interviews featuring members of the Deaf community.
Consult with Experts: Reach out to members of the Deaf community or experts in Deaf studies to gain insights into their experiences. They can provide invaluable guidance and help you avoid common misconceptions.
Diversity Within the Community: Understand that the Deaf and hard-of-hearing communities are diverse. Some individuals communicate using sign language, while others rely on lip-reading, cochlear implants, or hearing aids. Be aware of these differences when creating your character.
Character Development
Backstory and Identity: Consider your character's background. Were they born deaf, or did they become deaf later in life? How do they identify within the Deaf community? Understanding their identity and experiences will shape their character.
Language and Communication: Decide how your character communicates. Are they fluent in sign language, or do they primarily rely on lip-reading and spoken language? Their communication style will influence their interactions with other characters.
Cultural Awareness: Explore the cultural aspects of the Deaf community. Understand the importance of Deaf culture, including its history, art, and values. Incorporate these elements into your character's life when relevant.
Writing Tips
Dialogue and Communication: When writing dialogue for a deaf or hard-of-hearing character, be mindful of their unique communication style. Use visual cues, body language, and facial expressions to convey emotions and context.
Access to Information: Consider the challenges your character may face in accessing information. This could involve issues with closed captioning, subtitles, or accommodations in educational or work settings.
Social Interactions: Depict social interactions realistically. Show how your character navigates conversations, group dynamics, and social events within their community and with hearing individuals.
Preparation
Sensitivity Readers: Consider hiring sensitivity readers who are part of the Deaf or hard-of-hearing community to review your work and provide feedback. Their insights can help you avoid stereotypes and inaccuracies.
Learn Sign Language: If your character uses sign language, take the time to learn at least basic signs. This will not only enrich your writing but also demonstrate your commitment to accuracy.
Beta Readers: Seek feedback from a diverse group of beta readers who can assess the authenticity of your character and offer constructive criticism.
Engage with the Community: Attend Deaf community events, workshops, or online forums to immerse yourself in the culture and better understand the perspectives and experiences of deaf and hard-of-hearing individuals.
Creating a deaf or hard-of-hearing character that resonates with readers requires dedication, empathy, and thorough research. By following these steps and embracing the rich culture and diversity of the Deaf community, you can create a character that is not only authentic but also promotes understanding and inclusivity in your writing. In addition, when writing dialogue for your deaf or hard-of-hearing character, remember:
It's important to clarify why, when writing dialogue for a deaf character, you should continue to use structured English grammar and not sign language structured grammar.
Maintaining Structured English Grammar:
Readability: Writing in structured English grammar ensures that the text remains accessible and comprehensible to all readers, including those who may not be familiar with sign language or Deaf culture. It avoids potential confusion that could arise from using sign language grammar in written text.
Universal Understanding: English is a global language, and adhering to its grammar rules allows for a wider audience to understand and engage with your story. Sign language grammar varies between different sign languages, making it less universally applicable in written form.
Respect for the Medium: While sign language is a rich and expressive mode of communication, it is primarily a visual and gestural language. Attempting to replicate sign language grammar in written text can be cumbersome and may not fully capture the nuances of sign language communication.
Balance of Realism and Readability: Striking a balance between authenticity and readability is crucial in storytelling. Maintaining structured English grammar while depicting a deaf character's interactions helps convey the character's experience without compromising the reader's ability to follow the narrative.
As an illustration, consider the following text: Dialogues with Descriptive Sign Language:
Sarah greeted John with a warm smile, her hands moving gracefully as she signed, "Hi, how are you?"
John returned the greeting in sign language, his expressions mirroring his words. "I'm good, thanks. Did you see the new movie?"
Sarah's eyes lit up as she signed back enthusiastically, "Yes, I loved it!"
In summary, using structured English grammar when writing dialogue for a deaf character is a practical and respectful choice that ensures your writing remains inclusive and accessible to a broad audience while still authentically representing the character's identity and experiences.
Furthermore, it's essential to avoid creating a character who is overly perfect or one-dimensional. In real life, we understand that everyone has imperfections and complexities, regardless of whether they are deaf or hard of hearing. Therefore, it's entirely acceptable to depict your character as a villain with a hearing issue if that aligns with your storytelling goals.
#writing deaf characters#hard of hearing#writing tips#writing resources#sign language#bsl#asl#auslan#fiction writing#building a character#writing guilde#writing characters with disibilities
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Christmas Prompt - A Scrooge 🎄
Write about someone who hates Christmas.
What reason do they hate Christmas? Was there a particular event that sparked their aversion? Or was it a recurring theme?
How do they try to avoid the festivities?
Do they resolve their issues?
#writer academia#writing#romantic writer aesthetic#romantic writer#romantic academia#cottagecore#aesthetic#dark academia#christmas#prompt#christmas prompt#writing about christmas#scrooge#someone who hates christmas#creative writing#creative writing prompt#fiction writing#prose writing#character#building a character
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
tried out apothecary diaries the other day, got inspired to do a study, redrew jinmao as Gustav Klimt's "The Kiss", died


