#data source: github
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How to install NewPipe on Android
NewPipe is a YouTube replacement client for Android devices. It's open-source (meaning, you can see all of their code as you please), privacy-oriented, lightweight, and supports features that are normally locked behind a YouTube Premium paywall.
Disclaimer: I am not affiliated with NewPipe, YouTube, Android, Google, Alphabet Inc, or any other brand or name mentioned here. I made this guide to help my friends who were curious.
NewPipe's Website: https://newpipe.net/
The GitHub Repository
Step 0. Compatibility check
Make sure you're running an Android device! This won't work on an Apple device of any kind! Also, for those more tech-savvy among you, if you have the F-Droid store installed, you can download NewPipe straight from there!
Step 1. Downloading
Go to NewPipe's Github repo (repository, the codebase or where all of the code is stored). Scroll to the bottom of the page until you see "Releases". Click on the one that says "Latest" next to it in a little green bubble:

Your version number (v#...) will be different if you're reading this in the future! That's okay. Scroll past the changelog (unless you want to read it!) until you find "Assets":

Click on the first one, the one with the little cube ending in .apk. APK files are Android Package (Kit) and are the main format for downloading apps. Once you click on the link, it should begin downloading or your browser will ask you to confirm that you want to download this file. You should always verify the filename matches what you expect it to be (namely, the file format) before attempting to install! It might take a few moments for the file to download depending on your internet connection.
Step 2. Installation
Once you have the file downloaded, you can click the download popup in your notification bar or find the file in your device's file system. One of 2 things will happen:
You will get a popup asking if you want to install an APK by the name of NewPipe - confirm that you do (and make sure the app is really NewPipe!) and it will install automatically. You can then click "Open" to open the app and begin using it.
You will get a popup warning you that you have the ability to install apps from unknown sources disabled and that you can't install this. This is normal and does not mean that you downloaded the wrong thing.
If you got the first popup, continue past this step. For those of you who got the second, let's go over what this means.
By default, most Androids have this setting disabled. This is for security purposes, so you can't accidentally install a malicious app from the whole internet. If you enable this setting (allow installations from unknown/unsigned sources), you are theoretically putting yourself at risk. Realistically, you're probably fine. But, after installing NewPipe, you can always re-disable the setting if it makes you more comfortable. That will prevent you from installing updates in the future, but it can always be re-enabled.
Ready to turn that setting on? It will vary by your individual device! Some devices will take you directly to the page with the setting upon failed installation, and some you will just have to find it yourself using the searchbar in settings.
Once you've allowed installations from unknown sources (wording may vary slightly), try to repeat the steps above of clicking the download popup or finding the APK in your files and trying to install it. It should work correctly this time!
Step 3. Updating NewPipe
Like most apps, NewPipe is in development currently and frequently has new versions released to improve it and fix bugs. Unlike most apps, NewPipe needs to be manually updated, since we haven't downloaded through the Google Play store.
To update NewPipe, all you have to do is follow the above steps for installing the app, except that when you get the popup asking to install it, it will instead say "Update". That's it! NewPipe and Android handle the rest.
NewPipe also has popup notifications for when the app has a new update, so you don't have to worry about checking the GitHub for a new release. Just click on the "A new version is available" popup and it should take you directly to the webpage.
That's it! Enjoy browsing videos in peace without ads and with the ability to download and so much more. Pro tip: you can copy paste YouTube links into the NewPipe search bar to go directly to that video/playlist/channel.
#newpipe#youtube#youtube client#youtube replacement#how to install newpipe#android#android apk#android app#images#text#links#image descriptions#privacy#data privacy#internet privacy#big tech#data security#github#software#database#opensource#open source#newpipe app
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
obnoxious that I can't just use a computer to do the things I've always used computers to do, now I have to use two different computers including one with specialized hardware for interfacing with an entirely different network of interdevice communication. I don't wanna turn on goddamn mfa, and it's insufferable when I have to goddamn pull out another hundreds of dollars of tech just to be allowed to use your site's search (because you forbid it unauthenticated)
#on the one hand I get that having stronger security for authentication is nice.#on the other hand though. if you don't trust the individual with whom you have to authenticate for the service they have a monopoly over#then you have to fuckin sacrifice your operational security in the name of making some other individual feel better about their lax securit#which like. fine whatever dont do business with people you dont wanna do business with. except for like. fucking github#like you want the gpl'ed source code for the quake engine#youre gonna have to endure microsoft and github and a million petty tyrants who demand every bit of data just for fundamental functionality#ugh I don't know I have any coherent complaints I'm just whinging bc I had to use two computers for a task one computer can do
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
how to build a digital music collection and stuff
spotify sucks aaaass. so start downloading shit!!
file format glossary
.wav is highest quality and biggest
.mp3 is very small, but uses lossy compression which means it's lower quality
.flac is smaller than .wav, but uses lossless compression so it's high quality
.m4a is an audio file format that apple uses. that's all i really know
downloading the music
doubledouble.top is a life saver. you can download from a variety of services including but not limited to apple music, spotify, soundcloud, tidal, deezer, etc.
i'd recommend ripping your music from tidal or apple music since they're the best quality (i think apple music gives you lossless audio anyway. .m4a can be both lossy and lossless, but from the text on doubledouble i assume they're ripping HQ files off apple music)
i also love love love cobalt.tools for ripping audio/video from youtube (they support a lot of other platforms too!)
of course, many artists have their music on bandcamp — purchase or download directly from them if you can. bandcamp offers a variety of file formats for download
file conversion
if you're downloading from apple music with doubledouble, it spits out an .m4a file.
.m4a is ok for some people but if you prefer .flac, you may wanna convert it. ffmpeg is a CLI (terminal) tool to help with media conversion
if you're on linux or macOS, you can use parameter expansion to batch convert all files in a folder. put the files in one place first, then with your terminal, cd into the directory and run:
for i in *.m4a; do ffmpeg -i "$i" "${i%.*}.flac"; done
this converts from .m4a to .flac — change the file extensions if needed.
soulseek
another way to get music is through soulseek. soulseek is a peer-to-peer file sharing network which is mainly used for music. nicotine+ is a pretty intuitive (and open-source) client if you don't like the official one.
you can probably find a better tutorial on soulseek somewhere else. just wanted to make this option known
it's bad etiquette to download from people without sharing files of your own, so make sure you've got something shared. also try to avoid queuing up more than 1-2 albums from one person in a row
tagging & organizing your music
tagging: adding metadata to a music file (eg. song name, artist name, album) that music players can recognize and display
if you've ripped music from a streaming platform, chances are it's already tagged. i've gotten files with slightly incorrect tags from doubledouble though, so if you care about that then you might wanna look into it
i use musicbrainz picard for my tagging. they've got pretty extensive documentation, which will probably be more useful than me
basically, you can look up album data from an online database into the program, and then match each track with its file. the program will tag each file correctly for you (there's also options for renaming the file according to a certain structure if you're into that!)
