#slavery economics
Text
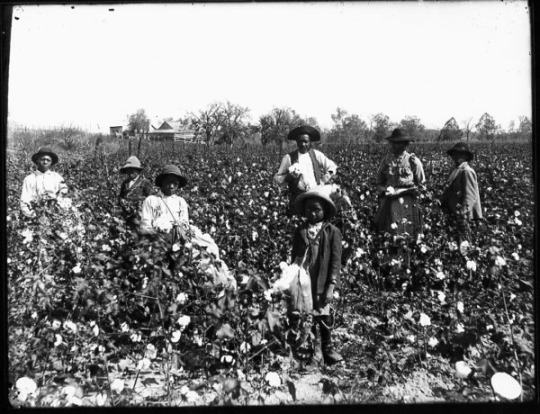

The enslavement of African people in the Americas by the nations and peoples of Western Europe, created the economic engine that funded modern capitalism. Therefore it comes as no surprise that most of the major corporations that were founded by Western European and American merchants prior to roughly 100 years ago, benefited directly from slavery.

Lehman Brothers, whose business empire started in the slave trade, recently admitted their part in the business of slavery.
According to the Sun Times, the now-defunct financial services firm acknowledged that its founding partners owned not one, but several enslaved Africans during the Civil War era and that, “in all likelihood,” it “profited significantly” from slavery.
“This is a sad part of our heritage …We’re deeply apologetic … It was a terrible thing … There’s no one sitting in the United States in the year 2005, hopefully, who would ever, in a million years, defend the practice,” said Joe Polizzotto, general counsel of Lehman Brothers.
Aetna, Inc., the United States’ largest health insurer, apologized for selling policies in the 1850s that reimbursed slave owners for financial losses when the enslaved Africans they owned died.
“Aetna has long acknowledged that for several years shortly after its founding in 1853 that the company may have insured the lives of slaves,” said Aetna spokesman Fred Laberge in 2002. “We express our deep regret over any participation at all in this deplorable practice.”

“Today, we are reporting that this research found that, between 1831 and 1865, two of our predecessor banks — Citizens Bank and Canal Bank in Louisiana — accepted approximately 13,000 enslaved individuals as collateral on loans and took ownership of approximately 1,250 of them when the plantation owners defaulted on the loans,” the company wrote in a statement.
New York Life Insurance Company is the largest mutual life insurance company in the United States. They also took part in slavery by selling insurance policies on enslaved Africans.
According to USA Today, evidence of 10 more New York Life slave policies comes from an 1847 account book kept by the company’s Natchez, Miss., agent, W.A. Britton. The book, part of a collection at Louisiana State University, contains Britton’s notes on slave policies he wrote for amounts ranging from $375 to $600. A 1906 history of New York Life says 339 of the company’s first 1,000 policies were written on the lives of slaves.

USA Today reported that Wachovia Corporation (now owned by Wells Fargo) has apologized for its ties to slavery after disclosing that two of its historical predecessors owned enslaved Africans and accepted them as payment.
“On behalf of Wachovia Corporation, I apologize to all Americans, and especially to African-Americans and people of African descent,” said Ken Thompson, Wachovia chairman and chief executive officer, in the statement. “We are deeply saddened by these findings.”

N M Rothschild & Sons Bank in London was linked to slavery. The company that was one of the biggest names in the City of London had previously undisclosed links to slavery in the British colonies. Documents seen by the Financial Times have revealed that Nathan Mayer Rothschild, the banking family’s 19th-century patriarch, made personal gains by using enslaved Africans as collateral in dealings with a slave owner.
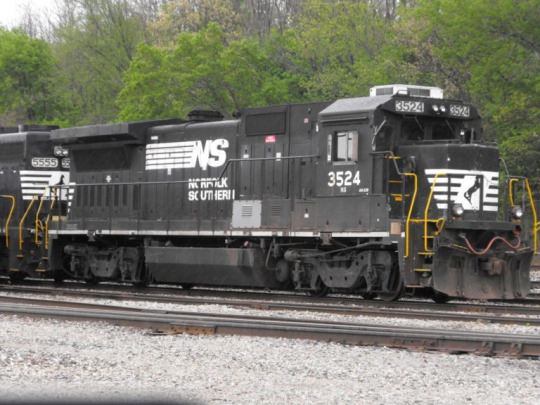

Norfolk Southern also has a history in the slave trade. The Mobile & Girard company, which is now part of Norfolk Southern, offered slaveholders $180 ($3,379 today) apiece for enslaved Africans they would rent to the railroad for one year, according to the records. The Central of Georgia, another company aligned with Norfolk Southern line today, valued its slaves at $31,303 ($663,033 today) on record.
USA Today has found that their own parent company, E.W. Scripps and Gannett, has had links to the slave trade.