ive been sick for a while so excuse the messiness
#I've only seen up to ep24 and i quite like it#i appreciate how human all the characters feel despite leaning on anime tropes#its a great example of expanding and building on ideas in character building!#i heard something about frogs having to do with them so i added frogs but lack. Context#nobody spoil me pretty please#anyway. smooch#jinmao#the apothecary diaries#maomao#jinshi#apothecary diaries
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
One of my favourite questions for figuring out a character’s motivations is which qualities they most fear being assigned to them. Are they afraid (consciously or unconsciously) of being seen as stupid? Ungrateful? Weak? Incompetent? Lazy? Cowardly? Intimidating? Like they actually care? etc.
It’s such a fun way to explore into who they are, why they do what they do, what they don’t do out of fear, and how they might be affected by the events of the story. And I love when characters have negative motivations—trying to avoid something (in this case, being seen a particular way) as much as they’re trying to achieve a goal.
#it’s also a great question to think about yourself lmfao#ttrpgs#(is usually where I think about this but it’s good for other character building too)#my stuff
35K notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing References: Character Development
50 Questions ⚜ Backstory ⚜ Character-driven Story
Basics: How to Write a Character ⚜ A Story-Worthy Hero
Basics: Character-Building ⚜ Character Creation
Types of Characters: Key Characters ⚜ Literary Characters ⚜ Flat & Round Characters ⚜ Morally Grey ⚜ Narrators ⚜ Allegorical Characters ⚜ Archetypes ⚜ Stereotypical Characters
Worksheets: Backstory ⚜ Character ⚜ Kill your Characters ⚜ Antagonist; Villain; Fighting ⚜ Change; Adding Action; Conflict ⚜ Character Sketch & Bible ⚜ Protagonist & Antagonist ⚜ Name; Quirks; Flaws; Motivation ⚜ "Interviewing" your Characters ⚜ "Well-Rounded" Character
Personality Traits
5 Personality Traits (OCEAN) ⚜ 16 Personality Traits (16PF)
600+ Personality Traits ⚜ 170 Quirks
East vs. West Personalities ⚜ Trait Theories
Tips/Editing
Character Issues ⚜ Character Tropes for Inspiration
"Strong" Characters ⚜ Unlikable to Likable
Tips from Rick Riordan
Writing Notes
Binge ED ⚜ Hate ⚜ Love ⚜ Identifying Character Descriptions
Childhood Bilingualism ⚜ Children's Dialogue ⚜ On Children
Culture ⚜ Culture: Two Views ⚜ Culture Shock
Dangerousness ⚜ Flaws ⚜ Fantasy Creatures
Emotional Intelligence ⚜ Genius (Giftedness)
Emotions (1) (2) ⚜ Anger ⚜ Fear ⚜ Happiness ⚜ Sadness
Emotional Universals ⚜ External & Internal Journey
Goals & Motivations ⚜ Grammar Development ⚜ Habits
Facial Expressions ⚜ Jargon ⚜ Swearing & Taboo Expressions
Happy/Excited Body Language ⚜ Laughter & Humor
Health ⚜ Frameworks of Health ⚜ Memory
Mutism ⚜ Shyness ⚜ Parenting Styles ⚜ Generations
Psychological Reactions to Unfair Behavior
Rhetoric ⚜ The Rhetorical Triangle ⚜ Logical Fallacies
Thinking ⚜ Thinking Styles ⚜ Thought Distortions
Uncommon Words: Body ⚜ Emotions
Villains ⚜ Voice & Accent
More References: Plot ⚜ World-building ⚜ Writing Resources PDFs
#writing reference#character building#writing tips#writing advice#character inspiration#writeblr#dark academia#spilled ink#literature#writing prompt#creative writing#fiction#writers on tumblr#story#novel#light academia#writing resources#compilation requested by anon#still a bit messy & incomplete - will edit soon#will also update this every few weeks/months
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
Zoom In, Don’t Glaze Over: How to Describe Appearance Without Losing the Plot
You’ve met her before. The girl with “flowing ebony hair,” “emerald eyes,” and “lips like rose petals.” Or him, with “chiseled jawlines,” “stormy gray eyes,” and “shoulders like a Greek statue.”
We don’t know them.
We’ve just met their tropes.
Describing physical appearance is one of the trickiest — and most overdone — parts of character writing. It’s tempting to reach for shorthand: hair color, eye color, maybe a quick body scan. But if we want a reader to see someone — to feel the charge in the air when they enter a room — we need to stop writing mannequins and start writing people.
So let’s get granular. Here’s how to write physical appearance in a way that’s textured, meaningful, and deeply character-driven.
1. Hair: It’s About Story, Texture, and Care
Hair says a lot — not just about genetics, but about choices. Does your character tame it? Let it run wild? Is it dyed, greying, braided, buzzed, or piled on top of her head in a hurry?
Good hair description considers:
Texture (fine, coiled, wiry, limp, soft)
Context (windblown, sweat-damp, scorched by bleach)
Emotion (does she twist it when nervous? Is he ashamed of losing it?)
Flat: “Her long brown hair framed her face.”