there's also beets, which is a CLI tool for... a lot of music collection management stuff. i haven't really used it myself, but if you feel up to it then they've got extensive documentation too. for most people, though, it's not really a necessity
how you wanna organize your music is completely up to you. my preferred filestructure is:
artist > album > track # track

using a music player
the options for this are pretty expansive. commonly used players i see include VLC, foobar2000, clementine (or a fork of it called strawberry), and cmus (for the terminal)
you can also totally use iTunes or something. i don't know what audio players other systems come with
i personally use dopamine. it's a little bit slow, but it's got a nice UI and is themeable plus has last.fm support (!!!)
don't let the github page fool you, you don't have to build from source. you can find the releases here
click the "assets" dropdown on the most recent release, and download whichever one is compatible with your OS
syncing
if you're fine with your files just being on one device (perhaps your computer, but perhaps also an USB drive or an mp3 player), you don't have to do this
you can sync with something like google drive, but i hate google more than i hate spotify
you can get a free nextcloud account from one of their providers with 2GB of free storage. you can use webDAV to access your files from an app on your phone or other device (documents by readdle has webDAV support, which is what i use)
disroot and blahaj.land are a couple providers i know that offer other services as well as nextcloud (so you get more with your account), but accounts are manually approved. do give them a look though!!
if you're tech-savvy and have an unused machine lying around, look into self-hosting your own nextcloud, or better yet, your own media server. i've heard that navidrome is a pretty good audio server. i unfortunately don't have experience with self-hosting at the moment so i have like zero advice to give here. yunohost seems to be a really easy way to manage a server
afterword
i don't know if any of this is helpful, but i just wanted to consolidate my personal advice in one place. fuck big tech. own your media, they could take it away from you at any moment
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
ShadowDragon sells a tool called SocialNet that streamlines the process of pulling public data from various sites, apps, and services. Marketing material available online says SocialNet can “follow the breadcrumbs of your target’s digital life and find hidden correlations in your research.” In one promotional video, ShadowDragon says users can enter “an email, an alias, a name, a phone number, a variety of different things, and immediately have information on your target. We can see interests, we can see who friends are, pictures, videos.”
The leaked list of targeted sites include ones from major tech companies, communication tools, sites focused around certain hobbies and interests, payment services, social networks, and more. The 30 companies the Mozilla Foundation is asking to block ShadowDragon scrapers are Amazon, Apple, BabyCentre, BlueSky, Discord, Duolingo, Etsy, Meta’s Facebook and Instagram, FlightAware, Github, Glassdoor, GoFundMe, Google, LinkedIn, Nextdoor, OnlyFans, Pinterest, Reddit, Snapchat, Strava, Substack, TikTok, Tinder, TripAdvisor, Twitch, Twitter, WhatsApp, Xbox, Yelp, and YouTube.
437 notes
·
View notes
Text
The main reason to use Firefox and Linux and other free and open source software is that otherwise the big tech monopolies will fuck you as the customer over in search of profits. They will seek to control how you use their products and sell your data. When a company dominates the market, things can only get worse for ordinary people.
Like take Google Chrome for example, which together with its chromium reskins dominate the web browser market. Google makes a lot of money from ads, and consequently the company hates adblockers. They already are planning to move to manifest V3, which will nerf adblockers significantly. The manifest V3 compatible chrome version of Ublock Orgin is a "Lite" version for a reason. Ublock's Github page has an entire page explaining why the addon works best in Firefox.
And Google as we speak are trying to block adblockers from working on Youtube, If you want to continue blocking Youtube ads, and since Youtube ads make the site unuseable you ought to want that, it makes the most sense to not use a browser controlled by Google.
And there is no reason to think things won't get worse. There is for example nothing stopping Google from kicking adblockers off their add-on stores completely. They do regard it as basically piracy if the youtube pop-ups tell us anything, so updating the Chrome extensions terms of service to ban adblocking is a natural step. And so many people seem to think Chrome is the only browser that exists, so they are not going to switch to alternatives, or if they do, they will switch to another chrominum-based browser.
And again, they are fucking chromium itself for adblockers with Manifest V3, so only Firefox remains as a viable alternative. It's the only alternative to letting Google control the internet.
And Microsoft is the same thing. I posted before about their plans to move Windows increasingly into the cloud. This already exists for corporate customers, as Windows 365. And a version for ordinary users is probably not far off. It might not be the only version of Windows for awhile, the lack of solid internet access for a good part of the Earth's population will prevent it. But you'll probably see cheap very low-spec chromebookesque laptops running Windows for sale soon, that gets around Windows 11's obscene system requirements by their Windows being a cloud-based version.
And more and more of Windows will require Internet access or validation for DRM reasons if nothing else. Subscription fees instead of a one-time license are also likely. It will just be Windows moving in the direction Microsoft Office has already gone.
There is nothing preventing this, because again on the desktop/laptop market Windows is effectively a monopoly, or a duopoly with Apple. So there is no competition preventing Microsoft from exercising control over Windows users in the vein of Apple.
For example, Microsoft making Windows a walled garden by only permitting programs to be installed from the Microsoft Store probably isn't far off. This already exists for Win10 and 11, it's called S-mode. There seem to be more and more laptops being sold with Windows S-mode as the default.
Now it's not the only option, and you can turn it off with some tinkering, but there is really nothing stopping Microsoft from making it the only way of using Windows. And customers will probably accept it, because again the main competition is Apple where the walled garden has been the default for decades.
Customers have already accepted all sorts of bad things from Microsoft, because again Windows is a near-monopoly, and Apple and Google are even worse. That’s why there has been no major negative reaction to how Windows has increasingly spies on its users.
Another thing is how the system requirements for Windows seem to grow almost exponentially with each edition, making still perfectly useable computers unable to run the new edition. And Windows 11 is the worst yet. Like it's hard to get the numbers of how many computers running Win10 can't upgrade to Win11, but it's probably the majority of them, at least 55% or maybe even 75%. This has the effect of Windows users abandoning still perfectly useable hardware and buying new computers, creating more e-waste.
For Windows users, the alternative Windows gives them is to buy a new computer or get another operating system, and inertia pushes them towards buying another computer to keep using Windows. This is good for Windows and the hardware manufacturers selling computers with Windows 11 pre-installed, they get to profit off people buying Windows 11 keys and new computers, while the end-users have to pay, as does the environment. It’s planned obsolescence.
And it doesn’t have to be like that. Linux distros prove that you can have a modern operating system that has far lower hardware requirements. Even the most resource taxing Linux distros, like for example Ubuntu running the Gnome desktop, have far more modest system requirements than modern Windows. And you can always install lightweight Linux Distros that often have very low system requirements. One I have used is Antix. The ballooning Windows system requirements comes across as pure bloat on Microsoft’s part.
Now neither Linux or Firefox are perfect. Free and open source software don’t have a lot of the polish that comes with the proprietary products of major corporations. And being in competition with technology monopolies does have its drawbacks. The lacking website compatibility with Firefox and game compatibility with Linux are two obvious examples.