According to reports, FleetBoston evolved from an earlier financial institution, Providence Bank, founded by a John Brown, who was a slave trader and owned ships used to transport enslaved Africans.
The bank financed Brown’s slave voyages and profited from them. Brown even reportedly helped charter what became Brown University.

CSX used slave labor to construct portions of some U.S. rail lines under the political and legal system that was in place more than a century ago.
Two enslaved Africans whom the company rented were identified as John Henry and Reuben. The record states, “they were to be returned clothed when they arrived to work for the company.”
Individual enslaved Africans cost up to $200 — the equivalent of $3,800 today — to rent for a season and CSX took full advantage.

Brown Brothers Harriman is the oldest and largest private investment bank and securities firm in the United States, founded in 1818. USA Todayfound that the New York merchant bank of James and William Brown, currently known as Brown Bros. Harriman owned hundreds of enslaved Africans and financed the cotton economy by lending millions to southern planters, merchants and cotton brokers.

USA Today reported that New York-based AIG completed the purchase of American General Financial Group, a Houston-based insurer that owns U.S. Life Insurance Company. A U.S. Life policy on an enslaved African living in Kentucky was reprinted in a 1935 article about slave insurance in The American Conservationist magazine.
AIG says it has “found documentation indicating” U.S. Life insured enslaved Africans.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text

Beron Vanserra is a capitalist first, Fae second
#if i had a nickel for every fanfic that has made me enjoy beron vanserra#the man sees the economical downsides of slavery and went “nope not doing this. time to fight for humanity rights”#he doesn't care if people are queer or women or whatever#he just wants benefits#beron vanserra#acotar#autumn court#s
158 notes
·
View notes
Link
The WE's agenda becomes clearer and clearer as time goes on.
#wef#world economic forum#slavery#one world government#globalists#bill gates#joe biden#fjb#jfk jr#green new deal
238 notes
·
View notes
Text
The fighting was over in Ephebe. It hadn't lasted long, especially when the slaves joined in. There were too many narrow streets, too many ambushes and, above all, too much terrible determination. It's generally held that free men will always triumph over slaves, but perhaps it all depends on your point of view.
Besides, the Ephebian garrison commander had declared somewhat nervously that slavery would henceforth be abolished, which infuriated the slaves. What would be the point of saving up to become free if you couldn't own slaves afterwards? Besides, how'd they eat?
The Omnians couldn't understand, and uncertain people fight badly.
Terry Pratchett, Small Gods
#ephebians#omnians#small gods#discworld#terry pratchett#war#crusade#tactics#urban warfare#familiarity#cultural differences#determination#slavery#freedom#economics#perspective#dignity#uncertainty#depends on your point of view#terrible determination
55 notes
·
View notes
Text

Survive the economy
#Survive the economy#economics#economy#poverty#homeless#company#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#eat the rich#eat the fucking rich#class war#slavery#wage slavery#slave wages#oppression#repression#anti capitalism#anti slavery#antiwork#fuck the gop#fuck the idf#fuck the police
67 notes
·
View notes
Text

#jt#jatavia#black twitter#pan africanism#slavery#pro black#juneteenth#black lives matter#black business#black musicians#black tumblr#self mastery#black entrepreneurship#black excellence#level up journey#black girl luxury#therapyforblackpeople#melanin#african american#black economics#black is beautiful#black moodboard#beatiful black women#moodboard#black literature#black education#black power#black people#black positivity#freedom
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
So we’re in a “selective recession” because wealthy people are still doing just fine? The vast majority of Americans are struggling to pay bills and working extra part-time jobs (or stringing together part-time gigs because they can’t find a full-time job), but it’s all OK because rich people can still afford luxury vacations? By this definition, the 1930’s were a “Selective Great Depression” because a few wealthy people were still out sailing their yachts. How stupid do they think we are? Who believes this propaganda?
#save america#leadership#biden economy#economic collapse#bidenomics#bidenflation#debt slavery#americans are angry#Americans are fed up#propaganda#official lies
43 notes
·
View notes
Text