Better: “Her ponytail was too tight, the kind that whispered of control issues and caffeine-fueled 4 a.m. library shifts.”
You don’t need to romanticise it. You need to make it feel real.
2. Eyes: Less Color, More Connection
We get it: her eyes are violet. Cool. But that doesn’t tell us much.
Instead of focusing solely on eye color, think about:
What the eyes do (do they dart, linger, harden?)
What others feel under them (seen, judged, safe?)
The surrounding features (dark circles, crow’s feet, smudged mascara)
Flat: “His piercing blue eyes locked on hers.”
Better: “His gaze was the kind that looked through you — like it had already weighed your worth and moved on.”
You’re not describing a passport photo. You’re describing what it feels like to be seen by them.
3. Facial Features: Use Contrast and Texture
Faces are not symmetrical ovals with random features. They’re full of tension, softness, age, emotion, and life.
Things to look for:
Asymmetry and character (a crooked nose, a scar)
Expression patterns (smiling without the eyes, habitual frowns)
Evidence of lifestyle (laugh lines, sun spots, stress acne)
Flat: “She had a delicate face.”
Better: “There was something unfinished about her face — as if her cheekbones hadn’t quite agreed on where to settle, and her mouth always seemed on the verge of disagreement.”
Let the face be a map of experience.
4. Bodies: Movement > Measurement
Forget dress sizes and six packs. Think about how bodies occupy space. How do they move? What are they hiding or showing? How do they wear their clothes — or how do the clothes wear them?
Ask:
What do others notice first? (a presence, a posture, a sound?)
How does their body express emotion? (do they go rigid, fold inwards, puff up?)
Flat: “He was tall and muscular.”
Better: “He had the kind of height that made ceilings nervous — but he moved like he was trying not to take up too much space.”
Describing someone’s body isn’t about cataloguing. It’s about showing how they exist in the world.
5. Let Emotion Tint the Lens
Who’s doing the describing? A lover? An enemy? A tired narrator? The emotional lens will shape what’s noticed and how it’s described.
In love: The chipped tooth becomes charming.
In rivalry: The smirk becomes smug.
In mourning: The face becomes blurred with memory.
Same person. Different lens. Different description.
6. Specificity is Your Superpower
Generic description = generic character. One well-chosen detail creates intimacy. Let us feel the scratch of their scarf, the clink of her earrings, the smudge of ink on their fingertips.
Examples:
“He had a habit of adjusting his collar when he lied — always clockwise, always twice.”
“Her nail polish was always chipped, but never accidentally.”
Make the reader feel like they’re the only one close enough to notice.
Describing appearance isn’t just about what your character looks like. It’s about what their appearance says — about how they move through the world, how others see them, and how they see themselves.
Zoom in on the details that matter. Skip the clichés. Let each description carry weight, story, and emotion. Because you’re not building paper dolls. You’re building people.
#writeblr#writing community#writers of tumblr#writing tips#character development#creative writing#writing advice#character description#descriptive writing#show don't tell#world building#narrative voice#writing help#fiction writing#amwriting#writing characters
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Worksheets & Templates
will update this every few weeks/months. alternatively, here are all my tagged Writing Worksheets & Templates
Chapter Outline ⚜ Character- or Plot-Driven Story
Death & Sacrifice ⚜ Magic & Rituals ⚜ Plot-Planning
Editing: Sentence Check ⚜ Writing Your Novel: 20 Questions
Tension ⚜ Thought Distortions ⚜ What's at Stake
Character Development
50 Questions ⚜ Backstory ⚜ Character Creation
Antagonist; Villain; Fighting ⚜ Protagonist & Antagonist
Character: Change; Adding Action; Conflict
Character: Creator; Name; Quirks; Flaws; Motivation
Character Profile (by Rick Riordan) ⚜ Character Sheet Template
Character Sketch & Bible ⚜ Interview your Character
Story-Worthy Hero ⚜ "Well-Rounded" Character Worksheet
Worldbuilding
20 Questions ⚜ Decisions & Categories ⚜ Worksheet
Setting ⚜ Dystopian World ⚜ Magic System (AALC Method)
Templates: Geography; World History; City; Fictional Plant
References: Worldbuilding ⚜ Plot ⚜ Character ⚜ Writing Resources PDFs
all posts are queued. send questions/requests here.
#writing tips#writeblr#dark academia#spilled ink#writers on tumblr#fiction#creative writing#character development#character building#original character#character design#booklr#writing prompts#novel#worldbuilding#writing inspiration#writing ideas#bookblr#writing reference#writing prompt#writing resources
10K notes
·
View notes
Text
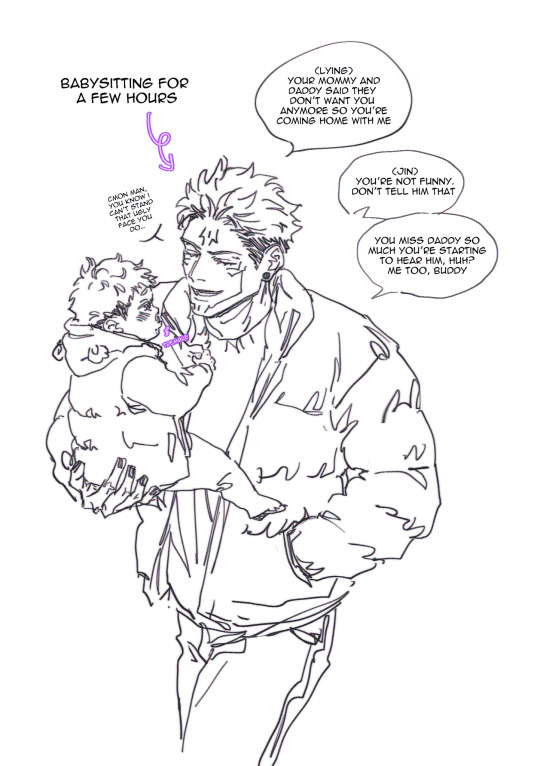