Yet Firefox and Linux have the capacity to grow, to become better. Being open source helps. Even if Firefox falls, developers can create a fork of it. If a Linux distro is not to your taste, there is usually another one. Whereas Windows and Chrome will only get worse as they will continue to abuse their monopolistic powers over the tech market.
846 notes
·
View notes
Text
alright y'all are driving me insane; let's talk about shinigami eyes
im tempted to be sarcastic here but im just going to state it as plainly and clearly as possible: no, shinigami eyes isn't made by a terf, you just don't understand how the plugin works. deciding to mass uninstall the plugin and not contribute actively makes the plugin worse
let's take a look at the extension's actual webpage together
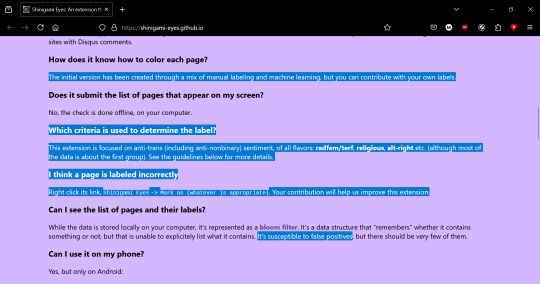
the extension explicitly states within its own documentation that it was initially created by a mix of manual labeling and machine learning, but you can contribute with your own labels. if you understand anything about machine learning, you'll know that it's going to constantly adapt itself based on the inputs it receives
so, when a bunch of terfs install the plugin for the purposes of driving transgender communities apart, transgender people don't make any contributions to shinigami eyes, claim it's run by a terf, and mass uninstall the plugin, what do you think the new data set is for the program?
it also tells you the basic criteria, literally how to use the plugin (it's not passive! it's active!), and warns that it's susceptible to false positives
and if you scroll down slightly further:

the developer explicitly states they're transgender and why the plugin was made
now let's look at the actual guidelines, so you know how you're supposed to use the plugin:

initial primer: do not flag unless you're reasonably confident about your decision
not enough to mark as anti-trans: being a conservative, a swerf, a bad or mediocre ally, ace-phobic, being concerned with, "free speech," and giving voice to, "both sides," with examples of each
the purpose of the plugin is to mark people as trans-friendly or anti-trans (and has a clear function! you can remove either marking!), not for other sociopolitical issues
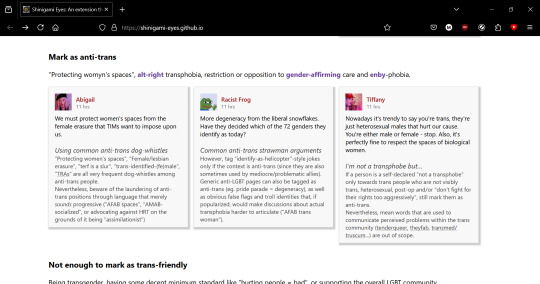
mark as anti-trans: "protecting wombyn's spaces," alt-right transphobia, restriction or opposition to gender-affirming care and enby-phobia, with examples of each
and, yes, that means that the plugin being used to fraudulently mark trans men and nonbinary people people as anti-trans is using the plugin incorrectly if that's your only basis for flagging them; you shouldn't flag someone based on them being trans, as it immediately points out in the literal next section:

not enough to mark as trans-friendly: being transgender, having some decent minimum standard like, "hurting people = bad," or supporting the overall LGBT community, with examples of each
vague statements don't equate someone as trans-friendly
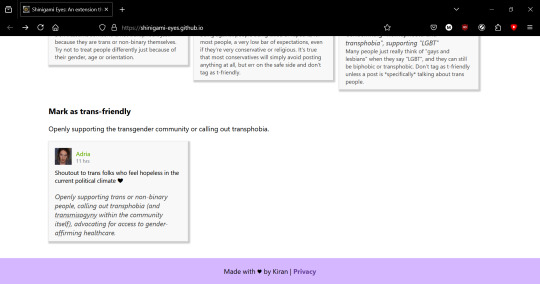
and finally, mark as trans-friendly: openly supporting the transgender community or calling out transphobia, with an example
and at the very bottom, you can see, "made with [love] by kiran"
additionally, if you go to the actual github page:

it's open source. if you think the code is borked you have an opportunity to figure out what's wrong with it
if the point wasn't clear enough: ignorance of functionality and lack of participation make problems worse via attrition. if you want to make shinigami eyes better, you need to reinstall it and actively participate in fixing the data, not just getting angry at a computer program
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
"how do I keep my art from being scraped for AI from now on?"
if you post images online, there's no 100% guaranteed way to prevent this, and you can probably assume that there's no need to remove/edit existing content. you might contest this as a matter of data privacy and workers' rights, but you might also be looking for smaller, more immediate actions to take.
...so I made this list! I can't vouch for the effectiveness of all of these, but I wanted to compile as many options as possible so you can decide what's best for you.
Discouraging data scraping and "opting out"
robots.txt - This is a file placed in a website's home directory to "ask" web crawlers not to access certain parts of a site. If you have your own website, you can edit this yourself, or you can check which crawlers a site disallows by adding /robots.txt at the end of the URL. This article has instructions for blocking some bots that scrape data for AI.
HTML metadata - DeviantArt (i know) has proposed the "noai" and "noimageai" meta tags for opting images out of machine learning datasets, while Mojeek proposed "noml". To use all three, you'd put the following in your webpages' headers:
<meta name="robots" content="noai, noimageai, noml">
Have I Been Trained? - A tool by Spawning to search for images in the LAION-5B and LAION-400M datasets and opt your images and web domain out of future model training. Spawning claims that Stability AI and Hugging Face have agreed to respect these opt-outs. Try searching for usernames!
Kudurru - A tool by Spawning (currently a Wordpress plugin) in closed beta that purportedly blocks/redirects AI scrapers from your website. I don't know much about how this one works.
ai.txt - Similar to robots.txt. A new type of permissions file for AI training proposed by Spawning.
ArtShield Watermarker - Web-based tool to add Stable Diffusion's "invisible watermark" to images, which may cause an image to be recognized as AI-generated and excluded from data scraping and/or model training. Source available on GitHub. Doesn't seem to have updated/posted on social media since last year.
Image processing... things
these are popular now, but there seems to be some confusion regarding the goal of these tools; these aren't meant to "kill" AI art, and they won't affect existing models. they won't magically guarantee full protection, so you probably shouldn't loudly announce that you're using them to try to bait AI users into responding
Glaze - UChicago's tool to add "adversarial noise" to art to disrupt style mimicry. Devs recommend glazing pictures last. Runs on Windows and Mac (Nvidia GPU required)
WebGlaze - Free browser-based Glaze service for those who can't run Glaze locally. Request an invite by following their instructions.