Slavery was never ended, it was only expanded.
🔥 Fuel Our Work: https://bit.ly/TFTPSubs
🎙 TFTP Podcast: https://bit.ly/TFTPPodcast
#TheFreeThoughtProject #TFTP
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
Alabama Is Generating Billions by Trapping People in Prison
youtube
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
#anti capitalism#leftism#communism#socialism#anarchy#communists#communist#twitter post#fudgepacker#trumphater#libturds#obama#liberals#liberal#leftists#conservatives#republicans#progressives#gop#economics#capitalism#poverty#twitter x#wage slavery#late stage capitalism#debt
29 notes
·
View notes
Text

F.2.2 Do “libertarian”-capitalists support slavery?
Yes. It may come as a surprise to many people, but right-“Libertarianism” is one of the few political theories that justifies slavery. For example, Robert Nozick asks whether “a free system would allow [the individual] to sell himself into slavery” and he answers “I believe that it would.” [Anarchy, State and Utopia, p. 371] While some right-“libertarians” do not agree with Nozick, there is no logical basis in their ideology for such disagreement.
This can be seen from “anarcho”-capitalist Walter Block, who, like Nozick, supports voluntary slavery. As he puts it, “if I own something, I can sell it (and should be allowed by law to do so). If I can’t sell, then, and to that extent, I really don’t own it.” Thus agreeing to sell yourself for a lifetime “is a bona fide contract” which, if “abrogated, theft occurs.” He critiques those other right-wing “libertarians” (like Murray Rothbard) who oppose voluntary slavery as being inconsistent to their principles. Block, in his words, seeks to make “a tiny adjustment” which “strengthens libertarianism by making it more internally consistent.” He argues that his position shows “that contract, predicated on private property [can] reach to the furthest realms of human interaction, even to voluntary slave contracts.” [“Towards a Libertarian Theory of Inalienability: A Critique of Rothbard, Barnett, Smith, Kinsella, Gordon, and Epstein,” pp. 39–85, Journal of Libertarian Studies, vol. 17, no. 2, p. 44, p. 48, p. 82 and p. 46]
So the logic is simple, you cannot really own something unless you can sell it. Self-ownership is one of the cornerstones of laissez-faire capitalist ideology. Therefore, since you own yourself you can sell yourself.
This defence of slavery should not come as a surprise to any one familiar with classical liberalism. An elitist ideology, its main rationale is to defend the liberty and power of property owners and justify unfree social relationships (such as government and wage labour) in terms of “consent.” Nozick and Block just takes it to its logical conclusion. This is because his position is not new but, as with so many other right-“libertarian” ones, can be found in John Locke’s work. The key difference is that Locke refused the term “slavery” and favoured “drudgery” as, for him, slavery mean a relationship “between a lawful conqueror and a captive” where the former has the power of life and death over the latter. Once a “compact” is agreed between them, “an agreement for a limited power on the one side, and obedience on the other … slavery ceases.” As long as the master could not kill the slave, then it was “drudgery.” Like Nozick, he acknowledges that “men did sell themselves; but, it is plain, this was only to drudgery, not to slavery: for, it is evident, the person sold was not under an absolute, arbitrary, despotical power: for the master could not have power to kill him, at any time, whom, at a certain time, he was obliged to let go free out of his service.” [Locke, Second Treatise of Government, Section 24] In other words, voluntary slavery was fine but just call it something else.
Not that Locke was bothered by involuntary slavery. He was heavily involved in the slave trade. He owned shares in the “Royal Africa Company” which carried on the slave trade for England, making a profit when he sold them. He also held a significant share in another slave company, the “Bahama Adventurers.” In the “Second Treatise”, Locke justified slavery in terms of “Captives taken in a just war,” a war waged against aggressors. [Section 85] That, of course, had nothing to do with the actual slavery Locke profited from (slave raids were common, for example). Nor did his “liberal” principles stop him suggesting a constitution that would ensure that “every freeman of Carolina shall have absolute power and authority over his Negro slaves.” The constitution itself was typically autocratic and hierarchical, designed explicitly to “avoid erecting a numerous democracy.” [The Works of John Locke, vol. X, p. 196]
So the notion of contractual slavery has a long history within right-wing liberalism, although most refuse to call it by that name. It is of course simply embarrassment that stops many right-“libertarians” calling a spade a spade. They incorrectly assume that slavery has to be involuntary. In fact, historically, voluntary slave contracts have been common (David Ellerman’s Property and Contract in Economics has an excellent overview). Any new form of voluntary slavery would be a “civilised” form of slavery and could occur when an individual would “agree” to sell their lifetime’s labour to another (as when a starving worker would “agree” to become a slave in return for food). In addition, the contract would be able to be broken under certain conditions (perhaps in return for breaking the contract, the former slave would have pay damages to his or her master for the labour their master would lose — a sizeable amount no doubt and such a payment could result in debt slavery, which is the most common form of “civilised” slavery. Such damages may be agreed in the contract as a “performance bond” or “conditional exchange.”