#jjk#jujutsu kaisen#fanart#my art#ryomen sukuna#au#sketch#hes a bully but thats ok cus it builds character#itadori yuuji#little man yuuji#unckuna au
19K notes
·
View notes
Text
Principles and Laws of Magic for Fantasy Writers
Fundamental Laws
1. Law of Conservation of Magic- Magic cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
3. Law of Equivalent Exchange- To gain something, an equal value must be given.
5. Law of Magical Exhaustion- Using magic drains the user’s energy or life force.
Interaction and Interference
4. Law of Magical Interference- Magic can interfere with other magical effects.
6. Law of Magical Contamination- Magic can have unintended side effects.
8. Law of Magical Inertia- Magical effects continue until stopped by an equal or greater force.
Resonance and Conditions
7. Law of Magical Resonance- Magic resonates with certain materials, places, or times.
9. Law of Magical Secrecy- Magic must be kept secret from the non-magical world.
11. Law of Magical Hierarchy- Different types of magic have different levels of power and difficulty.
Balance and Consequences
10. Law of Magical Balance- Every positive magical effect has a negative consequence.
12. Law of Magical Limitation- Magic has limits and cannot solve every problem.
14. Law of Magical Rebound- Misused magic can backfire on the user.
Special Conditions
13. Law of Magical Conduits- Certain objects or beings can channel magic more effectively.
15. Law of Magical Cycles- Magic may be stronger or weaker depending on cycles (e.g., lunar phases).
17. Law of Magical Awareness- Some beings are more attuned to magic and can sense its presence.
Ethical and Moral Laws
16. Law of Magical Ethics- Magic should be used responsibly and ethically.
18. Law of Magical Consent- Magic should not be used on others without their consent.
20. Law of Magical Oaths- Magical promises or oaths are binding and have severe consequences if broken.
Advanced and Rare Laws
19. Law of Magical Evolution- Magic can evolve and change over time.
20. Law of Magical Singularities- Unique, one-of-a-kind magical phenomena exist and are unpredictable.
Unique and Imaginative Magical Laws
- Law of Temporal Magic- Magic can manipulate time, but with severe consequences. Altering the past can create paradoxes, and using time magic ages the caster rapidly.
- Law of Emotional Resonance- Magic is amplified or diminished by the caster’s emotions. Strong emotions like love or anger can make spells more powerful but harder to control.
- Law of Elemental Harmony- Magic is tied to natural elements (fire, water, earth, air). Using one element excessively can disrupt the balance and cause natural disasters.
- Law of Dream Magic- Magic can be accessed through dreams. Dreamwalkers can enter others’ dreams, but they risk getting trapped in the dream world.
- Law of Ancestral Magic- Magic is inherited through bloodlines. The strength and type of magic depend on the caster’s ancestry, and ancient family feuds can influence magical abilities.
- Law of Symbiotic Magic- Magic requires a symbiotic relationship with magical creatures. The caster and creature share power, but harming one affects the other.
- Law of Forgotten Magic- Ancient spells and rituals are lost to time. Discovering and using forgotten magic can yield great power but also unknown dangers.
- Law of Magical Echoes- Spells leave behind echoes that can be sensed or traced. Powerful spells create stronger echoes that linger longer.
- Law of Arcane Geometry- Magic follows geometric patterns. Spells must be cast within specific shapes or alignments to work correctly.
- Law of Celestial Magic- Magic is influenced by celestial bodies. Spells are stronger during certain astronomical events like eclipses or planetary alignments.
- Law of Sentient Magic- Magic has a will of its own. It can choose to aid or hinder the caster based on its own mysterious motives.
- Law of Shadow Magic- Magic can manipulate shadows and darkness. Shadowcasters can travel through shadows but are vulnerable to light.