Mist - Another adversarial noise tool, by Psyker Group. Runs on Windows and Linux (Nvidia GPU required) or on web with a Google Colab Notebook.
Nightshade - UChicago's tool to distort AI's recognition of features and "poison" datasets, with the goal of making it inconvenient to use images scraped without consent. The guide recommends that you do not disclose whether your art is nightshaded. Nightshade chooses a tag that's relevant to your image. You should use this word in the image's caption/alt text when you post the image online. This means the alt text will accurately describe what's in the image-- there is no reason to ever write false/mismatched alt text!!! Runs on Windows and Mac (Nvidia GPU required)
Sanative AI - Web-based "anti-AI watermark"-- maybe comparable to Glaze and Mist. I can't find much about this one except that they won a "Responsible AI Challenge" hosted by Mozilla last year.
Just Add A Regular Watermark - It doesn't take a lot of processing power to add a watermark, so why not? Try adding complexities like warping, changes in color/opacity, and blurring to make it more annoying for an AI (or human) to remove. You could even try testing your watermark against an AI watermark remover. (the privacy policy claims that they don't keep or otherwise use your images, but use your own judgment)
given that energy consumption was the focus of some AI art criticism, I'm not sure if the benefits of these GPU-intensive tools outweigh the cost, and I'd like to know more about that. in any case, I thought that people writing alt text/image descriptions more often would've been a neat side effect of Nightshade being used, so I hope to see more of that in the future, at least!
246 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hypothetical Decentralised Social Media Protocol Stack
if we were to dream up the Next Social Media from first principles we face three problems. one is scaling hosting, the second is discovery/aggregation, the third is moderation.
hosting
hosting for millions of users is very very expensive. you have to have a network of datacentres around the world and mechanisms to sync the data between them. you probably use something like AWS, and they will charge you an eye-watering amount of money for it. since it's so expensive, there's no way to break even except by either charging users to access your service (which people generally hate to do) or selling ads, the ability to intrude on their attention to the highest bidder (which people also hate, and go out of their way to filter out). unless you have a lot of money to burn, this is a major barrier.
the traditional internet hosts everything on different servers, and you use addresses that point you to that server. the problem with this is that it responds poorly to sudden spikes in attention. if you self-host your blog, you can get DDOSed entirely by accident. you can use a service like cloudflare to protect you but that's $$$. you can host a blog on a service like wordpress, or a static site on a service like Github Pages or Neocities, often for free, but that broadly limits interaction to people leaving comments on your blog and doesn't have the off-the-cuff passing-thought sort of interaction that social media does.
the middle ground is forums, which used to be the primary form of social interaction before social media eclipsed them, typically running on one or a few servers with a database + frontend. these are viable enough, often they can be run with fairly minimal ads or by user subscriptions (the SomethingAwful model), but they can't scale indefinitely, and each one is a separate bubble. mastodon is a semi-return to this model, with the addition of a means to use your account on one bubble to interact with another ('federation').
the issue with everything so far is that it's an all-eggs-in-one-basket approach. you depend on the forum, instance, or service paying its bills to stay up. if it goes down, it's just gone. and database-backend models often interact poorly with the internet archive's scraping, so huge chunks won't be preserved.
scaling hosting could theoretically be solved by a model like torrents or IPFS, in which every user becomes a 'server' for all the posts they download, and you look up files using hashes of the content. if a post gets popular, it also gets better seeded! an issue with that design is archival: there is no guarantee that stuff will stay on the network, so if nobody is downloading a post, it is likely to get flushed out by newer stuff. it's like link rot, but it happens automatically.
IPFS solves this by 'pinning': you order an IPFS node (e.g. your server) not to flush a certain file so it will always be available from at least one source. they've sadly mixed this up in cryptocurrency, with 'pinning services' which will take payment in crypto to pin your data. my distaste for a technology designed around red queen races aside, I don't know how pinning costs compare to regular hosting costs.
theoretically you could build a social network on a backbone of content-based addressing. it would come with some drawbacks (posts would be immutable, unless you use some indirection to a traditional address-based hosting) but i think you could make it work (a mix of location-based addressing for low-bandwidth stuff like text, and content-based addressing for inline media). in fact, IPFS has the ability to mix in a bit of address-based lookup into its content-based approach, used for hosting blogs and the like.
as for videos - well, BitTorrent is great for distributing video files. though I don't know how well that scales to something like Youtube. you'd need a lot of hard drive space to handle the amount of Youtube that people typically watch and continue seeding it.
aggregation/discovery
the next problem is aggregation/discovery. social media sites approach this problem in various ways. early social media sites like LiveJournal had a somewhat newsgroup-like approach, you'd join a 'community' and people would post stuff to that community. this got replaced by the subscription model of sites like Twitter and Tumblr, where every user is simultaneously an author and a curator, and you subscribe to someone to see what posts they want to share.
this in turn got replaced by neural network-driven algorithms which attempt to guess what you'll want to see and show you stuff that's popular with whatever it thinks your demographic is. that's gotta go, or at least not be an intrinsic part of the social network anymore.
it would be easy enough to replicate the 'subscribe to see someone's recommended stuff' model, you just need a protocol for pointing people at stuff. (getting analytics such as like/reblog counts would be more difficult!) it would probably look similar to RSS feeds: you upload a list of suitably formatted data, and programs which speak that protocol can download it.
the problem of discovery - ways to find strangers who are interested in the same stuff you are - is more tricky. if we're trying to design this as a fully decentralised, censorship-resistant network, we face the spam problem. any means you use to broadcast 'hi, i exist and i like to talk about this thing, come interact with me' can be subverted by spammers. either you restrict yourself entirely to spreading across a network of curated recommendations, or you have to have moderation.
moderation
moderation is one of the hardest problems of social networks as they currently exist. it's both a problem of spam (the posts that users want to see getting swamped by porn bots or whatever) and legality (they're obliged to remove child porn, beheading videos and the like). the usual solution is a combination of AI shit - does the robot think this looks like a naked person - and outsourcing it to poorly paid workers in (typically) African countries, whose job is to look at reports of the most traumatic shit humans can come up with all day and confirm whether it's bad or not.
for our purposes, the hypothetical decentralised network is a protocol to help computers find stuff, not a platform. we can't control how people use it, and if we're not hosting any of the bad shit, it's not on us. but spam moderation is a problem any time that people can insert content you did not request into your feed.
possibly this is where you could have something like Mastodon instances, with their own moderation rules, but crucially, which don't host the content they aggregate. so instead of having 'an account on an instance', you have a stable address on the network, and you submit it to various directories so people can find you. by keeping each one limited in scale, it makes moderation more feasible. this is basically Reddit's model: you have topic-based hubs which people can subscribe to, and submit stuff to.
the other moderation issue is that there is no mechanism in this design to protect from mass harassment. if someone put you on the K*w*f*rms List of Degenerate Trannies To Suicidebait, there'd be fuck all you can do except refuse to receive contact from strangers. though... that's kind of already true of the internet as it stands. nobody has solved this problem.
to sum up
primarily static sites 'hosted' partly or fully on IPFS and BitTorrent
a protocol for sharing content you want to promote, similar to RSS, that you can aggregate into a 'feed'
directories you can submit posts to which handle their own moderation
no ads, nobody makes money off this
honestly, the biggest problem with all this is mostly just... getting it going in the first place. because let's be real, who but tech nerds is going to use a system that requires you to understand fuckin IPFS? until it's already up and running, this idea's got about as much hope as getting people to sign each others' GPG keys. it would have to have the sharp edges sanded down, so it's as easy to get on the Hypothetical Decentralised Social Network Protocol Stack as it is to register an account on tumblr.
but running over it like this... I don't think it's actually impossible in principle. a lot of the technical hurdles have already been solved. and that's what I want the Next Place to look like.