In summary, right-“libertarians” are talking about “civilised” slavery (or, in other words, civil slavery) and not forced slavery. While some may have reservations about calling it slavery, they agree with the basic concept that since people own themselves they can sell themselves, that is sell their labour for a lifetime rather than piecemeal.
We must stress that this is no academic debate. “Voluntary” slavery has been a problem in many societies and still exists in many countries today (particularly third world ones where bonded labour — i.e. where debt is used to enslave people — is the most common form). With the rise of sweat shops and child labour in many “developed” countries such as the USA, “voluntary” slavery (perhaps via debt and bonded labour) may become common in all parts of the world — an ironic (if not surprising) result of “freeing” the market and being indifferent to the actual freedom of those within it.
Some right-“libertarians” are obviously uneasy with the logical conclusion of their definition of freedom. Murray Rothbard, for example, stressed the “unenforceability, in libertarian theory, of voluntary slave contracts.” Of course, other “libertarian” theorists claim the exact opposite, so “libertarian theory” makes no such claim, but never mind! Essentially, his objection revolves around the assertion that a person “cannot, in nature, sell himself into slavery and have this sale enforced — for this would mean that his future will over his own body was being surrendered in advance” and that if a “labourer remains totally subservient to his master’s will voluntarily, he is not yet a slave since his submission is voluntary.” However, as we noted in section F.2, Rothbard emphasis on quitting fails to recognise the actual denial of will and control over ones own body that is explicit in wage labour. It is this failure that pro-slave contract “libertarians” stress — they consider the slave contract as an extended wage contract. Moreover, a modern slave contract would likely take the form of a “performance bond,” on which Rothbard laments about its “unfortunate suppression” by the state. In such a system, the slave could agree to perform X years labour or pay their master substantial damages if they fail to do so. It is the threat of damages that enforces the contract and such a “contract” Rothbard does agree is enforceable. Another means of creating slave contracts would be “conditional exchange” which Rothbard also supports. As for debt bondage, that too, seems acceptable. He surreally notes that paying damages and debts in such contracts is fine as “money, of course, is alienable” and so forgets that it needs to be earned by labour which, he asserts, is not alienable! [The Ethics of Liberty, pp. 134–135, p. 40, pp. 136–9, p. 141 and p. 138]
It should be noted that the slavery contract cannot be null and void because it is unenforceable, as Rothbard suggests. This is because the doctrine of specific performance applies to all contracts, not just to labour contracts. This is because all contracts specify some future performance. In the case of the lifetime labour contract, then it can be broken as long as the slave pays any appropriate damages. As Rothbard puts it elsewhere, “if A has agreed to work for life for B in exchange for 10,000 grams of gold, he will have to return the proportionate amount of property if he terminates the arrangement and ceases to work.” [Man, Economy, and State, vol. I , p. 441] This is understandable, as the law generally allows material damages for breached contracts, as does Rothbard in his support for the “performance bond” and “conditional exchange.” Needless to say, having to pay such damages (either as a lump sum or over a period of time) could turn the worker into the most common type of modern slave, the debt-slave.
And it is interesting to note that even Murray Rothbard is not against the selling of humans. He argued that children are the property of their parents who can (bar actually murdering them by violence) do whatever they please with them, even sell them on a “flourishing free child market.” [The Ethics of Liberty, p. 102] Combined with a whole hearted support for child labour (after all, the child can leave its parents if it objects to working for them) such a “free child market” could easily become a “child slave market” — with entrepreneurs making a healthy profit selling infants and children or their labour to capitalists (as did occur in 19th century Britain). Unsurprisingly, Rothbard ignores the possible nasty aspects of such a market in human flesh (such as children being sold to work in factories, homes and brothels). But this is besides the point.
Of course, this theoretical justification for slavery at the heart of an ideology calling itself “libertarianism” is hard for many right-“libertarians” to accept and so they argue that such contracts would be very hard to enforce. This attempt to get out of the contradiction fails simply because it ignores the nature of the capitalist market. If there is a demand for slave contracts to be enforced, then companies will develop to provide that “service” (and it would be interesting to see how two “protection” firms, one defending slave contracts and another not, could compromise and reach a peaceful agreement over whether slave contracts were valid). Thus we could see a so-called “free” society producing companies whose specific purpose was to hunt down escaped slaves (i.e. individuals in slave contracts who have not paid damages to their owners for freedom). Of course, perhaps Rothbard would claim that such slave contracts would be “outlawed” under his “general libertarian law code” but this is a denial of market “freedom”. If slave contracts are “banned” then surely this is paternalism, stopping individuals from contracting out their “labour services” to whom and however long they “desire”. You cannot have it both ways.