- Law of Sympathetic Magic- Magic works through connections. A spell cast on a representation of a person (like a doll or portrait) affects the actual person.
- Law of Magical Artifacts- Certain objects hold immense magical power. These artifacts can only be used by those deemed worthy or who possess specific traits.
- Law of Arcane Paradoxes- Some spells create paradoxes that defy logic. These paradoxes can have unpredictable and often dangerous outcomes.
- Law of Elemental Fusion- Combining different elemental magics creates new, hybrid spells with unique properties and effects.
- Law of Ethereal Magic- Magic can interact with the spirit world. Ethereal mages can communicate with spirits, but prolonged contact can blur the line between life and death.
- Law of Arcane Symbiosis- Magic can bond with technology, creating magical machines or enchanted devices with extraordinary capabilities.
- Law of Dimensional Magic- Magic can open portals to other dimensions. Dimensional travelers can explore alternate realities but risk getting lost or encountering hostile beings.
- Law of Arcane Sacrifice- Powerful spells require a sacrifice, such as a cherished memory, a personal item, or even a part of the caster’s soul.
#writer#writing#writer things#writerblr#writerscorner#writing inspiration#writing tips#author#writers and poets#ao3 writer#writeblr#fantasy writer#sci fi and fantasy#writing inspo#writing resources#dnd campaign#dnd character#character development#original character#amwriting#writers community#writer stuff#writing blog#writers block#writerscommunity#worldbuilding#world building#fantasy series
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
what will your character do..
(reblog and brainstorm, lovelies! u can also write drabbles with theseee )
if they're met face to face with their plot, with no warning?
if they're stressed?
if they're happy? who will they want to share it with?
if they're sad? will they go to anyone for comfort? if yes, who?
if they're forced into a life of death situation?
if they're being threatened?
if they're kissed by their ex?
if they're confessed to by someone who they had no clue liked them? (given, they're single or not)
if their lover betrays them?
if they're coughing up blood out of the blue?
if there's a strange presence in the room, and it feels ominous?
if they discovered a dead body?
^ if the dead body is their best friend? (great question to start and develop a plot)
if their enemy is at their doorstep, bruised and injured?
if they had to share a bed with someone they don't particularly hate? ahem
if they had to be fed by someone they didn't like/their crush?
if their partner-to-be? enemy? pulls them into a secluded and shushes them? (their bodies pressing and all that!!)
when asked to choose between their family and their lover? (given the circumstances of ur story)
when kissed on their head by their enemy after a near death experience?
if they're dancing with a stranger, and the stranger says 'stop dancing, sweetheart and you'll hunted. do u wanna die?' ?
if they find out the food that served to them has glass dust on it? (who is it served by?)
when being pulled into a hug when they most need it by someone they least expect?
when they have to hold someone they loved at a gun point? why would it even occur?
when they have to choose between their own life and their lover's?
when they've to give up something (of great importance to the character) to save their lover?
#writer prompts#otp prompts#dialogue prompts#romance writing#urfriendlywriter#imagine your otp#writeblr#writing prompts#writing inspiration#romance prompts writing#how to write#how to write a character#character tropes#build a character#writing characters#character traits#character sheet#writing prompt#writing#writing list#romance prompts#bookblr#writing advice#writing inspo#writing help#otp drabble prompts#otp writing#otp meme#otp things#otp ideas
8K notes
·
View notes
Text