245 notes
·
View notes
Text
I made a Minecraft mod! It adds kiwi birds.

This is a mod I made as a moving present for a friend who went to live in New Zealand last year. I finally decided to polish it up and release it to the public. It is inspired by the Cute Kiwi Birds mod by Lordloss_ which hasn't been updated since 1.16. All code and assets are original.
FEATURES
Kiwi birds spawn in most forest biomes.
They will occasionally dig for items, including seeds, berries, and sometimes nuggets of iron and gold, according to a loot table that can be configured using a data pack.
They can be bred with seeds, and they lay eggs which work the same way as chicken eggs.
If you slay a kiwi bird (you monster) they will drop kiwifruit which can be eaten or crafted into delicious pavlova.
Just like real life, kiwi birds are vulnerable to invasive predators. Don't let your pet cats get too close!
NOTES
This mod requires Forge for Minecraft 1.20.1.
You have permission to use this mod in mod packs. Refer to the license for other questions about distribution.
The source code and issue tracker are available on Github.
DOWNLOAD LINK
It's also available via the CurseForge app, and awaiting moderator approval on Modrinth.
364 notes
·
View notes
Text
For context, I have been using Firefox since I made my first Myspace theme in 2005. I don't know how many times I can post this but I'm just so fucking sick of Firefox, and particularly Mozilla. A company full of a bunch of 2012 political and social Tumblr activists that will do literally everything except make Firefox better. The degradation in performance over this last year in particular, the slow adoption of web standards (that they advocated for!! when websites don't work on firefox it's because devs don't want to deal with their workarounds!!!), the laughable developer experience, the constant firing of devs while throwing millions at random organizations throughout Africa and constant rebranding efforts, the sudden shift to pushing news (and therefore, ads) directly into the new tab page by default, the further push for AI in the browser...
To top it all off, they suddenly add a ToS out of nowhere (which has been the trend in annoying activist tech circles) that has the most absurd legalese speech ever that goes directly against the entire point of Firefox for decades. from: https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/about/legal/terms/firefox/ "When you upload or input information through Firefox, you hereby grant us a nonexclusive, royalty-free, worldwide license to use that information to help you navigate, experience, and interact with online content as you indicate with your use of Firefox." (something which the Mozilla team made a clarification on, by being extremely vague about what information means) from: https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/about/legal/acceptable-use/ "You may not use any of Mozilla’s services to … Upload, download, transmit, display, or grant access to content that includes graphic depictions of sexuality or violence,"
The second one you can make an argument that Mozilla services does not include Firefox, but things like sync or the VPN for example are - and more importantly it is VAGUE. On purpose I'd wager.
Which was already bad enough, but the icing on the cake is found on the Data Privacy FAQ, where it now says: from: https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/privacy/faq/ Mozilla doesn’t sell data about you (in the way that most people think about “selling data“), and we don’t buy data about you. Since we strive for transparency, and the LEGAL definition of “sale of data“ is extremely broad in some places, we’ve had to step back from making the definitive statements you know and love. from: https://github.com/mozilla/bedrock/ Combined with a new push to github, where it USED to clearly state: "Unlike other companies, we don't sell access to your data." "Does firefox sell your personal data? - Nope. Never have, never will. And we protect you from many advertisers who do." for those unaware of how github works, the lines with red backgrounds are removed. ----- The fucking camels back is breaking, and it's entirely because Mozilla is full of performative corporate hacks that don't understand the first thing about development in any capacity. Mozilla would rather put all their efforts into probably money laundering than they would to care about their primary product that not only generates them most of their money (from google, btw), but has most of their userbase. People go on and on about how the Firefox userbase is constantly dwindling and you don't have to look very far into it to understand why. Your marketshare is tanking because you fucking suck. The only people left using firefox are people with principles they believe in, and morons - sometimes I'm not sure which side I fall in with every fucking update they make. The ONLY benefit to still using firefox (especially as a dev tbh) is containers and ublock, and nothing else. Firefox itself has become a garbage product, ran by a completely garbage company that should not be trusted. At least Google admits they're fucking you while they're doing it. So where do I go from here? I'm not sure. Zen Browser is doing extremely good work and is a fork of the Firefox source, I'm going to start daily driving it more. With some luck, they will force Firefox to get back on the correct path but I doubt it. Brave exists too I guess. Ladybird is looking like it has a bright path ahead of it, ditching both Chromium AND Gecko (the engine powering Firefox) but it's in the early stages and not really ready for the average user. The future is not in Firefox. They've been too shitty for too long and they've only gotten worse with every month that passes. I need one of these projects to succeed so I can get off this piece of shit software.
#long post#mozilla#firefox#getting mad about a browser at 11am on a friday#honestly you'd think this got me all riled up but you know what actually did?#the way firefox renders gradients#fucking pisses me the fuck off#so much banding looking like a flash game from 2002 it's PATHETIC
13 notes
·
View notes
Text



Resources and study tips to get you in cyber forensics
Master post • Part1 • part2
let's get you prepped to be a cyber sleuth without spending any cash. Here’s the ultimate tips and resources.
Ps: you can't become one while doing these pointers but you can experience the vibe so you can finally find your career interest


### 1. **Digital Scavenger Hunts**
- **CTF Challenges (Capture The Flag)**: Dive into platforms like [CTFtime](https://ctftime.org/) where you can participate in cyber security challenges. It's like playing *Among Us* but with hackers—find the imposter in the code!
- **Hunt A Killer (Digitally)**: Create your own digital crime scenes. Ask friends to send you files (like images, PDFs) with hidden clues. Your job? Find the Easter eggs and solve the case.
### 2. **YouTube University**
- **Cyber Sleuth Tutorials**: Channels like *HackerSploit* and *The Cyber Mentor* have playlists covering digital forensics, cybersecurity, and more. Binge-watch them like your fave Netflix series, but here you're learning skills to catch bad guys.
- **Live Streams & Q&A**: Jump into live streams on platforms like Twitch where cybersecurity experts solve cases in real-time. Ask questions, get answers, and interact with the pros.