So, ironically, an ideology proclaiming itself to support “liberty” ends up justifying and defending slavery. Indeed, for the right-“libertarian” the slave contract is an exemplification, not the denial, of the individual’s liberty! How is this possible? How can slavery be supported as an expression of liberty? Simple, right-“libertarian” support for slavery is a symptom of a deeper authoritarianism, namely their uncritical acceptance of contract theory. The central claim of contract theory is that contract is the means to secure and enhance individual freedom. Slavery is the antithesis to freedom and so, in theory, contract and slavery must be mutually exclusive. However, as indicated above, some contract theorists (past and present) have included slave contracts among legitimate contracts. This suggests that contract theory cannot provide the theoretical support needed to secure and enhance individual freedom.
As Carole Pateman argues, “contract theory is primarily about a way of creating social relations constituted by subordination, not about exchange.” Rather than undermining subordination, contract theorists justify modern subjection — “contract doctrine has proclaimed that subjection to a master — a boss, a husband — is freedom.” [The Sexual Contract, p. 40 and p. 146] The question central to contract theory (and so right-Libertarianism) is not “are people free” (as one would expect) but “are people free to subordinate themselves in any manner they please.” A radically different question and one only fitting to someone who does not know what liberty means.
Anarchists argue that not all contracts are legitimate and no free individual can make a contract that denies his or her own freedom. If an individual is able to express themselves by making free agreements then those free agreements must also be based upon freedom internally as well. Any agreement that creates domination or hierarchy negates the assumptions underlying the agreement and makes itself null and void. In other words, voluntary government is still government and a defining characteristic of an anarchy must be, surely, “no government” and “no rulers.”
This is most easily seen in the extreme case of the slave contract. John Stuart Mill stated that such a contract would be “null and void.” He argued that an individual may voluntarily choose to enter such a contract but in so doing “he abdicates his liberty; he foregoes any future use of it beyond that single act. He therefore defeats, in his own case, the very purpose which is the justification of allowing him to dispose of himself…The principle of freedom cannot require that he should be free not to be free. It is not freedom, to be allowed to alienate his freedom.” He adds that “these reasons, the force of which is so conspicuous in this particular case, are evidently of far wider application.” [quoted by Pateman, Op. Cit., pp. 171–2]
And it is such an application that defenders of capitalism fear (Mill did in fact apply these reasons wider and unsurprisingly became a supporter of a market syndicalist form of socialism). If we reject slave contracts as illegitimate then, logically, we must also reject all contracts that express qualities similar to slavery (i.e. deny freedom) including wage slavery. Given that, as David Ellerman points out, “the voluntary slave … and the employee cannot in fact take their will out of their intentional actions so that they could be ‘employed’ by the master or employer” we are left with “the rather implausible assertion that a person can vacate his or her will for eight or so hours a day for weeks, months, or years on end but cannot do so for a working lifetime.” [Property and Contract in Economics, p. 58] This is Rothbard’s position.
The implications of supporting voluntary slavery is quite devastating for all forms of right-wing “libertarianism.” This was proven by Ellerman when he wrote an extremely robust defence of it under the pseudonym “J. Philmore” called The Libertarian Case for Slavery (first published in The Philosophical Forum, xiv, 1982). This classic rebuttal takes the form of “proof by contradiction” (or reductio ad absurdum) whereby he takes the arguments of right-libertarianism to their logical end and shows how they reach the memorably conclusion that the “time has come for liberal economic and political thinkers to stop dodging this issue and to critically re-examine their shared prejudices about certain voluntary social institutions … this critical process will inexorably drive liberalism to its only logical conclusion: libertarianism that finally lays the true moral foundation for economic and political slavery.” Ellerman shows how, from a right-“libertarian” perspective there is a “fundamental contradiction” in a modern liberal society for the state to prohibit slave contracts. He notes that there “seems to be a basic shared prejudice of liberalism that slavery is inherently involuntary, so the issue of genuinely voluntary slavery has received little scrutiny. The perfectly valid liberal argument that involuntary slavery is inherently unjust is thus taken to include voluntary slavery (in which case, the argument, by definition, does not apply). This has resulted in an abridgement of the freedom of contract in modern liberal society.” Thus it is possible to argue for a “civilised form of contractual slavery.” [“J. Philmore,”, Op. Cit.]
So accurate and logical was Ellerman’s article that many of its readers were convinced it was written by a right-“libertarian” (including, we have to say, us!). One such writer was Carole Pateman, who correctly noted that ”[t]here is a nice historical irony here. In the American South, slaves were emancipated and turned into wage labourers, and now American contractarians argue that all workers should have the opportunity to turn themselves into civil slaves.” [Op. Cit., p. 63]).