my feelings never reached you
#mdzs#mdzs fanart#mo dao zu shi#lan wangji#wei wuxian#lan zhan#wei ying#wangxian#mxtx#y'know what hell yeah#finally finished this thing#it sat in my folder for A While#anyway#something something post 33 lashes something#ouch#yippie yippie yippie#heartache builds character once again
2K notes
·
View notes
Text




Astarion’s first impressions of my tav Cain, because playing a good aligned paladin with a charlatan background is really, truly, deeply hilarious. I loved lying at every possible opportunity to make my life easier. I wish there wasn’t a cap on inspiration points because I was getting it left and right from cain and astarion combined.
#you can see me progressively put more effort into this#baldurs gate 3#astarion#bg3#bg3 art#bg3 tav#bg3 astarion#bg3 fanart#oc: cain#he’s named that bc when i built him i ripped his build from my dnd character at the time#whose name was abel#in my mind they’re brothers and in this universe abel doesn’t become an adventurer#and runs a butchery in baldurs gate
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
🍖 How to Build a Culture Without Just Inventing Spices and Necklaces
(a worldbuilding roast. with love.)
So. You’re building a fantasy world, and you’ve just invented: → Three types of ceremonial jewelry → A spice that tastes like cinnamon if it were bitter and cursed → A holiday where everyone wears gold and screams at dawn
Cute. But that’s not culture. That’s aesthetics.
And if your worldbuilding is all outfits, dances, and spice blends with vaguely mystical names, your story’s probably going to feel like a cosplay convention held inside a Pinterest board.
Here’s how to fix that—aka: how to build a real, functioning culture that shapes your story, not just its vibes.
─────── ✦ ───────
🔗 Culture Is Built on Power, Not Just Style
Ask yourself: → Who’s in charge, and why? → Who has land? Who doesn’t? → What’s considered taboo, sacred, or punishable by death?
Culture is shaped by who gets to make the rules and who gets crushed by them. That’s where things like religion, family structure, class divisions, gender roles, and social expectations actually come from.
Start there. Not at the embroidery.
─────── ✦ ───────
2.🪓 Culture Comes From Conflict
Did this society evolve peacefully? Was it colonized? Did it colonize? Was it rebuilt after a war? Is it still in one?
→ What was destroyed and mythologized? → What do the survivors still whisper about? → What do children get taught in school that’s… suspiciously sanitized?
No culture is neutral. Every tradition has a history, and that history should taste like blood, loss, or propaganda.
─────── ✦ ───────
3.🧠 Belief Systems > Customs Lists
Sure, rituals and holidays are cool. But what do people believe about: → Death? → Love? → Time? → The natural world? → Justice?
Example: A society that believes time is cyclical vs. one that sees time as linear will approach everything—from prison sentences to grief—completely differently.
You don’t need to invent 80 gods. You need to know what those gods mean to the people who pray to them.
─────── ✦ ───────
4.🫀 Culture Controls Behavior (Quietly)
Culture shows up in: → What people apologize for → What insults cut deepest → What people are embarrassed about → What’s praised publicly vs. what’s hidden privately
For instance: → A culture obsessed with stoicism won’t say “I love you.” They’ll say “Have you eaten?” → A culture built on legacy might prioritize ancestor veneration, archival writing, name inheritance.
This stuff? Way more immersive than giving everyone matching earrings.
─────── ✦ ───────
5. 🏠 Culture = Daily Life, Not Just Festivals
Sure, your MC might attend a funeral where people paint their faces blue. But what about: → Breakfast routines? → How people greet each other on the street? → Who cooks, and who eats first? → What’s considered “clean” or “proper”? → How is parenting handled? Divorce?
Culture is what happens between plot points. It should shape your character’s assumptions, language, fears, and habits—whether or not a festival is going on.
─────── ✦ ───────
6. 💬 Let Your Characters Disagree With Their Own Culture
A culture isn’t a monolith.
Even in deeply traditional societies, people: → Rebel → Question → Break rules → Misinterpret laws → Mock sacred things → Act hypocritically → Weaponize or resist what’s expected
Let your characters wrestle with the culture around them. That’s where realism (and tension) lives.
─────── ✦ ───────
7.🧼 Beware the “Pretty = Good” Trap
Worldbuilding gets boring fast when: → The protagonist’s homeland is beautiful and pure → The enemy’s culture is dark and “barbaric” → Every detail just reinforces who the reader should like
You can—and should—challenge the aesthetic hierarchy. → Let ugly things be beloved. → Let beautiful things be corrupt. → Let your MC romanticize their culture and then get disillusioned by it later.
─────── ✦ ───────
📍 TL;DR (but like, spicy): → Culture is not food and jewelry. → Culture is power, fear, memory, contradiction. → Stop inventing spices until you know who starved last winter. → Let your world feel lived in, not curated.
The best cultural worldbuilding doesn’t look like a list. It feels like a system. A pressure. A presence your characters can’t escape—even if they try.
Now go. Build something real. (You can add spices later.)
—rin t. // writing advice for worldbuilders with rage and range // thewriteadviceforwriters
Sometimes the problem isn’t your plot. It’s your first 5 pages. Fix it here → 🖤 Free eBook: 5 Opening Pages Mistakes to Stop Making:
🕯️ download the pack & write something cursed:
#worldbuilding#writing advice#writeblr#fantasy writing#writing tips#amwriting#writing community#culturebuilding#fiction writing#writing realism#storybuilding#fantasy worldbuilding#speculative fiction#writer resources#writing help#character development#society building#writing immersion#realistic worldbuilding#rin t speaks#thewriteadviceforwriters#writing#writers block#writers on tumblr#writers and poets#on writing#how to write#creative writing#how to start a novel#writing resources
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