### 3. **Public Libraries & eBook Treasure Hunts**
- **Library eBooks**: Most libraries have eBooks or online resources on digital forensics. Check out titles like *"Hacking Exposed"* or *"Digital Forensics for Dummies"*. You might have to dig through the catalog, but think of it as your first case.
- **LinkedIn Learning via Library**: Some libraries offer free access to LinkedIn Learning. If you can snag that, you've got a goldmine of courses on cybersecurity and forensics.
### 4. **Virtual Study Groups**
- **Discord Servers**: Join cybersecurity and hacking communities on Discord. They often have study groups, challenges, and mentors ready to help out. It's like joining a digital Hogwarts for hackers.
- **Reddit Threads**: Subreddits like r/cybersecurity and r/hacking are packed with resources, advice, and study buddies. Post your questions, and you’ll get a whole thread of answers.
### 5. **DIY Labs at Home**
- **Build Your Own Lab**: Got an old PC or laptop? Turn it into a practice lab. Install virtual machines (VMware, VirtualBox) and play around with different operating systems and security tools. It’s like Minecraft but for hacking.
- **Log Your Own Activity**: Turn on logging on your own devices and then try to trace your own steps later. You’re basically spying on yourself—no NSA required.
### 6. **Community College & University Open Courses**
- **Free Audit Courses**: Many universities offer free auditing of cybersecurity courses through platforms like Coursera, edX, and even YouTube. No grades, no stress, just pure learning.
- **MOOCs**: Massive Open Online Courses often have free tiers. Try courses like "Introduction to Cyber Security" on platforms like FutureLearn or edX.
### 7. **Scour GitHub**
- **Open-Source Tools**: GitHub is full of open-source forensic tools and scripts. Clone some repositories and start tinkering with them. You’re basically getting your hands on the tools real investigators use.
- **Follow the Code**: Find projects related to digital forensics, follow the code, and see how they work. Contribute if you can—bonus points for boosting your resume.
### 8. **Local Meetups & Online Conferences**
- **Free Virtual Conferences**: Many cybersecurity conferences are virtual and some offer free access. DEF CON has a lot of free content, and you can find tons of talks on YouTube.
- **Hackathons**: Look for free entry hackathons—often universities or tech companies sponsor them. Compete, learn, and maybe even win some gear.
### 9. **DIY Challenges**
- **Create Your Own Scenarios**: Get a friend to simulate a hack or data breach. You try to solve it using whatever tools and resources you have. It's like escape rooms, but digital.
- **Pen & Paper Simulation**: Before diving into digital, try solving forensic puzzles on paper. Map out scenarios and solutions to get your brain wired like a detective.
### 10. **Stay Updated**
- **Podcasts & Blogs**: Tune into cybersecurity podcasts like *Darknet Diaries* or follow blogs like *Krebs on Security*. It’s like getting the tea on what’s happening in the cyber world.
### 11. **Free Software & Tools**
- **Autopsy**: Free digital forensics software that helps you analyze hard drives and mobile devices. Think of it as your magnifying glass for digital clues.
- **Wireshark**: A free tool to see what's happening on your network. Catch all the data packets like you're a digital fisherman.
### 12. **Online Forensics Communities**
- **Free Webinars & Workshops**: Join communities like the *SANS Institute* for free webinars. It's like attending a masterclass but from the comfort of your gaming chair.
- **LinkedIn Groups**: Join groups like *Digital Forensics & Incident Response (DFIR)*. Network with pros, get job tips, and stay in the loop with the latest trends.
### 13. **Practice Cases & Mock Trials**
- **Set Up Mock Trials**: Role-play with friends where one is the hacker, another the victim, and you’re the investigator. Recreate cases from famous cybercrimes to see how you'd solve them.
- **Case Studies**: Research and recreate famous digital forensic cases. What steps did the investigators take? How would you handle it differently?

There you have it—your roadmap to becoming a cyber sleuth without dropping a dime. You don't have time find your interest after paying pennies to different ppl and colleges. You can explore multiple things from comfort of your home only if you want to.

#light academia#study blog#academic validation#academic weapon#student life#study motivation#study with me#study#studyblr#studyblr community#masterpostjam#codeblr
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Compact Pi Compute Module Backpack 🍓🥧📸🎒
We used to stock a PiCam Module
that would plug into a Pi CM4 or CM5 - recently we went to restock it, but the vendor hasn't replied to our emails for many months. So, it could be a good time for us to design something that works similarly but with more capabilities. So we tasked Timon
with designing something for us - we just said, "Make the best thing ya can," and he delivered! Check this board out that plugs onto the compute module and provides many great accessories: USB connection for bootloading/USB gadget, USB 3.0 host type A for CM5, micro HDMI, micro SD card for data storage on 'Lite modules, camera connection, and mount, two DSI connectors, fan connect, Stemma QT / Qwiic connection, and RTC battery. There's one shutdown button for CM5 and two GPIO buttons plus one LED. Timon's gonna try to add an EYESPI connector for our next rendering so we can get some I2C/SPI/PWM outputs easily. What do you think? We wanted to keep it compact and not too pricey (aiming for <$30 cost. We'll see if we can get it there) but were able to craft fairly complex projects in a small space.
#raspberrypi#computeModule#electronics#maker#hardware#embedded#engineering#diy#tech#innovation#pcbdesign#usb3#microsd#hdmi#camera#stemmaqt#qwiic#gpio#fan#rtc#devboard#prototyping#opensource#electronicsdesign#robotics#automation#coding#hobbyelectronics#hackerspace#geekstuff
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
Since Russian troops invaded Ukraine more than three years ago, Russian technology companies and executives have been widely sanctioned for supporting the Kremlin. That includes Vladimir Kiriyenko, the son of one of Vladimir Putin’s top aides and the CEO of VK Group, which runs VK, Russia’s Facebook equivalent that has increasingly shifted towards the regime’s repressive positioning.
Now cybersecurity researchers are warning that a widely used piece of open source code—which is linked to Kiriyenko’s company and managed by Russian developers—may pose a “persistent” national security risk to the United States. The open source software (OSS), called easyjson, has been widely used by the US Department of Defense and “extensively” across software used in the finance, technology, and healthcare sectors, say researchers at security company Hunted Labs, which is behind the claims. The fear is that Russia could alter easyjson to steal data or otherwise be abused.
“You have this really critical package that’s basically a linchpin for the cloud native ecosystem, that’s maintained by a group of individuals based in Moscow belonging to an organization that has this suspicious history,” says Hayden Smith, a cofounder at Hunted Labs.
For decades, open source software has underpinned large swathes of the technology industry and the systems people rely on day to day. Open source technology allows anyone to see and modify code, helping to make improvements, detect security vulnerabilities, and apply independent scrutiny that’s absent from the closed tech of corporate giants. However, the fracturing of geopolitical norms and the specter of stealthy supply chain attacks has led to an increase in questions about risk levels of "foreign" code.