The aim of Ellerman’s article was to show the problems that employment (wage labour) presents for the concept of self-government and how contract need not result in social relationships based on freedom. As “Philmore” put it, ”[a]ny thorough and decisive critique of voluntary slavery or constitutional non-democratic government would carry over to the employment contract — which is the voluntary contractual basis for the free-market free-enterprise system. Such a critique would thus be a reductio ad absurdum.” As “contractual slavery” is an “extension of the employer-employee contract,” he shows that the difference between wage labour and slavery is the time scale rather than the principle or social relationships involved. [Op. Cit.] This explains why the early workers’ movement called capitalism “wage slavery” and why anarchists still do. It exposes the unfree nature of capitalism and the poverty of its vision of freedom. While it is possible to present wage labour as “freedom” due to its “consensual” nature, it becomes much harder to do so when talking about slavery or dictatorship (and let us not forget that Nozick also had no problem with autocracy — see section B.4). Then the contradictions are exposed for all to see and be horrified by.
All this does not mean that we must reject free agreement. Far from it! Free agreement is essential for a society based upon individual dignity and liberty. There are a variety of forms of free agreement and anarchists support those based upon co-operation and self-management (i.e. individuals working together as equals). Anarchists desire to create relationships which reflect (and so express) the liberty that is the basis of free agreement. Capitalism creates relationships that deny liberty. The opposition between autonomy and subjection can only be maintained by modifying or rejecting contract theory, something that capitalism cannot do and so the right-wing “libertarian” rejects autonomy in favour of subjection (and so rejects socialism in favour of capitalism).
So the real contrast between genuine libertarians and right-“libertarians” is best expressed in their respective opinions on slavery. Anarchism is based upon the individual whose individuality depends upon the maintenance of free relationships with other individuals. If individuals deny their capacities for self-government through a contract the individuals bring about a qualitative change in their relationship to others — freedom is turned into mastery and subordination. For the anarchist, slavery is thus the paradigm of what freedom is not, instead of an exemplification of what it is (as right-“libertarians” state). As Proudhon argued:
“If I were asked to answer the following question: What is slavery? and I should answer in one word, It is murder, my meaning would be understood at once. No extended argument would be required to show that the power to take from a man his thought, his will, his personality, is a power of life and death; and that to enslave a man is to kill him.” [What is Property?, p. 37]
In contrast, the right-“libertarian” effectively argues that “I support slavery because I believe in liberty.” It is a sad reflection of the ethical and intellectual bankruptcy of our society that such an “argument” is actually proposed by some people under the name of liberty. The concept of “slavery as freedom” is far too Orwellian to warrant a critique — we will leave it up to right-“libertarians” to corrupt our language and ethical standards with an attempt to prove it.
From the basic insight that slavery is the opposite of freedom, the anarchist rejection of authoritarian social relations quickly follows:
“Liberty is inviolable. I can neither sell nor alienate my liberty; every contract, every condition of a contract, which has in view the alienation or suspension of liberty, is null: the slave, when he plants his foot upon the soil of liberty, at that moment becomes a free man .. . Liberty is the original condition of man; to renounce liberty is to renounce the nature of man: after that, how could we perform the acts of man?” [P.J. Proudhon, Op. Cit., p. 67]
The employment contract (i.e. wage slavery) abrogates liberty. It is based upon inequality of power and “exploitation is a consequence of the fact that the sale of labour power entails the worker’s subordination.” [Carole Pateman, Op. Cit., p. 149] Hence Proudhon’s support for self-management and opposition to capitalism — any relationship that resembles slavery is illegitimate and no contract that creates a relationship of subordination is valid. Thus in a truly anarchistic society, slave contracts would be unenforceable — people in a truly free (i.e. non-capitalist) society would never tolerate such a horrible institution or consider it a valid agreement. If someone was silly enough to sign such a contract, they would simply have to say they now rejected it in order to be free — such contracts are made to be broken and without the force of a law system (and private defence firms) to back it up, such contracts will stay broken.
The right-“libertarian” support for slave contracts (and wage slavery) indicates that their ideology has little to do with liberty and far more to do with justifying property and the oppression and exploitation it produces. Their theoretical support for permanent and temporary voluntary slavery and autocracy indicates a deeper authoritarianism which negates their claims to be libertarians.
#libertarians#libertarianism#libertarian capitalism#slavery#faq#anarchy faq#revolution#anarchism#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#climate change#climate crisis#climate#ecology#anarchy works#environmentalism#environment#solarpunk
18 notes
·
View notes
Text