“It’s closed! Where should we eat?”
#original characters#furry art#eventually someone will realize all my furry drawings have been a slowly building horror story#read the signs
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
transformers one hunger games simulator with drawings!!! PART TWO!!!
part 1
this is technically round 5 but im not posting all of them here
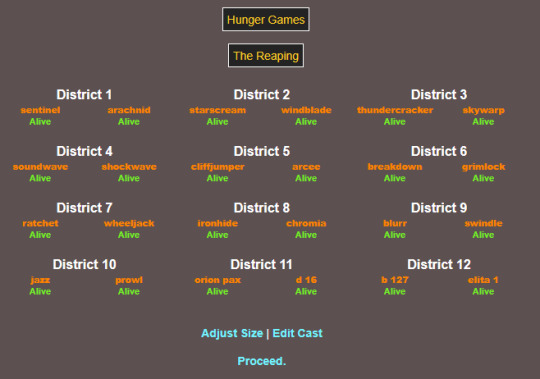

sentinel keeps getting murdered first and i think its so great LOOL




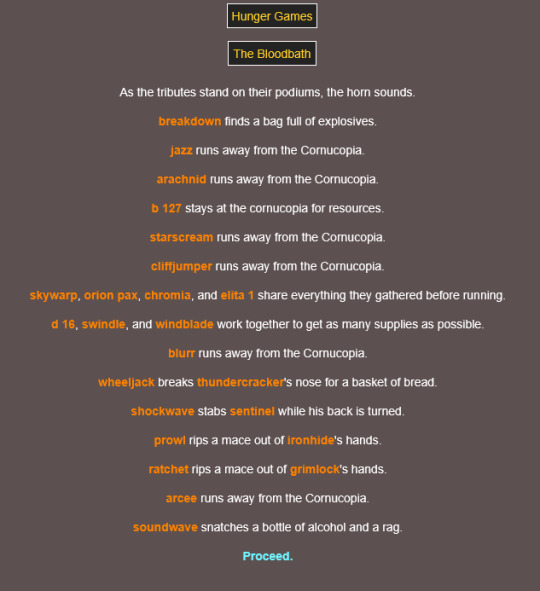
...orion. 😭

every time

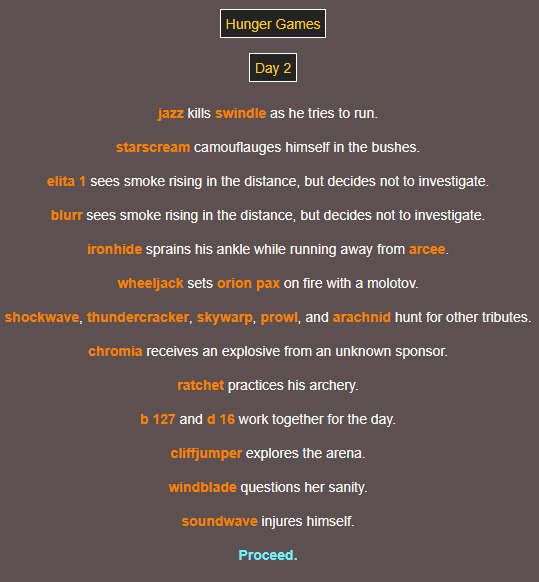
does he know 😭😭

dee and bee together again!

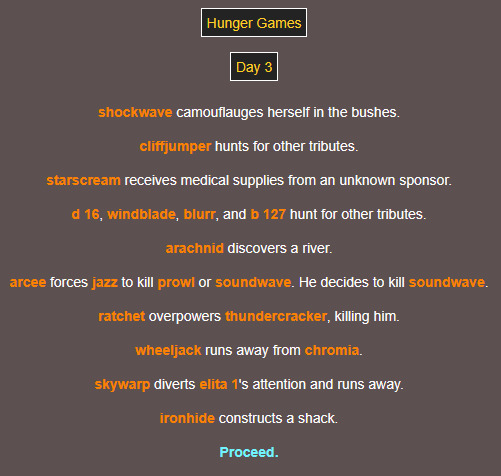
hey this feels familiar

dear god 😭

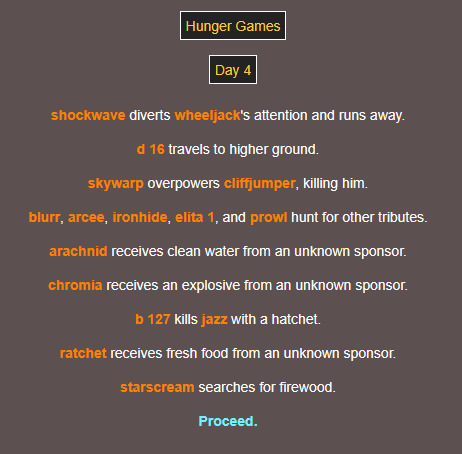
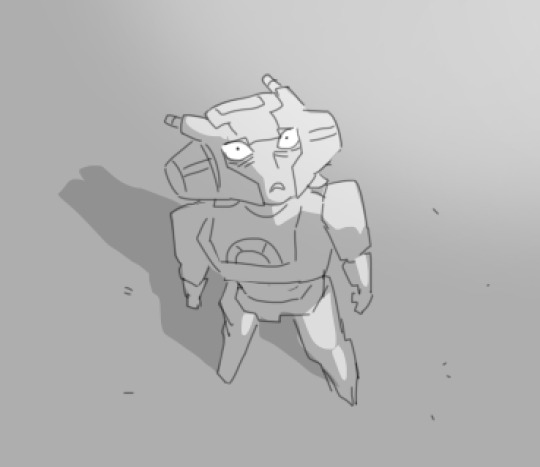
half the friend group reunited!!!
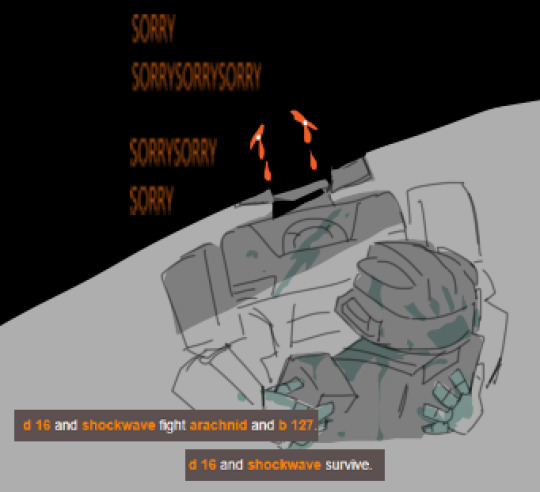
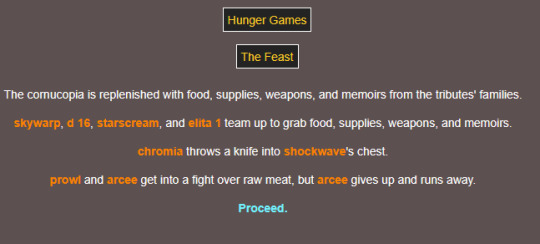