Easyjson is a code serialization tool for the Go programming language and is often used across the wider cloud ecosystem, being present in other open source software, according to Hunted Labs. The package is hosted on GitHub by a MailRu account, which is owned by VK after the mail company rebranded itself in 2021. The VK Group itself is not sanctioned. Easyjson has been available on Github since 2016, with most of its updates coming before 2020. Kiriyenko became the CEO of VK Group in December 2021 and was sanctioned in February 2022.
Hunted Labs’ analysis shared with WIRED shows the most active developers on the project in recent years have listed themselves as being based in Moscow. Smith says that Hunted Labs has not identified vulnerabilities in the easyjson code.
However, the link to the sanctioned CEO’s company, plus Russia’s aggressive state-backed cyberattacks, may increase potential risks, Smith says. Research from Hunted Labs details how code serialization tools could be abused by malicious hackers. “A Russian-controlled software package could be used as a ‘sleeper cell’ to cause serious harm to critical US infrastructure or for espionage and weaponized influence campaigns,” it says.
“Nation states take on a strategic positioning,” says George Barnes, a former deputy director at the National Security Agency, who spent 36 years at the NSA and now acts as a senior advisor and investor in Hunted Labs. Barnes says that hackers within Russia’s intelligence agencies could see easyjson as a potential opportunity for abuse in the future.
“It is totally efficient code. There’s no known vulnerability about it, hence no other company has identified anything wrong with it,” Barnes says. “Yet the people who actually own it are under the guise of VK, which is tight with the Kremlin,” he says. “If I’m sitting there in the GRU or the FSB and I’m looking at the laundry list of opportunities… this is perfect. It’s just lying there,” Barnes says, referencing Russia’s foreign military and domestic security agencies.
VK Group did not respond to WIRED’s request for comment about easyjson. The US Department of Defense did not respond to a request for comment about the inclusion of easyjson in its software setup.
“NSA does not have a comment to make on this specific software,” a spokesperson for the National Security Agency says. “The NSA Cybersecurity Collaboration Center does welcome tips from the private sector—when a tip is received, NSA triages the tip against our own insights to fully understand the threat and, if corroborated, share any relevant mitigations with the community.” A spokesperson for the US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, which has faced upheaval under the second Trump administration, says: “We are going to refer you back to Hunted Labs.”
GitHub, a code repository owned by Microsoft, says that while it will investigate issues and take action where its policies are broken, it is not aware of malicious code in easyjson and VK is not sanctioned itself. Other tech companies’ treatment of VK varies. After Britain sanctioned the leaders of Russian banks who own stakes in VK in September 2022, for example, Apple removed its social media app from its App Store.
Dan Lorenc, the CEO of supply chain security firm Chainguard, says that with easyjson, the connections to Russia are in “plain sight” and that there is a “slightly higher” cybersecurity risk than those of other software libraries. He adds that the red flags around other open source technology may not be so obvious.
“In the overall open source space, you don’t necessarily even know where people are most of the time,” Lorenc says, pointing out that many developers do not disclose their identity or locations online, and even if they do, it is not always possible to verify the details are correct. “The code is what we have to trust and the code and the systems that are used to build that code. People are important, but we’re just not in a world where we can push the trust down to the individuals,” Lorenc says.
As Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine has unfolded, there has been increased scrutiny on the use of open source systems and the impact of sanctions upon entities involved in the development. In October last year, a Linux kernel maintainer removed 11 Russian developers who were involved in the open souce project, broadly citing sanctions as the reason for the change. Then in January this year, the Linux Foundation issued guidance covering how international sanctions can impact open source, saying developers should be cautious of who they interact with and the nature of interactions.
The shift in perceived risk is coupled with the threat of supply chain attacks. Last year, corporate developers and the open source world were rocked as a mysterious attacker known as Jia Tan stealthily installed a backdoor in the widely used XZ Utils software, after spending two years diligently updating it without any signs of trouble. The backdoor was only discovered by chance.
“Years ago, OSS was developed by small groups of trusted developers who were known to one another,” says Nancy Mead, a fellow of the Carnegie Mellon University Software Engineering Institute. “In that time frame, no one expected a trusted developer of being a hacker, and the relatively slower pace provided time for review. These days, with automatic release, incorporation of updates, and the wide usage of OSS, the old assumptions are no longer valid.”
Scott Hissam, a senior member of technical staff also from the Carnegie Software Engineering Institute, says there can often be consideration about how many maintainers and the number of organizations that work on an open source project, but there is currently not a “mass movement” to consider other details about OSS projects. “However, it is coming, and there are several activities that collect details about OSS projects, which OSS consumers can use to get more insight into OSS projects and their activities,” Hissam says, pointing to two examples.
Hunted Lab’s Smith says he is currently looking into the provenance of other open source projects and the risks that could come with them, including scrutinizing countries known to have carried out cyberattacks against US entities. He says he is not encouraging people to avoid open source software at all, more that risk considerations have shifted over time. “We’re telling you to just make really good risk informed decisions when you're trying to use open source,” he says. “Open source software is basically good until it's not.”
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Brave Software launched Cookiecrumbler, an open-source tool (April 2025) that detects and neutralizes deceptive cookie consent pop-ups using AI, preserving privacy while maintaining site functionality.
The tool scans websites via proxies, uses open-source LLMs to classify cookie banners, and suggests precise blocking rules—avoiding invasive tracking or site breakage.
Detected pop-ups undergo human review to minimize errors, with findings published on GitHub for collaborative refinement by developers and ad-blockers.
Unlike traditional blockers (which risk breaking sites), Cookiecrumbler tailors rules per website and processes data on Brave’s backend—never on users’ devices.
The tool exposes the failure of GDPR-like regulations to enforce true consent, offering a stopgap until stronger legal accountability emerges. It signifies a shift toward usable privacy.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
pulling out a section from this post (a very basic breakdown of generative AI) for easier reading;
AO3 and Generative AI
There are unfortunately some massive misunderstandings in regards to AO3 being included in LLM training datasets. This post was semi-prompted by the ‘Knot in my name’ AO3 tag (for those of you who haven’t heard of it, it’s supposed to be a fandom anti-AI event where AO3 writers help “further pollute” AI with Omegaverse), so let’s take a moment to address AO3 in conjunction with AI. We’ll start with the biggest misconception:
1. AO3 wasn’t used to train generative AI.
Or at least not anymore than any other internet website. AO3 was not deliberately scraped to be used as LLM training data.
The AO3 moderators found traces of the Common Crawl web worm in their servers. The Common Crawl is an open data repository of raw web page data, metadata extracts and text extracts collected from 10+ years of web crawling. Its collective data is measured in petabytes. (As a note, it also only features samples of the available pages on a given domain in its datasets, because its data is freely released under fair use and this is part of how they navigate copyright.) LLM developers use it and similar web crawls like Google’s C4 to bulk up the overall amount of pre-training data.