Most history books will tell you that slavery was abolished in 1865 when Abraham Lincoln and other leaders of the anti-slavery Republican Party formed the 13th Amendment stating that “neither slavery nor involuntary servitude… shall exist within the United States of America, or any place subject to their jurisdiction.” This was certainly a step in the right direction, however, it only led to a more creative way for oppressive regimes to use slavery in the States, which quite unbelievably is still going on to this day.
The American prison system is a huge business and allows many companies to use the labour (which is comprised mainly of black males) to increase their bottom line. Prison as a business is one of the largest and fastest-growing industries in the United States. As taken from- Prison Privatization: The Many Facets of a Controversial Industry:
Now prison labor based in private prisons is a multimillion-dollar industry with its own trade exhibitions, conventions, websites, and mail-order/Internet catalogs (Pelaez 2008). . . . The industry also has direct advertising campaigns, architecture companies, construction companies, investment houses on Wall Street, plumbing supply companies, food supply companies, armed security, and padded cell manufacturing, all of which rival those of any other private industry (Pelaez 2008). Furthermore, private prisoners at the state level produce a variety of goods and services, from clothing to toys to telemarketing and customer service (Erlich 2005). The private federal prison industry also produces nearly all military goods, from uniform helmet to ammunition, along with durable goods ranging from paint to office furniture (Pelaez 2008). (source)
If we look into the roots of the US prison system it become clear that it was born to continue the systematic use of slavery for profit under the guise of reform:
Prison labor has its roots in slavery. After the 1861-1865 Civil War, a system of “hiring out prisoners” was introduced in order to continue the slavery tradition. Freed slaves were charged with not carrying out their sharecropping commitments (cultivating someone else’s land in exchange for part of the harvest) or petty thievery – which were almost never proven – and were then “hired out” for cotton picking, working in mines and building railroads. From 1870 until 1910 in the state of Georgia, 88% of hired-out convicts were Black. In Alabama, 93% of “hired-out” miners were Black. In Mississippi, a huge prison farm similar to the old slave plantations replaced the system of hiring out convicts. The notorious Parchman plantation existed until 1972.(source)
This may seem like something that sits in the dark past of American history, however, this is far from the truth. Today there are still many well known corporations using modern day slavery to profit. This list of 7 companies that are profiting from modern day slavery in America was compiled by Arjun Walia from Collective Evolution:
Whole Foods
The state allows inmates to work for the profit of a private corporation, and Whole Foods is one of many companies that takes advantage, buying fish and cheese produced by prison inmates and paying them a rate of .74 cents a day. They then increase the price of the product astronomically – tilapia raised by inmates, for example, sells for $11.99 a pound at Whole Foods — and enjoy all the profits. (source)
McDonalds
It’s no secret that McDonalds is suffering right now; in a world where people are steadily waking up and moving towards a healthier lifestyle, there is no place for such heavily processed and unethical ‘food.’ Yet despite being the world’s most successful fast-food chain, they still source many of their goods from prisons, including their containers, uniforms, and cutlery. The inmates who sew the uniforms hardly make anything. (source)
Wal-Mart
Although their company policy expressly outlines that forced labor, as well as prison labour, is unacceptable, a large portion of products sold in their stores have been supplied by third-party prison labor factories. Wal-Mart purchases its products from prison farms, where workers are put through several hours of intense labor, in difficult conditions, without sunscreen, water, or food —not to mention, basically working for free. (source)
Victoria’s Secret
Undergarments and casual wear are sewn by female inmates for Victoria’s Secret. In fact, in the late 1990s 2 prisoners were placed in solitary confinement for telling journalists that they were hired to replace “Made in Honduras” garment tags with “Made in U.S.A” tags. (source)
BP
This is a surprising one. When BP spilled several million barrels of oil into the Ocean (Gulf Coast), the company sent a workforce of prison inmates — almost all of them African-American — to handle cleanup, despite there being scores of displaced coastal residents desperate for work. The move sparked considerable outrage, particularly since BP not only saved money by hiring inmates over locals, but also through the significant tax breaks they received as a result. (source)
AT&T
In 1993 the company laid off thousands of telephone operators, who were all union members, in order to increase their profits. Despite being vocally against prison labour, they went on to hire inmates to work in their call centres, paying them a mere $2 per day. (source)
Aramark
This is a company that provides food to hospitals, schools, and colleges. They also have a monopoly on food served in approximately 600 prisons. They have a history of poor food service, a problem which led to a prison riot in Kentucky in 2009. (source)
Conclusion
There are many other shocking facts about the prison system such as:
Corporate stockholders of companies which are profiting from prison labor are lobbying for increased prison sentences.
America is home to 4% of the global population, yet houses approximately 25% of its prison population.
America has the highest global incarceration rate, which is growing every year.
Almost 50% of American juveniles will be arrested before their 23rd birthday.
Each U.S. resident is paying roughly $260 per year on the prison system
This means that all this slave labour that big corporations are profiting from is paid for by the taxpayers of the United States. Thanks to Collective Evolution for putting this article together, where I sourced most of the information. Much love, Luke
#7 Companies That Are Profiting From Modern Day Slavery In America#slavery in america#slavery economics
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