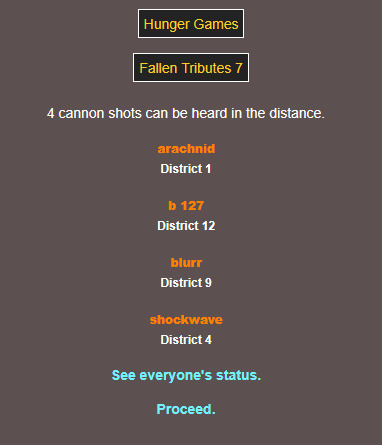

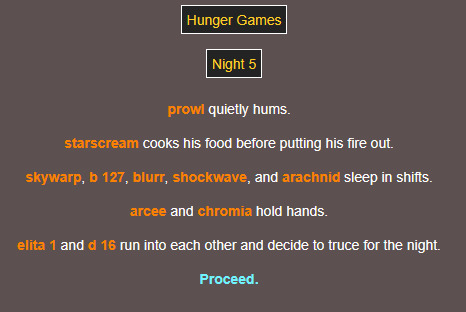
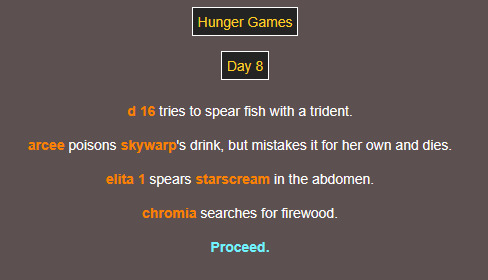
sorry elita

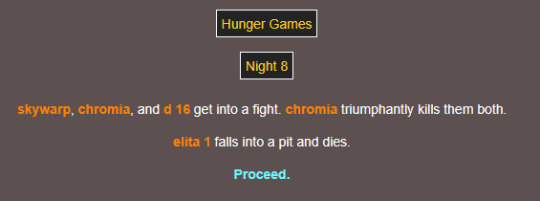

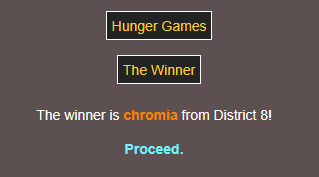

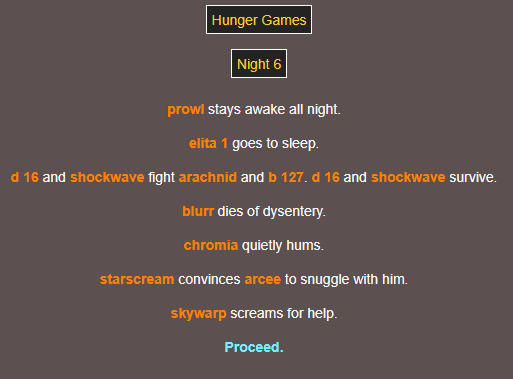
THE WINNER IS CHROMIA 😭😭 STEALING THE WIN FROM MINERS ONCE AGAIN!!!! 😭
#transformers one#hunger games simulator#for a moment it really felt like it was building to something and then chromia won IJOBKGKHMFLKG#WHICH IS ALSO ACTUALLY REALLY IN CHARACTER???#AND THATS SO FUNNY 😭😭#i make the drawings as i generate the simulation#so i end up being just as surprised as everyone else#i was building something with elita and dee but then elita fell in a hole and dee lost a 2 v 1#u cannot be serious 😭#COME ON ELITA#the simulator is geniunly so fun i love how random everything is#at the same time i can still attempt to build something out of it and its really fun
2K notes
·
View notes