AO3 is big to an individual user, but it’s actually a small website when it comes to the amount of data used to pre-train LLMs. It’s also just a bad candidate for training data. As a comparison example, Wikipedia is often used as high quality training data because it’s a knowledge corpus and its moderators put a lot of work into maintaining a consistent quality across its web pages. AO3 is just a repository for all fanfic -- it doesn’t have any of that quality maintenance nor any knowledge density. Just in terms of practicality, even if people could get around the copyright issues, the sheer amount of work that would go into curating and labeling AO3’s data (or even a part of it) to make it useful for the fine-tuning stages most likely outstrips any potential usage.
Speaking of copyright, AO3 is a terrible candidate for training data just based on that. Even if people (incorrectly) think fanfic doesn’t hold copyright, there are plenty of books and texts that are public domain that can be found in online libraries that make for much better training data (or rather, there is a higher consistency in quality for them that would make them more appealing than fic for people specifically targeting written story data). And for any scrapers who don’t care about legalities or copyright, they’re going to target published works instead. Meta is in fact currently getting sued for including published books from a shadow library in its training data (note, this case is not in regards to any copyrighted material that might’ve been caught in the Common Crawl data, its regarding a book repository of published books that was scraped specifically to bring in some higher quality data for the first training stage). In a similar case, there’s an anonymous group suing Microsoft, GitHub, and OpenAI for training their LLMs on open source code.
Getting back to my point, AO3 is just not desirable training data. It’s not big enough to be worth scraping for pre-training data, it’s not curated enough to be considered for high quality data, and its data comes with copyright issues to boot. If LLM creators are saying there was no active pursuit in using AO3 to train generative AI, then there was (99% likelihood) no active pursuit in using AO3 to train generative AI.
AO3 has some preventative measures against being included in future Common Crawl datasets, which may or may not work, but there’s no way to remove any previously scraped data from that data corpus. And as a note for anyone locking their AO3 fics: that might potentially help against future AO3 scrapes, but it is rather moot if you post the same fic in full to other platforms like ffn, twitter, tumblr, etc. that have zero preventative measures against data scraping.
2. A/B/O is not polluting generative AI
…I’m going to be real, I have no idea what people expected to prove by asking AI to write Omegaverse fic. At the very least, people know A/B/O fics are not exclusive to AO3, right? The genre isn’t even exclusive to fandom -- it started in fandom, sure, but it expanded to general erotica years ago. It’s all over social media. It has multiple Wikipedia pages.
More to the point though, omegaverse would only be “polluting” AI if LLMs were spewing omegaverse concepts unprompted or like…associated knots with dicks more than rope or something. But people asking AI to write omegaverse and AI then writing omegaverse for them is just AI giving people exactly what they asked for. And…I hate to point this out, but LLMs writing for a niche the LLM trainers didn’t deliberately train the LLMs on is generally considered to be a good thing to the people who develop LLMs. The capability to fill niches developers didn’t even know existed increases LLMs’ marketability. If I were a betting man, what fandom probably saw as a GOTCHA moment, AI people probably saw as a good sign of LLMs’ future potential.
3. Individuals cannot affect LLM training datasets.
So back to the fandom event, with the stated goal of sabotaging AI scrapers via omegaverse fic.
…It’s not going to do anything.
Let’s add some numbers to this to help put things into perspective:
LLaMA’s 65 billion parameter model was trained on 1.4 trillion tokens. Of that 1.4 trillion tokens, about 67% of the training data was from the Common Crawl (roughly ~3 terabytes of data).
3 terabytes is 3,000,000,000 kilobytes.
That’s 3 billion kilobytes.
According to a news article I saw, there has been ~450k words total published for this campaign (*this was while it was going on, that number has probably changed, but you’re about to see why that still doesn’t matter). So, roughly speaking, ~450k of text is ~1012 KB (I’m going off the document size of a plain text doc for a fic whose word count is ~440k).
So 1,012 out of 3,000,000,000.
Aka 0.000034%.
And that 0.000034% of 3 billion kilobytes is only 2/3s of the data for the first stage of training.
And not to beat a dead horse, but 0.000034% is still grossly overestimating the potential impact of posting A/B/O fic. Remember, only parts of AO3 would get scraped for Common Crawl datasets. Which are also huge! The October 2022 Common Crawl dataset is 380 tebibytes. The April 2021 dataset is 320 tebibytes. The 3 terabytes of Common Crawl data used to train LLaMA was randomly selected data that totaled to less than 1% of one full dataset. Not to mention, LLaMA’s training dataset is currently on the (much) larger size as compared to most LLM training datasets.
I also feel the need to point out again that AO3 is trying to prevent any Common Crawl scraping in the future, which would include protection for these new stories (several of which are also locked!).
Omegaverse just isn’t going to do anything to AI. Individual fics are going to do even less. Even if all of AO3 suddenly became omegaverse, it’s just not prominent enough to influence anything in regards to LLMs. You cannot affect training datasets in any meaningful way doing this. And while this might seem really disappointing, this is actually a good thing.
Remember that anything an individual can do to LLMs, the person you hate most can do the same. If it were possible for fandom to corrupt AI with omegaverse, fascists, bigots, and just straight up internet trolls could pollute it with hate speech and worse. AI already carries a lot of biases even while developers are actively trying to flatten that out, it’s good that organized groups can’t corrupt that deliberately.
#generative ai#pulling this out wasnt really prompted by anything specific#so much as heard some repeated misconceptions and just#sighs#nope#incorrect#u got it wrong#sorry#unfortunately for me: no consistent tag to block#sigh#ao3
101 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ive been going down a rabbit hole of open source robotics and really want to build a 6 axis arm just so I can stick a dildo on the end of it.
On a tangential project, there's a control mechanism that can be theoretically used to control each axis of the arm by using a contraption that looks the same, but has encoders instead of motors for each joint. By moving the end of the arm on the controller, I can move the arm of the robot.
SO, what does this mean? I could hook a fleshlight up to one unit and the dildo up to the other, and experience some odd mechanized sensation of fucking myself in either direction.
That got me thinking about gathering data about how I fuck myself. I could hook up some electrodes and analyze physical response tagged vocally while I use robots to masturbate. I could then analyze the data, pull out movement sequences that I really like, then build a second arm to join the first. With the data I could just sit back and have some automated gooning.
BUT Wait, there's more! With that kind of automation, I could either rig up the program to a model in unreal and fuck a character in VR, or I could add trackers to the physical robots and have the assets rigged to the trackers and if I decide to take manual control, the scene would be dynamic (of course I could close loop my motors and pull that data but that get into a different realm of expense plus a big redesign). Maybe an existing dev would be willing to add trackable characters if I could sell them on gonners wanting to track dolls. Hmmmm...
These aren't even sexy androids, they are automation hardware that I'm trying to use to turn myself into a cum factory. My brain broke. Anyhow, just thought I'd share my day browsing github and Ali express while actively resisting the urge to buy the gyno chair for sale on govdeals.com.
26 notes
·
View notes