"In a pathbreaking account of the way Americans financed slavery, Murphy connects the vast sweep of that tragedy to the banking that made it possible. Detail by dollar detail, she exposes the structures that transmuted enslaved people into assets and collateral, building white wealth all the while. A powerful--and chilling--book."
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
The earlier HTTYD books occasionally refer to Hiccup as 'the last great viking hero' which is already a bit melancholy but grows even more so with the context of the later books. I doubt viking society as it was known and understood just totally imploded into dust during Hiccup's lifetime, it's even implied in his old man monologues that that doesn't happen. But it does imply that the end of the viking age, the death of the viking world and way of life is rapidly approaching. Just as the dragon time is over, and the dragons are slowly, slowly leaving as Hiccup grows up and old, the Viking time ends and they too slowy, slowly, die out. I wonder if Hiccup saw this coming decline and thought it was because the vikings couldn't live without dragons, economically and spiritually. How awful, to lose the thing you fought to save and sent away and then your culture year after year.
#httyd books#httyd book spoilers#realistically 'culture death' is a lot more complicated outside of 'and then something happened and everyone here died oops'#The actual viking age ended but people were obviously still living in Scandinavia & it was a very long and messy transition#The 'viking age' was more of a thing historians imposed onto history rather than a clear cut rise of x culture abrupt end of x culture#But#The HTTYD vikings have been DEPENDING on dragons for centuries#it's a huge part of their culture their farming their very survival#Slavery human and dragon was lowkey the backbone of a huge portion of viking society.#idk if Hiccup and a centralised government/sovereign could have pulled them out of the tailspin loosing dragons would eventually put them i#Economics aside the loss of dragons after a couple of generations would start affecting culture aesthetics etc which might have led#to a new culture divorced from a lot of OG HTTYD viking society#either way I don't think the vikings as a culture and society survive the loss of dragons#shut up flynn
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Project 2025 Calls For Raising Taxes On Working Class Americans By 25%
youtube
You wanna become angry about some thing?
This includes you too, white 'trash' & any other poor folk!
Here's what your 'god' really wants from you - & it's not profit sharing!!
You've committed crimes for someone who wants more than just your love!
The Felon Rump wants all of your money, property & land...
That's what's going to happen when you can't pay your tax bill - you'll lose everything.
Are you happy now?
You've punished everyone else for your own political blindness & racism.
How happy will you feel when you have nothing left & must serve as chatel to your smug Con Man?
That's all that will be left: economic slaves working - without rest - until you finally die...
And, your family unable to ever rise above the poverty line.
Every day, more Republicans are leaving the False Prophet that is tRump.
Join the real patriots & end the Rump's economic apocalypse!!
You'll be saving your own self...
End.
#project 2025#TAX#HIKE!!#for working#folk#Less Taxes For#Rich & Corporations!!#political aside#Poor#Would Be Forced Into#Economic Slavery#vote like it matters#cause it does#Youtube
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

1984 - Trickle-Down Theory
#1984 - Trickle-Down Theory#trickle down economics#theory#trickle down theory#poverty#homeless#slavery#wage slavery#slave wages#eat the rich#eat the fucking rich#class war#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#antiwork#anti slavery#anti capitalism#antifascist#fuck work#antiauthoritarian#antinazi#anti colonialism
16 notes
·
View notes